



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1257-1266. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016366 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016366
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2016-12-26
接受日期:2017-07-01
出版日期:2017-12-20
发布日期:2017-12-10
通讯作者:
唐赛春
基金资助:
Yumei Pan, Saichun Tang*( ), Chunqiang Wei, Xiangqin Li
), Chunqiang Wei, Xiangqin Li
Received:2016-12-26
Accepted:2017-07-01
Online:2017-12-20
Published:2017-12-10
Contact:
Tang Saichun
摘要:
为探讨鬼针草属(Bidens)入侵种的入侵性, 利用同质园种植实验比较了该属入侵种三叶鬼针草(Bidens pilosa)和大狼耙草(B. frondosa)与本地种金盏银盘(B. biternata)和狼耙草(B. tripartita)在光照与水分交互作用下的形态、生长、生物量分配、光合特征及其表型可塑性的差异。结果表明: 入侵种的株高和生物量在低光低水条件下与本地种相似, 在有利的光照和水分条件(高光高水)下显著高于本地种, 相对生长速率在高光条件下均高于本地种。入侵种在高光处理下增加了对地下部分的资源投入, 在低光处理下增加了对叶的投入, 且低光低水条件下比叶面积显著高于本地种。这些特性可能提高了入侵种对资源的捕获和利用能力, 使其既能耐受不利的环境, 又能在有利的条件下表现最大化。入侵种和本地种的形态、生长和光合生理等参数对水分变化的可塑性指数均较小, 对光照变化的可塑性指数均较大。入侵种的多数变量对光照响应的可塑性指数大于本地种, 较大的表型可塑性可能促进其成功入侵。另外, 入侵种和本地种的光合生理参数无显著差异。相对于光合特征, 形态、生长、生物量分配和表型可塑性等可能对鬼针草属入侵种的入侵性更为重要。
潘玉梅, 唐赛春, 韦春强, 李象钦 (2017) 不同光照和水分条件下鬼针草属入侵种与本地种生长、光合特征及表型可塑性的比较. 生物多样性, 25, 1257-1266. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016366.
Yumei Pan, Saichun Tang, Chunqiang Wei, Xiangqin Li (2017) Comparison of growth, photosynthesis and phenotypic plasticity between invasive and native Bidens species under different light and water conditions. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1257-1266. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016366.
| 变量 Variables | 光照 Light (L) (df = 1) | 水分 Water (W) (df = 1) | 来源 Origin (O) (df = 1) | 物种(来源) Species (origin) (df = 2) | L × W (df = 1) | L × O (df = 1) | W × O (df = 1) | L × W × O (df = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 194.98*** | 39.31*** | 0.39 | 30.70*** | 50.92*** | 8.11** | 1.24 | 5.96* |
| 比叶面积 SLA | 467.90*** | 11.36** | 15.32 | 0.78 | 6.36* | 7.38* | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 494.65*** | 76.66*** | 0.544 | 25.33*** | 73.15*** | 11.2** | 3.45 | 3.7 |
| 相对生长速率 RGR | 1,747.95*** | 29.13*** | 0.89 | 101.44*** | 33.78*** | 5.70* | 3.37 | 1.02 |
| 根生物量比 RMR | 46.92*** | 0.03 | 0.09 | 9.07*** | 3.16 | 15.43*** | 0.04 | 0.001 |
| 茎生物量比 SMR | 0.101 | 9.09** | 4.27 | 2.44 | 1.30 | 11.05** | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| 叶生物量比 LMR | 5.53* | 8.07** | 5.13 | 1.49 | 3.19 | 22.38*** | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| 光补偿点 LCP | 220.98*** | 0.01 | 0.01 | 2.17 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.005 |
| 光饱和点 LSP | 117.78*** | 0.06 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.03 |
| 最大净光合速率 Amax | 132.73*** | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.10 |
| 暗呼吸速率 Rday | 119.90*** | 0.064 | 0.036 | 3.45* | 0.002 | 0.054 | 0.052 | 0.279 |
表1 光照、水分、物种来源及其交互作用对鬼针草属入侵种和本地种形态、生长及光合参数的影响(F值)
Table 1 Effects of light, water, origin and their interactions on morphology, growth and photosynthetic parameters of invasive and native Bidens species (F-values)
| 变量 Variables | 光照 Light (L) (df = 1) | 水分 Water (W) (df = 1) | 来源 Origin (O) (df = 1) | 物种(来源) Species (origin) (df = 2) | L × W (df = 1) | L × O (df = 1) | W × O (df = 1) | L × W × O (df = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 194.98*** | 39.31*** | 0.39 | 30.70*** | 50.92*** | 8.11** | 1.24 | 5.96* |
| 比叶面积 SLA | 467.90*** | 11.36** | 15.32 | 0.78 | 6.36* | 7.38* | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 494.65*** | 76.66*** | 0.544 | 25.33*** | 73.15*** | 11.2** | 3.45 | 3.7 |
| 相对生长速率 RGR | 1,747.95*** | 29.13*** | 0.89 | 101.44*** | 33.78*** | 5.70* | 3.37 | 1.02 |
| 根生物量比 RMR | 46.92*** | 0.03 | 0.09 | 9.07*** | 3.16 | 15.43*** | 0.04 | 0.001 |
| 茎生物量比 SMR | 0.101 | 9.09** | 4.27 | 2.44 | 1.30 | 11.05** | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| 叶生物量比 LMR | 5.53* | 8.07** | 5.13 | 1.49 | 3.19 | 22.38*** | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| 光补偿点 LCP | 220.98*** | 0.01 | 0.01 | 2.17 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.005 |
| 光饱和点 LSP | 117.78*** | 0.06 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.03 |
| 最大净光合速率 Amax | 132.73*** | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 0.10 |
| 暗呼吸速率 Rday | 119.90*** | 0.064 | 0.036 | 3.45* | 0.002 | 0.054 | 0.052 | 0.279 |
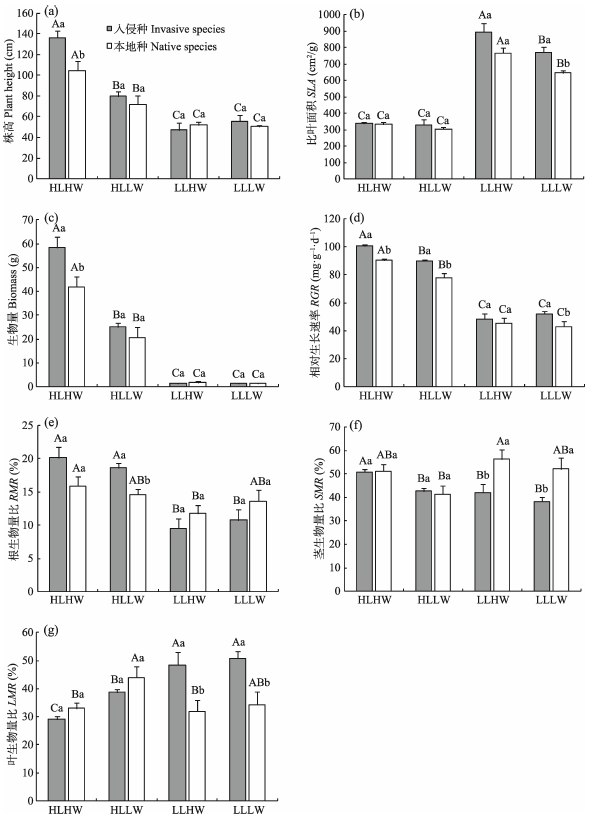
图1 不同光照和水分条件下鬼针草属入侵种与本地种的形态、生长及生物量分配特征(平均值±标准误)。不同大、小写字母分别代表物种在不同处理下和相同处理下入侵种和本地种间差异显著(P < 0.05)。HLHW: 高光高水; HLLW: 高光低水; LLHW: 低光高水; LLLW: 低光低水。
Fig. 1 Morphology, growth and biomass allocation characteristics of the invasive and native Bidens species under different light and water conditions (means ± SE). Different capital and small letters indicate significant differences among treatments for the same species and differences between invasive and native species at the same treatment, respectively (P < 0.05). HLHW, High light and high water; HLLW, High light and low water; LLHW, Low light and high water; LLLW, Low light and low water; SLA, Specific leaf area; RGR, Relative growth rate; RMR, Root mass ratio; SMR, Stem mass ratio; LMR, Leaf mass ratio.
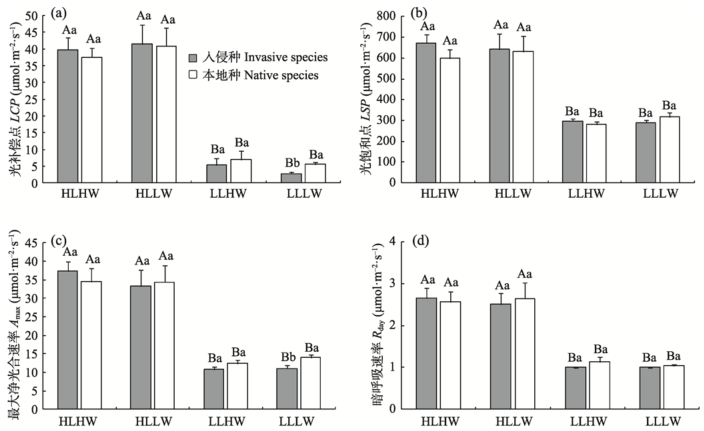
图2 不同光照和水分条件下鬼针草属入侵种和本地种的光合参数(平均值±标准误)。不同大、小写字母分别代表物种在不同处理下和相同处理下入侵种和本地种间差异显著(P < 0.05)。HLHW: 高光高水; HLLW: 高光低水; LLHW: 低光高水; LLLW: 低光低水。
Fig. 2 Photosynthetic parameters of the invasive and native Bidens species under different light and water conditions (means ± SE). Different capital and small letters indicate significant differences among treatments for the same species and differences between invasive and native species at the same treatment, respectively (P < 0.05). HLHW, High light and high water; HLLW, High light and low water; LLHW, Low light and high water; LLLW, Low light and low water; LCP, Light compensation point; LSP, Light saturation point; Amax, Maximum net photosynthetic rate; Rday, Dark respiration rate.
| 变量 Variables | 入侵种 Invasive species | 本地种 Native species | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光照 Light | 水分 Water | 光照 Light | 水分 Water | |||||
| 高水处理 High water | 低水处理 Low water | 高光处理 High light | 低光处理 Low light | 高水处理 High water | 低水处理 Low water | 高光处理 High light | 低光处理 Low light | |
| 株高 Plant height | 0.65 | 0.302 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.298 | 0.31 | 0.03 |
| 比叶面积 SLA | 0.62 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.135 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.09 | 0.16 |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.51 | 0.24 |
| 根生物量比 RMR | 0.53 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.14 |
| 茎生物量比 SMR | 0.17 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.07 |
| 叶生物量比 LMR | 0.4 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.07 |
| 相对生长速率 RGR | 0.52 | 0.42 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.5 | 0.45 | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| 最大净光合速率 Amax | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.005 | 0.12 |
| 光补偿点 LCP | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 0.21 |
| 光饱和点 LSP | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.53 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| 平均值 Mean value | 0.6 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
表2 鬼针草属入侵种和本地种各变量对光照和水分响应的表型可塑性指数
Table 2 Phenotypic plasticity indices for the variables of invasive and native Bidens species to light and/or water conditions
| 变量 Variables | 入侵种 Invasive species | 本地种 Native species | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光照 Light | 水分 Water | 光照 Light | 水分 Water | |||||
| 高水处理 High water | 低水处理 Low water | 高光处理 High light | 低光处理 Low light | 高水处理 High water | 低水处理 Low water | 高光处理 High light | 低光处理 Low light | |
| 株高 Plant height | 0.65 | 0.302 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.298 | 0.31 | 0.03 |
| 比叶面积 SLA | 0.62 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.135 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.09 | 0.16 |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.51 | 0.24 |
| 根生物量比 RMR | 0.53 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.14 |
| 茎生物量比 SMR | 0.17 | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.07 |
| 叶生物量比 LMR | 0.4 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.07 |
| 相对生长速率 RGR | 0.52 | 0.42 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.5 | 0.45 | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| 最大净光合速率 Amax | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.005 | 0.12 |
| 光补偿点 LCP | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 0.21 |
| 光饱和点 LSP | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.53 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| 平均值 Mean value | 0.6 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| [20] | [洪岚, 沈浩, 杨期和, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉 (2004) 外来入侵植物三叶鬼针草种子萌发与贮藏特性研究. 武汉植物学研究, 22, 433-437.] |
| [21] | Hou YP, Peng SL, Lin ZG, Huang QQ, Ni GY, Zhao N (2015) Fast-growing and poorly shade-tolerant invasive species may exhibit higher physiological but not morphological plasticity compared with non-invasive species. Biological Invasions, 17, 1555-1567. |
| [22] | Huang H, Guo SL (2005) Study on reproductive biology of the invasive plant Solidago canadensis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2795-2803. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄华, 郭水良 (2005) 外来入侵植物加拿大一枝黄花繁殖生物学研究. 生态学报, 25, 2795-2803.] | |
| [23] | Johnson NC, Rowland DL, Corkidi L, Allen EB (2008) Plant winners and losers during grassland N-eutrophication differ in biomass allocation and mycorrhizas. Ecology, 89, 2868-2878. |
| [24] | Mao DJ, Xie JF, Quan GM, Zhang JE (2010) Effects of Bidens pilosa aqueous extracts on germination and seedling growth of two pastures. Journal of Foshan University (Natural and Science Edition), 28(5), 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [毛丹鹃, 谢俊芳, 全国明, 章家恩 (2010) 三叶鬼针草水浸提液对两种牧草种子萌发与幼苗生长的影响. 佛山科学技术学院学报(自然科学版), 28(5), 7-11.] | |
| [25] | McDowell SCL (2002) Photosynthetic characteristics of invasive and noninvasive species of Rubus (Rosaceae). American Journal of Botany, 89, 1431-1438. |
| [26] | Mozdzer TJ, Megonigal JP (2012) Jack-and-master trait responses to elevated CO2 and N: a comparison of native and introduced Phragmites australis. PLoS ONE, 7, e42794. |
| [27] | Pan YM, Liu MC, Tang SC, Wei CQ, Pu GZ, Cen YX (2012a) Effect of light intensity on the growth characteristics of Bidens pilosa. Guihaia, 32, 77-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘玉梅, 刘明超, 唐赛春, 韦春强, 蒲高忠, 岑艳喜 (2012a) 光照对三叶鬼针草生长特征的影响. 广西植物, 32, 77-82.] | |
| [28] | Pan YM, Tang SC, Wei CQ, Liu MC (2012b) Response of growth characteristics of Bidens pilosa L. to soil nitrogen level. Weed Science, 30, 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘玉梅, 唐赛春, 韦春强, 刘明超 (2012b) 三叶鬼针草生长特征对土壤氮素水平的响应. 杂草科学, 30, 11-16.] | |
| [29] | Pan YM, Tang SC, Wei CQ, Li XQ (2016) Effects of global risks — nitrogen additions on growth and competitive relations among invasive and native congeneric species — Bidens frondosa. Polish Journal of Ecology, 64, 443-452. |
| [30] | Poorter L (1999) Growth response of 15 rain forest tree species to a light gradient: the relative importance of morphological and physiological traits. Functional Ecology, 13, 396-410. |
| [31] | Poorter L (2001) Light-dependent changes in biomass allocation and their importance for growth of rain forest tree species. Functional Ecology, 15, 113-123. |
| [32] | Pyšek P, Richardson DM (2007) Ecological studies: traits associated with invasiveness in alien plants, where do we stand? In: Biological Invasions (ed. Nentwig W), pp. 97-126. Springer-Verlag, Berlin & Heidelberg. |
| [33] | Quan GM, Mao DJ, Zhang JE, Xie JF, Xu HQ (2011) Reproductive capacity and seed germination characteristics of Chromolaena odorata. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(1), 72-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [全国明, 毛丹鹃, 章家恩, 谢俊芳, 徐华勤 (2011) 飞机草的繁殖能力与种子的萌发特性. 生态环境学报, 20(1), 72-78.] | |
| [34] | Quero JL, Villar R, Mrańön T, Zamora R (2006) Interactions of drought and shade effects on seedlings of four Quercus species: physiological and structural leaf responses. New Phytologist, 170, 819-834. |
| [35] | Ruprecht E, Fenesi A, Nijs I (2014) Are plasticity in functional traits and constancy in performance traits linked with invasiveness? An experimental test comparing invasive and naturalized plant species. Biological Invasions, 16, 1359-1372. |
| [36] | Smith MD, Knapp AK (2001) Physiological and morphological traits of exotic, invasive exotic, and native plant species in tallgrass prairie. International Journal of Plant Science, 162, 785-792. |
| [37] | Song LY, Peng CL, Peng SL (2009) Comparison of leaf construction costs between three invasive species and three native species in South China. Biodiversity Science, 17, 378-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋莉英, 彭长连, 彭少麟 (2009) 华南地区3种入侵植物与本地植物叶片建成成本的比较. 生物多样性, 17, 378-384.] | |
| [38] | Valladares F, Wright SJ, Lasso E, Kitajima K, Pearcy RW (2000) Plastic phenotypic response to light of 16 congeneric shrubs from a Panamanian rainforest. Ecology, 81, 1925-1936. |
| [39] | Wang K, Yang J, Chen JK (2009) The applications of congeneric comparisons in plant invasion ecology. Biodiversity Science, 17, 353-361. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王坤, 杨继, 陈家宽 (2009) 近缘种比较研究在植物入侵生态学中的应用. 生物多样性, 17, 353-361.] | |
| [40] | Wang K, Yang J, Chen JK (2010) Comparison of morphological traits between alligator weed and two congeners under different water and nutrient conditions. Biodiversity Science, 18, 615-621. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王坤, 杨继, 陈家宽 (2010) 不同土壤水分和养分条件下喜旱莲子草与同属种生长状况的比较研究. 生物多样性, 18, 615-621.] | |
| [41] | Wang XH, Ji MS (2013) Photosynthetic characteristics of an invasive plant Conyza canadensis and its associated plants. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王晓红, 纪明山 (2013) 入侵植物小飞蓬及其伴生植物的光合特性. 应用生态学报, 24, 71-77.] | |
| [1] | Albert KR, Ro-Poulsen H, Mikkelsen TN, Michelsen A, van der Linden L, Beier C (2011) Interactive effects of elevated CO2, warming, and drought on photosynthesis of Deschampsia flexuosia in a temperate health ecosystem. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62, 4253-4266. |
| [2] | Annapurna C, Singh JS (2003) Variation of Parthenium hysterophorus in response to soil quality: implications for invasiveness. Weed Research, 43, 190-198. |
| [42] | Wei CQ, Liu MC, Tang SC, Pan YM, Pu GZ (2012) Effects of light and temperature on seed germination of Eupatorium odoratum. Guihaia, 32, 527-530. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韦春强, 刘明超, 唐赛春, 潘玉梅, 蒲高忠 (2012) 光照和温度对飞机草种子萌发的影响. 广西植物, 32, 527-530.] | |
| [43] | Yan BG, Fan B, He GX, Shi LT, Pan ZX, Li JC, Yue XW, Liu GC (2016) Biomass allocations and their response to environmental factors for grass species in an arid-hot valley. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 3173-3181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫帮国, 樊博, 何光熊, 史亮涛, 潘志贤, 李建查, 岳学文, 刘刚才 (2016) 干热河谷草本植物生物量分配及其对环境因子的响应. 应用生态学报, 27, 3173-3181.] | |
| [3] | Burns JH (2004) A comparison of invasive and noninvasive dayflowers (Commelinaceae) across experimental nutrient and water gradients. Diversity and Distributions. 10, 387-397. |
| [4] | Cannell MGR, Thornley JHM (1998) Temperature and CO2 responses of leaf and canopy photosynthesis: a clarification using the non-rectangular hyperbola model of photosynthesis. Annals of Botany, 82, 883-892. |
| [5] | Daehler CC (2003) Performance comparisons of co-occurring native and alien invasive plants: implications for conservation and restoration. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution,& Systematics, 34, 183-211. |
| [44] | Yan XH, Zeng JJ, Zhou B, Wang N, Xiang HH, Kang YY (2012) Allelopathic potential of the extracts from alien invasive plant Bidens frondosa. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agriculture and Life Science Edition), 33, 88-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫小红, 曾建军, 周兵, 王宁, 项欢欢, 康媛媛 (2012) 外来入侵植物大狼耙草提取物的化感潜力. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 33, 88-94.] | |
| [6] | Davidson AM, Jennions M, Nicotra AB (2011) Do invasive species show higher phenotypic plasticity than native species and, if so, is it adaptive? A meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, 14, 419-431. |
| [7] | Deng X, Ye WH, Feng HL, Yang QH, Cao HL, Xu KY, Zhang Y (2004) Gas exchange characteristics of the invasive species Mikania micrantha and its indigenous congener M. cordata (Asteraceae) in South China. Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica, 45, 213-220. |
| [45] | Yan XH, Zhou B, Yin ZF, Wang N, Zhang ZG (2016) Reproductive biological characteristics potentially contributed to invasiveness in an alien invasive plant Bidens frondosa. Plant Species Biology, 31, 107-116. |
| [46] | Zhao XJ, Liu WY, Zhou M, Ma WZ (2009) Comparison of growth and reproduction characters among different populations of Eupatorium adenophorum in Yunnan. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 29, 1252-1258. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵相健, 刘文耀, 周蒙, 马文章 (2009) 不同地理种群紫茎泽兰生长繁殖特征的比较研究. 西北植物学报, 29, 1252-1258.] | |
| [47] | Zheng YL, Feng YL, Liu WX, Liao ZY (2009) Growth, biomass allocation, morphology, and photosynthesis of invasive Eupatorium adenophorum and its native congeners grown at four irradiances. Plant Ecology, 203, 263-271. |
| [8] | Droste T, Flory SL, Clay K (2010) Variation for phenotypic plasticity among populations of an invasive exotic grass. Plant Ecology, 207, 297-306. |
| [9] | Endo AT, Okuda T, Tamura M, Yasuoka Y (2001) Estimation of net photosynthetic rate based on in-situ hyperspectral data. Proceeding of Spie, 15, 214-221. |
| [10] | Feng YL (2008) Photosynthesis, nitrogen allocation and specific leaf area in invasive Eupatorium adenophorum and native Eupatorium japonicum grown at different irradiances. Physiologia Plantarum, 133, 318-326. |
| [48] | Zhou CQ, Tang SC, Pan YM, Wei CQ (2015) Effects of light and temperature on germination of heteromorphic achenes of Bidens frondosa L. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 23, 662-668. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周超群, 唐赛春, 潘玉梅, 韦春强 (2015) 光照和温度对入侵植物大狼耙草异形瘦果萌发的影响. 热带亚热带植物学报, 23, 662-668.] | |
| [11] | Feng YL, Fu GL (2008) Nitrogen allocation, partitioning and use efficiency in three invasive plant species in comparison with their native congeners. Biological Invasions, 10, 891-902. |
| [12] | Geng YP, Pan XY, Xu CY, Zhang WJ, Li B, Chen JK (2006) Phenotypic plasticity of invasive Alternathera philoxeroides in relation to different water availability, compared to its native congener. Acta Oecologica, 30, 380-385. |
| [13] | Geng YP, Zhang WJ, Li B, Chen JK (2004) Phenotypic plasticity and invasiveness of alien plants. Biodiversity Science, 12, 447-455. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [耿宇鹏, 张文驹, 李博, 陈家宽 (2004) 表型可塑性与外来植物的入侵能力. 生物多样性, 12, 447-455.] | |
| [14] | Godoy O, Valladares F, Castro-Diez P (2011) Multispecies comparison reveals that invasive and native plants differ in their traits but not in their plasticity. Functional Ecology, 25, 1248-1259. |
| [15] | Graeme TH, Andrew JD, Gabrielle VS (2008) Predicting invasiveness in exotic species: do subtropical native and invasive exotic aquatic plants differ in their growth response to macronutrients? Diversity and Distributions, 14, 243-251. |
| [16] | Grotkopp E, Rejmánek M (2007) High seedling relative growth rate and specific leaf area are traits of invasive species: phylogenetically independent contrasts of woody angiosperms. American Journal of Botany, 94, 526-532. |
| [17] | Guo AY, Yang Q, Zhang FJ, Meng XD (2010) Effects of the leaf extract from railway beggar ticks and Ageratum conyzoides on seeds germination of upland rice. Journal of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technololy, 24(3), 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭艾英, 杨晴, 张风娟, 孟宪东 (2010) 三叶鬼针草和胜红蓟的叶浸提液对旱稻种子萌发的影响. 河北科技师范学院学报, 24(3), 28-31.] | |
| [18] | Gupta S, Narayan R (2012) Phenotypic plasticity of Chenopodium murale across contrasting habitat conditions in peri-urban areas in Indian dry tropics, is it indicative of its invasiveness? Plant Ecology, 213, 493-503. |
| [19] | Hao JH, Liu QQ, Qiang S (2009) Reproductive traits associated with invasiveness in Bidens Pilosa (Asteraceae). Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 44, 656-665. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郝建华, 刘倩倩, 强胜 (2009) 菊科入侵植物三叶鬼针草的繁殖特征及其与入侵性的关系. 植物学报, 44, 656-665.] | |
| [20] | Hong L, Shen H, Yang QH, Cao HL, Ye WH (2004) Studies on seed germination and storage of the invasive alien species Bidens pilosa L. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 22, 433-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [49] | Zou JW, Rogers WE, Siemann E (2009) Plasiticity of Sapium sebiferum seedling growth to light and water resources: inter- and intraspecific comparisons. Basic and Applied Ecollogy, 10, 79-88. |
| [1] | 龙诗怡, 张博博, 夏宇辰, 费杨帆, 孟亚妮, 吕冰薇, 宋月青, 郑普, 郭陶然, 张健, 黎绍鹏. 本地群落多样性和时间稳定性对加拿大一枝黄花生物量的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [2] | 邵雯雯, 范国祯, 何知舟, 宋志平. 多地同质园实验揭示普通野生稻的表型可塑性与本地适应性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22311-. |
| [3] | 邓铭先, 黄河燕, 沈诗韵, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 斯确多吉, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草在青藏高原对模拟增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1198-1205. |
| [4] | 黄河燕, 朱政财, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 周永洪, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对模拟全天增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 419-427. |
| [5] | 于良瑞, 朱政财, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对同基因型邻体根系的表型可塑性: 入侵地和原产地的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 651-657. |
| [6] | 陈俊, 姚兰, 艾训儒, 朱江, 吴漫玲, 黄小, 陈思艺, 王进, 朱强. 基于功能性状的水杉原生母树种群生境适应策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 296-302. |
| [7] | 杨倩倩, 刘苏汶, 茹炜岽, 刘光富, 俞晓平. 基于DNA条形码技术对浙江省外来入侵福寿螺进行分子鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(3): 341-350. |
| [8] | 张紫妍, 张致杰, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对遮荫的可塑性反应:入侵地与原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1): 18-22. |
| [9] | 张晴柔, 蒋赏, 鞠瑞亭, 潘晓云. 上海市外来入侵物种[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(6): 732-737. |
| [10] | 施雯, 耿宇鹏, 欧晓昆. 遗传多样性与外来物种的成功入侵: 现状和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(6): 590-587. |
| [11] | 王坤, 杨继, 陈家宽. 不同土壤水分和养分条件下喜旱莲子草与同属种生长状况的比较研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(6): 615-621. |
| [12] | 强胜, 陈国奇, 李保平, 孟玲. 中国农业生态系统外来种入侵及其管理现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(6): 647-659. |
| [13] | 张亦默, 王卿, 卢蒙, 贾昕, 耿宇鹏, 李博. 中国东部沿海互花米草种群生活史特征的纬度变异与可塑性[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(5): 462-469. |
| [14] | 干晓静, 李博, 陈家宽, 马志军. 生物入侵对鸟类的生态影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(5): 548-557. |
| [15] | 贾昕, 傅东静, 潘晓云, 李博, 陈家宽. 陆生生境中喜旱莲子草的生长模式[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(3): 241-246. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()