



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1330-1338. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019281 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019281
• Research Bulletin • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rijin Jiang1,2,Linlin Zhang1,2,Kaida Xu1,2,*( ),Pengfei Li1,2,Yi Xiao1,2,Ziwei Fan1,2
),Pengfei Li1,2,Yi Xiao1,2,Ziwei Fan1,2
Received:2019-09-08
Accepted:2019-11-23
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2020-01-14
Contact:
Xu Kaida
Rijin Jiang,Linlin Zhang,Kaida Xu,Pengfei Li,Yi Xiao,Ziwei Fan. Characteristics and diversity of nekton functional groups in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1330-1338.
| 功能群 Functional group | 丰度百分比 Abundance percentage (%) | 生物量百分比 Biomass percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4月 April | 5月 May | 4月 April | 5月 May | |
| 浮游动物食性 Zooplanktivores functional group (FG1) | 8.36 | 10.83 | 6.43 | 12.02 |
| 浮游动物/游泳动物食性 Zooplanktivores /Piscivores functional group (FG2) | 33.19 | 61.23 | 17.13 | 25.09 |
| 游泳动物食性 Piscivores functional group (FG3) | 7.11 | 7.73 | 27.55 | 30.74 |
| 底栖动物食性 Benthivores functional group (FG4) | 1.89 | 1.00 | 9.17 | 8.87 |
| 碎屑食性 Detritivores functional group (FG5) | 15.22 | 7.63 | 4.60 | 3.76 |
| 杂食性 Omnivores functional group (FG6) | 34.22 | 11.58 | 35.12 | 19.52 |
Table 1 Abundance percentage and biomass percentage of different nekton functional groups in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May
| 功能群 Functional group | 丰度百分比 Abundance percentage (%) | 生物量百分比 Biomass percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4月 April | 5月 May | 4月 April | 5月 May | |
| 浮游动物食性 Zooplanktivores functional group (FG1) | 8.36 | 10.83 | 6.43 | 12.02 |
| 浮游动物/游泳动物食性 Zooplanktivores /Piscivores functional group (FG2) | 33.19 | 61.23 | 17.13 | 25.09 |
| 游泳动物食性 Piscivores functional group (FG3) | 7.11 | 7.73 | 27.55 | 30.74 |
| 底栖动物食性 Benthivores functional group (FG4) | 1.89 | 1.00 | 9.17 | 8.87 |
| 碎屑食性 Detritivores functional group (FG5) | 15.22 | 7.63 | 4.60 | 3.76 |
| 杂食性 Omnivores functional group (FG6) | 34.22 | 11.58 | 35.12 | 19.52 |
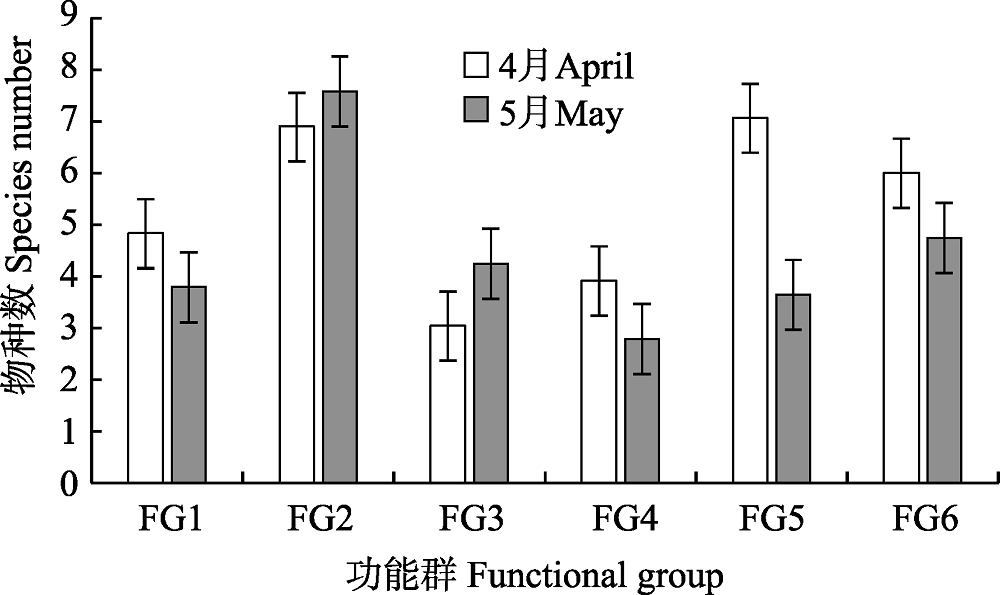
Fig. 2 Species number of each nekton functional group in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May. Functional group codes are the same as in Table 1.
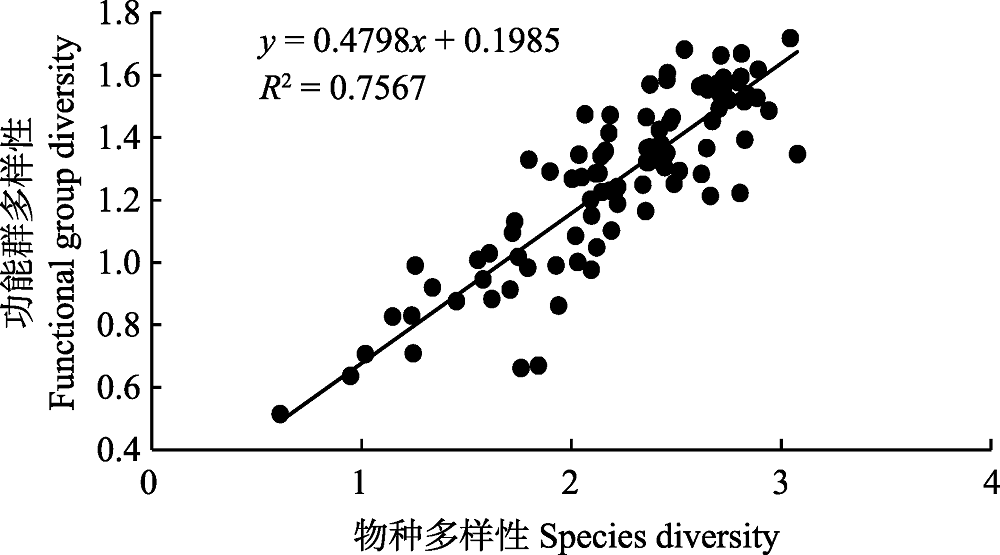
Fig. 3 The linear relationship between species diversity and functional diversity for the nekton community in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province
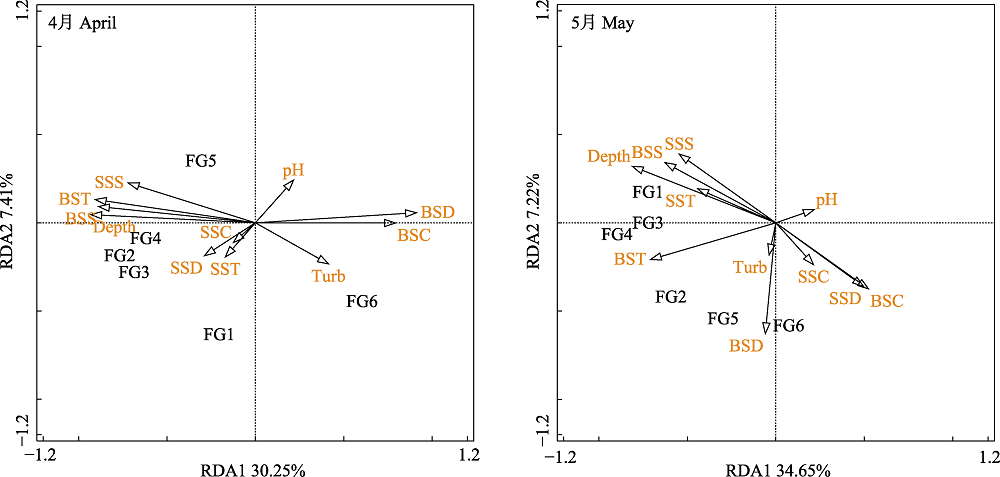
Fig. 4 Redundancy analysis ordination diagrams for nekton functional groups and environmental factors in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May. SST, Surface temperature; SSS, Surface salinity; SSC, Surface chlorophyll; SSD, Surface dissolved oxygen; BST, Bottom temperature; BSS, Bottom salinity; BSC, Bottom chlorophyll; BSD, Bottom dissolved oxygen; Turb, Turbidity; Depth, Depth of water. Functional group codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 环境参数 Environmental variables | 4月 April | 5月 May | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 (30.25%) | RDA2 (7.41%) | RDA1 (34.65% ) | RDA2 (7.22% ) | |
| 表层温度 Surface temperature (SST) | -0.15 | -0.13 | -0.40 | 0.12 |
| 表层盐度 Surface salinity (SSS) | -0.62 | 0.16 | -0.49 | 0.24 |
| 表层叶绿素 Surface chlorophyll (SSC) | -0.11 | -0.08 | 0.19 | -0.15 |
| 表层溶解氧 Surface dissolved oxygen (SSD) | -0.25 | -0.13 | 0.45 | -0.22 |
| 底层温度 Bottom temperature (BST) | -0.78 | 0.09 | -0.64 | -0.13 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom salinity (BSS) | -0.76 | 0.06 | -0.56 | 0.21 |
| 底层叶绿素 Bottom chlorophyll (BSC) | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.47 | -0.23 |
| 底层溶解氧 Bottom dissolved oxygen (BSD) | 0.78 | 0.04 | -0.05 | -0.38 |
| pH | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 浑浊度 Turbidity (Turb) | 0.36 | -0.16 | -0.03 | -0.11 |
| 水深 Depth of water (Depth) | -0.80 | 0.03 | -0.73 | 0.20 |
Table 2 Results of redundancy analysis of nekton functional groups and environmental factors in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May
| 环境参数 Environmental variables | 4月 April | 5月 May | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 (30.25%) | RDA2 (7.41%) | RDA1 (34.65% ) | RDA2 (7.22% ) | |
| 表层温度 Surface temperature (SST) | -0.15 | -0.13 | -0.40 | 0.12 |
| 表层盐度 Surface salinity (SSS) | -0.62 | 0.16 | -0.49 | 0.24 |
| 表层叶绿素 Surface chlorophyll (SSC) | -0.11 | -0.08 | 0.19 | -0.15 |
| 表层溶解氧 Surface dissolved oxygen (SSD) | -0.25 | -0.13 | 0.45 | -0.22 |
| 底层温度 Bottom temperature (BST) | -0.78 | 0.09 | -0.64 | -0.13 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom salinity (BSS) | -0.76 | 0.06 | -0.56 | 0.21 |
| 底层叶绿素 Bottom chlorophyll (BSC) | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.47 | -0.23 |
| 底层溶解氧 Bottom dissolved oxygen (BSD) | 0.78 | 0.04 | -0.05 | -0.38 |
| pH | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 浑浊度 Turbidity (Turb) | 0.36 | -0.16 | -0.03 | -0.11 |
| 水深 Depth of water (Depth) | -0.80 | 0.03 | -0.73 | 0.20 |
| [1] | Arenas F, Iñigo S, Jenkins HSR ( 2006) The invasibility of marine algal assemblages: Role of functional diversity and identity. Ecology, 87, 2851-2861. |
| [2] | Bai YF, Li LH, Huang JH, Chen ZZ ( 2001) The influence of plant diversity and functional composition on ecosystem stability of four Stipa communities in the Inner Mongolia Plateau. Acta Botanica Sinica, 43, 280-287. |
| [3] | Begon M, Harper JL, Towsend CR ( 1996) Ecology: Individuals, Populations and Communities. Blackwell Scientific, Victoria (Australia). |
| [4] | Bellwood DR, Hoey A, Choat JH ( 2003) Limited functional redundancy in high diversity systems: Resilience and ecosystem function on coral reefs. Ecology Letters, 6, 281-285. |
| [5] | Cheng JS, Zhu JS ( 1997) Study on feeding characteristics and nutrient level of main economic invertebrates in the Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 19(6), 102-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程济生, 朱金声 ( 1997) 黄海主要经济无脊椎动物摄食特征及其营养层次的研究. 海洋学报, 19(6), 102-108.] | |
| [6] | Clarke KR ( 1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18, 117-143. |
| [7] | Dai LB, Tian SQ, Peng X, Gao CX, Ye S, Du XX, Liu P ( 2018) Distribution of Larimichthys polyactis and its relationship with environmental factors in offshore water of southern Zhejiang. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 1352-1358. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴黎斌, 田思泉, 彭欣, 高春霞, 叶深, 杜晓雪, 刘攀 ( 2018) 浙江南部近海小黄鱼资源分布及其与环境因子的关系. 应用生态学报, 29, 1352-1358.] | |
| [8] | Deng JY, Zhao CY ( 1991) Marine Fishery Biology. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邓景耀, 赵传絪 ( 1991) 海洋渔业生物学. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Dolbeth M, Teixeira H, Marques JC, Pardal MÂ ( 2009) Feeding guild composition of a macrobenthic subtidal community along a depth gradient. Scientia Marina, 73, 225-237. |
| [10] | Floeter SR, Ferreira CEL, Dominici-Arosemena A, Zalmon IR ( 2004) Latitudinal gradients in Atlantic reef fish communities: Trophic structure and spatial use patterns. Journal of Fish Biology, 64, 1680-1699. |
| [11] | Garrison LP ( 2000) Spatial and dietary overlap in the Georges Bank ground fish community. Canadian Journal of Fishery and Aquatic Sciences, 57, 1679-1691. |
| [12] | Greenstreet SPR, Rogers S ( 2006) Indicators of the health of the North Sea fish community: Identifying reference levels for an ecosystem approach to management. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 63, 573-593. |
| [13] | Hu CY, Shui YY, Tian K, Li L, Qin HL, Zhang CC, Ji MM, Shui BN ( 2016) Functional group classification and niche identification of major fish species in the Qixing Islands Marine Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 24, 175-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡成业, 水玉跃, 田阔, 李良, 覃胡林, 张春草, 冀萌萌, 水柏年 ( 2016) 浙江七星列岛海洋特别保护区主要鱼类功能群划分及生态位分析. 生物多样性, 24, 175-184.] | |
| [14] | Jiang RJ, Xu HX, Jin HW, Zhou YD, He ZT ( 2012) Feeding habits of blue mackerel scad Decapterus maruadsi Temminck et Schlegel in the East China Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China, 36, 216-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋日进, 徐汉祥, 金海卫, 周永东, 贺舟挺 ( 2012) 东海蓝圆鰺的摄食习性研究. 水产学报, 36, 216-227.] | |
| [15] | Jiang YZ, Cheng JH, Li SF ( 2008) Variation in fish community structure and biodiversity in the north of the East China Sea between two periods. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 15, 453-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜亚洲, 程家骅, 李圣法 ( 2008) 东海北部鱼类群落多样性及其结构特征的变化. 中国水产科学, 15, 453-459.] | |
| [16] | Jiang YZ, Lin N, Yuan XW, Jiao HF, Li SF ( 2014) Functional group composition and functional diversity of nekton community in the Xiangshan Bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 45, 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜亚洲, 林楠, 袁兴伟, 焦海峰, 李圣法 ( 2014) 象山港游泳动物群落功能群组成与功能群多样性. 海洋与湖沼, 45, 108-114.] | |
| [17] | Jiao HF, Peng XM, You ZJ, Shi HX, Lou ZJ, Liu HD ( 2011) Species diversity of macrobenthos in the rocky intertidal zone of Yushan Island. Biodiversity Science, 19, 511-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 焦海峰, 彭小明, 尤仲杰, 施慧雄, 楼志军, 刘红丹 ( 2011) 渔山岛岩石相潮间带大型底栖动物物种多样性. 生物多样性, 19, 511-518.] | |
| [18] | Kong DL, Wu HF, Zeng H, Lü XT, Simmons M, Wang M, Sun XF, Han XG ( 2011) Plant functional group removal alters root biomass and nutrient cycling in a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Plant and Soil, 346, 133-144. |
| [19] | Lanta V, Lepš J ( 2006) Effect of functional group richness and species richness in manipulated productivity-diversity studies: A glasshouse pot experiment. Acta Oecologica, 29, 85-96. |
| [20] | Lepš J, Šmolauer P ( 2003) Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, New York. |
| [21] | Li GG, Fan ZG ( 2011) Marine Ecology. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李冠国, 范振刚 ( 2011) 海洋生态学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Lie HJ, Cho CH ( 2002) Recent advances in understanding the circulation and hydrography of the East China Sea. Fisheries Oceanography, 11, 318-328. |
| [23] | Lin LS, Yan LP, Ling JZ, Liu Y, Zhou RK ( 2005) Food habits of hairtail in the East China Sea region. Marine Fisheries, 27, 187-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林龙山, 严利平, 凌建忠, 刘勇, 周荣康 ( 2005) 东海带鱼摄食习性的研究. 海洋渔业, 27, 187-192.] | |
| [24] | Liu K, Lin HS, He XB, Huang YQ, Lin JH, Mou JF, Zhang SY, Wang JJ ( 2016) Functional feeding group of macrozoobenthos and their relationships to environmental factors in Xiamen coastal waters. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 38, 95-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘坤, 林和山, 何雪宝, 黄雅琴, 林俊辉, 牟剑锋, 张舒怡, 王建军 ( 2016) 厦门近岸海域大型底栖动物摄食功能群及其与环境因子的关系. 海洋学报, 38, 95-105.] | |
| [25] | Liu RY ( 2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Sea. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘瑞玉 ( 2008) 中国海洋生物名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] | Liu Y, Li SF, Cheng JH ( 2006) A study on seasonal changes of the fish communities in the East China Sea and the Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 28(4), 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘勇, 李圣法, 程家骅 ( 2006) 东海、黄海鱼类群落结构的季节变化研究. 海洋学报, 28(4), 108-114.] | |
| [27] | Long H ( 2005) The effect of temperature on fish survival. Fishery Modernization, 32(2), 20-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 龙华 ( 2005) 温度对鱼类生存的影响. 渔业现代化, 32(2), 20-22.] | |
| [28] | Lü ZB, Li F, Xu BQ, Wang B ( 2012) Fish community diversity during spring and autumn in the Yellow Sea off the coast of Shandong. Biodiversity Science, 20, 207-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕振波, 李凡, 徐炳庆, 王波 ( 2012) 黄海山东海域春、秋季鱼类群落多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 207-214.] | |
| [29] | Ma WJ, Zhang Q, Niu JM, Kang S, Liu PT, He X, Yang Y, Zhang YN, Wu JG ( 2013) Relationship of ecosystem primary productivity to species diversity and functional group diversity: Evidence from Stipa breviflora grassland in Nei Mongol. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 620-630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马文静, 张庆, 牛建明, 康萨如拉, 刘朋涛, 何欣, 杨艳, 张艳楠, 邬建国 ( 2013) 物种多样性和功能群多样性与生态系统生产力的关系——以内蒙古短花针茅草原为例. 植物生态学报, 37, 620-630.] | |
| [30] | Micheli F, Halpern BS ( 2005) Low functional redundancy in coastal marine assemblages. Ecology Letters, 8, 391-400. |
| [31] | Poff NL, Allan JD ( 1995) Functional organization of stream fish assemblages in relation to hydrological variability. Ecology, 76, 606-627. |
| [32] | Qian YQ, Ma KP ( 1994) Principle and Method of Biodiversity Studies. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 钱迎倩, 马克平 ( 1994) 生物多样性研究的原理与方法. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Shan XJ, Jin XS, Zhou ZP, Dai FQ ( 2011) Fish community diversity in the middle continental shelf of the East China Sea. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29, 1199-1208. |
| [34] | Sheng FL, Zeng XQ, Xue Y ( 2009) Study on propagation and feeding habits of Oratosquilla oratoria in the inshore waters of Qingdao. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39, 326-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 盛福利, 曾晓起, 薛莹 ( 2009) 青岛近海口虾蛄的繁殖及摄食习性研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 39, 326-332.] | |
| [35] | Sun BB, Yu CG, Liu H, Yan WC, Zhang WJ, Dai DX ( 2019) Spring and autumn shrimp and crab biodiversity in the east Nanji Islands. Biodiversity Science, 27, 787-795. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙蓓蓓, 俞存根, 刘惠, 颜文超, 张文俊, 戴冬旭 ( 2019) 南麂列岛东侧海域春秋季虾蟹类生物多样性. 生物多样性, 27, 787-795.] | |
| [36] | Tang QS, Su JL, Zhang J ( 2005) Key processes and sustainable mechanisms of ecosystem food production in the coastal ocean of China. Advance in Earth Sciences, 20, 1280-1287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐启升, 苏纪兰, 张经 ( 2005) 我国近海生态系统食物产出的关键过程及其可持续机理. 地球科学进展, 20, 1280-1287.] | |
| [37] | Thrush SF, Hewitt JE, Gibbs M, Lundquist G, Norkko A ( 2006) Functional role of large organisms in intertidal communities: Community effects and ecosystem function. Ecosystem, 9, 1029-1040. |
| [38] | Wang K, Zhang SY, Wang ZH, Zhao J, Jiang RJ ( 2014) Dietary composition and feeding strategy of Agrammus agrammus off the Ma’an Archipelago Special Marine Reserves. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 23, 251-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王凯, 章守宇, 汪振华, 赵静, 蒋日进 ( 2014) 马鞍列岛海洋特别保护区斑头六线鱼的摄食习性. 上海海洋大学学报, 23, 251-257.] | |
| [39] | Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB ( 2014) Advancements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 ( 2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [40] | Woodward G, Ebenman B, Emmerson M, Montoya JM, Olesen JM, Valido A, Warren PH ( 2005) Body size in ecological networks. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 20, 402-409. |
| [41] | Xu KD, Lu KE, Lu ZH, Dai Q ( 2018) Ecological niche analysis of dominant shrimp species in the Jiushan Islands Marine Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 26, 601-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐开达, 卢衎尔, 卢占晖, 戴乾 ( 2018) 韭山列岛自然保护区虾类优势种生态位. 生物多样性, 26, 601-610.] | |
| [42] | Xue Y, Xu BD, Gao TX, Xu H, Lin LS ( 2010) Preliminary study on the feeding habit of Lophius litulon during autumn in the North Yellow Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40, 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 薛莹, 徐宾铎, 高天翔, 徐浩, 林龙山 ( 2010) 北黄海秋季黄鮟鱇摄食习性的初步研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 40, 39-44.] | |
| [43] | Zhang B, Jin XS, Tang QS ( 2009) Functional groups of high trophic level communities in adjacent waters of Changjiang estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20, 344-351. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张波, 金显仕, 唐启升 ( 2009) 长江口及邻近海域高营养层次生物群落功能群及其变化. 应用生态学报, 20, 344-351.] | |
| [44] | Zhang B, Tang QS, Jin XS ( 2007) Functional groups of fish assemblages and their major species at high trophic level in the East China Sea. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 14, 939-949. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张波, 唐启升, 金显仕 ( 2007) 东海高营养层次鱼类功能群及其主要种类. 中国水产科学, 14, 939-949.] | |
| [45] | Zhang HL, Song ZQ, Pan GL, Chen F, Zhou YD ( 2013) Diversity analysis of fish in the coastal area of Zhejiang during spring. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 44, 126-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张洪亮, 宋之琦, 潘国良, 陈峰, 周永东 ( 2013) 浙江南部近海春季鱼类多样性分析. 海洋与湖沼, 44, 126-134.] | |
| [46] | Zhang LL, Jiang RJ, Yin R, Xu KD, Fang F, Xu YP, Ke AY ( 2019) Spatial niche and differentiation of major nekton species in Yueqing Bay, Zhejiang, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30, 3911-3920. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张琳琳, 蒋日进, 印瑞, 徐开达, 方芳, 徐义平, 柯爱英 ( 2019) 乐清湾主要游泳动物空间生态位及其分化. 应用生态学报, 30, 3911-3920.] | |
| [47] | Zhao SL, Xu HX, Zhong JS, Chen J ( 2016) Zhejiang Marine Ichthyology. Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵盛龙, 徐汉祥, 钟俊生, 陈健 ( 2016) 浙江海洋鱼类志. 浙江科学技术出版社, 杭州.] | |
| [48] | Zhao YQ, Zeng JN, Gao AG, Chen QZ, Liao YB, Shou L ( 2009) Community pattern and diversity of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat, Jiaojiang Estuary. Biodiversity Science, 17, 303-309. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵永强, 曾江宁, 高爱根, 陈全震, 廖一波, 寿鹿 ( 2009) 椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物群落格局与多样性. 生物多样性, 17, 303-309.] | |
| [49] | Zhuang P, Luo G, Zhang T, Zhang LZ, Liu J, Feng GP, Hou JL ( 2010) Food comparison among juvenile Acipen sersinensis and other six economic fishes in the Yangtze estuary. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 5544-5554. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 庄平, 罗刚, 张涛, 章龙珍, 刘健, 冯广朋, 侯俊利 ( 2010) 长江口水域中华鲟幼鱼与6种主要经济鱼类的食性及食物竞争. 生态学报, 30, 5544-5554.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()