



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (6): 533-548. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.09253
所属专题: 群落中的物种多样性:格局与机制
方精云1,*( ), 王襄平1,2, 沈泽昊1, 唐志尧1, 贺金生1, 于丹3, 江源4, 王志恒1, 郑成洋1, 朱江玲1, 郭兆迪1
), 王襄平1,2, 沈泽昊1, 唐志尧1, 贺金生1, 于丹3, 江源4, 王志恒1, 郑成洋1, 朱江玲1, 郭兆迪1
收稿日期:2009-10-29
接受日期:2009-11-27
出版日期:2009-11-20
发布日期:2009-11-20
通讯作者:
方精云
作者简介:*E-mail: jyfang@urban.pku.edu.cn基金资助:
Jingyun Fang1,*( ), Xiangping Wang1,2, Zehao Shen1, Zhiyao Tang1, Jinsheng He1, Dan Yu3, Yuan Jiang4, Zhiheng Wang1, Chengyang Zheng1, Jiangling Zhu1, Zhaodi Guo1
), Xiangping Wang1,2, Zehao Shen1, Zhiyao Tang1, Jinsheng He1, Dan Yu3, Yuan Jiang4, Zhiheng Wang1, Chengyang Zheng1, Jiangling Zhu1, Zhaodi Guo1
Received:2009-10-29
Accepted:2009-11-27
Online:2009-11-20
Published:2009-11-20
Contact:
Jingyun Fang
摘要:
植物群落是不同植物在长期环境变化中相互作用、相互适应而形成的组合。它提供着人类赖以生存的主要物质资源, 维系着地球生态系统的健康和功能, 也为各种动物和其他生物提供食物来源和栖息地, 是人类生存和发展不可或缺的物质基础, 具有不可替代的作用。我国植物群落类型多样, 在世界上首屈一指, 但我国至今尚没有一次全面和系统的植物群落清查, 不仅影响了人们对我国植物资源的了解、利用和保护, 也不利于我国生态学、环境科学和地理学等相关学科的发展。采用统一的方法体系和技术规范开展我国植物群落的清查工作势在必行, 并具有紧迫性。本文基于作者长期的野外工作实践和国内外的群落调查方法, 首先简要定义了与植物群落清查有关的重要概念, 在此基础上, 论述了调查样地的设置原则和体系、群落清查的技术指标和方法、主要优势种生态属性的测定方法和规范, 并介绍了大样地调查的主要步骤。通过本文的介绍、归纳和总结, 试图为制定我国植物群落清查的技术规范提供基础材料和技术储备。
方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 (2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253.
Jingyun Fang, Xiangping Wang, Zehao Shen, Zhiyao Tang, Jinsheng He, Dan Yu, Yuan Jiang, Zhiheng Wang, Chengyang Zheng, Jiangling Zhu, Zhaodi Guo (2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253.
| 分级 Scale | + | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盖度范围 Range of coverage (%) | 少有出现 Rare | 0-5 | 5-25 | 25-50 | 50-75 | >75 |
表1 Braun-Blanquet的盖度分级标准
Table 1 Braun-Blanquet scales of species coverage in plant communities
| 分级 Scale | + | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盖度范围 Range of coverage (%) | 少有出现 Rare | 0-5 | 5-25 | 25-50 | 50-75 | >75 |
| 分级 Scale | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 符号 Symbol | soc | cop3 | cop2 | cop1 | sp | sol | un |
| 描述 Description | 极多 | 很多 | 多 | 尚多 | 不多 | 稀少 | 单株 |
表2 Drude的多度分级标准
Table 2 Drude scales of the species abundance in plant communities
| 分级 Scale | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 符号 Symbol | soc | cop3 | cop2 | cop1 | sp | sol | un |
| 描述 Description | 极多 | 很多 | 多 | 尚多 | 不多 | 稀少 | 单株 |
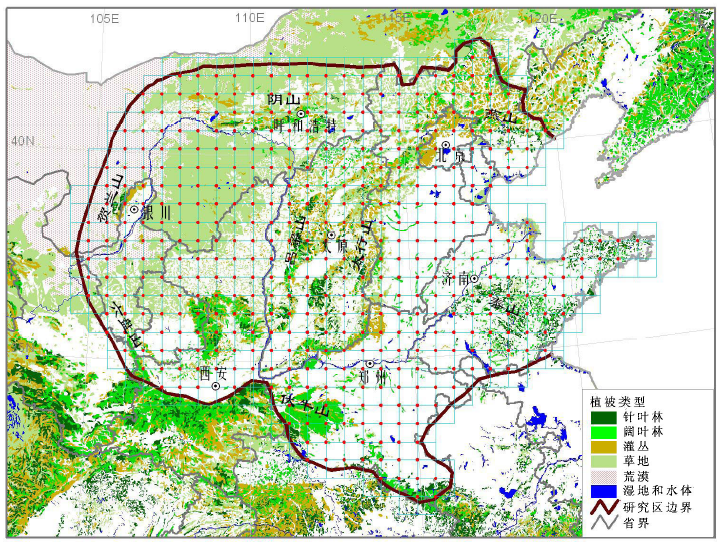
图2 华北及邻近地区植物群落清查的系统布点样地位置示意图。底图取自1: 100万中国植被图(侯学煜, 2001)。
Fig. 2 Systematic sampling sites for plant community inventory in the North China and the adjacent areas. The background shows the distribution of vegetation based on the Vegetation Atlas of China (1:1,000,000) (Hou, 2001).

图3 植物群落剖面示意图。引自《福建植被》 (林鹏, 1990)。调查地点为翠安县三港二里坪, 海拔770 m。1: 甜槠; 2: 青冈; 3: 东南石栎; 4: 光叶石楠; 5: 南岭山矾; 6: 鹿角杜鹃; 7: 马银花; 8: 粗叶木; 9: 肿节竹; 10: 细齿叶柃; 11: 中华里白。
Fig. 3 Illustration of vertical structure of the forest comm- unity (from Lin, 1990). The plot is located at Erliping, Cuian County, Fujian, at an altitude of 770 m above sea level. The species are: 1, Castanopsis eyrei; 2, Cyclobalanopsis glauca; 3, Lithocarpus harlandii; 4, Photinia glabra; 5, Symplocos confusa; 6, Rhododendron latoucheae; 7, R. ovatum; 8, Lasianthus chinensis; 9, Oligostachyum oedogonatum; 10, Eurya nitida; 11, Hicriopteris chinensis.
| 样方编号 | 群落类型 | 样方面积 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 调查地点 | 省 县(林业局) 乡(林场) 村(林班) | |||||||||
| 具体位置描述: | ||||||||||
| 纬度 | 地形 | ( )山地 ( )洼地 ( )丘陵 ( )平原 ( )高原 | ||||||||
| 经度 | 坡位 | ( )谷地 ( )下部 ( )中下部 ( )中部 | ||||||||
| 海拔 | ( )中上部 ( )山顶 ( )山脊 | |||||||||
| 坡向 | 森林起源 | ( )原始林 ( )次生林 ( )人工林 | ||||||||
| 坡度 | 干扰程度 | ( )无干扰 ( )轻微 ( )中度 ( )强度 | ||||||||
| 土壤类型 | 林龄 | 群落剖面图: | ||||||||
| 垂直结构 | 层高(m) | 盖度(%) | 优势种 | |||||||
| 乔木层 | ||||||||||
| 亚乔木层 | ||||||||||
| 灌木层 | ||||||||||
| 草本层 | ||||||||||
| 调查人 | ||||||||||
| 记录人 | 调查日期 | |||||||||
附表1 森林群落样方基本信息表
Appendix 1 Records for forest plots
| 样方编号 | 群落类型 | 样方面积 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 调查地点 | 省 县(林业局) 乡(林场) 村(林班) | |||||||||
| 具体位置描述: | ||||||||||
| 纬度 | 地形 | ( )山地 ( )洼地 ( )丘陵 ( )平原 ( )高原 | ||||||||
| 经度 | 坡位 | ( )谷地 ( )下部 ( )中下部 ( )中部 | ||||||||
| 海拔 | ( )中上部 ( )山顶 ( )山脊 | |||||||||
| 坡向 | 森林起源 | ( )原始林 ( )次生林 ( )人工林 | ||||||||
| 坡度 | 干扰程度 | ( )无干扰 ( )轻微 ( )中度 ( )强度 | ||||||||
| 土壤类型 | 林龄 | 群落剖面图: | ||||||||
| 垂直结构 | 层高(m) | 盖度(%) | 优势种 | |||||||
| 乔木层 | ||||||||||
| 亚乔木层 | ||||||||||
| 灌木层 | ||||||||||
| 草本层 | ||||||||||
| 调查人 | ||||||||||
| 记录人 | 调查日期 | |||||||||
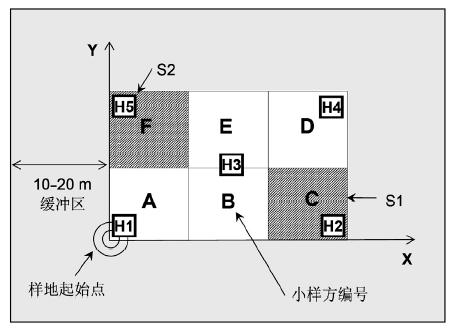
图4 森林群落样方设置和样格编号方法。样方面积20 m×30 m, 由6个10 m×10 m的样格组成, A-F为样格编号, S1和S2(阴影部分)为灌木层调查样格; H1-5为草本调查小样方。样方四边应各留有10-20 m以上的缓冲区。
Fig. 4 Plot setting and quadrate coding for forest communities. The 20 m × 30 m plot is composed of six quadrates (A-F), each with an area of 10 m×10 m. The shadowed quadrates (S1 and S2) were selected for shrub layer investigation, and subplots (H1-5) were selected for herbaceous layer investigation. A buffering zone of 10-20 m at each side of the plot is necessary to keep the plot away from apparent human activities.
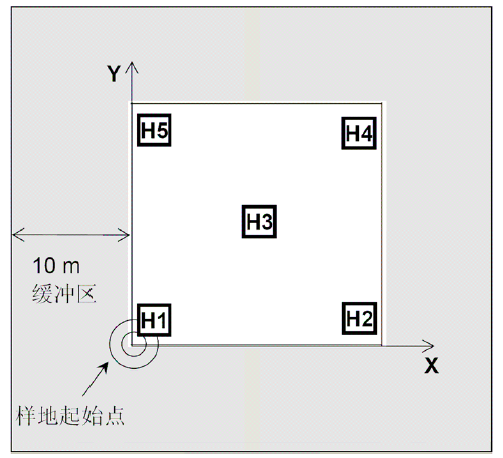
图7 灌丛(草地)样方设置方法。样方面积10 m × 10 m, 其中H1-5为详细调查小样方。样方四边应各留有10 m的缓冲区。对于灌丛, 需要调查整个样方(10 m × 10 m); 对于草地, 一般只调查5个小样方。
Fig. 7 Plot setting of shrub (grassland) communities. Five subplots (H1-5) were selected within each 10 m ×10 m plot. A buffering zone of 10 m at each side of the plot is necessary to keep the plot away from apparent human activities. For shrubs, whole plot (10 m × 10 m) should be investigated, and for grasslands, five subplots will be investigated.
| 属性 Traits | 建议的计量单位Unit suggested | 范围 Range | 最小重复数 Minimum replications | 推荐的重复数 Suggested replications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片属性 Leaf | |||||
| 叶片大小 Leaf size | mm2 | 1-106 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness | mm | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 叶片干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content | mg/g | 50-700 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | mm2/mg | 2-80 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 叶寿命 Leaf lifespan | month | 0.5-200 | 3, 12 | 10, 12 | |
| 叶片N Leaf N concentration | mg/g | 10-60 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 叶片P Leaf P concentration | mg/g | 0.5-5 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 最大光合速率 Maximum photosynthetic rate | μmol·m-2·s-1 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 气孔导度 Leaf stomatal water conductance | mol·m-2·s-1 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 蒸腾速率 Leaf transpiration | mol·m-2·s-1 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 枝干属性 Stem | |||||
| 树皮厚度 Bark thickness | mm | 5 | 10 | ||
| 树干密度 Stem specific density | mg/mm3 | 0.4-1.2 | 5 | 10 | |
| 心材/边材比率 Heartwood to sapwood area ratio | unitless | 5 | 10 | ||
| 树干高度 Stem height | m | ? -100 | 10 | 25 | |
| 根系属性 Root | |||||
| 类型 Root type | cat. | 5 | 10 | ||
| 比根长 Specific root length | m/g | 10-500 | 5, 10 | 10, 10 | |
| 细根直径 Fine root diameter | mm | 5, 10 | 10, 10 | ||
| 组织密度 Tissue density | mg/mm3 | 5, 10 | 10, 10 | ||
| 细根N Fine root N concentration | mg/g | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 细根P Fine root P concentration | mg/g | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 繁殖属性 Reproduction | |||||
| 种子大小 Seed mass | mg | 10-3-107 | 3, 5 | 10, 5 | |
| 传播类型 Dispersal mode | cat. | 3 | 3 | ||
| 萌枝能力 Resprouting capacity | unitless | 0-100 | 5 | 25 | |
表3 植物属性的计量单位、一般数值范围、要求的最小重复数和推荐的重复数。在最小重复数和推荐重复数中, 第一个数值代表个体数, 第2个数值代表器官数。此表基于Cornelissen等(2003a)、Pregitzer等(2002)以及He等(2006b)等归纳。
Table 3 Metric units, range, minimum and suggested replications for plant trait measurements. The first and second numbers in the minimum (and suggested) replications represent replications of individuals and organs, respectively. This table is summarized from Cornelissen et al. (2003a), Pregitzer et al. (2002), and He et al. (2006b)
| 属性 Traits | 建议的计量单位Unit suggested | 范围 Range | 最小重复数 Minimum replications | 推荐的重复数 Suggested replications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片属性 Leaf | |||||
| 叶片大小 Leaf size | mm2 | 1-106 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness | mm | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 叶片干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content | mg/g | 50-700 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | mm2/mg | 2-80 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 叶寿命 Leaf lifespan | month | 0.5-200 | 3, 12 | 10, 12 | |
| 叶片N Leaf N concentration | mg/g | 10-60 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 叶片P Leaf P concentration | mg/g | 0.5-5 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | |
| 最大光合速率 Maximum photosynthetic rate | μmol·m-2·s-1 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 气孔导度 Leaf stomatal water conductance | mol·m-2·s-1 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 蒸腾速率 Leaf transpiration | mol·m-2·s-1 | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 枝干属性 Stem | |||||
| 树皮厚度 Bark thickness | mm | 5 | 10 | ||
| 树干密度 Stem specific density | mg/mm3 | 0.4-1.2 | 5 | 10 | |
| 心材/边材比率 Heartwood to sapwood area ratio | unitless | 5 | 10 | ||
| 树干高度 Stem height | m | ? -100 | 10 | 25 | |
| 根系属性 Root | |||||
| 类型 Root type | cat. | 5 | 10 | ||
| 比根长 Specific root length | m/g | 10-500 | 5, 10 | 10, 10 | |
| 细根直径 Fine root diameter | mm | 5, 10 | 10, 10 | ||
| 组织密度 Tissue density | mg/mm3 | 5, 10 | 10, 10 | ||
| 细根N Fine root N concentration | mg/g | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 细根P Fine root P concentration | mg/g | 5, 2 | 10, 2 | ||
| 繁殖属性 Reproduction | |||||
| 种子大小 Seed mass | mg | 10-3-107 | 3, 5 | 10, 5 | |
| 传播类型 Dispersal mode | cat. | 3 | 3 | ||
| 萌枝能力 Resprouting capacity | unitless | 0-100 | 5 | 25 | |
| 属性 Traits | 测定方法 Measuring methods |
|---|---|
| 叶片属性 Leaf 叶片大小 Leaf size | 叶面积仪(如Delta-T (Cambridge, UK), Li-Cor (Lincoln, Nebraska, USA)), 或扫描仪 |
| 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness | 显微镜或游标卡尺测量 |
| 叶片干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content | 叶片装入自封袋, 加水浸湿, 保持12 h以上, 吸掉多余水分, 称鲜重; 60℃烘干至少72 h(或80℃至少48 h), 称干重, 计算 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 面积测定: 叶面积仪(如Delta-T (Cambridge, UK), Li-Cor (Lincoln, Nebraska, USA)。干重测定: 烘箱60℃烘烤至少72 h(或80℃至少48 h), 称干重。由叶面积和干重计算比叶面积。 |
| 叶寿命 Leaf lifespan | 双子叶植物: 叶片标记法; 单子叶植物: 测定叶片特定区域的生产和死亡动态, 具体见 |
| 叶片N Leaf N concentration | 元素分析仪法(2400Ⅱ CHNS/O Elemental Analyzer, Perkin-Elmer, Boston, MA,USA)( |
| 叶片P Leaf P concentration | 钼蓝比色法 ( |
| 最大光合速率 Pnmax | Li-6400便携式光合仪测定, 建议设光照=1,500 μmol/(m2·s1), [CO2] = 380 ppm |
| 气孔导度 Gs | Li-6400便携式光合仪测定 |
| 蒸腾速率 Tr | Li-6400便携式光合仪测定 |
| 枝干属性 Stem | |
| 树皮厚度 Bark thickness | 游标卡尺测量 |
| 树干密度 Stem specific density | 体积替代法: 鲜树干完全浸于盛水的量筒中约5 s, 读取增加的体积; 烘箱中60℃烘烤至少72 h (小树干)或96 h (大树干), 称干重。由体积和重量计算树干密度 |
| 心材/边材比率 Heartwood to sapwood area ratio | 钻取生长芯, 经打磨处理后, 用高精度扫描仪进行图像扫描, 据心材和边材颜色区分其界限, 用年轮分析软件测量每个生长芯的树皮厚度、边材宽度和边材年轮数。以树干横断面为标准圆形计算心材/边材比率 |
| 树干高度 Stem height | 直接测量法(如激光测距仪)和三角函数法 |
| 根系属性 Root | |
| 类型 Root type | 参照 |
| 比根长 Specific root length | 解剖镜下区分出活的、完整的根, 用目镜测微尺测量长度; 或用WinRHIZO根系分析系统, 60℃下至少烘烤72 h(或80℃至少48 h), 称重, 然后计算比根长 |
| 细根直径 Fine root diameter | 解剖镜下区分出活的、完整的根, 用目镜测微尺校正细根直径 |
| 组织密度 Tissue density | 根干重/根体积, 详细内容参见 |
| 细根N Fine root N concentration | 元素分析仪法(如CHNS/O Elemental Analyzer, Perkin-Elmer, Boston, MA, USA)或微量凯氏定氮法 |
| 细根P Fine root N concentration | 钼蓝比色法 ( |
| 繁殖属性 Reproduction | |
| 种子大小 Seed mass | 野外采成熟果实, 清理(洗)出种子, 统计种子数目, 80℃下至少烘烤48 h, 直到恒重, 称重。 |
| 传播类型 Dispersal mode | 记录所有与传播有关的分类学特征, 据重要性按降序排列。具体分类特征见 |
| 萌枝能力 Resprouting capacity | 根据萌枝数, 划分等级 |
表4 植物生态属性的常见测定方法
Table 4 Measuring methods for ecological traits of plants
| 属性 Traits | 测定方法 Measuring methods |
|---|---|
| 叶片属性 Leaf 叶片大小 Leaf size | 叶面积仪(如Delta-T (Cambridge, UK), Li-Cor (Lincoln, Nebraska, USA)), 或扫描仪 |
| 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness | 显微镜或游标卡尺测量 |
| 叶片干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content | 叶片装入自封袋, 加水浸湿, 保持12 h以上, 吸掉多余水分, 称鲜重; 60℃烘干至少72 h(或80℃至少48 h), 称干重, 计算 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 面积测定: 叶面积仪(如Delta-T (Cambridge, UK), Li-Cor (Lincoln, Nebraska, USA)。干重测定: 烘箱60℃烘烤至少72 h(或80℃至少48 h), 称干重。由叶面积和干重计算比叶面积。 |
| 叶寿命 Leaf lifespan | 双子叶植物: 叶片标记法; 单子叶植物: 测定叶片特定区域的生产和死亡动态, 具体见 |
| 叶片N Leaf N concentration | 元素分析仪法(2400Ⅱ CHNS/O Elemental Analyzer, Perkin-Elmer, Boston, MA,USA)( |
| 叶片P Leaf P concentration | 钼蓝比色法 ( |
| 最大光合速率 Pnmax | Li-6400便携式光合仪测定, 建议设光照=1,500 μmol/(m2·s1), [CO2] = 380 ppm |
| 气孔导度 Gs | Li-6400便携式光合仪测定 |
| 蒸腾速率 Tr | Li-6400便携式光合仪测定 |
| 枝干属性 Stem | |
| 树皮厚度 Bark thickness | 游标卡尺测量 |
| 树干密度 Stem specific density | 体积替代法: 鲜树干完全浸于盛水的量筒中约5 s, 读取增加的体积; 烘箱中60℃烘烤至少72 h (小树干)或96 h (大树干), 称干重。由体积和重量计算树干密度 |
| 心材/边材比率 Heartwood to sapwood area ratio | 钻取生长芯, 经打磨处理后, 用高精度扫描仪进行图像扫描, 据心材和边材颜色区分其界限, 用年轮分析软件测量每个生长芯的树皮厚度、边材宽度和边材年轮数。以树干横断面为标准圆形计算心材/边材比率 |
| 树干高度 Stem height | 直接测量法(如激光测距仪)和三角函数法 |
| 根系属性 Root | |
| 类型 Root type | 参照 |
| 比根长 Specific root length | 解剖镜下区分出活的、完整的根, 用目镜测微尺测量长度; 或用WinRHIZO根系分析系统, 60℃下至少烘烤72 h(或80℃至少48 h), 称重, 然后计算比根长 |
| 细根直径 Fine root diameter | 解剖镜下区分出活的、完整的根, 用目镜测微尺校正细根直径 |
| 组织密度 Tissue density | 根干重/根体积, 详细内容参见 |
| 细根N Fine root N concentration | 元素分析仪法(如CHNS/O Elemental Analyzer, Perkin-Elmer, Boston, MA, USA)或微量凯氏定氮法 |
| 细根P Fine root N concentration | 钼蓝比色法 ( |
| 繁殖属性 Reproduction | |
| 种子大小 Seed mass | 野外采成熟果实, 清理(洗)出种子, 统计种子数目, 80℃下至少烘烤48 h, 直到恒重, 称重。 |
| 传播类型 Dispersal mode | 记录所有与传播有关的分类学特征, 据重要性按降序排列。具体分类特征见 |
| 萌枝能力 Resprouting capacity | 根据萌枝数, 划分等级 |
| [1] |
Arrhenius O (1921) Species and area. Journal of Ecology, 9, 95-99.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bekker RM, van der Maarel E, Bruelheide H, Woods K (2007) Long-term datasets: from descriptive to predictive data using ecoinformatics. Journal of Vegetation Science, 18, 458-462.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Braun-Blanquet J (1964) Pflanzensoziologie, Grundzüge der Vegetationskunde, 3rd edn. Springer-Verlag, Wien, New York. |
| [4] |
Cannon WA (1949) A tentative classification of root systems. Ecology, 30, 542-548.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chave J, Coomes D, Jansen S, Lewis SL, Swenson NG, Zanne AE (2009) Towards a worldwide wood economics spectrum. Ecology Letters, 12, 351-366.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots, pp.1-224. Springer, Berlin. |
| [7] |
Condit R, Hubbell SP, Lafrankie JV, Sukumar R, Manokaran N, Foster RB, Ashton PS (1996) Species-area and species-individual relationships for tropical trees: a comparison of three 50-ha plots. Journal of Ecology, 84, 549-562.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Condit R, Pitman N, Leigh EG, Chave J, Terborgh J, Foster RB, Núñez P, Aguilar S, Valencia R, Villa G, Losos E, Hubbell SP (2002) Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees. Science, 295, 666-669.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Cornelissen JHC, Cerabolini B, Castro-Díaz P, Villar-Salvador P, Montserrat-Martí G, Puyravaud JP, Maestro M, Werger MJA, Aerts R (2003a) Functional traits of woody plants: correspondence of species rankings between field adults and laboratory-grown seedlings? Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 311-322.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Cornelissen JHC, Lavorel S, Garnier E, Diaz S, Buchmann N, Gurvich DE, Reich PB, ter Steege H, Morgan HD, van der Heijden MGA, Pausas JG, Poorter H (2003b) A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Australian Journal of Botany, 51, 335-380.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Dalling JW, Muller-Landau HC, Wright SJ, Hubbell SP (2002) Role of dispersal in the recruitment limitation of neotropical pioneer species. Journal of Ecology, 90, 714-727. |
| [12] |
De Deyn GB, Cornelissen JHC, Bardgett RD (2008) Plant functional traits and soil carbon sequestration in contrasting biomes. Ecology Letters, 11, 516-531.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Dong M (董鸣) (1996) Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Chinese Ecosystem Research Network: Survey, Observation and Analysis of Terrestrial Biocommunities (中国生态系统研究网络观测与分析标准方法: 陆地生物群落调查观测与分析). Standards Press of China, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [14] |
Drakare S, Lennon JJ, Hillebrand H (2006) The imprint of the geographical, evolutionary and ecological context on species-area relationships. Ecology Letters, 9, 215-227.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] | Fang JY, Brown S, Tang YH, Naruurs G-J, Wang XP, Shen H (2006) Overestimated biomass carbon pools of the northern mid- and high latitude forests. Climatic Change, 74, 355-368. |
| [16] | Gleason HA (1925) Species and area. Ecology, 6, 66-74. |
| [17] | Gurevitch J, Scheiner SM, Fox GA (2002) The Ecology of Plants. Sinauer Associates Inc., Massachusetts. |
| [18] |
He JS, Fang JY, Wang ZH, Guo DL, Flynn DFB, Geng Z (2006a) Stoichiometry and large-scale patterns of leaf carbon and nitrogen in the grassland biomes of China. Oecologia, 149, 115-122.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
He JS, Wang L, Flynn DFB, Wang XP, Ma WH, Fang JY (2008) Leaf nitrogen: phosphorus stoichiometry across Chinese grassland biomes. Oecologia, 155, 301-310.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | He JS, Wang XP, Flynn DFB, Wang L, Schmid B, Fang JY (2009) Taxonomic, phylogenetic and environmental trade- offs between leaf productivity and persistence. Ecology, 90, 2779-2791. |
| [21] | He JS, Wang ZH, Wang XP, Schmid B, Zuo WY, Zhou M, Zheng CY, Wang M, Fang JY (2006b) A test of the generality of leaf trait relationships on the Tibetan Plateau. New Phytologist, 170, 835-848. |
| [22] | Hou XY (侯学煜) (2001) Vegetation Atlas of China (1: 1000000) (1:100万中国植被图图集). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Hubbell SP (2001) The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography: a synopsis of the theory and some challenges ahead. In: Integrating Ecology and Evolution in a Spatial Context (eds Silvertown J, Amtonovics J), pp. 393-411. Blackwell Science, Oxford. |
| [24] |
Hubbell SP (2006) Neutral theory and the evolution of ecological equivalence. Ecology, 87, 1387-1398.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1983) Diversity of canopy trees in a neotropical forest and implications for conservation. In: Tropical Rain Forest: Ecology and Management (eds Sutton SL, Whitmore TC, Chadwick AC), pp. 25-41. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. |
| [26] |
Hubbell SP, Foster RB, O’Brien ST, Harms KE, Condit R, Wechsler B, Wright SJ, Lao S (1999) Light-gap disturbances, recruitment limitation, and tree diversity in a Neotropical forest. Science, 283, 554-557.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Kuo S (1996) Phosphorus. In: Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3, Chemical Methods (ed. Sparks DL), pp. 869-919. Soil Science Society of America, Inc., American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin. |
| [28] | Lieth H (1975) Modeling the primary productivity of the world. In: Primary Productivity of the Biosphere (eds Lieth H, Whittaker R), pp. 237-263. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [29] | Lin P (林鹏) (1990) Vegetation of Fujian Province (福建植被). Fujian Science and Technology Press, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | Ma KP (马克平) (1994) The measurement of community diversity. In: Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies (生物多样性研究的原理与方法) (eds Qian YQ (钱迎倩), Ma KP (马克平)), pp. 141-165. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Magurran AE (1988) Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [32] |
Moles AT, Ackerly DD, Webb CO, Tweddle JC, Dickie JB, Westoby M (2005) A brief history of seed size. Science, 307, 576-580.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | Petchey OL, Hector A, Gaston KJ (2004) How do different measures of functional diversity perform? Ecology, 11, 847-857. |
| [34] | Pregitzer KS, DeForest JL, Burton AJ, Allen MF, Ruess RW, Hendrick RL (2002) Fine root architecture of nine north American trees. Ecological Monographs, 72, 293-309. |
| [35] | Ryser P (1996) The importance of tissue density for growth and life span of leaves and roots: a comparison of five ecologically contrasting grasses. Functional Ecology, 10, 717-723. |
| [36] | Schaminée JHJ, Hennekens SM, Chytrý C, Rodwell JS (2009) Vegetation-plot data and databases in Europe: an overview. Preslia, 81, 173-185. |
| [37] | Sheil D, Burslem DFRP (2003) Disturbing hypotheses in tropical forests. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 18, 18-26. |
| [38] | Spellerberg IF, Fedor PJ (2001) A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916-2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness, species diversity and the Shannon-Wiener index. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 177-179. |
| [39] | Tang ZY (唐志尧), Qiao XJ (乔秀娟), Fang JY (方精云) (2009) Species-area relationship in biological communities. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 549-559. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] | Veech JA, Summerville KS, Crist TO, Gering JC (2002) The additive partitioning of species diversity: recent revial of an old idea. Oikos, 99, 3-9. |
| [41] | Wang ZH, Brown J, Tang ZY, Fang JY (2009) Temperature dependence, spatial scale, and tree species diversity in eastern Asia and North America. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 13388-13392. |
| [42] |
Weaver JE (1958) Classification of root systems of forbs of grassland and a consideration of their significance. Ecology, 39, 393-401.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution of measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251. |
| [44] |
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee WJ, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas M-L, Niinemets U, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov V I, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature, 428, 821-827.
URL PMID |
| [45] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1980) Vegetation of China (中国植被). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [46] | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Ding Hu Shan, China . Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Zhang XS (张新时) (2007) Vegetation Map of the People’s Republic of China (1:1 000 000) (1:100万中华人民共和国植被图). Geological Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [48] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gu Tian Shan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 钟欣艺, 赵凡, 姚雪, 吴雨茹, 许银, 鱼舜尧, 林静芸, 郝建锋. 三星堆遗址城墙不同维护措施下草本植物物种多样性与土壤抗冲性的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23169-. |
| [3] | 周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平. 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| [4] | 崔家鹤, 李智勇, 王宇池, 孙蔷, 莎娜, 李紫晶, 武艳涛, 史亚博, 韩瀛, 李明乐, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 垫状驼绒藜群落特征及地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23172-. |
| [5] | 王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23144-. |
| [6] | 李世雄, 王彦龙, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽. 土壤细菌群落特征对高寒草甸退化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 53-64. |
| [7] | 高趁光, 郭柯, 乔鲜果, 陆帅志, 刘长成, 侯东杰, 王孜. 草原模式植物群落监测方法应用样例[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 266-273. |
| [8] | 陈龙, 秦帅, 旭日, 杨柳, 赵利清. 阴山山脉天然侧柏林的基本特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 66-74. |
| [9] | 杨济达, 张志明, 沈泽昊, 欧晓昆, 耿宇鹏, 杨明玉. 云南干热河谷植被与环境研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 462-474. |
| [10] | 张志明, 沈蕊, 张建利, 徐倩, 罗园, 遇翘楚, 张秋霞, 欧晓昆. 元江流域干热河谷灌草丛土壤种子库与地上植物群落的物种组成比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 431-439. |
| [11] | 郭柯, 刘长成, 潘庆民. 中国草原/荒漠植物多样性监测网 模式植物群落监测方案[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(11): 1220-1226. |
| [12] | 潘开文, 张林, 邵元虎, 傅声雷. 中国土壤动物多样性监测: 探知土壤中的奥秘[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(11): 1234-1239. |
| [13] | 潘声旺, 胡明成, 罗竞红, 吴云霄. 绿化植物的生活型对边坡植被物种多样性及护坡性能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 341-350. |
| [14] | 韩大勇, 杨允菲. 松嫩草地植物群落物种多度–分布关系及其解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 348-357. |
| [15] | 王勇, 许洁, 杨刚, 李宏庆, 吴时英, 唐海明, 马波, 王正寰. 城市公共绿地常见木本植物组成对鸟类群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(2): 196-207. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn