



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (9): 1045-1055. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016062 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016062
出版日期:2016-09-20
发布日期:2016-10-09
通讯作者:
刘录三
基金资助:
Wenqian Cai, Jing Liu, Juan Zhou, Yang Xia, Lusan Liu*( )
)
Online:2016-09-20
Published:2016-10-09
Contact:
Liu Lusan
摘要:
基于2011年5月和9月2个航次获取的生物及环境数据, 分析了渤海湾大型底栖动物的功能摄食群组成, 并首次利用以生物量构建的摄食均匀度指数(the feeding evenness index, bjFD)和多元AZTI海洋生物指数(multivariate-biomass AZTI marine biotic index, M-bAMBI)对渤海湾生态质量进行评价。结果表明, 渤海湾大型底栖动物功能群由4类组成, 分别是肉食者、碎屑食者、浮游生物食者和杂食者, 未发现植食者。2个航次均以浮游生物食者和杂食者的生物量最高, 碎屑食者最低。聚类分析结果表明海河口内大型底栖动物群落功能摄食群组成与其他区域明显不同。两个航次均以海河口的重金属潜在生态风险指数值(risk index, RI)较低, 且5月航次该指数沿河口向外有明显的空间分布梯度。bjFD平均值为0.28, 指示研究区大部分区域生态质量较差, 其中低值区集中在海河口、北塘口及其附近海域, 与风险指数值的低值区基本吻合。BEST分析表明温度、盐度、重金属及营养盐等是影响bjFD变化的主要环境因子。与M-bAMBI相比, bjFD对海河口及北塘口较差的环境质量状况更为敏感。总体上, bjFD适用于评价渤海湾的生态质量。
蔡文倩, 刘静, 周娟, 夏阳, 刘录三 (2016) 基于生物量的大型底栖动物功能摄食群结构 及生态质量评价. 生物多样性, 24, 1045-1055. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016062.
Wenqian Cai, Jing Liu, Juan Zhou, Yang Xia, Lusan Liu (2016) Composition of macrozoobenthos functional feeding groups and assessment of ecological quality using the feeding evenness index calculated from biomass data. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1045-1055. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016062.
| 物种 Species | 摄食群 Feeding group | 物种 Species | 食性 Feeding group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中华内卷齿虫 Aglaophamus sinensis | CA | 双栉虫 Ampharete acutifrons | DE | ||
| 日本鼓虾 Alpheus japonicus | CA | 中华倍棘蛇尾 Amphioplus sinicus | DE | ||
| 白毛钩虫 Cabira pilargiformis | CA | 小双鳞蛇尾 Amphipholis squamata | DE | ||
| 日本浪漂水虱 Cirolana japonensis | CA | 小头虫 Capitella capitata | DE | ||
| 小头栉孔鰕虎鱼 Ctenotrypauchen chinensis | CA | 刚毛虫 Chaetozone setosa | DE | ||
| 黄海埃刺梳磷虫 Ehersileanira incisa hwanghaiensis | CA | 细丝鳃虫 Cirratulus filiformis | DE | ||
| 内肋蛤 Eocylichna braunsi | CA | 须鳃虫 Cirriformia tentaculata | DE | ||
| 渤海格鳞虫 Gattyana pohaiensis | CA | 三叶针尾涟虫 Diastylis tricincta | DE | ||
| 长吻沙蚕 Glycera chirori | CA | 内肋蛤 Endopleura lubrica | DE | ||
| 锥唇吻沙蚕 Glycera onomichiensis | CA | 塞切尔泥钩虾 Eriopisella sechellensis | DE | ||
| 寡节甘吻沙蚕 Glycinde gurjanovae | CA | 丝异须虫 Heteromastus filiforms | DE | ||
| 日本角吻沙蚕 Goniada japonica | CA | 异足科索沙蚕 Kuwaita heteropoda | DE | ||
| 色斑角吻沙蚕 Goniada maculata | CA | 中华后指虫 Laonice sinica | DE | ||
| 软背鳞虫 Lepidonotus helotypus | CA | 短吻铲荚鎰 Listriolobus brevirostris | DE | ||
| 含糊拟刺虫 Linopherus ambigua | CA | 中国索沙蚕 Lumbrineris sinensis | DE | ||
| 岩虫 Marphysa sanguinea | CA | 索沙蚕属一种 Lumbrineris sp. | DE | ||
| 红带织纹螺 Nassarius succinctus | CA | 尖叶长手沙蚕 Magelona cincta | DE | ||
| 全刺沙蚕 Nectoneanthes oxypoda | CA | 彩虹明樱蛤 Moerella iridescens | DE | ||
| 纽虫一种 Nemertinea sp. | CA | 多齿沙蚕 Nereis multignatha | DE | ||
| 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nepthys oligobranchia | CA | 背蚓虫 Notomastus latericeus | DE | ||
| 狭细蛇潜虫 Ophiodromus angustifrons | CA | 豆形核桃蛤 Nucula faba | DE | ||
| 拟特须虫 Paralacydonia paradoxa | CA | 梳鳃虫 Terebellides stroemii | DE | ||
| 格陵兰半突虫 Phyllodoce groenlandica | CA | 对称拟蚶 Arcopsis symmetrica | DE | ||
| 乳突半突虫 Phyllodoce papillosa | CA | 双纹须蚶 Barbatia bistrigata | DE | ||
| 肥壮巴豆蟹 Pinnixa tumida | CA | 大螺赢蜚 Corophium major | PL | ||
| 耳口露齿螺 Ringicula doliaris | CA | 中华螺赢蜚 Corophium sinensis | PL | ||
| 深钩毛虫 Sigambra bassi | CA | 小刀蛏 Cultellus attenuatus | PL | ||
| 叉毛卷须虫 Cirrophorus furcatus | OM | 津知圆蛤 Cycladicama tsuchi | PL | ||
| 异足倒颚蟹 Asthenognathus inaequipes | OM | 凸镜蛤 Dosinia derupta | PL | ||
| 黄色刺沙蚕 Neanthes flava | OM | 细螯虾 Leptochela gracilis | PL | ||
| 豆形拳蟹 Philyra pisum | OM | 微黄镰玉螺 Lunatia yokoyamai | PL | ||
| 扁形动物门一种 Platyhelminthes sp. | OM | 长偏顶蛤 Modiolus elongatus | PL | ||
| 杂毛虫属一种 Poecilochaetus sp. | OM | 凸壳肌蛤 Musculus senhousei | PL | ||
| 锯额瓷蟹 Porcellana serratifrons | OM | 黑龙江篮蛤 Potamocorbula amurensis | PL | ||
| 绒毛细足蟹 Raphidopus ciliatus | OM | 光滑篮蛤 Potamocorbula laevis | PL | ||
| 哈氏刻肋海胆 Temnopleurus hardwickii | OM | 秀丽波纹蛤 Raetellops pulchella | PL | ||
| 短角双眼钩虾 Ampelisca brevicornis | DE | 金星碟铰蛤 Trigonothracia jinxingae | PL | ||
表1 渤海湾主要大型底栖动物功能摄食群
Table 1 Functional feeding groups for the key macrozoobenthos species in the Bohai Bay
| 物种 Species | 摄食群 Feeding group | 物种 Species | 食性 Feeding group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中华内卷齿虫 Aglaophamus sinensis | CA | 双栉虫 Ampharete acutifrons | DE | ||
| 日本鼓虾 Alpheus japonicus | CA | 中华倍棘蛇尾 Amphioplus sinicus | DE | ||
| 白毛钩虫 Cabira pilargiformis | CA | 小双鳞蛇尾 Amphipholis squamata | DE | ||
| 日本浪漂水虱 Cirolana japonensis | CA | 小头虫 Capitella capitata | DE | ||
| 小头栉孔鰕虎鱼 Ctenotrypauchen chinensis | CA | 刚毛虫 Chaetozone setosa | DE | ||
| 黄海埃刺梳磷虫 Ehersileanira incisa hwanghaiensis | CA | 细丝鳃虫 Cirratulus filiformis | DE | ||
| 内肋蛤 Eocylichna braunsi | CA | 须鳃虫 Cirriformia tentaculata | DE | ||
| 渤海格鳞虫 Gattyana pohaiensis | CA | 三叶针尾涟虫 Diastylis tricincta | DE | ||
| 长吻沙蚕 Glycera chirori | CA | 内肋蛤 Endopleura lubrica | DE | ||
| 锥唇吻沙蚕 Glycera onomichiensis | CA | 塞切尔泥钩虾 Eriopisella sechellensis | DE | ||
| 寡节甘吻沙蚕 Glycinde gurjanovae | CA | 丝异须虫 Heteromastus filiforms | DE | ||
| 日本角吻沙蚕 Goniada japonica | CA | 异足科索沙蚕 Kuwaita heteropoda | DE | ||
| 色斑角吻沙蚕 Goniada maculata | CA | 中华后指虫 Laonice sinica | DE | ||
| 软背鳞虫 Lepidonotus helotypus | CA | 短吻铲荚鎰 Listriolobus brevirostris | DE | ||
| 含糊拟刺虫 Linopherus ambigua | CA | 中国索沙蚕 Lumbrineris sinensis | DE | ||
| 岩虫 Marphysa sanguinea | CA | 索沙蚕属一种 Lumbrineris sp. | DE | ||
| 红带织纹螺 Nassarius succinctus | CA | 尖叶长手沙蚕 Magelona cincta | DE | ||
| 全刺沙蚕 Nectoneanthes oxypoda | CA | 彩虹明樱蛤 Moerella iridescens | DE | ||
| 纽虫一种 Nemertinea sp. | CA | 多齿沙蚕 Nereis multignatha | DE | ||
| 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nepthys oligobranchia | CA | 背蚓虫 Notomastus latericeus | DE | ||
| 狭细蛇潜虫 Ophiodromus angustifrons | CA | 豆形核桃蛤 Nucula faba | DE | ||
| 拟特须虫 Paralacydonia paradoxa | CA | 梳鳃虫 Terebellides stroemii | DE | ||
| 格陵兰半突虫 Phyllodoce groenlandica | CA | 对称拟蚶 Arcopsis symmetrica | DE | ||
| 乳突半突虫 Phyllodoce papillosa | CA | 双纹须蚶 Barbatia bistrigata | DE | ||
| 肥壮巴豆蟹 Pinnixa tumida | CA | 大螺赢蜚 Corophium major | PL | ||
| 耳口露齿螺 Ringicula doliaris | CA | 中华螺赢蜚 Corophium sinensis | PL | ||
| 深钩毛虫 Sigambra bassi | CA | 小刀蛏 Cultellus attenuatus | PL | ||
| 叉毛卷须虫 Cirrophorus furcatus | OM | 津知圆蛤 Cycladicama tsuchi | PL | ||
| 异足倒颚蟹 Asthenognathus inaequipes | OM | 凸镜蛤 Dosinia derupta | PL | ||
| 黄色刺沙蚕 Neanthes flava | OM | 细螯虾 Leptochela gracilis | PL | ||
| 豆形拳蟹 Philyra pisum | OM | 微黄镰玉螺 Lunatia yokoyamai | PL | ||
| 扁形动物门一种 Platyhelminthes sp. | OM | 长偏顶蛤 Modiolus elongatus | PL | ||
| 杂毛虫属一种 Poecilochaetus sp. | OM | 凸壳肌蛤 Musculus senhousei | PL | ||
| 锯额瓷蟹 Porcellana serratifrons | OM | 黑龙江篮蛤 Potamocorbula amurensis | PL | ||
| 绒毛细足蟹 Raphidopus ciliatus | OM | 光滑篮蛤 Potamocorbula laevis | PL | ||
| 哈氏刻肋海胆 Temnopleurus hardwickii | OM | 秀丽波纹蛤 Raetellops pulchella | PL | ||
| 短角双眼钩虾 Ampelisca brevicornis | DE | 金星碟铰蛤 Trigonothracia jinxingae | PL | ||
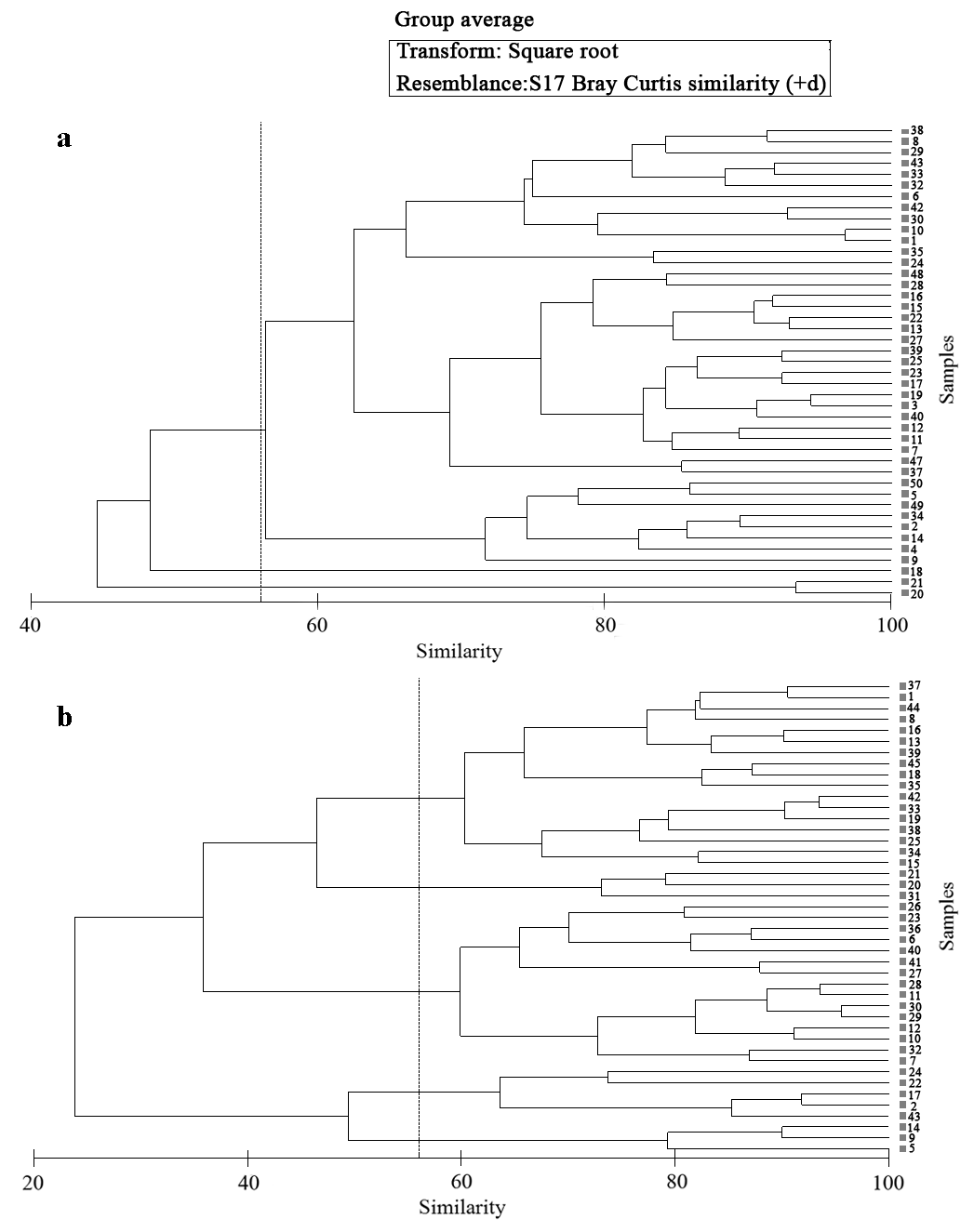
图4 2011年5月(a)和9月(b)航次摄食均匀度指数聚类分析结果
Fig. 4 Cluster analysis on the bjFD for the voyages of May and September, 2011 in the Bohai Bay. a, May; b, September.
| 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September | 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September | 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September | 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 14 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 27 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 40 | 0.19 | 0.46 |
| 2 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 15 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 28 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 41 | - | 0.06 |
| 3 | 0.55 | - | 16 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 29 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 42 | 0.75 | 0.21 |
| 4 | 0.16 | - | 17 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 30 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 43 | 0.27 | 0.05 |
| 5 | 0.38 | 0.00 | 18 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 31 | - | 0.11 | 44 | - | 0.50 |
| 6 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 19 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 32 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 45 | - | 0.35 |
| 7 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 33 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 47 | 0.33 | - |
| 8 | 0.61 | 0.76 | 21 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 34 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 48 | 0.18 | - |
| 9 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 22 | 0.48 | 0.64 | 35 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 49 | 0.37 | - |
| 10 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 23 | 0.15 | 0.58 | 36 | - | 0.31 | 50 | 0.42 | - |
| 11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 24 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 37 | 0.38 | 0.64 | |||
| 12 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 25 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 38 | 0.64 | 0.37 | |||
| 13 | 0.30 | 0.78 | 26 | - | 0.62 | 39 | 0.22 | 0.43 |
表2 渤海湾各样点摄食均匀度指数值
Table 2 The values of the feeding evenness index for all the stations in the Bohai Bay
| 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September | 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September | 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September | 样点 Station | 5月 May | 9月 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 14 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 27 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 40 | 0.19 | 0.46 |
| 2 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 15 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 28 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 41 | - | 0.06 |
| 3 | 0.55 | - | 16 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 29 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 42 | 0.75 | 0.21 |
| 4 | 0.16 | - | 17 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 30 | 0.66 | 0.01 | 43 | 0.27 | 0.05 |
| 5 | 0.38 | 0.00 | 18 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 31 | - | 0.11 | 44 | - | 0.50 |
| 6 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 19 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 32 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 45 | - | 0.35 |
| 7 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 33 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 47 | 0.33 | - |
| 8 | 0.61 | 0.76 | 21 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 34 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 48 | 0.18 | - |
| 9 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 22 | 0.48 | 0.64 | 35 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 49 | 0.37 | - |
| 10 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 23 | 0.15 | 0.58 | 36 | - | 0.31 | 50 | 0.42 | - |
| 11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 24 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 37 | 0.38 | 0.64 | |||
| 12 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 25 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 38 | 0.64 | 0.37 | |||
| 13 | 0.30 | 0.78 | 26 | - | 0.62 | 39 | 0.22 | 0.43 |
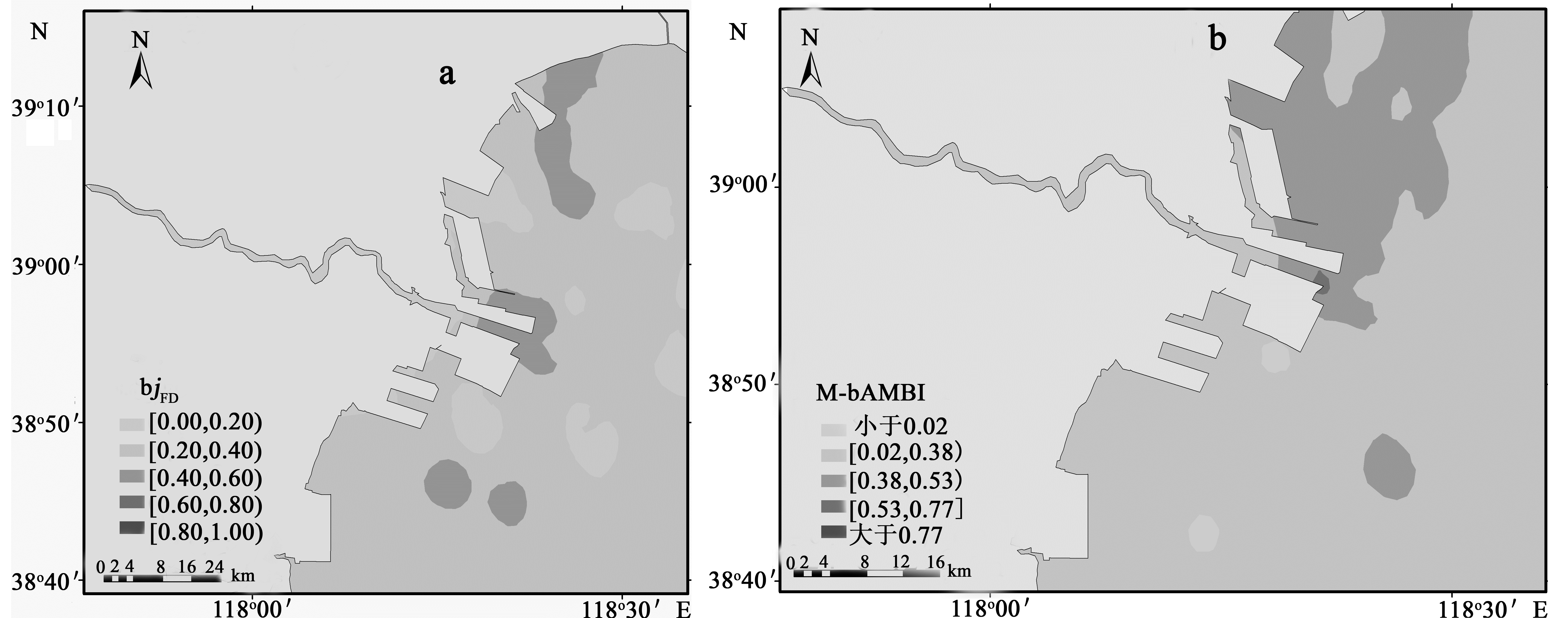
图5 2011年5月和9月航次的渤海湾各样点bjFD (a)和M-bAMBI (b)空间分布
Fig. 5 Spatial distributions of bjFD (a) and M-bAMBI (b) for each sampling station for the voyages of May and September, 2011 in the Bohai Bay
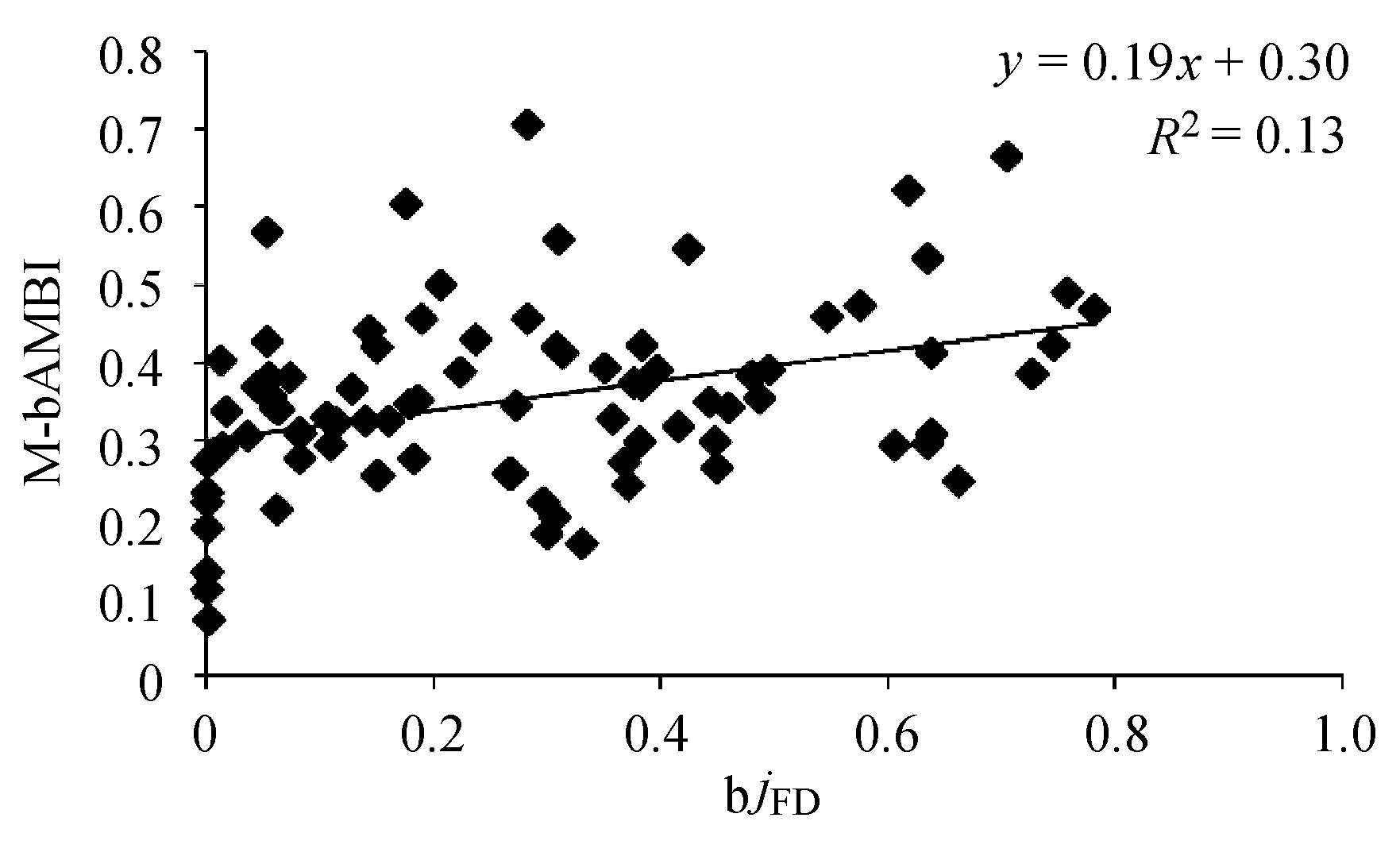
图6 渤海湾2011年5月和9月航次M-bAMBI和bjFD线性回归分析
Fig. 6 Linear regression analysis on the M-bAMBI and bjFD for the voyages of May and September, 2011 in the Bohai Bay
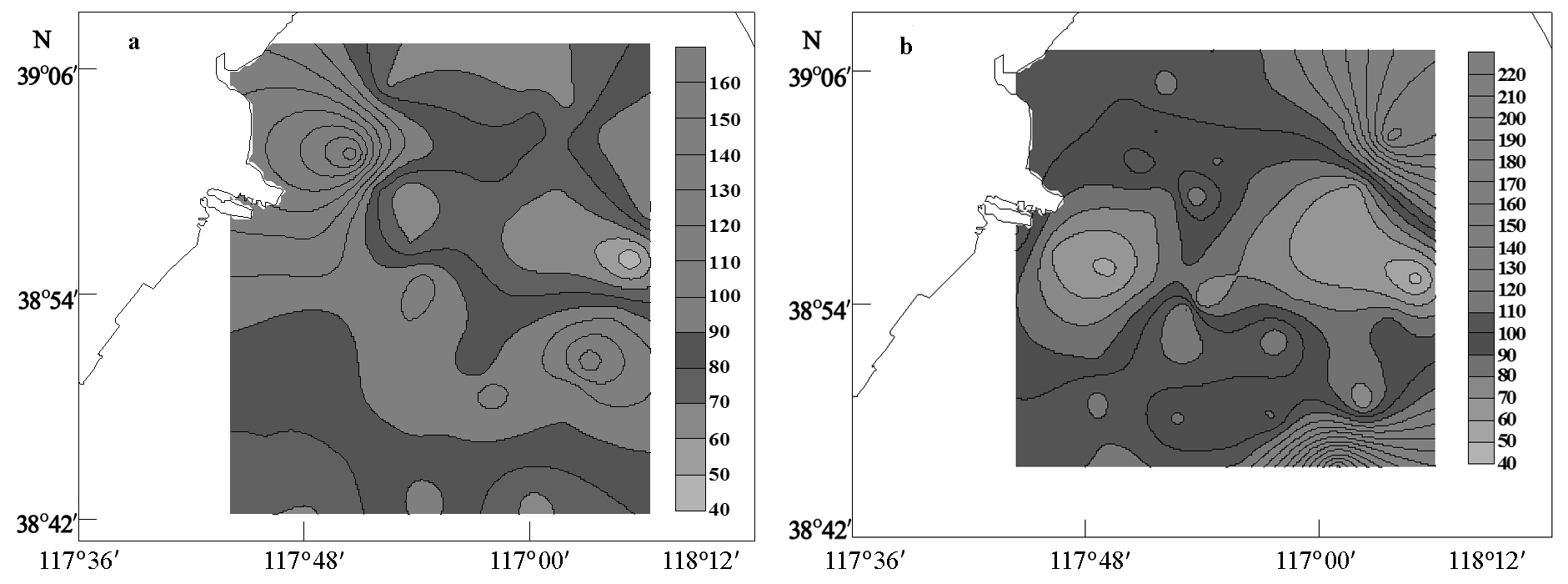
图7 渤海湾2011年5月(a)和9月(b)航次生态风险指数(RI)空间分布
Fig. 7 Spatial distribution of the risk index for the voyages of May (a) and September (b), 2011 in the Bohai Bay
| [1] | Borja Á (2014) Grand challenges in marine ecosystems ecology. Frontiers in Marine Science, 1, 1-6. |
| [2] | Cai WQ, Liu LS, Qiao F, Lin KX, Zhou J (2012) Study on the changes of macrobenthos communities and their causes in Bohai Bay. Environmental Science, 33, 3104-3109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蔡文倩, 刘录三, 乔飞, 林岿璇, 周娟 (2012) 渤海湾大型底栖生物群落结构变化及原因探讨. 环境科学, 33, 3104-3109.] | |
| [3] | Cai WQ, Meng W, Liu LS, Zhu YZ, Zhou J (2013) Long-term trends of the dominant macrozoobenthos in Bohai Bay. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 33, 2332-2340. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蔡文倩, 孟伟, 刘录三, 朱延忠, 周娟 (2013) 渤海湾大型底栖动物群落优势种长期变化研究. 环境科学学报, 33, 2332-2340.] | |
| [4] | Cai WQ, Borja Á, Liu LS, Muxika I, German JR (2014a) Assessing benthic health under multiple human pressures in Bohai Bay (China), using density and biomass in calculating AMBI and M-AMBI. Marine Ecology, 35, 180-192. |
| [5] | Cai WQ, Meng W, Liu LS, Lin KX (2014b) Evaluation of the ecological status with benthic indices in the coastal system: the case of Bohai Bay (China). Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering, 8, 737-746. |
| [6] | Cai WQ, Borja Á, Lin KX, Zhu YZ, Zhou J, Liu LS (2015) Assessing the benthic quality status of the Bohai Bay (China) with proposed modifications of M-AMBI. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(10), 111-121. |
| [7] | Chen JS, Zhou JY (1992) Study on the Heavy Metals in the Chinese Watershed. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈静生, 周家义 (1992) 中国水环境重金属研究. 中国环境科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Cui YH, Sun DY (1983) Preliminary report on the macrobenthos in the outlets of Bohai Bay. Marine Sciences, (3), 29-35. (in Chinese) |
| [崔玉珩, 孙道元 (1983) 渤海湾排污区底栖动物调查初步报告. 海洋科学, (3), 29-35.] | |
| [9] | Dauer DM, Luckenbach MW, Rodi AJ (1993) Abundance-biomass comparison (ABC method): effects of an estuarine gradient, anoxic/hypoxic events and contaminated sediments. Marine Biology, 116, 507-518. |
| [10] | Fang M, Wu YJ, Liu H, Jia Y, Zhang Y, Wang XT, Wu MH, Zhang CL (2013) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 33, 563-569. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [方明, 吴友军, 刘红, 贾英, 张媛, 王学彤, 吴明红, 张春雷 (2013) 长江口沉积物重金属的分布、来源及潜在生态风险评价. 环境科学学报, 33, 563-569.] | |
| [11] | Gamito S, Furtado R (2009) Feeding diversity in macroinvertebrate communities: a contribution to estimate the ecological status in shallow waters. Ecological Indicators, 9, 1009-1019. |
| [12] | Gamito S, Patrício J, Neto JM, Teixeira H, Marques JC (2012) Feeding diversity index as complementary information in the assessment of ecological quality status. Ecological Indicators, 19(8), 73-78. |
| [13] | Gray NF, Delaney E (2008) Comparison of benthic macroinvertebrate indices for the assessment of the impact of acid mine drainage on an Irish river below an abandoned Cu-S mine. Environmental Pollution, 155, 31-40. |
| [14] | Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975-1001. |
| [15] | Hoey GV, Permuy DC, Vandendriessche S, Vincx M, Hostens K (2013) An ecological quality status assessment procedure for soft-sediment benthic habitats: weighing alternative approaches. Ecological Indicators, 25, 266-278. |
| [16] | Huntley ME, Lopez MGD (1992) Temperature dependent production of marine copepods: a global synthesis. The American Naturalist, 140, 202-242. |
| [17] | Li SY, Miao FM, Liu GX, Hao J (1995) Preliminary study on the environmental background values of heavy metals in the Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 17(2), 78-85. (in Chinese) |
| [李淑媛, 苗丰民, 刘国贤, 郝静 (1995) 渤海底质重金属环境背景值初步研究. 海洋学报, 17(2), 78-85.] | |
| [18] | Liu C, Wang ZY, He Y, Wu YS (2003) Investigation on sediment quality of the river mouths around Bohai Bay. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 23, 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘成, 王兆印, 何耘, 吴永胜 (2003) 环渤海湾诸河口底质现状的调查研究. 环境科学学报, 23, 58-63.] | |
| [19] | Liu SG, Lou S, Kuang CP, Huang WR, Chen WJ, Zhang JL, Zhong GH (2011) Water quality assessment by pollution-index method in the coastal waters of Hebei Province in western Bohai Sea, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 2220-2229. |
| [20] | Maret TR, Cain DJ, MacCoy DE (2003) Response of benthic invertebrate assemblages to metal exposure and bioaccumulation associated with hard-rock mining in northwestern streams, USA. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 22, 598-620. |
| [21] | Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China(2002) Determination Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家环保总局(2002) 水和废水监测分析方法. 中国环境科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Muxika I, Borja Á, Bald J (2007) Using historical data, expert judgement and multivariate analysis in assessing reference conditions and benthic ecological status, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55, 16-29. |
| [23] | Ning X, Lin C, Su J, Liu CG, Hao Q, Le FF, Tang QS (2010) Long-term environmental changes and the responses of the ecosystems in the Bohai Sea during 1960-1996. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57, 1079-1091. |
| [24] | Peng ST, Zhou R, Qin XB, Shi HH, Ding DW (2013) Application of macrobenthos functional groups to estimate the ecosystem health in a semi-enclosed bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 74, 302-310. |
| [25] | Qin YW, Zhang L, Zheng BH, Cao W, Liu XB, Jia J (2012) Impact of shoreline changes on the coastal water quality of Bohai Bay (2003-2011). Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32, 2149-2159. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦延文, 张雷, 郑丙辉, 曹伟, 刘宪斌, 贾静 (2012) 渤海湾岸线变化(2003-2011年)对近岸海域水质的影响. 环境科学学报, 32, 2149-2159.] | |
| [26] | Sanders HL (1956) Oceanography of Long Island Sound, 1952-4, X. The biology of marine bottom communities. Bulletin of the Bingham Oceanographic Collection, 15, 345-414. |
| [27] | Sola C, Prat N (2006) Monitoring metal and metalloid bioaccumulation in Hydropsyche (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) to evaluate metal pollution in a mining river. Whole body versus tissue content. Science of the Total Environment, 359, 221-231. |
| [28] | Steneck RS, Watling L (1982) Feeding capabilities and limitations of herbivorous molluscs: a functional group approach. Marine Biology, 68, 299-319. |
| [29] | Sun DY, Liu YC (1991) Species composition and quantitative distributions of biomass and density of the microbenthic infauna in the Bohai Sea. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 9(1), 42-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙道元, 刘银城 (1991) 渤海底栖动物种类组成和数量分布. 黄渤海海洋, 9(1), 42-50.] | |
| [30] | Warwick RM, Clarke KR, Somerfield PJ (2010) Exploring the marine biotic index (AMBI): variations on a theme by Ángel Borja. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60, 554-559. |
| [31] | Wu ZL, Zhang SY, Chen Y, Bi YX (2015) Analysis of functional feeding groups of macroinvertebrates communities in the macroalgae beds of Gouqi Island, Zhejiang Province. Journal of Fisheries of China, 39, 382-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴祖立, 章守宇, 陈彦, 毕远新 (2015) 枸杞岛海藻场大型底栖无脊椎动物摄食类群研究. 水产学报, 39, 382-391.] | |
| [32] | Xu SS (2011) Decline Mechanisms of Fishery Resources in the Bohai Sea Under Anthropogenic Activities. PhD dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许思思 (2011) 人为影响下渤海渔业资源的衰退机制. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 青岛.] | |
| [33] | Zhang PY (2005) Studies on Ecology of Zoobenthos and Environmental Quality Assessment in Coastal Waters of Bohai Bay. PhD dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张培玉 (2005) 渤海湾近岸海域底栖生物生态学与环境质量评价研究. 博士学位论文, 中国海洋大学, 青岛.] | |
| [34] | Zhang YZ, Liu DE, Fang QS, Wang HS, Qin ZQ (2009) Effects of temperature and salinity on growth and survival rate of young Epinephelus coioides. Journal of Jimei University, 14(1), 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张雅芝, 刘冬娥, 方琼珊, 王涵生, 秦志清 (2009) 温度和盐度对斜带石斑鱼幼鱼生长与存活的影响. 集美大学学报, 14(1), 8-13.] | |
| [35] | Zhou H, Zhang ZN (2003) Rationale of the multivariate statistical software PRIMER and its application in benthic community ecology. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 33, 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周红, 张志南 (2003) 大型多元统计软件PRIMER的方法原理及在底栖群落生态学中的应用. 青岛海洋大学学报, 33, 58-64.] | |
| [36] | Zhou H, Zhang ZN, Liu XS, Tu LH, Yu ZS (2007) Changes in the shelf macrobenthic community over large temporal and spatial scales in the Bohai Sea, China. Journal of Marine Systems, 67, 312-321. |
| [37] | Zhu YZ, Zhou J, Lin KX, Liu J, Cai WQ, Liu LS (2015) Assessment on the macrozoobenthos community health in Xiamen Bay using macrozoobenthos community index. Guangxi Sciences, 22, 549-557. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱延忠, 周娟, 林岿璇, 刘静, 蔡文倩, 刘录三 (2015) 基于MCI的厦门湾大型底栖动物群落健康状况评价. 广西科学, 22, 549-557.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [3] | 尹星元, 安慧, 邢彬彬, 苏诗玉, 文志林, 郭建超, 刘小平, 王波. 养分添加和降水变化对荒漠草原地上和地下生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24073-. |
| [4] | 吴乐婕, 刘泽康, 田星, 张群, 李博, 吴纪华. 海三棱藨草基因型多样性对种群营养生长和繁殖策略的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23478-. |
| [5] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [6] | 吴浩, 余玉蓉, 王佳钰, 赵媛博, 高娅菲, 李小玲, 卜贵军, 薛丹, 吴林. 低水位增加灌木多样性和生物量但降低土壤有机碳含量: 以鄂西南贫营养泥炭地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22600-. |
| [7] | 周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平. 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| [8] | 欧阳园丽, 张参参, 林小凡, 田立新, 顾菡娇, 陈伏生, 卜文圣. 中国亚热带不同菌根树种的根叶形态学性状特征与生长差异: 以江西新岗山为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 746-758. |
| [9] | 王爱霞, 马婧婧, 龚会蝶, 范国安, 王茂, 赵红梅, 程军回. 北疆一年生早春短命植物物种丰富度分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 735-745. |
| [10] | 朱杰, 吴安驰, 邹顺, 熊鑫, 刘世忠, 褚国伟, 张倩媚, 刘菊秀, 唐旭利, 闫俊华, 张德强, 周国逸. 南亚热带常绿阔叶林树木多样性与生物量和生产力的关联及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1435-1446. |
| [11] | 李宝泉, 姜少玉, 吕卷章, 陈琳琳, 闫朗, 刘春云, 李晓静, 宋博, 李新正. 黄河三角洲潮间带及近岸浅海大型底栖动物物种组成及长周期变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1511-1522. |
| [12] | 张田田, 王璇, 任海保, 余建平, 金毅, 钱海源, 宋小友, 马克平, 于明坚. 浙江古田山次生与老龄常绿阔叶林群落特征的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1069-1080. |
| [13] | 宋瑞玲, 王昊, 张迪, 吕植, 朱子云, 张璐, 刘炎林, 才文公保, 吴岚. 基于MODIS-EVI评估三江源高寒草地的保护成效[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 149-157. |
| [14] | 谭珊珊, 王忍忍, 龚筱羚, 蔡佳瑶, 沈国春. 群落物种及结构多样性对森林地上生物量的影响及其尺度效应: 以巴拿马BCI样地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(10): 1054-1064. |
| [15] | 刘鸿雁, 杨超杰, 张沛东, 李文涛, 杨晓龙, 张秀梅. 青岛崂山湾人工鱼礁区底层游泳动物群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(8): 896-906. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn