



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 22407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022407 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022407
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuyuan Bao1, Yinkang Li2,3, Wuying Lin4, Zhiqin Zhou5, Xiaobo Xiao6, Xiaoyong Xie2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-16
Accepted:2022-11-10
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
* E-mail: About author:# Co-first authors
Yuyuan Bao, Yinkang Li, Wuying Lin, Zhiqin Zhou, Xiaobo Xiao, Xiaoyong Xie. The current situation of horseshoe crabs in the offshore waters of northern South China Sea with analysis of the potential habitat distribution of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus in Beibu Gulf[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22407.
| 编号 Number | 站位 Survey station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 平均高潮位 Mean high tide level (m) | 平均低潮位 Mean low tide level (m) | 参考潮汐站位 The closest tidal station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 渔洲坪 Yuzhouping | 108°22′ E | 21°38′ N | 3.7 | 1.15 | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 螃蟹档 Pangxiedang | 108°49′ E | 21°37′ N | 3.88 | 1.37 | 龙门 Longmen |
| 3 | 中三墩 Zhongsandun | 108°52′ E | 21°37′ N | |||
| 4 | 西背岭 Xibeiling | 109°10′ E | 21°24′ N | 4.0 | 1.3 | 北海 Beihai |
| 5 | 下村 Xiacun | 109°12′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 6 | 竹林盐场 Zhulinyanchang | 109°16′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 7 | 坡尾底 Poweidi | 109°33′ E | 21°31′ N | 5.05 | 2.16 | 铁山港 Tieshangang (石头埠) (Shitoubu) |
| 8 | 沙田 Shatian | 109°39′ E | 21°30′ N | |||
| 9 | 榕根山 Ronggenshan | 109°40′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 10 | 乌坭 Wuni | 109°45′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 11 | 草潭 Caotan | 109°48′ E | 21°21′ N | 4.07 | 1.51 | 下泊 Xiabo |
| 12 | 澄迈湾 Chengmaiwan | 109°59′ E | 19°56′ N | 2.46 | 0.92 | 马村港 Macungang |
| 13 | 新盈 Xinying (I) | 109°31′ E | 19°54′ N | 3.15 | 1.07 | 新盈 Xinying |
| 14 | 新英 Xinying (II) | 109°16′ E | 19°43′ N | 3.07 | 1.05 | 洋浦 Yangpu |
Table 1 Tide level information of survey stations of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus in Beibu Gulf
| 编号 Number | 站位 Survey station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 平均高潮位 Mean high tide level (m) | 平均低潮位 Mean low tide level (m) | 参考潮汐站位 The closest tidal station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 渔洲坪 Yuzhouping | 108°22′ E | 21°38′ N | 3.7 | 1.15 | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 螃蟹档 Pangxiedang | 108°49′ E | 21°37′ N | 3.88 | 1.37 | 龙门 Longmen |
| 3 | 中三墩 Zhongsandun | 108°52′ E | 21°37′ N | |||
| 4 | 西背岭 Xibeiling | 109°10′ E | 21°24′ N | 4.0 | 1.3 | 北海 Beihai |
| 5 | 下村 Xiacun | 109°12′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 6 | 竹林盐场 Zhulinyanchang | 109°16′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 7 | 坡尾底 Poweidi | 109°33′ E | 21°31′ N | 5.05 | 2.16 | 铁山港 Tieshangang (石头埠) (Shitoubu) |
| 8 | 沙田 Shatian | 109°39′ E | 21°30′ N | |||
| 9 | 榕根山 Ronggenshan | 109°40′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 10 | 乌坭 Wuni | 109°45′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 11 | 草潭 Caotan | 109°48′ E | 21°21′ N | 4.07 | 1.51 | 下泊 Xiabo |
| 12 | 澄迈湾 Chengmaiwan | 109°59′ E | 19°56′ N | 2.46 | 0.92 | 马村港 Macungang |
| 13 | 新盈 Xinying (I) | 109°31′ E | 19°54′ N | 3.15 | 1.07 | 新盈 Xinying |
| 14 | 新英 Xinying (II) | 109°16′ E | 19°43′ N | 3.07 | 1.05 | 洋浦 Yangpu |
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 平均海表温度 Mean sea surface temperature (sst) | 45.9 | 10.2 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of the wettest quarter (bio 8) | 36 | 21.3 |
| 距海岸线欧氏距离 Euclidean distance to the coastline (coastline) | 4.4 | 44.4 |
| 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of the warmest month (bio 5) | 3.1 | 3.9 |
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature (bio 1) | 2.4 | 5.2 |
| 海底地形高程 Seabed topographic elevation (etopo 1) | 2.3 | 9.4 |
| 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation (bio 12) | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month (bio 14) | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 平均海表盐度 Mean sea surface salinity (sss) | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| 气温季节性变化 Temperature seasonality (bio 4) | 0.4 | 1 |
| 等温性 Isothermality (bio 3) | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (bio 2) | 0.2 | 0.5 |
Table 2 Contribution and importance of major environmental variables to the distribution of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 平均海表温度 Mean sea surface temperature (sst) | 45.9 | 10.2 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of the wettest quarter (bio 8) | 36 | 21.3 |
| 距海岸线欧氏距离 Euclidean distance to the coastline (coastline) | 4.4 | 44.4 |
| 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of the warmest month (bio 5) | 3.1 | 3.9 |
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature (bio 1) | 2.4 | 5.2 |
| 海底地形高程 Seabed topographic elevation (etopo 1) | 2.3 | 9.4 |
| 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation (bio 12) | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month (bio 14) | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 平均海表盐度 Mean sea surface salinity (sss) | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| 气温季节性变化 Temperature seasonality (bio 4) | 0.4 | 1 |
| 等温性 Isothermality (bio 3) | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (bio 2) | 0.2 | 0.5 |
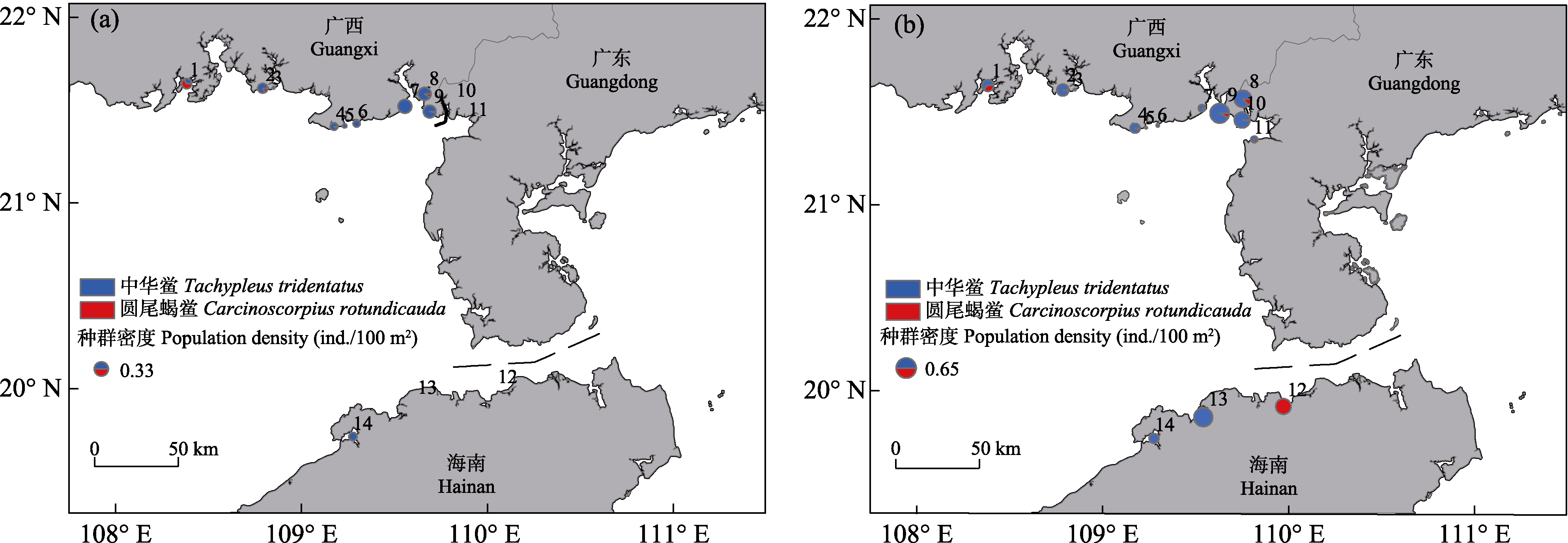
Fig. 3 Juvenile horseshoe crab distribution in the intertidal zone of Beibu Gulf in 2019 (a) and 2020 (b). 1, Yuzhouping; 2, Pangxiedang; 3, Zhongsandun; 4, Xibeiling; 5, Xiacun; 6, Zhulinyanchang; 7, Poweidi; 8, Shatian; 9, Ronggenshan; 10, Wuni; 11, Caotan; 12, Chengmaiwan; 13, Xinying (I); 14, Xinying (II).
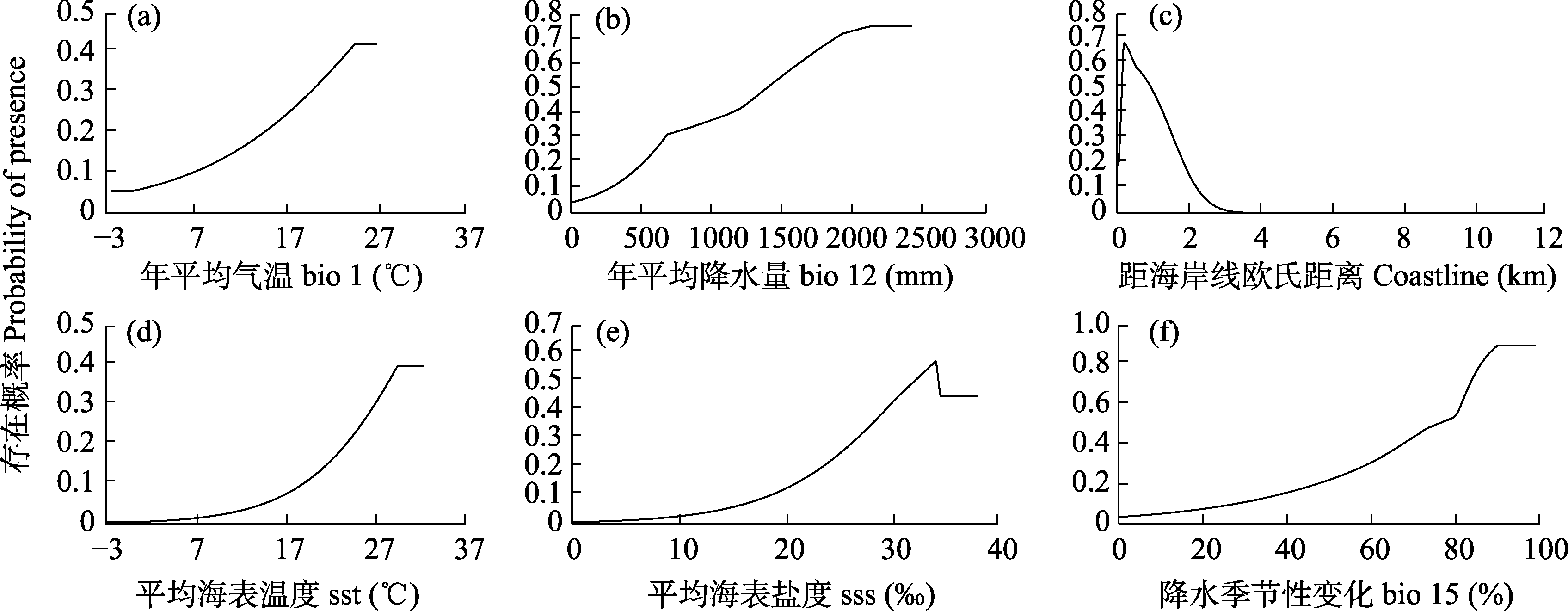
Fig. 5 Response curves of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus to environmental variables in MaxEnt models. The meanings of the environmental variables are shown in Table 2.
| [1] | Arnold C (2020) Horseshoe crab blood is key to making a COVID-19 vaccined—but the ecosystem may suffer. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/covid-vaccine-needs-horseshoe-crab-blood. (accessed on 2022-05-20) |
| [2] | Brockmann HJ, Smith MD (2009) Reproductive competition and sexual selection in horseshoe crabs. In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp. 199-221. Springer, New York. |
| [3] |
Cartwright-Taylor L, Yap VB, Hsu CC, Lou ST (2011) Distribution and abundance of horseshoe crabs Tachypleus gigas and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda around the main island of Singapore. Aquatic Biology, 13, 127-136.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Chakraborty A, Joshi PK, Sachdeva K (2016) Predicting distribution of major forest tree species to potential impacts of climate change in the central Himalayan region. Ecological Engineering, 97, 593-609.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chao BX, Hu WJ, Chen B, Zhang D, Chen GC, Yu WW, Ma ZY, Lei GC, Wang YY (2020) Potential suitable habitat of mangroves and conservation gap analysis in Guangdong Province with MaxEnt Modeling. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 3785-3794. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [晁碧霄, 胡文佳, 陈彬, 张典, 陈光程, 俞炜炜, 马志远, 雷光春, 王玉玉 (2020) 基于MaxEnt模型的广东省红树林潜在适生区和保护空缺分析. 生态学杂志, 39, 3785-3794.] | |
| [6] |
Chen CP, Yang MC, Fan LF, Qiu G, Liao YY, Hsieh HL (2015) Co-occurrence of juvenile horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in an estuarine bay, southwestern China. Aquatic Biology, 24, 117-126.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Cheng H, Chabot CC, Watson WH (2015) The life history cycle of Limulus polyphemus in the Great Bay Estuary, New Hampshire, USA. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp.237-253. Springer, Cham. |
| [8] |
Chiu HMC, Morton B (2003) The morphological differentiation of two horseshoe crab species, Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda (Xiphosura), in Hong Kong with a regional Asian comparison. Journal of Natural History, 37, 2369-2382.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Gallagher RV, Hughes L, Leishman MR, Wilson PD (2010) Predicted impact of exotic vines on an endangered ecological community under future climate change. Biological Invasions, 12, 4049-4063.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Gelviz-Gelvez SM, Pavón NP, Illoldi-Rangel P, Ballesteros-Barrera C (2015) Ecological niche modeling under climate change to select shrubs for ecological restoration in Central Mexico. Ecological Engineering, 74, 302-309.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Hong SG (2011) Biology of Horseshoe Crabs, Tachypleus tridentatus. Xiamen University Press, Xiamen. (in Chinese) |
| [洪水根 (2011) 中国鲎生物学研究. 厦门大学出版社, 厦门.] | |
| [12] | Hsieh HL, Chen CP (2015) Current status of Tachypleus tridentatus in Taiwan for Red List assessment. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp.383-396. Springer, Cham. |
| [13] | Hu MH, Kwan BKY, Wong YJ, Cheung SG, Shin PKS (2015) Population structure and growth of juvenile horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda (Xiphosura) in Southern China. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp. 167-180. Springer, Cham. |
| [14] | International Union for Conservation of Nature IUCN (2012) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (Version 3.1), 2nd edn. https://portals.iucn.org/library/node/10315. (accessed on 2022-05-24) |
| [15] |
Jayasinghe SL, Kumar L (2019) Modeling the climate suitability of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in Sri Lanka in response to current and future climate change scenarios. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 272/273, 102-117.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kwan BKY, Hsieh HL, Cheung SG, Shin PKS (2016) Present population and habitat status of potentially threatened Asian horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in Hong Kong: A proposal for marine protected areas. Biodiversity and Conservation, 25, 673-692.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Laurie K, Chen CP, Cheung SG, Do V, Hsieh HL, John AB, Mohamad F, Seino S, Nishida S, Shin PKS, Yang M (2019) Tachypleus tridentatus (errata version published in 2019). http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T21309A149768986.en. (accessed on 2022-05-24) |
| [18] |
Lee CNW, Morton B (2016) Changes in the distributions of juvenile horseshoe crabs (Arthropoda: Chelicerata) (2002-2014) related to environmental perturbations at Pak Nai and Ha Pak Nai, Deep Bay, Hong Kong SAR, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 108, 134-146.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Li XJ, Mao FJ, Du HQ, Zhou GM, Xing LQ, Liu TY, Han N, Liu YL, Zhu DE, Zheng JL, Dong LF, Zhang M (2019) Spatiotemporal evolution and impacts of climate change on bamboo distribution in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109265.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Liang GY (1985) Preliminary investigation on horseshoe crabs resources in Beibu Gulf. Guangxi Agricultural Science, (2), 18-20, 16. (in Chinese) |
| [梁广耀 (1985) 北部湾鲎资源的初步调查. 广西农业科学, (2), 18-20, 16.] | |
| [21] | Liao YY, Li XM (2001) Present situation of horseshoe crab resources in the sea area of China and tactics of preservation. Resources Science, 23(2), 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖永岩, 李晓梅 (2001) 中国海域鲎资源现状及保护策略. 资源科学, 23(2), 53-57.] | |
| [22] |
Liao YY, Hsieh HL, Xu SQ, Zhong QP, Lei J, Liang MZ, Fang HY, Xu LL, Lin WY, Xiao XB, Chen CP, Cheung SG, Kwan BKY (2019) Wisdom of crowds reveals decline of Asian horseshoe crabs in Beibu Gulf, China. Oryx, 53, 222-229.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Luo Z, Miao FZ, Hu MH, Wang YJ (2020) Research development on horseshoe crab: A 30-year bibliometric analysis. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 41.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Mamun MD, Kim S, An KG (2018) Distribution pattern prediction of an invasive alien species largemouth bass using a maximum entropy model (MaxEnt) in the Korean Peninsula. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity, 11, 516-524.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Merow C, Smith MJ, Silander JA (2013) A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: What it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography, 36, 1058-1069.
DOI URL |
| [26] | National Marine Data and Information Service (2019) Tide Table 2020 (Vol. 3): From Taiwan Straits to the Beibu Gulf. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家海洋信息中心 (2019) 2020年潮汐表(第3册): 台湾海峡至北部湾. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Novitsky TJ (2015) Biomedical implications for managing the Limulus polyphemus harvest along the northeast coast of the United States. In: Changing Global Perspectives on Horseshoe Crab Biology, Conservation and Management (eds Carmichael RH, Botton ML, Shin PKS, Cheung SG), pp. 483-500. Springer, Cham. |
| [28] |
Padalia H, Srivastava V, Kushwaha SPS (2014) Modeling potential invasion range of alien invasive species, Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit. in India: Comparison of MaxEnt and GARP. Ecological Informatics, 22, 36-43.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Pati S, Shahimi S, Nandi D, Sarkar T, Acharya S, Sheikh H, Acharya DK, Choudhury T, John A, Nelson B, Dash BP, Edinur HA (2021) Predicting Tachypleus gigas spawning distribution with climate change in northeast coast of India. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 22, 211-220.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Rudkin DM, Young GA (2009) Horseshoe crabs—An ancient ancestry revealed. In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp.25-44. Springer, New York. |
| [31] | Seino S, Uda T, Maeda K, Yamaji K (2000) Dispersion mechanism of hatchlings of horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus at tidal flat off the Yasaka rivermouth in Moriye Bay. Proceedings of Hydraulic Engineering, 44, 1209-1214. (in Japanese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Sekiguchi K (1988) Biology of Horseshoe Crabs. Science House Company Limited, Tokyo. |
| [33] | Sekiguchi K, Shuster CN Jr (2009) Limits on the global distribution of horseshoe crabs (Limulacea): Lessons learned from two lifetimes of observations:Asia and America. In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp. 5-24. Springer, New York. |
| [34] | Shuster CN, Sekiguchi K (2009) Basic habitat requirements of the extant species of horseshoe crabs (Limulacea). In: Biology and Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs (eds Tanacredi JT, Botton ML, Smith DR), pp.115-129. Springer, New York. |
| [35] | Tang QX, Wang YS (2021) Characteristics and distribution pattern of mangrove community in the Leizhou Peninsula. Ecological Science, 40(5), 23-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐秋霞, 王友绍 (2021) 雷州半岛红树林群落特征及其分布格局. 生态科学, 40(5), 23-32.] | |
| [36] | Wang DX, Su YQ, Wang J, Liang JR (2001) Influence of environmental factors on development of embryo and larvae in Tachypleus tridentatues. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 8(3), 10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王德祥, 苏永全, 王军, 梁军荣 (2001) 几种因子对中国鲎胚胎和幼体发育的影响. 中国水产科学, 8(3), 10-14.] | |
| [37] | Wang T, Huang HH, Zhang P, Zhang SF, Wu FX, Liu QX, Liao XL, Xie B (2020) Acoustic survey of fisheries resources and spatial distribution in the Guishan wind farm area. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 27, 1496-1504. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王腾, 黄洪辉, 张鹏, 张书飞, 吴风霞, 刘庆霞, 廖秀丽, 谢斌 (2020) 珠海桂山风电场水域渔业资源声学评估与空间分布. 中国水产科学, 27, 1496-1504.] | |
| [38] | Wang YH (1984) The northern distribution of Tachypleus tridentatus leach in China Seas. Marine Sciences, 8(4), 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王彝豪 (1984) 中国鲎在我国分布之北界. 海洋科学, 8(4), 38.] | |
| [39] | Waycott B (2020) Can Farming Horseshoe Crabs Help the COVID-19 Cause? https://www.aquaculturealliance.org/advocate/can-farming-horseshoe-crabs-help-the-covid-19-cause. (accessed on 2022-05-20) |
| [40] |
Wei B, Wang R, Hou K, Wang X, Wu W (2018) Predicting the current and future cultivation regions of Carthamus tinctorius L. using MaxEnt model under climate change in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 16, e00477.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Weng ZH, Xie YJ, Xiao ZQ, Huang LM, Li J, Wang SH, Zhang YZ (2012) Distribution and resource of Chinese horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) in Fujian and other coast water of China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 47, 40-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [翁朝红, 谢仰杰, 肖志群, 黄良敏, 李军, 王淑红, 张雅芝 (2012) 福建及中国其他沿岸海域中国鲎资源分布现状调查. 动物学杂志, 47, 40-48.] | |
| [42] |
Xie XY, Wu Z, Wang CC, Fu YJ, Wang XP, Xu P, Huang X, Liao YY, Huang SL, Kwan KY (2020) Nursery habitat for Asian horseshoe crabs along the northern Beibu Gulf, China: Implications for conservation management under baseline gaps. Aquatic Conservation Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 30, 260-272.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Yan H, Feng L, Zhao Y, Feng L, Zhu C, Qu Y, Wang H (2020) Predicting the potential distribution of an invasive species, Erigeron canadensis L., in China with a maximum entropy model. Global Ecology and Conservation, 21, e00822. |
| [44] | Yan MY, Li QZ, Song J, Wang ZH, Wang YJ, Hu MH (2019) Prediction of potential distribution areas of Chinese horseshoe crab and mangrove horseshoe crab in the Beibu Gulf of Guangxi based on MaxEnt model and their population conservation strategies. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 3100-3109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [颜明艳, 李琼珍, 宋洁, 王振华, 王有基, 胡梦红 (2019) 基于MaxEnt模型评估北部湾潮间带中国鲎和圆尾鲎稚鲎的潜在地理分布及种群保育对策. 生态学报, 39, 3100-3109.] | |
| [45] | Yan R, Fan JT, Xu SN, Xu YW, Sun MS, Chen ZZ (2018) Distribution characteristics of jack mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) habitat in the offshore waters of northern South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 2430-2435. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [晏然, 范江涛, 徐姗楠, 许友伟, 孙铭帅, 陈作志 (2018) 南海北部近海竹荚鱼栖息地分布特征. 生态学杂志, 37, 2430-2435.] |
| [1] | Yan Kang Jing Gan Linlin Yu Chenjing He Jingbin Wu Liqing Zhang. Design pattern and network development of urban microhabitat based on natural-based solutions (NbS): A case study of habitat gardens in Changning District, Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24528-. |
| [2] | Huan Xu, Fengfei Xin, Hongliang Shi, Lin Yuan, Shunqi Bo, Xinyi Zhao, Shuaitao Deng, Tingting Pan, Jing Yu, Saisai Sun, Cheng Xue. Evaluation of effects of integrated ecological restoration technology on habitat and bird diversity improvement in the northern branch of Yangtze River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [3] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [4] | Rongfei Su, Ruishan Chen, Linlin Yu, Jingbin Wu, Yan Kang. Biodiversity in community habitat gardens in Changning District, Shanghai based on camera trapping [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| [5] | Jiaqi Li, Yidi Feng, Lei Wang, Penyan Pan, Xiaoru Liu, Xueyang Li, Yihan Wang, Fang Wang. Diet and habitat selection of raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Shanghai, a rapidly urbanizing megacity in eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [6] | Yanli Wang, Ying Zhang, Chunlin Qi, Changda Zhang, Youhai Shi, Yanjun Du, Qiong Ding. Identifying biodiversity hotspots and conservation gaps in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park based on macrofungi and plants perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [7] | Mingjun Zhang, Hesheng Wang, Wenbo Yan, Yunnan Fu, Qi Wang, Zhigao Zeng. Diel activity and habitat selection of small Indian civets (Viverricula indica) in Hainan Datian National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [8] | Peng Wang, Jiarong Sui, Xinyao Ding, Weizhong Wang, Xueqian Cao, Haipeng Zhao, Yanping Wang. Nested distribution patterns of bird assemblages and their influencing factors in Zhengzhou urban parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23359-. |
| [9] | Haolin Wang, Huaisheng Zhang, Jianqiang Zhu, Zhongyi Chen, Yulin Ke, Tao Yang, Hui Chen. Research progress of diet composition and its research methods for Père David’s deer [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23057-. |
| [10] | Churan Zhang, Shengfa Li, Fengchang Li, Zhizhong Tang, Huiyan Liu, Lihong Wang, Rong Gu, Yun Deng, Zhiming Zhang, Luxiang Lin. Habitat association and community classification of woody plants in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [11] | Cailian Liu, Xiong Zhang, Enyuan Fan, Songlin Wang, Yan Jiang, Baian Lin, Lu Fang, Yuqiang Li, Lebin Liu, Min Liu. Species diversity, ecological characteristics and conservation measures of seahorses (Hippocampus) in China’s waters [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23282-. |
| [12] | Shuhan Yang, He Wang, Lei Chen, Yingfei Liao, Guang Yan, Yining Wu, Hongfei Zou. Effects of heterogeneous habitat on soil nematode community characteristics in the Songnen Plain [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [13] | Minghui Wang, Zhaoquan Chen, Shuaifeng Li, Xiaobo Huang, Xuedong Lang, Zihan Hu, Ruiguang Shang, Wande Liu. Spatial pattern of dominant species with different seed dispersal modes in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Pu’er, Yunnan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [14] | Wei Liu, Ruge Wang, Tianqiao Fan, Nayiman Abudulijiang, Xinhang Song, Shuping Xiao, Ning Guo, Lingying Shuai. Habitat suitability for the Aviceda leuphotes in Mingxi County, Fujian Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [15] | Rongfei Su, Ruishan Chen, Xiaona Guo. Conservation strategies for biodiversity in urban community renewal: A case study of habitat garden in Changning District, Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23118-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn