



Biodiv Sci ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 499-506. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014270 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014270
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qiong Xiao1, Zhi Yang2, Huiyuan Tang2, Pengxiang Duan1, Xiaoqing Wang1, Tiaoyi Xiao1, Xiaoyan Liu1,*( )
)
Received:2014-12-28
Accepted:2015-06-23
Online:2015-07-20
Published:2015-08-03
Contact:
Liu Xiaoyan
About author:# Co-first authors
Qiong Xiao, Zhi Yang, Huiyuan Tang, Pengxiang Duan, Xiaoqing Wang, Tiaoyi Xiao, Xiaoyan Liu. Species diversity of fish and its conservation in the mainstream of the lower reaches of Wu River[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(4): 499-506.
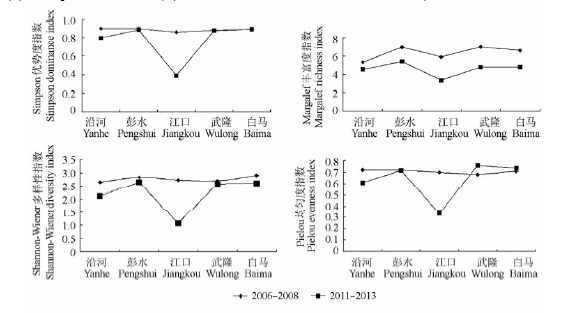
Fig. 2 Indices of fish biodiversity among all investigated sections in the mainstream of the lower reaches of the Wu River during 2006 and 2008 and during 2011 and 2013
| 2006-2008 | 2011-2013 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种类 Species | 重量百分比 Percentage of Weight (%) | 尾均重 Average body Weight (g) | 种类 Species | 重量百分比 Percentage of weight (%) | 尾均重 Average body weight (g) |
| 大鳍鳠 Mystus macropterus | 9.39 | 35.5 | | 15.8 | 20 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus (Cyprinus) carpio | 7.93 | 228.3 | 草鱼 Ctenopharyngodon idellus | 11.6 | 520.8 |
| 瓦氏黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus vachelli | 7.84 | 38.7 | 瓦氏黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus vachelli | 10.39 | 40 |
| 粗唇鮠 Leiocassis crassilabris | 7.60 | 24.3 | 泉水鱼 Semilabeo prochilus | 6.5 | 101.2 |
| 中华倒刺鲃 Spinibarbus sinensis | 7.44 | 84.4 | 黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | 5.08 | 5.1 |
| 泉水鱼 Semilabeo prochilus | 7.29 | 70.2 | 鳜 Siniperca chuatsi | 4.72 | 121.1 |
| 墨头鱼 Garra pingi pingi | 6.91 | 214.6 | 鲤 Cyprinus (Cyprinus) carpio | 4.21 | 104.5 |
| 瓣结鱼 Tor (Folifer) brevifilis brevifilis | 5.44 | 63.5 | 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | 3.41 | 61.7 |
| 南方鲇 Silurus meridionalis | 5.21 | 424.8 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 3.14 | 50.9 |
| 白甲鱼 Onychostoma sima | 3.86 | 114.9 | 粗唇鮠 Leiocassis crassilabris | 2.73 | 30.2 |
| 铜鱼 Coreius heterodon | 3.14 | 253.0 | 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 2.61 | 28.7 |
| 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | 2.91 | 70.3 | 鲇 Silurus asotus | 2.59 | 144 |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 2.36 | 49.2 | 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 2.44 | 23.3 |
| 鲇 Silurus asotus | 2.30 | 130.3 | 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 2.2 | 22.5 |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 2.23 | 16.4 | |||
| 总计 Total | 81.86 | 总计 Total | 77.42 | ||
Table 1 Structures of fishery catches in the mainstream of the lower reaches of Wu River during 2006 and 2008 and during 2011 and 2013
| 2006-2008 | 2011-2013 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种类 Species | 重量百分比 Percentage of Weight (%) | 尾均重 Average body Weight (g) | 种类 Species | 重量百分比 Percentage of weight (%) | 尾均重 Average body weight (g) |
| 大鳍鳠 Mystus macropterus | 9.39 | 35.5 | | 15.8 | 20 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus (Cyprinus) carpio | 7.93 | 228.3 | 草鱼 Ctenopharyngodon idellus | 11.6 | 520.8 |
| 瓦氏黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus vachelli | 7.84 | 38.7 | 瓦氏黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus vachelli | 10.39 | 40 |
| 粗唇鮠 Leiocassis crassilabris | 7.60 | 24.3 | 泉水鱼 Semilabeo prochilus | 6.5 | 101.2 |
| 中华倒刺鲃 Spinibarbus sinensis | 7.44 | 84.4 | 黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | 5.08 | 5.1 |
| 泉水鱼 Semilabeo prochilus | 7.29 | 70.2 | 鳜 Siniperca chuatsi | 4.72 | 121.1 |
| 墨头鱼 Garra pingi pingi | 6.91 | 214.6 | 鲤 Cyprinus (Cyprinus) carpio | 4.21 | 104.5 |
| 瓣结鱼 Tor (Folifer) brevifilis brevifilis | 5.44 | 63.5 | 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | 3.41 | 61.7 |
| 南方鲇 Silurus meridionalis | 5.21 | 424.8 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 3.14 | 50.9 |
| 白甲鱼 Onychostoma sima | 3.86 | 114.9 | 粗唇鮠 Leiocassis crassilabris | 2.73 | 30.2 |
| 铜鱼 Coreius heterodon | 3.14 | 253.0 | 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 2.61 | 28.7 |
| 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | 2.91 | 70.3 | 鲇 Silurus asotus | 2.59 | 144 |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 2.36 | 49.2 | 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 2.44 | 23.3 |
| 鲇 Silurus asotus | 2.30 | 130.3 | 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 2.2 | 22.5 |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 2.23 | 16.4 | |||
| 总计 Total | 81.86 | 总计 Total | 77.42 | ||
| 1 | Anderson EP, Freeman MC, Pringle CM (2006) Ecological consequences of hydropower development in Central Ame- rica: impacts of small dams and water diversion on neotrop- ical stream fish assemblages.River Research and Applica- tions, 22, 397-411. |
| 2 | Blanchard F, LeLoc’h F, Hily C, Boucher J (2004) Fishing effects on diversity, size and community structure of the benthic invertebrate and fish megafauna on the Bay of Biscay coast of France.Marine Ecology Progress Series, 280, 249-260. |
| 3 | Chen YY (陈宜瑜) (1998) Fauna Sinica (Osteichthyes): Cypriniformes II (中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(中卷)). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 4 | Chu XL (禇新洛), Zheng BS (郑葆珊), Dai DY (戴定远) (1999) Fauna Sinica (Osteichthyes): Siluriformes (中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲇形目). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 5 | Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER V6: User Manual/ Tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth. |
| 6 | Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E, Plymouth. |
| 7 | Dai YG (代应贵), Chen YF (陈毅峰) (2007) Fish fauna and its ecological types of Qingshui River in Guizhou Province, Southwest China.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 26, 682-687. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 8 | Ding RH (丁瑞华) (1994) The Fishes of Sichuan (四川鱼类志). Sichuan Publishing House of Science & Technology, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| 9 | Dudgeon D (2011) Asian river fishes in the Anthropocene: threats and conservation challenges in an era of rapid envi- ronmental change.Journal of Fish Biology, 79, 1487-1524. |
| 10 | Everitt BS, Hothorn T (2006) A Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using R. Taylor and Francis Group, Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton. |
| 11 | Fan XG, Wei QW, Chang JB, Rosenthal H, He JX, Chen DQ, Shen L, Du H, Yang DG (2006) A review on conservation issues in the upper Yangtze River—a last chance for a big challenge: Can Chinese paddlefish (Psephurus gladius), Dabry’s sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus) and other fish species still be saved?Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 22(Suppl.1), 32-39. |
| 12 | Gao X, Zeng Y, Wang JW, Liu HZ (2010) Immediate impacts of the second impoundment on fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir.Environmental Biology of Fishes, 87, 163-173. |
| 13 | He GH (何光宏) (2014) Study on automatic generation control and its application in cascade hydropower stations in Wujiang River.Hydropower and New Energy(水电与新能源), (7), 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Hu ML, Wu ZQ, Liu YL (2009) The fish fauna of mountain streams in the Guanshan National Nature Reserve, Jiangxi, China.Environmental Biology of Fishes, 86, 23-27. |
| 15 | Hudman SP, Gido KB (2013) Multi-scale effects of impoundments on genetic structure of creek chub (Semotilus atromaculatus) in the Kansas River basin.Freshwater Biology, 58, 441-453. |
| 16 | Jellyman PG, Harding JS (2012) The role of dams in altering freshwater fish communities in New Zealand.Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 46, 475-489. |
| 17 | Kumar NAS, Kumar J, Mahesh V, Benakappa S (2013) Assessment of fish diversity of Tunga River, Karnataka, India.Nature and Science, 11(2), 82-87. |
| 18 | Li KJ (李寇军), Qiu YS (邱永松), Wang YZ (王跃中) (2007) Influence of natural environment variation on fishery resources in Beibu Gulf.South China Fisheries Science(南方水产), 3(1), 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 19 | Lin ML (林明利), Zhang TL (张堂林), Ye SW (叶少文), Li W (李文), Ren P (任鹏), Yang ZW (杨战伟), Liu JS (刘家寿), Li ZJ (李钟杰) (2013) Status of fish resources, historical variation and fisheries management strategies in Hongze Lake.Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica(水生生物学报), 37, 1118-1127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Liu JK (刘建康), Cao WX (曹文宣) (1992) Fish resources of the Yangtze River Basin and the tactics for their conservation.Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Valley(长江流域资源与环境), 1(1), 17-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Manuwadi H, Wilaiwan U, Penjai S, Watanee H (2002) Possible impact of dam reservoirs and river diversions on material fluxes to the Gulf of Thailand.Marine Chemistry, 79, 185-191. |
| 22 | Paul WW (2008) The impact of changes in water level and human development on forage fish assemblages in Great Lakes coastal marshes.Journal of Great Lakes Research, 34, 615-630. |
| 23 | Sun SS (孙莎莎), Tang WQ (唐文乔), Guo HY (郭弘艺), Li HH (李辉华), Liu D (刘东), Zhou TS (周天舒), Chen HZ (陈浩洲), Shen LH (沈林宏), Gu SX (顾树信) (2013) Composition and changes in abundance and biomass of fish assemblages along the Jingjiang section of the Yangtze River over the last decade.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 21, 688-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 24 | Tarkan AS, Copp GH, Top N, Özdemir N, Önsoy B, Bikge G, Filiz H, Yapici S, Ekmmei FG, Kirankaya ŞG, Emiroglu Ö, Gaygusuz Ö, Gursoy G, Oymark A, Özcan G, Sa G (2012) Are introduced gibel carp Carassius gibelio in Turkey more invasive in artificial than in natural waters?Fisheries Management and Ecology, 19, 178-187. |
| 25 | Waples RS, Zabel RW, Scheuerell MD, Sanderson BL (2008) Evolutionary responses by native species to major anthropogenic changes to their ecosystems: Pacific salmon in the Columbia River hydropower system.Molecular Ecology, 17, 84-96. |
| 26 | Xie P (2003) Three-Gorges Dam: risk to ancient fish.Science, 302, 1149. |
| 27 | Xiong LF (熊六凤), Ouyang S (欧阳珊), Chen TH (陈堂华), Qi T (祁涛), Wu XP (吴小平) (2010) The resource status and spatio-temporal variation of freshwater mussel in Qinglan Lake of Jiangxi Province.Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报), 32, 1257-1264. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 28 | Yang SR, Gao X, Li MZ, Ma BS, Liu HZ (2012) Interannual variations of the fish assemblage in the transitional zones of the Three Gorges Reservoir: persistence and stability.Environmental Biology of Fishes, 93, 295-304. |
| 29 | Yang Z (杨志), Zheng HT (郑海涛), Xiong MH (熊美华), Hu JX (胡菊香), Qiao Y (乔晔), Wang X (王翔), Zhang YC (张轶超), Chang JB (常剑波) (2011) Variation characteristics of fish community structure and biodiversity in autumn before and after impoundment of Pengshui Hydropower Station.Environmental Science and Technology(环境科学与技术), 34(8), 22-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 30 | Yemane D, Field JG, Leslie R (2005) Exploring the effects of fishing on fish assemblages using abundance biomass comparison (ABC) curves.Journal of Marine Science, 62, 374-379. |
| 31 | Yu XD (于晓东), Luo TH (罗天宏), Zhou HZ (周红章) (2005) Large-scale patterns in species diversity of fishes in the Yangtze River Basin.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 13, 473-495. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 32 | Yue PQ (乐佩琦) (2000) Fauna Sinica (Osteichthyes): Cypriniformes III (中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(下卷)). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 33 | Zhang T (张涛), Zhuang P (庄平), Zhang LZ (章龙珍), Hou JL (侯俊利), Liu JY (刘鉴毅), Wang YL (王云龙), Liu J (刘健) (2010) Composition and diversity of fish species in the coast of the Yangtze River Estuary.Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology(应用与环境生物学报), 16, 817-821. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 34 | Zhang JT (张金屯) (2004) Quantified Ecology (数量生态学). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 35 | Zhang JM (张觉民), He ZH (何志辉) (1991) Manual of Investigation for Fisheries Resources in Inland Waters (内陆水域渔业自然资源调查手册), pp. 242-298. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 36 | Zhu SQ (朱松泉) (1995) Synopsis of Freshwater Fishes of China (中国淡水鱼类检索). Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Jingyi Yuan, Xu Zhang, Zhenpeng Tian, Zizhe Wang, Yongping Gao, Dizhao Yao, Hongcan Guan, Wenkai Li, Jing Liu, Hong Zhang, Qin Ma. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [5] | Ma Wenjun, Liu Sijia, Li Kemao, Jian Shenglong, Xue Chang’an, Han Qingxiango, Wei Jinliang, Chen Shengxue, Niu Yimeng, Cui Zhouping, Sui Ruichen, Tian Fei, Zhao Kai. Fish diversity and distribution in the source region of the Yangtze River in Qinghai Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [6] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [7] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [8] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [9] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [10] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [11] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [13] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [14] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [15] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn