



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 25142. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025142 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025142
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lijie Niu1,3( ), Yingying Hou1,3, Shijia Wen1, Haiping Zhang2,3, Aqie Qubi1,3, Yuansheng Fu1,4, Hong Wang1, Zongxin Ren1,3,*(
), Yingying Hou1,3, Shijia Wen1, Haiping Zhang2,3, Aqie Qubi1,3, Yuansheng Fu1,4, Hong Wang1, Zongxin Ren1,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-18
Accepted:2025-07-07
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
*E-mail: renzongxin@mail.kib.ac.cn
Supported by:Lijie Niu, Yingying Hou, Shijia Wen, Haiping Zhang, Aqie Qubi, Yuansheng Fu, Hong Wang, Zongxin Ren. Floral nectar: Secretion behavior, cost and regulation[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(8): 25142.
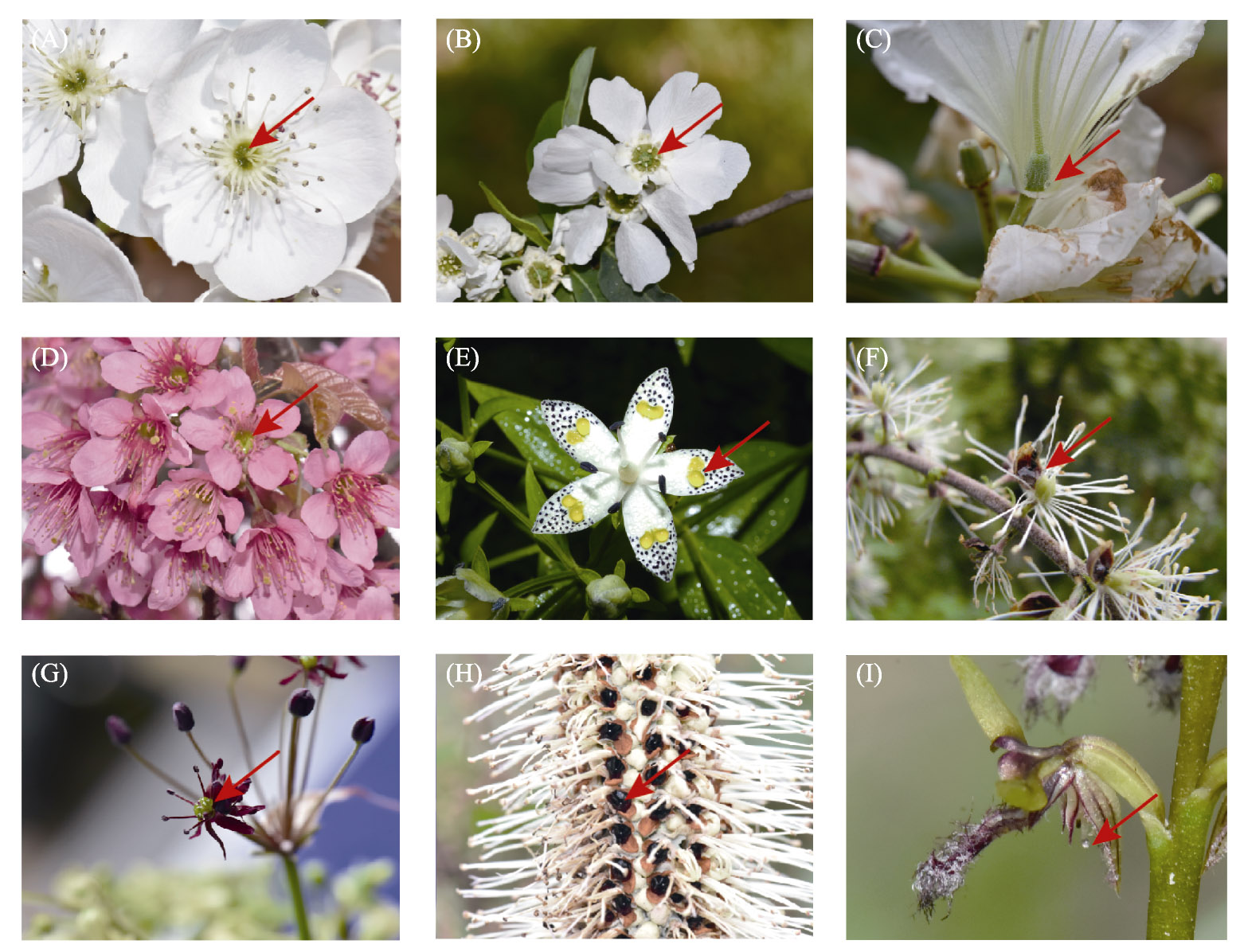

Fig. 1 Floral nectar and nectaries diversity in flowering plants. A, Sticky floral nectar of Pyrus spp. in early spring; B, Crystallized sugar on the nectaries of Exochorda racemosa; C, Nectar drops at the base of corolla of Rhododendron decorum; D, Flowers of Prunus cerasoides produce a large amount of diluted nectar, it is pollinated by birds and bees; E, The nectaries of Swertia bimaculata locate at the middle of tepals with two yellow anther-like marks; F, Tepals of Actaea cimicifuga have evolved into nectaries, secreting nectar drops; G, Nectar drops at the base of ovary of Allium wallichii; H, Flowers of bird pollinated Leucosceptrum canum contain black colored nectar; I, Nectar droplet on the terminus of the auricle of column of Corunastylis fimbriata (Orchidaceae) from Australia. Red arrows indicate nectar or nectary.
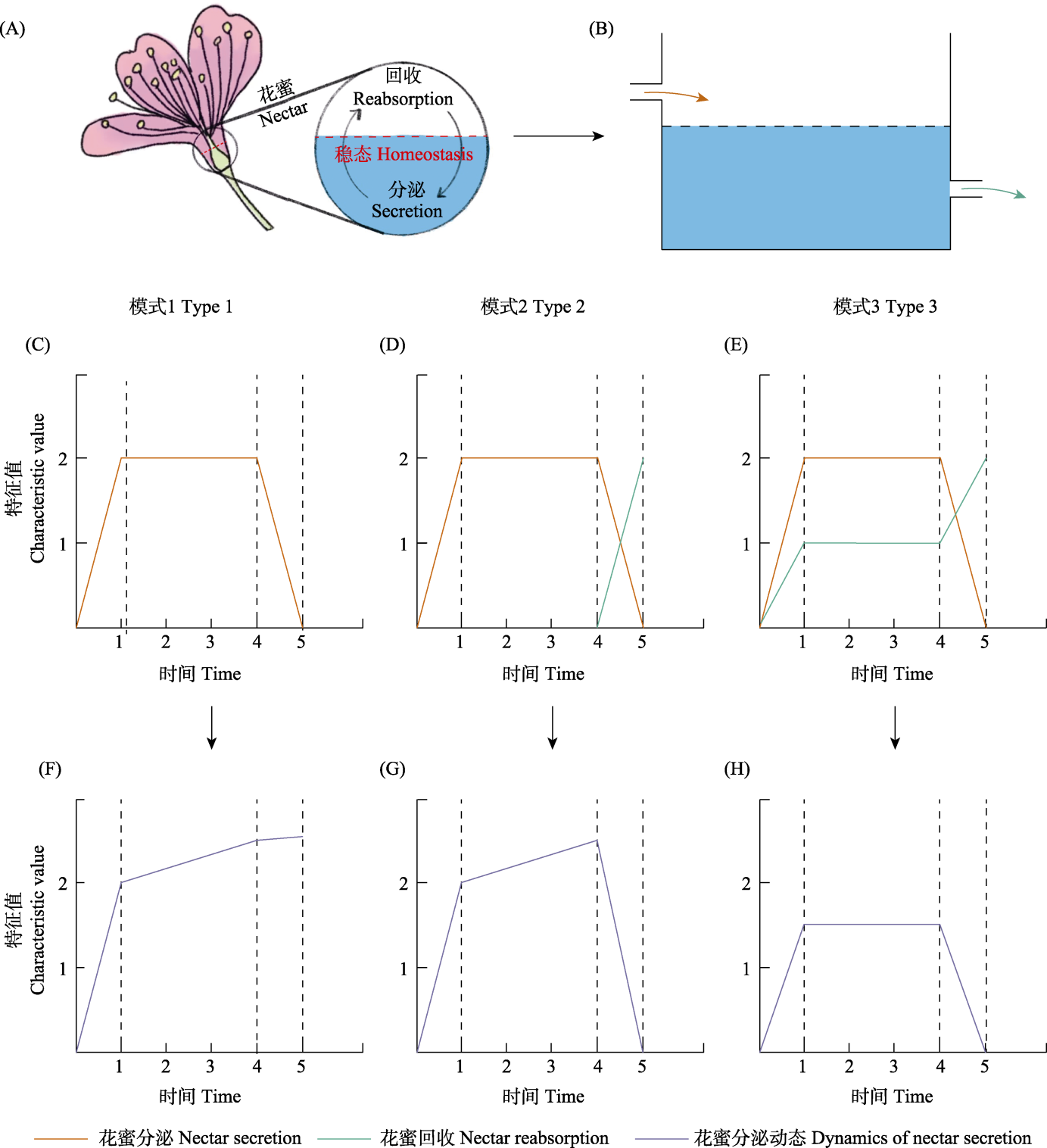
Fig. 2 Floral nectar secretion and regulation. A-B, In general, floral nectaries of many plant species have secretion and reabsorption function to regulate nectar production to reach sugar homeostasis. However, time and dynamic of nectar secretion and reabsorption remain unclear. Usually, floral nectar production can be subdivided into three stages, beginning, continuous secretion and decline secretion at the end of floral longevity. Both sugar and water could be reabsorbed or not, absorption could happen at the end of flower age or begin since the secretion starts. Therefore, there are three major types of floral nectar dynamics. Type 1, Secretion but without reabsorption (C), floral nectar values (volume and sugar concentration) accumulated (F); Type 2, Secretion and reabsorption at the end of floral age (D), floral nectar values continue to increase but decline at the end of floral age (G); Type 3, Secretion and absorption at the same time (E), in this case, nectar values keep in a stable level until flower wilts (H). The characteristic value represents nectar volume, sugar concentration or sugar mass.
| [1] |
Adler LS, Wink M, Distl M, Lentz A (2006) Leaf herbivory and nutrients increase nectar alkaloids. Ecology Letters, 9, 960-967.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Aizen M, Basilio A (1998) Sex differential nectar secretion in protandrous Alstroemeria aurea (Alstroemeriaceae): Is production altered by pollen removal and receipt? American Journal of Botany, 85, 245.
PMID |
| [3] | Armbruster S (2006) Evolutionary and ecological aspects of specialized pollination:Views from the Arctic to the tropics. In: Plant-pollinator Interactions:From Specialization to Generalization (eds Waser N, Ollerton J), pp. 260-282. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [4] |
Ballarin CS, Fontúrbel FE, Rech AR, Oliveira PE, Goés GA, Polizello DS, Oliveira PH, Hachuy-Filho L, Amorim FW (2024) How many animal-pollinated angiosperms are nectar-producing? New Phytologist, 243, 2008-2020.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Barberis M, Nepi M, Galloni M (2024) Floral nectar: Fifty years of new ecological perspectives beyond pollinator reward. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 62, 125764.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Barman M, Tenhaken R, Dötterl S (2024) Negative and sex-specific effects of drought on flower production, resources and pollinator visitation, but not on floral scent in monoecious Cucurbita pepo. New Phytologist, 244, 1013-1023.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Bernardello G (2007) A systematic survey of floral nectaries. In: Nectaries and Nectar (eds Nicolson SW, Nepi M, Pacini E), pp.19-128. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht. |
| [8] |
Bernardello L, Galetto L, Rodriguez IG (1994) Reproductive biology, variability of nectar features and pollination of Combretum fruticosum (Combretaceae) in Argentina. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 114, 293-308.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bertsch A (1983) Nectar production of Epilobium angustifolium L. at different air humidities: Nectar sugar in individual flowers and the optimal foraging theory. Oecologia, 59, 40-48.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Bogo G, Fisogni A, Rabassa-Juvanteny J, Bortolotti L, Nepi M, Guarnieri M, Conte L, Galloni M (2021) Nectar chemistry is not only a plant’s affair: Floral visitors affect nectar sugar and amino acid composition. Oilos, 130, 1180-1192. |
| [11] | Bonnier G (1878) Les nectaires. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Botanique, Série 6, 8, 5-212. |
| [12] |
Boose DL (1997) Sources of variation in floral nectar production rate in Epilobium canum (Onagraceae): Implications for natural selection. Oecologia, 110, 493-500.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Brandenburg A, Dell’Olivo A, Bshary R, Kuhlemeier C (2009) The sweetest thing: Advances in nectar research. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 12, 486-490.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Brito Vera GA, Pérez F (2024) Floral nectar (FN): Drivers of variability, causes, and consequences. Brazilian Journal of Botany, 47, 473-483.
DOI |
| [15] |
Bukovics P, Orosz-Kovács Z, Szabó L, Farkas Á, Bubán T (2003) Composition of floral nectar and its seasonal variability in sour cherry cultivars. Acta Botanica Hungarica, 45, 259-271.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Burkle LA, Irwin RE (2010) Beyond biomass: Measuring the effects of community-level nitrogen enrichment on floral traits, pollinator visitation and plant reproduction. Journal of Ecology, 98, 705-717.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Búrquez A, Corbet SA (1991) Do flowers reabsorb nectar? Functional Ecology, 5, 369-379.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Cardoso-Gustavson P, Davis AR (2015) Is nectar reabsorption restricted by the stalk cells of floral and extrafloral nectary trichomes? Plant Biology, 17, 134-146.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Carlson JE, Harms KE (2006) The evolution of gender-biased nectar production in hermaphroditic plants. The Botanical Review, 72, 179-205.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Castellanos MC, Wilson P, Thomson JD (2002) Dynamic nectar replenishment in flowers of Penstemon (Scrophulariaceae). American Journal of Botany, 89, 111-118. |
| [21] |
Cawoy V, Kinet JM, Jacquemart AL (2008) Morphology of nectaries and biology of nectar production in the distylous species Fagopyrum esculentum. Annals of Botany, 102, 675-684.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Clearwater MJ, Noe ST, Manley-Harris M, Truman GL, Gardyne S, Murray J, Obeng-Darko SA, Richardson SJ (2021) Nectary photosynthesis contributes to the production of mānuka (Leptospermum scoparium) floral nectar. New Phytologist, 232, 1703-1717.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Corbet SA (2003) Nectar sugar content: Estimating standing crop and secretion rate in the field. Apidologie, 34, 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Corbet SA, Unwin DM, Prŷs-Jones OE (1979) Humidity, nectar and insect visits to flowers, with special reference to Crataegus, Tilia and Echium. Ecological Entomology, 4, 9-22.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Corbet SA, Willmer PG (1981) The nectar of Justicia and Columnea: Composition and concentration in a humid tropical climate. Oecologia, 51, 412-418.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Cruden RW, Hermann SM, Peterson S (1983) Patterns of nectar production and plant-pollinator coevolution. In: The Biology of Nectaries (eds Bentley B, Elias T), pp. 259. Columbia University Press, New York. |
| [27] | Davis JK, Aguirre LA, Barber NA, Stevenson PC, Adler LS (2019) From plant fungi to bee parasites: Mycorrhizae and soil nutrients shape floral chemistry and bee pathogens. Ecology, 100, e02801. |
| [28] |
De la Barrera E, Nobel PS (2004) Nectar: Properties, floral aspects, and speculations on origin. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 65-69.
PMID |
| [29] |
Dong K, Dong Y, Su R, Zhang J, Qing Z, Yang X, Ren X, Ma Y, He S (2016) Effect of nectar reabsorption on plant nectar investment in Cerasus cerasoides. Current Science, 110, 251-256.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Dreisig H (2012) How long to stay on a plant: The response of bumblebees to encountered nectar levels. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 6, 315-325.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Dutton EM, Luo EY, Cembrowski AR, Shore JS, Frederickson ME (2016) Three’s a crowd: Trade-offs between attracting pollinators and ant bodyguards with nectar rewards in Turnera. The American Naturalist, 188, 38-51.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Fahn A (1979) Secretory Tissues in Plants. Academic Press, London. |
| [33] | Fahn A (2000) Structure and function of secretory cells. Advances in Botanical Research, 31, 37-75. |
| [34] |
Farkas Á, Orosz-Kovács Z (2003) Nectar secretion dynamics of Hungarian local pear cultivars. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 238, 57-67.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Fernandes N, Luz L, Alves Filho E, de Aragão FA, Zocolo G, Freitas B (2023) Differences in the chemical composition of Melon (Cucumis melo L.) nectar explain flower gender preference by its pollinator, Apis mellifera. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 34, 976-986. |
| [36] |
Fischer M, Matthies D (1997) Mating structure and inbreeding and outbreeding depression in the rare plant Gentianella germanica (Gentianaceae). American Journal of Botany, 84, 1685-1692.
PMID |
| [37] |
Galetto L, Araujo FP, Grilli G, Amarilla LD, Torres C, Sazima M (2018) Flower trade-offs derived from nectar investment in female reproduction of two Nicotiana species (Solanaceae). Acta Botanica Brasilica, 32, 473-478.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Galetto L, Bernardello G (1993) Nectar secretion pattern and removal effects in three species of Solanaceae. Canadian Journal of Botany, 71, 1394-1398.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Galetto L, Bernardello G (2004) Floral nectaries, nectar production dynamics and chemical composition in six Ipomoea species (Convolvulaceae) in relation to pollinators. Annals of Botany, 94, 269-280.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Galetto L, Bernardello LM, Juliani H (1994) Characteristics of secretion of nectar in Pyrostegia venusta (Ker-Gawl.) Miers (Bignoniaceae). New Phytologist, 127, 465-471.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Gillespie LH, Henwood MJ (1994) Temporal changes of floral nectar-sugar composition in Polyscias sambucifolia (Sieb. ex Dc.) Harms (Araliaceae). Annals of Botany, 74, 227-231.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Golubov J, Mandujano MC, Montaña C, López-Portillo J, Eguiarte LE (2004) The demographic costs of nectar production in the desert perennial Prosopis glandulosa (Mimosoideae): A modular approach. Plant Ecology, 170, 267-275.
DOI |
| [43] | González-Teuber M, Heil M (2009) Nectar chemistry is tailored for both attraction of mutualists and protection from exploiters. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 4, 809-813. |
| [44] |
Grierson ERP, Thrimawithana AH, van Klink JW, Lewis DH, Carvajal I, Shiller J, Miller P, Deroles SC, Clearwater MJ, Davies KM, Chagné D, Schwinn KE (2024) A phosphatase gene is linked to nectar dihydroxyacetone accumulation in mānuka (Leptospermum scoparium). New Phytologist, 242, 2270-2284.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Halpern SL, Adler LS, Wink M (2010) Leaf herbivory and drought stress affect floral attractive and defensive traits in Nicotiana quadrivalvis. Oecologia, 163, 961-971.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Heil M (2011) Nectar: Generation, regulation and ecological functions. Trends in Plant Science, 16, 191-200.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Hoover SER, Ladley JJ, Shchepetkina AA, Tisch M, Gieseg SP, Tylianakis JM (2012) Warming, CO2, and nitrogen deposition interactively affect a plant-pollinator mutualism. Ecology Letters, 15, 227-234.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Jabbour F (2017) A study of the anatomy and physiology of nectaries: A translation of Gaston Bonnier’s seminal work (1878, Bulletin de la Société Botanique de France). Botany Letters, 164, 293-302.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Jakobsen HB, Kritjánsson K (1994) Influence of temperature and floret age on nectar secretion in Trifolium repens L. Annals of Botany, 74, 327-334.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Kato S, Sakai S (2008) Nectar secretion strategy in three Japanese species: Changes in nectar volume and sugar concentration dependent on flower age and flowering order. Botany, 86, 337-345.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Keasar T, Sadeh A, Shmida A (2008) Variability in nectar production and standing crop, and their relation to pollinator visits in a Mediterranean shrub. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 2, 117-123.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Kim W, Gilet T, Bush JWM (2011) Optimal concentrations in nectar feeding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 16618-16621. |
| [53] | Klein AM, Vaissière BE, Cane JH, Steffan-Dewenter I, Cunningham SA, Kremen C, Tscharntke T (2007) Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 274, 303-313. |
| [54] |
Koopowitz H, Marchant T (1998) Postpollination nectar reabsorption in the African epiphyte Aerangis verdickii (Orchidaceae). American Journal of Botany, 85, 508.
PMID |
| [55] |
Koptur S, Palacios-Rios M, Díaz-Castelazo C, MacKay WP, Rico-Gray V (2013) Nectar secretion on fern fronds associated with lower levels of herbivore damage: Field experiments with a widespread epiphyte of Mexican cloud forest remnants. Annals of Botany, 111, 1277-1283.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Kuo J, Pate JS (1985) The extrafloral nectaries of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp). I. Morphology, anatomy and fine structure. Planta, 166, 15-27.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
Lake JC, Hughes L (1999) Nectar production and floral characteristics of Tropaeolum majus L. grown in ambient and elevated carbon dioxide. Annals of Botany, 84, 535-541.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Langenberger M, Davis A (2002) Temporal changes in floral nectar production, reabsorption, and composition associated with dichogamy in annual caraway (Carum carvi; Apiaceae). American Journal of Botany, 89, 1588-1598.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Leiss KA, Vrieling K, Klinkhamer PGL (2004) Heritability of nectar production in Echium vulgare. Heredity, 92, 446-451.
PMID |
| [60] |
Liao H, Fu XH, Zhao HQ, Cheng J, Zhang R, Yao X, Duan XS, Shan HY, Kong HZ (2020) The morphology, molecular development and ecological function of pseudonectaries on Nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae) petals. Nature Communications, 11, 1777.
DOI |
| [61] |
Liao IT, Hileman LC, Roy R (2021) On the horizon for nectar-related research. American Journal of Botany, 108, 2326-2330.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Lun HN, Yang CF (2025) Quantitative analyses reveal interactions of community plants and insect flower visitors are associated with relative composition of nectar amino acids. Plant Ecology, 226, 451-463.
DOI |
| [63] |
Lunau K, Ren ZX, Fan XQ, Trunschke J, Pyke GH, Wang H (2020) Nectar mimicry: A new phenomenon. Scientific Reports, 10, 7039.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Luo EY, Ogilvie JE, Thomson JD (2014) Stimulation of flower nectar replenishment by removal: A survey of eleven animal-pollinated plant species. Journal of Pollination Ecology, 12, 52-62.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Luyt R, Johnson SD (2002) Postpollination nectar reabsorption and its implications for fruit quality in an epiphytic orchid. Biotropica, 34, 442-446.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Marazzi B, Bronstein JL, Koptur S (2013) The diversity, ecology and evolution of extrafloral nectaries: Current perspectives and future challenges. Annals of Botany, 111, 1243-1250.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Millard J, Outhwaite CL, Kinnersley R, Freeman R, Gregory RD, Adedoja O, Gavini S, Kioko E, Kuhlmann M, Ollerton J, Ren ZX, Newbold T (2021) Global effects of land-use intensity on local pollinator biodiversity. Nature Communications, 12, 2902.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Nachev V, Stich KP, Winter C, Bond A, Kamil A, Winter Y (2017) Cognition-mediated evolution of low-quality floral nectars. Science, 355, 75-78.
DOI PMID |
| [69] | Nachev V, Winter Y (2017) Response to Comment on “Cognition-mediated evolution of low-quality floral nectars”. Science, 358, eaao2622. |
| [70] |
Nardone E, Dey T, Kevan PG (2013) The effect of sugar solution type, sugar concentration and viscosity on the imbibition and energy intake rate of bumblebees. Journal of Insect Physiology, 59, 919-933.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | Nepi M (2017) New perspectives in nectar evolution and ecology: Simple alimentary reward or a complex multiorganism interaction? Acta Agrobotanica, 70, 1704. |
| [72] |
Nepi M, Grasso DA, Mancuso S (2018) Nectar in plant-insect mutualistic relationships: From food reward to partner manipulation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1063.
DOI PMID |
| [73] |
Nepi M, Guarnieri M, Pacini E (2001) Nectar secretion, reabsorption, and sugar composition in male and female flowers of Cucurbita pepo. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 162, 353-358.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Nepi M, Pacini E, Willemse MTM (1996) Nectary biology of Cucurbita pepo: Ecophysiological aspects. Acta Botanica Neerlandica, 45, 41-54.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Nepi M, Stpiczyńska M (2008a) The complexity of nectar: Secretion and resorption dynamically regulate nectar features. Naturwissenschaften, 95, 177-184.
DOI URL |
| [76] | Nepi M, Stpiczyńska M (2008b) Do plants dynamically regulate nectar features through sugar sensing? Plant Signaling & Behavior, 3, 874-876. |
| [77] |
Ng M, Yanofsky MF (2000) Three ways to learn the ABCs. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 3, 47-52.
PMID |
| [78] |
Nicolson SW (1995) Direct demonstration of nectar reabsorption in the flowers of Grevillea robusta (Proteaceae). Functional Ecology, 9, 584-588.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Nicolson SW (2022) Sweet solutions: Nectar chemistry and quality. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 377, 20210163.
DOI URL |
| [80] | Nicolson SW, Nepi M, Pacini E (2007) Nectaries and Nectar. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht. |
| [81] | Nicolson SW, de Veer L, Köhler A, Pirk CWW (2013) Honeybees prefer warmer nectar and less viscous nectar, regardless of sugar concentration. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280, 20131597. |
| [82] |
Ollerton J (2017) Pollinator diversity: Distribution, ecological function, and conservation. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 48, 353-376.
DOI URL |
| [83] | Ollerton J, Johnson S, Hingston AB (2006) Geographical variation in diversity and specificity of pollination systems. In: Plant-Pollinator Interactions: From Specialization to Generalization (eds Ollerton J, Waser N), pp,283-308, University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [84] |
Ollerton J, Winfree R, Tarrant S (2011) How many flowering plants are pollinated by animals? Oikos, 120, 321-326.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Osborne J, Awmack C, Clark S, Williams I, Mills VCJA (1997) Nectar and flower production in Vicia faba L. (field bean) at ambient and elevated carbon dioxide. Apidologie, 28, 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Pacini E, Nepi M, Vesprini JL (2003) Nectar biodiversity: A short review. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 238, 7-21.
DOI URL |
| [87] | Pan C, Chen Z, Zhang M, Chen X, Smagghe G, Fan M, Chang Z, Zhao L, Long J (2024) Effects of flowering period on floral traits, pollinator behavior and seed production of David’s mountain laurel (Sophora davidii). Plant Signaling & Behavior, 19, 2383823. |
| [88] |
Parachnowitsch AL, Manson JS, Sletvold N (2019) Evolutionary ecology of nectar. Annals of Botany, 123, 247-261.
DOI PMID |
| [89] |
Patiño S, Grace J (2002) The cooling of convolvulaceous flowers in a tropical environment. Plant, Cell & Environment, 25, 41-51.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Pattrick JG, Symington HA, Federle W, Glover BJ (2020) The mechanics of nectar offloading in the bumblebee Bombus terrestris and implications for optimal concentrations during nectar foraging. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 17, 20190632.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
Pedersen MW, LeFevre CW, Wiebe HH (1958) Absorption of C14-labeled sucrose by alfalfa nectaries. Science, 127, 758-759.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
Phillips BB, Shaw RF, Holland MJ, Fry EL, Bardgett RD, Bullock JM, Osborne JL (2018) Drought reduces floral resources for pollinators. Global Change Biology, 24, 3226-3235.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Prasifka JR, Mallinger RE, Portlas ZM, Hulke BS, Fugate KK, Paradis T, Hampton ME, Carter CJ (2018) Using nectar-related traits to enhance crop-pollinator interactions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 812.
DOI PMID |
| [94] |
Pyke GH (1991) What does it cost a plant to produce floral nectar? Nature, 350, 58-59.
DOI |
| [95] |
Pyke GH (2016a) Floral nectar: Pollinator attraction or manipulation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 339-341.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Pyke GH (2016b) Plant-pollinator co-evolution: It’s time to reconnect with Optimal Foraging Theory and Evolutionarily Stable Strategies. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 19, 70-76.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Pyke GH, Ren ZX (2023) Floral nectar production: What cost to a plant? Biological Reviews, 98, 2078-2090.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
Pyke GH, Ren ZX, Trunschke J, Lunau K, Wang H (2020a) Changes in floral nectar are unlikely adaptive responses to pollinator flight sound. Ecology Letters, 23, 1421-1422.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
Pyke GH, Ren ZX, Trunschke J, Lunau K, Wang H (2020b) Salvage of floral resources through re-absorption before flower abscission. Scientific Reports, 10, 15960.
DOI |
| [100] |
Pyke GH, Waser NM (1981) The production of dilute nectars by hummingbird and honeyeater flowers. Biotropica, 13, 260-270.
DOI URL |
| [101] | Pyke GH, Waser NM (2017) Comment on “Cognition-mediated evolution of low-quality floral nectars”. Science, 358, eaao1962. |
| [102] |
Quevedo-Caraballo S, de Vega C, Lievens B, Fukami T, Álvarez-Pérez S (2025) Tiny but mighty? Overview of a decade of research on nectar bacteria. New Phytologist, 245, 1897-1910.
DOI PMID |
| [103] |
Ren G, Healy RA, Klyne AM, Horner HT, James MG, Thornburg RW (2007) Transient starch metabolism in ornamental tobacco floral nectaries regulates nectar composition and release. Plant Science, 173, 277-290.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Rivera GL, Galetto L, Bernardello L (1996) Nectar secretion pattern, removal effects, and breeding system of Ligaria cuneifolia (Loranthaceae). Canadian Journal of Botany, 74, 1996-2001.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
Roy R, Schmitt AJ, Thomas JB, Carter CJ (2017) Nectar biology: From molecules to ecosystems. Plant Science, 262, 148-164.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Schaeffer RN, Mei Y, Andicoechea J, Manson JS, Irwin RE (2017) Consequences of a nectar yeast for pollinator preference and performance. Functional Ecology, 31, 613-621.
DOI URL |
| [107] | Shi L, Nicolson SW, Yang Y, Wu J, Yan S, Wu Z (2020) Drinking made easier: Honey bee tongues dip faster into warmer and/or less viscous artificial nectar. Journal of Experimental Biology, 223, jeb229799. |
| [108] |
Silvertown J, Gordon DM (1989) A framework for plant behavior. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 20, 349-366.
DOI URL |
| [109] |
Southwick EE (1984) Photosynthate allocation to floral nectar: A neglected energy investment. Ecology, 65, 1775-1779.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
Stevenson PC, Nicolson SW, Wright GA, Manson J (2017) Plant secondary metabolites in nectar: Impacts on pollinators and ecological functions. Functional Ecology, 31, 65-75.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Stpiczyńska M (2003a) Floral longevity and nectar secretion of Platanthera chlorantha (Custer) Rchb. (Orchidaceae). Annals of Botany, 92, 191-197.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Stpiczyńska M (2003b) Incorporation of [3H] sucrose after the resorption of nectar from the spur of Platanthera chlorantha (Custer) Rchb. Canadian Journal of Botany, 81, 927-932.
DOI URL |
| [113] | Stpiczyńska M, Milanesi C, Faleri C, Cresti M (2005) Ultrastructure of the nectary spur of Platanthera chlorantha (Custer) Rchb. (Orchidaceae) during successive stages of nectar secretion. Acta Biologica Cracoviensia Series Botanica, 472, 111-119. |
| [114] |
Tadey M, Aizen MA (2001) Why do flowers of a hummingbird-pollinated mistletoe face down? Functional Ecology, 15, 782-790.
DOI URL |
| [115] | Tong ZY, Wu LY, Feng HH, Zhang M, Armbruster WS, Renner SS, Huang SQ (2023) New calculations indicate that 90% of flowering plant species are animal-pollinated. National Science Review, 10, nwad219. |
| [116] | Torres C, Galetto L (1998) Patterns and implications of floral nectar secretion, chemical composition, removal effects and standing crop in Mandevilla pentlandiana (Apocynaceae). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 127, 207-223. |
| [117] |
Vannette RL (2020) The floral microbiome: Plant, pollinator, and microbial perspectives. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 51, 363-386.
DOI |
| [118] |
Vannette RL, Fukami T (2016) Nectar microbes can reduce secondary metabolites in nectar and alter effects on nectar consumption by pollinators. Ecology, 97, 1410-1419.
PMID |
| [119] | VanValkenburg E, Gonçalves-Souza T, Sanders NJ, CaraDonna P (2024) Sodium-enriched nectar shapes plant-pollinator interactions in a subalpine meadow. Ecology and Evolution, 14, e70026. |
| [120] |
Vassilyev AE (2010) On the mechanisms of nectar secretion: Revisited. Annals of Botany, 105, 349-354.
DOI PMID |
| [121] |
Veiga-Blanco T, Galetto L, Machado IC (2013) Nectar regulation in Euphorbia tithymaloides L., a hummingbird- pollinated Euphorbiaceae. Plant Biology, 15, 910-918.
DOI PMID |
| [122] |
Veits M, Khait I, Obolski U, Zinger E, Boonman A, Goldshtein A, Saban K, Seltzer R, Ben-Dor U, Estlein P, Kabat A, Peretz D, Ratzersdorfer I, Krylov S, Chamovitz D, Sapir Y, Yovel Y, Hadany L (2019) Flowers respond to pollinator sound within minutes by increasing nectar sugar concentration. Ecology Letters, 22, 1483-1492.
DOI PMID |
| [123] |
Villarreal AG, Freeman CE (1990) Effects of temperature and water stress on some floral nectar characteristics in Ipomopsis longiflora (Polemoniaceae) under controlled conditions. Botanical Gazette, 151, 5-9.
DOI URL |
| [124] |
Wei J, Huo Z, Gorb SN, Rico-Guevara A, Wu Z, Wu J (2020) Sucking or lapping: Facultative feeding mechanisms in honeybees (Apis mellifera). Biology Letters, 16, 20200449.
DOI URL |
| [125] | Wen SJ, Chen S, Rech AR, Ji L, Wang H, Wang ZY, Wu D, Ren ZX (2024) The functional dilemma of nectar mimic staminodes in Parnassia wightiana (Celastraceae): Attracting pollinators and florivorous beetles. Ecology and Evolution, 14, e70380. |
| [126] |
Wen SJ, Deng MX, Wu D, Wang ZY, Ren ZX (2024) Comparative floral nectar attributes in four Swertia species (Gentianaceae). Biodiversity Science, 32, 23297. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[文诗嘉, 邓敏学, 吴丁, 王志勇, 任宗昕 (2024) 獐牙菜属四种植物花蜜特征的比较. 生物多样性, 32, 23297.]
DOI |
|
| [127] |
Wenzler M, Hölscher D, Oerther T, Schneider B (2008) Nectar formation and floral nectary anatomy of Anigozanthos flavidus: A combined magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy study. Journal of Experimental Botany, 59, 3425-3434.
DOI URL |
| [128] | Willmer P (2011) Pollination and Floral Ecology. Princeton University Press. Princeton. |
| [129] |
Wist TJ, Davis AR (2006) Floral nectar production and nectary anatomy and ultrastructure of Echinacea purpurea (Asteraceae). Annals of Botany, 97, 177-193.
DOI URL |
| [130] |
Witt T, Jürgens A, Geyer R, Gottsberger G (1999) Nectar dynamics and sugar composition in flowers of Silene and Saponaria species (Caryophyllaceae). Plant Biology, 1, 334-345.
DOI URL |
| [131] |
Zhang HP, Wen SJ, Wang H, Ren ZX (2023) Floral nectar reabsorption and a sugar concentration gradient in two long-spurred Habenaria species (Orchidaceae). BMC Plant Biology, 23, 331.
DOI |
| [132] | Zhao XN (2018) The Study of Reproductive Ecology on Nectar Presenting Strategies in Four Nectariferous Plants. PhD dissertation, Northeast Normal University, Changchun. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵兴楠 (2018) 花蜜呈现策略的繁殖生态学研究. 博士学位论文, 东北师范大学, 长春.] |
| [1] | Li Motong, He Tuo, Li Wei, Liao Jing, Zeng Yan. Regulating international trade in wild fauna and flora: An analysis of CITES terminology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [2] | Su Hongqiao, Yu Deguang, Mou Kunlun. Discussion on the integration path between national parks and territorial space planning and utilization regulation system [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24570-. |
| [3] | Liu Zhixiang, Xie Hua, Zhang Hui, Huang Xiaolei. Functional diversity and regulation of cuticular hydrocarbons in social insects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [4] | Nan Chen, Quan-Guo Zhang. The experimental evolution approach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [5] | Suyan Ba, Chunyan Zhao, Yuan Liu, Qiang Fang. Constructing a pollination network by identifying pollen on insect bodies: Consistency between human recognition and an AI model [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24088-. |
| [6] | Qiaoxia Li, Youlong Li, Jigang Li, Chenlong Chen, Kun Sun. Effects of photoperiods on the development of chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers in Viola monbeigii and V. dissecta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23484-. |
| [7] | Xiaohu Shen, Guanyu Li, Hongfei Shi, Chuanzhi Wang. Ensemble learning strategy for birdsong recognition under data imbalance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24215-. |
| [8] | Shijia Wen, Minxue Deng, Ding Wu, Zhiyong Wang, Zongxin Ren. Comparative floral nectar attributes in four Swertia species (Gentianaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23297-. |
| [9] | Xiaofeng Yang, Xiaomeng Li, Wanjin Liao. Advances in the genetic regulating pathways of plant flowering time [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 825-842. |
| [10] | Hui Zhang, Qian Liu, Xiaolei Huang. Mechanisms regulating caste and behavior differentiation in social insects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(4): 507-516. |
| [11] | Zhihua Zhou, Xiaohua Jin. Analysis and suggestions on policies and regulations on conservation and management of wild plants in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1583-1590. |
| [12] | Chen Qiangqiang, Li Meiling, Wang Xu, Mueen Qamer Faisal, Wang Peng, Yang Jianwei, Wang Muyang, Yang Weikang. Identification of potential ecological corridors for Marco Polo sheep in Taxkorgan Wildlife Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(2): 186-199. |
| [13] | Zeyu Tong,Huanli Xu,Shuangquan Huang. Examining methodologies of pollinator detection in the field [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(5): 433-444. |
| [14] | Xiangcheng Mi, Jing Guo, Zhanqing Hao, Zongqiang Xie, Ke Guo, Keping Ma. Chinese forest biodiversity monitoring: scientific foundations and strategic planning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(11): 1203-1219. |
| [15] | Shan Sun, Zhiqiang Zhang, Bo Zhang, Yongping Yang. Perspectives on plant-pollinator interactions from the evolution of cooperation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(3): 250-263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()