



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 23497. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023497 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023497
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Binyue Lu1,#( ), Kun Li1,#(
), Kun Li1,#( ), Chenxi Wang2(
), Chenxi Wang2( ), Sheng Li1,*(
), Sheng Li1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-12-27
Accepted:2024-03-10
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
E-mail: About author:#Co-first authors
Binyue Lu, Kun Li, Chenxi Wang, Sheng Li. The application and outlook of wildlife tracking using sensor-based tags in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23497.

Fig. 1 Examples of traditional (a-c) and sensor-based (d-i) tracking technologies used in wildlife studies in China. a, Metal leg band used for Siberian rubythroat (Calliope calliope); b, Ear tag used for Chinese takin (Budorcas taxicolor); c, Marked number on the wing of Glanville fritillary (Melitaea cinxia); d, RFID tag implanted under skin of Asiatic toad (Bufo gargarizans); e, Backpacked VHF transmitter used for Chinese brown frog (Rana chensinensis); f, VHF transmitter implanted in the abdominal cavity of Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus); g, Backpacked light-level geolocator used for common swift (Apus apus); h, Satellite-tracking device used for steppe eagle (Aquila nipalensis); i, Satellite-tracking colloar used for snow leopard (Panthera uncia). Photos were provided by Sheng Li (Fig. 1a, b), Rongjiang Wang (Fig. 1c), Cheng Li (Fig. 1d, e), Lu Zhang (Fig. 1f), Yang Liu (Fig. 1g), Pinjia Que (Fig. 1h) and Dingqian Xiang (Fig. 1i).
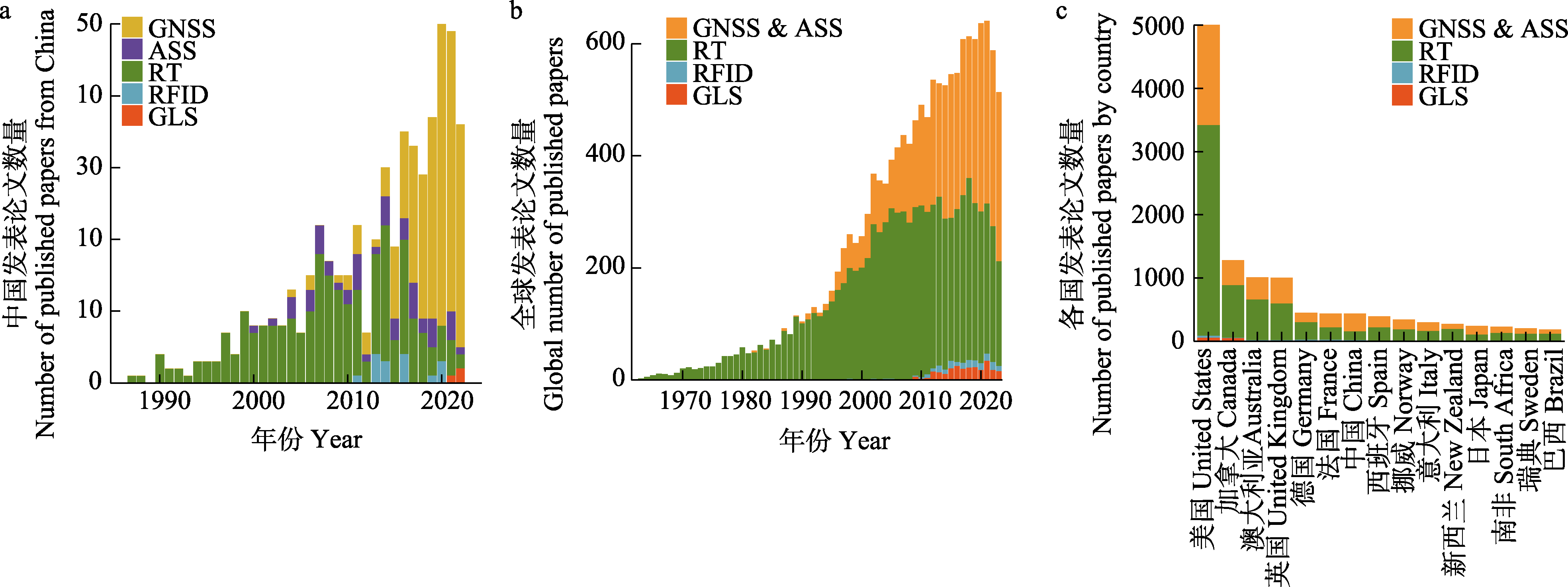
Fig. 2 Publication trends of articles on sensor-based wildlife tracking studies in China (a) and around the world (b), and the top 15 countries with the largest number of publications in English (c). GNSS, Global navigation satellite system; ASS, Argos satellite system; RT, Radio telemetry; RFID, Radio frequency identification; GLS, Light-level global location sensor.
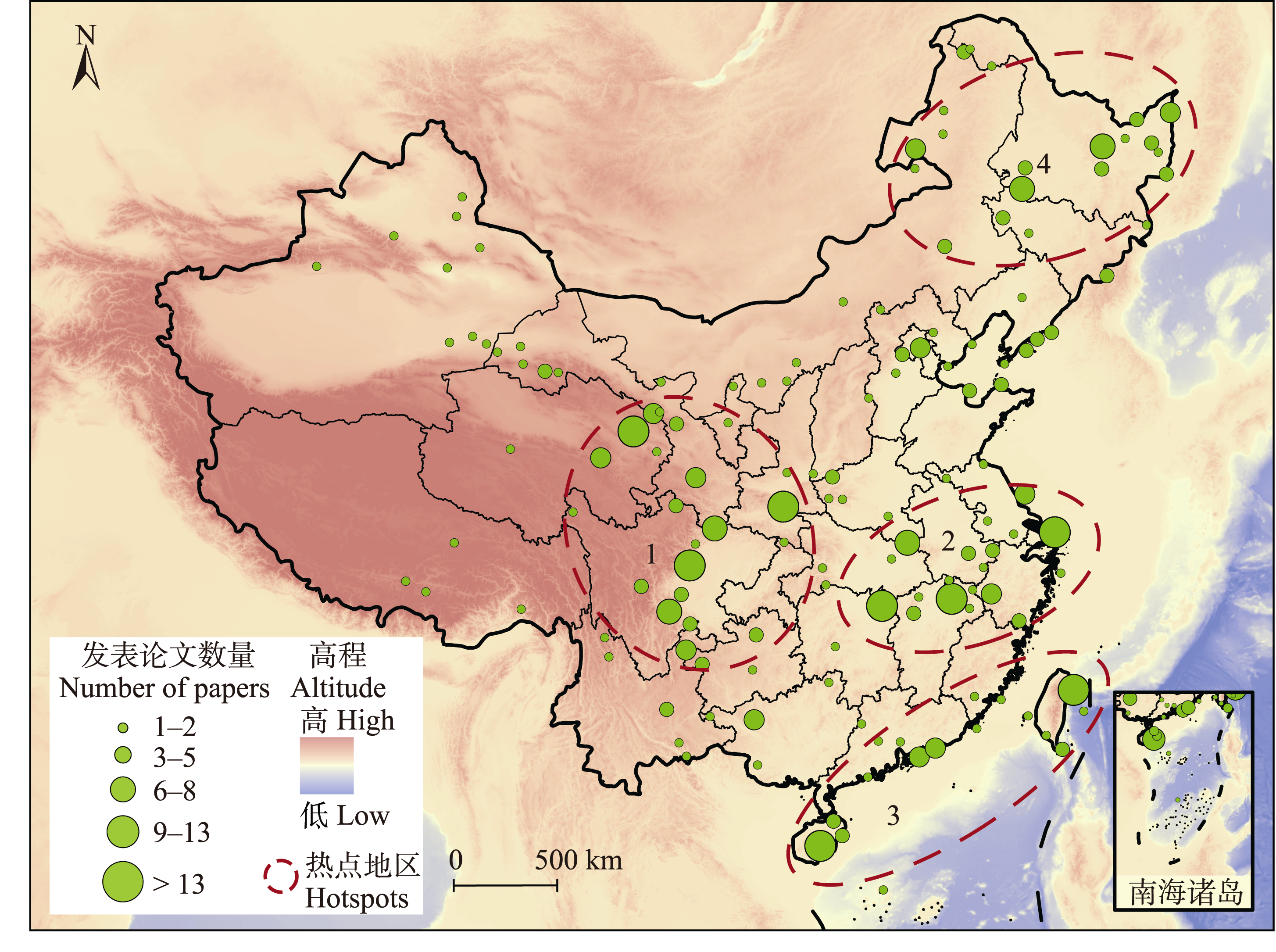
Fig. 3 The distribution of study sites and hotspots (1-4) of wildlife tracking research in China. (1) Eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and surrounding mountainous regions; (2) Middle and lower reaches region of the Yangtze River; (3) Coastal regions from East China to South China; (4) Northeastern region of China.
| 追踪技术 Tracking techniques | 定位追踪原理 Principle of positioning and tracking | 数据收回方式 Data recall mode | 是否需要再 次捕捉动物 Whether recapture needed | 定位精度 Accuracy of positioning | 单个体数据量 Data amount of each individual | 文献数量 No. of publications | 应用动物类群 Applied animal groups | 涉及物种数 No. of species involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无线射频识别技术 Radio frequency identification | RFID扫描 RFID scanning | RFID近距扫描 RFID proximity scanning | 不一定 Uncertain | +++ | + | 17 | 无脊椎动物、两栖类、爬行类、小型兽类 Invertebrates, amphibians, reptiles, small mammals | 8 |
| 无线电遥测技术 Radio telemetry | 无线电测向 与三角定位 Radio direction finding and triangulation | 无线电遥测 Radio telemetry | 否 No | ++ | ++ | 256 | 兽类、鸟类、两栖类、爬行类 Mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles | 108 |
| 光敏全球定位传感器技 术 Light-level global location sensor | 记录光强变化, 推断经纬度 Record changes in light intensity and infer latitude and longitude | 芯片数据下载 Chip data download | 是 Yes | + | ++ | 3 | 鸟类 Birds | 2 |
| Argos卫星技术 Argos satellite system | 多普勒原理 The Doppler principle | 卫星传输Satellite transmission | 否 No | + | ++ | 50 | 鸟类、爬行类 Birds, reptiles | 28 |
| 全球定位导航系统技术 Global navigation satellite system | 定位卫星星 座3维测量 Positioning satellite constellation 3-dimensional measurements | 本地存储, 回收后有线下载Local storage, wired download after recycling | 不一定 Uncertain | +++ | +++ | 211 | 大中型动物(兽类, 鸟类, 爬行类) Large and medium-sized animals (mammals, birds, reptiles) | 79 |
| 短距离UHF无线下载 Short-range UHF wireless download | 否 No | +++ | +++ | |||||
| GSM网络无线下载 Wireless download over GSM network | 否 No | +++ | +++ | |||||
| 卫星传输Satellite transmission | 否 No | +++ | +++ |
Table 1 Comparison of sensor-based tracking techniques used in wildlife tracking studies in China
| 追踪技术 Tracking techniques | 定位追踪原理 Principle of positioning and tracking | 数据收回方式 Data recall mode | 是否需要再 次捕捉动物 Whether recapture needed | 定位精度 Accuracy of positioning | 单个体数据量 Data amount of each individual | 文献数量 No. of publications | 应用动物类群 Applied animal groups | 涉及物种数 No. of species involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无线射频识别技术 Radio frequency identification | RFID扫描 RFID scanning | RFID近距扫描 RFID proximity scanning | 不一定 Uncertain | +++ | + | 17 | 无脊椎动物、两栖类、爬行类、小型兽类 Invertebrates, amphibians, reptiles, small mammals | 8 |
| 无线电遥测技术 Radio telemetry | 无线电测向 与三角定位 Radio direction finding and triangulation | 无线电遥测 Radio telemetry | 否 No | ++ | ++ | 256 | 兽类、鸟类、两栖类、爬行类 Mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles | 108 |
| 光敏全球定位传感器技 术 Light-level global location sensor | 记录光强变化, 推断经纬度 Record changes in light intensity and infer latitude and longitude | 芯片数据下载 Chip data download | 是 Yes | + | ++ | 3 | 鸟类 Birds | 2 |
| Argos卫星技术 Argos satellite system | 多普勒原理 The Doppler principle | 卫星传输Satellite transmission | 否 No | + | ++ | 50 | 鸟类、爬行类 Birds, reptiles | 28 |
| 全球定位导航系统技术 Global navigation satellite system | 定位卫星星 座3维测量 Positioning satellite constellation 3-dimensional measurements | 本地存储, 回收后有线下载Local storage, wired download after recycling | 不一定 Uncertain | +++ | +++ | 211 | 大中型动物(兽类, 鸟类, 爬行类) Large and medium-sized animals (mammals, birds, reptiles) | 79 |
| 短距离UHF无线下载 Short-range UHF wireless download | 否 No | +++ | +++ | |||||
| GSM网络无线下载 Wireless download over GSM network | 否 No | +++ | +++ | |||||
| 卫星传输Satellite transmission | 否 No | +++ | +++ |
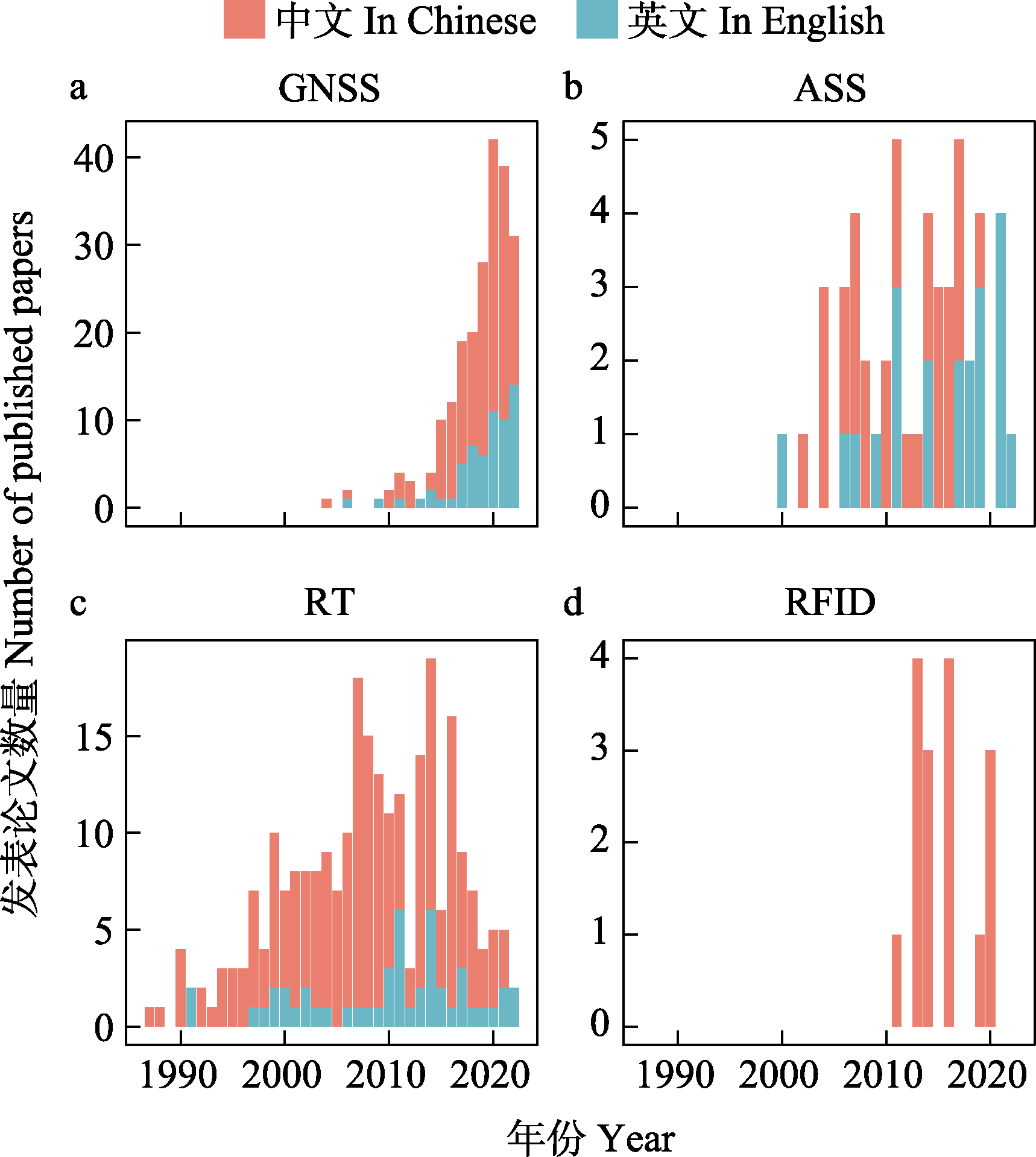
Fig. 4 Publication trends of Chinese and English articles on GNSS, ASS, RF and RFID technologies in wildlife tracking and localization research in China from 1980 to 2022 (see details for technique abbreviations in Fig. 1)
| 类群 Group | 所含分类类群 Taxonomic groups included | 论文数量 No. of papers |
|---|---|---|
| 大中型哺乳动物 Large and medium-sized mammals | 鲸偶蹄目、食肉目、灵长目、鳞甲目、奇蹄目 Cetartiodactyla, Carnivora, Primates, Pholidota, and Perissodactyla | 152 |
| 小型哺乳动物 Small mammals | 啮齿目、翼手目、攀鼩目、劳亚食虫目 Rodentia, Chiroptera, Scandentia, and Lipotyphla | 37 |
| 猛禽 Raptorial birds | 鹰形目、隼形目、鸮形目 Accipitriformes, Falconiformes, and Strigiformes | 22 |
| 涉禽 Wading birds | 鹤型目、鹳形目、鹈形目(鹭科、鹮科)、鸻形目(除鸥科、贼鸥科、海雀科外的其他科) Gruiformes, Ciconiiformes, Pelecaniformes (Ardeidae, Threskiornithidae), and Charadriiformes (other families except Laridae, Stercorariidea and Alcidae) | 109 |
| 游禽 Swimming birds | 雁形目、鸻形目(鸥科)、鲣鸟目 Anseriformes, Charadriiformes (Laridae), and Suliformes | 131 |
| 陆禽 Terrestrial birds | 鸡形目、鸨形目 Galliformes and Otidiformes | 68 |
| 其他鸟类 Other birds | 雀形目、夜鹰目、佛法僧目、鸽形目 Passeriformes, Caprimulgiformes, Coraciiformes, and Columbiformes | 14 |
| 其他脊椎动物 Other vertebrates | 龟鳖目、鳄目、有鳞目、有尾目、无尾目、须鲨目、鲀形目、鲟形目 Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, Caudata, Anura, Orectolobiformes, Tetraodontiformes, and Acipenseriformes | 53 |
| 无脊椎动物 Invertebrates | 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 7 |
Table 2 The animal groups covered by the sensor-based wildlife tracking studies in China
| 类群 Group | 所含分类类群 Taxonomic groups included | 论文数量 No. of papers |
|---|---|---|
| 大中型哺乳动物 Large and medium-sized mammals | 鲸偶蹄目、食肉目、灵长目、鳞甲目、奇蹄目 Cetartiodactyla, Carnivora, Primates, Pholidota, and Perissodactyla | 152 |
| 小型哺乳动物 Small mammals | 啮齿目、翼手目、攀鼩目、劳亚食虫目 Rodentia, Chiroptera, Scandentia, and Lipotyphla | 37 |
| 猛禽 Raptorial birds | 鹰形目、隼形目、鸮形目 Accipitriformes, Falconiformes, and Strigiformes | 22 |
| 涉禽 Wading birds | 鹤型目、鹳形目、鹈形目(鹭科、鹮科)、鸻形目(除鸥科、贼鸥科、海雀科外的其他科) Gruiformes, Ciconiiformes, Pelecaniformes (Ardeidae, Threskiornithidae), and Charadriiformes (other families except Laridae, Stercorariidea and Alcidae) | 109 |
| 游禽 Swimming birds | 雁形目、鸻形目(鸥科)、鲣鸟目 Anseriformes, Charadriiformes (Laridae), and Suliformes | 131 |
| 陆禽 Terrestrial birds | 鸡形目、鸨形目 Galliformes and Otidiformes | 68 |
| 其他鸟类 Other birds | 雀形目、夜鹰目、佛法僧目、鸽形目 Passeriformes, Caprimulgiformes, Coraciiformes, and Columbiformes | 14 |
| 其他脊椎动物 Other vertebrates | 龟鳖目、鳄目、有鳞目、有尾目、无尾目、须鲨目、鲀形目、鲟形目 Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, Caudata, Anura, Orectolobiformes, Tetraodontiformes, and Acipenseriformes | 53 |
| 无脊椎动物 Invertebrates | 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 7 |
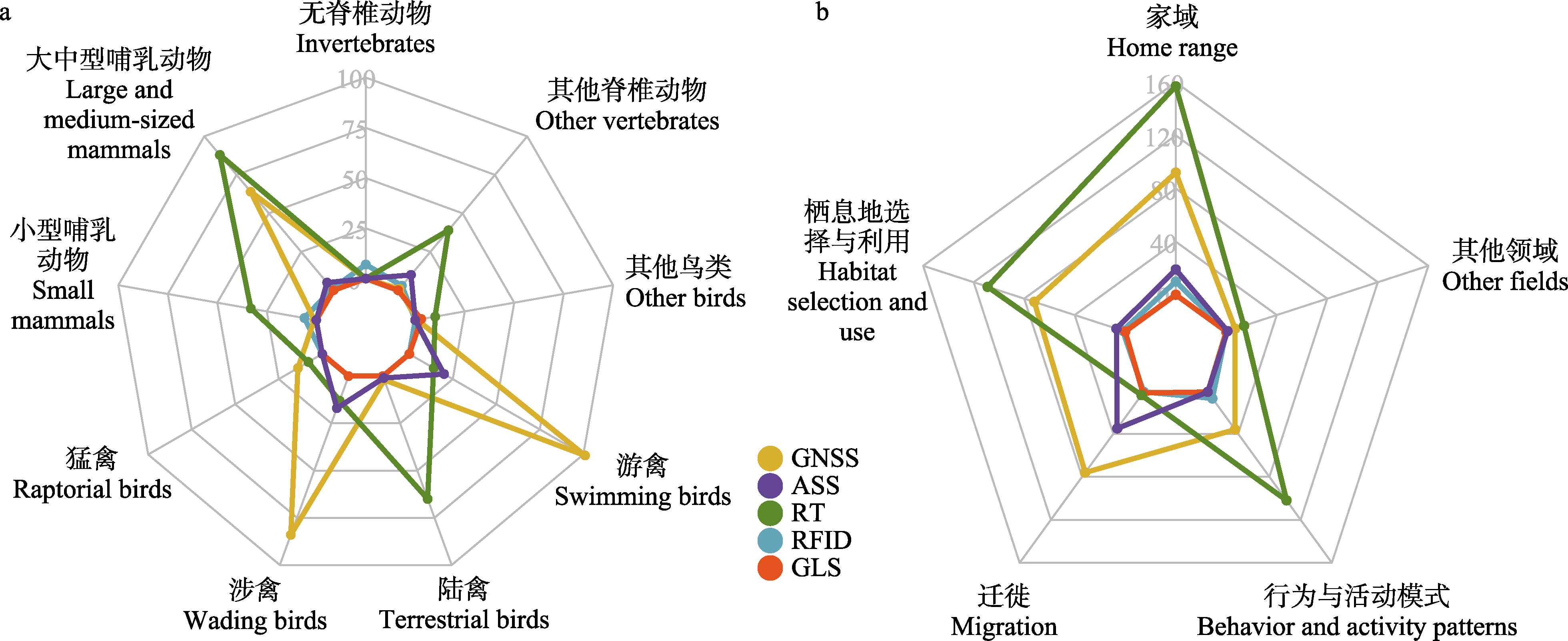
Fig. 5 Number of published articles of each technique used in different animal groups (a) and different research fields (b) (see details for technique abbreviations in Fig. 1)
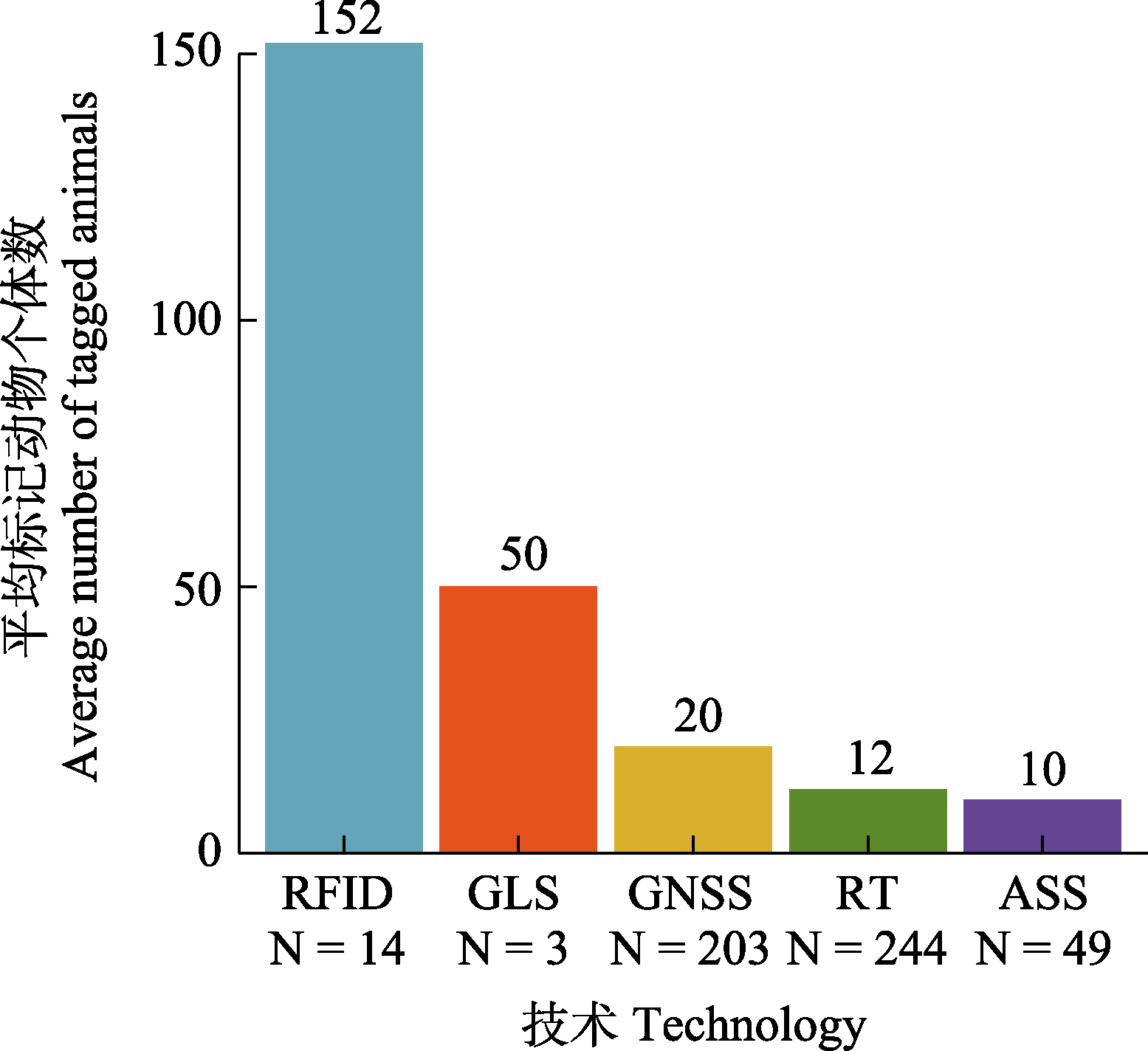
Fig. 6 The average number of animal individuals tracked by each technique in each study. N stands for the number of studies. See details for technique abbreviations in Fig. 1.
| [1] | Anderson GQA, Green RE (2009) The value of ringing for bird conservation. Ringing & Migration, 24, 205-212. |
| [2] | Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences, (2023) China checklist of animals. In: Catalogue of Life China: 2023 Annual Checklist. Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. |
| [3] | Bridge ES, Thorup K, Bowlin MS, Chilson PB, Diehl RH, Fléron RW, Hartl P, Kays RW, Kelly JF, Robinson WD, Wikelski M (2011) Technology on the move: Recent and forthcoming innovations for tracking migratory birds. BioScience, 61, 689-698. |
| [4] | Burt WH (1943) Territoriality and home range concepts as applied to mammals. Journal of Mammalogy, 24, 346-352. |
| [5] | Cai LY, Xu YP, Jiang PP, Ding P, Yao XH, Xu XR, Wang GB (2007) Home range and daily moving distance of Elliot’s pheasant. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 34, 679-683. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蔡路昀, 徐言朋, 蒋萍萍, 丁平, 姚小华, 徐向荣, 王国兵 (2007) 白颈长尾雉的活动区和日活动距离. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 34, 679-683.] | |
| [6] | Catry T, Granadeiro JP, Gutiérrez JS, Correia E (2022) Stopover use of a large estuarine wetland by dunlins during spring and autumn migrations: Linking local refuelling conditions to migratory strategies. PLoS ONE, 17, e0263031. |
| [7] | Chen JH, Zhuang P, Wu JH, Huang SL, Liu J, Yang JP, Xu JN, Zheng YP, Zhao F, Zhang T (2011) Migration and distribution of released Acipenser sinensis in the sea based on Pop-up Archival Tag technique. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18, 437-442. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈锦辉, 庄平, 吴建辉, 黄硕琳, 刘健, 杨吉平, 徐嘉楠, 郑跃平, 赵峰, 张涛 (2011) 应用弹式卫星数据回收标志技术研究放流中华鲟幼鱼在海洋中的迁移与分布. 中国水产科学, 18, 437-442.] | |
| [8] | Chen MT, Liang YJ, Kuo CC, Pei KJC (2016) Home ranges, movements and activity patterns of leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis) and threats to them in Taiwan. Mammal Study, 41, 77-86. |
| [9] | Chen YW, Yu YT, Meng FJ, Deng XQ, Cao L, Fox AD (2021) Migration routes, population status and important sites used by the globally threatened Black-faced Spoonbill (Platalea minor): A synthesis of surveys and tracking studies. Avian Research, 12, 74. |
| [10] | Cheng IJ (2000) Post-nesting migrations of green turtles (Chelonia mydas) at Wan-An Island, Penghu Archipelago, Taiwan. Marine Biology, 137, 747-754. |
| [11] | Choi C, Gan XJ, Hua N, Wang Y, Ma Z (2014) The habitat use and home range analysis of dunlin (Calidris alpina) in Chongming Dongtan, China and their conservation implications. Wetlands, 34, 255-266. |
| [12] | Chu B, Liu L, Ji CP, Zhou YS, Zhou JW, Wang ZP, Hua LM (2020) Preliminary study on dispersal characteristics of populations of plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi) on a small scale. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 28, 734-742. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[楚彬, 刘丽, 姬程鹏, 周延山, 周建伟, 王志鹏, 花立民 (2020) 基于小尺度的高原鼢鼠(Myospalax baileyi)扩散初探. 草地学报, 28, 734-742.]
DOI |
|
| [13] | Chu GZ, Hou YQ, Zhang GG, Liu DP, Dai M, Jiang HX, Zhang DH (2008) Satellite-tracking migration route of great black-headed gulls breeding at Qinghai Lake, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 44(4), 99-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [楚国忠, 侯韵秋, 张国钢, 刘冬平, 戴铭, 江红星, 张德海 (2008) 卫星跟踪青海湖繁殖地渔鸥的迁徙路线. 林业科学, 44(4), 99-104.] | |
| [14] | Combreau O, Qiao J, Lawrence M, Gao X, Yao J, Yang W, Launay F (2002) Breeding success in a houbara bustard Chlamydotis [undulata] macqueenii population on the eastern fringe of the Jungar Basin, People’s Republic of China. Ibis, 144, E45-E56. |
| [15] | Cong PH, Zheng GM (2008) The roosting behavior and roost-site selection of Temminck’s tragopan (Tragopan temminckii) in Laojunshan Natural Reserve, Sichuan, China. Biodiversity Science, 16, 332-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[丛培昊, 郑光美 (2008) 四川老君山地区红腹角雉的夜栖行为和夜栖地选择. 生物多样性, 16, 332-338.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Cooke SJ, Hinch SG, Wikelski M, Andrews RD, Kuchel LJ, Wolcott TG, Butler PJ (2004) Biotelemetry: A mechanistic approach to ecology. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 334-343. |
| [17] | Cui DY, Du Y, Liu J, Zhao YQ, Wu XY, Cheng H, Lv SC, Jia T, Zhang JG (2017) Movement range and variation of re-introduced red-crowned cranes (Grus japonensis) in the early stages after release in the wild. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 38(1), 28-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔多英, 杜洋, 刘佳, 赵永强, 吴晓宇, 成海, 吕士成, 贾婷, 张金国 (2017) 重引入丹顶鹤野放初期活动范围及变化规律. 野生动物学报, 38(1), 28-34.] | |
| [18] | D’Eon RG, Delparte D (2005) Effects of radio-collar position and orientation on GPS radio-collar performance, and the implications of PDOP in data screening. Journal of Applied Ecology, 42, 383-388. |
| [19] |
Demšar U, Buchin K, Cagnacci F, Safi K, Speckmann B, Van de Weghe N, Weiskopf D, Weibel R (2015) Analysis and visualisation of movement: An interdisciplinary review. Movement Ecology, 3, 5.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Deng XQ, Zhao QS, Fang L, Xu ZG, Wang X, He HR, Cao L, Fox AD (2019) Spring migration duration exceeds that of autumn migration in Far East Asian Greater White-fronted Geese (Anser albifrons). Avian Research, 10, 19. |
| [21] | Dingle H (2014) Migration:The Biology of Life on the Move. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [22] | Duan XN, Chu WW, Wang Y, Du CC, He L, Chu HJ (2016) The largest gray wolf (Canis lupus) home ranges in the world may exist in the Mount Kalamaili Ungulate Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36, 452-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [端肖楠, 初雯雯, 王渊, 杜聪聪, 何雷, 初红军 (2016) 新疆卡拉麦里山有蹄类自然保护区冬季狼的家域. 兽类学报, 36, 452-458.] | |
| [23] | Duan YB, Liu L, Huang YL, Mi HX, Rong K, Ma JZ (2015) Bed-site habitat use of Burmese python (Python bivittatus) during early reintroduction in Hainan Yinggeling National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 2848-2854. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [段玉宝, 刘磊, 黄云龙, 米红旭, 戎可, 马建章 (2015) 海南鹦哥岭缅甸蟒放归初期停卧地的利用. 生态学杂志, 34, 2848-2854.] | |
| [24] | Fudickar AM, Wikelski M, Partecke J (2012) Tracking migratory songbirds: Accuracy of light-level loggers (geolocators) in forest habitats. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 47-52. |
| [25] | Ga RD, Fan SJ, Cao L, Zhang BX, Wang YX, Zhu BG, Dong SB, Zhao GRLT (2022) Migration strategy of the Bohai Bay wintering population of juvenile Oriental Storks (Ciconia boyciana). Biodiversity Science, 30, 21232. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[嘎日迪, 樊淑娟, 曹垒, 张贝西, 王昱熙, 朱宝光, 董树斌, 赵格日乐图 (2022) 东方白鹳幼鸟渤海湾越冬群体的迁徙策略. 生物多样性, 30, 21232.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Ge BM, Guan TP, Chen LM, Ma WH, Song YL (2012) The applications of the GPS collar system in wild animal management and monitoring. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 31, 311-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [葛宝明, 官天培, 谌利民, 马文虎, 宋延龄 (2012) GPS项圈系统在野生动物管理与监测中的应用. 四川动物, 31, 311-316.] | |
| [27] | Gu HX, Xia ZR, Chen HL, Lin RJ, Li PP (2007) Review of tagging methods of sea turtles in China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 26, 458-460. (in Chinese) |
| [古河祥, 夏中荣, 陈华灵, 林日锦, 李丕鹏 (2007) 中国海龟标志方法纵览. 四川动物, 26, 458-460.] | |
| [28] | Gu XD, Wang HJ, Zhang SN, Dai Q, Zhu LF, Gu HJ, Wang YZ, Wei FW (2011) Home range and activity rhythm of the reintroduced giant Panda “Shenglin 1” in Dujiangyan, Sichuan Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 30, 493-497. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [古晓东, 王鸿加, 张陕宁, 戴强, 朱立峰, 顾海军, 王跃招, 魏辅文 (2011) 放归大熊猫“盛林1号”的活动范围和活动节律监测. 四川动物, 30, 493-497.] | |
| [29] |
Guo ST, Qiang M, Luan XR, Xu PF, He G, Yin XY, Xi L, Jin XL, Shao JB, Chen XJ, Fang DY, Li BG (2015) The application of the internet of things to animal ecology. Integrative Zoology, 10, 572-578.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Ha LY, Rong K (2013) Ranging distance of squirrels in fragmented habitat during autumn and winter. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 41, 13587-13589. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [哈丽亚, 戎可 (2013) 斑块化生境中松鼠的秋冬季活动距离研究. 安徽农业科学, 41, 13587-13589.] | |
| [31] |
Hahsler M, Piekenbrock M, Doran D (2019) dbscan: Fast density-based clustering with R. Journal of Statistical Software, 91, 1-30.
DOI |
| [32] | Hall LS, Krausman PR, Morrison ML (1997) The habitat concept and a plea for standard terminology. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 25, 173-182. |
| [33] | Han JB, Lu ZC, Tian JS, Ma ZQ, Wang ZH, Yang Y, Wang QG, Song XR, Peng ZP (2013) Release studies on spotted seals (Phoca largha) using satellite telemetry tracking technique. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 33, 300-307. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩家波, 鹿志创, 田甲申, 马志强, 王召会, 杨勇, 王勤国, 宋新然, 彭志平 (2013) 基于卫星信标跟踪的斑海豹放流效果研究. 兽类学报, 33, 300-307.] | |
| [34] | Han ZX, Hu JC, Yang JD (2006) Daily activity rhythm of red pandas (Ailurus fulgens) in summer and autumn. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 25, 597-602. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩宗先, 胡锦矗, 杨建东 (2006) 小熊猫夏秋季的昼夜活动节律. 四川动物, 25, 597-602.] | |
| [35] | Han ZX, Wei FW, Li M, Zhang ZJ, Hu JC (2005) Daily activity rhythm of captive red pandas (Ailurus fulgens). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 25, 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩宗先, 魏辅文, 李明, 张泽钧, 胡锦矗 (2005) 圈养小熊猫的昼夜活动节律. 兽类学报, 25, 97-101.] | |
| [36] | He K, Lei JL, Jia YF, Wu ET, Sun GQ, Lu C, Zeng Q, Lei GC (2022) Temporal dynamics of the goose habitat in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Remote Sensing, 14, 1883. |
| [37] |
He X, Pei EL, Yuan X, Cai F, Shen GP, Zhang ED, Xu GL, Chen M (2016) Habitat selection and movement range of re-introduced Chinese water deer after release in Shanghai Binjiang Forest Park, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36, 36-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[何鑫, 裴恩乐, 袁晓, 蔡锋, 沈国平, 张恩迪, 徐桂林, 陈珉 (2016) 上海滨江森林公园重引入獐野放后的活动范围与栖息地选择. 兽类学报, 36, 36-45.]
DOI |
|
| [38] | He XJ, Zeng ZJ, Wang WX, Wu XB, Yan WY, Wang ZL (2010) The application potential of RFID technology in honeybees. Apiculture of China, 61(11), 19-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何旭江, 曾志将, 王文祥, 吴小波, 颜伟玉, 王子龙 (2010) RFID技术在蜜蜂研究中的应用. 中国蜂业, 61(11), 19-21.] | |
| [39] | Heberling JM, Miller JT, Noesgaard D, Weingart SB, Schigel D (2021) Data integration enables global biodiversity synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2018093118. |
| [40] | Hsu HH, Joung SJ, Liao YY, Liu KM (2007) Satellite tracking of juvenile whale sharks, Rhincodon typus, in the Northwestern Pacific. Fisheries Research, 84, 25-31. |
| [41] | Hu CS (2016) The Home Range and Dispersal Ecology of Crested Ibis (Nipponia Nippon). PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡灿实 (2016) 朱鹮(Nipponia nippon)活动性及其扩散模式研究. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Huang MX, Li LH, Xu LJ, Shen YL, Jia LY (2018) Application progress of RFID technology in individual animal behavior recognition. China Poultry, 40(22), 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄孟选, 李丽华, 许利军, 申艳路, 贾兰英 (2018) RFID技术在动物个体行为识别中的应用进展. 中国家禽, 40(22), 39-44.] | |
| [43] | Huang S, Shi DW, Wu YT, Hou JH, Cao F, Meng FJ (2022) The preliminary study on the potential bird strike risk due to flight behavior of domestic pigeon around airports. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 57, 821-835. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄尚, 史大伟, 吴永涛, 侯建华, 曹飞, 孟凡娟 (2022) 机场周边家鸽飞行行为的潜在鸟击风险初步研究. 动物学杂志, 57, 821-835.] | |
| [44] | Huang SL, Hu DF, Chen L (2016) Study on application of passive integrated transponder (PIT) in wildlife individual identification. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 37, 172-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄松林, 胡德夫, 陈力 (2016) PIT标记在野生动物个体识别中的应用研究. 野生动物学报, 37, 172-177.] | |
| [45] | Huang T, Xu ZG, Peng J, Zhao YL (2018) Study on the migration routes of overwintering Cygnus columbianus in Dongting Lake based on satellite tracking. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 37, 361-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄田, 徐正刚, 彭姣, 赵运林 (2018) 基于卫星跟踪的洞庭湖越冬小天鹅迁徙路线研究. 四川动物, 37, 361-372.] | |
| [46] | Huang X, Zhao YY, Liu Y (2021) Using light-level geolocations to monitor incubation behaviour of a cavity- nesting bird Apus apus pekinensis. Avian Research, 12, 9. |
| [47] | Hut RA, Paolucci S, Dor R, Kyriacou CP, Daan S (2013) Latitudinal clines:An evolutionary view on biological rhythms. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280, 20130433. |
| [48] | Jeltsch F, Bonte D, Pe’er G, Reineking B, Leimgruber P, Balkenhol N, Schröder B, Buchmann CM, Mueller T, Blaum N, Zurell D, Böhning-Gaese K, Wiegand T, Eccard JA, Hofer H, Reeg J, Eggers U, Bauer S (2013) Integrating movement ecology with biodiversity research—Exploring new avenues to address spatiotemporal biodiversity dynamics. Movement Ecology, 1, 6. |
| [49] | Jia CX, Zheng GM, Zhou XP, Zhang HM (2004) Home range and habitat characteristics of blood pheasant in summer. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 23, 349-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾陈喜, 郑光美, 周小平, 张和民 (2004) 血雉繁殖期活动区与栖息地特征. 四川动物, 23, 349-352.] | |
| [50] | Kanazawa I, Cheng WWW, Pun HSF, Sakiyama Y, Doi H,(2015) First migration record of Chestnut Tiger Butterfly, Parantica sita niphonica (Moore, 1883) (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae: Danainae) from Japan to Hong Kong and longest recorded movement by the species. The Pan-Pacific Entomologist, 91, 91-97. |
| [51] | Kang MJ, Zheng GM (2007) Roost-site selection of lady amherst’s pheasant. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 2929-2934. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [康明江, 郑光美 (2007) 白腹锦鸡(Chrysolophus amherstiae)的夜栖地选择. 生态学报, 27, 2929-2934.] | |
| [52] | Kauhala K, Holmala K, Lammers W, Schregel J (2006) Home ranges and densities of medium-sized carnivores in south-east Finland, with special reference to rabies spread. Acta Theriologica, 51, 1-13. |
| [53] | Kays R, Crofoot MC, Jetz W, Wikelski M (2015) Terrestrial animal tracking as an eye on life and planet. Science, 348, aaa2478. |
| [54] | Kays R, Davidson SC, Berger M, Bohrer G, Fiedler W, Flack A, Hirt J, Hahn C, Gauggel D, Russell B, Kölzsch A, Lohr A, Partecke J, Quetting M, Safi K, Scharf A, Schneider G, Lang I, Schaeuffelhut F, Landwehr M, Storhas M, van Schalkwyk L, Vinciguerra C, Weinzierl R, Wikelski M (2022) The Movebank system for studying global animal movement and demography. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 13, 419-431. |
| [55] | Kenward RE (2000) A Manual for Wildlife Radio Tagging. Academic Press, Cambridge. |
| [56] | Khan M, Barron DG, Patil R, Nannemann M, Courson M (2020) Internet of Things Based Remote Sensing for Ornithological Monitoring. 2020 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech), Oklahoma City, OK, USA. |
| [57] | Kissling WD, Pattemore DE, Hagen M (2014) Challenges and prospects in the telemetry of insects. Biological Reviews, 89, 511-530. |
| [58] | Knight A, Brower LP, Williams EH (2008) Spring remigration of the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) in north-central Florida: Estimating population parameters using mark-recapture. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 68, 531-556. |
| [59] | Kong F, Zhu QJ, Xiao FR, Hong Z, Zhang HX, Shi HT (2021) Home ranges and movement patterns of the Chinese softshell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) in the Yellow River, Northwestern China. Chelonian Conservation and Biology, 20, 2-9. |
| [60] | Kong YJ, Liu YL, He CW, Li TT, Li QL, Ma CX, Wang DJ, Li S (2022) Determining the daily activity pattern of Chinese mountain cat (Felis bieti): A comparative study based on camera-trapping and satellite collar tracking data. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22081. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[孔玥峤, 刘炎林, 贺成武, 李天醍, 李全亮, 马存新, 王大军, 李晟 (2022) 评估荒漠猫的日活动节律:基于红外相机与卫星颈圈数据的对比. 生物多样性, 30, 22081.]
DOI |
|
| [61] | Kuang FL, Wu W, Li D, Hassell CJ, Maglio G, Leung KSK, Coleman JT, Cheng CY, Tomkovich PS, Ma ZJ (2022) Detecting the non-breeding region and migration route of whimbrels (Numenius phaeopus rogachevae) in the East Asian-Australasian Flyway. Avian Research, 13, 100011. |
| [62] | Kuang SX, Yang ZZ, Tu XB, Zou CL, Shu HL, Huang MG, Wang ZR (2020) Preliminary study on rescue and return monitoring of wild Siberian crane (Grus leucogeranus) in Poyang Lake. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 41, 207-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [况绍祥, 杨长志, 涂晓斌, 邹畅林, 舒惠理, 黄秒根, 汪志如 (2020) 鄱阳湖野生白鹤的救护及异地放归监测初步研究. 野生动物学报, 41, 207-210.] | |
| [63] | Li BV, Pimm SL, Li S, Zhao LJ, Luo CP (2017) Free-ranging livestock threaten the long-term survival of giant pandas. Biological Conservation, 216, 18-25. |
| [64] | Li X, Huo ZP, Yu XP (2013) Cause of death of the crested ibis of a reintroduced population in Ningshan, Shaanxi. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 48, 701-706. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李夏, 霍志萍, 于晓平 (2013) 陕西宁陕朱鹮再引入种群个体死亡原因分析. 动物学杂志, 48, 701-706.] | |
| [65] | Li XM, Xu JH, Qian FW (2016) Migration routes of Siberian crane (Grus leucogeranus) in spring and autumn by satellite tracking. Wetland Science, 14, 347-353. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李秀明, 徐家慧, 钱法文 (2016) 卫星跟踪的白鹤春季和秋季迁徙路线. 湿地科学, 14, 347-353.] | |
| [66] | Li YH, Hu YM (2021) The contributions of animal movement network researches to landscape ecology. Biodiversity Science, 29, 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李月辉, 胡远满 (2021) 动物移动网络研究对景观生态学的贡献. 生物多样性, 29, 98-108.] | |
| [67] | Li YP, Wang HY, Jiang ZG, Song YC, Yang DD, Li L (2022) Seasonal differences of the Milu’s home range at the early rewilding stage in Dongting Lake area, China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 35, e02057. |
| [68] | Liu DP, Li CQ, Zhang GG, Lu J, Chen G (2014) Satellite tracking of scaly-sided merganser (Mergus squamatus) breeding in lesser Xingan Mountains, China. Waterbirds, 37, 432-438. |
| [69] | Liu H, He XY, Liu Q, Jian HB, Zhang Q, Huang JZ, Zhi SY, Liang J, Peng Z, Sun YX, Peng XW, Liu ZX, Zhang LB (2017) Radio-tracking studies on foraging areas of short-nosed fruit bats Cynopterus sphinx in Macau. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 52, 373-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘会, 何向阳, 刘奇, 简汉彪, 张琴, 黄继展, 植诗雅, 梁捷, 彭真, 孙云霄, 彭兴文, 刘志霄, 张礼标 (2017) 无线电遥测技术研究澳门犬蝠的捕食区面积. 动物学杂志, 52, 373-380.] | |
| [70] | Liu JH, Wang Y, Bian K, Tang J, Wang WF, Guo LW, Wang B, Fang G, Zhao L, Qi XG (2020) Home range utilization and individual dispersal of re-introduced forest musk deer (Moschus berezovskii). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 40, 109-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘嘉辉, 王艳, 边坤, 唐婕, 王伟峰, 郭林文, 王波, 方谷, 赵兰, 齐晓光 (2020) 重引入林麝的家域利用与个体迁移. 兽类学报, 40, 109-119.] | |
| [71] | Liu QX (2009) Activity Rhythm, Home Range and Habitat Selection of the Tibetan Fox. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘群秀 (2009) 藏狐的活动规律、家域特征及生境选择的研究. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [72] | Liu XH, Cheng XN, Skidmore AK (2011) Potential solar radiation pattern in relation to the monthly distribution of giant pandas in Foping Nature Reserve, China. Ecological Modelling, 222, 645-652. |
| [73] |
Liu XH, Wang TJ, Wang T, Skidmore AK, Songer M (2015) How do two giant panda populations adapt to their habitats in the Qinling and Qionglai Mountains, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22, 1175-1185.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | Long TL, Shao KQ, Guo G, Cheng CY, Zou XY, Zhou FL (1998) Winter ecological tracking and observation study of Chinese monal. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 17, 104-105. (in Chinese) |
| [隆廷伦, 邵开清, 郭耕, 程彩云, 邹学英, 周方林 (1998) 绿尾虹雉冬季生态的跟踪观测研究. 四川动物, 17, 104-105.] | |
| [75] | Lu S, Liu ZX, Tian S, Song K, Hu Q, Li JQ, Xu JL (2022) Sex-specific movement responses of Reeves’s pheasant to human disturbance: Importance of body characteristics and reproductive behavior. Animals, 12, 1619. |
| [76] | Lv SB, Liu YW, Liu YM, Xu SG, Li YF, Yuan M, He TT, Lin DD (2020) Impact of “Elaphurus davidianus return home project” on the transmission of schistosomiasis in Poyang Lake areas. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control, 32, 498-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吕尚标, 刘亦文, 刘跃民, 徐圣国, 李宜锋, 袁敏, 何婷婷, 林丹丹 (2020) 鄱阳湖区实施“麋鹿回家计划”对血吸虫病传播影响的调查. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 32, 498-501.] | |
| [77] | Ma ZJ, Ding CQ, Li XH, Lu BZ, Zhai TQ, Zheng GM (2001) Feeding site selection of crested ibis in winter. Zoological Research, 22(1), 46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马志军, 丁长青, 李欣海, 路宝忠, 翟天庆, 郑光美 (2001) 朱鹮冬季觅食地的选择. 动物学研究, 22(1), 46-50.] | |
| [78] | Ma ZJ, Hua N, Peng HB, Choi CY, Battley PF, Zhou QY, Chen Y, Ma Q, Jia N, Xue WJ, Bai QQ, Wu W, Feng XS, Tang CD (2013) Differentiating between stopover and staging sites: Functions of the southern and northern Yellow Sea for long‐distance migratory shorebirds. Journal of Avian Biology, 44, 504-512. |
| [79] | McKinnon EA, Love OP (2018) Ten years tracking the migrations of small landbirds: Lessons learned in the golden age of bio-logging. The Auk, 135, 834-856. |
| [80] | McShea WJ, Shen XL, Liu F, Wang TM, Xiao ZS, Li S (2020) China’s wildlife camera-trap monitoring needs a unified standard. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1125-1131. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [William J. McShea, 申小莉, 刘芳, 王天明, 肖治术, 李晟 (2020) 中国的野生动物红外相机监测需要统一的标准. 生物多样性, 28, 1125-1131.] | |
| [81] | Merkel B, Aars J, Laidre KL, Fox JW (2023) Light-level geolocation as a tool to monitor polar bear (Ursus maritimus) denning ecology: A case study. Animal Biotelemetry, 11, 11. |
| [82] | Misra P, Enge P (2006) Global Positioning System: Signals, Measurements, and Performance. Ganga-Jamuna Press, Lincoln. |
| [83] | Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Gil PR (1997) Megadiversity: Earth’s Biologically Wealthiest Nations. Cemex, San Pedro. |
| [84] | Moore FR, Gauthreaux SAJ, Kerlinger P, Simons TR (1995) Habitat requirements during migration:Important link in conservation. In: Ecology and Management of Neotropical Migratory Birds (eds Martin TE, Finch DM), pp. 121-144. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [85] |
Morris DW (2003) Toward an ecological synthesis: A case for habitat selection. Oecologia, 136, 1-13.
PMID |
| [86] | Nakazawa M (2019) fmsb: Functions for Medical Statistics Book with some Demographic Data. Version 0.7.6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fmsb. (accessed on 2023-12-30) |
| [87] | Nathan R, Getz WM, Revilla E, Holyoak M, Kadmon R, Saltz D, Smouse PE (2008) A movement ecology paradigm for unifying organismal movement research. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 19052-19059. |
| [88] | Newton I (2007) The Migratxion Ecology of Birds. Academic Press, New York. |
| [89] |
Powell RA, Proulx G (2003) Trapping and marking terrestrial mammals for research: Integrating ethics, performance criteria, techniques, and common sense. ILAR Journal, 44, 259-276.
PMID |
| [90] | R Core Team (2023) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [91] | Rao XD, Yang CC, Liang W (2017) Breeding biology and novel reproductive behaviour in the Hainan partridge (Arborophila ardens). Avian Research, 8, 34. |
| [92] |
Ren BP, Li M, Long YC, Wei FW (2009) Influence of day length, ambient temperature, and seasonality on daily travel distance in the Yunnan snub-nosed monkey at Jinsichang, Yunnan, China. American Journal of Primatology, 71, 233-241.
DOI PMID |
| [93] | Roger DH (1994) Twelve. Theory of geolocation by light levels. In: Elephant Seals (eds Burney JLB, Richard ML), pp. 227-236. University of California Press, Berkeley. |
| [94] | Schaller GB, Hu J, Pan WS, Zhu J (1985) Pandas in the Wild:The Giant Pandas of Wolong. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [95] | Shang YC (1998) Behavior Ecology. Peking University Press, Beijng. (in Chinese) |
| [尚玉昌 (1998) 行为生态学. 北京大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [96] |
Shaw AK (2020) Causes and consequences of individual variation in animal movement. Movement Ecology, 8, 12.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | Shen W, Pei JC, Ji X (2017) The application of radio telemetry in biological studies. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 16, 284-289. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈纹, 裴剑驰, 计翔 (2017) 无线电遥测技术在生物学研究中的应用. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 16, 284-289.] | |
| [98] | Shi M, Sun YH, Wen AX, Fang Y (2013) Spring territory behavior of the Chinese grouse (Tetrastes sewerzowi) at Lianhuashan, Gansu, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 48, 665-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [石美, 孙悦华, 温安祥, 方昀 (2013) 甘肃莲花山斑尾榛鸡的春季领域行为. 动物学杂志, 48, 665-672.] | |
| [99] | Si YL, Wei J, Wu WZ, Zhang WY, Hou L, Yu L, Wielstra B (2020) Reducing human pressure on farmland could rescue China’s declining wintering geese. Movement Ecology, 8, 35. |
| [100] | Song YL, Zeng ZG (2006) Observation on group types of golden takin (Budorcas taxicolor bedfordi). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 19, 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋延龄, 曾治高 (2006) 秦岭羚牛的集群类型. 兽类学报, 19, 81-88.] | |
| [101] | Sullivan JD, Takekawa JY, Spragens KA, Newman SH, Xiao XM, Leader PJ, Smith B, Prosser DJ (2018) Waterfowl spring migratory behavior and avian influenza transmission risk in the changing landscape of the East Asian-Australasian flyway. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 206. |
| [102] | Sun NCM, Sompud J, Pei KJC (2018) Nursing period, behavior development, and growth pattern of a newborn Formosan pangolin (Manis pentadactyla pentadactyla) in the wild. Tropical Conservation Science, 11, 1-6. |
| [103] | Sun Y, Zhang YY (2009) Radio tracking in zoological research. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 45, 268-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙岳, 张雁云 (2009) 无线电遥测技术在动物学研究中的应用. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 45, 268-274.] | |
| [104] | Sun YH, Chiu MC, Li CF, Liu M, Wu HJ, Chiang PJ (2014) The seasonal home range and movements of Mandarin Ducks Aix galericulata on tributaries of the Tachia River, central Taiwan. Forktail, 30, 41-44. |
| [105] | Tang ZH, Chen Z, Ma J, Zhu GJ, Ma XF, Sheng LX, Li YX (2010) Foraging areas of Rousettus leschenaulti on the Hainan Island of China. Current Zoology, 56, 479-484. |
| [106] | Teitelbaum CS, Mueller T (2019) Beyond migration: Causes and consequences of nomadic animal movements. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34, 569-581. |
| [107] | Teng LW, Liu ZS, Song YL, Zeng ZG (2004) Forage and bed sites characteristics of Indian muntjac (Muntiacus muntjak) in Hainan Island, China. Ecological Research, 19, 675-681. |
| [108] |
Tian LQ, He XJ, Wu XB, Gan HY, Han X, Liu H, Zeng ZJ (2014) Study on foraging behaviors of honeybee Apis mellifera based on RFID technology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 831-835. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PMID |
| [田柳青, 何旭江, 吴小波, 甘海燕, 韩旭, 刘浩, 曾志将 (2014) 基于RFID技术的西方蜜蜂采集行为研究. 应用生态学报, 25, 831-835.] | |
| [109] | Tomkiewicz SM, Fuller MR, Kie JG, Bates KK (2010) Global positioning system and associated technologies in animal behaviour and ecological research. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365, 2163-2176. |
| [110] | Turbek SP, Schield DR, Scordato ESC, Contina A, Da XW, Liu Y, Liu Y, Pagani-Núñez E, Ren QM, Smith CCR, Stricker CA, Wunder M, Zonana DM, Safran RJ (2022) A migratory divide spanning two continents is associated with genomic and ecological divergence. International Journal of Organic Evolution, 76, 722-736. |
| [111] | Wang G, Li C, Wu J, Han JF, Jiang JP, Xie F (2016) Population ecology of Bufo gargarizans in zoige wetland based on artificial cover. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 5556-5563. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王刚, 李成, 吴军, 韩金锋, 江建平, 谢锋 (2016) 基于人工掩蔽物法的若尔盖湿地中华蟾蜍种群生态研究. 生态学报, 36, 5556-5563.] | |
| [112] | Wang HJ, Wang DX, Wang WZ, Song XJ, Liu B, Chen JF, Gu HX (2002) Experimental study of biotelemetry based on satellite traking during post-nesting migrations of green turtles. High Technology Letters, 12(11), 82-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王华接, 王东晓, 王文质, 宋晓军, 刘斌, 陈坚峰, 古河祥 (2002) 基于海龟洄游卫星追踪的生物遥测试验研究. 高技术通讯, 12(11), 82-86.] | |
| [113] | Wang JC, Shi HT (2002) Hainan peacock-pheasant. Bulletin of Biology, 11, 24. (in Chinese) |
| [汪继超, 史海涛 (2002) 海南孔雀雉. 生物学通报, 11, 24.] | |
| [114] |
Wang K, Ren JL, Chen HM, Lv ZT, Guo XG, Jiang K, Chen JM, Li JT, Guo P, Wang YY, Che J (2020) The updated checklists of amphibians and reptiles of China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 189-218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王剀, 任金龙, 陈宏满, 吕植桐, 郭宪光, 蒋珂, 陈进民, 李家堂, 郭鹏, 王英永, 车静 (2020) 中国两栖、爬行动物更新名录. 生物多样性, 28, 189-218.]
DOI |
|
| [115] | Wang PH, Fan JG, Chen XY, Yang JF, Hou JH, Gao LJ (2020) Autumn migration route of a saker falcon by satellite tracking in Hebei Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 55, 462-467. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王鹏华, 范俊功, 陈向阳, 杨俊峰, 侯建华, 高立杰 (2020) 卫星跟踪河北猎隼的秋季迁徙路线. 动物学杂志, 55, 462-467.] | |
| [116] | Wang W, Ma JZ, Yu HL, Hu LQ (2008) Food habits of Asiatic black bears in the Xiao Xing’anling Mountains. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 28, 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王文, 马建章, 余辉亮, 胡立清 (2008) 小兴安岭地区黑熊的食性分析. 兽类学报, 28, 7-13.] | |
| [117] | Wang ZH, Yao H, Ding YZ, Thorbjarnarson J, Wang XM (2011) Testing reintroduction as a conservation strategy for the critically endangered Chinese alligator: Movements and home range of released captive individuals. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56, 2586-2593. |
| [118] | Wei FW (2022) Taxonomy and Distribution of Mammals in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [魏辅文 (2022) 中国兽类分类与分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [119] | Wei FW, Yang QS, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Liu SY, Li BG, Yang G, Li M, Zhou J, Li S, Hu YB, Ge DY, Li S, Yu WH, Chen BY, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CQ, Wu SB, Zhang L, Chen ZZ, Chen SD, Deng HQ, Jiang TL, Zhang LB, Shi HY, Lu XL, Li Q, Liu Z, Cui YQ, Li YC (2021) Catalogue of mammals in China (2021). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 41, 487-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[魏辅文, 杨奇森, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 刘少英, 李保国, 杨光, 李明, 周江, 李松, 胡义波, 葛德燕, 李晟, 余文华, 陈炳耀, 张泽钧, 周材权, 吴诗宝, 张立, 陈中正, 陈顺德, 邓怀庆, 江廷磊, 张礼标, 石红艳, 卢学理, 李权, 刘铸, 崔雅倩, 李玉春 (2021) 中国兽类名录(2021版). 兽类学报, 41, 487-501.]
DOI |
|
| [120] | Weng Y, McShea W, Diao YX, Yang HB, Zhang XF, Gu BJ, Bu HL, Wang F (2022) The incursion of free-ranging dogs into protected areas: A spatio-temporal analysis in a network of giant panda reserves. Biological Conservation, 265, 109423. |
| [121] | Whitney K (2022) History of Wildlife Tracking Technologies. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [122] | Wickham H (2016) ggplot2:Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [123] | Wilcove DS, Wikelski M (2008) Going, going, gone: Is animal migration disappearing. PLoS Biology, 6, e188. |
| [124] | Wu C, Chen L, Gao Y, Jiang W (2018a) Seaward migration behavior of juvenile second filial generation Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis in the Yangtze River, China. Fisheries Science, 84, 71-78. |
| [125] | Wu HF, Jin JF, Batbayar N, Li FS, Ding CQ (2018) Wintering home range variation of white-naped cranes Grus vipio and its correlation with water level and temperature in Poyang Lake. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 53, 497-506. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴海峰, 金杰锋, Nymbayar Batbayar, 李凤山, 丁长青 (2018) 鄱阳湖越冬白枕鹤活动区面积与水位和气温的关系. 动物学杂志, 53, 497-506.] | |
| [126] | Wu HQ, Yang XJ, Yang JX (2008) Review of satellite tracking in bird migratory studies. Zoological Research, 29, 346-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [伍和启, 杨晓君, 杨君兴 (2008) 卫星跟踪技术在候鸟迁徙研究中的应用. 动物学研究, 29, 346-352.] | |
| [127] | Wu YN, Yang YZ, Cao L, Yin HQ, Xu MY, Wang ZJ, Liu YY, Wang X, Deng Y (2018b) Habitat environments impacted the gut microbiome of long-distance migratory swan geese but central species conserved. Scientific Reports, 8, 13314. |
| [128] | Xia X, Ren J, Li L, Wang HY, Song YC, Yang DD, Jiang ZG (2021) Autumn-winter habitat selection by the re-wild Milu (Elaphurus davidianus) at the early stage after release in Dongting Lake Wetland, China. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1087-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏昕, 任静, 李立, 王海燕, 宋玉成, 杨道德, 蒋志刚 (2021) 洞庭湖区麋鹿再野化初期秋冬季生境选择. 生物多样性, 29, 1087-1096.] | |
| [129] | Xiao FR (2017) Ecomorphological Adaption of Habitat Use in Turtle and Its Empirical Study on Two Species of Asian Box Turtle (Cuora). PhD dissertation, Hainan Normal University, Haikou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖繁荣 (2017) 龟类生境利用的生态形态适应及两种闭壳龟的实证研究. 博士学位论文, 海南师范大学, 海口.] | |
| [130] | Xiao WH, Zhou QS, Zhu CD, Wu DH, Xiao ZS (2020) Advances in techniques and methods of wildlife monitoring. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 409-417. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[肖文宏, 周青松, 朱朝东, 吴东辉, 肖治术 (2020) 野生动物监测技术和方法应用进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 44, 409-417.]
DOI |
|
| [131] | Xie FJ, Li XZ, Xiao DN, He HS (2006) Post-fire habitat restoration of sables during winter season in northern slope of the Great Xing’an Mountains. Journal of Forestry Research, 17, 231-237. |
| [132] | Xu HY, Yang ZY, Liu DP, Jia R, Chen LX, Liang BS, Zhang ZW, Zhang GG (2022a) Autumn migration routes of fledgling Chinese egrets (Egretta eulophotes) in Northeast China and their implications for conservation. Avian Research, 13, 100018. |
| [133] | Xu HY, Zhao XB, Jia R, Chen LX, Yang ZY, Zhang GG (2022b) Behavioral plasticity mediates adaptation to changes in food provisioning following the COVID-19 lockdown in black-headed gulls (Larus ridibundus). Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1013244. |
| [134] | Xu WJ, Huang QY, Stabach J, Buho H, Leimgruber P (2019) Railway underpass location affects migration distance in Tibetan antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii). PLoS ONE, 14, e0211798. |
| [135] | Yan WB, Zeng ZG, Gong HS, He XB, Liu XY, Ma YS, Song YL (2017a) Seasonal variation and sexual difference of home ranges by takins. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 81, 938-942. |
| [136] | Yan WB, Zeng ZG, Gong HS, He XB, Liu XY, Si KC, Song YL (2017b) Habitat use and selection by takin in the Qinling Mountains, China. Wildlife Research, 43, 671-680. |
| [137] | Yang H, Ma JZ, Rong K (2013) Feasibility analysis of passive integrated transponders in population ecology studies of Siberian chipmunk. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 6634-6642. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨慧, 马建章, 戎可 (2013) 被动式电子标签用于花鼠种群动态研究的可行性. 生态学报, 33, 6634-6642.] | |
| [138] | Yang JD, Zhang ZJ, Li M, Hu JC, Wei FW (2006) Home range of red pandas (Ailurus fulgens) in Fengtongzhai Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 26, 13-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨建东, 张泽钧, 李明, 胡锦矗, 魏辅文 (2006) 蜂桶寨自然保护区小熊猫巢域初步研究. 兽类学报, 26, 13-17.] | |
| [139] | Yang XJ, Qian FW, Li FS, Gao LB, Wu HQ (2005) First satellite tracking of black-necked cranes in China. Zoological Research, 26, 657-658. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨晓君, 钱法文, 李凤山, 高立波, 伍和启 (2005) 中国首次卫星跟踪黑颈鹤研究初报. 动物学研究, 26, 657-658.] | |
| [140] | Ye SJ, Ma S, Zhou F, Wei X, Yue Q, Huang ML, Wu D, Jin HY, Bo SQ, Yuan X, Luo ZJ, Gu JM, Wang TH, Wang ZH (2021) Spatial behavior and habitat use of Anas poecilorhyncha and A. platyrhynchos in winter at Dongtan Wetland of Pudong, Shanghai. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 60, 451-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [叶思嘉, 马硕, 周锋, 韦旭, 岳衢, 黄美玲, 吴迪, 金惠宇, 薄顺奇, 袁晓, 罗梓菁, 顾建明, 王天厚, 王正寰 (2021) 上海浦东东滩湿地斑嘴鸭和绿头鸭的越冬期空间行为与栖息地利用. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 60, 451-461.] | |
| [141] | Yu GX, Xie MW, Chen YN, Chen LX, Wang YH, Liu DP (2022) Population dynamics and autumn migration of Pernis ptilorhynchus in Changdao of Shandong Province, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 58(4), 119-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于国祥, 谢茂文, 陈雅楠, 陈丽霞, 王毅花, 刘冬平 (2022) 山东长岛凤头蜂鹰的种群动态及秋季迁徙. 林业科学, 58(4), 119-127.] | |
| [142] |
Yu X, Wu NC, Ge LY, Li LS, Zhang ZW, Lei J (2022) Artificial shelters provide suitable thermal habitat for a cold-blooded animal. Scientific Reports, 12, 5879.
DOI PMID |
| [143] | Yuan BD, Yan YF, Cheng ZY, Lu CH (2017) Roost habitat characteristics and differences of Mrs Hume’s pheasant (Syrmaticus humiae) in spring and summer night. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 53(9), 143-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [原宝东, 闫永峰, 程志营, 鲁长虎 (2017) 黑颈长尾雉春夏夜栖地特征与差异性分析. 林业科学, 53(9), 143-150.] | |
| [144] | Yuan YH, Liu QX, Zhang X (2019) Preliminary studies on the home range and diurnal behaviour of Callosciurus erythraeus in an urban garden. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 39, 639-650. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁耀华, 刘群秀, 张欣 (2019) 城市公园中赤腹松鼠的家域特征及昼间活动规律初探. 兽类学报, 39, 639-650.] | |
| [145] | Zeng ZG, Song YL (2001) Daily activity rhythm and time budget of golden takin in spring and summer. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 21(1), 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾治高, 宋延龄 (2001) 秦岭羚牛春夏季昼夜活动节律与时间分配. 兽类学报, 21(1), 7-13.] | |
| [146] | Zhang FY, Zhou FF, Zhou JW, Zhou R, Bao DEH, Ye GH, Hua LM (2020a) Diurnal activity pattern of plateau zokor in breeding season and its influencing factors. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 55, 297-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张飞宇, 周富斐, 周建伟, 周睿, 包达尔罕, 叶国辉, 花立民 (2020a) 高原鼢鼠繁殖季日活动模式及其影响因素. 动物学杂志, 55, 297-305.] | |
| [147] | Zhang FY, Zhou JW, Zhou FF, Zhou R, Hua XZ, Hua LM (2020b) The change of home range of plateau zokor during courtship period and its relationship with body mass. Grassland and Turf, 40, 67-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张飞宇, 周建伟, 周富斐, 周睿, 华铣泽, 花立民 (2020b) 高原鼢鼠求偶期巢域变化与体重的研究. 草原与草坪, 40, 67-72.] | |
| [148] |
Zhang GG, Liu DP, Jiang HX, Hou YQ, Dai M, Chu GZ, Xing Z (2008) Movement of four breeding waterbirds at Qinghai Lake, China. Biodiversity Science, 16, 279-287. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张国钢, 刘冬平, 江红星, 侯韵秋, 戴铭, 楚国忠, 星智 (2008) 青海湖四种繁殖水鸟活动区域的研究. 生物多样性, 16, 279-287.]
DOI |
|
| [149] | Zhang JJ, Xie YB, Li LX, Batbayar N, Deng XQ, Damba I, Meng FJ, Cao L, Fox AD (2020) Assessing site-safeguard effectiveness and habitat preferences of bar-headed geese (Anser indicus) at their stopover sites within the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using GPS/GSM telemetry. Avian Research, 11, 49. |
| [150] | Zhang YG, Ma YD, Li XM (2018) The distribution of young Eurasian spoonbill (Platalea leucorodia) by GMS+GPS method in Taihu Nation Wetland Park of China. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 39, 579-583. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张余广, 马一丹, 李晓民 (2018) 基于GMS+GPS技术对白琵鹭幼鸟扩散的研究. 野生动物学报, 39, 579-583.] | |
| [151] | Zhao SS (2022) Study on the Impact of Onshore Wind Farm Developments on the Wintering Waterbirds and Their Conservation Strategies in the Coast of Yangtze River Delta, China. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵闪闪 (2022) 长江三角洲海岸带风电开发对越冬水鸟的影响及其保育策略研究. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [152] | Zhao TT, Kuang FL, Yuan X, Bao SQ, Liu YY, Wang ZH, Tan K, Ke MJ, Zhong CW, Tang XD, Ma ZJ (2021) Satellite-tracking on the movements and habitat use of three species in Ardeidae at Qingpu, Shanghai. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 60, 231-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵天天, 邝粉良, 袁晓, 薄顺奇, 刘雨邑, 王正寰, 谭坤, 柯娩娟, 钟晨威, 唐晓东, 马志军 (2021) 上海青浦地区3种鹭科鸟类活动性和栖息地利用的卫星追踪. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 60, 231-237.] | |
| [153] | Zhao YY, Zhao XR, Wu L, Mu T, Yu F, Kearsley L, Liang X, Fu JP, Hou XR, Peng P, Li XY, Zhang T, Yan S, Newell D, Hewson CM, Townshend T, Åkesson S, Liu Y (2022) A 30,000-km journey by Apus apus pekinensis tracks arid lands between northern China and south-western Africa. Movement Ecology, 10, 29. |
| [154] | Zheng GM (2023) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 4rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美 (2023) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第四版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [155] | Zheng ZY, Li JH, Su RM, Lin Y, Chen Y, Chen FZ, Liang Q (2013) The out hive activity of honeybee (Apis cerana cerana) in winter using RFID. Apiculture of China, 64(Z3), 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑志阳, 李江红, 苏荣茂, 林燕, 陈颖, 陈奋泽, 梁勤 (2013) 利用电子标签技术研究中华蜜蜂冬季出巢活动规律. 中国蜂业, 64(Z3), 7-11.] | |
| [156] | Zhou JW, Hua LM, Zuo ST, Ji WH (2013) Field evaluation of three types of radio transmitters in ecological study on plateau zokor Myospalax baileyi. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, 24, 486-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周建伟, 花立民, 左松涛, 纪维红 (2013) 3种无线发射器在高原鼢鼠生态学研究中的效果测试. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 24, 486-490.] | |
| [157] | Zhou SQ, Huang JY, Zhang YH, Liu D, Li RG, Zhou XP, Huang Y, Tang CX, Wei RP, Zhang GQ, Li DS, Wang PY, Zhang HM (2012) Comparison of spatial positioning between radio telemetry (RT) and GPS in temperate mountain forests: A case study on tracking the reintroduction of captive giant pandas. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 32, 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周世强, 黄金燕, 张亚辉, 刘巅, 李仁贵, 周小平, 黄炎, 汤纯香, 魏荣平, 张贵权, 李德生, 王鹏彦, 张和民 (2012) 高山峡谷地区无线电遥测与GPS空间定位的比较: 野外放归大熊猫的跟踪定位. 兽类学报, 32, 193-202.] | |
| [158] | Zhou SQ, Zhang JD, Hull V, Huang JY, Liu D, Zhou JQ, Sun MM, Zhang HM (2019) Comparative activity patterns of wild giant pandas and livestock. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 1071-1081. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周世强, 张晋东, Hull Vanessa, 黄金燕, 刘巅, 周季秋, 孙萌萌, 张和民 (2019) 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜的活动格局比较. 生态学报, 39, 1071-1081.] | |
| [159] | Zhu BR, Verhoeven MA, Loonstra AHJ, Sanchez-Aguilar L, Hassell CJ, Leung KKS, Lei WP, Zhang ZW, Piersma T (2021) Identification of breeding grounds and annual routines of the newly discovered bohaii subspecies of black-tailed godwits. Emu-Austral Ornithology, 121, 292-302. |
| [160] | Zhu Q (2020) Investigating the Migratory Connectivity of the Swan Goose Anser cygnoides by Genetic, Satellite Tracking and Stable Isotope Methods. PhD dissertation, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝芹 (2020) 基于分子生物学、卫星追踪和稳定同位素溯源的贝叶斯模型研究鸿雁(Anser cygnoides)的迁徙连通性. 博士学位论文, 中国科学技术大学, 合肥.] |
| [1] | Wang Dawei, Cheng Shuai, Feng Jiawei, Wang Tianming. The wildlife camera-trapping dataset of Zhangguangcai Mountains in Northeast China (2015-2020) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24384-. |
| [2] | Yueqiao Kong, Yanlin Liu, Chengwu He, Tianti Li, Quanliang Li, Cunxin Ma, Dajun Wang, Sheng Li. Determining the daily activity pattern of Chinese mountain cat (Felis bieti): A comparative study based on camera-trapping and satellite collar tracking data [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(9): 22081-. |
| [3] | Zhishu Xiao, Wenhong Xiao, Tianming Wang, Sheng Li, Xinming Lian, Dazhao Song, Xueqin Deng, Qihai Zhou. Wildlife monitoring and research using camera-trapping technology across China: The current status and future issues [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22451-. |
| [4] | Sheng Li, Dajun Wang, Xianghui Chen, Hongliang Bu, Xiaogeng Liu, Tong Jin. The wildlife camera-trapping dataset of Laohegou Protected Area, Sichuan Province (2011-2015) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1170-1174. |
| [5] | Xin Xia, Jing Ren, Li Li, Haiyan Wang, Yucheng Song, Daode Yang, Zhigang Jiang. Autumn-winter habitat selection by the re-wild Milu (Elaphurus davidianus) at the early stage after release in Dongting Lake Wetland, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(8): 1087-1096. |
| [6] | Yueqiao Kong, Sheng Li, Baoquan Liu, Jiajun Zhou, Cheng Li, Jianping Yu. Distribution records and conservation status of Chinese pangolin (Manis pentadactyla) in China during 2010-2020 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(7): 910-917. |
| [7] | Yingrong Guo, Wenjun Lan, Sicheng Zou, Rongbin Yuan, Xiaoyu Dong, Jirui Cao, Qingpei Yang, Qingni Song. Camera-trapping survey of wild mammals and ground-dwelling birds in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 811-818. |
| [8] | Jia Tian, Shuyi Zhu, Xiaofeng Zhang, Liwen He, Xiaodong Gu, Tianpei Guan, Sheng Li. The diversity of large- and medium-sized terrestrial mammals and birds in the Giant Panda National Park: A meta-analysis based on camera-trapping data [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1490-1504. |
| [9] | Xuehua Liu, Yuke Zhang, Xiangyu Zhao, Xiangbo He, Qiong Cai, Yun Zhu, Baisuo He, Qiang Jiu. Introduction to the wildlife camera-trapping database of the middle Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1075-1080. |
| [10] | Xiaoli Shen, Jianping Yu, Sheng Li, Huiyun Xiao, Xiaonan Chen, Shengwen Chen, Mingzhang Liu, Keping Ma. Progress overview of the camera-trapping monitoring platform for the Qianjiangyuan National Park, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1110-1114. |
| [11] | Jia Li, Xiulei Wang, Mingwei Yang, Daxiang Chen, Xiaoju Wang, Ping Luo, Fang Liu, Yadong Xue, Guangliang Li, Yuguang Zhang, Yu Zhang, Diqiang Li. Construction progress of camera-trapping database from the Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1081-1089. |
| [12] | Xuemin Lang, Gankhuyag Purev-Ochir, Oyunchimeg Terbish, Dashdorj Khurelbaatar, Baasansuren Erdenechimeg, Amarkhuu Gungaa, Chunrong Mi, Yumin Guo. Luan River upper reaches: The important stopover site of the white-naped crane (Grus vipio) western population [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(10): 1213-1221. |
| [13] | Mu Jun, Wang Jiaojiao, Zhang Lei, Li Yunbo, Li Zhumei, Su Haijun. Field monitoring using infrared cameras and activity rhythm analysis on mammals and birds in Xishui National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(6): 683-688. |
| [14] | Jianping Yu,Jiangyue Wang,Huiyun Xiao,Xiaonan Chen,Shengwen Chen,Sheng Li,Xiaoli Shen. Camera-trapping survey of mammalian and avian biodiversity in Qianjiangyuan National Park, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1339-1344. |
| [15] | Xixi Hu, Weichao Zheng, Jiaqi Li, Sheng Li, Han Yang, Xing Chen, Tianpei Guan. Preliminary survey on mammal and bird diversity at Siguniang Mountains National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(12): 1325-1331. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn