



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1320-1329. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019219 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019219
• Original Papers: Microbial Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhiyuan Chen1,Jun Liu1,Xingpeng Yang1,Meng Liu1,Ya Wang2,Zhibin Zhang1,*( ),Du Zhu1,2,*
),Du Zhu1,2,*
Received:2019-07-07
Accepted:2019-10-20
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2020-02-22
Contact:
Zhang Zhibin,Zhu Du
Zhiyuan Chen, Jun Liu, Xingpeng Yang, Meng Liu, Ya Wang, Zhibin Zhang, Du Zhu. Community composition and diversity of cultivable endophytic bacteria isolated from Dongxiang wild rice[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1320-1329.
| 代表菌株 | NCBI库中相似度最高菌种 | 基因登录号 | 序列相 | 分离菌株数 | 培养基分离菌株数 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representative strains | (登录号) | GenBank accession | 似度 | No. of strains | No. of strains from medium | |||||||||||||
| Closest relatives in NCBI | no. | Identity | ||||||||||||||||
| (GenBank accession no.) | (%) | 根 | 茎 | 叶 | NA | BPA | R2A | TSA | NA×10 | |||||||||
| Root | Stem | Leaf | ||||||||||||||||
| 变形菌门 Proteobacteria | ||||||||||||||||||
| 泛菌属 Pantoea | 5 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR10 | Pantoea sp. (JX994157.1) | KP980595 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS8 | Pantoea sp. (KJ733870.1) | KP980579 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL1 | Pantoea sp. (KJ733870.1) | KP980566 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 鞘氨醇单胞菌属 Sphingomonas | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | ||||||||||
| JXR34 | Sphingomonas yanoikuyae (KJ009425.1) | KP980605 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL6 | Sphingomonas sanguinis (NR113637.1) | KP980568 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 土壤杆菌属 Agrobacterium | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXS10 | Agrobacterium sp. (GQ169803.1) | KP980581 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL9 | Agrobacterium sp. (KJ184856.1) | KP980570 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 甲烷细菌属 Methylobacterium | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR16 | Methylobacterium sp. (KM083547.1) | KP980599 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS9 | Methylobacterium sp. (AB604650.1) | KP980580 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL16 | Methylobacterium sp. (KM083546.1) | KP980572 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR26 | Pseudomonas sp. (HE978359.1) | KP980602 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL21 | Pseudomonas fulva (AY741159.1) | KP980573 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 寡养单胞菌属Stenotrophomonas | - | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXS14 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (JN571747.1) | KP980583 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 根瘤菌属 Rhizobium | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| JXS18 | Rhizobium sp. (JN082742.1) | KP980584 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| JXR29 | Acinetobacter oleivorans (KJ806471.1) | KP980603 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria | ||||||||||||||||||
| 微小菌属 Microbacterium | 1 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||
| JXR14 | Microbacterium trichothecenolyticum (KF953537.1) | KP980598 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS2 | Microbacterium sp. (AB773218.1) | KP980577 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL7 | Microbacterium sp. (EU741023.1) | KP980569 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL12 | Microbacterium laevaniformans | KP980571 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| (KC252695.1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 短杆菌属 Curtobacterium | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR24 | Curtobacterium citreum (KC329830.1) | KP980601 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS1 | Curtobacterium luteum (JQ660182.1) | KP980576 | 97 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL30 | Curtobacterium sp. (KC841444.1) | KP980575 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 分支杆菌属 Mycobacterium | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR17 | Mycobacterium sp. (AB605021.1) | KP980600 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 节杆菌属 Arthrobacter | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR12 | Arthrobacter phenanthrenivorans (KC934897.1) | KP980596 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 代表菌株 | NCBI库中相似度最高菌种 | 基因登录号 | 序列相 | 分离株数 | 培养基分离株数 | |||||||||||||
| Representative strains | (登录号) | GenBank accession | 似度 | No. of strains | No. of strains from medium | |||||||||||||
| Closest relatives in NCBI | no. | Identity | ||||||||||||||||
| (GenBank accession no.) | (%) | 根 | 茎 | 叶 | NA | BPA | R2A | TSA | NA×10 | |||||||||
| Root | Stem | Leaf | ||||||||||||||||
| 雷弗森菌属 Leifsonia | 3 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR6 | Leifsonia sp. (KJ944083.1) | KP980592 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 红球菌属 Rhodococcus | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | ||||||||||
| JXR8 | Rhodococcus equi (NR041910.1) | KP980594 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes | ||||||||||||||||||
| 类芽孢杆菌属 Paenibacillus | 3 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | |||||||||||
| JXR1 | Paenibacillus agarexedens (KC355292.1) | KP980588 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXR5 | Paenibacillus sp. (KJ000069.1) | KP980591 | 99 | |||||||||||||||
| JXR30 | Paenibacillus vulneris (KM272755.1) | KP980604 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 芽孢杆菌属 Bacillus | 7 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||||
| JXR2 | Bacillus cereus (KF831402.1) | KP980589 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXR3 | Bacillus sp. (JX566646.1) | KP980590 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS6 | Bacillus subtilis (KP229430.1) | KP980578 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS20 | Bacillus sp. (KM555037.1) | KP980585 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS25 | Bacillus mojavensis (HQ123468.1) | KP980587 | 97 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL24 | Bacillus sp. (KP119613.1) | KP980574 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属 Lysinibacillus | 4 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR13 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus (KM070813.1) | KP980597 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL2 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis (JN867122.1) | KP980567 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 总计 Total | 34 | 28 | 32 | 23 | 18 | 16 | 12 | 25 | ||||||||||
Table 1 The distribution of endophytic bacteria isolated from different tissues of Dongxiang wild rice
| 代表菌株 | NCBI库中相似度最高菌种 | 基因登录号 | 序列相 | 分离菌株数 | 培养基分离菌株数 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representative strains | (登录号) | GenBank accession | 似度 | No. of strains | No. of strains from medium | |||||||||||||
| Closest relatives in NCBI | no. | Identity | ||||||||||||||||
| (GenBank accession no.) | (%) | 根 | 茎 | 叶 | NA | BPA | R2A | TSA | NA×10 | |||||||||
| Root | Stem | Leaf | ||||||||||||||||
| 变形菌门 Proteobacteria | ||||||||||||||||||
| 泛菌属 Pantoea | 5 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR10 | Pantoea sp. (JX994157.1) | KP980595 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS8 | Pantoea sp. (KJ733870.1) | KP980579 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL1 | Pantoea sp. (KJ733870.1) | KP980566 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 鞘氨醇单胞菌属 Sphingomonas | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | ||||||||||
| JXR34 | Sphingomonas yanoikuyae (KJ009425.1) | KP980605 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL6 | Sphingomonas sanguinis (NR113637.1) | KP980568 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 土壤杆菌属 Agrobacterium | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXS10 | Agrobacterium sp. (GQ169803.1) | KP980581 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL9 | Agrobacterium sp. (KJ184856.1) | KP980570 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 甲烷细菌属 Methylobacterium | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR16 | Methylobacterium sp. (KM083547.1) | KP980599 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS9 | Methylobacterium sp. (AB604650.1) | KP980580 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL16 | Methylobacterium sp. (KM083546.1) | KP980572 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR26 | Pseudomonas sp. (HE978359.1) | KP980602 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL21 | Pseudomonas fulva (AY741159.1) | KP980573 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 寡养单胞菌属Stenotrophomonas | - | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXS14 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (JN571747.1) | KP980583 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 根瘤菌属 Rhizobium | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| JXS18 | Rhizobium sp. (JN082742.1) | KP980584 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| JXR29 | Acinetobacter oleivorans (KJ806471.1) | KP980603 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria | ||||||||||||||||||
| 微小菌属 Microbacterium | 1 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||
| JXR14 | Microbacterium trichothecenolyticum (KF953537.1) | KP980598 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS2 | Microbacterium sp. (AB773218.1) | KP980577 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL7 | Microbacterium sp. (EU741023.1) | KP980569 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL12 | Microbacterium laevaniformans | KP980571 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| (KC252695.1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 短杆菌属 Curtobacterium | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR24 | Curtobacterium citreum (KC329830.1) | KP980601 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS1 | Curtobacterium luteum (JQ660182.1) | KP980576 | 97 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL30 | Curtobacterium sp. (KC841444.1) | KP980575 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 分支杆菌属 Mycobacterium | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR17 | Mycobacterium sp. (AB605021.1) | KP980600 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 节杆菌属 Arthrobacter | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR12 | Arthrobacter phenanthrenivorans (KC934897.1) | KP980596 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 代表菌株 | NCBI库中相似度最高菌种 | 基因登录号 | 序列相 | 分离株数 | 培养基分离株数 | |||||||||||||
| Representative strains | (登录号) | GenBank accession | 似度 | No. of strains | No. of strains from medium | |||||||||||||
| Closest relatives in NCBI | no. | Identity | ||||||||||||||||
| (GenBank accession no.) | (%) | 根 | 茎 | 叶 | NA | BPA | R2A | TSA | NA×10 | |||||||||
| Root | Stem | Leaf | ||||||||||||||||
| 雷弗森菌属 Leifsonia | 3 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 2 | ||||||||||
| JXR6 | Leifsonia sp. (KJ944083.1) | KP980592 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 红球菌属 Rhodococcus | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | ||||||||||
| JXR8 | Rhodococcus equi (NR041910.1) | KP980594 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes | ||||||||||||||||||
| 类芽孢杆菌属 Paenibacillus | 3 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | |||||||||||
| JXR1 | Paenibacillus agarexedens (KC355292.1) | KP980588 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXR5 | Paenibacillus sp. (KJ000069.1) | KP980591 | 99 | |||||||||||||||
| JXR30 | Paenibacillus vulneris (KM272755.1) | KP980604 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 芽孢杆菌属 Bacillus | 7 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||||
| JXR2 | Bacillus cereus (KF831402.1) | KP980589 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXR3 | Bacillus sp. (JX566646.1) | KP980590 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS6 | Bacillus subtilis (KP229430.1) | KP980578 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS20 | Bacillus sp. (KM555037.1) | KP980585 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXS25 | Bacillus mojavensis (HQ123468.1) | KP980587 | 97 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL24 | Bacillus sp. (KP119613.1) | KP980574 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属 Lysinibacillus | 4 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| JXR13 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus (KM070813.1) | KP980597 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| JXL2 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis (JN867122.1) | KP980567 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| 总计 Total | 34 | 28 | 32 | 23 | 18 | 16 | 12 | 25 | ||||||||||
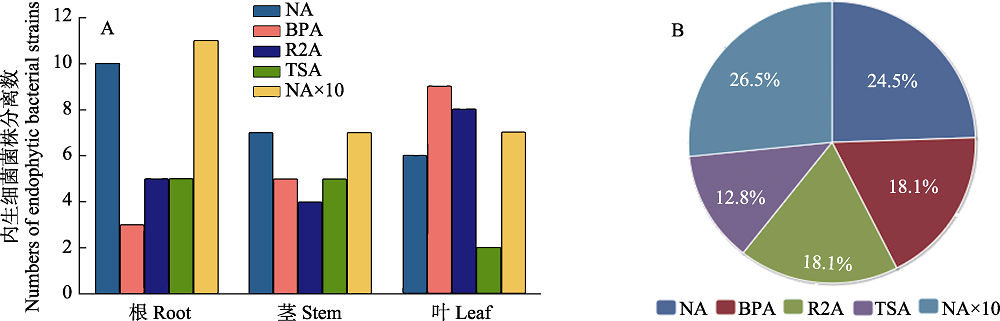
Fig. 1 The endophytic bacteria isolated by nutrient agar, Baird-Parker agar, Reasoner’s 2A agar Tryptone soy agar and 10-fold nutrient agar from each tissues of Dongxiang wild rice. (A) The amount of endophytic bacterial, derived from any tissues of Dongxiang wild rice, isolated from different mediums; (B) The percentage of the isolated strains from each medium.
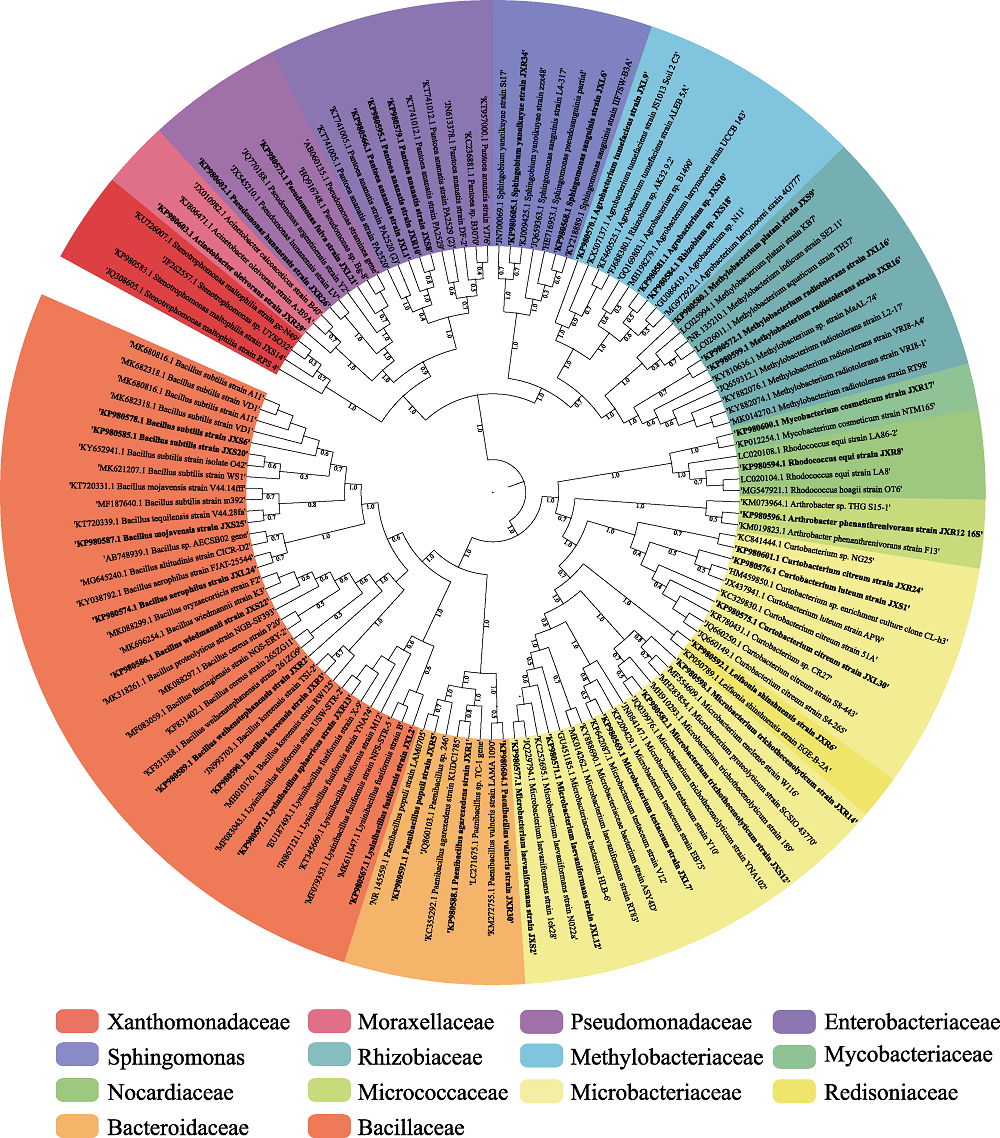
Fig. 2 Neighbor-joining tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the phylogenetic relationships among the strains and their closely related taxa. The thicker branches represent endophytic bacteria of Dongxiang wild rice and the others represent related strains.
| 组织名称 Tissue | 细菌属数 Genus | 多样性指数 Shannon- Wiener index | 优势度指数 Simpson index | 均匀度指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 14 | 2.52 | 0.88 | 0.72 |
| 茎 Stem | 8 | 1.81 | 0.80 | 0.54 |
| 叶 Leaf | 9 | 2.09 | 0.74 | 0.60 |
Table 2 Diversity analysis of endophytic bacteria in different tissues of Dongxiang wild rice (according to genera)
| 组织名称 Tissue | 细菌属数 Genus | 多样性指数 Shannon- Wiener index | 优势度指数 Simpson index | 均匀度指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 14 | 2.52 | 0.88 | 0.72 |
| 茎 Stem | 8 | 1.81 | 0.80 | 0.54 |
| 叶 Leaf | 9 | 2.09 | 0.74 | 0.60 |
| [1] | Baldan E, Nigris S, Populin F, Zottini M, Squartini A, Baldan B ( 2014) Identification of culturable bacterial endophyte community isolated from tissues of Vitis vinifera “Glera”. Plant Biosystems, 148, 508-516. |
| [2] | Brundrett MC, Tedersoo L ( 2018) Evolutionary history of mycorrhizal symbioses and global host plant diversity. New Phytologist, 220, 1108-1115. |
| [3] | Chen JK, Wang HY, He GQ ( 1998) A survey on the habitats of Oryza rufipogon and Isoetes sinensis in Jiangxi Province. Chinese Biodiversity, 6, 260-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈家宽, 王海洋, 何国庆 ( 1998) 江西境内珍稀植物普通野生稻和中华水韭产地的考察. 生物多样性, 6, 260-266.] | |
| [4] | Dai F, Huang YH, Peng WM, Li LM, Long ZE ( 2011) Studies on the microbial community in the rhizosphere soil of Dongxiang wild rice. Agricultural Science & Technology, 12, 527-529. |
| [5] | Dominika T, Michal Z, Renata GK, Sonia S, Christel B, Katarzyna H ( 2018) Cadmium-induced changes in the production of siderophores by a plant growth promoting strain of Pseudomonas fulva. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 58, 623-632. |
| [6] | Dong XZ, Cai MY ( 2001) Manual for Systematic Identification of Common Bacteria. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 东秀珠, 蔡妙英 ( 2001) 常见细菌系统鉴定手册. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Faria DC, Dias ACF, Melo IS, de Carvalho Costa FE ( 2013) Endophytic bacteria isolated from orchid and their potential to promote plant growth. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 29, 217-221. |
| [8] | Gerry AJ, Rashid AY, Mahmoud WY ( 2017) Genome sequencing of Microbacterium sp. Yaish 1, a bacterial strain isolated from the rhizosphere of date palm trees affected by salinity. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 5, e01247-17. |
| [9] | Greenberg JH ( 1956) The measurement of linguistic diversity. Language, 32, 105-119. |
| [10] | Hu GP, You MS, Liu B, Zhu YJ, Zheng XF, Lin YZ ( 2010) Relationship between the stem endophytic and rhizosphere bacteria and the variety characteristics of Oryza sativa. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 31, 1026-1030. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡桂萍, 尤民生, 刘波, 朱育菁, 郑雪芳, 林营志 ( 2010) 水稻茎部内生细菌及根际细菌与水稻品种特性的相关性. 热带作物学报, 31, 1026-1030.] | |
| [11] | James EK, Olivares FL ( 1998) Infection and colonization of sugar cane and other graminaceous plants by endophytic diazotrophs. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 17, 77-119. |
| [12] | Li F, Guo SY, Zhao Y, Chen DZ, Chong K, Xu YY ( 2010) Overexpression of a homopeptide repeat-containing bHLH protein gene (OrbHLH001) from Dongxiang wild rice confers freezing and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Reports, 29, 977-986. |
| [13] | Li GC, Zhang SY, Xiao W, Long ZY, Zhang NM ( 2015) Research progress on endophytes in rice. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 31(12), 157-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李龚程, 张仕颖, 肖炜, 龙智勇, 张乃明 ( 2015) 水稻中内生菌研究进展. 中国农学通报, 31(12), 157-162.] | |
| [14] | Li NN, Li N, Cao YH, Zhang X, Xiao M, Liu Y, Wang WP ( 2017) Diversity of endophytic bacterial communities in three parental seeds of hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) at maturity stage. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 35(4), 56-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李南南, 黎妮, 曹艳花, 张欣, 肖明, 刘洋, 王伟平 ( 2017) 3个杂交水稻亲本成熟期种子内生细菌多样性研究. 食品科学技术学报, 35(4), 56-64.] | |
| [15] | Li QQ, Jiao C, Nong Q, Yuan GQ, Lin W, Huang YL ( 2010) Dynamic distribution of endophytic bacteria in rice from Guangxi and their antagonism to the pathogen of rice sheath blight. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 26, 312-319. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黎起秦, 焦成, 农倩, 袁高庆, 林纬, 黄永禄 ( 2010) 广西水稻内生细菌的动态分布及其对水稻纹枯病菌的拮抗作用. 中国生物防治, 26, 312-319.] | |
| [16] | Liu XM, Yao Z, Shim JM, Lee KW, Kim HJ, Kim JH ( 2017) Properties of antimicrobial substances produced by Bacillus species isolated from rice straw. Microbiology and Biotechnology Letters, 45, 133-142. |
| [17] | Loaces I, Ferrando L, Scavino AF ( 2011) Dynamics, diversity and function of endophytic siderophore-producing bacteria in rice. Microbial Ecology, 61, 606-618. |
| [18] | Luo F, Wang Y, Zeng QG, Yan RM, Zhang ZB, Zhu D ( 2011) Diversity and plant growth promoting activities of the cultivable rhizo-bacteria of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Biodiversity Science, 19, 476-484. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗菲, 汪涯, 曾庆桂, 颜日明, 张志斌, 朱笃 ( 2011) 东乡野生稻根际可培养细菌多样性及其植物促生活性分析. 生物多样性, 19, 476-484.] | |
| [19] | Mano H, Morisaki H ( 2008) Endophytic bacteria in the rice plant. Microbes and Environments, 23, 109-117. |
| [20] | Marcus S, Ajay S, Owen PW ( 2004) Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 50, 1-17. |
| [21] | Nelson EB ( 2004) Microbial dynamics and interactions in the spermosphere. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 42, 271-309. |
| [22] | Pavlova AS, Leontieva MR, Smirnova TA, Kolomeitseva GL, Netrusov AI, Tsavkelova EA ( 2017) Colonization strategy of the endophytic plant growth-promoting strains of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Klebsiella oxytoca on the seeds, seedlings and roots of the epiphytic orchid, Dendrobium nobile Lindl. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 123, 217-232. |
| [23] | Pielou EC ( 1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13, 131-144. |
| [24] | Quan RD, Wang J, Hui J, Bai HB, Lyu XL, Zhu YX, Zhang HW, Zhang ZJ, Li SH, Huang RF ( 2018) Improvement of salt tolerance using wild rice genes. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 2269-2280. |
| [25] | Rangjaroen C, Rerkasem B, Teaumroong N, Sungthong R, Lumyong S ( 2014) Comparative study of endophytic and endophytic diazotrophic bacterial communities across rice landraces grown in the highlands of northern Thailand. Archives of Microbiology, 196, 35-49. |
| [26] | Reinhold-Hurek B, Hurek T ( 2011) Living inside plants: Bacterial endophytes. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 14, 435-443. |
| [27] | Ryan RP, Germaine K, Franks A, Ryan DJ, Dowling DN ( 2008) Bacterial endophytes: Recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 278, 1-9. |
| [28] | Santoyo G, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Orozco-Mosqueda MDC, Glick BR ( 2016) Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiological Research, 183, 92-99. |
| [29] | Sha YX, Zeng QC, Wang X, Shen RQ, Liu H, Wang XG ( 2018) Screening and control efficiency evaluation of Bacillus against rice blast Magnaporthe oryzae. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 34, 414-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沙月霞, 曾庆超, 王昕, 沈瑞清, 刘浩, 王喜刚 ( 2018) 防治稻瘟病芽胞杆菌的筛选及效果评价. 中国生物防治学报, 34, 414-422.] | |
| [30] | Shahzad R, Waqas M, Khan AL, Al-Hosni K, Kang SM, Seo WC, Lee IJ ( 2017) Indoleacetic acid production and plant growth promoting potential of bacterial endophytes isolated from rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds. Acta Biologica Hungarica, 68, 175-186. |
| [31] | Shannon CE ( 1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379-423. |
| [32] | Shao SC, Burgess KS, Jennifer CJ, Liu Q, Fan XL, Hui H, Gao JY ( 2017) Using in situ symbiotic seed germination to restore over-collected medicinal orchids in Southwest China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 888-898. |
| [33] | Shylla A, Shivaprakash MK, Shashidhar HE, Vishwakarma P, Sudradhar M ( 2016) Production of phytohormones by endophytic bacteria isolated from aerobic rice. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 10, 2127-2133. |
| [34] | Silo-Suh LA, Lethbridge BJ, Raffel SJ, Yin HH, Clardy J, Handelsman J ( 1994) Biological activities of two fungistatic antibiotics produced by Bacillus cereus UW85. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 2023-2030. |
| [35] | Song ZP, Chen JK, Zhao Y ( 2018) Rice domestication and the Yangtze River civilization. Biodiversity Science, 26, 346-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋志平, 陈家宽, 赵耀 ( 2018) 水稻驯化与长江文明. 生物多样性, 26, 346-356.] | |
| [36] | Sun L ( 2006) Endophytic Bacteria and Root-Associated Bacteria with Rice by Culture-Independent and Culture-Dependent Approaches. PhD dissertation, Capital Normal University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙磊 ( 2006) 非培养方法和培养方法对水稻内生细菌和根结合细菌的研究. 博士学位论文, 首都师范大学, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Tan ZY, Peng GX, Xu PZ, Ai SY, Tang SH, Zhang GX, Zeng FY ( 2009) Diversity and high nitrogenase activity of endophytic diazotrophs isolated from Oryza rufipogon Griff. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54, 2839-2848. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭志远, 彭桂香, 徐培智, 艾绍英, 唐拴虎, 张国霞, 曾凤云 ( 2009) 普通野生稻(Oryza rufipogon)内生固氮菌多样性及高固氮酶活性. 科学通报, 54, 2839-2848.] | |
| [38] | Tsavkelova EA, Cherdyntseva TA, Botina SG, Netrusov AI ( 2007) Bacteria associated with orchid roots and microbial production of auxin. Microbiological Research, 162, 69-76. |
| [39] | Tsavkelova EA, Egorova MA, Leontieva MR, Malakho SG, Kolomeitseva GL ( 2016) Dendrobium nobile Lindl. seed germination in co-cultures with diverse associated bacteria. Plant Growth Regulation, 80, 79-91. |
| [40] | Wang XJ, Jia RZ, Guo YL, Xu L, Zuo J, Kong H, Guo AP ( 2015) Diversity of culturable endobacterial communities in rice (Oryza sativa L.) stem at different growth stages. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 36, 1078-1085. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王雪君, 贾瑞宗, 郭运玲, 徐林, 左娇, 孔华, 郭安平 ( 2015) 水稻4个生长时期茎部可培养内生菌多样性分析. 热带作物学报, 36, 1078-1085.] | |
| [41] | Whittaker RH ( 1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251. |
| [42] | Xia H, Lu BR, Su J, Chen R, Rong J, Song ZP, Wang F ( 2009) Normal expression of insect-resistant transgene in progeny of common wild rice crossed with genetically modified rice: Its implication in ecological biosafety assessment. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 119, 635-644. |
| [43] | Xie ZC, Chu YK, Zhang WJ, Lang DY, Zhang XH ( 2019) Bacillus pumilus alleviates drought stress and increases metabolite accumulation in Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 158, 99-106. |
| [44] | Yang B, Chen Y, Li X, Ren CG, Dai CC ( 2013) Research progress on endophyte-promoted plant nitrogen assimilation and metabolism. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 2656-2664. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨波, 陈晏, 李霞, 任承钢, 戴传超 ( 2013) 植物内生菌促进宿主氮吸收与代谢研究进展. 生态学报, 33, 2656-2664.] | |
| [45] | Yang JH, Liu HX, Zhu GM, Pan YL, Xu LP, Guo JH ( 2008) Diversity analysis of antagonists from rice-associated bacteria and their application in biocontrol of rice diseases. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 104, 91-104. |
| [46] | Zhang FT, Xu T, Mao LY, Yan SY, Chen XW, Wu ZF, Chen R, Luo XD, Xie JK, Gao S ( 2016) Genome-wide analysis of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) to investigate lost/acquired genes during rice domestication. BMC Plant Biology, 16, 103-114. |
| [47] | Zhao J, Liu T, Pan L, Jin BH, Zhao D, Chen C, Zhu YY, He XH ( 2015) Isolation and identification of root endophytic and rhizosphere bacteria of rice landraces in Yuanyang terrace, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26, 3737-3745. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵娟, 刘涛, 潘磊, 靳百慧, 赵丹, 陈晨, 朱有勇, 何霞红 ( 2015) 元阳梯田地方水稻品种根部内生菌及根际微生物的分离与鉴定. 应用生态学报, 26, 3737-3745.] | |
| [48] | Zhou Y, Yang P, Cui FL, Zhang FT, Luo XD, Xie JK ( 2016) Transcriptome analysis of salt stress responsiveness in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). PLoS ONE, 11, e014624. |
| [1] | Hong Deyuan. A brief discussion on methodology in taxonomy [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [2] | Yajun Sun. What do higher or lower organisms mean—Clarify the meaning and validity of the biological ladder implied by On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [3] | Hua He, Dunyan Tan, Xiaochen Yang. Cryptic dioecy in angiosperms: Diversity, phylogeny and evolutionary significance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [4] | Yanyu Ai, Haixia Hu, Ting Shen, Yuxuan Mo, Jinhua Qi, Liang Song. Vascular epiphyte diversity and the correlation analysis with host tree characteristics: A case in a mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forest, Ailao Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [5] | Yanwen Lv, Ziyun Wang, Yu Xiao, Zihan He, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu. Advances in lineage sorting theories and their detection methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [6] | Chen-Kun Jiang, Wen-Bin Yu, Guang-Yuan Rao, Huaicheng Li, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. Plant Phylogeny Posters—An educational project on plant diversity from an evolutionary perspective [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [7] | Wanjun Hu, Zezhou Hao, Canwei Xia, Jiangjian Xie. Wetland soundscape recording scheme and feature selection for soundscape classification [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24121-. |
| [8] | Churan Zhang, Shengfa Li, Fengchang Li, Zhizhong Tang, Huiyan Liu, Lihong Wang, Rong Gu, Yun Deng, Zhiming Zhang, Luxiang Lin. Habitat association and community classification of woody plants in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [9] | Yun Han, Xiaofeng Chi, Jingya Yu, Xujie Ding, Shilong Chen, Faqi Zhang. A checklist of wild vascular plants in Qinghai, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [10] | Qing Zeng, Chao Xiong, Mei Yin, Anhui Ge, Lili Han, Limei Zhang. Research progress on ecological functions and community assembly of plant microbiomes [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22667-. |
| [11] | Yufei Huang, Chunyan Lu, Mingming Jia, Zili Wang, Yue Su, Yanlin Su. Plant species classification of coastal wetlands based on UAV images and object- oriented deep learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22411-. |
| [12] | Wenwen Shao, Guozhen Fan, Zhizhou He, Zhiping Song. Phenotypic plasticity and local adaptation of Oryza rufipogon revealed by common garden trials [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22311-. |
| [13] | Zhizhong Li, Shuai Peng, Qingfeng Wang, Wei Li, Shichu Liang, Jinming Chen. Cryptic diversity of the genus Ottelia in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22394-. |
| [14] | Huiyin Song, Zhengyu Hu, Guoxiang Liu. Assessing advances in taxonomic research on Chlorellaceae (Chlorophyta) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22083-. |
| [15] | Tao Yang, Zehao Shen, Xiaofeng Wang, Jiesheng Rao, Wencong Liu, Xi Tian, Xi Chen, Qiuyu Zhang, Qian Liu, Hengjun Qian, Yuyang Xie, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Mengling Tu, Ziming Shan, Yukun Zhang, Bo Hou, Jianbin Li, Xiaokun Ou. Characteristics of plant community diversity in a subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Central Yunnan Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn