



Biodiv Sci ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (4): 362-368. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07314 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.07314
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ruili Zhang, Yin Jia, Qixiang Zhang*( )
)
Received:2007-10-19
Accepted:2008-04-01
Online:2008-07-20
Published:2008-07-20
Contact:
Qixiang Zhang
Ruili Zhang, Yin Jia, Qixiang Zhang. Phenotypic variation of natural populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(4): 362-368.
| 群体编号 Population No. | 地点 Origin | 经纬度 Locality | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSM 1 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'165" N 100°06'403" E | 3,330 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing north |
| CSM 2 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'749" N 100°06'557" E | 2,800 | 干燥山坡坡地, 杜鹃林缘, 西向 Dry slope, beneath Rhododendron shrubs, facing west |
| MX | 漾濞美翕 Meixi, Yangbi | 25°43'213" N 100°03'175" E | 3,050 | 山间开敞坡地, 林缘, 西向 Grassy slope, beneath the woodlands, facing west |
| TCL | 云龙天池 Tianchi Lake, Yunlong | 25°51'422" N 99°19'389" E | 2,330 | 干燥坡地, 乔木林下, 东南向 Dry slope, under the woodlands, facing southeast |
| LDP | 丽江梨地坪 Lidiping, Lijiang | 27°12'389" N 99°24'478" E | 3,400 | 山坡坡地, 南向 Grassy slope, facing south |
| PTG | 维西攀天阁 Pantiange, Weixi | 27°20'983" N 99°11'976" E | 2,900 | 开阔缓坡, 沼泽地, 南向 Moist meadow, facing south |
| SBM | 双柏百竹山 Baizhu Mountain, Shuangbai | 24°33'404" N 100°48'615" E | 2,500 | 山顶开阔地带, 潮湿林缘, 东南向 Open forest, moist, beneath the woodlands, facing southeast |
| YLM | 丽江玉龙雪山 Yulong Mountains, Lijiang | 27°07'791'' N 100°15'114'' E | 2,800 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 东北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing northeast |
| SCH | 景东山厂河 Shanchanghe, Jingdong | 24°18'151" N 100°43'882" E | 2,210 | 干燥的开阔地带, 北向 Dry slope, facing north |
| ZZ | 腾冲自治 Zizhi, Tengchong | 26°34'309" N 99°53'572" E | 2,500 | 开阔地带, 干燥, 南向 Open forest, dry, facing south |
Table 1 Locations and ecological factors of the sampled populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 群体编号 Population No. | 地点 Origin | 经纬度 Locality | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSM 1 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'165" N 100°06'403" E | 3,330 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing north |
| CSM 2 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'749" N 100°06'557" E | 2,800 | 干燥山坡坡地, 杜鹃林缘, 西向 Dry slope, beneath Rhododendron shrubs, facing west |
| MX | 漾濞美翕 Meixi, Yangbi | 25°43'213" N 100°03'175" E | 3,050 | 山间开敞坡地, 林缘, 西向 Grassy slope, beneath the woodlands, facing west |
| TCL | 云龙天池 Tianchi Lake, Yunlong | 25°51'422" N 99°19'389" E | 2,330 | 干燥坡地, 乔木林下, 东南向 Dry slope, under the woodlands, facing southeast |
| LDP | 丽江梨地坪 Lidiping, Lijiang | 27°12'389" N 99°24'478" E | 3,400 | 山坡坡地, 南向 Grassy slope, facing south |
| PTG | 维西攀天阁 Pantiange, Weixi | 27°20'983" N 99°11'976" E | 2,900 | 开阔缓坡, 沼泽地, 南向 Moist meadow, facing south |
| SBM | 双柏百竹山 Baizhu Mountain, Shuangbai | 24°33'404" N 100°48'615" E | 2,500 | 山顶开阔地带, 潮湿林缘, 东南向 Open forest, moist, beneath the woodlands, facing southeast |
| YLM | 丽江玉龙雪山 Yulong Mountains, Lijiang | 27°07'791'' N 100°15'114'' E | 2,800 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 东北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing northeast |
| SCH | 景东山厂河 Shanchanghe, Jingdong | 24°18'151" N 100°43'882" E | 2,210 | 干燥的开阔地带, 北向 Dry slope, facing north |
| ZZ | 腾冲自治 Zizhi, Tengchong | 26°34'309" N 99°53'572" E | 2,500 | 开阔地带, 干燥, 南向 Open forest, dry, facing south |
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.122 | ||||||
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 0.056 | -0.511 | |||||
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | -0.157 | 0.053 | 0.645* | ||||
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 0.562 | -0.399 | -0.017 | -0.335 | |||
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | -0.396 | -0.448 | 0.281 | 0.100 | -0.417 | ||
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.696* | -0.006 | 0.193 | 0.079 | 0.496 | -0.219 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.316 | 0.079 | 0.293 | 0.140 | -0.069 | 0.016 | 0.463 |
Table 2 Pearson correlation coefficient (r) for eight morphological traits and their significance in the Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata populations
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.122 | ||||||
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 0.056 | -0.511 | |||||
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | -0.157 | 0.053 | 0.645* | ||||
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 0.562 | -0.399 | -0.017 | -0.335 | |||
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | -0.396 | -0.448 | 0.281 | 0.100 | -0.417 | ||
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.696* | -0.006 | 0.193 | 0.079 | 0.496 | -0.219 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.316 | 0.079 | 0.293 | 0.140 | -0.069 | 0.016 | 0.463 |
| 群体编号 Population | 变异系数 CV (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 平均 Average | |
| CSM 1 | 11.51 | 10.28 | 6.88 | 10.12 | 6.62 | 16.64 | 5.17 | 5.04 | 9.03 |
| CSM 2 | 8.56 | 9.45 | 6.32 | 5.26 | 4.57 | 11.43 | 3.98 | 3.77 | 6.67 |
| MX | 5.92 | 4.92 | 5.32 | 4.78 | 6.82 | 3.34 | 3.76 | 2.95 | 4.73 |
| TCL | 8.65 | 13.47 | 7.18 | 6.51 | 7.34 | 17.68 | 4.77 | 6.07 | 8.96 |
| LDP | 8.16 | 9.05 | 5.98 | 4.77 | 3.49 | 10.57 | 4.99 | 3.52 | 6.32 |
| PTG | 15.26 | 12.62 | 8.76 | 7.99 | 6.48 | 15.24 | 6.14 | 6.68 | 9.90 |
| SBM | 4.55 | 4.17 | 4.75 | 4.14 | 3.49 | 12.58 | 3.59 | 4.02 | 5.16 |
| YLM | 7.96 | 8.14 | 7.82 | 4.62 | 2.32 | 7.78 | 2.86 | 3.25 | 5.59 |
| SCH | 8.54 | 8.26 | 6.51 | 3.35 | 4.48 | 4.39 | 4.09 | 3.88 | 5.44 |
| ZZ | 13.49 | 10.86 | 8.13 | 9.33 | 4.58 | 13.46 | 5.61 | 6.29 | 8.97 |
Table 3 Coefficients of variance (CV) of morphological traits within each population of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 群体编号 Population | 变异系数 CV (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 平均 Average | |
| CSM 1 | 11.51 | 10.28 | 6.88 | 10.12 | 6.62 | 16.64 | 5.17 | 5.04 | 9.03 |
| CSM 2 | 8.56 | 9.45 | 6.32 | 5.26 | 4.57 | 11.43 | 3.98 | 3.77 | 6.67 |
| MX | 5.92 | 4.92 | 5.32 | 4.78 | 6.82 | 3.34 | 3.76 | 2.95 | 4.73 |
| TCL | 8.65 | 13.47 | 7.18 | 6.51 | 7.34 | 17.68 | 4.77 | 6.07 | 8.96 |
| LDP | 8.16 | 9.05 | 5.98 | 4.77 | 3.49 | 10.57 | 4.99 | 3.52 | 6.32 |
| PTG | 15.26 | 12.62 | 8.76 | 7.99 | 6.48 | 15.24 | 6.14 | 6.68 | 9.90 |
| SBM | 4.55 | 4.17 | 4.75 | 4.14 | 3.49 | 12.58 | 3.59 | 4.02 | 5.16 |
| YLM | 7.96 | 8.14 | 7.82 | 4.62 | 2.32 | 7.78 | 2.86 | 3.25 | 5.59 |
| SCH | 8.54 | 8.26 | 6.51 | 3.35 | 4.48 | 4.39 | 4.09 | 3.88 | 5.44 |
| ZZ | 13.49 | 10.86 | 8.13 | 9.33 | 4.58 | 13.46 | 5.61 | 6.29 | 8.97 |
| 性状 Traits | 均方(自由度) MS (df) | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | ||
| 株高 Plant height | 207.53 (9) | 9.99 (290) | 1.3962 | 20.76** | 7.16** | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 13.31 (9) | 1.42 (290) | 0.5663 | 9.35** | 2.51** | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 280.42 (9) | 17.5 (290) | 2.5684 | 15.97** | 6.84** | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 23.90 (9) | 2.36 (290) | 0.2382 | 10.14** | 9.89** | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 118.23 (9) | 13.52 (290) | 0.7212 | 8.75** | 18.74** | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 21.31 (9) | 1.35 (290) | 0.2076 | 15.74** | 6.52** | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 43.41 (9) | 5.23 (290) | 1.7746 | 8.3** | 2.94** | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.1525 (9) | 0.0325 (290) | 0.0115 | 4.69** | 2.83** | |
Table 4 Variance analysis of morphological traits among and within populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 性状 Traits | 均方(自由度) MS (df) | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | ||
| 株高 Plant height | 207.53 (9) | 9.99 (290) | 1.3962 | 20.76** | 7.16** | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 13.31 (9) | 1.42 (290) | 0.5663 | 9.35** | 2.51** | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 280.42 (9) | 17.5 (290) | 2.5684 | 15.97** | 6.84** | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 23.90 (9) | 2.36 (290) | 0.2382 | 10.14** | 9.89** | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 118.23 (9) | 13.52 (290) | 0.7212 | 8.75** | 18.74** | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 21.31 (9) | 1.35 (290) | 0.2076 | 15.74** | 6.52** | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 43.41 (9) | 5.23 (290) | 1.7746 | 8.3** | 2.94** | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.1525 (9) | 0.0325 (290) | 0.0115 | 4.69** | 2.83** | |
| 性状 Traits | 方差分量 Variance component | 方差分量百分比 % of variation | 表型分化系数 Vst | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | |||
| 株高 Plant height | 2.1948 | 3.1992 | 1.3962 | 32.32 | 47.11 | 20.56 | 0.4069 | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.1321 | 0.2858 | 0.5663 | 13.43 | 29.05 | 57.53 | 0.3161 | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 2.9207 | 4.9973 | 2.5684 | 27.84 | 47.67 | 24.50 | 0.3017 | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 0.2394 | 0.7058 | 0.2382 | 19.42 | 57.25 | 19.32 | 0.2533 | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 1.1635 | 4.2651 | 0.7212 | 18.94 | 69.43 | 11.74 | 0.2143 | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 0.2219 | 0.3821 | 0.2076 | 27.34 | 47.08 | 25.58 | 0.3674 | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.4242 | 1.1521 | 1.7746 | 12.66 | 34.38 | 52.96 | 0.2691 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.0004 | 0.0021 | 0.0115 | 2.72 | 14.93 | 82.34 | 0.1541 | |
| 平均值 Mean | 19.33 | 43.36 | 37.31 | 0.2854 | ||||
Table 5 Variance portions and differentiation coefficients of variance of morphological traits among and within populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 性状 Traits | 方差分量 Variance component | 方差分量百分比 % of variation | 表型分化系数 Vst | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | |||
| 株高 Plant height | 2.1948 | 3.1992 | 1.3962 | 32.32 | 47.11 | 20.56 | 0.4069 | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.1321 | 0.2858 | 0.5663 | 13.43 | 29.05 | 57.53 | 0.3161 | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 2.9207 | 4.9973 | 2.5684 | 27.84 | 47.67 | 24.50 | 0.3017 | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 0.2394 | 0.7058 | 0.2382 | 19.42 | 57.25 | 19.32 | 0.2533 | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 1.1635 | 4.2651 | 0.7212 | 18.94 | 69.43 | 11.74 | 0.2143 | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 0.2219 | 0.3821 | 0.2076 | 27.34 | 47.08 | 25.58 | 0.3674 | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.4242 | 1.1521 | 1.7746 | 12.66 | 34.38 | 52.96 | 0.2691 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.0004 | 0.0021 | 0.0115 | 2.72 | 14.93 | 82.34 | 0.1541 | |
| 平均值 Mean | 19.33 | 43.36 | 37.31 | 0.2854 | ||||
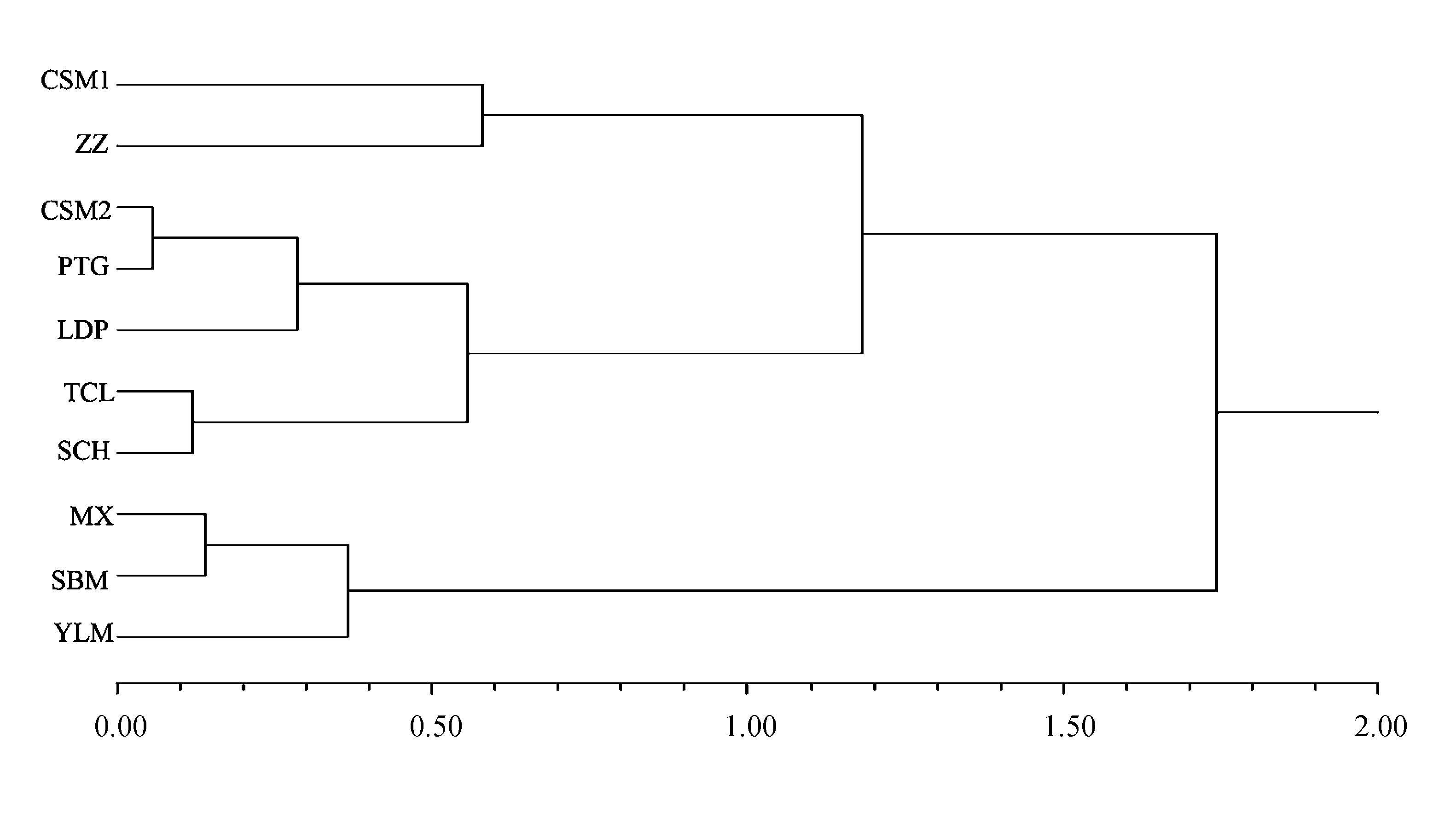
Fig. 1 UPGMA dendrogram of ten natural populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata based on eight morphological traits. Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| [1] | Antrobus S, Lack AJ (1993) Genetics of colonizing and established populations of Primula veris. Heredity, 71,252-258. |
| [2] | Christoph R, Anja A, Markus R (2005) Molecular variation within and between ten populations of Primula farinosa (Primulaceae) along an altitudinal gradient in the north Alps. Basic and Applied Ecology, 6,35-45. |
| [3] | Ge S (葛颂), Wang MX (王明庥), Chen YW (陈岳武) (1988) An analysis of population genetic structure of masson pine by isozyme technique. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 24,399-409. (in Chinese with English abstract ). |
| [4] | Gu WC (顾万春), Li WY (李文英) (2007) Analysis and suggestions of benefit sharing policies relating to forest tree germplasm resources in China. World Forestry Research (世界林业研究), 20 (1),66-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1990) Allozyme diversity in plant species. In:Plant Population Genetics, Breeding, and Genetic Resources (eds Brown AHD, Clegg MT, Kahler AL),pp.43-63. Sinauer Association Inc.,Massachusetts. |
| [6] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1992) Factors influencing levels of genetic diversity in woody plant species. New Forest, 6,95-124. |
| [7] | Honjo M, Ueno S, TsumuraY, Washitani I, Ohsawa R (2004) Phylogeographic study based on intraspecific sequence variation of chloroplast DNA for the conservation of genetic diversity in the Japanese endangered species Primula sieboldii. Biological Conservation, 120,215-224. |
| [8] | Hu QM (胡启明) (1994) On the geographical distribution of the Primulaceae. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报), 2 (4),1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Ishihama F, Nakano C, Ueno S, Ajima M, Tsumura Y, Washitani I (2003) Seed set and gene flow patterns in an experimental population of an endangered heterostylous herb with controlled local opposite-morph density. Functional Ecology, 17,680-689. |
| [10] |
Jacquemyn H, Honnay O, Galbusera P, Roldan-Ruiz I (2004) Genetic structure of the forest herb Primula elatior in a changing landscape. Molecular Ecology, 13,211-219.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Jin Y (金燕), Lu BR (卢宝荣) (2003) Sampling strategy of genetic diversity. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 11,155-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Kitamoto N, Honjo M, Ueno S, Takenaka A,TsumuraY, Washitani I, Ohsawa R (2005) Spatial genetic structure among and within populations of Primula sieboldii growing beside separate streams. Molecular Ecology, 14,149-157.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Liang SL (梁树乐), Zhang QX (张启翔) (2004) Investigation on resources of the Primula L. in the Cangshan Mountains of Dali. Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College (莱阳农学院学报), 21,63-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Liang SL (梁树乐) (2006) Studies on the Introduction and Crossbreeding of Wild Primula L. from the Southwest of China (我国西南地区部分野生报春的引种与杂交育种研究). PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | Li B (李斌), Gu WC (顾万春), Lu BM (卢宝明) (2002) A study on phenotypic diversity of seeds and cones characteristics in Pinus bungeana. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 10,181-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Li J (李进), Chen KY (陈可咏), Li BS (李渤生) (1998) The variation of genetic diversity of Quercus aquifolioides in different elevations. Acta Botanica Sinica(植物学报), 40,761-767. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Luo SB (罗少波), Li ZJ (李智军), Zhou WB (周微波), Kenichihida , Takehiko (1996) Technique for identification of heat tolerance in heading Chinese cabbage (中国蔬菜), 2,16-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Ming J (明军), Gu WC (顾万春) (2006a) Genetic diversity in natural populations of Syringa oblata detected by AFLP markers. Acta Horticulturae Sinica (园艺学报), 33,1269-1274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Ming J (明军), Gu WC (顾万春) (2006b) Phenotypic variation of Syringa oblata Lindl. Forest Research (林业科学研究), 19,199-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] |
Nan P, Shi SH, Peng SL, Tian CJ, Zhong Y (2003) Genetic diversity in Primula obconica (Primulaceae) from central and south-west China as revealed by ISSR markers. Annals of Botany, 91,329-333.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Richards J (1993) Primula. B. T. Bastford Ltd., London. |
| [22] | Rossum F, Echchgadda G, Szabadi I, Triest L (2002) Commonness and long-term survival in fragmented habitats: Primula elatior as a study case . Conservation Biology, 16,1286-1295. |
| [23] | Van Rossum F, Echchgadda G, Szabadi I, Triest L (2002) Commonness and long-term survival in fragmented habitats: Primula elatior as a study case. Conservation Biology, 16,1286-1295. |
| [24] | Wang FY (王凤英), Ge XJ (葛学军), Hao G (郝刚), Hu QM (胡启明) (2005) Genetic diversity and differentiation in Primula sikkimensis (Primulaceae) in Himalyan- Hengduan Mountains. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany (热带亚热带植物学报), 13,149-153. (in the Chinese with English abstract). |
| [25] | Wsahitani I, Ishihama F, Matsumura C, Nagai M, Nishihiro J, Ajima M (2005) Conservation ecology of Primula sieboldii: synthesis of information towards the prediction of the genetic/demographic fate of a population. Plant Species Biology, 20,3-15. |
| [26] | Xue DW, Ge XJ, Hao G, Zhang CQ (2004) High genetic diversity in a rare, narrowly endemic Primrose species: Primula interjacens by ISSR analysis. Acta Botanica Sinica, 46,1163-1169. |
| [1] | Xiangxiang Chen, Zhongshuai Gai, Juntuan Zhai, Jindong Xu, Peipei Jiao, Zhihua Wu, Zhijun Li. Genetic diversity and construction of core conservation units of the natural populations of Populus euphratica in Northwest China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1638-1649. |
| [2] | Xueqin Wu,Gangbiao Xu,Yan Liang,Xiangbao Shen. Genetic diversity of natural and planted populations of Tsoongiodendron odorum from the Nanling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(1): 71-79. |
| [3] | Lei Li, Tong Liu, Bin Liu, Zhongquan Liu, Langming Si, Rong Zhang. Phenotypic variation and covariation among natural populations of Arabidopsis thaliana in North Xinjiang [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(5): 497-508. |
| [4] | Bin Zeng, Shuping Luo, Jiang Li, Wenkui Nie, Feng Zhang, Hailong Li. Morphological variations in natural populations ofAmygdalus ledebouriana [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(5): 484-491. |
| [5] | Haili Ke, Xiqiang Song, Zhiqiong Tan, Hongxia Liu, Yibo Luo. Endophytic fungi diversity in root of Doritis pulcherrima (Orchidaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2007, 15(5): 456-462. |
| [6] | Huifang Wu, Zuozhou Li, Hongwen Huang. Genetic differentiation among natural populations of Gastrodia elata (Orchidaceae) in Hubei and germplasm assessment of the cultivated populations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(4): 315-326. |
| [7] | Xiaoyun Pan, Hanzhao Liang, Alejandro Sosa, Yupeng Geng, Bo Li, Jiakuan Chen. Patterns of morphological variation of alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides): from native to invasive regions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(3): 232-240. |
| [8] | Haiqin Sun, Ang Li, Wei Ban, Xiaoming Zheng, Song Ge. Morphological variation and its adaptive significance for Changnienia amoena, an endangered orchid [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2005, 13(5): 376-386. |
| [9] | LI Bin, GU Wan-Chun. A study on phenotypic diversity of seeds and cones characteristics in Pinus bungeana [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2002, 10(2): 181-188. |
| [10] | CHEN Wei-Lun, GUO Dong-Hong, AN He-Xiang, ZHU Zhi-Qing. In vitro conservation of Actinidia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1998, 06(4): 278-281. |
| [11] | Wang Shaoping, Wang Renging, Li Li. Studies on the diversity of Naidong Camellia in Qingdao Ⅰ Distribution and morphological variation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1995, 03(3): 139-142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn