



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (6): 696-703. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14225 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.14225
Special Issue: 野生动物的红外相机监测
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lvbing Zhang1,2, Shaopeng Cui1,2, Yuanjun Huang1,2, Daiqiang Chen1,2, Huijie Qiao1, Chunwang Li1, Zhigang Jiang1,*( )
)
Received:2014-10-23
Accepted:2014-11-23
Online:2014-11-20
Published:2014-12-11
Contact:
Jiang Zhigang
Lvbing Zhang, Shaopeng Cui, Yuanjun Huang, Daiqiang Chen, Huijie Qiao, Chunwang Li, Zhigang Jiang. Infrared camera traps in wildlife research and monitoring in China: issues and insights[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(6): 696-703.
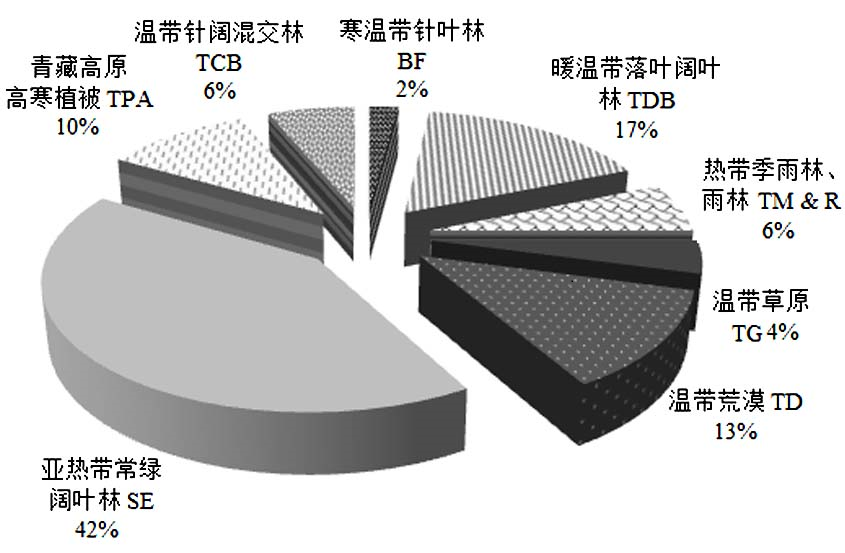
Fig. 2 Efforts of camera-trap researches in vegetation and habitats types. BF, boreal forests; TDB, temperate deciduous broad-leaved forests; TM & R, tropical monsoon forests and rain forests; TG, temperate grassland; TD, temperate desert; SE, subtropical evergreen forests; TPA, alpine of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; TCB, temperate coniferous broad-leaved forest
| 动物类群 Taxon | 种群或多样性研究 Researches on population ecology or biodiversity | 行为学研究 Researches on animal behavior | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 频数* Frequency | 种类数* Species number | 频数 Frequency | 种类数 Species number | |||
| 哺乳纲 Mammalia | ||||||
| 食肉目 Carnivora | ||||||
| 犬科 Canidae | 8 | 5 | ||||
| 猫科 Felidae | 27 | 7 | 3 | 1 | ||
| 鼬科 Mustelidae | 46 | 8 | ||||
| 熊猫科和熊科 Ailuropodidae, Ursidae | 7 | 2 | ||||
| 灵猫科 Viverridae | 18 | 4 | ||||
| 偶蹄目 Artiodactyla | ||||||
| 鹿科 Cervidae | 30 | 9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 牛科 Bovidae | 24 | 9 | ||||
| 猪科 Suidae | 16 | 1 | ||||
| 麝科 Moschidae | 4 | 3 | ||||
| 骆驼科 Camelidae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 灵长目 Primates | ||||||
| 猴科 Cercopithecidae | 8 | 4 | ||||
| 懒猴科 Lorisidae | 2 | 2 | ||||
| 啮齿目 Rodentia | ||||||
| 松鼠科 Sciuridae | 33 | 9 | ||||
| 鼠科 Muridae | 14 | >4 | ||||
| 鼹形鼠科 Spalacidae | 2 | 2 | ||||
| 豪猪科 Hystricidae | 5 | 1 | ||||
| 兔形目 Lagomorpha | ||||||
| 兔科 Leporidae | 10 | 5 | ||||
| 鼠兔科 Ochotonidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 奇蹄目 Perissodactyla | ||||||
| 马科 Equidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 食虫类 Insectivora | ||||||
| 鼩鼱科 Soricidae | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 猬科 Erinaceidae | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 鳞甲目 Pholidota | ||||||
| 鲮鲤科 Manidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 树鼩目 Scandentia | ||||||
| 树鼩科 Tupaiidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 翼手目 Chiroptera | ||||||
| 狐蝠科 Pteropodidae | 1 | 2 | ||||
| 鸟纲 Aves | ||||||
| 雀形目 Passeriformes | 151 | - | ||||
| 鸡形目 Galliformes | 17 | - | 3 | 2 | ||
| 鸽形目 Columbiformes | 4 | - | ||||
| 隼形目 Falconiformes | 8 | - | ||||
| 鸮形目 Strigiformes | 3 | - | ||||
| 鴷形目 Coraciiformes | 8 | - | ||||
| 鸻形目 Charadriiformes | 1 | - | ||||
Table S1 Mammal and bird groups captured with infrared-camera traps in wildlife research and monitoring of China http://www.biodiversity-science.net/fileup/PDF/w2014-225-1.pdf
| 动物类群 Taxon | 种群或多样性研究 Researches on population ecology or biodiversity | 行为学研究 Researches on animal behavior | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 频数* Frequency | 种类数* Species number | 频数 Frequency | 种类数 Species number | |||
| 哺乳纲 Mammalia | ||||||
| 食肉目 Carnivora | ||||||
| 犬科 Canidae | 8 | 5 | ||||
| 猫科 Felidae | 27 | 7 | 3 | 1 | ||
| 鼬科 Mustelidae | 46 | 8 | ||||
| 熊猫科和熊科 Ailuropodidae, Ursidae | 7 | 2 | ||||
| 灵猫科 Viverridae | 18 | 4 | ||||
| 偶蹄目 Artiodactyla | ||||||
| 鹿科 Cervidae | 30 | 9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 牛科 Bovidae | 24 | 9 | ||||
| 猪科 Suidae | 16 | 1 | ||||
| 麝科 Moschidae | 4 | 3 | ||||
| 骆驼科 Camelidae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 灵长目 Primates | ||||||
| 猴科 Cercopithecidae | 8 | 4 | ||||
| 懒猴科 Lorisidae | 2 | 2 | ||||
| 啮齿目 Rodentia | ||||||
| 松鼠科 Sciuridae | 33 | 9 | ||||
| 鼠科 Muridae | 14 | >4 | ||||
| 鼹形鼠科 Spalacidae | 2 | 2 | ||||
| 豪猪科 Hystricidae | 5 | 1 | ||||
| 兔形目 Lagomorpha | ||||||
| 兔科 Leporidae | 10 | 5 | ||||
| 鼠兔科 Ochotonidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 奇蹄目 Perissodactyla | ||||||
| 马科 Equidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 食虫类 Insectivora | ||||||
| 鼩鼱科 Soricidae | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 猬科 Erinaceidae | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 鳞甲目 Pholidota | ||||||
| 鲮鲤科 Manidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 树鼩目 Scandentia | ||||||
| 树鼩科 Tupaiidae | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 翼手目 Chiroptera | ||||||
| 狐蝠科 Pteropodidae | 1 | 2 | ||||
| 鸟纲 Aves | ||||||
| 雀形目 Passeriformes | 151 | - | ||||
| 鸡形目 Galliformes | 17 | - | 3 | 2 | ||
| 鸽形目 Columbiformes | 4 | - | ||||
| 隼形目 Falconiformes | 8 | - | ||||
| 鸮形目 Strigiformes | 3 | - | ||||
| 鴷形目 Coraciiformes | 8 | - | ||||
| 鸻形目 Charadriiformes | 1 | - | ||||
| [1] | Badru M, Douglas S, Peter S, Miriam van H, Pontious E (2013) A camera trap assessment of terrestrial vertebrates in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda.African Journal of Ecology, 51, 21-31. |
| [2] | Brackman LS (2000) Not-So-Candid camera, please: law enforcement officers violate the fourth amendment when the media tags along. Missouri Law Review, 65, 743. |
| [3] | Carbone C, Christie S, Conforti K, Coulson T, Franklin N, Ginsberg JR, Griffiths M, Holden J, Kawanishi K, Kinnaird M, Laidlaw R, Lynam A, Macdonald DW, Martyr D, McDougal C, Nath L, O’Brien T, Seidensticker J, Smith DJL, Sunquist M, Tilson R, Wan Shahruddin WN (2006) The use of photographic rates to estimate densities of tigers and other cryptic mammals.Animal Conservation, 4, 75-79. |
| [4] | Chen XR (陈小荣), Xu DM (许大明), Bao YX (鲍毅新), Zhang SS (章书声) (2013) Mammalian species diversity in Baishanzu National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province of East China based on G-F index. Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 32, 1421-1427. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Efford MG (2009) Secr—Spatially Explicit Capture-recapture in R, version 1.2.10. Department of Zoology, University of Otago, Dunedin. (10/10/2014 |
| [6] | Gopalaswamy AM, Royle JA, Hines JE, Singh P, Jathanna D, Kumar N, Karanth KU (2012) Program SPACECAP: software for estimating animal density using spatially explicit capture-recapture models.Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 1067-1072. |
| [7] | Hemmi JM, Maddess T, Mark RF (2000) Spectral sensitivity of photoreceptors in an Australian marsupial, the tammar wallaby (Macropus eugenii).Vision Research, 40, 591-599. |
| [8] | Hines JE (2010) Capture 2. Patuxent: USGS PWRC.(10/10/ |
| 1)2014) | |
| [9] | Hu TH (胡天华), Li YG (李元刚) (2013) Application of camera traps in wildlife monitoring of Helan Mountain Natural Reserve, Ningxia.Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology(宁夏农林科技), 54, 57-59. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Huang GT, Rosowski JJ, Peake WT (2000) Relating middle-ear acoustic performance to body size in the cat family: measurements and models.Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 186, 447-465. |
| [11] | Huang G, Rosowski J, Ravicz M, Peake W (2002) Mammalian ear specializations in arid habitats: structural and functional evidence from sand cat (Felis margarita).Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 188, 663-681. |
| [12] | Isley TE, Gysel LW (1975) Sound-source localization by the red fox. Journal of Mammalogy, 56, 397-404. |
| [13] | Jiang ZG (蒋志刚) (2004) Animal Behavioral Principles and Species Conservation Methods (动物行为原理与物种保护方法). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Jiang ZG (蒋志刚), Sun JZ (孙吉周), Cui SP (崔绍朋), Chen DQ (陈代强), Zhang LB (张履冰), Li CW (李春旺), Tang SH (汤宋华), Chu HJ (初红军) (2014) Moose Alces alces alces in Mt. Altay, Xinjiang.Chinese Journal of Zoology(动物学杂志), 49, 303-304. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Larrucea ES, Brussard PF, Jaeger MM, Barrett RH (2007) Cameras, coyotes and the assumption of equal detectability.Journal of Wildlife Management, 71, 1682-1689. |
| [16] | Lehner PN, Krumm R, Cringan AT (1976) Tests for olfactory repellents for coyotes and dogs.Journal of Wildlife Management, 40, 145-150. |
| [17] | Li F (李峰), Jiang ZG (蒋志刚) (2014) Is nocturnal rhythm of Asian badger (Meles leucurus) caused by human activity? A case study in the eastern area of Qinghai Lake.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22, 758-763. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Li M (李敏), Wang JC (汪继超), Liu HW (刘海伟), Shi HT (史海涛) (2014) Simulation of Cuora galbinifrons nest predation.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 33, 1629-1633. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Li S, McShea WJ, Wang DJ, Shao LK, Shi XG (2010) The use of infrared-triggered cameras for surveying phasianids in Sichuan Province, China.IBIS, 152, 299-309. |
| [20] | Li ZX (李志兴) (2003) China’s first photo of wild tiger using infrared camera.Chinese Journal of Wildlife(野生动物学报), (5), 35-38. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Li ZL (李治霖), Kang AL (康霭黎), Lang JM (郎建民), Xue YG (薛延刚), Ren Y (任毅), Zhu ZW (朱志文), Ma JZ (马建章), Liu PQ (刘培琦), Jiang GS (姜广顺) (2014) On the assessment of big cats and their prey populations based on camera trap data.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22, 725-732. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Liu DZ (刘东志), Jiang ZG (蒋志刚), Chu HJ (初红军), Huang XW (黄效文), Zhang F (张帆), Chen G (陈刚) (2013) Summer nocturnal activity rhythms and time budgets of the Sino-Mongolia beaver (Castor fiber birulai) in Xinjiang, China.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 33, 319-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Liu F (刘芳), Li DQ (李迪强), Wu JG (吴记贵) (2012) Using infra-red cameras to survey wildlife in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 32, 730-739. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Lu XL (卢学理), Jiang ZG (蒋志刚), Tang JR (唐继荣), Wang XJ (王学杰), Xiang DQ (向定乾), Zhang JP (张建平) (2005) Auto-trigger camera traps for studying giant panda and its sympatric wildlife species.Acta Zoologica Sinica(动物学报), 51, 495-500. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Ma M (马鸣), Xu F (徐峰), Chundawat RS, Jumabay K, Wu YQ (吴逸群), Ai ZZ (艾则孜), Zhu MH (朱玛洪) (2006) Camera trapping of snow leopards for the photo capture rate and population size in the Muzat Valley of Tianshan Mountains.Acta Zoologica Sinica(动物学报), 52, 788-793. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Meek PD, Ballard G, Fleming PJS, Schaefer M, Williams W, Falzon G (2014) Camera traps can be heard and seen by animals.PLoS ONE, 9, e110832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone. 0110832. |
| [27] | Mokany K, Jones MM, Harwood DT (2013) Scaling pairwise β-diversity and α-diversity with area.Journal of Biogeography, 40, 2299-2309. |
| [28] | Newbold HG, King CM (2009) Can a predator see ‘invisible’ light? Infrared vision in ferrets (Mustela furo).Wildlife Research, 36, 309-318. |
| [29] | O’Brien TG, Kinnaird MF, Wibisono HT (2003) Crouching tigers, hidden prey: Sumatran tiger and prey populations in a tropical forest landscape.Animal Conservation, 6, 131-139. |
| [30] | O’Brien T, Baillie J, Krueger L, Cuke M (2010) The Wildlife Picture Index: monitoring top trophic levels.Animal Conservation, 13, 335-343. |
| [31] | O’Connell AF, Nichols JD, Karanth KU (2011) Camera Traps in Animal Ecology: Methods and Analyses. Springer, New York. |
| [32] | Pater L (2001) Defining auditory thresholds for animal species. ALIS. |
| [33] | Ping X, Li C, Jiang Z, Liu W, Zhu H (2011a) Sexual difference in seasonal patterns of salt lick use by south China sika deer Cervus nippon.Mammalian Biology, 76, 196-200. |
| [34] | Ping X, Li C, Jiang Z, Liu W, Zhu H (2011b) Interference competition and group size effect in sika deer (Cervus nippon) at salt licks.Ethologica, 14, 43-49. |
| [35] | Price MA, Attenborough K, Heap NW (1988) Sound attenuation through trees: measurements and models.Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 84, 1836-1844. |
| [36] | Rowcliffe JM, Kays R, Kranstauber B, Carbone C, Jansen PA (2014) Quantifying levels of animal activity using camera trap data.Methods in Ecology and Evolution , doi:10.1111/2041-210X.12278 (2014/10/15) |
| [37] | Rovero F, Martin E, Rosa M, Ahumada JA, Spitale D (2014) Estimating species richness and modelling habitat preferences of tropical forest mammals from camera trap data.PLoS ONE, 9, e103300. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103300 (2014/10/12) |
| [38] | Schipper J (2007) Camera-trap avoidance by Kinkajous Potos flavus: rethinking the “non invasive” paradigm.Small Carnivore Conservation, 36, 38-41. |
| [39] | Séquin ES, Jaeger MM, Brussard PF, Barrett RH (2003) Wariness of coyotes to camera traps relative to social status and territory boundaries.Canadian Journal of Zoology, 81, 2015-2025. |
| [40] | Si XF, Kays R, Ding P (2014) How long is enough to detect terrestrial animals? Estimating the minimum trapping effort on camera traps.PeerJ, 2, e374. |
| [41] | Tremaine G, Farah CR, Jessica D, Joseph K, Alfonso A (2014) Arboreal camera trapping: taking a proven method to new heights.Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 443-451. |
| [42] | Trolle M, Kéry M (2003) Estimation of ocelot density in the Pantanal using capture-recapture analysis of camera-trapping data.Journal of Mammalogy, 84, 607-614. |
| [43] | Wang JJ (王佳佳), Yu ZG (余志刚), Li ZM (李筑眉), Jiang H (蒋鸿), Liang W (梁伟) (2014) Identifying predators of ground nests of birds in Kuankuoshui Nature Reserve, Guizhou, southwestern China.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 33, 352-357. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [44] | Wang Y (王云), Piao ZJ (朴正吉), Guan L (关磊), Kong YP (孔亚平) (2013) Influence of Ring Changbai Mountain Scenic Highway on wildlife.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 32, 425-435. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [45] | Wearn OR, Rowcliffe JM, Carbone C, Bernard H, Ewers RM (2013) Assessing the status of wild felids in a highly- disturbed commercial forest reserve in Borneo and the implications for camera trap survey design.PLoS ONE, 8, e77598. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077598. |
| [46] | Wegge P, Pokheral CP, Jnawali SR (2004) Effects of trapping effort and trap shyness on estimates of tiger abundance from camera trap studies.Animal Conservation, 7, 251-256. |
| [47] | Windberg LA (1996) Coyote responses to visual and olfactory stimuli related to familiarity with an area.Canadian Journal of Zoology, 74, 2248-2253. |
| [48] | Xiao ZS (肖治术), Wang XZ (王学志), Li XH (李欣海) (2014a) An introduction to CameraData: an online database of wildlife camera trap data.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22, 712-716. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [49] | Xiao ZS (肖治术), Li XH (李欣海), Wang XZ (王学志), Zhou QH (周岐海), Quan RC (权锐昌), Shen XL (申小莉), Li S (李晟) (2014b) Developing camera-trapping protocols for wildlife monitoring in Chinese forests.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22, 704-711. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [50] | Xu AC, Jiang ZG, Li CW, Guo JX, Da SL, Cui QH, Yu SY, Wu GS (2008) Status and conservation of the snow leopard Panthera uncia in the Gouli Region, Kunlun Mountains, China.Oryx, 42, 460-463. |
| [51] | Xue YD (薛亚东), Liu F (刘芳), Guo TZ (郭铁征), Yuan L (袁磊), Li DQ (李迪强) (2014) Using camera traps to survey wildlife at water sources on the northern slope of the Altun Mountains, China.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 34, 164-171. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [52] | Zhang SS (章书声), Bao YX (鲍毅新), Wang YN (王艳妮), Fang PF (方平福), Ye B (叶彬) (2012) Activity rhythms of black muntjac (Muntiacus crinifron) revealed with infrared camera.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 32, 368-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [53] | Zhang SS (章书声), Bao YX (鲍毅新), Wang YN (王艳妮), Fang PF (方平福), Ye B (叶彬) (2013) Estimating rodent density using infrared-triggered camera technology.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 33, 3241-3247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [54] | Zhao YZ (赵玉泽), Wang ZC (王志臣), Xu JL (徐基良), Luo X (罗旭), An LD (安丽丹) (2013) Activity rhythm and behavioral time budgets of wild Reeves’s pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesii) using infrared camera. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 33, 6021-6027. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [55] | Zheng WC (郑伟成), Zhang SS (章书声), Pan CC (潘成椿), Liu JL (刘菊莲), Ji GH (季国华) (2014) Mammal and avian diversity detected by infrared cameras in Jiulongshan National Nature Reserve.Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology(浙江林业科技), 34, 17-22. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Min Luo, Yongchuan Yang, Cheng Jin, Lihua Zhou, Yuxiao Long. Composition profile and response to human activity of mammals in the urban forests of central Chongqing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [10] | Murong Yi, Ping Lu, Yong Peng, Yong Tang, Jiuheng Xu, Haoping Yin, Luyang Zhang, Xiaodong Weng, Mingxiao Di, Juan Lei, Chenqi Lu, Rujun Cao, Nianhua Dai, Deyang Zhan, Mei Tong, Zhiming Lou, Yonggang Ding, Jing Chai, Jing Che. Population status and habitat of Critically Endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [11] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [12] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [13] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [14] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [15] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()