



Biodiv Sci ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 190-196. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07030 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07030
Special Issue: 中国的森林生物多样性监测
Previous Articles Next Articles
Kai Song1,2, Xiangcheng Mi1,*( ), Qi Jia1,3, Haibao Ren1, Dan Bebber4, Keping Ma1
), Qi Jia1,3, Haibao Ren1, Dan Bebber4, Keping Ma1
Received:2011-02-22
Accepted:2011-03-04
Online:2011-03-20
Published:2011-06-01
Contact:
Xiangcheng Mi
Supported by:Kai Song, Xiangcheng Mi, Qi Jia, Haibao Ren, Dan Bebber, Keping Ma. Variation in phylogenetic structure of forest communities along a human disturbance gradient in Gutianshan forest, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(2): 190-196.
| 样地 Plot | 群落类型 Community type | 物种数 Species richness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | DBH≤5 cm | 5 cm <DBH≤ 10 cm | DBH> 10 cm | ||
| 1 | I | 81 | 77 | 31 | 22 |
| 2 | IV | 114 | 96 | 56 | 73 |
| 3 | II | 100 | 100 | 66 | 25 |
| 4 | IV | 89 | 83 | 50 | 39 |
| 5 | III | 105 | 96 | 53 | 43 |
| 6 | III | 123 | 113 | 68 | 46 |
| 7 | I | 90 | 86 | 32 | 18 |
| 8 | II | 95 | 89 | 58 | 25 |
| 9 | II | 85 | 76 | 53 | 19 |
| 10 | IV | 118 | 96 | 68 | 72 |
| 11 | I | 98 | 90 | 40 | 16 |
| 12 | III | 87 | 80 | 45 | 34 |
Table 1 Community types and species richness of 12 1-ha plots
| 样地 Plot | 群落类型 Community type | 物种数 Species richness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | DBH≤5 cm | 5 cm <DBH≤ 10 cm | DBH> 10 cm | ||
| 1 | I | 81 | 77 | 31 | 22 |
| 2 | IV | 114 | 96 | 56 | 73 |
| 3 | II | 100 | 100 | 66 | 25 |
| 4 | IV | 89 | 83 | 50 | 39 |
| 5 | III | 105 | 96 | 53 | 43 |
| 6 | III | 123 | 113 | 68 | 46 |
| 7 | I | 90 | 86 | 32 | 18 |
| 8 | II | 95 | 89 | 58 | 25 |
| 9 | II | 85 | 76 | 53 | 19 |
| 10 | IV | 118 | 96 | 68 | 72 |
| 11 | I | 98 | 90 | 40 | 16 |
| 12 | III | 87 | 80 | 45 | 34 |
| 群落类型 Community type | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| II | 0.2146 | ||
| III | 0.2239 | 0.1910 | |
| IV | 0.2920 | 0.2161 | 0.2177 |
Table 2 The S?rensen index between different community types
| 群落类型 Community type | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| II | 0.2146 | ||
| III | 0.2239 | 0.1910 | |
| IV | 0.2920 | 0.2161 | 0.2177 |
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | s2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type | 3 | 64.5689 | 21.5230 | 19.09 | <0.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 296 | 333.7407 | 1.1275 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 299 | 398.3096 |
Table 3 LSD’s one-way ANOVA for Net Relatedness Index of communities with different disturbance types
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | s2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type | 3 | 64.5689 | 21.5230 | 19.09 | <0.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 296 | 333.7407 | 1.1275 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 299 | 398.3096 |
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | S2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type (DT) | 3 | 210.0901 | 70.03 | 42.76 | <.0001 |
| 径级结构 DBH | 2 | 489.0633 | 244.5317 | 149.31 | <.0001 |
| 干扰类型× 径级结构 DT× DBH | 6 | 69.703 | 11.6172 | 7.09 | <.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 859 | 1406.8081 | 1.6377 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 870 | 2175.6645 |
Table 4 Two-way ANOVA for Net Relatedness Index of communities with different disturbance types and DBH classes
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | S2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type (DT) | 3 | 210.0901 | 70.03 | 42.76 | <.0001 |
| 径级结构 DBH | 2 | 489.0633 | 244.5317 | 149.31 | <.0001 |
| 干扰类型× 径级结构 DT× DBH | 6 | 69.703 | 11.6172 | 7.09 | <.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 859 | 1406.8081 | 1.6377 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 870 | 2175.6645 |
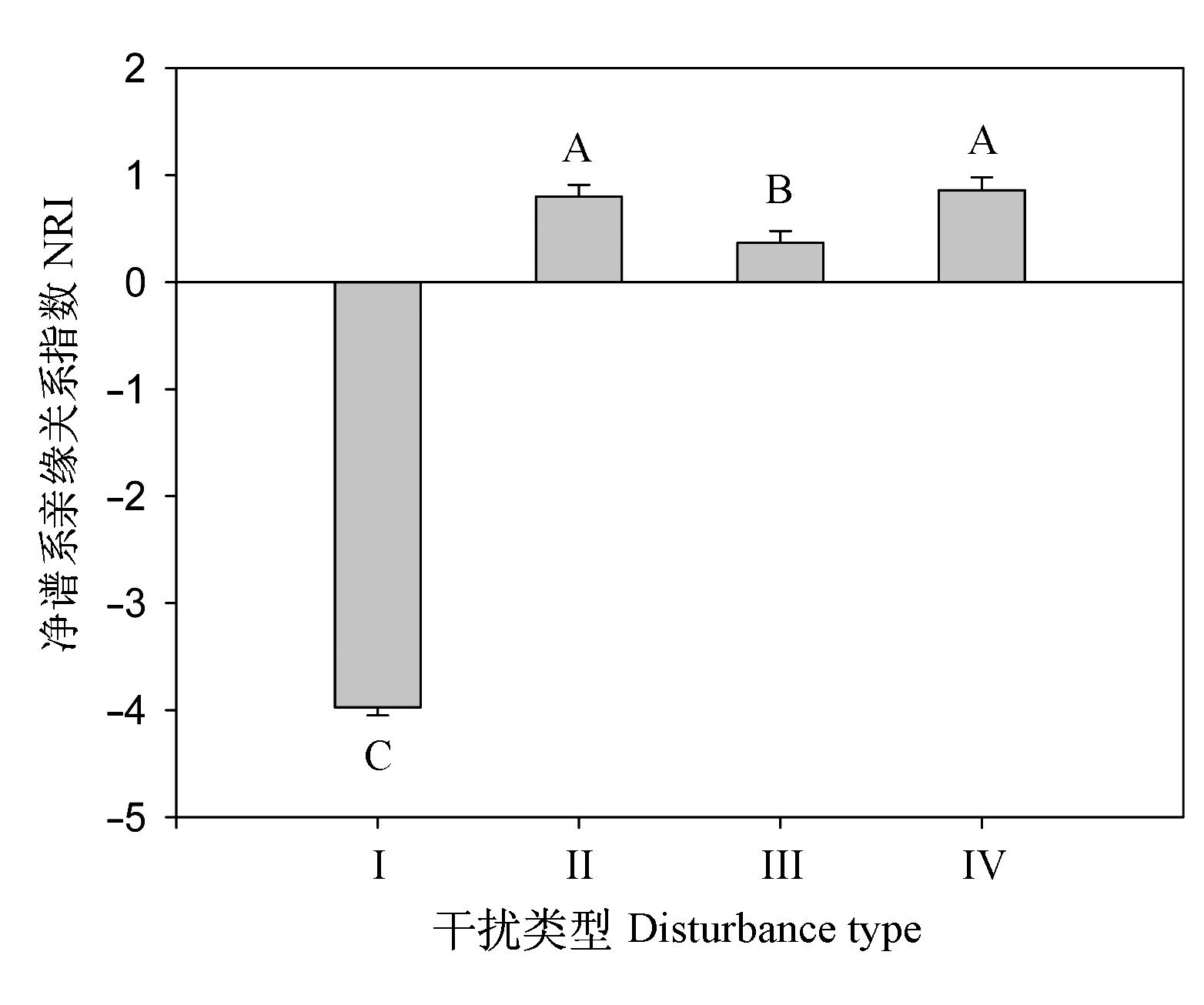
Fig. 1 The mean value of Net Relatedness Index of communities of different human disturbance types. I, II, III, IV, see Table 1. The letters on bars are the results of multiple comparison for different community types.
| 地形因子 Topographical factor | 海拔 Elevation | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 凹凸度 Convexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.3916 | 0.1153 | 0.3711 | 0.043* |
| R2 | 0.0025 | 0.0083 | 0.0027 | 0.0137 |
Table 5 Effects of different topographical factors on Net Relatedness Index of communities
| 地形因子 Topographical factor | 海拔 Elevation | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 凹凸度 Convexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.3916 | 0.1153 | 0.3711 | 0.043* |
| R2 | 0.0025 | 0.0083 | 0.0027 | 0.0137 |
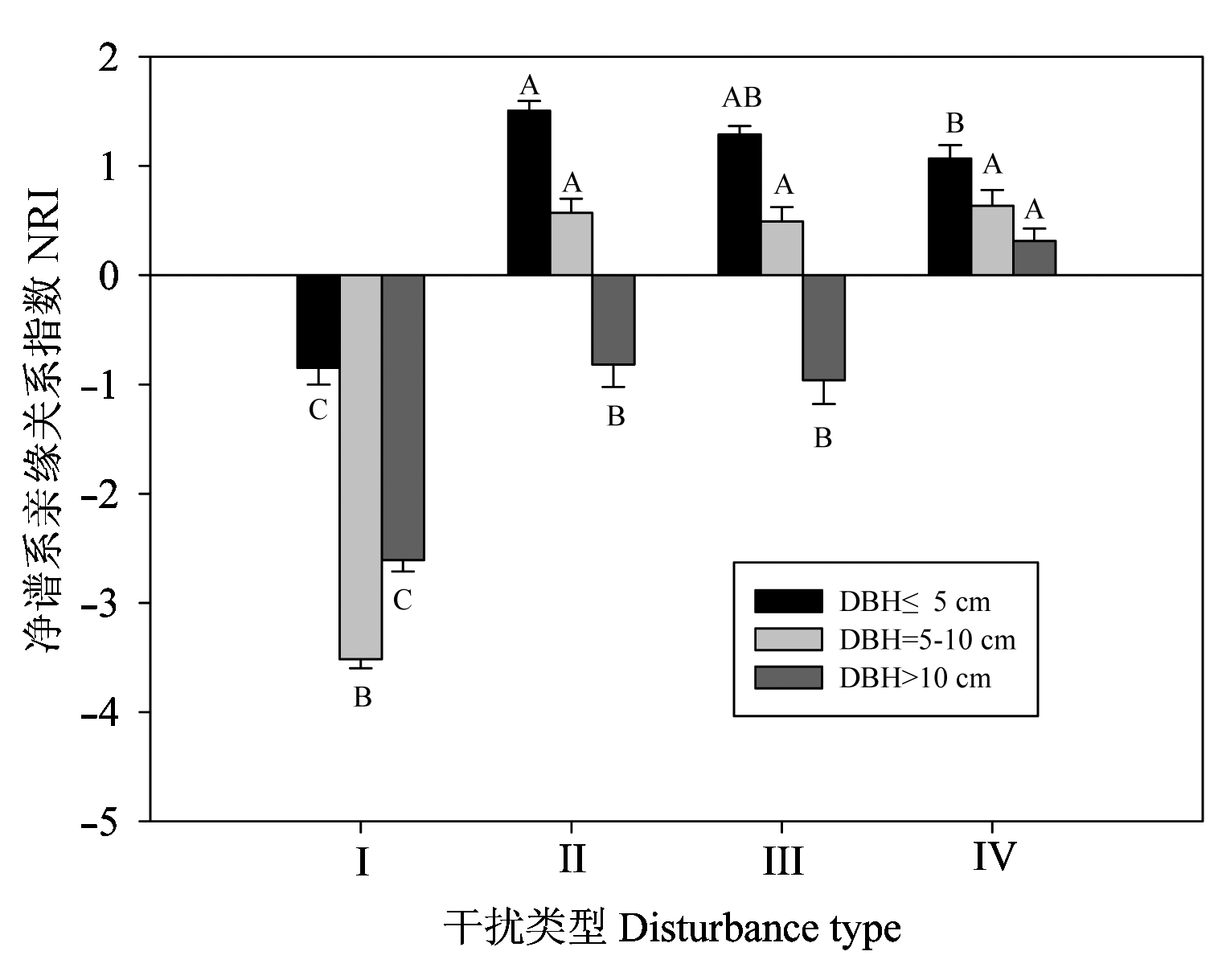
Fig. 2 The mean value Net Relatedness Index of communities of different DBH classes. The letters on bars are the results of multiple comparison for different community types for the same DBH class. I, II, III, IV, see Table 1.
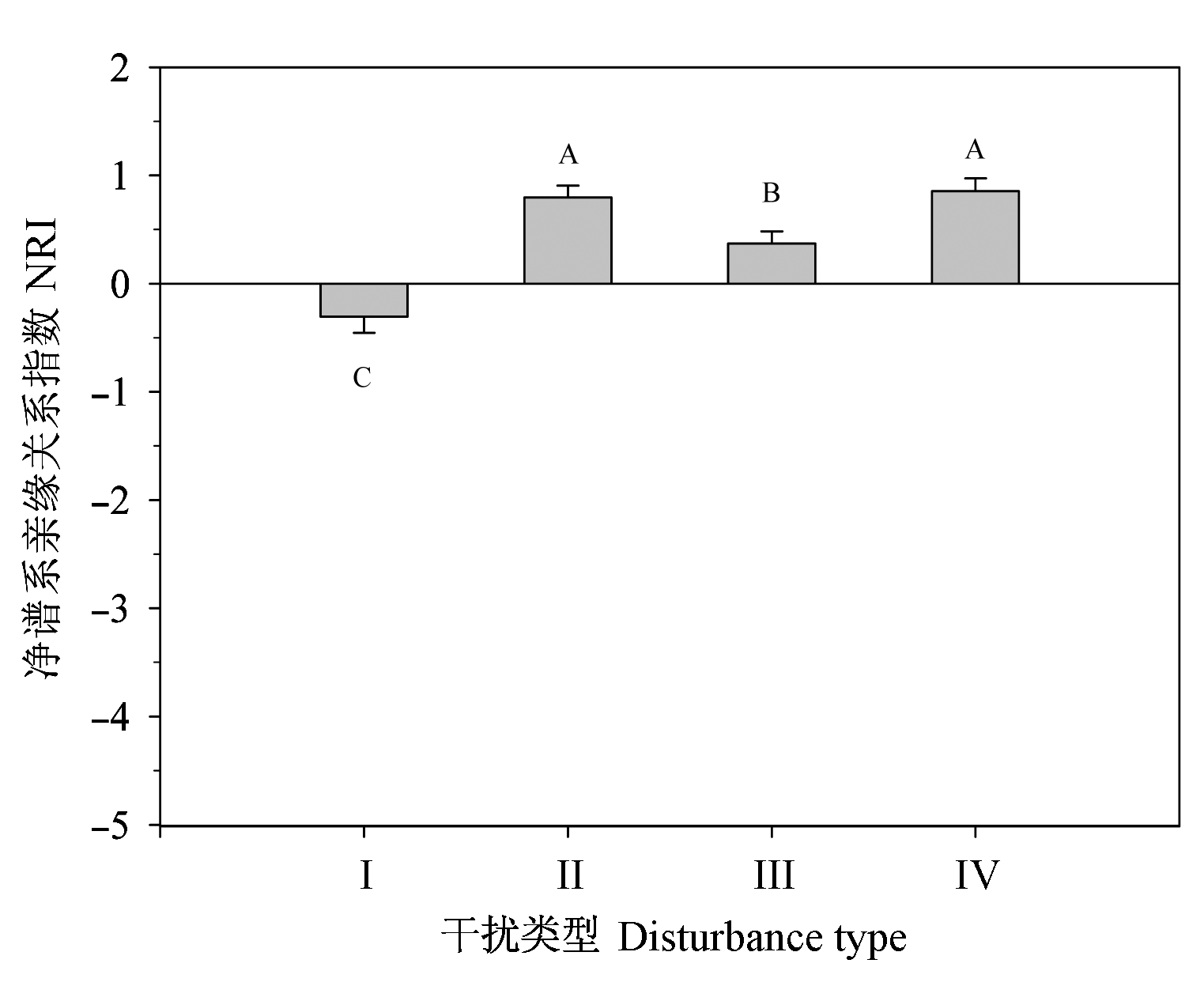
Fig. 3 The mean value of Net Relatedness Index of communities with different human disturbance after excluding Cunninghamia lanceolata from plantation forest. The letters on bars are the results of multiple comparison for different community types. I, II, III, IV, see Table 1.
| [1] | Belsky AJ (1986) Regeneration of artificial disturbance in grasslands of the Serengeti National Park, Tanzania: II. Five years of successional change. Journal of Ecology, 74, 937-952. |
| [2] | Brown KA, Gurevitch J (2004) Long-term impacts of logging on forest diversity in Madagascar. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 6045-6049. |
| [3] | Buckley DS, Crow TR, Nauertz EA (2003) Influence of skid trails and haul roads on understory plant richness and composition in managed forest landscapes in Upper Michigan, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 175, 509-520. |
| [4] |
Cannon CH, Peart DR, Leighton M (1998) Tree species diversity in commercially logged Bornean rainforest. Science, 281, 1366-1368.
URL PMID |
| [5] |
Cavender-Bares J, Ackerly DD, Baum DA, Bazzaz FA (2004) Phylogenetic overdispersion in Floridian oak communities. The American Naturalist, 163, 823-843.
URL PMID |
| [6] |
Cavender-Bares J, Adrienne K, Brianna M (2006) Phylogenetic structure of Floridian plant communities depends on taxonomic and spatial scale. Ecology, 87, S109-S122.
URL PMID |
| [7] | Chazdon RL (2003) Tropical forest recovery: legacies of human impact and natural disturbances. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 6, 51-71. |
| [8] | Collins SL, Barber SC (1985) Effects of disturbance on diversity on mixed grass prairie. Vegetatio, 64, 87-94. |
| [9] | Gong GQ (宫贵权), Cheng JM (程积民), Mi XC (米湘成), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾) (2007) Habitat association of wood species in the Gutianshan subtropical broad-leaved evergreen forest. Science of Soil and Water Conservation (中国水土保持科学), 5(3), 79-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] |
Helmus MR, Keller W, Paterson MJ (2009) Communities contain closely related species during ecosystem disturbance. Ecology Letters, 13, 162-174.
URL PMID |
| [11] | Huang JX (黄建雄), Zheng FY (郑凤英), Mi XC (米湘成) (2010) Influence of environmental factors on phylogenetic structure at multiple spatial scales in an evergreen broad- leaved forest of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 34, 309-315. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [13] |
Kembel SW, Hubbell SP (2006) The phylogenetic structure of a neotropical forest tree community. Ecology, 87, S86-S99.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Koleff P, Gaston KJ, Lennon JJ (2003) Measuring beta diversity for presence-absence data. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 367-382. |
| [15] |
Letcher SG (2009) Phylogenetic structure of angiosperm communities during tropical forest succession. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277, 97-104.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Liu ZM (刘志民), Zhao XY (赵晓英), Liu XM (刘新民) (2002) Relationship between disturbance and vegetation. Acta Prataculturae Sinica (草业学报), 11(4), 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] |
Losos JB (2008) Phylogenetic niche conservatism, phylogenetic signal and the relationship between phylogenetic relatedness and ecological similarity among species. Ecology Letters, 11, 995-1007.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Lou LH (楼炉焕), Jin SH (金水虎) (2000) Spermatophyta flora of Gutianshan Nature Reserve in Zhejiang. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (北京林业大学学报), 22(5), 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Pickett S TA, White PS (1985) The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics. Academic Press, London. |
| [20] | R Development Core Team (2009) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org. (accessed 2010-09) |
| [21] |
Swenson NG, Enquist BJ, Pither J, Thompson J, Zimmerman JK (2006) The problem and promise of scale dependence in community phylogenetics. Ecology, 87, 2418-2424.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Swenson NG, Enquist BJ, Thompson J, Zimmerman JK (2007) The influence of spatial and size scale on phylogenetic relatedness in tropical forest communities. Ecology, 88, 1770-1780.
URL PMID |
| [23] | Verdu M, Rey PJ, Alcantara JM, Siles G, Valiente-Banuet A (2009) Phylogenetic signatures of facilitation and competition in successional communities. Journal of Ecology, 97, 1171-1180. |
| [24] | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, Kembel S (2008a) Phylocom: software for the analysis of phylogenetic community structure and character evolution. Version 4.0. http://phylodiversity.net/ phylocom. (accessed 2010-09) |
| [25] | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 475-505. |
| [26] | Webb CO, Cannon CH, Davies SJ (2008b) Ecological organization, biogeography, and the phylogenetic structure of tropical forest tree communities. In: Tropical Forest Community Ecology (eds Carson WP, Schnizer SA). Wiley Blackwell, Oxford. |
| [27] | Webb CO, Donoghue MJ (2005) Phylomatic: tree assembly for applied phylogenetics. Molecular Ecology Notes, 5, 181-183. |
| [28] | Wiens JJ, Graham CH (2005) Niche conservatism: integrating evolution, ecology and conservation biology. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 36, 519-539. |
| [29] |
Wikstrom N, Savolainen V, Chase MW (2001) Evolution of the angiosperms: calibrating the family tree. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268, 2211-2220.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Ye LQ (叶林奇) (2000) The relationship between disturbance and biodiversity. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science)(贵州大学学报自然科学版), 17(2), 129-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [2] | Li Hualiang, Zhang Mingjun, Zhang Xibin, Tan Rong, Li Shichuan, Feng Erhui, Lin Xueyun, Chen Min, Yan enbo, Zeng Zhigao. Composition and influencing factors of the amphibian community in Hainan Dongzhaigang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [3] | Yang Ding, Yingqun Feng, Jinyu Zhang, Bo Wang. Seed predation and dispersal by animals of an endangered endemic species Pinus dabeshanensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23401-. |
| [4] | Minghui Wang, Zhaoquan Chen, Shuaifeng Li, Xiaobo Huang, Xuedong Lang, Zihan Hu, Ruiguang Shang, Wande Liu. Spatial pattern of dominant species with different seed dispersal modes in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Pu’er, Yunnan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [5] | Jiming Cheng, Huimin He, Hongyu Niu, Hongmao Zhang. Research progress on the effect of intraspecific personality differences on seed dispersal in rodents [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22446-. |
| [6] | Xinyang Zhou, Yutao Wang, Jianping Li. Response of plant community composition to precipitation changes in typical grasslands in the Loess Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| [7] | Chaoya Wang, Jintao Li, Chang Liu, Bo Wang, Baige Miao, Yanqiong Peng. Interannual stability in butterfly diversity and the larvae-plant interaction network structure at Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23305-. |
| [8] | Jinhua Liu, Feng Li, Tao Tian, Haifeng Xiao. Response of soil bacteria and nematodes to litter identity and diversity of dominant plants in a tropical rainforest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23276-. |
| [9] | Chao Zhang, Juan Li, Haiyun Cheng, Jiachong Duan, Zhao Pan. Patterns and environmental drivers of the butterfly diversity in the western region of Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22272-. |
| [10] | Xiaotong Liu, Yijia Tian, Hanwen Liu, Cuiying Liang, Siwei Jiang, Wenju Liang, Xiaoke Zhang. Seasonal variation in cropland soil nematode community composition in the lower reaches of Liaohe Plain [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22222-. |
| [11] | Yu Ren, Shengli Tao, Tianyu Hu, Haitao Yang, Hongcan Guan, Yanjun Su, Kai Cheng, Mengxi Chen, Huawei Wan, Qinghua Guo. The outlook and system construction for monitoring Essential Biodiversity Variables based on remote sensing: The case of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22530-. |
| [12] | Xiangcheng Mi, Xugao Wang, Guochun Shen, Xubin Liu, Xiaoyang Song, Xiujuan Qiao, Gang Feng, Jie Yang, Zikun Mao, Xuehong Xu, Keping Ma. Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network (CForBio): Twenty years of exploring community assembly mechanisms and prospects for future research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22504-. |
| [13] | Zusheng Yi, Yuanjun Huang, Hui Yi, Xinwang Zhang, Wenjun Li. Biodiversity of macrozoobenthos in the Chebaling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 680-687. |
| [14] | Lei Dong, Jing Wang, Yonggang Liu, Zhiping Zhao, Xiangcheng Mi, Ke Guo. Phylogenetic structure of Vitex negundo var. heterophylla shrub communities and Spiraea trilobata shrub communities in the North Taihang Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(1): 21-31. |
| [15] | Xifu Yang, Hongmao Zhang, Zhibin Zhang. Mast seeding and its relationship to animal hoarding behaviour [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(7): 821-832. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()