



Biodiv Sci ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (4): 378-384. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09077 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.09077
Special Issue: 保护生物学: 现状和挑战
• Special Issue • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liying Song1,2,*( ), Changlian Peng1, Shaolin Peng2,*(
), Changlian Peng1, Shaolin Peng2,*( )
)
Received:2009-03-31
Accepted:2009-07-08
Online:2009-07-20
Published:2009-07-20
Contact:
Liying Song,Shaolin Peng
Liying Song, Changlian Peng, Shaolin Peng. Comparison of leaf construction costs between three invasive species and three native species in South China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(4): 378-384.
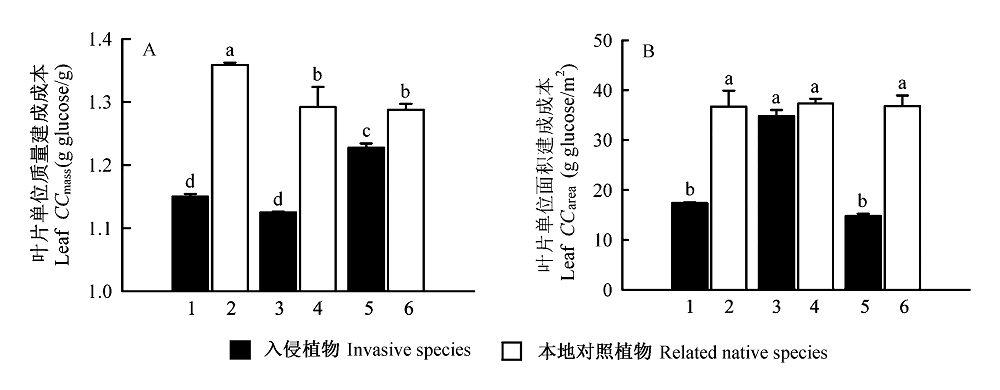
Fig. 1 Leaf construction cost per unit mass (CCmass) (A) and per unit area (CCarea) (B) in three invasive species and the native species in South China. 1, Mikania micrantha; 2, Paederia scandens; 3, Wedelia trilobata; 4, W. chinensis; 5, Ipomoea cairica; 6, I.pescaprae. Different lowercase letters show significant difference at P= 0.05.
| 来源 Origin | 物种 Species | 比叶面积 SLA (m2/kg) | 碳浓度 Carbon content (%) | 氮浓度 Nitrogen content (%) | 灰分含量 Ash (%) | 去灰分热值 Hc(kJ/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入侵种 Invasive | 薇甘菊 Mikania micrantha | 65.98±0.64b | 33.23±0.51e | 4.49±0.15a | 22.29±0.15b | 18.97±0.04b |
| 三裂叶蟛蜞菊 Wedelia trilobata | 32.44±5.79c | 33.69±0.53e | 3.27±0.10b | 26.22±0.37a | 19.64±0.09b | |
| 五爪金龙 Ipomoea cairica | 83.47±1.57a | 36.03±0.48d | 4.73±0.31a | 16.90±0.76c | 18.94±0.20b | |
| 本地种 Native | 鸡矢藤 Paederia scandens | 40.22±0.81c | 41.73±0.39a | 4.13±0.39a | 13.66±0.09d | 20.22±0.09ab |
| 蟛蜞菊 Wedelia chinensis | 34.59±0.80c | 37.78±0.07c | 4.53±0.03a | 21.35±1.71b | 21.02±0.94a | |
| 厚藤 Ipomoea pescaprae | 33.62±0.38c | 39.80±0.46b | 4.88±0.16a | 18.21±1.57c | 20.14±0.26ab |
Table 1 Specific leaf area (SLA), carbon content, nitrogen content, ash content (Ash) and ash-free heat of combustion (Hc) of three invasive species and three native species in South China
| 来源 Origin | 物种 Species | 比叶面积 SLA (m2/kg) | 碳浓度 Carbon content (%) | 氮浓度 Nitrogen content (%) | 灰分含量 Ash (%) | 去灰分热值 Hc(kJ/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入侵种 Invasive | 薇甘菊 Mikania micrantha | 65.98±0.64b | 33.23±0.51e | 4.49±0.15a | 22.29±0.15b | 18.97±0.04b |
| 三裂叶蟛蜞菊 Wedelia trilobata | 32.44±5.79c | 33.69±0.53e | 3.27±0.10b | 26.22±0.37a | 19.64±0.09b | |
| 五爪金龙 Ipomoea cairica | 83.47±1.57a | 36.03±0.48d | 4.73±0.31a | 16.90±0.76c | 18.94±0.20b | |
| 本地种 Native | 鸡矢藤 Paederia scandens | 40.22±0.81c | 41.73±0.39a | 4.13±0.39a | 13.66±0.09d | 20.22±0.09ab |
| 蟛蜞菊 Wedelia chinensis | 34.59±0.80c | 37.78±0.07c | 4.53±0.03a | 21.35±1.71b | 21.02±0.94a | |
| 厚藤 Ipomoea pescaprae | 33.62±0.38c | 39.80±0.46b | 4.88±0.16a | 18.21±1.57c | 20.14±0.26ab |
| 变量 Variable | 入侵种 Invasive species | 本地种 Native species | F值 F-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片单位质量建成成本 CCmass(g glucose/g) | 1.17±0.02 | 1.32±0.01 | 47.604** |
| 叶片单位面积建成成本 CCarea(g glucose/m2) | 22.34±3.16 | 36.93±1.25 | 16.776** |
| 比叶面积 SLA (m2/kg) | 60.52±7.49 | 35.89±1.25 | 9.330** |
| 碳浓度 Carbon content (%) | 34.32±0.50 | 40.02±0.61 | 52.529** |
| 氮浓度 Nitrogen content (%) | 4.16±0.25 | 4.51±0.18 | 1.250NS |
| 灰分含量 Ash (%) | 21.80±1.37 | 17.29±1.31 | 5.593* |
| 去灰分热值 Hc (kJ/g) | 19.18±0.13 | 20.39±0.24 | 20.432** |
Table 2 Average leaf construction cost per unit mass (CCmass) and per unit area (CCarea), specific leaf area (SLA), carbon content, nitrogen content, ash content (Ash) and ash-free heat of combustion (Hc) of three invasive species and three native species in South China
| 变量 Variable | 入侵种 Invasive species | 本地种 Native species | F值 F-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片单位质量建成成本 CCmass(g glucose/g) | 1.17±0.02 | 1.32±0.01 | 47.604** |
| 叶片单位面积建成成本 CCarea(g glucose/m2) | 22.34±3.16 | 36.93±1.25 | 16.776** |
| 比叶面积 SLA (m2/kg) | 60.52±7.49 | 35.89±1.25 | 9.330** |
| 碳浓度 Carbon content (%) | 34.32±0.50 | 40.02±0.61 | 52.529** |
| 氮浓度 Nitrogen content (%) | 4.16±0.25 | 4.51±0.18 | 1.250NS |
| 灰分含量 Ash (%) | 21.80±1.37 | 17.29±1.31 | 5.593* |
| 去灰分热值 Hc (kJ/g) | 19.18±0.13 | 20.39±0.24 | 20.432** |
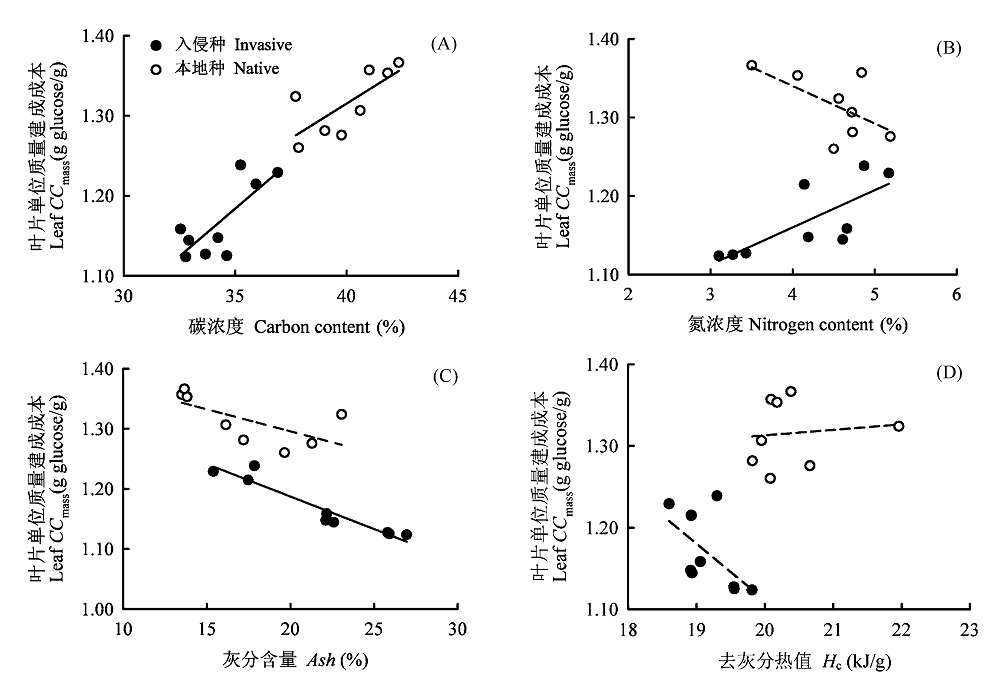
Fig. 2 The correlations between leaf construction cost per unit mass (Leaf CCmass) and carbon content (A), nitrogen content (B), ash content (Ash) (C), ash-free heat of combustion (Hc) (D), respectively. Solid lines represent significant correlations, and dashed lines insignificant correlations.
| [1] |
Baruch Z, Goldstein G (1999) Leaf construction cost, nutrient concentration, and net CO2 assimilation of native and invasive species in Hawaii. Oecologia, 121,183-192.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Baruch Z, Gómez JA (1996) Dynamics of energy and nutrient concentration and construction cost in a native and two alien C 4 grasses from two neotropical savannas. Plant and Soil, 181,175-184. |
| [3] |
Callaway RM, Aschehoug ET (2000) Invasive plants versus their new and old neighbors: a mechanism for exotic invasion. Science, 290,521-523.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Daehler CC (1998) Variation in self-fertility and the reproductive advantage of self-fertility for an invading plant (Spartina alterniflora). Evolutionary Ecology, 12,553-568. |
| [5] | Daehler CC (2003) Performance comparisons of co-occurring native and alien invasive plants: implications for conservation and restoration. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34,183-211. |
| [6] | Deng X, Ye WH, Feng HL, Yang QH, Cao HL, Xu KY, Zhang Y (2004) Gas exchange characteristics of the invasive species Mikania micrantha and its indigenous congener M. cordata (Asteraceae) in South China. Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica, 45,213-220. |
| [7] |
Dukes JS, Mooney HA (1999) Does global change increase the success of biological invaders? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 14,135-139.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Ewe SML, Sternberg LSL (2005) Growth and gas exchange responses of Brazilian pepper (Schinus terebinthifolius) and native South Florida species to salinity. Trees (Berlin), 19,119-128. |
| [9] | Griffin KL (1994) Calorimetric estimates of CC and their use in ecological studies. Functional Ecology, 8,551-562. |
| [10] | Hertling UM, Lubke RA (2000) Assessing the potential for biological invasion—the case of Ammophila arenarian. South African Journal of Science, 96,520-527. |
| [11] | Lambers H, Poorter H (1992) Inherent variation in growth rate between higher plants: a search for physiological causes and ecological consequences. Advances in Ecological Research, 23,188-261. |
| [12] | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology global consequences and control. Ecological Applications, 10,689-710. |
| [13] | Martínez F, Lazo YO, Fernández-Galiano RM, Merino JA (2002) Chemical composition and construction cost for roots of Mediterranean trees, shrub species and grassland communities. Plant, Cell and Environment, 25,601-608. |
| [14] |
McDowell SCL (2002) Photosynthetic characteristics of invasive and noninvasive species of Rubus (Rosaceae). American Journal of Botany, 89,1431-1438.
URL PMID |
| [15] |
Nagel JM, Griffin KL (2001) Construction cost and invasive potential: comparing Lythrum salcaria (Lythraceae) with co-occurring native species along pond banks. American Journal of Botany, 88,2252-2258.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Nagel JM, Huxman TE, Griffin KL, Smith SD (2004) CO2 enrichment reduces the energetic cost of biomass construction in an invasive desert grass. Ecology, 85,100-106. |
| [17] |
Penning de Vries FWT, Brunsting AHM, Van Laar HH (1974) Products, requirements and efficiency of biosynthesis: a quantitative approach. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 45,339-377.
URL PMID |
| [18] | Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of non-indigenous species in the United States. BioScience, 50,53-65. |
| [19] |
Poorter H, Pepin S, Rijkers T, de Jong Y, Evans JR, Körner C (2006) Construction costs, chemical composition and payback time of high and low-irradiance leaves. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57,355-371.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Poorter H, Van Berkel Y, Baxter R, Den Hertog J, Dijkstra P, Gifford RM, Griffin KL, Roumet C, Roy J, Wong SC (1997) The effect of elevated CO2 on the chemical composition and construction costs of leaves of 27 C3 species. Plant, Cell and Environment, 20,472-482. |
| [21] | Poorter H, Villar R (1997) The fate of acquired carbon in plants:chemical composition and construction costs. In: Plant Resource Allocation (eds Bazzaz FA, Grace J),pp.39-72. Academic Press, New York. |
| [22] | Reich PB, Walters MB, Ellsworth DS (1997) From tropics to tundra: global convergence in plant functioning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 94,13730-13734. |
| [23] | Song LY, Ni GY, Chen BM, Peng SL (2007) Energetic cost of leaf construction in the invasive weed Mikania micrantha H.B.K. and its co-occurring species: implications for invasiveness. Botanical Studies, 48,331-338. |
| [24] | Tsialtas JT, Kassioumi M, Veresoglou DS (2002) Leaf construction cost of the most abundant species in an upland grassland area of northern Greece. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 3,360-363. |
| [25] | Villar R, Merino J (2001) Comparison of leaf construction costs in woody species with differing leaf life-spans in contrasting ecosystems. New Phytologist, 151,213-226. |
| [26] | Williams K, Percival F, Merino J, Mooney HA (1987) Estimation of tissue construction cost from heat of combustion and organic nitrogen content. Plant, Cell and Environment, 10,725-734. |
| [27] | Wu JR (吴锦容), Peng SL (彭少麟) (2005) Allelopathy: “novel weapons” of exotic invasive plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 25,3093-3097. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Xu RM (徐汝梅), Ye WH (叶万辉) (2003) Biological Invasions: Theory and Practice (生物入侵:理论与实践). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [29] | Zha TS, Wang KY, Ryyppo A, Kellomaki S (2002) Needle dark respiration in relation to within-crown position in Scots pine trees grown in long-term elevation of CO2 concentration and temperature. New Phytologist, 156,33-41. |
| [1] | Minhao Chen, Chao Zhang, Jiadong Wang, Zhenjie Zhan, Junzhi Chen, Xiaofeng Luan. Distribution and niche overlap of American mink and Eurasian otter in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22289-. |
| [2] | Weifeng Xiao, Lüxing Zuo, Wentao Yang, Chaokui Li. Generating pseudo-absence samples of invasive species based on the similarity of geographical environment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22094-. |
| [3] | Rongzhou Qiu, Jian Zhao, Hong Chen, Xiaoqing Xian, Meixiang Chi, Qiyong Weng. Research and application of a big data collection method for invasive species surveys [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(10): 1377-1385. |
| [4] | Li Meng, Wei Tingting, Shi Boyang, Hao Xiyang, Xu Haigen, Sun Hongying. Biodiversity monitoring of freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates using environmental DNA [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(5): 480-490. |
| [5] | Le Wang, Chen Shi, Jinyan Tian, Xiaonan Song, Mingming Jia, Xiaojuan Li, Xiaomeng Liu, Ruofei Zhong, Dameng Yin, Shanshan Yang, Xianxian Guo. Researches on mangrove forest monitoring methods based on multi-source remote sensing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(8): 838-849. |
| [6] | Yumei Pan, Saichun Tang, Chunqiang Wei, Xiangqin Li. Comparison of growth, photosynthesis and phenotypic plasticity between invasive and native Bidens species under different light and water conditions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(12): 1257-1266. |
| [7] | Yue Xu, Peng Li, Ye Liu, Wanjun Zhang, Siyu Qin, Zehao Shen. Spatial patterns and determinants of species richness of alien and native plants in the Nujiang River valley [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(4): 389-398. |
| [8] | Qianqian Yang, Suwen Liu, Weidong Ru, Guangfu Liu, Xiaoping Yu. Molecular identification of invasive golden apple snails in Zhejiang Province based on DNA barcoding [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(3): 341-350. |
| [9] | Juan Qiu,Dilinuer Shalimu,Dunyan Tan. Reproductive characteristics of the invasive species Solanum rostratum in different habitats of Xinjiang, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(5): 590-600. |
| [10] | Xiaojing Gan, Bo Li, Jiakuan Chen, Zhijun Ma. The ecological effects of biological invasions on birds [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2007, 15(5): 548-557. |
| [11] | Zhongyi Chen, Bo Li, Jiakuan Chen. Some growth characteristics and relative competitive ability of invasive Spartina alterniflora and native Scirpus mariqueter [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2005, 13(2): 130-136. |
| [12] | XU Hai-Gen, QIANG Sheng, HAN Zheng-Min, GUO Jian-Ying, HUANG Zong-Guo, SUN Hong-Ying, 6, HE Shun-Ping, 7, DING Hui, WU Hai-Rong, WAN Fang-Hao. The distribution and introduction pathway of alien invasive species in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2004, 12(6): 626-638. |
| [13] | HUANG Jian-Hui, HAN Xing-Guo, YANG Qin-Er, BAI Yong-Fei. Fundamentals of invasive species biology and ecology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2003, 11(3): 240-247. |
| [14] | WAN Fang-Hao, GUO Jian-Ying, WANG De-Hui. Alien invasive species in China: their damages and management strategies [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2002, 10(1): 119-125. |
| [15] | Sean Nee. Correlates of invasion success: evidence from New Zealand [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2002, 10(1): 106-108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()