



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 25190. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025190
• Original Papers: Microbial Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xinyi Hong1, Yilang Cai1, Jiale Fang1, Kekan Yao2, Jiale Li3, Yixiang Wang4, Shangbin Bai1, Nan Wang1, Xiumei Zhou1,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-22
Accepted:2025-07-26
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-10-31
Contact:
*E-mail: zhouxm0324@163.com
Supported by:Xinyi Hong, Yilang Cai, Jiale Fang, Kekan Yao, Jiale Li, Yixiang Wang, Shangbin Bai, Nan Wang, Xiumei Zhou. Soil viral diversity and carbon metabolism genes profiling in Xixi Wetland[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(9): 25190.
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature (℃) | 土壤湿度 Soil moisture (%) | pH | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (g/kg) | 土壤全氮 Total nitrogen (g/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔灌草地 Trees, shrubs and grasslands | 9.1 ± 0.2ab | 32.60 ± 14.06bc | 6.84 ± 0.44a | 41.3 ± 24.5a | 3.4 ± 1.8a |
| 灌草地 Shrub grasslands | 8.9 ± 1.4b | 25.29 ± 3.67c | 6.36 ± 0.50a | 30.8 ± 9.6ab | 2.8 ± 0.3ab |
| 芦苇地 Reed marshes | 7.1 ± 0.3c | 39.24 ± 11.89b | 5.57 ± 0.41b | 26.0 ± 10.4b | 2.2 ± 0.8b |
| 池塘 Ponds | 7.4 ± 0.1c | 51.70 ± 10.56ab | 6.56 ± 0.04a | 13.6 ± 0.8c | 1.1 ± 0.1c |
| 浅滩 Shoals | 11.1 ± 0.5a | 74.13 ± 8.35a | 5.47 ± 0.12b | 16.2 ± 1.1bc | 1.4 ± 0.1c |
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties across different habitat types in Xixi Wetland. The data is the mean ± SD.
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature (℃) | 土壤湿度 Soil moisture (%) | pH | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (g/kg) | 土壤全氮 Total nitrogen (g/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔灌草地 Trees, shrubs and grasslands | 9.1 ± 0.2ab | 32.60 ± 14.06bc | 6.84 ± 0.44a | 41.3 ± 24.5a | 3.4 ± 1.8a |
| 灌草地 Shrub grasslands | 8.9 ± 1.4b | 25.29 ± 3.67c | 6.36 ± 0.50a | 30.8 ± 9.6ab | 2.8 ± 0.3ab |
| 芦苇地 Reed marshes | 7.1 ± 0.3c | 39.24 ± 11.89b | 5.57 ± 0.41b | 26.0 ± 10.4b | 2.2 ± 0.8b |
| 池塘 Ponds | 7.4 ± 0.1c | 51.70 ± 10.56ab | 6.56 ± 0.04a | 13.6 ± 0.8c | 1.1 ± 0.1c |
| 浅滩 Shoals | 11.1 ± 0.5a | 74.13 ± 8.35a | 5.47 ± 0.12b | 16.2 ± 1.1bc | 1.4 ± 0.1c |
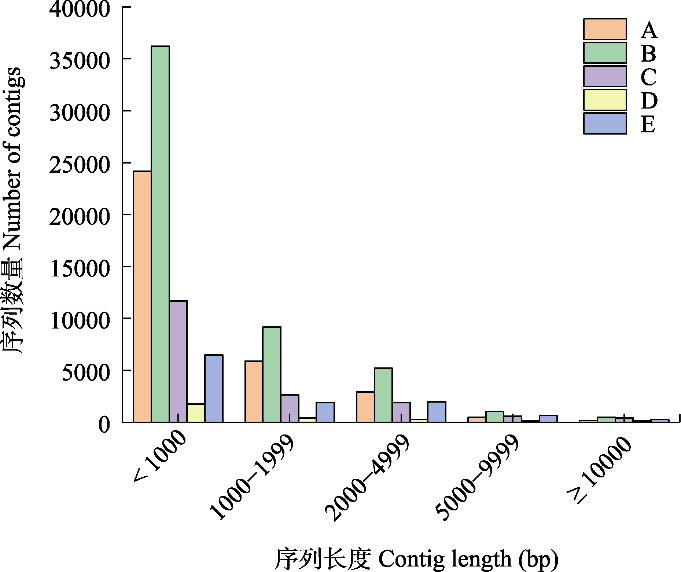
Fig. 1 The distribution of contig lengths for different habitat types in Xixi Wetland. A, Trees, shrubs and grasslands; B, Shrub grasslandes; C, Reed marshes; D, Ponds; E, Shoals.
| 宿主属 Host genus | 病毒序列数量 Number of viral sequences | 占总预测病毒宿主序 列数的比值 Proportion of predicted viral host sequences (%) | 乔灌草地 Trees, shrubs and grasslands | 灌草地 Shrub grasslands | 芦苇地 Reed marshes | 池塘 Ponds | 浅滩 Shoals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter | 76 | 1.23 | 57 | 69 | 12 | 2 | 2 |
| 伯克霍尔德氏菌属 Burkholderia | 105 | 1.70 | 58 | 87 | 45 | 2 | 2 |
| 汉密尔顿菌属(暂定类群) Candidatus_Hamiltonella | 76 | 1.23 | 33 | 64 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 蛭弧菌属 Bdellovibrio | 1,939 | 31.38 | 1,372 | 1,563 | 99 | 4 | 2 |
| 柄杆菌属 Caulobacter | 155 | 2.51 | 105 | 136 | 55 | 2 | 2 |
| 埃希氏菌属 Escherichia | 375 | 6.07 | 257 | 320 | 62 | 6 | 1 |
| 地芽孢杆菌属 Geobacillus | 63 | 1.02 | 39 | 52 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 螺杆菌属 Helicobacter | 61 | 0.99 | 39 | 46 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
| 黏液乳杆菌属 Limosilactobacillus | 104 | 1.68 | 55 | 82 | 14 | 1 | 0 |
| 李斯特菌属 Listeria | 120 | 1.94 | 50 | 86 | 27 | 10 | 0 |
| 中慢生根瘤菌属 Mesorhizobium | 76 | 1.23 | 52 | 60 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| 分枝杆菌属 Mycolicibacterium | 114 | 1.84 | 71 | 89 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 副拟杆菌属 Parabacteroides | 68 | 1.10 | 51 | 54 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 土球腔菌属 Pedosphaera | 50 | 0.81 | 31 | 47 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 普雷斯科特氏菌属 Prescottella | 77 | 1.25 | 53 | 70 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 原绿球藻属 Prochlorococcus | 50 | 0.81 | 39 | 32 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas | 203 | 3.28 | 109 | 173 | 34 | 2 | 2 |
| 红杆菌属 Rhodobacter | 69 | 1.12 | 57 | 61 | 26 | 2 | 3 |
| 红育菌属 Rhodovulum | 53 | 0.86 | 34 | 45 | 14 | 2 | 2 |
| 罗格氏菌属 Ruegeria | 54 | 0.87 | 38 | 41 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| 中华根瘤菌属 Sinorhizobium | 57 | 0.92 | 40 | 42 | 32 | 1 | 1 |
| 弧菌属 Vibrio | 129 | 2.09 | 84 | 102 | 26 | 4 | 2 |
| 未知 Unknown | 266 | 4.30 | 161 | 213 | 105 | 3 | 2 |
Table 2 Summary of the predicted viral hosts with over 50 sequence counts and their distribution across different habitat types
| 宿主属 Host genus | 病毒序列数量 Number of viral sequences | 占总预测病毒宿主序 列数的比值 Proportion of predicted viral host sequences (%) | 乔灌草地 Trees, shrubs and grasslands | 灌草地 Shrub grasslands | 芦苇地 Reed marshes | 池塘 Ponds | 浅滩 Shoals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter | 76 | 1.23 | 57 | 69 | 12 | 2 | 2 |
| 伯克霍尔德氏菌属 Burkholderia | 105 | 1.70 | 58 | 87 | 45 | 2 | 2 |
| 汉密尔顿菌属(暂定类群) Candidatus_Hamiltonella | 76 | 1.23 | 33 | 64 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 蛭弧菌属 Bdellovibrio | 1,939 | 31.38 | 1,372 | 1,563 | 99 | 4 | 2 |
| 柄杆菌属 Caulobacter | 155 | 2.51 | 105 | 136 | 55 | 2 | 2 |
| 埃希氏菌属 Escherichia | 375 | 6.07 | 257 | 320 | 62 | 6 | 1 |
| 地芽孢杆菌属 Geobacillus | 63 | 1.02 | 39 | 52 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 螺杆菌属 Helicobacter | 61 | 0.99 | 39 | 46 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
| 黏液乳杆菌属 Limosilactobacillus | 104 | 1.68 | 55 | 82 | 14 | 1 | 0 |
| 李斯特菌属 Listeria | 120 | 1.94 | 50 | 86 | 27 | 10 | 0 |
| 中慢生根瘤菌属 Mesorhizobium | 76 | 1.23 | 52 | 60 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| 分枝杆菌属 Mycolicibacterium | 114 | 1.84 | 71 | 89 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| 副拟杆菌属 Parabacteroides | 68 | 1.10 | 51 | 54 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 土球腔菌属 Pedosphaera | 50 | 0.81 | 31 | 47 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 普雷斯科特氏菌属 Prescottella | 77 | 1.25 | 53 | 70 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 原绿球藻属 Prochlorococcus | 50 | 0.81 | 39 | 32 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas | 203 | 3.28 | 109 | 173 | 34 | 2 | 2 |
| 红杆菌属 Rhodobacter | 69 | 1.12 | 57 | 61 | 26 | 2 | 3 |
| 红育菌属 Rhodovulum | 53 | 0.86 | 34 | 45 | 14 | 2 | 2 |
| 罗格氏菌属 Ruegeria | 54 | 0.87 | 38 | 41 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| 中华根瘤菌属 Sinorhizobium | 57 | 0.92 | 40 | 42 | 32 | 1 | 1 |
| 弧菌属 Vibrio | 129 | 2.09 | 84 | 102 | 26 | 4 | 2 |
| 未知 Unknown | 266 | 4.30 | 161 | 213 | 105 | 3 | 2 |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 乔灌草地 Trees, shrubs and grasslands | 灌草地 Shrub grasslands | 芦苇地 Reed marshes | 池塘 Ponds | 浅滩 Shoals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 6.30b | 8.26a | 7.50ab | 3.88c | 5.83bc |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.95a | 0.96a | 0.88b | 0.84b | 0.86b |
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 15,357.66ab | 20,083.64a | 4,650.26b | 257.23c | 543.23bc |
Table 3 Shannon index, Simpson index and Chao1 index of virus across different habitat types in Xixi Wetland
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 乔灌草地 Trees, shrubs and grasslands | 灌草地 Shrub grasslands | 芦苇地 Reed marshes | 池塘 Ponds | 浅滩 Shoals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 6.30b | 8.26a | 7.50ab | 3.88c | 5.83bc |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.95a | 0.96a | 0.88b | 0.84b | 0.86b |
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 15,357.66ab | 20,083.64a | 4,650.26b | 257.23c | 543.23bc |
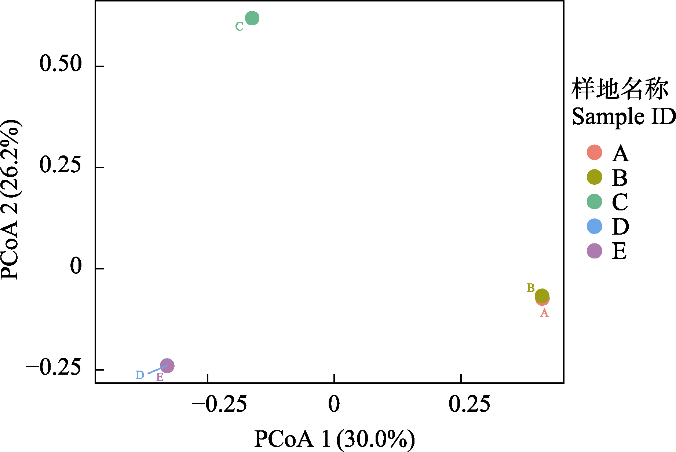
Fig. 2 Viral community structure of different habitat types in Xixi Wetland. A, Trees, shrubs and grasslands; B, Shrub grasslands; C, Reed marshes; D, Ponds; E, Shoals.
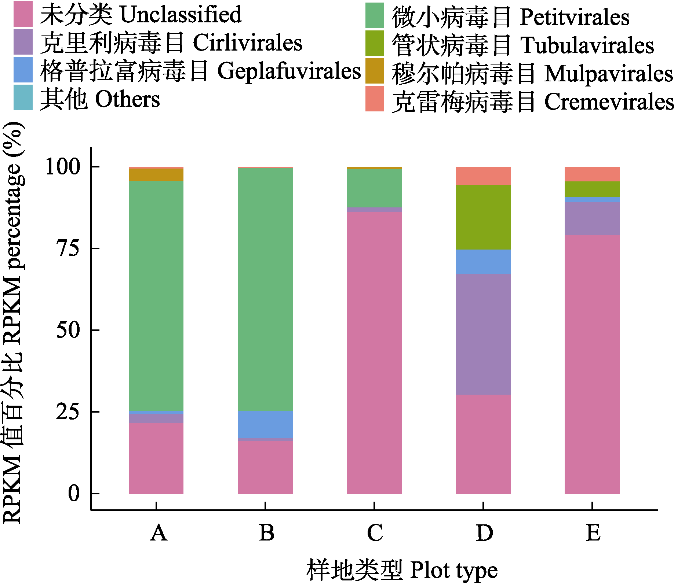
Fig. 3 Composition of horizontal community structure of viral order level in different habitat types of Xixi Wetland. RPKM, Reads per Kilobase per Million mapped reads.
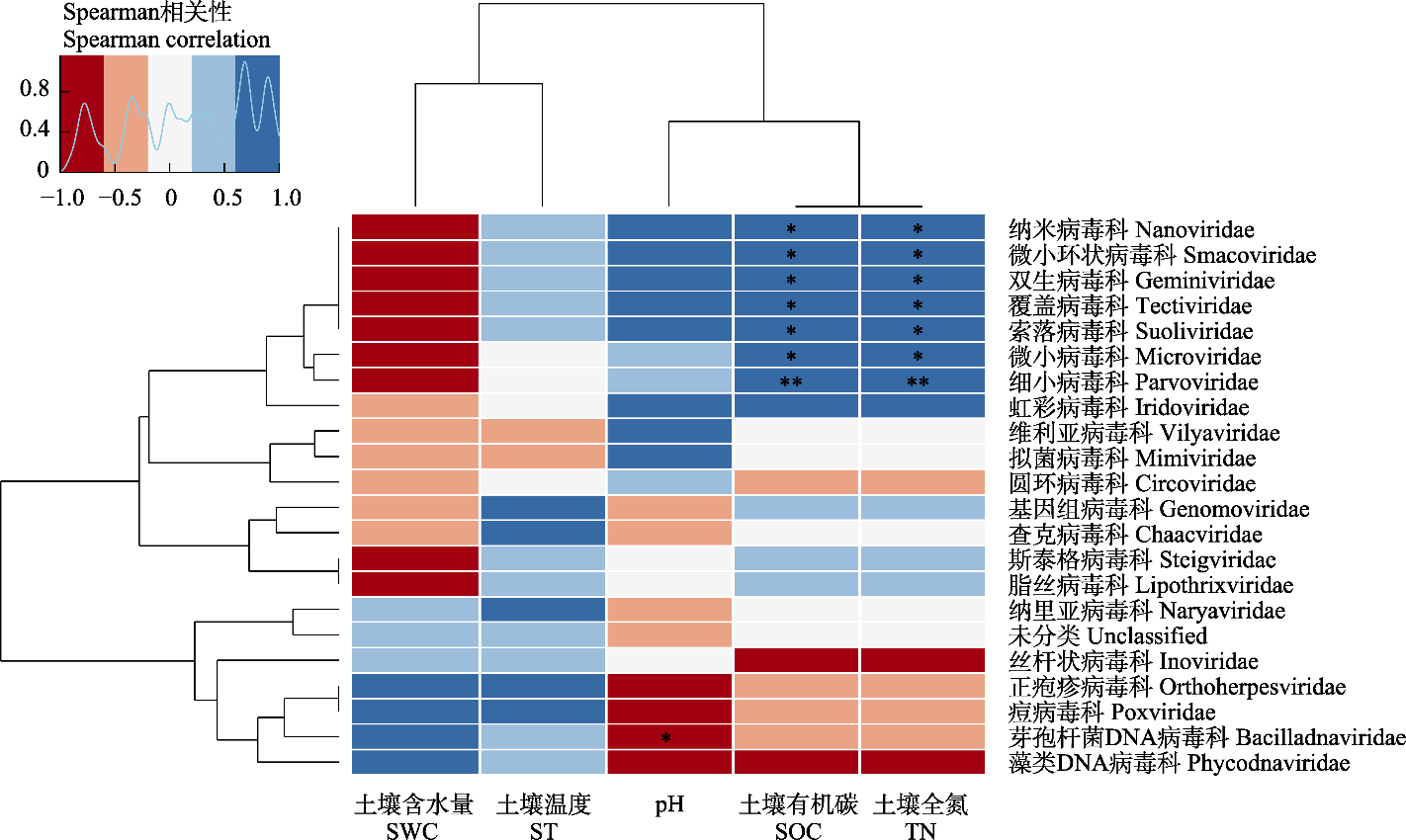
Fig. 4 Correlation between viral families composition and soil physicochemical properties in Xixi Wetland. SWC, Soil water content; ST, Soil temperature; SOC, Soil organic carbon; TN, Total nitrogen. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
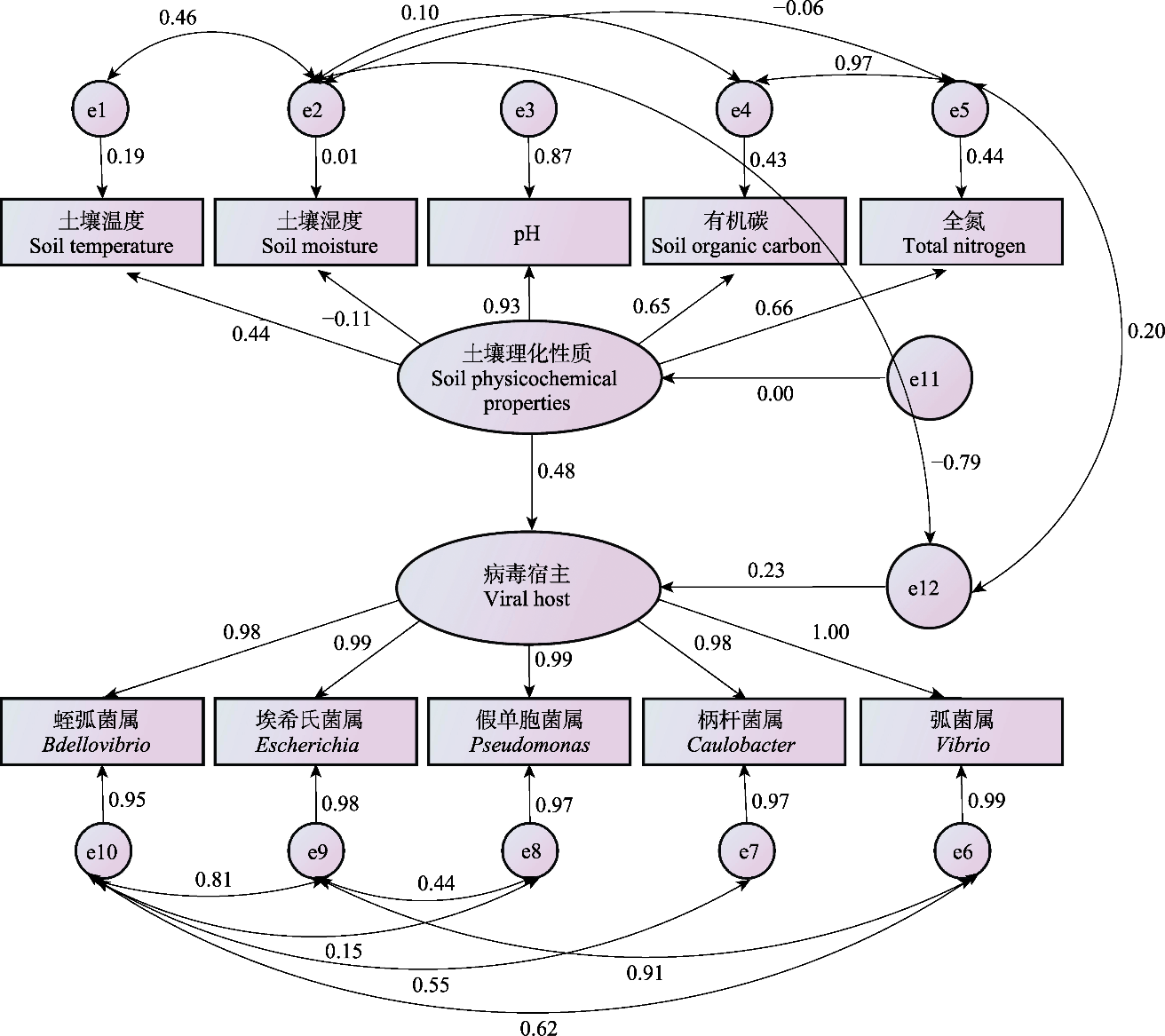
Fig. 5 The structural equation modeling of soil physicochemical properties and viral host. The e represents the residual term; The one-way arrow indicates the direct effect relationship between variables, where positive values indicate a positive correlation (the higher the value, the stronger the correlation) and negative values indicate a negative correlation (the larger the absolute value, the stronger the correlation); The double arrow indicates fitted lines, with positive values meaning observed values are greater than model-predicted values and negative values meaning observed values are less than model-predicted values.
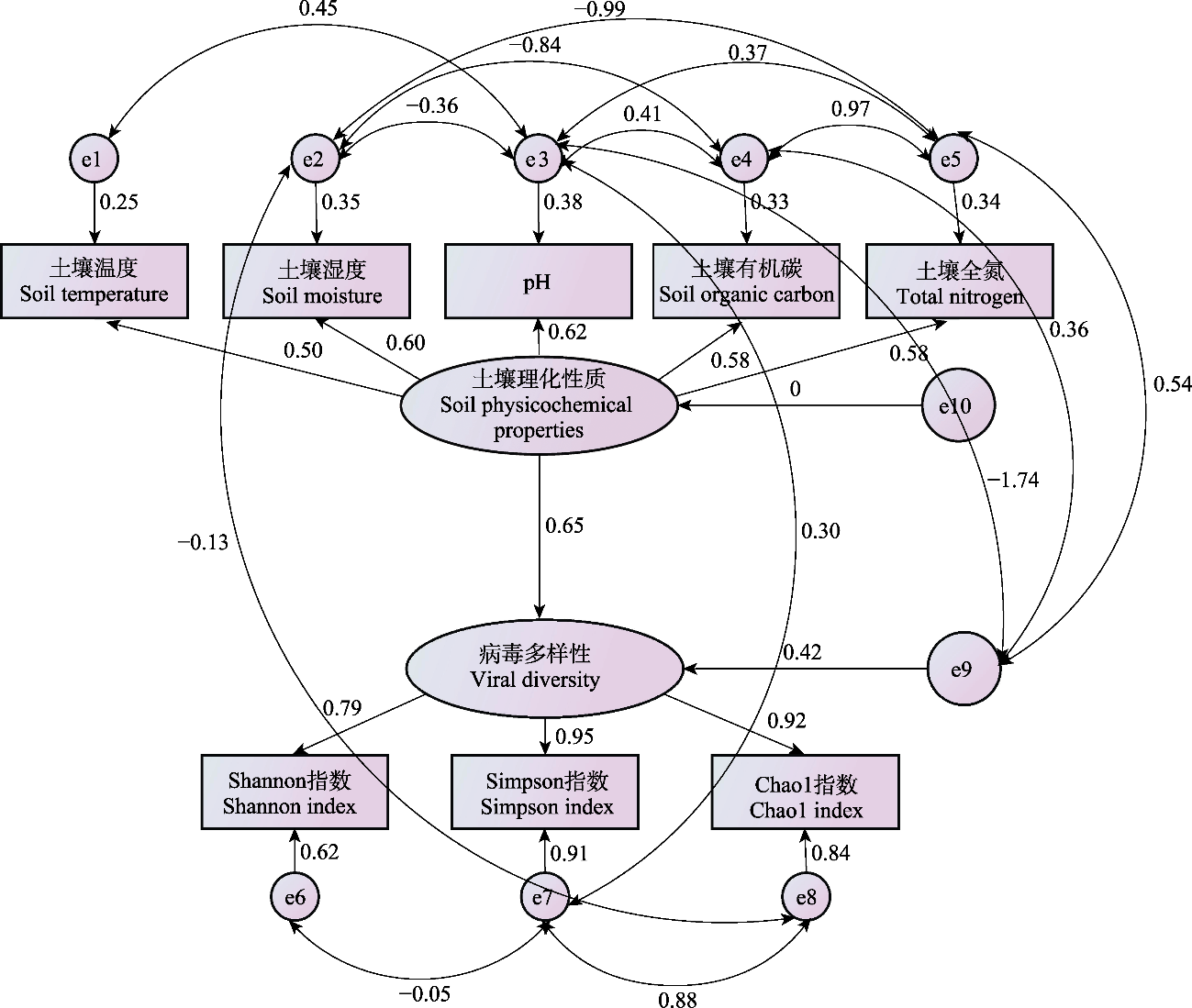
Fig. 6 The structural equation modeling of soil physicochemical properties and viral diversity. The e represents the residual term; The one-way arrow indicates the direct effect relationship between variables, where positive values indicate a positive correlation (the higher the value, the stronger the correlation) and negative values indicate a negative correlation (the larger the absolute value, the stronger the correlation); The double arrow indicates fitted lines, with positive values meaning observed values are greater than model-predicted values and negative values meaning observed values are less than model-predicted values.
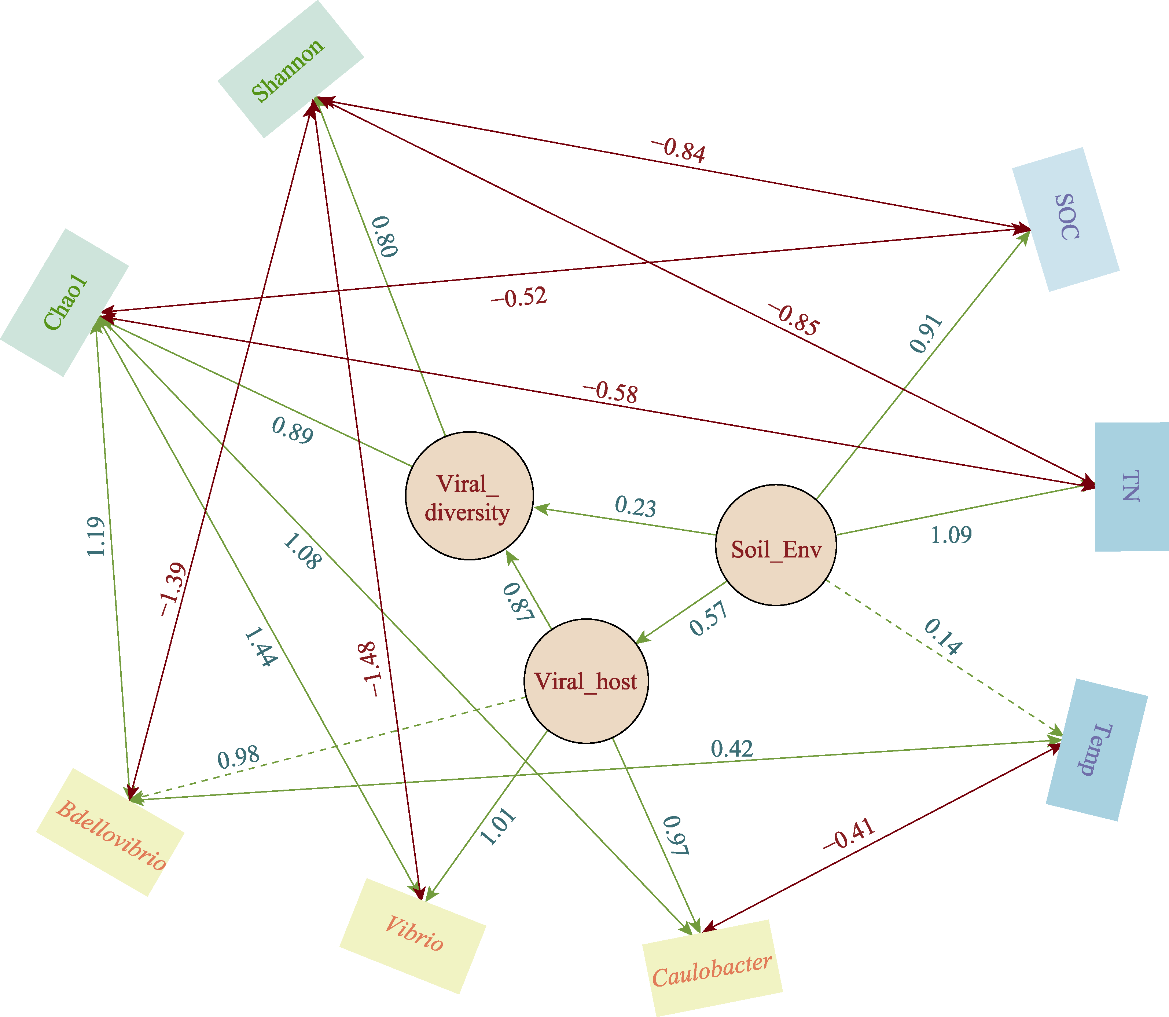
Fig. 7 The structural equation modeling of soil physicochemical properties-viral host-viral diversity. A solid green one-way arrow (pointing to the observed variable) indicates a direct positive correlation, while a dashed green one-way arrow indicates an indirect correlation, and the double arrow indicates the fitting line, the solid red line indicates a direct negative correlation. Negative values represent a negative (inhibitory) effect, while positive values represent a positive effect. Chao1, Chao1 index; Shannon, Shannon index; SOC, Soil organic carbon; TN, Total nitrogen; Temp, Temperature; Viral_diversity, Viral diversity; Viral_host, Viral host; Soil_Env, Soil environment.
| [1] | Angly FE, Felts B, Breitbart M, Salamon P, Edwards RA, Carlson C, Chan AM, Haynes M, Kelley S, Liu H, Mahaffy JM, Mueller JE, Nulton J, Olson R, Parsons R, Rayhawk S, Suttle CA, Rohwer F (2006) The marine viromes of four oceanic regions. PLoS Biology, 4, e368. |
| [2] |
Aziz RK, Breitbart M, Edwards RA (2010) Transposases are the most abundant, most ubiquitous genes in nature. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, 4207-4217.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. Journal of Computational Biology, 19, 455-477.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Bi L, Du S, Yu DT, Zhang LM, He JZ, Han LL (2021) Compositional and functional characteristics of viruses in soil under two types of land-use in Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 2728-2737. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [毕丽, 杜帅, 于丹婷, 张丽梅, 贺纪正, 韩丽丽 (2021) 新疆两种土地利用方式下土壤病毒的群落组成与功能特征. 生态学报, 41, 2728-2737.] | |
| [5] |
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, 30, 2114-2120.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Brussaard CPD, Wilhelm SW, Thingstad F, Weinbauer MG, Bratbak G, Heldal M, Kimmance SA, Middelboe M, Nagasaki K, Paul JH, Schroeder DC, Suttle CA, Vaqué D, Wommack KE (2008) Global-scale processes with a nanoscale drive: The role of marine viruses. The ISME Journal, 2, 575-578.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Córdova-Kreylos AL, Cao YP, Green PG, Hwang HM, Kuivila KM, Lamontagne MG, Van De Werfhorst LC, Holden PA, Scow KM (2006) Diversity, composition, and geographical distribution of microbial communities in California salt marsh sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 3357-3366.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Dell’Anno A, Corinaldesi C, Danovaro R (2015) Virus decomposition provides an important contribution to benthic deep-sea ecosystem functioning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, E2014-E2019. |
| [9] |
Ding J, Wang Y, Yu S (2025) Ecotone-driven vegetation transitions reshape soil nitrogen cycling functional genes in black soils of Northeast China. Biology, 14, 1474.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Gao RC, Hu M, Li FB, Chen GH, Fang LP (2022) Research progress and ecological function of phages in soil. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 43, 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高瑞川, 胡敏, 李芳柏, 陈冠虹, 方利平 (2022) 土壤噬菌体的研究进展及生态功能解析. 华南农业大学学报, 43, 1-11.] | |
| [11] |
Guo JR, Bolduc B, Zayed AA, Varsani A, Dominguez-Huerta G, Delmont TO, Akbar Pratama, Mart Krupovic, Dean V, Sullivan BM (2021) VirSorter2: A multi-classifier, expert-guided approach to detect diverse DNA and RNAviruses. Microbiome, 9, 37.
DOI URL |
| [12] | He L, Yan YT, Yuan CY, Lin QS, Yu DT (2024) Characteristics of soil viral communities in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations with different stand ages. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 2543-2551. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[和莉, 严雨亭, 袁程昱, 林秋沙, 于丹婷 (2024) 不同林龄杉木人工林土壤病毒群落特征. 应用生态学报, 35, 2543-2551.]
DOI |
|
| [13] | Hulo C, de Castro E, Masson P, Bougueleret L, Bairoch A, Xenarios I, Le Mercier P (2011) ViralZone: A knowledge resource to understand virus diversity. Nucleic Acids Research, 39, D576-D582. |
| [14] | Jiang JZ, Yuan WG, Shang J, Ying HS, Yang LL, Li M, Zhang P, Jiang T, Sun YN, Li HY (2023) Virus classification for viral genomic fragments using PhaGCN2. Brief Bioinformatics, 24, bbac505. |
| [15] |
Kuzyakov Y, Mason-Jones K (2018) Viruses in soil: Nano-scale undead drivers of microbial life, biogeochemical turnover and ecosystem functions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 127, 305-317.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics, 25, 1754-1760.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Li RQ, Li YR, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2008) SOAP: Short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics, 24, 713-714.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Liang C, Amelung W, Lehmann J, Kästner M (2019) Quantitative assessment of microbial necromass contribution to soil organic matter. Global Change Biology, 25, 3578-3590.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Liang C, Schimel JP, Jastrow JD (2017) The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage. Nature Microbiology, 2, 17105.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Lu CY, Zhang Z, Cai ZN, Zhu ZZ, Qiu Y, Wu AP, Jiang TJ, Zheng HP, Peng YS (2021) Prokaryotic virus host predictor: A Gaussian model for host prediction of prokaryotic viruses in metagenomics. BMC Biology, 19, 5.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Lü MZ, Sheng LX, Zhang L (2013) A review on carbon fluxes for typical wetlands in different climates of China. Wetland Science, 11, 114-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吕铭志, 盛连喜, 张立 (2013) 中国典型湿地生态系统碳汇功能比较. 湿地科学, 11, 114-120.] | |
| [22] |
Ma B, Lu CY, Wang YL, Yu JW, Zhao KK, Xue R, Ren H, Lv XF, Pan RH, Zhang JB, Zhu YG, Xu JM (2023) A genomic catalogue of soil microbiomes boosts mining of biodiversity and genetic resources. Nature Communications, 14, 7318.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Man BY, Xiang X, Luo Y, Mao XT, Zhang C, Sun BH, Wang X (2021) Characteristics and influencing factors of soil fungal community of typical vegetation types in Mount Huangshan, East China. Mycosystema, 40, 2735-2751. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[满百膺, 向兴, 罗洋, 毛小涛, 张超, 孙丙华, 王希 (2021) 黄山典型植被类型土壤真菌群落特征及其影响因素. 菌物学报, 40, 2735-2751.]
DOI |
|
| [24] |
Mao YE, Zhou XM, Wang N, Li XX, You YK, Bai SB (2023) Impact of Phyllostachys edulis expansion to Chinese fir forest on the soil bacterial community. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22659. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌 (2023) 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响. 生物多样性, 31, 22659.]
DOI |
|
| [25] |
Nayfach S, Camargo AP, Schulz F, Eloe-Fadrosh E, Roux S, Kyrpides NC (2021) CheckV assesses the quality and completeness of metagenome-assembled viral genomes. Nature Biotechnology, 39, 578-585.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Peng Y, Leung HCM, Yiu SM, Chin FYL (2012) IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics, 28, 1420-1428.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Qin JQ, Xiao ZR, Ming AG, Zhu H, Teng JQ, Liang ZL, Tao Y, Qin L (2023) Effect of monoculture and mixed plantation with coniferous and broadleaved tree species on soil microbial carbon cycle functional gene abundance. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 32, 1719-1731. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[秦佳琪, 肖指柔, 明安刚, 朱豪, 滕金倩, 梁泽丽, 陶怡, 覃林 (2023) 针阔人工混交林及其纯林对土壤微生物碳循环功能基因丰度的影响. 生态环境学报, 32, 1719-1731.]
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Sakschewski B, von Bloh W, Boit A, Poorter L, Peña-Claros M, Heinke J, Joshi J, Thonicke K (2016) Resilience of Amazon forests emerges from plant trait diversity. Nature Climate Change, 6, 1032-1036.
DOI |
| [29] |
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics, 30, 2068-2069.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Shang JY, Sun YN (2022) CHERRY: A computational metHod for accuratE pRediction of virus-pRokarYotic interactions using a graph encoder-decoder model. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 23, bbac182. |
| [31] |
Srinivasiah S, Bhavsar J, Thapar K, Liles M, Schoenfeld T, Wommack KE (2008) Phages across the biosphere: Contrasts of viruses in soil and aquatic environments. Research in Microbiology, 159, 349-357.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Suttle CA (2005) Viruses in the sea. Nature, 437, 356-361.
DOI |
| [33] |
Trubl G, Hyman P, Roux S, Abedon ST (2020) Coming-of-age characterization of soil viruses: A user’s guide to virus isolation, detection within metagenomes, and viromics. Soil Systems, 4, 23.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Wang GH, Liu JJ, Zhu D, Ye M, Zhu YG (2020) A review of researches on viruses in soil, advancement and challenges. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57, 1319-1332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王光华, 刘俊杰, 朱冬, 叶茂, 朱永官 (2020) 土壤病毒的研究进展与挑战. 土壤学报, 57, 1319-1332.] | |
| [35] | Wu HQ, Ruan CJ, Han M, Wang G (2024) Mystery of soil viruses: Advances, challenges, and perspectives. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 64, 1824-1847. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴汉卿, 阮楚晋, 韩苗, 王钢 (2024) 土壤病毒之奥秘: 研究进展、挑战及未来展望. 微生物学报, 64, 1824-1847.] | |
| [36] | Yu HT, Huang SH, Liu YJ, Kou WB, Liu YZ, Wu L (2017) Profile distribution characteristics of soil enzymes and microbial biomass in the Poyang Lake Wetland. Research of Environmental Sciences, 30, 1715-1722. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于昊天, 黄时豪, 刘亚军, 寇文伯, 刘以珍, 吴兰 (2017) 鄱阳湖湿地土壤酶及微生物生物量的剖面分布特征. 环境科学研究, 30, 1715-1722.] | |
| [37] | Zhai XJ, Cui LJ, Li W, Zhao XS, Zhang MY, Kang XM (2024) Carbon sequestration by typical wetland ecosystems in China. Journal of Hydroecology, 45, 76-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [翟夏杰, 崔丽娟, 李伟, 赵欣胜, 张曼胤, 康晓明 (2024) 中国典型湿地生态系统的固碳价值研究. 水生态学杂志, 45, 76-85.] | |
| [38] |
Zhou GX, Chen L, Zhang CZ, Ma DH, Zhang JB (2023) Bacteria-virus interactions are more crucial in soil organic carbon storage than iron protection in biochar-amended paddy soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 57, 19713-19722.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Zhang Mingyi, Wang Xiaomei, Zheng Yanxin, Wu Nan, Li Donghao, Fan Enyuan, Li Na, Shan Xiujuan, Yu Tao, Zhao Chunnuan, Li Bo, Xu Shuai, Wu Yuping, Ren Liqun. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | Song Yuanhao, Gong Lü, Li Ben, Hu Yang, Li Xiuzhen. Impacts of different pond-to-wetland restoration methods on macrofauna in the Liao River Estuary, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | Chen Dingsong, Liu Zikai, He Ziyang, Chen Weidong. Advances in tardigrade diversity, distribution characteristics and ecological functions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [4] | Yuan Liu, Jianqing Du, Liyuan Ma, Gang Yang, Jianqing Tian. Diversity and distribution of methanogen communities in the riparian wetlands of the Nam Co basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24247-. |
| [5] | Naipeng Zhang, Hongru Liang, Yan Zhang, Chao Sun, Yong Chen, Lulu Wang, Jiangbao Xia, FangLei Gao. Effects of soil type and groundwater depth on spatial differentiation of typical salt marsh plant communities in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [6] | Baomin Yao, Qing Zeng, Limei Zhang. Research progress on the biodiversity and ecological function of soil protists [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22353-. |
| [7] | Shixiong Li, Yanlong Wang, Yuqin Wang, Yali Yin. Response of soil bacterial community characteristics to alpine meadow degradation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(1): 53-64. |
| [8] | Baoquan Li, Shaoyu Jiang, Juanzhang Lü, Linlin Chen, Lang Yan, Chunyun Liu, Xiaojing Li, Bo Song, Xinzheng Li. Species composition and long-term variation of macrobenthos in intertidal zone and offshore areas of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(12): 1511-1522. |
| [9] | Gongqi Sun, Mingxiang Zhang, Guangchun Lei. Wetland water bird biodiversity conservation strategies in the Yellow River basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(12): 1469-1482. |
| [10] | Jingqi Sun, Quan Chen, Hangyu Li, Yanfen Chang, Hede Gong, Liang Song, Huazheng Lu. Progress on the clonality of epiphytic ferns [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(11): 1184-1195. |
| [11] | Mengru Wang, Shenglei Fu, Haixiang Xu, Meina Wang, Leilei Shi. Ecological functions of millipedes in the terrestrial ecosystem [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(10): 1051-1059. |
| [12] | Xiaoke Zhang, Wenju Liang, Qi Li. Recent progress and future directions of soil nematode ecology in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(10): 1060-1073. |
| [13] | Xiuqin Yin, Yan Tao, Haixia Wang, Chen Ma, Xinchang Kou, Huan Xu, Dong Cui. Forest soil fauna ecology in Northeast China: Review and prospect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(10): 1083-1090. |
| [14] | Youzhi Li, Lijuan Cui, Xu Pan, Yu Ning, Wei Li, Xiaoming Kang, Kai Li, Baodi Sun, Jingjing Yu. Spatial distribution of plant diversity and functional groups in the Liaohe estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(4): 471-478. |
| [15] | Yanping Wu, Wenjing Yang*. Indicators and implementing methods of wetland biodiversity monitoring: taking Great Lakes coastal wetlands as an example [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(4): 527-535. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn