



Biodiv Sci ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 21458. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021458 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021458
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Nan Ye, Beibei Hou, Chao Wang, Ruiwu Wang, Jianxiao Song( )
)
Received:2021-11-15
Accepted:2022-02-28
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-04-11
Contact:
Jianxiao Song
Nan Ye, Beibei Hou, Chao Wang, Ruiwu Wang, Jianxiao Song. Spatial self-organization in microbial interactions[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21458.
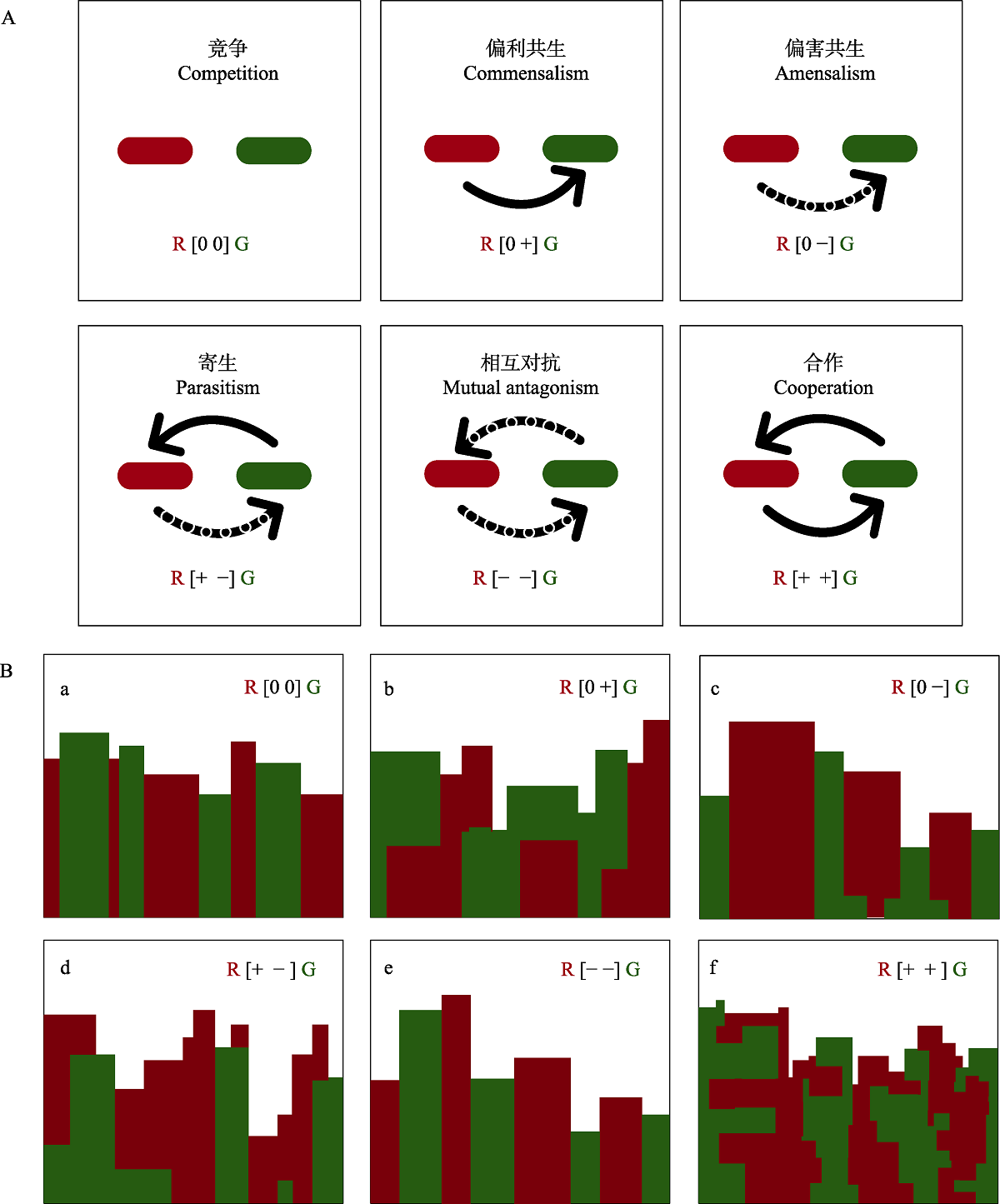
Fig. 1 Different ecological interaction types and vertical cross-sectional spatial patterns of microorganisms with model predictions (adapted from Momeni et al, 2013a). A, Different forms of interaction between two bacterial populations, with solid arrows indicating increased net fitness benefits (+), dashed connectors indicating decreased net fitness benefits (-), and no arrows indicating no fitness benefits (0). B, Two bacterial populations formed different distributions patterns in the vertical direction of the community. a-f corresponding to competition, commensalism, amensalism, parasitism, mutual antagonism and cooperation, respectively. The red and green colors indicate different bacterial populations, denoted by the R and G, respectively. The symbols in parentheses close to the alphabet represent fitness benefits: + indicates an increase in net fitness, - represents a decrease in net fitness, and 0 means no change in net fitness. For example, R [+ -] G describes a parasitic interaction in which the net fitness of the red colony increases while the net fitness of the green colony decreases.
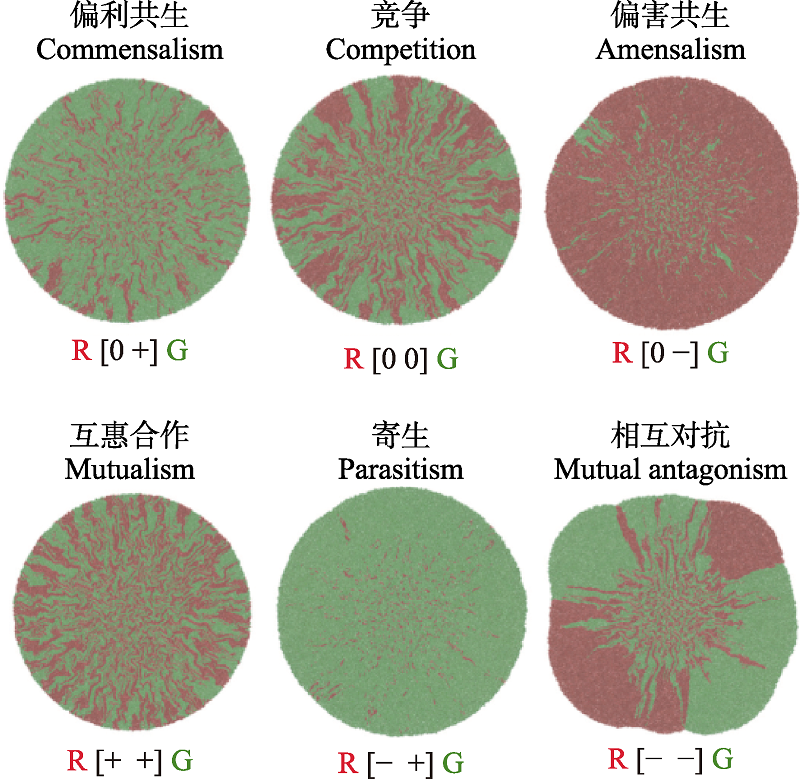
Fig. 2 Representative horizontal surface spatial patterns of different ecological interactions with computer simulation (adapted from Blanchard & Lu, 2015). The red and green colors indicate different bacterial populations, denoted by the R and G, respectively. The symbols in parentheses close to the alphabet represent fitness benefits: + indicates an increase in net fitness, - represents a decrease in net fitness, and 0 means no change in net fitness. For example, R [- +] G describes a parasitic interaction in which the net fitness of the red colony decreases while the net fitness of the green colony increases. Two bacterial communities form different types of horizontal surface spatial patterns during expansion with different forms of ecological interactions.
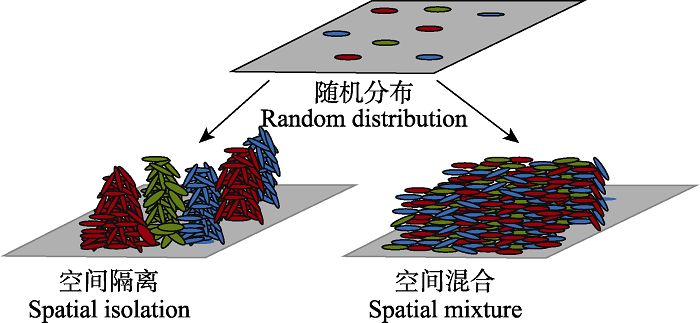
Fig. 3 Spatial self-organization process of competition and cooperation interactions. Different colors represent different bacterial species. Bacteria initially distribute randomly in the environment. During growth and dispersal, competitive interactions will lead to spatial segregation of different species, while cooperation among them allows different species to mix with each other spatially.
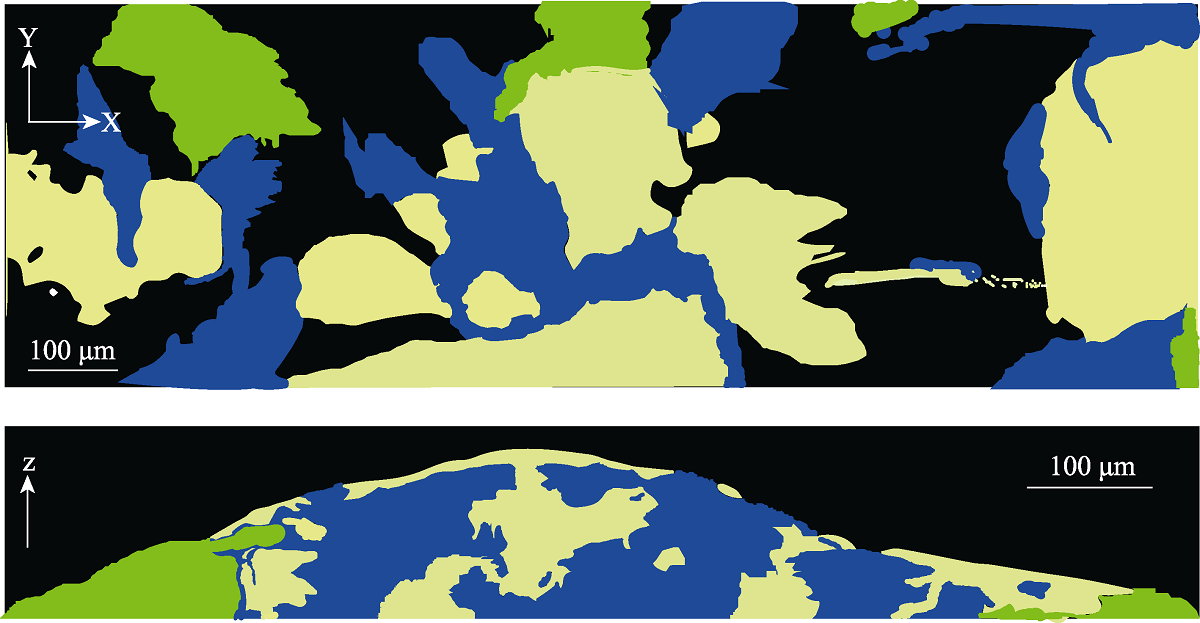
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of spatial pattern of the cheater invading the cooperative system. This figure was adapted from the study of Momeni et al (2013b). According to the experimental results of Momeni et al (2013b), the blue area represents the cooperative partner, the yellow area represents the cooperator, and the green area represented the cheater. Cooperators tend to mix with each other, while cheaters are crowded out of the community. This spatial pattern effectively increases the frequency of interaction of cooperators and avoids being exploited by cheaters.
| [1] |
Allen B, Gore J, Nowak MA (2013) Spatial dilemmas of diffusible public goods. eLife, 2, e01169.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Asfahl KL, Schuster M (2017) Social interactions in bacterial cell-cell signaling. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 41, 92- 107.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Axelrod R, Hamilton WD (1981) The evolution of cooperation. Science, 211, 1390-1396.
PMID |
| [4] | Bai Y, He CY, Long J, Li XF, Fu XF (2021) Spatial modulation of individual behaviors enables collective decision-making during bacterial group migration. bioRxiv, http://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.17.431709. |
| [5] | Bertalanffy L (1969) General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications. Georges Braziller, Inc., New York. |
| [6] |
Blanchard AE, Lu T (2015) Bacterial social interactions drive the emergence of differential spatial colony structures. BMC Systems Biology, 9, 59.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Book G, Ingham C, Ariel G (2017) Modeling cooperating micro-organisms in antibiotic environment. PLoS ONE, 12, e0190037.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Camazine S, Deneubourg JL, Franks NR, Sneyd J, Theraulaz G, Bonabeau E (2020) Self-organization in Biological Systems. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [9] | Chodkowski JL, Shade A (2017) A synthetic community system for probing microbial interactions driven by exometabolites. mSystems, 2, e00129-17. |
| [10] |
D’Souza GG, Povolo VR, Keegstra JM, Stocker R, Ackermann M (2021) Nutrient complexity triggers transitions between solitary and colonial growth in bacterial populations. The ISME Journal, 15, 2614-2626.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Dal Co A, van Vliet S, Kiviet DJ, Schlegel S, Ackermann M (2020) Short-range interactions govern the dynamics and functions of microbial communities. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 366-375. |
| [12] | Darch SE, Simoska O, Fitzpatrick M, Barraza JP, Stevenson KJ, Bonnecaze RT, Shear JB, Whiteley M (2018) Spatial determinants of quorum signaling in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, 4779-4784. |
| [13] | Dawkins R, Davis N (2017) The Selfish Gene. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [14] | Doekes HM, Hermsen R (2021) Multiscale selection in spatially structured populations. bioRxiv, http://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.21.473617. |
| [15] | Ebrahimi A, Schwartzman J, Cordero OX (2019) Cooperation and spatial self-organization determine rate and efficiency of particulate organic matter degradation in marine bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 23309-23316. |
| [16] |
Epstein S (2013) The phenomenon of microbial uncultivability. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 16, 636-642.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Falkowski PG, Fenchel T, Delong EF (2008) The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science, 320, 1034-1039.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Figueiredo ART, Kümmerli R (2020) Microbial mutualism: Will you still need me, will you still feed me? Current Biology, 30, R1041-R1043. |
| [19] | Fletcher JA, Doebeli M (2009) A simple and general explanation for the evolution of altruism. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 276, 13-19. |
| [20] |
Foster KR, Bell T (2012) Competition, not cooperation, dominates interactions among culturable microbial species. Current Biology, 22, 1845-1850.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Foster KR, Wenseleers T (2006) A general model for the evolution of mutualisms. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 19, 1283-1293.
PMID |
| [22] |
Frank SA (1994) Genetics of mutualism: The evolution of altruism between species. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 170, 393-400.
PMID |
| [23] |
Fu X, Kato S, Long J, Mattingly HH, He C, Vural DC, Zucker SW, Emonet T (2018) Spatial self-organization resolves conflicts between individuality and collective migration. Nature Communications, 9, 2177.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P (2005) Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends in Microbiology, 13, 34-40.
PMID |
| [25] | Gandhi SR, Yurtsev EA, Korolev KS, Gore J (2016) Range expansions transition from pulled to pushed waves as growth becomes more cooperative in an experimental microbial population. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 113, 6922-6927. |
| [26] |
Ge ZP, Liu QX (2020) More than the sum of its parts: Self-organized patterns and emergent properties of ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1431-1443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [葛振鹏, 刘权兴 (2020) 整体大于部分之和: 生态自组织斑图及其涌现属性. 生物多样性, 28, 1431-1443.] | |
| [27] |
Ghoul M, Mitri S (2016) The ecology and evolution of microbial competition. Trends in Microbiology, 24, 833-845.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
González-Cabaleiro R, Ofiţeru ID, Lema JM, Rodríguez J (2015) Microbial catabolic activities are naturally selected by metabolic energy harvest rate. The ISME Journal, 9, 2630-2641.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Griffin AS, West SA, Buckling A (2004) Cooperation and competition in pathogenic bacteria. Nature, 430, 1024-1027.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Haken H (1977) Synergetics. Physics Bulletin, 28, 412-414.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Hamilton WD (1964) The genetical evolution of social behaviour. II. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 7, 17-52. |
| [32] |
Healey D, Axelrod K, Gore J (2016) Negative frequency-dependent interactions can underlie phenotypic heterogeneity in a clonal microbial population. Molecular Systems Biology, 12, 877.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Karsenti E (2008) Self-organization in cell biology: A brief history. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 9, 255- 262.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Kauffman S, Kauffman SA (1995) At Home in the Universe:The Search for the Laws of Self-organization and Complexity. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [35] | Keller L (1999) Levels of Selection in Evolution. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [36] |
Kiers ET, Rousseau RA, West SA, Denison RF (2003) Host sanctions and the legume-rhizobium mutualism. Nature, 425, 78-81.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Kim HJ, Boedicker JQ, Choi JW, Ismagilov RF (2008) Defined spatial structure stabilizes a synthetic multispecies bacterial community. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 18188-18193. |
| [38] |
Konopka A (2009) What is microbial community ecology? The ISME Journal, 3, 1223-1230.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Korolev KS, Avlund M, Hallatschek O, Nelson DR (2010) Genetic demixing and evolution in linear stepping stone models. Reviews of Modern Physics, 82, 1691-1718.
PMID |
| [40] |
Koschwanez JH, Foster KR, Murray AW (2011) Sucrose utilization in budding yeast as a model for the origin of undifferentiated multicellularity. PLoS Biology, 9, e1001122.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Lam TKT, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Pocai A, Rossetti L (2005) Regulation of blood glucose by hypothalamic pyruvate metabolism. Science, 309, 943-947.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Lawton JH (1999) Are there general laws in ecology? Oikos, 84, 177-192.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Leventhal GE, Ackermann M, Schiessl KT (2019) Why microbes secrete molecules to modify their environment: The case of iron-chelating siderophores. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 16, 20180674.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Li L, Wu T, Wang Y, Ran M, Kang Y, Ouyang Q, Luo C (2019) Spatial coordination in a mutually beneficial bacterial community enhances its antibiotic resistance. Communications Biology, 2, 301.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Li ZJ, Chen XL, Zheng HL (2000) Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李振基, 陈小麟, 郑海雷 (2000) 生态学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [46] |
Little AEF, Robinson CJ, Peterson SB, Raffa KF, Handelsman J (2008) Rules of engagement: Interspecies interactions that regulate microbial communities. Annual Review of Microbiology, 62, 375-401.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Liu W, Jacquiod S, Brejnrod A, Russel J, Burmølle M, Sørensen SJ (2019) Deciphering links between bacterial interactions and spatial organization in multispecies biofilms. The ISME Journal, 13, 3054-3066.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Liu W, Tokuyasu TA, Fu X, Liu C (2021) The spatial organization of microbial communities during range expansion. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 63, 109-116.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Lovelock JE, Margulis L (1974) Atmospheric homeostasis by and for the biosphere: The gaia hypothesis. Tellus, 26, 2-10.
DOI URL |
| [50] | McFall-Ngai M, Hadfield MG, Bosch TCG, Carey HV, Domazet-Lošo T, Douglas AE, Dubilier N, Eberl G, Fukami T, Gilbert SF, Hentschel U, King N, Kjelleberg S, Knoll AH, Kremer N, Mazmanian SK, Metcalf JL, Nealson K, Pierce NE, Rawls JF, Reid A, Ruby EG, Rumpho M, Sanders JG, Tautz D, Wernegreen JJ (2013) Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 3229-3236. |
| [51] |
McGlynn SE, Chadwick GL, Kempes CP, Orphan VJ (2015) Single cell activity reveals direct electron transfer in methanotrophic consortia. Nature, 526, 531-535.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Mitri S, Clarke E, Foster KR (2016) Resource limitation drives spatial organization in microbial groups. The ISME Journal, 10, 1471-1482.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Mitri S, Foster KR (2013) The genotypic view of social interactions in microbial communities. Annual Review of Genetics, 47, 247-273.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | Mitri S, Xavier JB, Foster KR (2011) Social evolution in multispecies biofilms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 10839-10846. |
| [55] |
Momeni B, Brileya KA, Fields MW, Shou WY (2013a) Strong inter-population cooperation leads to partner intermixing in microbial communities. eLife, 2, e00230.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Momeni B, Waite AJ, Shou WY (2013b) Spatial self-organization favors heterotypic cooperation over cheating. eLife, 2, e00960.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Nadell CD, Drescher K, Foster KR (2016) Spatial structure, cooperation and competition in biofilms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14, 589-600.
DOI PMID |
| [58] |
Nowak MA (2006) Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science, 314, 1560-1563.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Nowak MA, Tarnita CE, Antal T (2010) Evolutionary dynamics in structured populations. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 365, 19-30. |
| [60] |
Nunan N, Wu K, Young IM, Crawford JW, Ritz K (2003) Spatial distribution of bacterial communities and their relationships with the micro-architecture of soil. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 44, 203-215.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Pande S, Kaftan F, Lang S, Svatoš A, Germerodt S, Kost C (2016) Privatization of cooperative benefits stabilizes mutualistic cross-feeding interactions in spatially structured environments. The ISME Journal, 10, 1413-1423.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Pande S, Shitut S, Freund L, Westermann M, Bertels F, Colesie C, Bischofs IB, Kost C (2015) Metabolic cross-feeding via intercellular nanotubes among bacteria. Nature Communi-cations, 6, 6238. |
| [63] |
Preussger D, Giri S, Muhsal LK, Oña L, Kost C (2020) Reciprocal fitness feedbacks promote the evolution of mutualistic cooperation. Current Biology, 30, 3580-3590.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Ran M, Wang Y, Wang S, Luo C (2015) Pump-free gradient- based micro-device enables quantitative and high- throughput bacterial growth inhibition analysis. Biomedical Microdevices, 17, 67.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Ratzke C, Barrere J, Gore J (2020) Strength of species interactions determines biodiversity and stability in microbial communities. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 376-383. |
| [66] |
Ratzke C, Gore J (2016) Self-organized patchiness facilitates survival in a cooperatively growing Bacillus subtilis population. Nature Microbiology, 1, 16022.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Satoh H, Miura Y, Tsushima I, Okabe S (2007) Layered structure of bacterial and archaeal communities and their in situ activities in anaerobic granules. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 7300-7307.
DOI URL |
| [68] | Smith MJ, Szathmary E (1997) The Major Transitions in Evolution. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [69] |
Strom SL (2008) Microbial ecology of ocean biogeochemistry: A community perspective. Science, 320, 1043-1045.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Sugden R (1989) Spontaneous order. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 3, 85-97.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Treves DS, Xia B, Zhou J, Tiedje JM (2003) A two-species test of the hypothesis that spatial isolation influences microbial diversity in soil. Microbial Ecology, 45, 20-28.
PMID |
| [72] |
Turner PE, Chao L (1999) Prisoner’s dilemma in an RNA virus. Nature, 398, 441-443.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
van de Koppel J, Gascoigne JC, Theraulaz G, Rietkerk M, Mooij WM, Herman PMJ (2008) Experimental evidence for spatial self-organization and its emergent effects in mussel bed ecosystems. Science, 322, 739-742.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | Wedlich-Söldner R, Betz T (2018) Self-organization: The fundament of cell biology. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 373, 20170103. |
| [75] |
Wingreen NS, Levin SA (2006) Cooperation among microorganisms. PLoS Biology, 4, e299.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Wootton JT (2001) Local interactions predict large-scale pattern in empirically derived cellular automata. Nature, 413, 841-844.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Xu H, Dauparas J, Das D, Lauga E, Wu Y (2019) Self- organization of swimmers drives long-range fluid transport in bacterial colonies. Nature Communications, 10, 1792.
DOI URL |
| [78] | Yanni D, Márquez-Zacarías P, Yunker PJ, Ratcliff WC (2019) Drivers of spatial structure in social microbial communities. Current Biology, 29, R545-R550. |
| [79] |
Zhang Z, van Kleunen M, Becks L, Thakur MP (2020) Towards a general understanding of bacterial interactions. Trends in Microbiology, 28, 783-785.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Nan Chen, Quan-Guo Zhang. The experimental evolution approach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [2] | Shidong Li. On the spatiotemporal development and driving factors of national parks in China and the United States [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23040-. |
| [3] | Hong Chen, Xiaoqing Xian, Yixue Chen, Na Lin, Miaomiao Wang, Zhipeng Li, Jian Zhao. Spatial pattern and driving factors on the prevalence of red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) in island cities: A case study of Haitan Island, Fujian [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22501-. |
| [4] | Shiyun Shen, Yuanfei Pan, Liru Chen, Yanli Tu, Xiaoyun Pan. Plant-soil feedbacks differ between native and introduced populations of Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [5] | Wei Zhang, Dongdong Zhai, Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Yuanyuan Chen, Ying Wang, Chuansong Liao, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Huatang Deng, Daqing Chen. Community structure and functional diversity of fishes in the Three Gorges Reservoir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22136-. |
| [6] | Wen Zhao, Dandan Wang, Mumin Reyila, Kaichuan Huang, Shun Liu, Baokai Cui. Soil microbial community structure of Larix gmelinii forest in the Aershan area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [7] | Xi Tian, Wencong Liu, Jiesheng Rao, Xiaofeng Wang, Tao Yang, Xi Chen, Qiuyu Zhang, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Xu Zhang, Zehao Shen. Patterns and causes of forest gap disturbance in a semi-humid evergreen broadleaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23219-. |
| [8] | Bing Yan, Qing Lu, Song Xia, Junsheng Li. An overview of advances in soil microbial diversity of urban environment [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 22186-. |
| [9] | Fei Fu, Huiyu Wei, Yuteng Chang, Beixin Wang, Kai Chen. Elevational patterns of life history and ecological trait diversity of aquatic insects in the middle of the Lancang River: The effects of climate and land use variables [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21332-. |
| [10] | Jiahuan Sun, Dong Liu, Jiaqi Zhu, Shuning Zhang, Meixiang Gao. Spatial distribution pattern of soil mite community and body size in wheat- maize rotation farmland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22292-. |
| [11] | Chengjun Song, Feng Sun. Effects of Zanthoxylum bungeanum agroforestry systems on soil microbial and nematode communities under drought [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(10): 1348-1357. |
| [12] | Tingting Li, Ximei Zhang. Research progress of the maintaining mechanisms of soil microbial diversity in Inner Mongolia grasslands under global change [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(6): 749-758. |
| [13] | Yaobin Song, Li Xu, Junpeng Duan, Weijun Zhang, Xiaolu Shentu, Tianxiang Li, Runguo Zang, Ming Dong. Sex ratio and spatial pattern of Taxus fuana, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations in Tibet [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(3): 269-276. |
| [14] | Zhenpeng Ge, Quanxing Liu. More than the sum of its parts: Self-organized patterns and emergent properties of ecosystems [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(11): 1431-1443. |
| [15] | Xiao Yaqian,Liu Chuan,Xiao Liang. The role of model animals in the study of symbiotic microorganisms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(5): 505-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()