



Biodiv Sci ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 21290. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021290 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021290
Special Issue: 数据论文
• Bioinventories • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhiwei Gao1, Tianyu Qian1, Jianping Jiang2, Dejia Hou1, Xuejian Deng3, Daode Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-22
Accepted:2021-12-12
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
Daode Yang
Zhiwei Gao, Tianyu Qian, Jianping Jiang, Dejia Hou, Xuejian Deng, Daode Yang. Species diversity and distribution of amphibians and reptiles in Hunan Province, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21290.
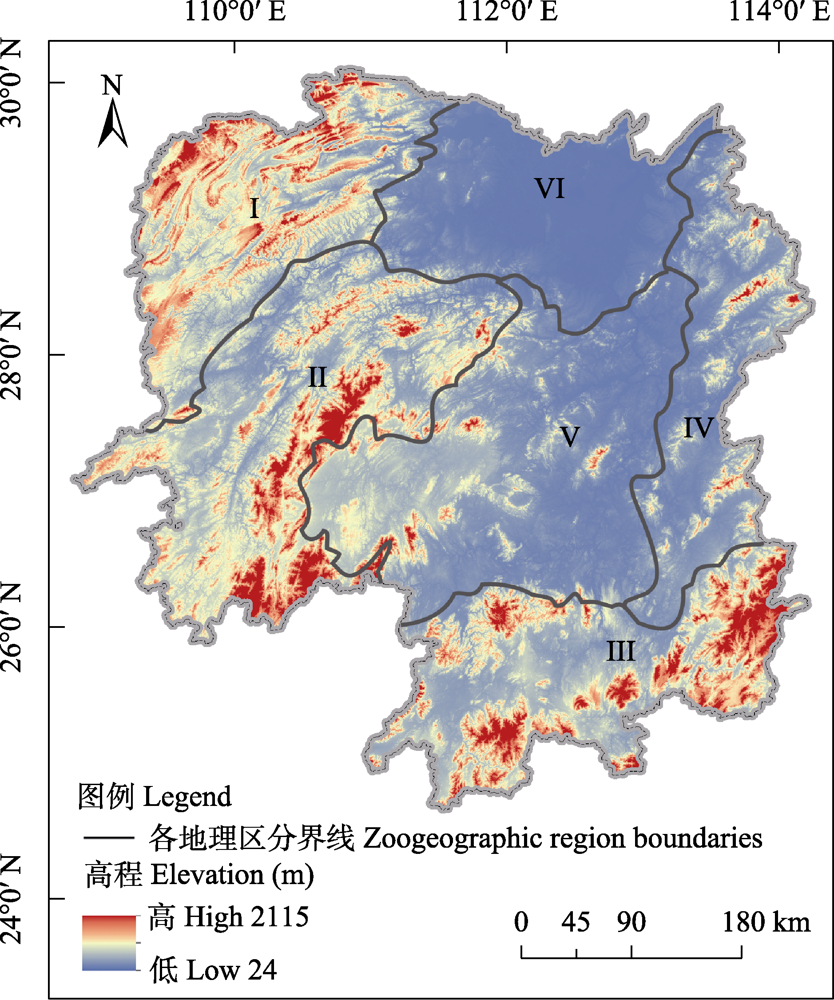
Fig. 1 Map of the geographic division of amphibians and reptiles in Hunan Province (adapted from Shen et al, 2014a). I, Mountain area in northwestern Hunan Province; II, Mountain area in western Hunan Province; III, Mountainous and hilly areas in southern Hunan Province; IV, Mountainous and hilly areas in eastern Hunan Province; V, Hilly area in central Hunan Province; VI, Dongting Lake plain in northern Hunan Province.
| 类别 Category | 种名 Species | 采集地 Locality | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 两栖纲 Amphibia | |||
| 新种 New species | 吴氏肥螈 Pachytriton wuguanfui | 道县 Daoxian County | Yuan et al, |
| 珀普短腿蟾 Megophrys popei | 炎陵县 Yanling County | Zhao et al, | |
| 陈氏角蟾 Megophrys cheni | 炎陵县 Yanling County | Wang et al, | |
| 林氏角蟾 Megophrys lini | 炎陵县 Yanling County | Wang et al, | |
| 舜皇角蟾 Megophrys shunhuangensis | 新宁县 Xinning County | Wang L et al, | |
| 幕阜山角蟾 Megophrys mufumontana | 平江县 Pingjiang County | Wang J et al, | |
| 南岭角蟾 Megophrys nanlingensis | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Wang J et al, | |
| 湘南角蟾 Megophrys xiangnanensis | 双牌县 Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 阳明山角蟾 Megophrys yangmingensis | 双牌县 Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 莽山掌突蟾 Leptobrachella mangshanensis | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Hou et al, | |
| 武陵掌突蟾 Leptobrachella wulingensis | 武陵源区、永定区 Wulingyuan District, Yongding District | Qian et al, | |
| 九岭山林蛙 Rana jiulingensis | 浏阳市、平江县 Liuyang City, Pingjiang County | Wan et al, | |
| 中华湍蛙 Amolops sinensis | 南岳区、双牌县 Nanyue District, Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 湘琴蛙 Nidirana xiangica | 浏阳市、双牌县 Liuyang City, Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 粤琴蛙 Nidrana guangdongensis | 桂东县 Guidong County | Lyu et al, | |
| 桑植臭蛙 Odorrana sangzhiensis | 桑植县 Sangzhi County | Zhang et al, | |
| 广东纤树蛙 Gracixalus guangdongensis | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Wang et al, | |
| 新记录种 New record species | 龙胜臭蛙 Odorrana lungshengensis | 绥宁县 Suining County | Liu et al, |
| 红吸盘棱皮树蛙 Theloderma rhododiscus | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Hou et al, | |
| 侏树蛙 Zhangixalus minimus | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Zhang et al, | |
| 爬行纲 Reptilia | |||
| 新种或新亚种 New species or subspecies | 都庞岭半叶趾虎 Hemiphyllodactylus dupanglingensis | 道县 Daoxian County | Zhang et al, |
| 广西棱蜥洪江亚种 Tropidophorus guangxiensis hongjiangensis | 洪江市 Hongjiang City | Guo et al, | |
| 桑植腹链蛇 Hebius sangzhiensis | 桑植县 Sangzhi County | Zhou et al, | |
| 赵氏后棱蛇 Opisthotropis zhaoermii | 古丈县 Guzhang County | Ren et al, | |
| 新记录种 New record species | 四川华蝮 Trimeresurus sichuanensis | 石门县 Shimen County | Unpublished data |
| 刘氏白环蛇 Lycodon liuchengchaoi | 石门县 Shimen County | Bai et al, | |
Table 1 List of new species (including subspecies) and new record of amphibians and reptiles found or distributed in Hunan Province since 2014
| 类别 Category | 种名 Species | 采集地 Locality | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 两栖纲 Amphibia | |||
| 新种 New species | 吴氏肥螈 Pachytriton wuguanfui | 道县 Daoxian County | Yuan et al, |
| 珀普短腿蟾 Megophrys popei | 炎陵县 Yanling County | Zhao et al, | |
| 陈氏角蟾 Megophrys cheni | 炎陵县 Yanling County | Wang et al, | |
| 林氏角蟾 Megophrys lini | 炎陵县 Yanling County | Wang et al, | |
| 舜皇角蟾 Megophrys shunhuangensis | 新宁县 Xinning County | Wang L et al, | |
| 幕阜山角蟾 Megophrys mufumontana | 平江县 Pingjiang County | Wang J et al, | |
| 南岭角蟾 Megophrys nanlingensis | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Wang J et al, | |
| 湘南角蟾 Megophrys xiangnanensis | 双牌县 Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 阳明山角蟾 Megophrys yangmingensis | 双牌县 Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 莽山掌突蟾 Leptobrachella mangshanensis | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Hou et al, | |
| 武陵掌突蟾 Leptobrachella wulingensis | 武陵源区、永定区 Wulingyuan District, Yongding District | Qian et al, | |
| 九岭山林蛙 Rana jiulingensis | 浏阳市、平江县 Liuyang City, Pingjiang County | Wan et al, | |
| 中华湍蛙 Amolops sinensis | 南岳区、双牌县 Nanyue District, Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 湘琴蛙 Nidirana xiangica | 浏阳市、双牌县 Liuyang City, Shuangpai County | Lyu et al, | |
| 粤琴蛙 Nidrana guangdongensis | 桂东县 Guidong County | Lyu et al, | |
| 桑植臭蛙 Odorrana sangzhiensis | 桑植县 Sangzhi County | Zhang et al, | |
| 广东纤树蛙 Gracixalus guangdongensis | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Wang et al, | |
| 新记录种 New record species | 龙胜臭蛙 Odorrana lungshengensis | 绥宁县 Suining County | Liu et al, |
| 红吸盘棱皮树蛙 Theloderma rhododiscus | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Hou et al, | |
| 侏树蛙 Zhangixalus minimus | 宜章县 Yizhang County | Zhang et al, | |
| 爬行纲 Reptilia | |||
| 新种或新亚种 New species or subspecies | 都庞岭半叶趾虎 Hemiphyllodactylus dupanglingensis | 道县 Daoxian County | Zhang et al, |
| 广西棱蜥洪江亚种 Tropidophorus guangxiensis hongjiangensis | 洪江市 Hongjiang City | Guo et al, | |
| 桑植腹链蛇 Hebius sangzhiensis | 桑植县 Sangzhi County | Zhou et al, | |
| 赵氏后棱蛇 Opisthotropis zhaoermii | 古丈县 Guzhang County | Ren et al, | |
| 新记录种 New record species | 四川华蝮 Trimeresurus sichuanensis | 石门县 Shimen County | Unpublished data |
| 刘氏白环蛇 Lycodon liuchengchaoi | 石门县 Shimen County | Bai et al, | |
| 动物地理区 Zoogeographic region | 东洋界种数 No. of Oriental species (%) | 广布种数 No. of widely- distributed species (%) | 合计 Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华中区 Central China | 华南区 South China | 西南区 Southwest China | 华中-华南区 Central & South China | 华中-西南区 Central & Southwest China | 华南-西南区 South & Southwest China | 华中-华南- 西南区 Central & South & Southwest China | |||
| 湘西北山地区 Mountain area in northwestern Hunan Province | 22(20.4) | 1(0.9) | 2(1.9) | 22(20.4) | 8(7.4) | 0(0.0) | 21(19.4) | 32(29.6) | 108 |
| 湘西山地区 Mountain area in western Hunan Province | 10(11.5) | 1(1.1) | 2(2.3) | 27(31.0) | 2(2.3) | 1(1.1) | 15(17.2) | 29(33.3) | 87 |
| 湘南山地丘陵区 Mountainous and hilly areas in southern Hunan Province | 24(17.4) | 3(2.2) | 0(0.0) | 53(38.4) | 3(2.2) | 0(0.0) | 22(15.9) | 32(23.9) | 138 |
| 湘东山地丘陵区 Mountainous and hilly areas in eastern Hunan Province | 8(13.6) | 1(1.7) | 0(0.0) | 15(25.4) | 1(1.7) | 0(0.0) | 10(16.9) | 24(40.7) | 59 |
| 湘中丘陵区 Hilly area in central Hunan Province | 5(6.0) | 1(1.2) | 0(0.0) | 27(32.1) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 21(25.0) | 30(35.7) | 84 |
| 湘北洞庭湖平原区 Dongting Lake plain in northern Hunan Province | 3(7.5) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 9(22.5) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 6(15.0) | 22(55.0) | 40 |
| 合计 Total | 51(26.7) | 3(1.6) | 2(1.0) | 62(32.5) | 8(4.2) | 1(0.5) | 28(14.7) | 36(18.8) | 191 |
Table 2 Fauna composition of amphibians and reptiles in different zoogeographic regions of Hunan Province
| 动物地理区 Zoogeographic region | 东洋界种数 No. of Oriental species (%) | 广布种数 No. of widely- distributed species (%) | 合计 Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华中区 Central China | 华南区 South China | 西南区 Southwest China | 华中-华南区 Central & South China | 华中-西南区 Central & Southwest China | 华南-西南区 South & Southwest China | 华中-华南- 西南区 Central & South & Southwest China | |||
| 湘西北山地区 Mountain area in northwestern Hunan Province | 22(20.4) | 1(0.9) | 2(1.9) | 22(20.4) | 8(7.4) | 0(0.0) | 21(19.4) | 32(29.6) | 108 |
| 湘西山地区 Mountain area in western Hunan Province | 10(11.5) | 1(1.1) | 2(2.3) | 27(31.0) | 2(2.3) | 1(1.1) | 15(17.2) | 29(33.3) | 87 |
| 湘南山地丘陵区 Mountainous and hilly areas in southern Hunan Province | 24(17.4) | 3(2.2) | 0(0.0) | 53(38.4) | 3(2.2) | 0(0.0) | 22(15.9) | 32(23.9) | 138 |
| 湘东山地丘陵区 Mountainous and hilly areas in eastern Hunan Province | 8(13.6) | 1(1.7) | 0(0.0) | 15(25.4) | 1(1.7) | 0(0.0) | 10(16.9) | 24(40.7) | 59 |
| 湘中丘陵区 Hilly area in central Hunan Province | 5(6.0) | 1(1.2) | 0(0.0) | 27(32.1) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 21(25.0) | 30(35.7) | 84 |
| 湘北洞庭湖平原区 Dongting Lake plain in northern Hunan Province | 3(7.5) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 9(22.5) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 6(15.0) | 22(55.0) | 40 |
| 合计 Total | 51(26.7) | 3(1.6) | 2(1.0) | 62(32.5) | 8(4.2) | 1(0.5) | 28(14.7) | 36(18.8) | 191 |
| 种名 Species | 国家重点保护野生动物名录 List of National Key Protected Wild Animals | CITES附录 CITES Appendix | 濒危等级Endangerment categories |
|---|---|---|---|
| 两栖纲 Amphibia | |||
| 挂榜山小鲵 Hynobius guabangshanensis | I | CR | |
| 黄斑拟小鲵 Pseudohynobius flavomaculatus | II | VU | |
| 大鲵 Andrias davidianus | II | I | CR |
| 宽脊疣螈 Tylototriton broadoridgus | II | II | NT |
| 莽山疣螈 Tylototriton lizhenchangi | II | II | VU |
| 浏阳疣螈 Tylototriton liuyangensis | II | II | DD |
| 尾斑瘰螈 Paramesotriton caudopunctatus | II | II | VU |
| 富钟瘰螈 Paramesotriton fuzhongensis | II | II | VU |
| 峨眉髭蟾 Leptobrachium boringii | II | EN | |
| 雷山髭蟾 Leptobrachium leishanense | II | VU | |
| 虎纹蛙 Hoplobatrachus chinensis | II | EN | |
| 爬行纲 Reptilia | |||
| 砂鳖 Pelodiscus axenaria | II | EN | |
| 小鳖 Pelodiscus parviformis | II | EN | |
| 平胸龟 Platysternon megacephalum | II | I | CR |
| 黄缘闭壳龟 Cuora flavomarginata | II | II | CR |
| 黄喉拟水龟 Mauremys mutica | II | II | EN |
| 乌龟 Mauremys reevesii | II | EN | |
| 眼斑水龟 Sacalia bealei | II | II | EN |
| 脆蛇蜥 Dopasia harti | II | EN | |
| 细脆蛇蜥 Dopasia gracilis | II | EN | |
| 井冈山脊蛇 Achalinus jinggangensis | II | CR | |
| 莽山原矛头蝮 Protobothrops mangshanensis | I | II | CR |
| 舟山眼镜蛇 Naja atra | II | VU | |
| 眼镜王蛇 Ophiophagus hannah | II | II | EN |
| 滑鼠蛇 Ptyas mucosa | II | EN | |
Table 3 The amphibian and reptile species listed in List of National Key Protected Wild Animals or CITES Appendix I and II in Hunan Province
| 种名 Species | 国家重点保护野生动物名录 List of National Key Protected Wild Animals | CITES附录 CITES Appendix | 濒危等级Endangerment categories |
|---|---|---|---|
| 两栖纲 Amphibia | |||
| 挂榜山小鲵 Hynobius guabangshanensis | I | CR | |
| 黄斑拟小鲵 Pseudohynobius flavomaculatus | II | VU | |
| 大鲵 Andrias davidianus | II | I | CR |
| 宽脊疣螈 Tylototriton broadoridgus | II | II | NT |
| 莽山疣螈 Tylototriton lizhenchangi | II | II | VU |
| 浏阳疣螈 Tylototriton liuyangensis | II | II | DD |
| 尾斑瘰螈 Paramesotriton caudopunctatus | II | II | VU |
| 富钟瘰螈 Paramesotriton fuzhongensis | II | II | VU |
| 峨眉髭蟾 Leptobrachium boringii | II | EN | |
| 雷山髭蟾 Leptobrachium leishanense | II | VU | |
| 虎纹蛙 Hoplobatrachus chinensis | II | EN | |
| 爬行纲 Reptilia | |||
| 砂鳖 Pelodiscus axenaria | II | EN | |
| 小鳖 Pelodiscus parviformis | II | EN | |
| 平胸龟 Platysternon megacephalum | II | I | CR |
| 黄缘闭壳龟 Cuora flavomarginata | II | II | CR |
| 黄喉拟水龟 Mauremys mutica | II | II | EN |
| 乌龟 Mauremys reevesii | II | EN | |
| 眼斑水龟 Sacalia bealei | II | II | EN |
| 脆蛇蜥 Dopasia harti | II | EN | |
| 细脆蛇蜥 Dopasia gracilis | II | EN | |
| 井冈山脊蛇 Achalinus jinggangensis | II | CR | |
| 莽山原矛头蝮 Protobothrops mangshanensis | I | II | CR |
| 舟山眼镜蛇 Naja atra | II | VU | |
| 眼镜王蛇 Ophiophagus hannah | II | II | EN |
| 滑鼠蛇 Ptyas mucosa | II | EN | |
| [1] | Bai LZ, Wang K, Kang ZJ, Liao QY, Liu MS (2018) Lycodon liuchengchaoi found in Hupingshan, Hunan, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 53, 640, 659. (in Chinese) |
| [ 白林壮, 王剀, 康祖杰, 廖庆义, 刘美斯 (2018) 湖南壶瓶山发现刘氏链蛇. 动物学杂志, 53, 640, 659.] | |
| [2] |
Biju SD, Garg S, Gokulakrishnan G, Chandrakasan S, Thammachoti P, Ren JL, Gopika C, Bisht K, Hamidy A, Shouche Y (2020) New insights on the systematics and reproductive behaviour in tree frogs of the genus Feihyla, with description of a new related genus from Asia (Anura, Rhacophoridae). Zootaxa, 4878, 1-55.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Cai B, Ji X, Wang YY, Rao DQ, Huang S, Wang YZ, Song ZB, Guo XG, Jiang JP (2022) An annotated list of lizards (Sauria: Squamata) recorded from the People’s Republic of China. Asian Herpetological Research, 13, 1-11. |
| [4] | Cai B, Lü K, Chen YY, Li JT, Wang YZ, Gu HJ, Gu XD (2018) The distributional list of amphibians and reptiles in Sichuan Province, China. China Scientific Data, 3, 11-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡波, 吕可, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 王跃招, 顾海军, 古晓东 (2018) 四川省两栖爬行动物分布名录. 中国科学数据, 3, 11-19.] | |
| [5] |
Cai B, Wang YZ, Chen YY, Li JT (2015) A revised taxonomy for Chinese reptiles. Biodiversity Science, 23, 365-382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 蔡波, 王跃招, 陈跃英, 李家堂 (2015) 中国爬行纲动物分类厘定. 生物多样性, 23, 365-382.]
DOI |
|
| [6] |
Chen JM, Poyarkov NA, Suwannapoom C, Lathrop A, Wu YH, Zhou WW, Yuan ZY, Jin JQ, Chen HM, Liu HQ, Nguyen TQ, Nguyen SN, Duong TV, Eto K, Nishikawa K, Matsui M, Orlov NL, Stuart BL, Brown RM, Rowley JJ, Murphy RW, Wang YY, Che J (2018) Large-scale phylogenetic analyses provide insights into unrecognized diversity and historical biogeography of Asian leaf-litter frogs, genus Leptolalax (Anura: Megophryidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 124, 162-171.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Chen YH (1998) Ophidian diversity in National Mt. Mang Nature Reserve, Hunan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 17, 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈远辉 (1998) 湖南莽山国家级自然保护区蛇类的多样性. 四川动物, 17, 86-90.] | |
| [8] | Chen YH, Yang DD, Gong SP (2012) Endangered status and conservation strategies of Protobothrops mangshanensis in China. Journal of Snake, 24, 387-388. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈远辉, 杨道德, 龚世平 (2012) 莽山烙铁头蛇的濒危现状与保护对策. 蛇志, 24, 387-388.] | |
| [9] |
David P, Vogel G, Dubois A (2011) On the need to follow rigorously the rules of the Code for the subsequent designation of a nucleospecies (type species) for a nominal genus which lacked one: The case of the nominal genus Trimeresurus Lacépède, 1804 (Reptilia: Squamata: Viperidae). Zootaxa, 2992, 1-51.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Deng WJ, Wei QL, Peng Q, Li JX, Lei YW, Zhang N, Mo XY (2021) Study on biodiversity and human disturbances of amphibians in the Xuefengshan Natural Reserve, Hunan Province. Life Science Research, 25, 338-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邓文静, 韦启浪, 彭琪, 李家兴, 雷有为, 张娜, 莫小阳 (2021) 湖南雪峰山自然保护区两栖动物多样性调查及人为干扰研究. 生命科学研究, 25, 338-346.] | |
| [11] | Deng XJ, Ye YY (1997) Eight new records of saurian in Hunan Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 32(6), 39-41. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邓学建, 叶贻云 (1997) 湖南蜥蜴类动物新纪录八种. 动物学杂志, 32(6), 39-41.] | |
| [12] | Deng XJ, Ye YY (1998) Reptile fauna and zoogeographic division in Hunan Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 17, 91-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邓学建, 叶贻云 (1998) 湖南爬行动物区系与地理区划. 四川动物, 17, 91-96.] | |
| [13] |
Djong HT, Matsui M, Kuramoto M, Nishioka M, Sumida M (2011) A new species of the Fejervarya limnocharis complex from Japan (Anura, Dicroglossidae). Zoological Science, 28, 922-929.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2006) Fauna Sinica•Amphibia (Vol. 1): General Accounts of Amphibia, Gymnophiona, Urodela. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2006) 中国动物志•两栖纲(上卷): 总论, 蚓螈目, 有尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [15] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2009a) Fauna Sinica•Amphibia (Vol. 2): Anura. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2009a) 中国动物志•两栖纲(中卷):无尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2009b) Fauna Sinica•Amphibia (Vol. 3): Anura, Ranidae. Science Press, Beijing.](in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2009b) 中国动物志•两栖纲(下卷):无尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Fei L, Ye CY (1992) Comments on the taxonomy of pelobatid toads of genus Leptolalax (Carpophrys) with description of a new species. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 38, 245-253. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 费梁, 叶昌媛 (1992) 中国锄足蟾科掌突蟾属的分类探讨暨一新种描述(Amphibia: Pelobatidae). 动物学报, 38, 245-253.] | |
| [18] | Fei L, Ye CY, Jiang JP (2010) Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 叶昌媛, 江建平 (2010) 中国两栖动物彩色图鉴. 四川科技出版社, 成都.] | |
| [19] | Fei L, Ye CY, Jiang JP (2012) Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians and Their Distributions. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 叶昌媛, 江建平 (2012) 中国两栖动物及其分布彩色图鉴. 四川科技出版社, 成都.] | |
| [20] | Frost DR (2021) Amphibian Species of the World. American Museum of Natural History, New York, USA. https://amphibiansoftheworld.amnh.org/. (accessed on 2021-11-27) |
| [21] | Guo KJ, Shu F, Wu NF, Chen SD, Hou M, Shi SC, Deng XJ (2021) Neotype designation and redescription of Tropidophorus guangxiensis Wen, 1992 (Squamata: Sauria: Scincidae), with description of a new subspecies from central South China. Zoological Research, 42, 606-613. |
| [22] |
Guo P, Wang YZ (2011) A new genus and species of cryptic Asian green pitviper (Serpentes: Viperidae: Crotalinae) from Southwest China. Zootaxa, 2918, 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Hou YM, Zhang MF, Chen J, Chen DS, Hu F, Wang B (2017) A new record of amphibian in Hunan Province: Theloderma rhododiscus. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 36, 718-719. (in Chinese) |
| [ 侯银梦, 张梦斐, 陈军, 陈德胜, 胡飞, 王斌 (2017) 湖南省两栖类新纪录--红吸盘棱皮树蛙. 四川动物, 36, 718-719.] | |
| [24] |
Hou YM, Zhang MF, Hu F, Li SY, Shi SC, Chen J, Mo XY, Wang B (2018) A new species of the genus Leptolalax (Anura, Megophryidae) from Hunan, China. Zootaxa, 4444, 247-266.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Huang S (2021) Atlas of Chinese Snakes. The Straits Publishing House, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 黄松 (2021) 中国蛇类图鉴. 海峡书局, 福州.] | |
| [26] | Jiang JP, Xie F, Li C, Wang B (2020) Species Catalogue of China (Vol.2): Animals•Vertebrates (IV)•Amphibia. Science Press. Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 江建平, 谢锋, 李成, 王斌 (2020) 中国生物物种名录(第二卷):动物•脊椎动物(IV)•两栖纲. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Jiang JP, Xie F, Li C, Wang B (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity•Vertebrates (Vol. IV):Amphibians. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 江建平, 谢锋, 李成, 王斌 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录•脊椎动物(第四卷):两栖动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [28] | Kang ZJ, Yang DD, Liao QY (2009) Two new records of snakes in Hunan Province, Lycodon fasciatus and Rhabdophis nuchalis, collected in Hunan Hupingshan National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 44, 145-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 康祖杰, 杨道德, 廖庆义 (2009) 壶瓶山发现湖南蛇类新纪录二种--双全白环蛇和颈槽蛇. 动物学杂志, 44, 145-147.] | |
| [29] | Li SZ, Xu N, Liu J, Lü JC, Wang B, Wei G (2020) A revised species list of amphibians in Guizhou Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 39, 694-710. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李仕泽, 徐宁, 刘京, 吕敬才, 王斌, 魏刚 (2020) 贵州省两栖动物名录修订. 四川动物, 39, 694-710.] | |
| [30] |
Li YM, Wu XB (2019) A revised species list of amphibians and reptiles in the Anhui Province. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1002-1011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李永民, 吴孝兵 (2019) 安徽省两栖爬行动物名录修订. 生物多样性, 27, 1002-1011.]
DOI |
|
| [31] | Li ZS, Mo JW, Gu YL, Liu S, Fei DB, Yang DD (2010) Investigation and analysis on amphibian and reptile resources in Nanyue Hengshan National Nature Reserve. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology, 37(1), 20-23, 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李祖实, 莫吉炜, 谷颖乐, 刘松, 费冬波, 杨道德 (2010) 南岳衡山国家级自然保护区两栖爬行动物资源调查与分析. 湖南林业科技, 37(1), 20-23, 29.] | |
| [32] | Liang QS, Liu SL, Gu HQ, Tang ZJ, Wu XJ (1982) New record of snakes in Hunan Province. Journal of Ji’nan University (Nature Science & Medicine Edition), (2), 107-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梁启燊, 刘素㛤, 顾辉青, 唐振杰, 吴先杰 (1982) 湖南省蛇类的新记录. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), (2), 107-117.] | |
| [33] | Liang QS, Liu SL, Tang DY, Gu HQ, Wu XJ (1981) Notes on reptiles of Ling County, Hunan, China. Journal of Ji’nan University (Nature Science & Medicine Edition), (1), 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梁启燊, 刘素㛤, 唐大由, 顾辉青, 吴先杰 (1981) 湖南酃县的爬行类调查报告. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), (1), 84-88.] | |
| [34] | Liu QC, Zhai XF, Wang TL, Wang JC (2018) Morphological identification and diversity of Polypedates species (Rhacophoridae, Anura, Amphibia) on Hainan Island. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 37, 490-496. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘秋成, 翟晓飞, 王同亮, 汪继超 (2018) 海南岛泛树蛙属(两栖纲: 无尾目: 树蛙科)物种的形态特征鉴定及其多样性研究. 四川动物, 37, 490-496.] | |
| [35] |
Liu S, Hou M, Wang J, Ananjeva NB, Rao DQ (2020) A new species of Diploderma (Squamata: Sauria: Agamidae) from Yunnan Province, China. Russian Journal of Herpetology, 27, 127-148.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Liu Z, Shi SC, Shu F, Liu Y, Wang L, Deng XJ (2018) A new record of amphibian in Hunan Province. Life Science Research, 22, 375-376, 396. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘钊, 石胜超, 舒服, 柳勇, 王璐, 邓学建 (2018) 湖南省两栖类新纪录--龙胜臭蛙. 生命科学研究, 22, 375-376, 396.] | |
| [37] | Luo J, Vogel G, Ryabov SA (2011) Three newsletters on snake research. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 28(3), 89-92. (in Chinese) |
| [ 罗键,Vogel G, Ryabov SA (2011) 蛇类研究简讯三则. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 28(3), 89-92.] | |
| [38] |
Lyu ZT, Dai KY, Li Y, Wan H, Liu ZY, Qi S, Lin SM, Wang J, Li YL, Zeng YJ, Li PP, Pang H, Wang YY (2020a) Comprehensive approaches reveal three cryptic species of genus Nidirana (Anura, Ranidae) from China. ZooKeys, 914, 127-159.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Lyu ZT, Huang LS, Wang J, Li YQ, Chen HH, Qi S, Wang YY (2019) Description of two cryptic species of the Amolops ricketti group (Anura, Ranidae) from southeastern China. ZooKeys, 812, 133-156.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Lyu ZT, Huang Z, Liao XW, Lin L, Huang Y, Wang YY, Mo YM (2021) A new species of music frog (Anura, Ranidae, Nidirana) from Mt. Daming, Guangxi, China. ZooKeys, 1059, 35-56.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Lyu ZT, Li YQ, Zeng ZC, Zhao J, Liu ZY, Guo GX, Wang YY (2020b) Four new species of Asian horned toads (Anura, Megophryidae, Megophrys) from Southern China. ZooKeys, 942, 105-140.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Malhotra A, Thorpe RS (2004) A phylogeny of four mitochondrial gene regions suggests a revised taxonomy for Asian pitvipers (Trimeresurus and Ovophis). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 32, 83-100.
PMID |
| [43] |
Ota H (2000) Japalura szechwanensis, a junior synonym of J. fasciata. Journal of Herpetology, 34, 611-614.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Pan D, Zhang B, Yang DD, Ding XY, Cui S, Hu XH (2018) White-striped treefrog Rhacophorus leucofasciatus found in Zhangjiajie, Hunan Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 53, 159-160. (in Chinese) |
| [ 潘丹, 张冰, 杨道德, 丁向运, 崔珊, 胡新华 (2018) 湖南省张家界发现白线树蛙. 动物学杂志, 53, 159-160.] | |
| [45] |
Qian TY, Xia X, Cao Y, Xiao NW, Yang DD (2020) A new species of Leptobrachella (Anura: Megophryidae) Smith, 1925 from Wuling Mountains in Hunan Province, China. Zootaxa, 4816, 491-526.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Ren JL, Wang K, Jiang K, Guo P, Li JT (2017) A new species of the Southeast Asian genus Opisthotropis (Serpentes: Colubridae: Natricinae) from western Hunan, China. Zoological Research, 38, 251-263. |
| [47] | Shen YH, Yang DD, Mo XY, Li HH, Chen D (2014a) The Fauna of Hunan:Amphibia. Hunan Science and Technology Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [ 沈猷慧, 杨道德, 莫小阳, 黎红辉, 陈丹 (2014a) 湖南动物志: 两栖纲. 湖南科学技术出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [48] | Shen YH, Ye YY, Deng XJ (2014b) The Fauna of Hunan:Reptilia. Hunan Science and Technology Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [ 沈猷慧, 叶贻云, 邓学建 (2014b) 湖南动物志: 爬行纲. 湖南科学技术出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [49] |
Tapley B, Cutajar T, Mahony S, Nguyen CT, Dau VQ, Nguyen TT, Luong HV, Rowley JJL (2017) The Vietnamese population of Megophrys kuatunensis (Amphibia: Megophryidae) represents a new species of Asian horned frog from Vietnam and southern China. Zootaxa, 4344, 465-492.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Uetz P, Freed P, Hošek J (2021) The Reptile Database.http://reptile-database.org/. (accessed on 2021-11-27) |
| [51] |
Wan H, Lyu ZT, Qi S, Zhao J, Li PP, Wang YY (2020) A new species of the Rana japonica group (Anura, Ranidae, Rana) from China, with a taxonomic proposal for the R. johnsi group. ZooKeys, 942, 141-158.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Wang J, Lyu ZT, Liu ZY, Liao CK, Zeng ZC, Zhao J, Li YL, Wang YY (2019a) Description of six new species of the subgenus Panophrys within the genus Megophrys (Anura, Megophryidae) from southeastern China based on molecular and morphological data. ZooKeys, 851, 113-164.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Wang J, Lyu ZT, Yang CY, Li YL, Wang YY (2019b) A new species of the genus Takydromus (Squamata, Lacertidae) from southwestern Guangdong, China. ZooKeys, 871, 119-139.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Wang J, Zeng ZC, Lyu ZT, Liu ZY, Wang YY (2018) Description of a new species of Gracixalus (Amphibia: Anura: Rhacophoridae) from Guangdong Province, southeastern China. Zootaxa, 4420, 251-269.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Wang K, Ren JL, Chen HM, Lyu ZT, Guo XG, Jiang K, Chen JM, Li JT, Guo P, Wang YY, Che J (2020) The updated checklists of amphibians and reptiles of China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 189-218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 王剀, 任金龙, 陈宏满, 吕植桐, 郭宪光, 蒋珂, 陈进民, 李家堂, 郭鹏, 王英永, 车静 (2020) 中国两栖、爬行动物更新名录. 生物多样性, 28, 189-218.]
DOI |
|
| [56] |
Wang K, Yu ZB, Vogel G, Che J (2021) Contribution to the taxonomy of the genus Lycodon H. Boie in Fitzinger, 1827 (Reptilia: Squamata: Colubridae) in China, with description of two new species and resurrection and elevation of Dinodon septentrionale chapaense Angel, Bourret, 1933. Zoological Research, 42, 62-86.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
Wang L, Deng XJ, Liu Y, Wu QQ, Liu Z (2019) A new species of the genus Megophrys (Amphibia: Anura: Megophryidae) from Hunan, China. Zootaxa, 4695, 301-330.
DOI |
| [58] | Wang YY, Chen CQ, Zhao J, Wu Y, Lyu ZT, Yang JH, Yu WH, Lin JS, Liu ZY, Wang J, Du Q, Zhang Z, Song YZ, Wang ZR, He GQ (2017) Colored Atlas of Terrestrial Vertebrates of the Jinggangshan Region in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王英勇, 陈春泉, 赵健, 吴毅, 吕植桐, 杨剑焕, 余文华, 林剑声, 刘祖尧, 王健, 杜卿, 张忠, 宋玉赞, 汪志如, 何桂强 (2017) 中国井冈山地区陆生脊椎动物彩色图谱. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [59] |
Wang YY, Zhang TD, Zhao J, Sung YH, Yang JH, Pang H, Zhang Z (2012) Description of a new species of the genus Xenophrys Günther, 1864 (Amphibia: Anura: Megophryidae) from Mount Jinggang, China, based on molecular and morphological data. Zootaxa, 3546, 53-67.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Wang YY, Zhao J, Yang JH, Zhou ZX, Chen GL, Liu Y (2014) Morphology, molecular genetics, and bioacoustics support two new sympatric Xenophrys toads (Amphibia: Anura: Megophryidae) in southeast China. PLoS ONE, 9, e93075.
DOI URL |
| [61] | Wang YZ, Cai B, Li JT (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity•Vertebrates (Vol. III):Reptiles. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 王跃招, 蔡波, 李家堂 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录•脊椎动物(第三卷):爬行动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [62] | Wu HP (1995) The research into the resources of classification of snakes and their ecology in the Nanyue Mountains (I). Journal of Hengyang Normal University, 13(2), 59-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 伍和平 (1995) 南岳衡山蛇类资源及生态研究(I). 衡阳师专学报(自然科学版), 13(2), 59-62.] | |
| [63] | Wu HP (1996) Preliminary report on the investigation of snakes in Nanyue Hengshan. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 31(1), 16-18. (in Chinese) |
| [ 伍和平 (1996) 南岳衡山蛇类调查初报. 动物学杂志, 31(1), 16-18.] | |
| [64] | Wu T, Liu ZX, Zhang YX, Wang BZ, Mao ZX, Huang TF (2019) Species diversity and faunal characteristics of amphibians and reptiles in the Xiaoxi National Nature Reserve, Hunan. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 38, 452-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴涛, 刘志霄, 张佑祥, 王本忠, 毛正祥, 黄太福 (2019) 湖南小溪国家级自然保护区两栖爬行动物多样性与区系特征. 四川动物, 38, 452-458.] | |
| [65] |
Wu YK, Wang YZ, Hanken J (2012) New species of Pachytriton (Caudata: Salamandridae) from the Nanling Mountain Range, southeastern China. Zootaxa, 3388, 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Xiang SJ, Deng XJ, Dong C, Xiao ZL (2008) A new record of amphibian in Hunan Province: Leptolalax oshanensis. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 43, 138-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 向孙军, 邓学建, 董超, 肖智力 (2008) 湖南省两栖动物新纪录--峨山掌突蟾. 动物学杂志, 43, 138-140.] | |
| [67] |
Yan F, Jiang K, Chen HM, Fang P, Jin JQ, Li Y, Wang SN, Robert WM, Che J, Zhang YP (2011) Matrilineal history of the Rana longicrus species group (Rana, Ranidae, Anura) and the description of a new species from Hunan, southern China. Asian Herpetological Research, 2, 61-71.
DOI URL |
| [68] | Yang K, Liu W, Deng XL (2017) A survey on the herpetological resources and species diversity in western Wuling Mountains. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 36, 708-717. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨孔, 刘伟, 邓熙龄 (2017) 武陵山西部两栖爬行动物资源调查及多样性研究. 四川动物, 36, 708-717.] | |
| [69] |
Yuan ZY, Zhang BL, Che J (2016) A new species of the genus Pachytriton (Caudata: Salamandridae) from Hunan and Guangxi, southeastern China. Zootaxa, 4085, 219-232.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Zhang B, Li Y, Hu K, Li PP, Gu ZR, Xiao NW, Yang DD (2021) A new species of Odorrana (Anura, Ranidae) from Hunan Province, China. ZooKeys, 1024, 91-115.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | Zhang B, Qian TY, Jiang XJ, Cai B, Deng XJ, Yang DD (2020) A new species of Hemiphyllodactylus Bleeker, 1860 (Reptilia: Squamata) from Hunan Province, China. Asian Herpetological Research, 11, 183-193. |
| [72] | Zhang MF, Hou YM, Chen DS, Li SY, Chen J, Hu F, Wang B (2018) Rhacophorus minimus found in Yizhang, Hunan. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 53, 475-478. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张梦斐, 侯银梦, 陈德胜, 李思源, 陈军, 胡飞, 王斌 (2018) 湖南宜章发现两栖动物侏树蛙. 动物学杂志, 53, 475-478.] | |
| [73] | Zhang MW, Zong Y, Ma JF (1998) Fauna Sinica•Reptilia (Vol. 1): General Accounts of Reptilia, Testudoformes, Crocodiliformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张孟闻, 宗愉, 马积藩 (1998) 中国动物志•爬行纲(第一卷): 总论, 龟鳖目, 鳄形目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [74] | Zhang RZ (2011) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 (2011) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [75] | Zhang XR, Wang J, Hou C, Fang YY, Yue CL, Li HP, Pan J (2020a) Species status and faunal analysis of amphibian in Zhejiang Province. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 41, 781-790. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 章旭日, 王珺, 侯楚, 房瑶瑶, 岳春雷, 李贺鹏, 潘杰 (2020a) 浙江省两栖动物物种现状及区系分析. 野生动物学报, 41, 781-790.] | |
| [76] | Zhang XR, Yue CL, Hou C, Wang J, Li HP (2020b) Species checklist and faunal characteristics of reptiles in Zhejiang Province, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 55, 189-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 章旭日, 岳春雷, 侯楚, 王珺, 李贺鹏 (2020b) 浙江省爬行动物物种现状及区系特征. 动物学杂志, 55, 189-203.] | |
| [77] | Zhang Y, Gong DJ, Huang S, Gao J, Zhang MY (2020) Species diversity and fauna of amphibians and reptiles in Gansu Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 39, 579-591. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张勇, 龚大洁, 黄帅, 高军, 张明宇 (2020) 甘肃两栖爬行动物多样性及区系分析. 四川动物, 39, 579-591.] | |
| [78] | Zhao EM (1999) Diagnoses of a new frog and a new snake from China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 18(3), 96. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵尔宓 (1999) 中国一新种蛙及一新种蛇的鉴别特征. 四川动物, 18(3), 96.] | |
| [79] | Zhao EM (2006) Snakes of China. Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House, Hefei. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵尔宓 (2006) 中国蛇类. 安徽科学技术出版社, 合肥.] | |
| [80] | Zhao EM, Huang MH, Zong Y (1998) Fauna Sinica•Reptilia (Vol. 3): Squamata•Serpentes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵尔宓, 黄美华, 宗愉 (1998) 中国动物志•爬行纲(第三卷):有鳞目•蛇亚目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [81] | Zhao EM, Jiang YM, Huang QY, Zhao H, Zhao KT, Zhou KY, Liu YZ, Liu MY, Li DJ, Zhang YX (1999) Fauna Sinica•Reptilia (Vol.2): Squamata•Lacertilia. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵尔宓, 江耀明, 黄庆云, 赵惠, 赵肯堂, 周开亚, 刘月珍, 刘明玉, 李德俊, 张玉霞 (1999) 中国动物志•爬行纲(第二卷):有鳞目•蜥蜴亚目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [82] |
Zhao J, Yang JH, Chen GL, Chen CQ, Wang YY (2014) Description of a new species of the genus Brachytarsophrys Tian and Hu, 1983 (Amphibia: Anura: Megophryidae) from southern China based on molecular and morphological data. Asian Herpetological Research, 5, 150-160.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Zhong J, Liu ZQ, Wang YQ (2008) Phylogeography of the rice frog, Fejervarya multistriata (Anura: Ranidae), from China based on mtDNA D-loop sequences. Zoological Science, 25, 811-820.
DOI PMID |
| [84] |
Zhou ZY, Sun ZY, Qi S, Lu YY, Lyu ZT, Wang YY, Li PP, Ma JZ (2019) A new species of the genus Hebius (Squamata: Colubridae: Natricinae) from Hunan Province, China. Zootaxa, 4674, 68-82.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Wang Dawei, Cheng Shuai, Feng Jiawei, Wang Tianming. The wildlife camera-trapping dataset of Zhangguangcai Mountains in Northeast China (2015-2020) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24384-. |
| [2] | Li Hualiang, Zhang Mingjun, Zhang Xibin, Tan Rong, Li Shichuan, Feng Erhui, Lin Xueyun, Chen Min, Yan enbo, Zeng Zhigao. Composition and influencing factors of the amphibian community in Hainan Dongzhaigang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [3] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [4] | Shengxian Yang, Qing Yang, Xiaodong Li, Xin Chao, Huiqiu Liu, Lanruoxue Wei, Sang Ba. Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [5] | Cheng Du, Yuan Wang, Xiaoling Yan, Jing Yan, Huiru Li, Qingfei Zhang, Yonghong Hu. Composition and historical changes of plant species diversity in Shanghai and the updated checklist of Shanghai vascular plants (2022) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23093-. |
| [6] | Jingxuan Chen, Jiajun Zhou, Baoquan Liu. Records and population status of sea turtles in the Zhejiang sea area of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23082-. |
| [7] | Yixin Jiang, Yingying Shi, Shuo Gao, Supen Wang. The impact of anthropogenic noise, artificial light at night and road kills on amphibians [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [8] | Wenhong Xiao, Xueyou Li, Ruichang Quan, Xinming Lian, Ming Li, Yonggang Nie, Zuofu Xiang, Weikang Yang, Feng Xu, Jie Wang, Qihai Zhou, Pengfei Fan, Xifu Yang, Wei Liu, Yuehua Sun, Libiao Zhang, Zhipang Huang, Hua Huang, Zongji Fan, Zhishu Xiao. Construction of Sino BON Mammal Diversity Monitoring Network (Sino BON- Mammal): A 10-year review and future outlook [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23326-. |
| [9] | Cheng Li, Jianping Jiang, Feng Xie, Tian Zhao, Jing Che, Yiming Li, Weiguo Du, Weikang Yang, Feng Xu. Progress and prospect of Chinese biodiversity monitoring of amphibians and reptiles [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23382-. |
| [10] | Weinuo Liang, Liang Hu. Geographical distribution of freshwater and estuarial fish archaeological remains since the Neolithic Age in China and its biogeographical implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 21471-. |
| [11] | Peiliang Liu, Yuan Lu, Cheng Du, Zhenhai Wu, Lulu Xun, Bin Li, Ming Yue. A checklist of vascular plants in Shaanxi Province, China (Version 2021) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 22061-. |
| [12] | Yunfeng Song, Chuanwu Chen, Yanping Wang. A dataset on the life-history and ecological traits of Chinese amphibians [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(3): 22053-. |
| [13] | Jiang Qiao, Guoqing Jia, Huaming Zhou, Lin Gong, Yong Jiang, Nengwen Xiao, Xiaoqi Gao, Anxiang Wen, Jie Wang. Mammal and bird diversity recorded with camera traps in Gongga Mountain National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 20395-. |
| [14] | Jun Wang, Chao Zhao. Taxonomy, species diversity and distribution patterns of fungus-feeding Phlaeothripidae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22128-. |
| [15] | Zhishu Xiao, Wenhong Xiao, Tianming Wang, Sheng Li, Xinming Lian, Dazhao Song, Xueqin Deng, Qihai Zhou. Wildlife monitoring and research using camera-trapping technology across China: The current status and future issues [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22451-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn