



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 887-896. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020444 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020444
Special Issue: 传粉生物学
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Demei Hu1,2,3, Renxiu Yao1,2,3, Yan Chen1,2,3, Xiansong You3, Shunyu Wang3, Xiaoxin Tang1,3, Xiaoyue Wang1,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-29
Accepted:2021-02-04
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-03-23
Contact:
*Xiaoyue Wang E-mail: wang.xiaoyue1989@163.com
Demei Hu, Renxiu Yao, Yan Chen, Xiansong You, Shunyu Wang, Xiaoxin Tang, Xiaoyue Wang. Tirpitzia sinensis improves pollination accuracy by promoting the compatible pollen growth[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(7): 887-896.
| 居群 Population | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 短柱型 (株) S-morph (ind.) | 长柱型 (株) L-morph (ind.) | G-test | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,714 ± 3.0 | 104º49' | 23º94' | 55 | 43 | 1.237 | 0.266 |
| 2 | 1,315 ± 3.0 | 104º84' | 23º17' | 52 | 44 | 0.511 | 0.475 |
| 3 | 1,130 ± 3.0 | 104º85' | 23º17' | 46 | 41 | 0.184 | 0.668 |
| 4 | 1,286 ± 3.0 | 104º84' | 23º17' | 55 | 50 | 0.152 | 0.696 |
| 5 | 1,413 ± 3.0 | 104º80' | 23º17' | 48 | 50 | 0.010 | 0.92 |
Table 1 The comparison of the number of L-morph and S-morph of Tirpitzia sinensis in five populations by G-test of goodness-of-fit
| 居群 Population | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 短柱型 (株) S-morph (ind.) | 长柱型 (株) L-morph (ind.) | G-test | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,714 ± 3.0 | 104º49' | 23º94' | 55 | 43 | 1.237 | 0.266 |
| 2 | 1,315 ± 3.0 | 104º84' | 23º17' | 52 | 44 | 0.511 | 0.475 |
| 3 | 1,130 ± 3.0 | 104º85' | 23º17' | 46 | 41 | 0.184 | 0.668 |
| 4 | 1,286 ± 3.0 | 104º84' | 23º17' | 55 | 50 | 0.152 | 0.696 |
| 5 | 1,413 ± 3.0 | 104º80' | 23º17' | 48 | 50 | 0.010 | 0.92 |
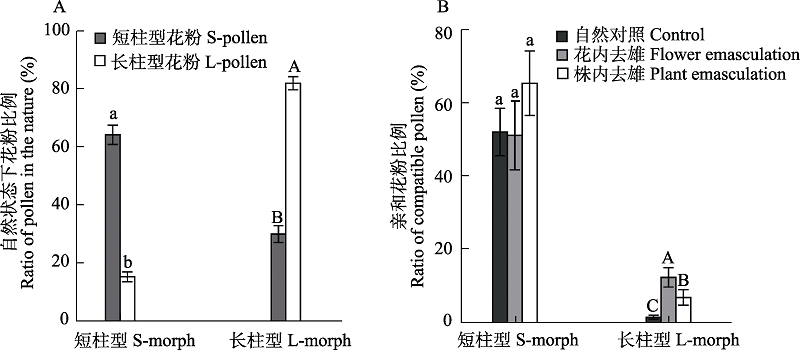
Fig. 1 The ratio of pollens in natural state and different emasculate treatments (A) Comparison of the proportion of different morphs of pollens deposited on the stigma of Tirpitzia sinensis in the natural state; (B) The ratio of compatible pollens on the stigma of Tirpitzia sinensis treated by different emasculate treatments. Different letters indicate significant difference among treatments.
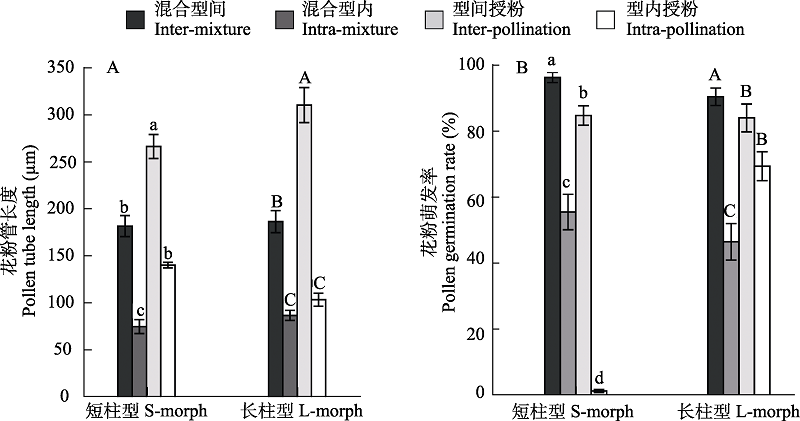
Fig. 2 Comparison of pollen tube length (A) and pollen germination rate (B) of Tirpitzia sinensis with different pollination treatments. Different letters indicate significant difference among treatments.
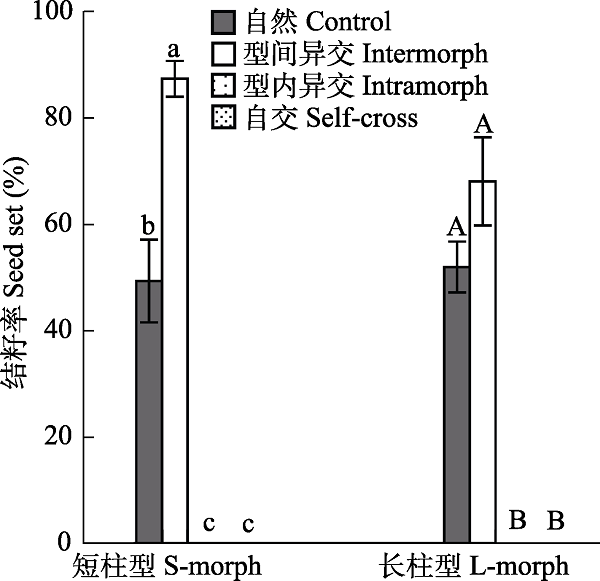
Fig. 3 Comparison of the seed set of Tirpitzia sinensis with different pollination treatments. The seed set ratio of intra-morph outcrossing and selfing were zero, different letters indicate significant difference among treatments.
| [1] |
Armbruster WS, Pérez-Barrales R, Arroyo J, Edwards ME, Vargas P (2006) Three-dimensional reciprocity of floral morphs in wild flax (Linum suffruticosum): A new twist on heterostyly. New Phytologist, 171, 581-590.
PMID |
| [2] | Barranco D, Arroyo J, Santos-Gally R (2019) Avoiding sexual interference: Herkogamy and dichogamy in style dimorphic flowers of Narcissus broussonetii (Amaryllidaceae). AoB PLANTS, 11, 038. |
| [3] |
Barrett SCH (1977) The breeding system of Pontederia rotundifolia L., a tristylous species. New Phytologist, 78, 209-220.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Barrett SCH (2019) ‘A most complex marriage arrangement’: Recent advances on heterostyly and unresolved questions. New Phytologist, 224, 1051-1067.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Barrett SCH, Glover DE (1985) On the Darwinian Hypothesis of the adaptive significance of tristyly. Evolution, 39, 766-774.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Barrett SCH (1992) Heterostylous genetic polymorphisms: Model systems for evolutionary analysis. In: Evolution and Function of Heterostyly, pp.1-29, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [7] |
Brys R, Jacquemyn H, Hermy M, Beeckman T (2008) Pollen deposition rates and the functioning of distyly in the perennial Pulmonaria officinalis (Boraginaceae). Plant Systematics and Evolution, 273, 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B (1979) A model for the evolution of distyly. The American Naturalist, 114, 467-498.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Costa J, Castro S, Loureiro J, Barrett SCH (2017) Experimental insights on Darwin’s cross-promotion hypothesis in tristylous purple loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria). American Journal of Botany, 104, 616-626.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Costa J, Torices R, Barrett SCH (2019) Evolutionary history of the buildup and breakdown of the heterostylous syndrome in Plumbaginaceae. New Phytologist, 224, 1278-1289.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Dafni A (1992) Pollination Ecology: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [12] | Darwin C (1892) The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species. John Murray, London. |
| [13] |
Dulberger R (1974) Structural dimorphism of stigmatic papillae in distylous Linum species. American Journal of Botany, 61, 238-243.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Dulberger R (1992) Floral polymorphisms and their functional significance in the heterostylous syndrome. In: Evolution and Function of Heterostyly (ed. Barrett SCH), pp. 41-84. Springer, Berlin. |
| [15] | Fetscher AE (2001) Resolution of male-female conflict in a hermaphroditic flower. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268, 525-529. |
| [16] |
Ganders FR (1974) Disassortative pollination in the distylous plant Jepsonia heterandra. Canadian Journal of Botany, 52, 2401-2406.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Ganders FR (1976) Pollen flow in distylous populations of Amsinckia (Boraginaceae). Canadian Journal of Botany, 54, 2530-2535.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Ganders FR (1979) The biology of heterostyly. New Zealand Journal of Botany, 17, 607-635.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Hu D, Gao SP, Li WJ, Lei T, Liu YQ, Li Q, Li JN, Jiang MY (2020) Dissecting the distyly response to pollination using metabolite profiling in heteromorphic incompatibility system interactions of Plumbago auriculata Lam. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 42, 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Keller B, Thomson JD, Conti E (2014) Heterostyly promotes disassortative pollination and reduces sexual interference in Darwin’s primroses: Evidence from experimental studies. Functional Ecology, 28, 1413-1425.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Kohn JR, Barrett SCH (1992) Experimental studies on the functional significance of heterostyly. Evolution, 46, 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Liu QR, Zhou LH (2008) Linaceae. In: Flora of China, Vol. 11 (eds Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY), Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Science Press, Beijing. |
| [23] | Liu SJ (2014) A Study of Adaptive Significance of Distyly in Primula species. PhD dissertation, Wuhan University, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘淑娟 (2014) 报春花属植物二型花柱的适应意义研究. 博士学位论文, 武汉大学, 武汉.] | |
| [24] |
Liu SJ, Wu LY, Huang SQ (2016) Shortened anther-stigma distance reduces compatible pollination in two distylous Primula species. Journal of Plant Ecology, 9, 224-232.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Lloyd DG, Webb CJ (1992) In: Evolution and Function of Heterostyly (ed. Barrett SCH), pp. 179-207. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [26] |
Lloyd DG, Yates JMA (1982) Intrasexual selection and the segregation of pollen and stigmas in hermaphrodite plants, exemplified by Wahlenbergia albomarginata (Campanulaceae). Evolution, 36, 903-913.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Massinga PH, Johnson SD, Harder LD (2005) Heteromorphic incompatibility and efficiency of pollination in two distylous Pentanisia species (Rubiaceae). Annals of Botany, 95, 389-399.
PMID |
| [28] |
Naiki A, Nagamasu H (2003) Distyly and pollen dimorphism in Damnacanthus (Rubiaceae). Journal of Plant Research, 116, 105-113.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Nicholls MS (1985) Pollen flow, population composition, and the adaptive significance of distyly in Linum tenuifolium L. (Linaceae). Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 25, 235-242.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Nishihiro J, Washitani I, Thomson JD, Thomson BA (2000) Patterns and consequences of stigma height variation in a natural population of a distylous plant Primula sieboldii. Functional Ecology, 14, 502-512.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Ornduff R (1966) The breeding system of Pontederia cordata L. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 93, 407-416.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Ornduff R (1970) Incompatibility and the pollen economy of Jepsonia parryi. American Journal of Botany, 57, 1036-1041.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Ornduff R (1970) The systematics and breeding system of Gelsemium (Loganiceae). Journal of the Arnold Arboretum, 51, 1-17.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Ornduff R, Perry JD (1964) Reproductive biology of Piriqueta caroliniana (Turneraceae). Rhodora, 66, 100-109. |
| [35] |
Piper J, Charlesworth B (1986) The evolution of distyly in Primula vulgaris. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 29, 123-137.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Raupp PP, Matias R, Furtado MT, Consolaro H (2020) The role of distyly in pollen flow of the hummingbird-pollinated Palicourea rigida (Rubiaceae). Flora, 271, 151681.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Ree RH (1997) Pollen flow, fecundity, and the adaptive significance of heterostyly in Palicourea padifolia (Rubiaceae). Biotropica, 29, 298-308.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Rodriguez-Riano T, Dafni A (2000) A new procedure to assess pollen viability. Sexual Plant Reproduction, 12, 241-244.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Vuilleumier BS (1967) The origin and evolutionary development of heterostyly in the angiosperms. Evolution, 21, 210-226.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Wang W, Yang SP, Cui GL, Zhang X, Liu Y, Chen Y (2015) Pollen viability and stigma receptivity of Artemisia annua L. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 37(2), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王卫, 杨水平, 崔广林, 张雪, 刘芸, 陈阳 (2015) 青蒿花粉活力及柱头可授性研究. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 37(2), 1-7.] | |
| [41] |
Wang XY, Quan QM, Wang B, Li YX, Huang SQ (2018) Pollen competition between morphs in a pollen-color dimorphic herb and the loss of phenotypic polymorphism within populations. Evolution, 72, 785-797.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Wolfe LM, Massinga PH, Johnson SD (2009) A quantitative evaluation of the distylous syndrome in Sebaea grandis (Gentianaceae). South African Journal of Botany, 75, 785-790.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Wu LY (2017) A Study of Evolution and Adaptive Significance of Distyly in Fagopyrum Species. PhD dissertation, Wuhan University, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴凌云 (2017) 荞麦属植物二型花柱的进化及适应性意义研究. 博士学位论文, 武汉大学, 武汉.] | |
| [44] |
Wu LY, Chang FF, Liu SJ, Scott Armbruster W, Huang SQ (2018) Heterostyly promotes compatible pollination in buckwheats: Comparisons of intraflower, intraplant, and interplant pollen flow in distylous and homostylous Fagopyrum. American Journal of Botany, 105, 108-116.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Wu LY, Wang B, Schoen DJ, Huang SQ (2017) Transitions from distyly to homostyly are associated with floral evolution in the buckwheat genus (Fagopyrum). American Journal of Botany, 104, 1232-1240.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Zhao ZT, Luo ZL, Yuan S, Mei LN, Zhang DX (2019) Global transcriptome and gene co-expression network analyses on the development of distyly in Primula oreodoxa. Heredity, 123, 784-794.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Zhou W, Barrett SCH, Wang H, Li DZ (2015) Reciprocal herkogamy promotes disassortative mating in a distylous species with intramorph compatibility. New Phytologist, 206, 1503-1512.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Yongguang Li, Hui Ren, Yingjie Zhang, Ruining Li, Hao Ai, Xianzhong Huang. Analysis of the molecular evolution of the PEBP gene family in cruciferous plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21545-. |
| [2] | Wang Xiaoyue,Zhu Xinxin,Yang Juan,Liu Yunjing,Tang Xiaoxin. Variation in style length and the effect on reproductive success in Chinese plums (Armeniaca mume) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(2): 159-167. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()