



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 667-676. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019013 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019013
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Weng Zhuoxian1,2,3,Huang Jiaqiong2,Zhang Shihao2,Yu Kaichun2,Zhong Fusheng1,2,3,Huang Xunhe2,3,*( ),Zhang Bin1,*(
),Zhang Bin1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-17
Accepted:2019-05-20
Online:2019-06-20
Published:2019-06-14
Contact:
Huang Xunhe,Zhang Bin
Weng Zhuoxian, Huang Jiaqiong, Zhang Shihao, Yu Kaichun, Zhong Fusheng, Huang Xunhe, Zhang Bin. Genetic diversity and population structure of black-bone chickens in China revealed by mitochondrial COI gene sequences[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(6): 667-676.
| 代号 Code | 品种名 Breed | 产地 Origin | 样本量 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|
| LY | 略阳乌鸡 Lueyang chicken | 陕西省略阳县 Lueyang, Shaanxi | 10 |
| WLS | 无量山乌骨鸡 Wuliangshan black-bone chicken | 云南省南涧县 Nanjian, Yunnan | 25 |
| YJ | 盐津乌骨鸡 Yanjin black-bone chicken | 云南省盐津县 Yanjin, Yunnan | 24 |
| ZX | 竹乡鸡 Zhuxiang chicken | 贵州省赤水市 Chishui, Guizhou | 32 |
| XF | 雪峰乌骨鸡 Xuefeng black-bone chicken | 湖南省洪江市 Hongjiang, Hunan | 19 |
| JS | 江山乌骨鸡 Jiangshan black-bone chicken | 浙江省江山市 Jiangshan, Zhejiang | 21 |
| SK | 丝羽乌骨鸡 Silkies | 江西省泰和县 Taihe, Jiangxi | 25 |
| YG | 余干乌骨鸡 Yugan black-bone chicken | 江西省余干县 Yugan, Jiangxi | 18 |
| HY | 黄羽黑鸡 Huangyu black chicken | 江西省宜春市 Yichun, Jiangxi | 18 |
| DH | 德化黑鸡 Dehua black chicken | 福建省德化县 Dehua, Fujian | 22 |
| JH | 金湖乌凤鸡 Jinhu black-bone chicken | 福建省泰宁县 Taining, Fujian | 24 |
| GX | 广西乌鸡 Guangxi black-bone chicken | 广西东兰县 Donglan, Guangxi | 17 |
Table 1 Sample information of this study
| 代号 Code | 品种名 Breed | 产地 Origin | 样本量 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|
| LY | 略阳乌鸡 Lueyang chicken | 陕西省略阳县 Lueyang, Shaanxi | 10 |
| WLS | 无量山乌骨鸡 Wuliangshan black-bone chicken | 云南省南涧县 Nanjian, Yunnan | 25 |
| YJ | 盐津乌骨鸡 Yanjin black-bone chicken | 云南省盐津县 Yanjin, Yunnan | 24 |
| ZX | 竹乡鸡 Zhuxiang chicken | 贵州省赤水市 Chishui, Guizhou | 32 |
| XF | 雪峰乌骨鸡 Xuefeng black-bone chicken | 湖南省洪江市 Hongjiang, Hunan | 19 |
| JS | 江山乌骨鸡 Jiangshan black-bone chicken | 浙江省江山市 Jiangshan, Zhejiang | 21 |
| SK | 丝羽乌骨鸡 Silkies | 江西省泰和县 Taihe, Jiangxi | 25 |
| YG | 余干乌骨鸡 Yugan black-bone chicken | 江西省余干县 Yugan, Jiangxi | 18 |
| HY | 黄羽黑鸡 Huangyu black chicken | 江西省宜春市 Yichun, Jiangxi | 18 |
| DH | 德化黑鸡 Dehua black chicken | 福建省德化县 Dehua, Fujian | 22 |
| JH | 金湖乌凤鸡 Jinhu black-bone chicken | 福建省泰宁县 Taining, Fujian | 24 |
| GX | 广西乌鸡 Guangxi black-bone chicken | 广西东兰县 Donglan, Guangxi | 17 |
| 品种名 Breed | 变异位点数 No. of variable sites | 平均核苷酸差异 Average K (k) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π) | 单倍型多样性 Haplotype diversity (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 略阳乌鸡 LY | 6 | 2.356 | 0.00339 ± 0.00064 | 0.733 ± 0.120 |
| 无量山乌骨鸡 WLS | 6 | 1.653 | 0.00238 ± 0.00026 | 0.743 ± 0.051 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | 10 | 2.036 | 0.00293 ± 0.00042 | 0.757 ± 0.075 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | 7 | 2.018 | 0.00290 ± 0.00028 | 0.730 ± 0.056 |
| 雪峰乌骨鸡 XF | 6 | 1.310 | 0.00188 ± 0.00069 | 0.380 ± 0.134 |
| 江山乌骨鸡 JS | 7 | 1.952 | 0.00281 ± 0.00048 | 0.729 ± 0.078 |
| 丝羽乌骨鸡 SK | 7 | 0.993 | 0.00143 ± 0.00044 | 0.537 ± 0.115 |
| 余干乌骨鸡 YG | 5 | 1.804 | 0.00260 ± 0.00025 | 0.680 ± 0.074 |
| 黄羽黑鸡 HY | 5 | 1.523 | 0.00219 ± 0.00051 | 0.634 ± 0.093 |
| 德化黑鸡 DH | 4 | 0.987 | 0.00142 ± 0.00047 | 0.455 ± 0.114 |
| 金湖乌凤鸡 JH | 5 | 1.486 | 0.00214 ± 0.00044 | 0.572 ± 0.095 |
| 广西乌鸡 GX | 3 | 1.456 | 0.00209 ± 0.00034 | 0.485 ± 0.079 |
Table 2 The number of variable sites, average K (k), nucleotide diversity (π) and haplotype diversity (h) of COI gene in the 12 black-bone chicken breeds. Breed codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 品种名 Breed | 变异位点数 No. of variable sites | 平均核苷酸差异 Average K (k) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π) | 单倍型多样性 Haplotype diversity (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 略阳乌鸡 LY | 6 | 2.356 | 0.00339 ± 0.00064 | 0.733 ± 0.120 |
| 无量山乌骨鸡 WLS | 6 | 1.653 | 0.00238 ± 0.00026 | 0.743 ± 0.051 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | 10 | 2.036 | 0.00293 ± 0.00042 | 0.757 ± 0.075 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | 7 | 2.018 | 0.00290 ± 0.00028 | 0.730 ± 0.056 |
| 雪峰乌骨鸡 XF | 6 | 1.310 | 0.00188 ± 0.00069 | 0.380 ± 0.134 |
| 江山乌骨鸡 JS | 7 | 1.952 | 0.00281 ± 0.00048 | 0.729 ± 0.078 |
| 丝羽乌骨鸡 SK | 7 | 0.993 | 0.00143 ± 0.00044 | 0.537 ± 0.115 |
| 余干乌骨鸡 YG | 5 | 1.804 | 0.00260 ± 0.00025 | 0.680 ± 0.074 |
| 黄羽黑鸡 HY | 5 | 1.523 | 0.00219 ± 0.00051 | 0.634 ± 0.093 |
| 德化黑鸡 DH | 4 | 0.987 | 0.00142 ± 0.00047 | 0.455 ± 0.114 |
| 金湖乌凤鸡 JH | 5 | 1.486 | 0.00214 ± 0.00044 | 0.572 ± 0.095 |
| 广西乌鸡 GX | 3 | 1.456 | 0.00209 ± 0.00034 | 0.485 ± 0.079 |
| 单倍型 Haplotype | 变异位点 Variation sites | 单倍型在品种的分布(频率) Haplotype distribution in breeds (frequency) | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|
AP003321 | 6666666666677777777777 7777788889900012233333 1146704890012331537788 0255272216776245331467 ACATGTTTAATGAGACAGTCCA | ||
| H1 | ...................... | LY5, WLS10, YJ4, ZX14, XF1, JS10, SK17, YG7, HY10, DH16, JH15, GX6 | 115 |
| H2 | T..................... | ZX1 | 1 |
| H3 | ...C.C...G............ | LY2, WLS2, YJ1, ZX9, XF15, JS4, SK2, YG8, HY2, DH3, JH5, GX11 | 64 |
| H4 | T..C.C...G............ | ZX2 | 2 |
| H5 | C..............T...... | ZX1 | 1 |
| H6 | ..GC.C...G............ | ZX1 | 1 |
| H7 | ...............T...... | WLS1, YJ1, ZX4, JS4, SK2, YG1, HY1, DH3, JH3 | 20 |
| H8 | .........G...A........ | WLS7, YJ11, XF2 | 20 |
| H9 | .........G..........T. | WLS5, YJ1 | 6 |
| H10 | ......C............... | YJ4 | 4 |
| H11 | ..G....C.G...A........ | YJ1 | 1 |
| H12 | .GG......G..........T. | YJ1 | 1 |
| H13 | ..................C... | SK1 | 1 |
| H14 | ................G..... | SK2 | 2 |
| H15 | ................GC.... | SK1 | 1 |
| H16 | ....................TG | LY1 | 1 |
| H17 | ...C.C...G..G......... | LY2 | 2 |
| H18 | ...............T...T.. | XF1 | 1 |
| H19 | ...C.C...G....G....... | JS1, JH1 | 2 |
| H20 | ...CAC...G............ | JS1 | 1 |
| H21 | ...........A...T...... | JS1 | 1 |
| H22 | .....C...G............ | YG1 | 1 |
| H23 | ..........A........... | YG1 | 1 |
| H24 | ........G......T...... | HY5 | 5 |
Table 3 COI haplotypes and their distributions in the 12 black-bone chicken breeds
| 单倍型 Haplotype | 变异位点 Variation sites | 单倍型在品种的分布(频率) Haplotype distribution in breeds (frequency) | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|
AP003321 | 6666666666677777777777 7777788889900012233333 1146704890012331537788 0255272216776245331467 ACATGTTTAATGAGACAGTCCA | ||
| H1 | ...................... | LY5, WLS10, YJ4, ZX14, XF1, JS10, SK17, YG7, HY10, DH16, JH15, GX6 | 115 |
| H2 | T..................... | ZX1 | 1 |
| H3 | ...C.C...G............ | LY2, WLS2, YJ1, ZX9, XF15, JS4, SK2, YG8, HY2, DH3, JH5, GX11 | 64 |
| H4 | T..C.C...G............ | ZX2 | 2 |
| H5 | C..............T...... | ZX1 | 1 |
| H6 | ..GC.C...G............ | ZX1 | 1 |
| H7 | ...............T...... | WLS1, YJ1, ZX4, JS4, SK2, YG1, HY1, DH3, JH3 | 20 |
| H8 | .........G...A........ | WLS7, YJ11, XF2 | 20 |
| H9 | .........G..........T. | WLS5, YJ1 | 6 |
| H10 | ......C............... | YJ4 | 4 |
| H11 | ..G....C.G...A........ | YJ1 | 1 |
| H12 | .GG......G..........T. | YJ1 | 1 |
| H13 | ..................C... | SK1 | 1 |
| H14 | ................G..... | SK2 | 2 |
| H15 | ................GC.... | SK1 | 1 |
| H16 | ....................TG | LY1 | 1 |
| H17 | ...C.C...G..G......... | LY2 | 2 |
| H18 | ...............T...T.. | XF1 | 1 |
| H19 | ...C.C...G....G....... | JS1, JH1 | 2 |
| H20 | ...CAC...G............ | JS1 | 1 |
| H21 | ...........A...T...... | JS1 | 1 |
| H22 | .....C...G............ | YG1 | 1 |
| H23 | ..........A........... | YG1 | 1 |
| H24 | ........G......T...... | HY5 | 5 |
| 品种名 Breed | 变异位点 Variation sites | 氨基酸变异 Amino acid variation | 变异数 Variation number |
|---|---|---|---|
AP003321 | 0000122 1235124 9010875 YLTEVDI | ||
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | F...... | 酪氨酸→苯丙氨酸 Tyrosine → Phenylalanine | 3 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | S...... | 酪氨酸→丝氨酸 Tyrosine → Serine | 1 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | ..A.... | 苏氨酸→丙氨酸 Threonine → Alanine | 1 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | ..A.... | 苏氨酸→丙氨酸 Threonine → Alanine | 1 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | .VA.... | 亮氨酸→缬氨酸, 苏氨酸→丙氨酸 Leucine → Valine, Threonine → Alanine | 1 |
| 丝羽乌骨鸡 SK | .....H. | 天冬氨酸→组氨酸 Asparagine → Histidine | 1 |
| 略阳乌鸡 LY | ......V | 异亮氨酸→缬氨酸 Isoleucine → Valine | 1 |
| 江山乌骨鸡 JS | ...K... | 谷氨酸→赖氨酸 Glutamic acid → Lysine | 1 |
| 余干乌骨鸡 YG | ....E.. | 缬氨酸→谷氨酸 Valine → Glutamic acid | 1 |
Table 4 Amino acid variation of COI gene and their distribution in these black-bone chicken breeds. Breed codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 品种名 Breed | 变异位点 Variation sites | 氨基酸变异 Amino acid variation | 变异数 Variation number |
|---|---|---|---|
AP003321 | 0000122 1235124 9010875 YLTEVDI | ||
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | F...... | 酪氨酸→苯丙氨酸 Tyrosine → Phenylalanine | 3 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | S...... | 酪氨酸→丝氨酸 Tyrosine → Serine | 1 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | ..A.... | 苏氨酸→丙氨酸 Threonine → Alanine | 1 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | ..A.... | 苏氨酸→丙氨酸 Threonine → Alanine | 1 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | .VA.... | 亮氨酸→缬氨酸, 苏氨酸→丙氨酸 Leucine → Valine, Threonine → Alanine | 1 |
| 丝羽乌骨鸡 SK | .....H. | 天冬氨酸→组氨酸 Asparagine → Histidine | 1 |
| 略阳乌鸡 LY | ......V | 异亮氨酸→缬氨酸 Isoleucine → Valine | 1 |
| 江山乌骨鸡 JS | ...K... | 谷氨酸→赖氨酸 Glutamic acid → Lysine | 1 |
| 余干乌骨鸡 YG | ....E.. | 缬氨酸→谷氨酸 Valine → Glutamic acid | 1 |
| 品种名 Breed | Tajima’s D | Fu’s Fs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | P | Fs | P | |
| 略阳乌鸡 LY | 0.45768 | 0.70000 | 0.96375 | 0.68900 |
| 无量山乌骨鸡 WLS | 0.12109 | 0.56400 | 0.49464 | 0.62700 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | -0.79944 | 0.25300 | -1.69126 | 0.17200 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | 0.99606 | 0.85100 | -0.31381 | 0.45400 |
| 雪峰乌骨鸡 XF | -0.76698 | 0.25300 | 0.57269 | 0.65900 |
| 江山乌骨鸡 JS | 0.01119 | 0.54100 | -0.25147 | 0.44900 |
| 丝羽乌骨鸡 SK | -1.43529 | 0.07300 | -1.92588 | 0.07000 |
| 余干乌骨鸡 YG | 0.76262 | 0.79100 | 0.24173 | 0.59100 |
| 黄羽黑鸡 HY | 0.15067 | 0.60000 | 0.87825 | 0.69200 |
| 德化黑鸡 DH | -0.28222 | 0.43600 | 1.28651 | 0.75700 |
| 金湖乌凤鸡 JH | 0.31722 | 0.67500 | 1.19223 | 0.77300 |
| 广西乌鸡 GX | 1.81444 | 0.97700 | 3.86919 | 0.94800 |
| 平均 Average | 0.11225 | 0.55950 | 0.44305 | 0.57342 |
| 方差 Squared deviation | 0.87539 | 0.26761 | 1.50012 | 0.25155 |
Table 5 Neutrality test in 12 breeds based on COI sequences. Breed codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 品种名 Breed | Tajima’s D | Fu’s Fs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | P | Fs | P | |
| 略阳乌鸡 LY | 0.45768 | 0.70000 | 0.96375 | 0.68900 |
| 无量山乌骨鸡 WLS | 0.12109 | 0.56400 | 0.49464 | 0.62700 |
| 盐津乌骨鸡 YJ | -0.79944 | 0.25300 | -1.69126 | 0.17200 |
| 竹乡鸡 ZX | 0.99606 | 0.85100 | -0.31381 | 0.45400 |
| 雪峰乌骨鸡 XF | -0.76698 | 0.25300 | 0.57269 | 0.65900 |
| 江山乌骨鸡 JS | 0.01119 | 0.54100 | -0.25147 | 0.44900 |
| 丝羽乌骨鸡 SK | -1.43529 | 0.07300 | -1.92588 | 0.07000 |
| 余干乌骨鸡 YG | 0.76262 | 0.79100 | 0.24173 | 0.59100 |
| 黄羽黑鸡 HY | 0.15067 | 0.60000 | 0.87825 | 0.69200 |
| 德化黑鸡 DH | -0.28222 | 0.43600 | 1.28651 | 0.75700 |
| 金湖乌凤鸡 JH | 0.31722 | 0.67500 | 1.19223 | 0.77300 |
| 广西乌鸡 GX | 1.81444 | 0.97700 | 3.86919 | 0.94800 |
| 平均 Average | 0.11225 | 0.55950 | 0.44305 | 0.57342 |
| 方差 Squared deviation | 0.87539 | 0.26761 | 1.50012 | 0.25155 |
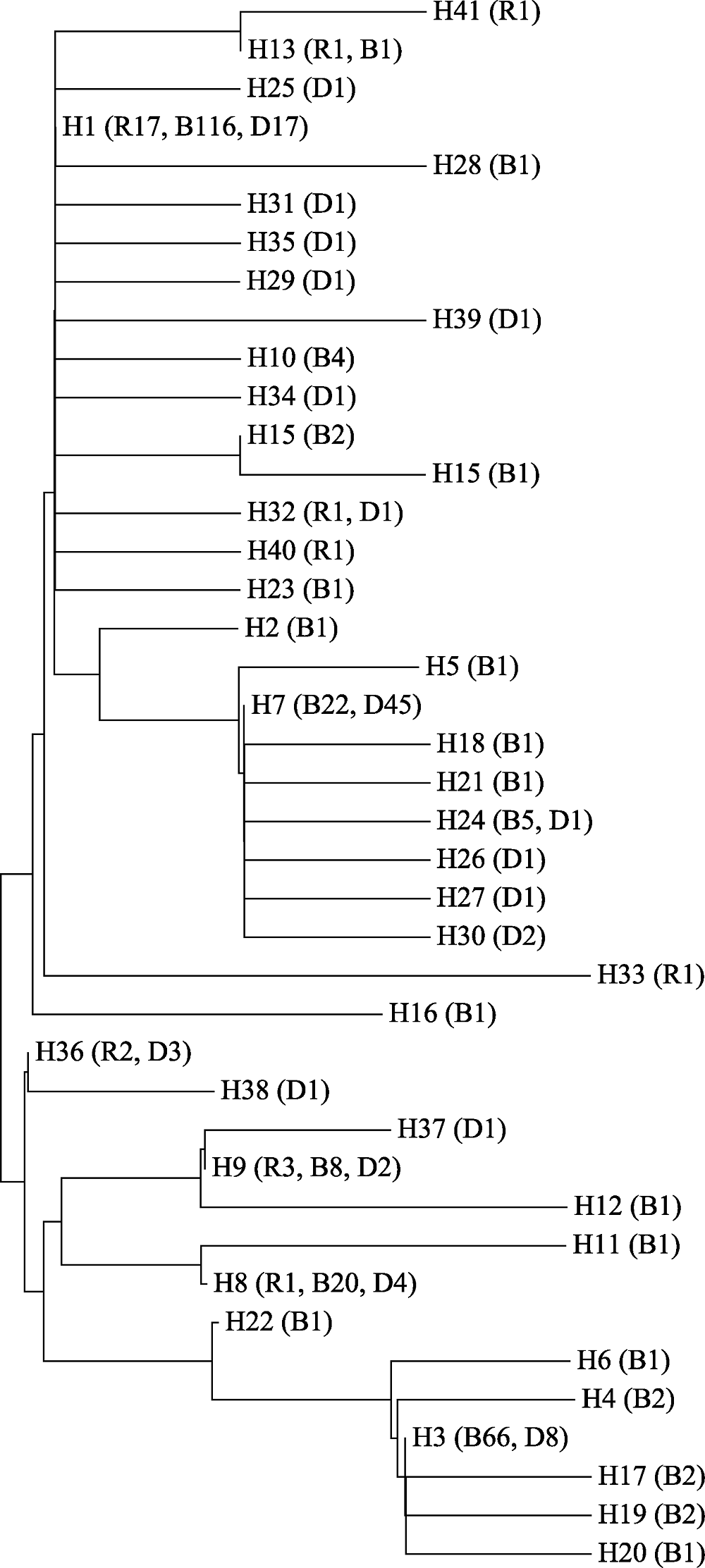
Fig. 2 Neighbor-joining tree of 41 COI haplotypes deteced in the samples of 384 chickens. R, Red junglefowl; B, Black-bone chicken; D, Domestic chicken. Numbers represent the sample size. Breed codes are the same as in Table 1.
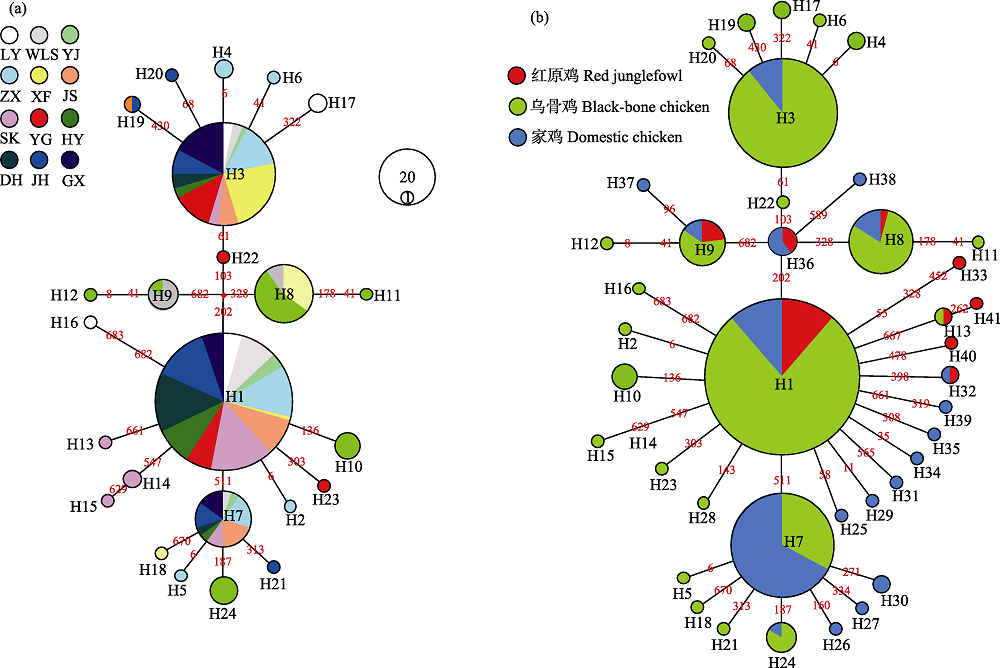
Fig. 3 Median-joining network based on COI gene. The links are labeled by the nucleotide positions to designate transitions. Cycle size is roughly proportional to the haplotype frequency, the breeds are indicated by different colors, breed codes are the same as in Table 1. (a) Median-joining network of 24 COI haplotypes deteced in the samples of 255 individuals of 12 Chinese black-bone breeds. (b) Median-joining network of 41 COI haplotypes deteced in the samples of 384 individuals.
| 变异起源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 Sum of squares | 方差组分 Variance components | 方差比例 Percentage of variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 11 | 52.622 | 0.18826 | 18.94 |
| 群体内 Within populations | 243 | 195.743 | 0.805553 | 81.06 |
| 总变异 Total variation | 254 | 248.365 | 0.99378 | 100 |
Table 6 AMOVA analysis of genetic variation of 12 black-bone chicken breeds
| 变异起源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 Sum of squares | 方差组分 Variance components | 方差比例 Percentage of variance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 11 | 52.622 | 0.18826 | 18.94 |
| 群体内 Within populations | 243 | 195.743 | 0.805553 | 81.06 |
| 总变异 Total variation | 254 | 248.365 | 0.99378 | 100 |
| Breed | LY | WLS | YJ | ZX | XF | JS | SK | YG | HY | DH | JH | GX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| WLS | 0.116* | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| YJ | 0.189* | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | |
| ZX | -0.018 | 0.134* | 0.207* | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| XF | 0.231* | 0.427* | 0.433* | 0.248* | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| JS | 0.004 | 0.121* | 0.196* | -0.014 | 0.341* | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| SK | 0.178* | 0.192* | 0.269* | 0.134* | 0.594* | 0.074* | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| YG | -0.035 | 0.170* | 0.234* | -0.011 | 0.158* | 0.032 | 0.250* | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| HY | 0.165* | 0.204* | 0.261* | 0.120* | 0.535* | 0.051 | 0.079* | 0.223* | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | |
| DH | 0.117 | 0.160* | 0.243* | 0.072 | 0.551* | 0.011 | -0.012 | 0.182* | 0.044 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| JH | 0.013 | 0.121* | 0.206* | -0.001 | 0.403* | -0.033 | 0.445 | 0.546 | 0.067 | -0.011 | 0.003 | |
| GX | 0.054 | 0.305* | 0.343* | 0.089* | 0.029 | 0.173* | 0.441* | -0.002 | 0.393* | 0.383* | 0.220* |
Table 7 K2P distance (above diagonal) and fixation index (Fst) (below diagonal) among 12 black-bone chicken breeds. Breed codes are the same as in Table 1.
| Breed | LY | WLS | YJ | ZX | XF | JS | SK | YG | HY | DH | JH | GX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| WLS | 0.116* | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| YJ | 0.189* | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | |
| ZX | -0.018 | 0.134* | 0.207* | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| XF | 0.231* | 0.427* | 0.433* | 0.248* | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| JS | 0.004 | 0.121* | 0.196* | -0.014 | 0.341* | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| SK | 0.178* | 0.192* | 0.269* | 0.134* | 0.594* | 0.074* | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| YG | -0.035 | 0.170* | 0.234* | -0.011 | 0.158* | 0.032 | 0.250* | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | |
| HY | 0.165* | 0.204* | 0.261* | 0.120* | 0.535* | 0.051 | 0.079* | 0.223* | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | |
| DH | 0.117 | 0.160* | 0.243* | 0.072 | 0.551* | 0.011 | -0.012 | 0.182* | 0.044 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| JH | 0.013 | 0.121* | 0.206* | -0.001 | 0.403* | -0.033 | 0.445 | 0.546 | 0.067 | -0.011 | 0.003 | |
| GX | 0.054 | 0.305* | 0.343* | 0.089* | 0.029 | 0.173* | 0.441* | -0.002 | 0.393* | 0.383* | 0.220* |
| [1] |
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A ( 1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48.
DOI URL |
| [2] | China National Commission of Animal Genetic Resources( 2011) Animal Genetic Resources in China: Poultry. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家畜禽遗传资源委员会( 2011) 中国畜禽遗传资源志: 家禽志. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [3] | Dharmayanthi AB, Terai Y, Sulandari S, Zein MSA, Akiyama T, Satta Y ( 2017) The origin and evolution of fibromelanosis in domesticated chickens: Genomic comparison of Indonesian Cemani and Chinese Silkie breeds. PLoS ONE, 4, e0173147. |
| [4] | Ekarius C ( 2007) Storey’s Illustrated Guide to Poultry Breeds. Storey Publishing, Massachusetts. |
| [5] |
Excoffier L, Lischer HE ( 2010) Arlequin suite ver. 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10, 564-567.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Feng CG, Gao Y, Dorshorst B, Song C, Gu XR, Li QY, Li JX, Liu TX, Rubin CJ, Zhao YQ, Wang YQ, Fei J, Li HF, Chen KW, Qu H, Shu DM, Ashwell C, Da Y, Andersson L, Hu X, Li N ( 2014) A cis-regulatory mutation of PDSS2 causes silky-feather in chickens. PLoS Genetics, 8, e1004576. |
| [7] |
Grant W, Bowen B ( 1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: Insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. Journal of Heredity, 89, 415-426.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Groeneveld LF, Lenstra JA, Eding H, Toro MA, Scherf B, Pilling D, Negrini R, Finlay EK, Han JL, Groeneveld E, Weigend S, GLOBALDIV Consortium ( 2010) Genetic diversity in farm animals—A review. Animal Genetics, 41, 6-31.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Hall TA ( 1999) Bioedit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95-98. |
| [10] | Hebert PDN, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, Francis CM ( 2004) Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biology, 2, 1657-1663. |
| [11] | Huang XH, Chen JB, He DL, Zhang XQ, Zhong FS ( 2016) DNA barcoding of indigenous chickens in China: A reevaluation. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 49, 2622-2633. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄勋和, 陈洁波, 何丹林, 张细权, 钟福生 ( 2016) DNA条形码技术鉴定中国地方鸡品种的重新评估. 中国农业科学, 49, 2622-2633.] | |
| [12] |
Huang XH, Wu YJ, Miao YW, Peng MS, Chen X, He DL, Suwannapoom C, Du BW, Li XY, Weng ZX, Jin SH, Song JJ, Wang MS, Chen JB, Li WN, Otecko NO, Geng ZY, Qu XY, Wu YP, Yang XR, Jin JQ, Han JL, Zhong FS, Zhang XQ, Zhang YP ( 2018) Was chicken domesticated in northern China? New evidence from mitochondrial genomes. Science Bulletin, 63, 743-746.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Jia XX, Tang XJ, Fan YF, Lu JX, Huang SH, Ge QL, Gao YS, Han W ( 2017) Genetic diversity of local chicken breeds in East China based on mitochondrial DNA D-loop region. Biodiversity Science, 25, 540-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贾晓旭, 唐修君, 樊艳凤, 陆俊贤, 黄胜海, 葛庆联, 高玉时, 韩威 ( 2017) 华东地区地方鸡品种mtDNA控制区遗传多样性. 生物多样性, 25, 540-548.] | |
| [14] | Kameshpandian P, Thomas S, Nagarajan M ( 2016) Genetic diversity and relationship of Indian Muscovy duck populations. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, 29, 1-5. |
| [15] | Li SZ ( 2005) Bencao Gangmu, 2nd edn. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李时珍 ( 2005) 本草纲目(第2版). 人民卫生出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Lin MM, Wang GQ, He ZG, Ma P, Liu Y ( 2017) Genetic diversity of Tianshui black-bone chicken based on DNA D-loop sequences. China Poultry, 39(1), 57-59. (in Chinese) |
| [ 林萌萌, 王国琪, 何振刚, 马平, 刘玉 ( 2017) 天水乌鸡线粒体DNA D-loop序列遗传多样性分析. 中国家禽, 39(1), 57-59.] | |
| [17] | Liu HT ( 2006) The formation, utilization and development of Dehua black-bone chicken. Fujian Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2(S1), 50-52. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘鸿涛 ( 2006) 德化黑鸡的形成、利用现状与发展思路. 福建畜牧兽医, 2(S1), 50-52.] | |
| [18] | Liu YP ( 2002) Genetic Diversity of Chinese Black-bone Chickens and Origin of Domestic Chickens. PhD dissertation, Sichuan Agricultural University, Ya’an, Sichuan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘益平 ( 2002) 中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性及家鸡起源研究. 博士学位论文, 四川农业大学, 四川雅安.] | |
| [19] |
Liu YP, Wu GS, Yao YG, Miao YW, Luikart GD, Baig M, Pereira AB, Ding ZL, Palanichamy MG, Zhang YP ( 2006) Multiple maternal origins of chickens: Out of the Asian jungles. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 38, 12-19.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Miao YW, Sun LM, Tong JJ, Li DL, Yuan YY, Yang MC, Hao WF, Huo JL, Yang R, Yu SL ( 2013) Maternal genetic analysis of Puer Maojiao and Nanjian Lver black-bone chicken using mtDNA D-loop sequences. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici, 34(7), 10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 苗永旺, 孙利民, 童晶晶, 李大林, 袁跃云, 杨满灿, 郝伟峰, 霍金龙, 杨润, 余仕亮 ( 2013) 普洱毛脚乌鸡与南涧绿耳乌鸡线粒体DNA母系遗传分析. 家畜生态学报, 34(7), 10-14.] | |
| [21] |
Peters J, Lebrasseur O, Deng H, Larson D ( 2016) Holocene cultural history of red jungle fowl (Gallus gallus) and its domestic descendant in East Asia. Quaternary Science Reviews, 142, 102-119.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Ren G, Ma H, Ma C, Wang W, Chen W, Ma L ( 2016) Genetic diversity and population structure of Portunus sanguinolentus (Herbst, 1783) revealed by mtDNA COI sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part A: DNA Mapping, Sequencing, and Analysis, 28, 740-746. |
| [23] | Rousset F ( 1997) Genetic differentiation and estimation of gene flow from F-statistics under isolation by distance. Genetics , 145, 1219-1228. |
| [24] |
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A ( 2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large datasets. Molecular Biology Evolution, 34, 3299-3302.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S ( 2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Molecular Biology & Evolution, 30, 2725-2729. |
| [26] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG ( 1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Tu YJ, Gao YS, Su YJ, Wang KH, Tong HB ( 2011) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic analysis of COI gene in some indigenous chicken breeds. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 38, 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 屠云洁, 高玉时, 苏一军, 王克华, 童海兵 ( 2011) 我国部分地方鸡种COI基因多态性及其分子系统进化研究. 安徽农业大学学报, 38, 39-42.] | |
| [28] | Wang L, Li Q, Kong LF, Yu H ( 2018) Population genetic structure and demographic history of Barbatia virescens along Chinese coast based on mitochondrial COI sequences. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 49, 87-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王玲, 李琪, 孔令锋, 于红 ( 2018) 基于COI基因的中国沿海青蚶野生群体遗传结构及种群动态研究. 海洋与湖沼, 49, 87-95.] | |
| [29] | Wei L, Liu SG, Shi XW ( 2008) Genetic diversity of the Xuefeng black bone chicken based on microsatellite markers. Biodiversity Science, 16, 503-508. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏麟, 刘胜贵, 史宪伟 ( 2008) 雪峰乌骨鸡自然群体遗传多样性的微卫星分析. 生物多样性, 16, 503-508.] | |
| [30] | Wu HH, Xie RQ ( 1999) The origin, history and usage of black-bone chickens. Guide to Chinese Poultry, 16(11), 56. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吾豪华, 谢若泉 ( 1999) 乌鸡产地、历史及作用浅议. 中国家禽导刊, 16(11), 56.] | |
| [31] | Xiang H, Gao J, Yu B, Xiang H, Gao JQ, Yu BQ, Zhou H, Cai DW, Zhang YW, Chen XY, Wang X, Hofreiter M, Zhao XB ( 2014) Early Holocene chicken domestication in northern China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 17564-17569. |
| [32] | Xu WJ, Zhu WQ, Shu JT, Song C, Chen KW ( 2014) Study on genetic diversity and phylogenetic evolution in Chinese main black-bone chicken. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 50(23), 10-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐文娟, 朱文奇, 束婧婷, 宋迟, 陈宽维 ( 2014) 我国主要乌骨鸡品种遗传多样性和系统进化研究. 中国畜牧杂志, 50(23), 10-14.] | |
| [33] | Yuan J ( 2010) Zooarchaeological study on the domestic animals in ancient China. Quaternary Science, 30, 298-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁靖 ( 2010) 中国古代家养动物的动物考古学研究. 第四纪研究, 30, 298-306.] | |
| [34] |
Zhang T, Du W, Lu H, Wang L ( 2018) Genetic diversity of mitochondrial DNA of Chinese black-bone chicken. Brazilian Journal of Poultry Science, 20, 565-572.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Jiajia Pu, Pingjun Yang, Yang Dai, Kexin Tao, Lei Gao, Yuzhou Du, Jun Cao, Xiaoping Yu, Qianqian Yang. Species identification and population genetic structure of non-native apple snails (Ampullariidea: Pomacea) in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [2] | Xingtong Wu, Lu Chen, Minqiu Wang, Yuan Zhang, Xueying Lin, Xinyu Li, Hong Zhou, Yafeng Wen. Population structure and genetic divergence in Firmiana danxiaensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(11): 1168-1179. |
| [3] | Shaoshuai Yu, Qicong Xu, Caili Lin, Shengjie Wang, Guozhong Tian. Genetic diversity of phytoplasmas: research status and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(2): 205-215. |
| [4] | Ni Xiang, Yannong Xiao, Canxing Duan, Xiaoming Wang, Zhendong Zhu. Genetic diversity in Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi based on SSR markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(6): 693-702. |
| [5] | Zhe Chen, Jiang Zhang, Hangfei Fu, Zhengzheng Xu, Kunzheng Deng, Jiayong Zhang. On the validity of the species Phenacoccus solenopsis based on morphological and mitochondrial COI data, with the description of a new body color variety [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(4): 443-450. |
| [6] | Bo Zhou, Haidong Jiang, Xiuxin Zhang, Jingqi Xue, Yantong Shi. Morphological diversity of some introduced tree peony cultivars [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(5): 543-550. |
| [7] | Biyun Chen, Qiong Hu, Christina Dixelius, Guoqing Li, Xiaoming Wu. Genetic diversity in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum assessed with SRAP markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(5): 509-515. |
| [8] | Changzhong Wang, Zhong Li, Hongwei Liang, Guangfu Hu, Qinchao Wu, Guiwei Zou, Xiangzhong Luo. Genetic diversity in fourProcambarus clarkii populations in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(5): 518-523. |
| [9] | Zhengfeng Wang, Xuejun Ge. Not only genetic diversity: advances in plant conservation genetics [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(4): 330-339. |
| [10] | Yinghui Ling, Yuejiao Cheng, Yanping Wang, Weijun Guan, Jianlin Han, Baoling Fu, Qianjun Zhao, Xiaohong He, Yabin Pu, Yuehui Ma. Genetic diversity of 23 Chinese indigenous horse breeds revealed by microsatellite markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 240-247. |
| [11] | Hongwei Liang, Zhong Li, Xiangzhong Luo, Changzhong Wang, Guangfu Hu, Guiwei Zou, Yongquan Yang. Genetic diversity based on microsatellite markers in five Nile tilapia strains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(1): 82-87. |
| [12] | Xueying Lu, Daoyuan Zhang, Wenbao Ma. Genetic variation and clonal diversity in fragmented populations of the desert plant Eremosparton songoricum based on ISSR markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2007, 15(3): 282-291. |
| [13] | Yongfa Luo, Zhigang Wang, Jiaqi Li, Guixiang Zhang, Yaosheng Chen, Yong Liang, Fuqing Yu, Weitao Song, Zifu Zhang . Genetic variation and genetic relationship among 13 Chinese and intro-duced cattle breeds using microsatellite DNA markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(6): 498-507. |
| [14] | Huifang Wu, Zuozhou Li, Hongwen Huang. Genetic differentiation among natural populations of Gastrodia elata (Orchidaceae) in Hubei and germplasm assessment of the cultivated populations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(4): 315-326. |
| [15] | Yingzhe Xia, Yan Sheng, Yiyu Chen. DNA sequence variation in the mitochondrial control region of lenok (Brachymystax lenok) populations in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(1): 48-54. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()