



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 306-313. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018269 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018269
Special Issue: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全; 传粉生物学; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tu Yanli1,Wang Liping2,3,Wang Xilong1,Wang Linlin2,3,*( ),Duan Yuanwen2
),Duan Yuanwen2
Received:2018-10-11
Accepted:2019-03-02
Online:2019-03-20
Published:2019-03-20
Contact:
Wang Linlin
Tu Yanli,Wang Liping,Wang Xilong,Wang Linlin,Duan Yuanwen. Status of invasive plants on local pollination networks: A case study of Tagetes minuta in Tibet based on pollen grains from pollinators[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(3): 306-313.
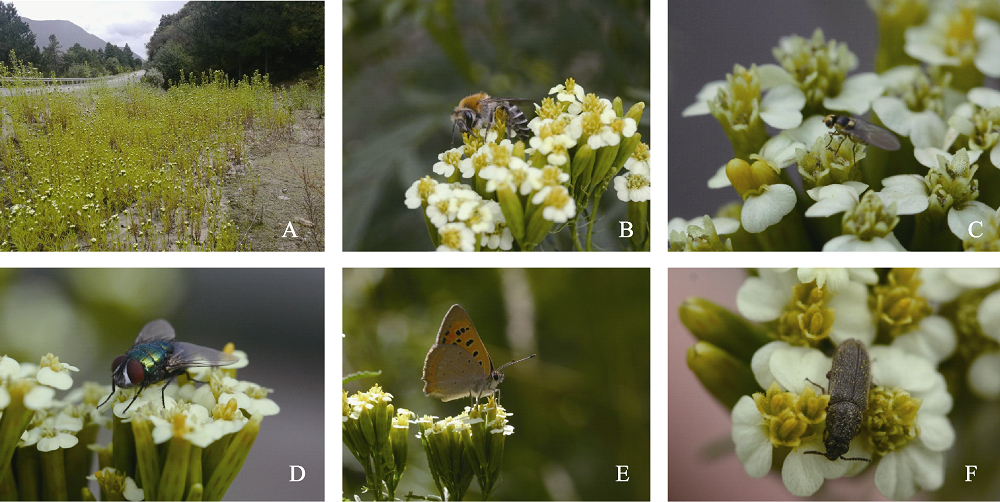

Fig. 1 Population of Tagetes minuta in Tibet and its pollinators. (A) T. minuta population; (B) Colletidae sp.; (C) Anthomyiidae sp.; (D) Calliphoridae sp.; (E) Lycaena phlaeas; (F) Tenebrionidae sp.
| 特征 Traits | 网络参数 Parameters |
|---|---|
| 植物种类数 No. of plant species | 12 |
| 访花昆虫种类数 No. of visiting species | 13 |
| 植物与昆虫的连接数量 No. of interactions | 63 |
| 连接度 Connectance | 0.404 |
| 嵌套度 Nestedness temperature | 14.57 |
| 加权嵌套度 Weighted nestedness | 0.683 |
| 特化水平 Specialization level (H°2) | 0.147 |
Table 1 Community level parameters of pollination network of Tagetes minuta population
| 特征 Traits | 网络参数 Parameters |
|---|---|
| 植物种类数 No. of plant species | 12 |
| 访花昆虫种类数 No. of visiting species | 13 |
| 植物与昆虫的连接数量 No. of interactions | 63 |
| 连接度 Connectance | 0.404 |
| 嵌套度 Nestedness temperature | 14.57 |
| 加权嵌套度 Weighted nestedness | 0.683 |
| 特化水平 Specialization level (H°2) | 0.147 |
| 代码 Codes | 植物 Plant species | 传粉者种类 Degree | 传粉昆虫比例 Normalised degree | 物种强度 Species strength | 特化水平 Specialization level (d°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 印加孔雀草 Tagetes minuta | 12 | 0.923 | 10.312 | 0.034 |
| B | 狭叶荆芥 Nepeta souliei | 8 | 0.615 | 0.85 | 0.095 |
| C | 无心菜 Arenaria serphyllifolia | 5 | 0.385 | 0.086 | 0.11 |
| D | 马先蒿属一种 Pedicularis sp. | 6 | 0.462 | 0.054 | 0.085 |
| E | 龙胆属一种 Gentiana sp. | 4 | 0.308 | 0.779 | 0.467 |
| F | 紫草科一种 Boraginaceae sp. | 6 | 0.462 | 0.107 | 0.046 |
| G | 蓝钟花属一种 Cyananthus sp. | 5 | 0.385 | 0.328 | 0.289 |
| H | 唇形科一种 Lamiaceae sp. | 4 | 0.308 | 0.197 | 0.099 |
| I | 唇形科一种 Lamiaceae sp. | 1 | 0.077 | 0.002 | 0.045 |
| J | 唇形科一种 Lamiaceae sp. | 3 | 0.231 | 0.037 | 0.332 |
| K | 百合科一种 Liliaceae sp. | 3 | 0.231 | 0.352 | 0.563 |
| L | 甘青老鹳草 Geranium pylzowianum | 6 | 0.462 | 0.063 | 0.117 |
Table 2 Several parameters of plants at the species levels in the pollination network of Tagetes minuta population
| 代码 Codes | 植物 Plant species | 传粉者种类 Degree | 传粉昆虫比例 Normalised degree | 物种强度 Species strength | 特化水平 Specialization level (d°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 印加孔雀草 Tagetes minuta | 12 | 0.923 | 10.312 | 0.034 |
| B | 狭叶荆芥 Nepeta souliei | 8 | 0.615 | 0.85 | 0.095 |
| C | 无心菜 Arenaria serphyllifolia | 5 | 0.385 | 0.086 | 0.11 |
| D | 马先蒿属一种 Pedicularis sp. | 6 | 0.462 | 0.054 | 0.085 |
| E | 龙胆属一种 Gentiana sp. | 4 | 0.308 | 0.779 | 0.467 |
| F | 紫草科一种 Boraginaceae sp. | 6 | 0.462 | 0.107 | 0.046 |
| G | 蓝钟花属一种 Cyananthus sp. | 5 | 0.385 | 0.328 | 0.289 |
| H | 唇形科一种 Lamiaceae sp. | 4 | 0.308 | 0.197 | 0.099 |
| I | 唇形科一种 Lamiaceae sp. | 1 | 0.077 | 0.002 | 0.045 |
| J | 唇形科一种 Lamiaceae sp. | 3 | 0.231 | 0.037 | 0.332 |
| K | 百合科一种 Liliaceae sp. | 3 | 0.231 | 0.352 | 0.563 |
| L | 甘青老鹳草 Geranium pylzowianum | 6 | 0.462 | 0.063 | 0.117 |
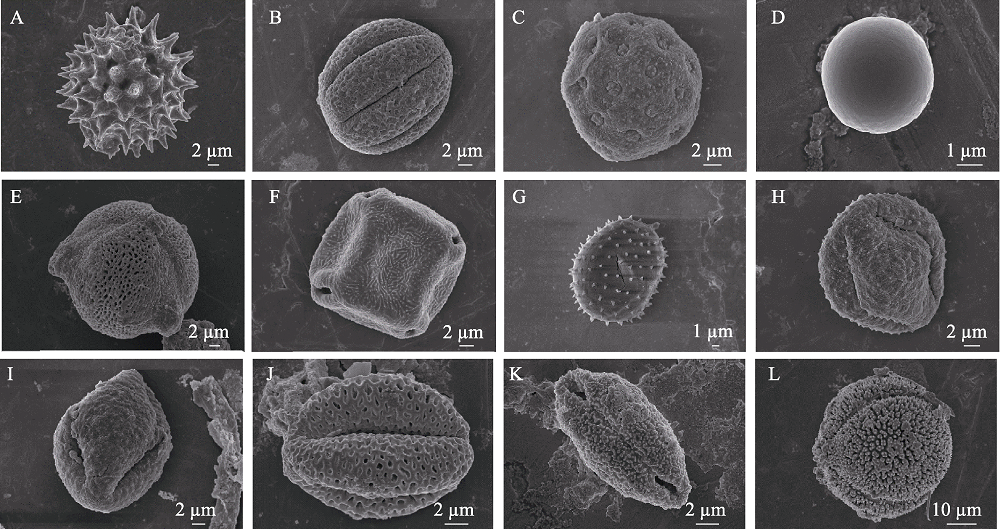
Fig. 2 A scan of pollens carried by pollinators of Tagetes minuta. (A) Tagetes minuta; (B) Nepeta souliei; (C) Arenaria serphyllifolia; (D) Pedicularis sp.; (E) Gentiana sp.; (F) Boraginaceae sp.; (G) Cyananthus sp.; (H-J) Lamiaceae spp.; (K) Liliaceae sp.; (L) Geranium pylzowianum.
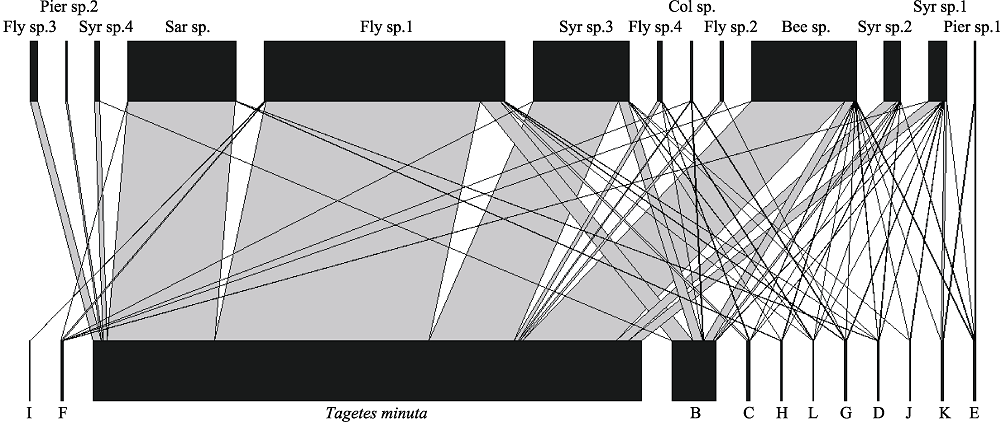
Fig. 3 Pollen network carried by pollinators of Tagetes minuta. Upper bars represent insect species and lower bars represent plant species. Bar width is proportional to the frequency of interactions. Lines are relative to the interaction between plants and insects. The codes of species are shown in Table 2 and Table 3.
| 代码 Codes | 传粉者 Pollinators | 昆虫数量 Samples | 植物物种 Degree | 植物物种比例 Normalised degree | 物种强度 Species strength | 特化水平 d° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bee sp. | 分舌花蜂科Colletidae | 32 | 11 | 0.917 | 1.611 | 0.006 |
| Syr sp.1 | 长尾管蚜蝇Eristalis tenax | 5 | 10 | 0.833 | 2.194 | 0.102 |
| Syr sp.2 | 黑带蚜蝇属Episyrpus | 3 | 7 | 0.583 | 0.64 | 0.024 |
| Syr sp.3 | 黑带蚜蝇属Episyrpus | 3 | 7 | 0.583 | 1.319 | 0.012 |
| Syr sp.4 | 食蚜蝇科Syrphidae | 1 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.013 | 0 |
| Fly sp.1 | 丽蝇科Calliphoridae | 2 | 8 | 0.667 | 4.072 | 0.016 |
| Fly sp.2 | 丽蝇科Calliphoridae | 1 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.299 | 0.139 |
| Fly sp.3 | 蝇科Muscidae | 1 | 1 | 0.083 | 0.014 | 0.017 |
| Fly sp.4 | 花蝇科Anthomyiidae | 1 | 4 | 0.333 | 0.303 | 0.034 |
| Sar sp. | 麻蝇科Sarcophadidae | 2 | 4 | 0.333 | 0.823 | 0.056 |
| Pier sp.1 | 东方菜粉蝶Pieris canidia | 1 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.501 | 0.803 |
| Pier sp.2 | 红灰蝶Lycaena phlaeas | 2 | 1 | 0.083 | 0.003 | 0.005 |
| Col sp. | 拟步甲科Tenebrionidae | 1 | 4 | 0.333 | 0.229 | 0.119 |
Table 3 Several parameters of pollinators at the species level in the pollination network of the Tagetes minuta population
| 代码 Codes | 传粉者 Pollinators | 昆虫数量 Samples | 植物物种 Degree | 植物物种比例 Normalised degree | 物种强度 Species strength | 特化水平 d° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bee sp. | 分舌花蜂科Colletidae | 32 | 11 | 0.917 | 1.611 | 0.006 |
| Syr sp.1 | 长尾管蚜蝇Eristalis tenax | 5 | 10 | 0.833 | 2.194 | 0.102 |
| Syr sp.2 | 黑带蚜蝇属Episyrpus | 3 | 7 | 0.583 | 0.64 | 0.024 |
| Syr sp.3 | 黑带蚜蝇属Episyrpus | 3 | 7 | 0.583 | 1.319 | 0.012 |
| Syr sp.4 | 食蚜蝇科Syrphidae | 1 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.013 | 0 |
| Fly sp.1 | 丽蝇科Calliphoridae | 2 | 8 | 0.667 | 4.072 | 0.016 |
| Fly sp.2 | 丽蝇科Calliphoridae | 1 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.299 | 0.139 |
| Fly sp.3 | 蝇科Muscidae | 1 | 1 | 0.083 | 0.014 | 0.017 |
| Fly sp.4 | 花蝇科Anthomyiidae | 1 | 4 | 0.333 | 0.303 | 0.034 |
| Sar sp. | 麻蝇科Sarcophadidae | 2 | 4 | 0.333 | 0.823 | 0.056 |
| Pier sp.1 | 东方菜粉蝶Pieris canidia | 1 | 2 | 0.167 | 0.501 | 0.803 |
| Pier sp.2 | 红灰蝶Lycaena phlaeas | 2 | 1 | 0.083 | 0.003 | 0.005 |
| Col sp. | 拟步甲科Tenebrionidae | 1 | 4 | 0.333 | 0.229 | 0.119 |
| 1 |
Arceo-Gómez G, Ashman TL ( 2016) Invasion status and phylogenetic relatedness predict cost of heterospecific pollen receipt: Implications for native biodiversity decline. Journal of Ecology, 104, 1003-1008.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
Bascompte J, Jordano P, Melián CJ, Olesen JM ( 2003) The nested assembly of plant-animal mutualistic networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 9383-9387.
DOI URL PMID |
| 3 |
Bascompte J, Jordano P, Olesen JM ( 2006) Asymmetric coevolutionary networks facilitate biodiversity maintenance. Science, 312, 431-433.
DOI URL PMID |
| 4 |
Bluthgen N, Menzel F, Bluthgen N ( 2006) Measuring specialization in species interaction networks. BMC Ecology, 6, 9.
DOI URL PMID |
| 5 |
Brennan AC, Harris SA, Hiscock SJ ( 2005) Modes and rates of selfing and associated inbreeding depression in the self-incompatible plant Senecio squalidus (Asteraceae): A successful colonizing species in the British Isles. New Phytologist, 168, 475-486.
DOI URL PMID |
| 6 |
Campbell LG, Husband BC ( 2007) Small populations are mate-poor but pollinator-rich in a rare, self-incompatible plant, Hymenoxys herbacea (Asteraceae). New Phytologist, 174, 915-925.
DOI URL PMID |
| 7 |
Dong ZG, Liu QX, Hu J, Deng MB, Xiong YN ( 2013) New records of naturalized plants from the Chinese Mainland. Guihaia, 33, 432-434. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 董振国, 刘启新, 胡君, 邓懋彬, 熊豫宁 ( 2013) 中国大陆归化植物新记录. 广西植物, 33, 432-434.]
DOI URL |
|
| 8 |
Eviner VT, Garbach K, Baty JH, Hoskinson SA ( 2012) Measuring the effects of invasive plants on ecosystem services: Challenges and prospects. Invasive Plant Science and Management, 5, 125-136.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Fang Q, Huang SQ ( 2012) Progress in pollination networks: Network structure and dynamics. Biodiversity Science, 20, 300-307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 方强, 黄双全 ( 2012) 传粉网络的研究进展: 网络的结构和动态. 生物多样性, 20, 300-307.]
DOI URL |
|
| 10 |
Flanagan RJ, Mitchell RJ, Karron JD ( 2010) Increased relative abundance of an invasive competitor for pollination, Lythrum salicaria, reduces seed number in Mimulus ringens. Oecologia, 164, 445-454.
DOI URL PMID |
| 11 |
Goodell K, Parker IM ( 2017) Invasion of a dominant floral resource: Effects on the floral community and pollination of native plants. Ecology, 98, 57-69.
DOI URL PMID |
| 12 |
Hao J, Sheng Q, Thomas C, Mark VK, Liu Q ( 2011) A test of baker’s law: Breeding systems of invasive species of Asteraceae in China. Biological Invasions, 13, 571-580.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Jeschke JM, Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Dick JTA, Essl F, Evans T, Gaertner M, Hulme PE, Kühn I, Mrugała A ( 2015) Defining the impact of non-native species. Conservation Biology, 28, 1188-1194.
DOI PMID |
| 14 |
Ju RT, Li H, Shi CJ, Li B ( 2012) Progress of biological invasions research in China over the last decade. Biodiversity Science, 20, 581-611. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 鞠瑞亭, 李慧, 石正人, 李博 ( 2012) 近十年中国生物入侵研究进展. 生物多样性, 20, 581-611.]
DOI URL |
|
| 15 |
Kaiser-Bunbury CN, Mougal J, Whittington AE, Valentin T, Gabriel R, Olesen JM, Bluthgen N ( 2017) Ecosystem restoration strengthens pollination network resilience and function. Nature, 542, 223-227.
DOI URL PMID |
| 16 |
Kearns CA, Inouye DW, Waser NM ( 1998) Endangered mutualisms: The conservation of plant-pollinator interactions. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics, 29, 83-112.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Lang DD, Tang M, Zhou X ( 2018) Qualitative and quantitative molecular construction of plant-pollinator network: Application and prospective. Biodiversity Science, 26, 445-456. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郎丹丹, 唐敏, 周欣 ( 2018) 传粉网络构建的定性定量分子研究: 应用与展望. 生物多样性, 26, 445-456.]
DOI URL |
|
| 18 |
Lopezaraiza-Mikel ME, Hayes RB, Whalley MR, Memmott J ( 2007) The impact of an alien plant on a native plant-pollinator network: An experimental approach. Ecology Letters, 10, 539-550.
DOI URL PMID |
| 19 |
McKinney AM, Goodell K ( 2011) Plant-pollinator interactions between an invasive and native plant vary between sites with different flowering phenology. Plant Ecology, 212, 1025-1035.
DOI URL |
| 20 | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ( 2005) Ecosystems and Human Well- Being: Synthesis. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| 21 |
Olesen JM, Bascompte J, Dupont YL, Jordano P ( 2007) The modularity of pollination networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 19891-19896.
DOI URL PMID |
| 22 |
Padrón B, Traveset A, Biedenweg T, Díaz D, Nogales M, Olesen JM ( 2009) Impact of alien plant invaders on pollination networks in two archipelagos. PLoS ONE, 4, e6275.
DOI URL PMID |
| 23 |
Potts SG, Imperatrizfonseca V, Ngo HT, Aizen MA, Biesmeijer JC, Breeze TD, Dicks LV, Garibaldi LA, Hill R, Settele J ( 2016) Safeguarding pollinators and their values to human well-being. Nature, 540, 220-229.
DOI URL PMID |
| 24 |
Powell KI, Krakos KN, Knight TM ( 2011) Comparing the reproductive success and pollination biology of an invasive plant to its rare and common native congeners: A case study in the genus Cirsium (Asteraceae). Biological Invasions, 13, 905-917.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Richardson RT, Lin CH, Sponsler DB, Quijia JO, Goodell K, Johnson RM ( 2015) Application of ITS2 metabarcoding to determine the provenance of pollen collected by honey bees in an agroecosystem. Applications in Plant Sciences, 3, 235-250.
DOI URL PMID |
| 26 | Schemske DW ( 1983) Limits to Specialization and Coevolution in Plant-Animal Mutualisms. Chicago University Press, Chicago. |
| 27 |
Sun SG, Lu B, Lu XM, Huang SQ ( 2018) On reproductive strategies of invasive plants and their impacts on native plants. Biodiversity Science, 26, 457-467. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 孙士国, 卢斌, 卢新民, 黄双全 ( 2018) 入侵植物的繁殖策略以及对本土植物繁殖的影响. 生物多样性, 26, 457-467.]
DOI URL |
|
| 28 |
Wan FH, Guo JY, Wang DH ( 2002) Alien invasive species in China: Their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 10, 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉 ( 2002) 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 10, 119-125.]
DOI URL |
|
| 29 |
Wang H, Cao GX, Wang LL, Yang YP, Zhang ZQ, Duan YW ( 2017) Evaluation of pollinator effectiveness based on pollen deposition and seed production in a gynodieocious alpine plant, Cyananthus delavayi. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 8156-8160.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
Weber E, Li B ( 2008) Plant invasions in China: What is to be expected in the wake of economic development? BioScience, 58, 437-444.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Weber E, Sun SG, Li B ( 2008) Invasive alien plants in China: Diversity and ecological insights. Biological Invasions, 10, 1411-1429.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Xie Y, Li ZY, Gregg WP, Dianmo L ( 2001) Invasive species in China—An overview. Biodiversity and Conservation, 10, 1317-1341.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Xu M, Tashi T ( 2015) A newly naturalized plant in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Guihaia, 35, 554-555. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 许敏, 扎西次仁 ( 2015) 青藏高原一新归化种. 广西植物, 35, 554-555.]
DOI URL |
|
| 34 | Zhang JL, Lü YF, Bian Y, Liu RS, Jiang L ( 2014) A new kind of invasive plant from mainland China—Tagetes minuta L. Plant Quarantine, 28(2), 65-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张劲林, 吕玉峰, 边勇, 刘若思, 江璐 ( 2014) 中国境内(内地)一种新的入侵植物——印加孔雀草. 植物检疫, 28(2), 65-67.] | |
| 35 |
Zhu SX, Qin HN, Chen YL ( 2005) Alien species of Compositae in China. Guihaia, 25, 69-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 朱世新, 覃海宁, 陈艺林 ( 2005) 中国菊科植物外来种概述. 广西植物, 25, 69-76.]
DOI URL |
| [1] | Zhang Chan, Zhao Suya, Zhang Xinran, Wang Yifan, Wang Linlin. Impacts of alien pollinators on native plant‒pollinator interactions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24443-. |
| [2] | Suyan Ba, Chunyan Zhao, Yuan Liu, Qiang Fang. Constructing a pollination network by identifying pollen on insect bodies: Consistency between human recognition and an AI model [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24088-. |
| [3] | Feifei Zhang, Tianfeng Yang, Lirong Chen, Dongmei Liu, Liuyuan Yang, Duyu Yang, Peng Ju, Lu Lu. Review of pollen color diversity in Angiosperms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23346-. |
| [4] | Xiaoqin Lü, Yang Li, Shunyu Wang, Renxiu Yao, Xiaoyue Wang. No significant differences found in chemical traits of pollen and nectar located in different positions across Aconitum piepunense racemes [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23371-. |
| [5] | Yong Li, Sanqing Li, Huan Wang. A dataset of wild vascular plants and their distributions in Tianjin, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23128-. |
| [6] | Jiajia Chen, Zhen Pu, Zhonghong Huang, Fengqin Yu, Jianjun Zhang, Donghua Xu, Junquan Xu, Peng Shang, Dilimulati·Parhati, Yaojiang Li, Jigme Tshering, Yumin Guo. Global distribution and number of overwintering black-necked crane (Grus nigricollis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22400-. |
| [7] | Fan Wu, Shenyun Liu, Huqiang Jiang, Qian Wang, Kaiwei Chen, Hongliang Li. Pollination difference between Apis cerana cerana and Apis mellifera ligustica during the late autumn and winter [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [8] | Qiujie Zhao, Huijun Guo, Guangtao Meng, Mingchuan Zhong, Jun Yin, Zhuocheng Liu, Pinrong Li, Li Chen, Yi Tao, Sheng Qiu, Hong Wang, Yanhui Zhao. Effects of grazing on bees and suggestions for its ecological restoration [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 23037-. |
| [9] | Yu Xiao, Yuran Li, Hexiang Duan, Zhengtao Ren, Shengbi Feng, Zhicheng Jiang, Jiahua Li, Pin Zhang, Jinming Hu, Yupeng Geng. Invasion status and control measures for alien plants within the Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [10] | Yaochu Sun, Yuanfei Pan, Mu Liu, Xiaoyun Pan. The specialist-to-generalist ratio affects growth and defense strategy of invasive plant Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22632-. |
| [11] | Xinyu Gong, Baorong Huang. Public welfare evaluation index system of national parks: A case study of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau National Park Cluster [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22571-. |
| [12] | Xia Cui, Quanru Liu, Chaoran Wu, Yufei He, Jinshuang Ma. The alien invasive plants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 21497-. |
| [13] | Jianming Wang, Mengjun Qu, Yin Wang, Yiming Feng, Bo Wu, Qi Lu, Nianpeng He, Jingwen Li. The drivers of plant taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic β-diversity in the gobi desert of northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [14] | Qinwen Lin, Cui Xiao, Jinshuang Ma. A dataset on catalogue of alien plants in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 22127-. |
| [15] | Guoping Shen, Rui Han, Zengqiang Miao, Jiangwa Xing, Yongzhen Li, Rong Wang, Derui Zhu. Bacterial diversity differences and influence factors of four types of hydrochemical characteristic lakes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21420-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()