



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 304-311. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016306 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016306
Special Issue: 土壤生物与土壤健康
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yali Jin1, Bicheng Li1, Long Geng2, Yun Bu1,*( )
)
Received:2016-10-21
Accepted:2016-12-31
Online:2017-03-20
Published:2017-04-07
Contact:
Bu Yun
Yali Jin, Bicheng Li, Long Geng, Yun Bu. Soil fauna community in different natural vegetation types of Dajinshan Island, Shanghai[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(3): 304-311.
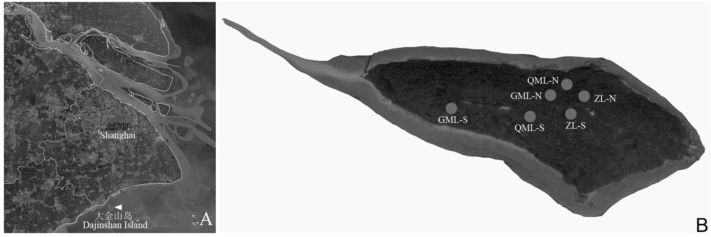
Fig. 1 The location of Dajinshan Island and soil fauna sampling sites. ZL, bamboo forest; QML, arboreal forest; GML, shrubbery; N, North slope; S, South slope.
| 类群 Group | 北坡 North slope | 南坡 South slope | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 Individuals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Dominance | 个体数 Individuals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Dominance | ||
| 蜱螨亚纲 Acari | 5,125 | 25,309 (74.26) | +++ | 3,833 | 18,928 (65.32) | +++ | |
| 弹尾纲 Collembola | 1,140 | 5,630 (16.52) | +++ | 1,320 | 6,519 (22.49) | +++ | |
| 线虫纲 Nematoda | 62 | 306 (0.90) | + | 198 | 978 (3.37) | ++ | |
| 原尾纲 Protura | 147 | 726 (2.13) | ++ | 42 | 207 (0.72) | + | |
| 线蚓科 Enchytraediae | 156 | 770 (2.26) | ++ | 28 | 138 (0.48) | + | |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 4 | 20 (0.06) | + | 132 | 652 (2.25) | ++ | |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 55 | 272 (0.80) | + | 78 | 385 (1.33) | ++ | |
| 双翅目幼虫 Diptera larvae | 48 | 237 (0.70) | + | 77 | 380 (1.31) | ++ | |
| 综合纲 Symphyla | 28 | 138 (0.41) | + | 24 | 119 (0.41) | + | |
| 等足目 Isopoda | 15 | 74 (0.22) | + | 36 | 178 (0.61) | + | |
| 少足纲 Pauropoda | 27 | 133 (0.39) | + | 17 | 84 (0.29) | + | |
| 倍足纲 Diplopoda | 25 | 123 (0.36) | + | 16 | 79 (0.27) | + | |
| 双尾纲 Diplura | 17 | 84 (0.25) | + | 15 | 74 (0.26) | + | |
| 鞘翅目成虫 Coleoptera adult | 10 | 49 (0.14) | + | 11 | 54 (0.19) | + | |
| 鞘翅目幼虫 Coleoptera larvae | 10 | 49 (0.14) | + | 7 | 35 (0.12) | + | |
| 拟蝎目 Pseudoscorpionida | 3 | 15 (0.14) | + | 10 | 49 (0.17) | + | |
| 石蜈蚣目 Lithobiomorpha | 7 | 35 (0.10) | + | 5 | 25 (0.09) | + | |
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 6 | 30 (0.09) | + | 4 | 20 (0.07) | + | |
| 缨翅目 Thysanoptera | 0 | 0 | 6 | 30 (0.10) | + | ||
| 鳞翅目幼虫 Lepodoptera larvae | 5 | 25 (0.07) | + | 1 | 5 (0.02) | + | |
| 等翅目 Isoptera | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 4 | 20 (0.07) | + | |
| 地蜈蚣目 Geophilomorpha | 2 | 10 (0.03) | + | 2 | 10 (0.03) | + | |
| 后孔寡毛目 Oligochaetaopisthopora | 4 | 20 (0.06) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 双翅目成虫 Diptera adult | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 1 | 5 (0.02) | + | |
| 直翅目 Orthptera | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 (0.02) | + | ||
| 啮目 Psocoptera | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 总数 Total | 6,901 | 34,079 | 5,868 | 28,978 | |||
Table 1 Soil fauna communities and densities (ind./m2) of south slope and north slope of Dajinshan Island
| 类群 Group | 北坡 North slope | 南坡 South slope | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 Individuals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Dominance | 个体数 Individuals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Dominance | ||
| 蜱螨亚纲 Acari | 5,125 | 25,309 (74.26) | +++ | 3,833 | 18,928 (65.32) | +++ | |
| 弹尾纲 Collembola | 1,140 | 5,630 (16.52) | +++ | 1,320 | 6,519 (22.49) | +++ | |
| 线虫纲 Nematoda | 62 | 306 (0.90) | + | 198 | 978 (3.37) | ++ | |
| 原尾纲 Protura | 147 | 726 (2.13) | ++ | 42 | 207 (0.72) | + | |
| 线蚓科 Enchytraediae | 156 | 770 (2.26) | ++ | 28 | 138 (0.48) | + | |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 4 | 20 (0.06) | + | 132 | 652 (2.25) | ++ | |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 55 | 272 (0.80) | + | 78 | 385 (1.33) | ++ | |
| 双翅目幼虫 Diptera larvae | 48 | 237 (0.70) | + | 77 | 380 (1.31) | ++ | |
| 综合纲 Symphyla | 28 | 138 (0.41) | + | 24 | 119 (0.41) | + | |
| 等足目 Isopoda | 15 | 74 (0.22) | + | 36 | 178 (0.61) | + | |
| 少足纲 Pauropoda | 27 | 133 (0.39) | + | 17 | 84 (0.29) | + | |
| 倍足纲 Diplopoda | 25 | 123 (0.36) | + | 16 | 79 (0.27) | + | |
| 双尾纲 Diplura | 17 | 84 (0.25) | + | 15 | 74 (0.26) | + | |
| 鞘翅目成虫 Coleoptera adult | 10 | 49 (0.14) | + | 11 | 54 (0.19) | + | |
| 鞘翅目幼虫 Coleoptera larvae | 10 | 49 (0.14) | + | 7 | 35 (0.12) | + | |
| 拟蝎目 Pseudoscorpionida | 3 | 15 (0.14) | + | 10 | 49 (0.17) | + | |
| 石蜈蚣目 Lithobiomorpha | 7 | 35 (0.10) | + | 5 | 25 (0.09) | + | |
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 6 | 30 (0.09) | + | 4 | 20 (0.07) | + | |
| 缨翅目 Thysanoptera | 0 | 0 | 6 | 30 (0.10) | + | ||
| 鳞翅目幼虫 Lepodoptera larvae | 5 | 25 (0.07) | + | 1 | 5 (0.02) | + | |
| 等翅目 Isoptera | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 4 | 20 (0.07) | + | |
| 地蜈蚣目 Geophilomorpha | 2 | 10 (0.03) | + | 2 | 10 (0.03) | + | |
| 后孔寡毛目 Oligochaetaopisthopora | 4 | 20 (0.06) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 双翅目成虫 Diptera adult | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 1 | 5 (0.02) | + | |
| 直翅目 Orthptera | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 (0.02) | + | ||
| 啮目 Psocoptera | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 1 | 5 (0.01) | + | 0 | 0 | ||
| 总数 Total | 6,901 | 34,079 | 5,868 | 28,978 | |||
| 类群 Group | 竹林 Bamboo forest | 乔木林 Arboreal forest | 灌木林 Shrubbery | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 Indivi- duals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Domin- ance | 个体数 Indi- viduals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Domin- ance | 个体数 Indi- viduals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Domin- ance | |||
| 蜱螨亚纲 Acari | 1,851 | 13,711 (60.65) | +++ | 2,929 | 21,696 (63.41) | +++ | 4,178 | 30,948 (81.95) | +++ | ||
| 弹尾纲 Collembola | 867 | 6,422 (28.41) | +++ | 1,087 | 8,052 (23.53) | +++ | 506 | 3,748 (9.93) | ++ | ||
| 线虫纲 Nematoda | 33 | 244 (1.08) | ++ | 169 | 1,252 (3.66) | ++ | 58 | 430 (1.14) | ++ | ||
| 原尾纲 Protura | 85 | 630 (2.79) | ++ | 85 | 630 (1.84) | ++ | 19 | 141 (0.37) | + | ||
| 线蚓科 Enchytraediae | 12 | 89 (0.39) | + | 100 | 741 (2.16) | ++ | 72 | 533 (1.41) | ++ | ||
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 3 | 22 (0.10) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | 131 | 970 (2.57) | ++ | ||
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 36 | 267 (1.18) | ++ | 74 | 548 (1.60) | ++ | 23 | 170 (0.45) | + | ||
| 双翅目幼虫 Diptera larvae | 37 | 274 (1.21) | ++ | 62 | 459 (1.34) | ++ | 26 | 193 (0.51) | + | ||
| 综合纲 Symphyla | 24 | 178 (0.79) | + | 15 | 111 (0.32) | + | 13 | 96 (0.26) | + | ||
| 等足目 Isopoda | 15 | 111 (0.49) | + | 20 | 148 (0.43) | + | 16 | 119 (0.31) | + | ||
| 少足纲 Pauropoda | 33 | 244 (1.08) | ++ | 5 | 37 (0.11) | + | 6 | 44 (0.12) | + | ||
| 倍足纲 Diplopoda | 18 | 133 (0.59) | + | 15 | 111 (0.32) | + | 8 | 59 (0.16) | + | ||
| 双尾纲 Diplura | 2 | 15 (0.07) | + | 23 | 170 (0.50) | + | 7 | 52 (0.14) | + | ||
| 鞘翅目成虫 Coleoptera adult | 10 | 74 (0.33) | + | 4 | 30 (0.09) | + | 7 | 52 (0.14) | + | ||
| 鞘翅目幼虫 Coleoptera larvae | 7 | 52 (0.23) | + | 6 | 44 (0.13) | + | 4 | 30 (0.08) | + | ||
| 拟蝎目 Pseudoscorpionida | 1 | 7 (0.03) | + | 11 | 81 (0.24) | + | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | ||
| 石蜈蚣目 Lithobiomorpha | 7 | 52 (0.23) | + | 4 | 30 (0.09) | + | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | ||
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 1 | 7 (0.03) | + | 4 | 30 (0.09) | + | 5 | 37 (0.10) | + | ||
| 缨翅目 Thysanoptera | 2 | 15 (0.07) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | ||
| 鳞翅目幼虫 Lepodoptera larvae | 2 | 15 (0.07) | + | 0 | 0 | 4 | 30 (0.08) | + | |||
| 等翅目 Isoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 37 (0.10) | + | ||||
| 地蜈蚣目 Geophilomorpha | 1 | 7 (0.03) | + | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | ||
| 后孔寡毛目 Oligochaetaopisthopora | 4 | 30 (0.13) | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 双翅目成虫 Diptera adult | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | ||||
| 直翅目 Orthptera | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 啮目 Psocoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | ||||
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 1 | 7 (0.13) | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 (0.02) | |||||
| 合计 Total | 3,052 | 22,607 (100) | 4,619 | 34,215 (100) | 5,098 | 37,763 (100) | |||||
Table 2 Soil fauna communities and densities (ind./m2) under different vegetation types on Dajinshan Island
| 类群 Group | 竹林 Bamboo forest | 乔木林 Arboreal forest | 灌木林 Shrubbery | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 Indivi- duals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Domin- ance | 个体数 Indi- viduals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Domin- ance | 个体数 Indi- viduals | 密度 Density (%) | 优势度 Domin- ance | |||
| 蜱螨亚纲 Acari | 1,851 | 13,711 (60.65) | +++ | 2,929 | 21,696 (63.41) | +++ | 4,178 | 30,948 (81.95) | +++ | ||
| 弹尾纲 Collembola | 867 | 6,422 (28.41) | +++ | 1,087 | 8,052 (23.53) | +++ | 506 | 3,748 (9.93) | ++ | ||
| 线虫纲 Nematoda | 33 | 244 (1.08) | ++ | 169 | 1,252 (3.66) | ++ | 58 | 430 (1.14) | ++ | ||
| 原尾纲 Protura | 85 | 630 (2.79) | ++ | 85 | 630 (1.84) | ++ | 19 | 141 (0.37) | + | ||
| 线蚓科 Enchytraediae | 12 | 89 (0.39) | + | 100 | 741 (2.16) | ++ | 72 | 533 (1.41) | ++ | ||
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 3 | 22 (0.10) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | 131 | 970 (2.57) | ++ | ||
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 36 | 267 (1.18) | ++ | 74 | 548 (1.60) | ++ | 23 | 170 (0.45) | + | ||
| 双翅目幼虫 Diptera larvae | 37 | 274 (1.21) | ++ | 62 | 459 (1.34) | ++ | 26 | 193 (0.51) | + | ||
| 综合纲 Symphyla | 24 | 178 (0.79) | + | 15 | 111 (0.32) | + | 13 | 96 (0.26) | + | ||
| 等足目 Isopoda | 15 | 111 (0.49) | + | 20 | 148 (0.43) | + | 16 | 119 (0.31) | + | ||
| 少足纲 Pauropoda | 33 | 244 (1.08) | ++ | 5 | 37 (0.11) | + | 6 | 44 (0.12) | + | ||
| 倍足纲 Diplopoda | 18 | 133 (0.59) | + | 15 | 111 (0.32) | + | 8 | 59 (0.16) | + | ||
| 双尾纲 Diplura | 2 | 15 (0.07) | + | 23 | 170 (0.50) | + | 7 | 52 (0.14) | + | ||
| 鞘翅目成虫 Coleoptera adult | 10 | 74 (0.33) | + | 4 | 30 (0.09) | + | 7 | 52 (0.14) | + | ||
| 鞘翅目幼虫 Coleoptera larvae | 7 | 52 (0.23) | + | 6 | 44 (0.13) | + | 4 | 30 (0.08) | + | ||
| 拟蝎目 Pseudoscorpionida | 1 | 7 (0.03) | + | 11 | 81 (0.24) | + | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | ||
| 石蜈蚣目 Lithobiomorpha | 7 | 52 (0.23) | + | 4 | 30 (0.09) | + | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | ||
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 1 | 7 (0.03) | + | 4 | 30 (0.09) | + | 5 | 37 (0.10) | + | ||
| 缨翅目 Thysanoptera | 2 | 15 (0.07) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | ||
| 鳞翅目幼虫 Lepodoptera larvae | 2 | 15 (0.07) | + | 0 | 0 | 4 | 30 (0.08) | + | |||
| 等翅目 Isoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 37 (0.10) | + | ||||
| 地蜈蚣目 Geophilomorpha | 1 | 7 (0.03) | + | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | ||
| 后孔寡毛目 Oligochaetaopisthopora | 4 | 30 (0.13) | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 双翅目成虫 Diptera adult | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 15 (0.04) | + | ||||
| 直翅目 Orthptera | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 啮目 Psocoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 (0.02) | + | ||||
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 1 | 7 (0.13) | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 (0.02) | |||||
| 合计 Total | 3,052 | 22,607 (100) | 4,619 | 34,215 (100) | 5,098 | 37,763 (100) | |||||
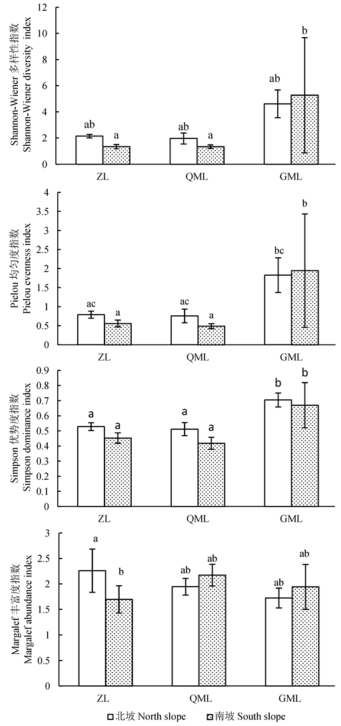
Fig. 2 Ecological indices of soil fauna communities of different vegetation types in Dajinshan Island (Mean ± SD). Different letters show the significant difference at P = 0.05 level. ZL, bamboo forest; QML, arboreal forest; GML, shrubbery.
| 1 | Addison JA, Trofymow JA, Marshall VG (2003) Abundance, species diversity, and community structure of Collembola in successional coastal temperate forests on Vancouver Island, Canada. Applied Soil Ecology, 24, 233-246. |
| 2 | Babenko AB (2010) The springtail (Hexapoda, Collembola) fauna of Wrangel Island. Entomological Review, 90, 571-584. |
| 3 | Chen XN, You WH, Wang XY, Yi L (2009a) Community traits of soil animal under different ground cover treatments in evergreen broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science, 17, 160-167.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈小鸟, 由文辉, 王向阳, 易兰 (2009a) 常绿阔叶林不同砍伐处理下土壤动物的群落特征. 生物多样性 17, 160-167.] | |
| 4 | Chen XN, You WH, Yi L (2009b) Community structure of soil fauna along an altitudinal gradient in Taibai Mountain of Tiantong Region, Zhejiang Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 28, 270-276.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈小鸟, 由文辉, 易兰 (2009b) 浙江天童太白山不同海拔土壤动物的群落结构. 生态学杂志 28, 270-276.] | |
| 5 | Cheng F, Cheng JP, Sang HC, Yu JL, Xi L, Pi SS (2013) Assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metals pollution in soil of Dajinshan Island. Environmental Science, 34, 1062-1066.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程芳, 程金平, 桑恒春, 于金莲, 席磊, 皮帅帅 (2013) 大金山岛土壤重金属污染评价及相关性分析. 环境科学 34, 1062-1066.] | |
| 6 | Čuchta P, Miklisová D, Kováč L (2012) A three-year study of soil Collembola communities in spruce forest stands of the High Tatra Mts (Slovakia) after a catastrophic windthrow event. European Journal of Soil Biology, 50, 151-158. |
| 7 | Da LJ, Yang YC, Chen YP (2004) The diversity of plant community on Dajinshan Island, Shanghai. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 2(3), 22-25.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [达良俊, 杨永川, 陈燕萍 (2004) 上海大金山岛的自然植物群落多样性. 城镇绿化 2(3), 22-25.] | |
| 8 | Decaënsa T, Jiménezb JJ, Gioiac C, Measeyb GJ, Lavelleb P (2006) The values of soil animals for conservation biology. European Journal of Soil Biology, 42, 23-38. |
| 9 | Gao Y, Bu Y, Luan YX, Yang YM, Ke X (2007) Community composition and diversity of soil fauna in the land use of city planning: a case study in Shanghai World Exposition Site. Biodiversity Science, 15, 207-214.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高艳, 卜云, 栾云霞, 杨毅明, 柯欣 (2007) 城市新规划地土壤动物群落组成和多样性: 以上海市世博会会址为例. 生物多样性 15, 207-214.] | |
| 10 | Gladys LM, Daniel I, France BR, Patrick L (2007) Soil fauna abundance and diversity in a secondary semi-evergreen forest in Guadeloupe (Lesser Antilles): influence of soil type and dominant tree species. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 44, 269-276. |
| 11 | Greenslade P, Convey P (2011) Exotic Collembola on subantarctic islands: pathways, origins and biology. Biological Invasions, 14, 405-417. |
| 12 | Gudleifsson BE, Bjarnadottir B (2008) Springtail (Collembola) populations in hayfields and pastures in northern Iceland. Icelandic Agricultural Sciences, 21, 49-59. |
| 13 | Hugo EA, Chown SL, McGeoch MA (2006) The microarthropods of sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Island: a quantitative assessment. Polar Biology, 30, 109-119. |
| 14 | Jin SK, Wang JJ, Zhu S, Zhang Q, Li X, Zheng WJ, You WH (2016) Soil meso- and micro-fauna community structures in different urban forest types in Shanghai, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 2363-2371.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [靳士科, 王娟娟, 朱莎, 张琪, 黎翔, 郑文静, 由文辉 (2016) 上海市不同类型城市森林中小型土壤动物群落结构特征. 应用生态学报 27, 2363-2371.] | |
| 15 | Jin YL, You WH, Yi L, Wang XY, Wang Q (2011) Ecological distribution of collembola in the litter of Tiantong forest ecosystems, Zhejiang. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20, 241-247.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [靳亚丽, 由文辉, 易兰, 王向阳, 王强 (2011) 天童森林生态系统凋落物层跳虫群落的生态学研究. 生态环境学报 20, 241-247.] | |
| 16 | Kardol P, Cregger MA, Campany CE, Classen AT (2010) Soil ecosystem functioning under climate change: plant species and community effects. Ecology, 91, 767-781. |
| 17 | Li BC (2014) Scientific Research Report of Dajinshan Island, Shanghai. Shanghai Science and Technology Education Publishing House, Shanghai.(in Chinese) |
| [李必成 (2014)大金山岛科学考察报告. 上海科技教育出版社, 上海.] | |
| 18 | Li W, Cui LJ, Zhao XS, Zhang MY, Gao CJ, Zhang Y, Wang YF (2015) Community structure and diversity of soil animals in the Lake Taihu ladeshore wetland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 944-955.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李伟, 崔丽娟, 赵欣胜, 张曼胤, 高常军, 张岩, 王义飞 (2015) 太湖岸带湿地土壤动物群落结构与多样性. 生态学报 35, 944-955.] | |
| 19 | Liao CH, Li JX, Huang HT (1997) Soil animal community diversity in the forest of the southern subtropical region, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 17, 549-555.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖崇惠, 李健雄, 黄海涛 (1997) 南亚热带森林土壤动物群落多样性研究. 生态学报 17, 549-555.] | |
| 20 | Lin YH, Zhang FD, Zhang JQ, Ouyang XJ, Mo DS, Zhou GY (2005) Preliminary investigation on temporal and spatial variation of structure of soil fauna community in different natural vegetations of Dinghushan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2616-2622.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林英华, 张夫道, 张俊清, 欧阳学军, 莫定生, 周国逸 (2005) 鼎湖山不同自然植被土壤动物群落结构时空变化. 生态学报 25, 2616-2622.] | |
| 21 | Liu Y, Zhang A, Yan Y, Li K, Fang Y (2011) Diversity of soil animal community under different land-use types in Chongming Island. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 50, 288-295.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘扬, 张岸, 严莹, 李恺, 方燕 (2011) 崇明岛不同土地利用类型下土壤动物群落多样性研究. 复旦学报(自然科学版) 50, 288-295.] | |
| 22 | Malmström A, Persson T, Ahlström K (2008) Effects of fire intensity on survival and recovery of soil microarthropods after a clearcut burning. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 38, 2465-2475. |
| 23 | Sadaka N, Ponge JF (2003) Soil animal communities in holm oak forests: influence of horizon, altitude and year. European Journal of Soil Biology, 39, 197-207. |
| 24 | Sterzynska M, Bloger T (2004) Collembola of North Bull Island—new records for the Irish coast. Fragmenta Faunistica, 47, 47-50. |
| 25 | Su YC, Gou YB, Yu D, Wang JY (2004) Diversity of soil invertebrate communities at Yushan Hill, Changshu, Jiangsu Province. Biodiversity Science, 12, 333-338. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [苏永春, 勾影波, 郁达, 王继元 (2004) 江苏常熟虞山土壤动物群落多样性研究. 生物多样性 12, 333-338.] | |
| 26 | Sun RY (2001) Principles of Animal Ecology, 3rd version. Beijing Normal University Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [孙儒泳 (2001) 动物生态学原理, 第3版. 北京师范大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 27 | Wang Q, Luo Y, Jin YL, You WH (2012) Community structure of soil fauna in forest belt of different areas of Shanghai in Fall. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 28, 669-674.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王强, 罗燕, 靳亚丽, 由文辉 (2012) 上海市外环林带秋季不同区域土壤动物群落结构. 生态与农村环境学报 28, 669-674.] | |
| 28 | Wardle DA, Bardtett RD, Klironomos JN, Setala H, Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science, 304, 1629-1633. |
| 29 | Wolters V (2001) Biodiversity of soil animals and its function. European Journal of Soil Biology, 37, 221-227. |
| 30 | Wu HT, Lü XG, Yang Q, Jiang M (2006) Ecological characteristics and functions of soil fauna community. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 43, 314-323.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [武海涛, 吕宪国, 杨青, 姜明 (2006) 土壤动物主要生态特征与生态功能研究进展. 土壤学报 43, 314-323.] | |
| 31 | Yang YC, Da LJ, Qin XK (2002) A study on the flora of Dajinshan Island in Shanghai, China. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 20, 433-437.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨永川, 达良俊, 秦祥堃 (2002) 上海大金山岛种子植物区系的研究.武汉植物学研究 20, 433-437.] | |
| 32 | Yi L (2005) Influences of Secondary Succession of the Damaged Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest on Soil Animal Community in Tiantong, Zhejiang Province. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [易兰 (2005) 浙江天童受损常绿阔叶林的次生演替对土壤动物群落的影响. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| 33 | Yi L, You WH, Song YC (2005) Soil animal communities in the litter of the evergreen broad-leaved forest at five succession stages in Tiantong. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 466-473.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [易兰, 由文辉, 宋永昌 (2005) 天童常绿阔叶林五个演替阶段凋落物中的土壤动物群落. 生态学报 25, 466-473.] | |
| 34 | Yin WY (1998) Pictorial Keys to Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1998) 中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 35 | Yin WY (1992) Subtropical Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1992) 中国亚热带土壤动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | Teng Wang, Chunhou Li, Guanghua Wang, Jinfa Zhao, Juan Shi, Hongyu Xie, Yong Liu, Yu Liu. Species composition and succession of coral reef fishes on Qilianyu Island, Xisha Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23481-. |
| [3] | Siqi Tao, Feiling Yang, Chaolang Hua, Ruidong Wu. Priority assessment for natural vegetation conservation in Yunnan Province by integrating threatened status and conservation value [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23324-. |
| [4] | Bin Wang, Yiqian Zhong, Meixue Yang, Miaorui Wu, Yanping Wang, Fang Lu, Wanglan Tao, Jianxing Li, Hongming Zhao, Shengyuan Liu, Wusheng Xiang, Xiankun Li. Spatial variation of non-structural carbohydrates in the leaves of dominant tree species and ecological driving factors in a karst seasonal rainforest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24325-. |
| [5] | Xiaodan Tan, Peng Zhang, Sirui Zhu, Xiang Liu, Shurong Zhou, Mu Liu. Effect of shrub encroachment on insect herbivory of Polygonum macrophyllum in alpine meadow of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23417-. |
| [6] | Yanqiu Xie, Hui Huang, Chunxiao Wang, Yaqin He, Yixuan Jiang, Zilin Liu, Chuanyuan Deng, Yushan Zheng. Determinants of species-area relationship and species richness of coastal endemic plants in the Fujian islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [7] | Hong Chen, Xiaoqing Xian, Yixue Chen, Na Lin, Miaomiao Wang, Zhipeng Li, Jian Zhao. Spatial pattern and driving factors on the prevalence of red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) in island cities: A case study of Haitan Island, Fujian [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22501-. |
| [8] | Xiaofan Shang, Jian Zhang, Haojie Gao, Weipeng Ku, Yuke Bi, Xiupeng Li, Enrong Yan. Island area and climate jointly impact seed plant richness patterns across the Zhoushan Archipelago [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [9] | Chang Cai, Xue Zhang, Chen Zhu, Yuhao Zhao, Gexia Qiao, Ping Ding. Nested assemblages of aphid species in the Thousand Island Lake: The importance of island area and host plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23183-. |
| [10] | Yanping Wang, Minchu Zhang, Chengxiu Zhan. A review on the nested distribution pattern (nestedness): Analysis methods, mechanisms and conservation implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [11] | De Gao, Yanping Wang. A review of the small-island effect detection methods and method advancement [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [12] | Yanjie Zuo, Mingchun Peng, Chongyun Wang, Zehao Shen, Yongping Li, Xinmao Zhou, Jie Zhou, Guangxin Zhou, Jiaxin Ren, Zhong’an Liu. Islandization and species diversity of semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forests in the Central Yunnan Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23252-. |
| [13] | Yajun Sun. Why do we believe in Darwin’s theory of evolution—On the 25 folds of aesthetic parsimony of On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(9): 22243-. |
| [14] | Qi Zhao, Jibao Jiang, Zenglu Zhang, Qing Jin, Jiali Li, Jiangping Qiu. Species composition and phylogenetic analysis of earthworms on Hainan Island [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| [15] | Wenyu Song, Xueyou Li, Hongjiao Wang, Zhongzheng Chen, Shuiwang He, Xuelong Jiang. Multi-dimensional evaluation of small mammal diversity in tree line habitats across the Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Areas: Implications for conservation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1215-1228. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn