



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 23299. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023299 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023299
• Special Feature: Celebrating Alfred Russel Wallace’s Bicentenary • Previous Articles Next Articles
De Gao1,2( ), Yanping Wang1,*(
), Yanping Wang1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-08-24
Accepted:2023-12-11
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2023-12-30
Contact:
E-mail: De Gao, Yanping Wang. A review of the small-island effect detection methods and method advancement[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23299.
| 模型形状 Model shape | 模型 Model | 公式 Equation1 | 参数数量 Number of parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 直线形 Linear shape | 线性模型 Linear | S = c + z × A | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 渐近模型 Asymptotic | S = d − c × z^A | 3 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 对数模型 Logarithmic | S = c + z × log(A) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 小林模型 Kobayashi | S = c × log(1 + A/z) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 莫诺模型 Monod | S = d/(1 + c × A^(−1)) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 负指数模型 Negative exponential | S = d × (1 − exp(−z × A)) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 持久性函数1模型 Persistence function 1 | S = c × A^z × exp(−d × A) | 3 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 幂函数模型 Power | S = c × A^z | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 罗森茨魏格幂函数模型 Power Rosenzweig | S = f + c × A^z | 3 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 有理函数模型 Rational | S = (c + z × A)/(1 + d × A) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 扩展幂函数2模型 Extended power 2 | S = c × A^(z − (d/A)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 冈珀茨模型 Gompertz | S = d × exp(−exp(−z × (A − c))) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 逻辑斯蒂模型 Logistic | S = c/(f + A^(−z)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 摩根-默瑟-弗洛丁模型 Morgan-Mercer-Flodin | S = d/(1 + c × A^(−z)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 持久性函数2模型 Persistence function 2 | S = c × A^z × exp(−d/A) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 威布尔-3模型 Weibull-3 | S = d × (1 − exp(−c × A^z)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 威布尔-4模型 Weibull-4 | S = d × (1 − exp(−c × A^z))^f | 4 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | Beta-P模型 Beta-P | S = d × (1 − (1 + (A/c)^z)^(−f)) | 4 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 查普曼-理查兹模型 Chapman-Richards | S = d × (1 − exp(−z × A)^c) | 3 |
| “C”形或“S”形 Convex or sigmoidal shape | 扩展幂函数1模型 Extended power 1 | S = c × A^(z × A^(−d)) | 3 |
Table 1 The 20 species-area relationship models available in the sars package (modified from Matthews et al, 2019)
| 模型形状 Model shape | 模型 Model | 公式 Equation1 | 参数数量 Number of parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 直线形 Linear shape | 线性模型 Linear | S = c + z × A | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 渐近模型 Asymptotic | S = d − c × z^A | 3 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 对数模型 Logarithmic | S = c + z × log(A) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 小林模型 Kobayashi | S = c × log(1 + A/z) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 莫诺模型 Monod | S = d/(1 + c × A^(−1)) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 负指数模型 Negative exponential | S = d × (1 − exp(−z × A)) | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 持久性函数1模型 Persistence function 1 | S = c × A^z × exp(−d × A) | 3 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 幂函数模型 Power | S = c × A^z | 2 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 罗森茨魏格幂函数模型 Power Rosenzweig | S = f + c × A^z | 3 |
| “C”形 Convex shape | 有理函数模型 Rational | S = (c + z × A)/(1 + d × A) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 扩展幂函数2模型 Extended power 2 | S = c × A^(z − (d/A)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 冈珀茨模型 Gompertz | S = d × exp(−exp(−z × (A − c))) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 逻辑斯蒂模型 Logistic | S = c/(f + A^(−z)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 摩根-默瑟-弗洛丁模型 Morgan-Mercer-Flodin | S = d/(1 + c × A^(−z)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 持久性函数2模型 Persistence function 2 | S = c × A^z × exp(−d/A) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 威布尔-3模型 Weibull-3 | S = d × (1 − exp(−c × A^z)) | 3 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 威布尔-4模型 Weibull-4 | S = d × (1 − exp(−c × A^z))^f | 4 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | Beta-P模型 Beta-P | S = d × (1 − (1 + (A/c)^z)^(−f)) | 4 |
| “S”形 Sigmoidal shape | 查普曼-理查兹模型 Chapman-Richards | S = d × (1 − exp(−z × A)^c) | 3 |
| “C”形或“S”形 Convex or sigmoidal shape | 扩展幂函数1模型 Extended power 1 | S = c × A^(z × A^(−d)) | 3 |
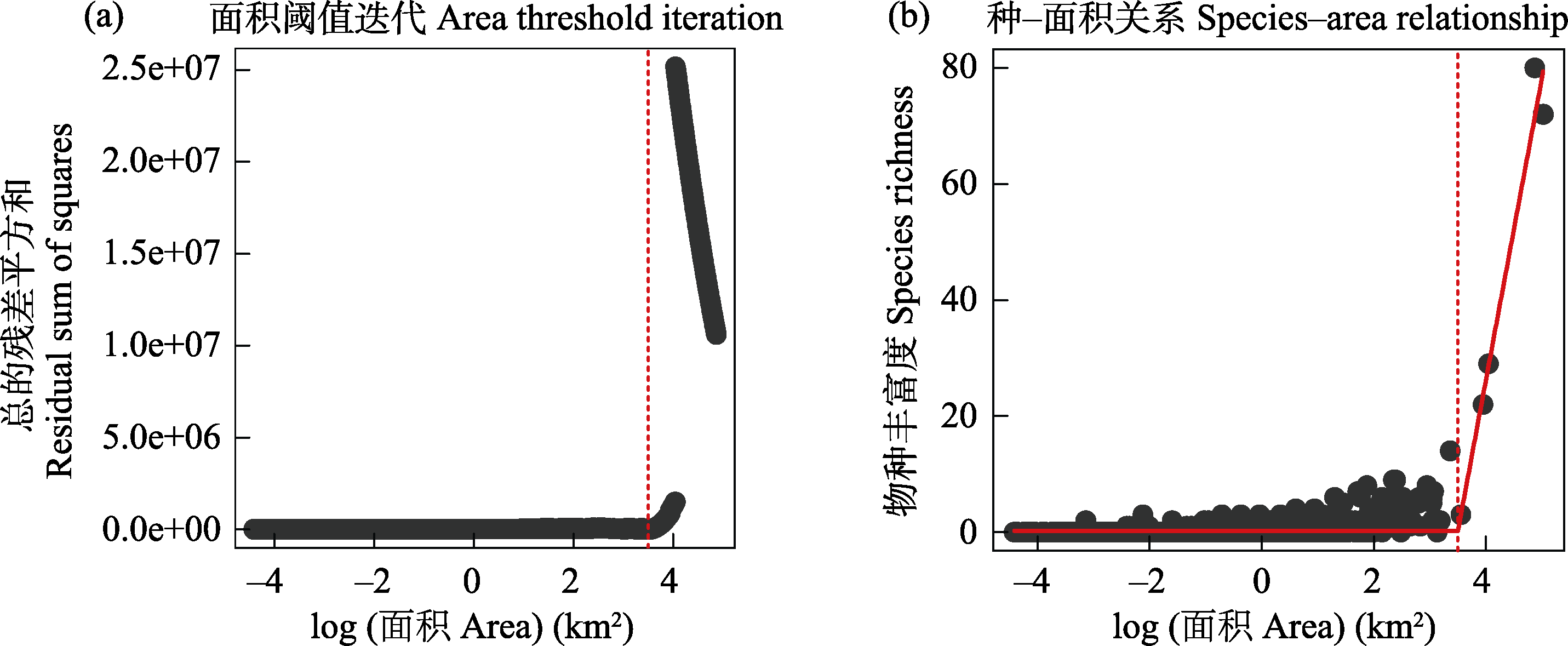
Fig. 2 Fitting the species-area relationship of amphibians of the West Indies using a two-segmented piecewise regression models with a flat slope within the area threshold (Model 4 in Gao & Wang, 2022). (a) The residual sum of squares varies with the iteration of the area threshold; (b) Fitting results of the species-area relationship. The data used for analysis are from Appendix 1.
| 模型 Model | 公式 Equation1 | 片段数量 Number of segments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 log A + (log A > T1) [z1 T1 + z2 (log A - T1)] | 2 |
| 2 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) [z1 log A + (z2 - z1) T1] + (log A > T1) z2 log A | 2 |
| 3 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1) (c2 + z2 log A) | 2 |
| 4 | Y = c1 + (log A > T1) z1 (log A - T1) | 2 |
| 5 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 T1 + (log A > T1) z1 log A | 2 |
| 6 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) c1 + (log A > T1) (c2 + z1 log A) | 2 |
| 7 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 log A + (log A > T1) z1 T1 | 2 |
| 8 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 (log A - T1) | 2 |
| 9 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1) c2 | 2 |
| 10 | Y = (log A ≤ T2) [c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 T1 + (log A > T1) z1 log A] + (log A > T2) (c2 + z2 log A) | 3 |
| 11 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) c1 + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) (c2 + z1 log A) + (log A > T2) (c3 + z2 log A) | 3 |
| 12 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) (c2 + z2 log A) + (log A > T2) (c3 + z3 log A) | 3 |
| 13 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) (c2 + z2 log A) + (log A > T2) c3 | 3 |
| 14 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) [(c1 - c2 + z1 T1 - z2 T2) (log A - T1) / (T1 -T2) + c1 + z1 T1] + (log A > T2) (c2 + z2 log A) | 3 |
Table 2 The 14 piecewise models for the detection of the small-island effect (organized from Gao et al, 2019)
| 模型 Model | 公式 Equation1 | 片段数量 Number of segments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 log A + (log A > T1) [z1 T1 + z2 (log A - T1)] | 2 |
| 2 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) [z1 log A + (z2 - z1) T1] + (log A > T1) z2 log A | 2 |
| 3 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1) (c2 + z2 log A) | 2 |
| 4 | Y = c1 + (log A > T1) z1 (log A - T1) | 2 |
| 5 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 T1 + (log A > T1) z1 log A | 2 |
| 6 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) c1 + (log A > T1) (c2 + z1 log A) | 2 |
| 7 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 log A + (log A > T1) z1 T1 | 2 |
| 8 | Y = c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 (log A - T1) | 2 |
| 9 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1) c2 | 2 |
| 10 | Y = (log A ≤ T2) [c1 + (log A ≤ T1) z1 T1 + (log A > T1) z1 log A] + (log A > T2) (c2 + z2 log A) | 3 |
| 11 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) c1 + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) (c2 + z1 log A) + (log A > T2) (c3 + z2 log A) | 3 |
| 12 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) (c2 + z2 log A) + (log A > T2) (c3 + z3 log A) | 3 |
| 13 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) (c2 + z2 log A) + (log A > T2) c3 | 3 |
| 14 | Y = (log A ≤ T1) (c1 + z1 log A) + (log A > T1 AND log A ≤ T2) [(c1 - c2 + z1 T1 - z2 T2) (log A - T1) / (T1 -T2) + c1 + z1 T1] + (log A > T2) (c2 + z2 log A) | 3 |
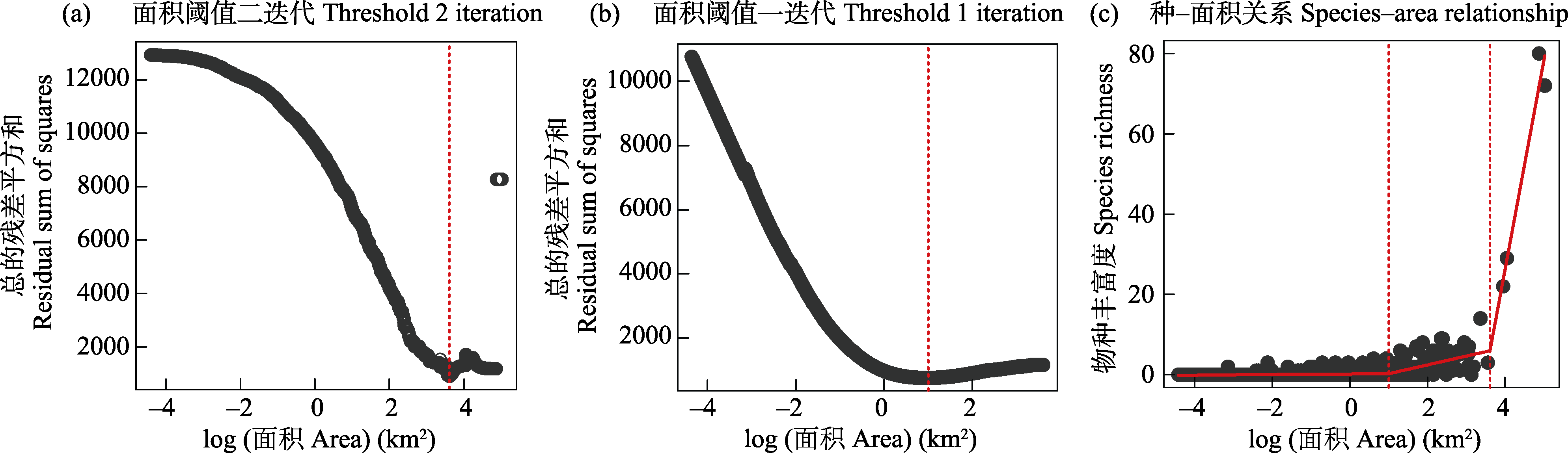
Fig. 3 Fitting the species-area relationship of amphibians of the West Indies using a three-segmented piecewise regression model (Model 6 in Gao & Wang, 2022). (a) The residual sum of squares varies with the iteration of the second area threshold; (b) The residual sum of squares varies with the iteration of the first area threshold; (c) Fitting results of the species-area relationship. The data used for analysis are from Appendix 1.
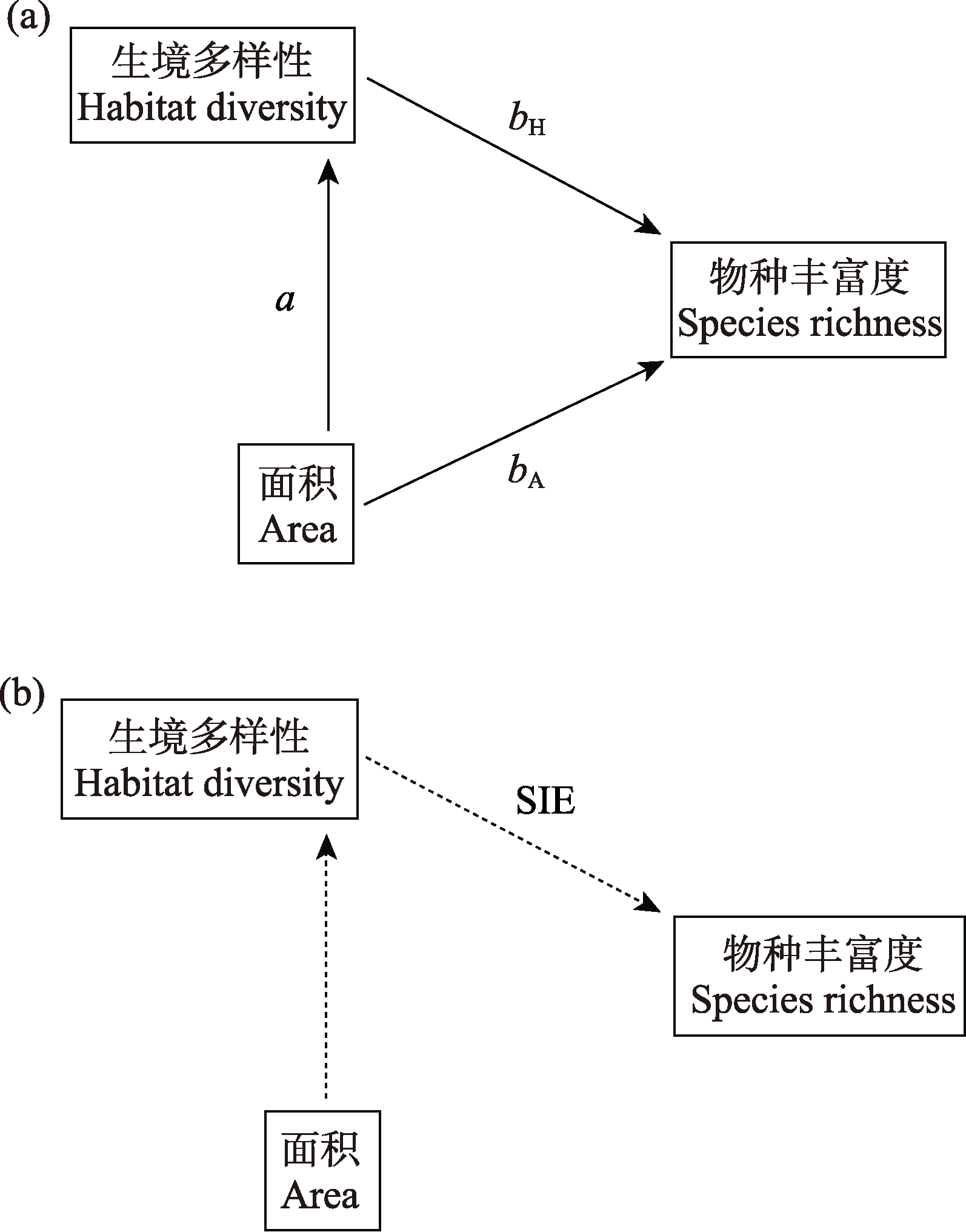
Fig. 4 A structural equation model for the effects of area and habitat diversity on species richness according to Triantis et al, 2006. (a) On large islands, area has both direct and indirect impacts on species richness; (b) On small islands, the direct impact of area on species richness disappears. a, bA, bH, and SIE are standardized regression coefficients. Solid and dashed lines represent the significant and non-significant effects at the 0.05 level respectively.
| 属性 Attribute | 种-面积关系形状比较法 SAR shape comparison | 断点回归法Breakpoint/piecewise regression | 零模型法Null model | 路径分析法Path analysis | 树模型法Tree-based model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 能否计算SIE面积阈值 Whether being able to calculate the SIE area threshold | 否 No | 是 Yes | 否 No | 是 Yes | 是 Yes |
| 能否判断SIE区间内SAR具有斜率 Whether being able to determine SAR slope within the limit of the SIE | 否 No | 是 Yes | 否 No | 否 No | 否 No |
| 是否只依赖岛屿面积和物种丰富度数据 Whether only relying on island area and species richness data | 是 Yes | 是 Yes | 是 Yes | 否 No | 否 No |
| 是否必须将岛屿面积对数转化 Whether logarithmic transformation is required for island area | 否 No | 是 Yes | 否 No | 否 No | 否 No |
| 犯I类错误的概率 Probability of making type I error1 | 低 Low | 高 High | 低 Low | 低 Low | 低 Low |
| 犯II类错误的概率 Probability of making type II error2 | 高 High | 低 Low | 低 Low | 高 High | 高 High |
| 使用这5种SIE检测方法的论文数 Number of publications using the five SIE detection methods | 5 | 45 | 4 | 9 | 1 |
Table 3 Attribute comparison among the five small-island effect (SIE) detection methods
| 属性 Attribute | 种-面积关系形状比较法 SAR shape comparison | 断点回归法Breakpoint/piecewise regression | 零模型法Null model | 路径分析法Path analysis | 树模型法Tree-based model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 能否计算SIE面积阈值 Whether being able to calculate the SIE area threshold | 否 No | 是 Yes | 否 No | 是 Yes | 是 Yes |
| 能否判断SIE区间内SAR具有斜率 Whether being able to determine SAR slope within the limit of the SIE | 否 No | 是 Yes | 否 No | 否 No | 否 No |
| 是否只依赖岛屿面积和物种丰富度数据 Whether only relying on island area and species richness data | 是 Yes | 是 Yes | 是 Yes | 否 No | 否 No |
| 是否必须将岛屿面积对数转化 Whether logarithmic transformation is required for island area | 否 No | 是 Yes | 否 No | 否 No | 否 No |
| 犯I类错误的概率 Probability of making type I error1 | 低 Low | 高 High | 低 Low | 低 Low | 低 Low |
| 犯II类错误的概率 Probability of making type II error2 | 高 High | 低 Low | 低 Low | 高 High | 高 High |
| 使用这5种SIE检测方法的论文数 Number of publications using the five SIE detection methods | 5 | 45 | 4 | 9 | 1 |
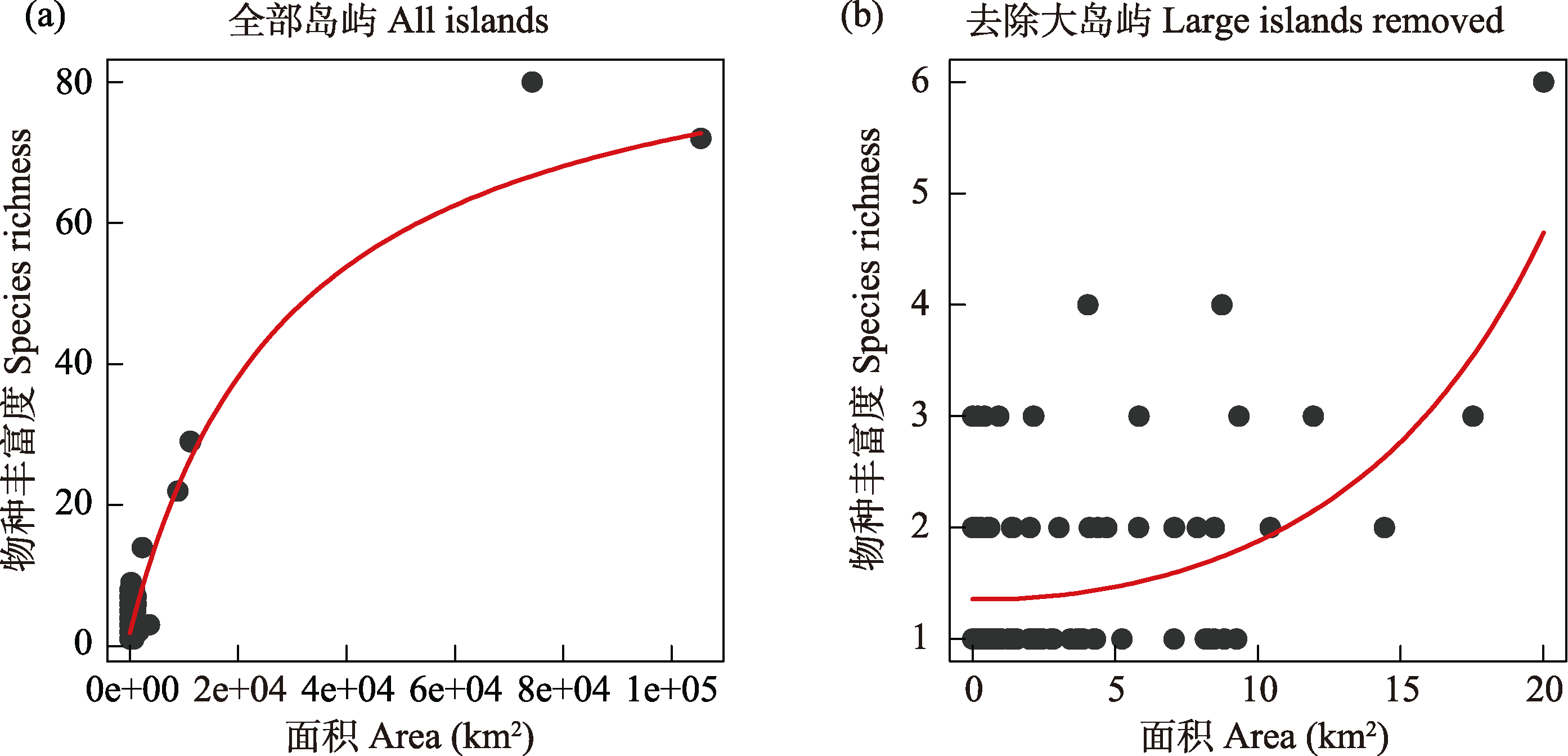
Fig. 7 The species-area relationship of amphibians of the West Indies. (a) All amphibian-inhabited islands; (b) Removing the top 40% of large islands from all amphibian-inhabited islands. The data used for analysis are from Appendix 1.
| [1] |
Arrhenius O (1921) Species and area. Journal of Ecology, 9, 95-99.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach. Springer, New York. |
| [3] |
Burns KC, McHardy PR, Pledger S (2009) The small-island effect: Fact or artefact? Ecography, 32, 269-276.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Chen CW, Xu AC, Wang YP (2021) Area threshold and trait-environment associations of butterfly assemblages in the Zhoushan Archipelago, China. Journal of Biogeography, 48, 785-797.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chen CW, Yang XR, Tan XW, Wang YP (2020) The role of habitat diversity in generating the small-island effect. Ecography, 43, 1241-1249.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Connor EF, McCoy ED (1979) The statistics and biology of the species-area relationship. The American Naturalist, 113, 791-833.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
De’ath G, Fabricius KE (2000) Classification and regression trees: A powerful yet simple technique for ecological data analysis. Ecology, 81, 3178-3192.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Dengler J (2010) Robust methods for detecting a small island effect. Diversity and Distributions, 16, 256-266.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Dengler J, Matthews TJ, Steinbauer MJ, Wolfrum S, Boch S, Chiarucci A, Conradi T, Dembicz I, Marcenò C, García‐Mijangos I, Nowak A, Storch D, Ulrich W, Campos JA, Cancellieri L, Carboni M, Ciaschetti G, De Frenne P, Dolezal J, Dolnik C, Essl F, Fantinato E, Filibeck G, Grytnes J-A, Guarino R, Güler B, Janišová M, Klichowska E, Kozub Ł, Kuzemko A, Manthey M, Mimet A, Naqinezhad A, Pedersen C, Peet RK, Pellissier V, Pielech R, Potenza G, Rosati L, Terzi M, Valkó O, Vynokurov D, White H, Winkler M, Biurrun I (2020) Species-area relationships in continuous vegetation: Evidence from Palaearctic grasslands. Journal of Biogeography, 47, 72-86.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Drakare S, Lennon JJ, Hillebrand H (2006) The imprint of the geographical, evolutionary and ecological context on species-area relationships. Ecology Letters, 9, 215-227.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Fattorini S (2007) To fit or not to fit? A poorly fitting procedure produces inconsistent results when the species-area relationship is used to locate hotspots. Biodiversity and Conservation, 16, 2531-2538.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Forster G (1777) A voyage around the world in his Majesty’s sloop, resolution, commanded by Captain James Cook, during the years 1772, 3, 4, and 5. B. Volume 1. White B, Robson J, Elmsly P, Robinson G, London. |
| [13] | Forster JR (1778) Observations made During a Voyage Round the World. Robinson G, London. |
| [14] |
Gao D, Cao Z, Xu P, Perry G (2019) On piecewise models and species-area patterns. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 8351-8361.
DOI |
| [15] |
Gao D, Perry G (2016) Detecting the small island effect and nestedness of herpetofauna of the West Indies. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 5390-5403.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Gao D, Wang YP (2022) A global synthesis of the small-island effect in amphibians and reptiles. Ecography, 2022, e05957. |
| [17] |
Gao D, Wang YP (2024) Non-linear thresholds in the effect of area on three dimensions of diversity of herpetofauna in the West Indies. Journal of Biogeography, 51, 439-453.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Gentile G, Argano R (2005) Island biogeography of the Mediterranean Sea: The species-area relationship for terrestrial isopods. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 1715-1726.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Gilpin ME, Diamond JM (1976) Calculation of immigration and extinction curves from the species-area-distance relation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 73, 4130-4134. |
| [20] |
Guilhaumon F, Mouillot D, Gimenez O (2010) mmSAR: An R-package for multimodel species-area relationship inference. Ecography, 33, 420-424.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Harcourt AH, Doherty DA (2005) Species-area relationships of primates in tropical forest fragments: A global analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology, 42, 630-637.
DOI URL |
| [22] | He F, Legendre P (2002) Species diversity patterns derived from species-area models. Ecology, 83, 1185-1198. |
| [23] | Henderson RW, Powell R (2001) Responses by the West Indian herpetofauna to human-influenced resources. Caribbean Journal of Science, 37, 41-54. |
| [24] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. |
| [25] |
Lomolino MV (2000) Ecology’s most general, yet protean pattern: The species-area relationship. Journal of Biogeography, 27, 17-26.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Lomolino MV, Weiser MD (2001) Towards a more general species-area relationship: Diversity on all islands, great and small. Journal of Biogeography, 28, 431-445.
DOI URL |
| [27] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. |
| [28] | Matthews TJ, Rigal F (2021) Thresholds and the species-area relationship: A set of functions for fitting, evaluating and plotting a range of commonly used piecewise models in R. Frontiers of Biogeography, 13, e49404. |
| [29] |
Matthews TJ, Rigal F, Kougioumoutzis K, Trigas P, Triantis KA (2020) Unravelling the small-island effect through phylogenetic community ecology. Journal of Biogeography, 47, 2341-2352.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Matthews TJ, Triantis KA, Whittaker RJ, Guihaumon F (2019) sar: An R package for fitting, evaluating and comparing species-area relationship models. Ecography, 42, 1446-1455.
DOI |
| [31] |
Menegotto A, Rangel TF, Schrader J, Weigelt P, Kreft H (2020) A global test of the subsidized island biogeography hypothesis. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 320-330.
DOI |
| [32] |
Morrison LW (2014) The small-island effect: Empty islands, temporal variability and the importance of species composition. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 1007-1017.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Muggeo VMR (2008) Segmented: An R package to fit regression models with broken-line relationships. R News, 8, 20-25. |
| [34] |
Neigel JE (2003) Species-area relationships and marine conservation. Ecological Applications, 13, 138-145.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Niering WA (1963) Terrestrial ecology of Kapingamarangi atoll, Caroline Islands. Ecological Monographs, 33, 131-160.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Qie L, Lee TM, Sodhi NS, Lim SLH (2011) Dung beetle assemblages on tropical land-bridge islands: Small island effect and vulnerable species. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 792-804.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Raxworthy CJ, Nussbaum RA (2000) Extinction and extinction vulnerability of amphibians and reptiles in Madagascar. Amphibian and Reptile Conservation, 2, 15-23. |
| [38] | Rosenzweig ML (1995) Species Diversity in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [39] | Rosenzweig ML (2004) Applying species-area relationships to the conservation of diversity. In: Frontiers of Biogeography: New Directions in the Geography of Nature (eds Lomolino MV, Heaney LR), pp. 325-343. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA. |
| [40] |
Rosindell J, Cornell SJ (2009) Species-area curves, neutral models, and long-distance dispersal. Ecology, 90, 1743-1750.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Schrader J, König C, Triantis KA, Trigas P, Kreft H, Weigelt P (2020) Species-area relationships on small islands differ among plant growth forms. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 814-829.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Schrader J, Moeljono S, Keppel G, Kreft H (2019) Plants on small islands revisited: The effects of spatial scale and habitat quality on the species-area relationship. Ecography, 42, 1405-1414.
DOI |
| [43] |
Sfenthourakis S (1996) The species-area relationship of terrestrial isopods (Isopoda; Oniscidea) from the Aegean Archipelago (Greece): A comparative study. Global Ecology and Biogeography Letters, 5, 149-157.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Sfenthourakis S, Triantis KA, Proios K, Rigal F (2021) The role of ecological specialization in shaping patterns of insular communities. Journal of Biogeography, 48, 243-252.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Sonderegger D (2020) SiZer: Significant Zero Crossings. R package version 0.1-7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=SiZer. (accessed on 2022-07-09) |
| [46] |
Stark SC, Bunker DE, Carson WP (2006) A null model of exotic plant diversity tested with exotic and native species-area relationships. Ecology Letters, 9, 136-141.
PMID |
| [47] |
Tjørve E (2003) Shapes and functions of species-area curves: A review of possible models. Journal of Biogeography, 30, 827-835.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
I) A review of new models and parameterizations. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 1435-1445.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Triantis KA, Guilhaumon F, Whittaker RJ (2012) The island species-area relationship: Biology and statistics. Journal of Biogeography, 39, 215-231.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Triantis KA, Sfenthourakis S (2012) Island biogeography is not a single-variable discipline: The small island effect debate. Diversity and Distributions, 18, 92-96.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Triantis KA, Vardinoyannis K, Tsolaki EP, Botsaris I, Lika K, Mylonas M (2006) Re-approaching the small island effect. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 914-923.
DOI URL |
| [52] | von Humboldt A (1807) Ideen zur einer Geographie der Pflanstzen nebst einem Naturgemälde der Tropenländer, Cotta, Tübringen. |
| [53] | Wang YP, Chen CW, Millien V (2018) A global synthesis of the small-island effect in habitat islands. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 285, 20181868. |
| [54] |
Wang YP, Chen CW, Millien V (2023) The integration of the small‐island effect and nestedness pattern. Journal of Biogeography, 50, 1234-1243.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Wang YP, Millien V, Ding P (2016) On empty islands and the small-island effect. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 1333-1345.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Wang YP, Wu Q, Wang X, Liu C, Wu LB, Chen CW, Ge DP, Song X, Chen CS, Xu AC, Ding P (2015) Small-island effect in snake communities on islands of an inundated lake: The need to include zeroes. Basic and Applied Ecology, 16, 19-27.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Wang YP, Zhang M, Wang SY, Ding ZF, Zhang JC, Sun JJ, Li P, Ding P (2012) No evidence for the small island effect in avian communities on islands of an inundated lake. Oikos, 121, 1945-1952.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Whitehead DR, Jones CE (1969) Small islands and the equilibrium theory of insular biogeography. Evolution, 23, 171-179.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | Whittaker RJ, Fernandez-Palacios JM (2007) Island Biogeography: Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [60] | Wintle BA, Kujala H, Whitehead A, Cameron A, Veloz S, Kukkala A, Moilanen A, Gordon A, Lentini PE, Cadenhead NCR, Bekessy SA (2019) Global synthesis of conservation studies reveals the importance of small habitat patches for biodiversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 909-914. |
| [61] |
Yan YZ, Jarvie S, Zhang Q, Han P, Liu QF, Zhang SS, Liu PT (2023) Habitat heterogeneity determines species richness on small habitat islands in a fragmented landscape. Journal of Biogeography, 50, 976-986.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Yan YZ, Jarvie S, Zhang Q, Zhang SS, Han P, Liu QF, Liu PT (2021) Small patches are hotspots for biodiversity conservation in fragmented landscapes. Ecological Indicators, 130, 108086.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Yu J, Li DD, Zhang ZY, Guo SL (2020) Species-area relationship and small-island effect of bryophytes on the Zhoushan Archipelago, China. Journal of Biogeography, 47, 978-992.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Yanqiu Xie, Hui Huang, Chunxiao Wang, Yaqin He, Yixuan Jiang, Zilin Liu, Chuanyuan Deng, Yushan Zheng. Determinants of species-area relationship and species richness of coastal endemic plants in the Fujian islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [2] | Yanping Wang, Minchu Zhang, Chengxiu Zhan. A review on the nested distribution pattern (nestedness): Analysis methods, mechanisms and conservation implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [3] | Xiaofan Shang, Jian Zhang, Haojie Gao, Weipeng Ku, Yuke Bi, Xiupeng Li, Enrong Yan. Island area and climate jointly impact seed plant richness patterns across the Zhoushan Archipelago [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [4] | Lan Xiao, Biao Dong, Linting Zhang, Chuanyuan Deng, Xia Li, Jianhui Liu, Duancong Wu. Distribution pattern of plant species richness of uninhabited islands in the Bohai Sea area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21231-. |
| [5] | Yunzhi Qin, Jiaxin Zhang, Jianming Liu, Mengting Liu, Dan Wan, Hao Wu, Yang Zhou, Hongjie Meng, Zhiqiang Xiao, Handong Huang, Yaozhan Xu, Zhijun Lu, Xiujuan Qiao, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and spatial structure in the Badagongshan 25 ha Forest Dynamics Plot in Hunan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(9): 1016-1022. |
| [6] | Xu Xiang, Zhang Huayong, Xie Ting, Sun Qingqing, Tian Yonglan. Elevational pattern of seed plant diversity in Xishuangbanna and its mechanisms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(7): 678-689. |
| [7] | Xingfeng Si, Yuhao Zhao, Chuanwu Chen, Peng Ren, Di Zeng, Lingbing Wu, Ping Ding. Beta-diversity partitioning: methods, applications and perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(5): 464-480. |
| [8] | Manyu Yan, Xiaojun Du, Aihua Zhao, Mingchun Peng. Individual woody species-area relationship in a deciduous broad-leaved forest in Baotianman, Henan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(5): 630-640. |
| [9] | Lei Zhong, Chia-Hao Chang-Yang, Pin Lu, Xueping Gu, Zupei Lei, Yanben Cai, Fangdong Zheng, I-Fang Sun, Mingjian Yu. Community structure and species composition of the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest: the analyses for a 9 ha forest dynamics plot in Wuyanling Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, East China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(5): 619-629. |
| [10] | Aichun Xu, Xingfeng Si, Yanping Wang, Ping Ding. Camera traps and the minimum trapping effort for ground-dwelling mammals in fragmented habitats in the Thousand Island Lake, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(6): 764-772. |
| [11] | Shikui Dong,Lin Tang,Xuexia Wang,Yinghui Liu,Shiliang Liu,Quanru Liu,Yu Wu,Yuanyuan Li,Xukun Su,Chen Zhao. Minimum plot size for estimating plant biodiversity of the alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(6): 651-657. |
| [12] | Zhiyao Tang, Xiujuan Qiao, Jingyun Fang. Species-area relationship in biological communities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(6): 549-559. |
| [13] | Wenhong Deng, Wei Gao. The effects of forest patch sizes on bird species diversity and individual density [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2005, 13(3): 204-212. |
| [14] | CHEN Bo, BAO Zhi-Yi. Indicators for monitoring biodiversity in urban and suburban parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2003, 11(2): 169-176. |
| [15] | BAI Yong-Fei, XU Zhi-Xin, LI De-Xin. Study on α diversity of four Stipa communities in Inner Mongolia Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2000, 08(4): 353-360. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn