



Biodiv Sci ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 907-915. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016100 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016100
Special Issue: 粮食安全
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Linhui Jiang1, Ling Luo1, Zhenggao Xiao1, Daming Li2, Xiaoyun Chen1, Manqiang Liu1,*( ), Feng Hu1
), Feng Hu1
Received:2016-04-08
Accepted:2016-05-19
Online:2016-08-20
Published:2016-09-02
Contact:
Liu Manqiang
Linhui Jiang, Ling Luo, Zhenggao Xiao, Daming Li, Xiaoyun Chen, Manqiang Liu, Feng Hu. Effects of soil biota influenced by long-term organic and chemical fertilizers on rice growth and resistance to insects[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(8): 907-915.
| 对照 Non-sterilized | 灭活 Sterilized | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | ||
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 4.34 ± 0.73 | 2.19 ± 0.53 | 18.36 ± 0.63 | 27.35 ± 0.38 | |
| 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg/kg) | 75.97 ± 9.73 | 147.13 ± 3.53 | 73.12 ± 3.65 | 143.23 ± 2.65 | |
| 可溶性有机碳 DOC (mg/kg) | 43.86 ± 11.90 | 34.27 ± 5.56 | 712.86 ± 4.71 | 1,074.73 ± 21.17 | |
| 速效磷 AP (mg/kg) | 135.34 ± 1.26 | 101.01 ± 0.68 | 21.88 ± 0.00 | 10.02 ± 0.39 | |
| 速效钾 AK (mg/kg) | 21.03 ± 0.00 | 34.96 ± 1.51 | 38.68 ± 1.38 | 67.00 ± 2.57 | |
| pH (H2O) | 6.01 ± 0.21 | 6.25 ± 0.26 | 5.77 ± 0.22 | 5.93 ± 0.23 | |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of original and sterilized soils (mean ± SD, n = 4)
| 对照 Non-sterilized | 灭活 Sterilized | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | ||
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 4.34 ± 0.73 | 2.19 ± 0.53 | 18.36 ± 0.63 | 27.35 ± 0.38 | |
| 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg/kg) | 75.97 ± 9.73 | 147.13 ± 3.53 | 73.12 ± 3.65 | 143.23 ± 2.65 | |
| 可溶性有机碳 DOC (mg/kg) | 43.86 ± 11.90 | 34.27 ± 5.56 | 712.86 ± 4.71 | 1,074.73 ± 21.17 | |
| 速效磷 AP (mg/kg) | 135.34 ± 1.26 | 101.01 ± 0.68 | 21.88 ± 0.00 | 10.02 ± 0.39 | |
| 速效钾 AK (mg/kg) | 21.03 ± 0.00 | 34.96 ± 1.51 | 38.68 ± 1.38 | 67.00 ± 2.57 | |
| pH (H2O) | 6.01 ± 0.21 | 6.25 ± 0.26 | 5.77 ± 0.22 | 5.93 ± 0.23 | |
| 自由度 | 铵态氮 | 硝态氮 | 可溶性有机碳 | pH | 茎叶重 | 根系重 | 根冠比 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | NH4+-N | NO3--N | DOC | (H2O) | Shoot mass | Root mass | R/S ratio | |
| 灭活 Sterilization (S) | 1 | 427.12** | 62.10** | 108.76** | 60.98** | 151.95** | 47.66** | 28.22** |
| 施肥 Fertilization (F) | 1 | 11.48** | 16.70** | 22.65** | 27.48** | 9.28** | 0.10NS | 1.24NS |
| 飞虱 Planthopper (P) | 1 | 2.08NS | 7.89** | 0.05NS | 0.07NS | 210.59** | 10.66** | 101.71** |
| 灭活×施肥 Sterilization × Fertilization (S × F) | 1 | 7.16* | 0.28NS | 11.46** | 0.94NS | 9.44** | 3.77NS | 8.18** |
| 灭活×飞虱 Sterilization × Planthopper (S × P) | 1 | 0.25NS | 3.60NS | 0.17NS | 6.05* | 20.62** | 2.39NS | 0.30NS |
| 施肥×飞虱 Fertilization × Planthopper (F × P) | 1 | 1.13NS | 2.51NS | 0.60NS | 0.17NS | 1.89NS | 5.06* | 1.51NS |
| 灭活×施肥×飞虱 Sterilization × Fertilization × Planthopper (S × F × P) | 1 | 0.19NS | 1.66NS | 1.52NS | 1.41NS | 1.99NS | 2.53NS | 2.74NS |
| Error | 24 |
Table 2 ANOVA results showing the effects of soil biological factor (non-sterilized vs. sterilized), fertilization management (chemical vs. organic fertilizer) and brown planthopper (with vs. without planthoppers) on content of soil NH4+-N, NO3--N, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), pH, shoot mass, root mass, R/S ratio.
| 自由度 | 铵态氮 | 硝态氮 | 可溶性有机碳 | pH | 茎叶重 | 根系重 | 根冠比 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | NH4+-N | NO3--N | DOC | (H2O) | Shoot mass | Root mass | R/S ratio | |
| 灭活 Sterilization (S) | 1 | 427.12** | 62.10** | 108.76** | 60.98** | 151.95** | 47.66** | 28.22** |
| 施肥 Fertilization (F) | 1 | 11.48** | 16.70** | 22.65** | 27.48** | 9.28** | 0.10NS | 1.24NS |
| 飞虱 Planthopper (P) | 1 | 2.08NS | 7.89** | 0.05NS | 0.07NS | 210.59** | 10.66** | 101.71** |
| 灭活×施肥 Sterilization × Fertilization (S × F) | 1 | 7.16* | 0.28NS | 11.46** | 0.94NS | 9.44** | 3.77NS | 8.18** |
| 灭活×飞虱 Sterilization × Planthopper (S × P) | 1 | 0.25NS | 3.60NS | 0.17NS | 6.05* | 20.62** | 2.39NS | 0.30NS |
| 施肥×飞虱 Fertilization × Planthopper (F × P) | 1 | 1.13NS | 2.51NS | 0.60NS | 0.17NS | 1.89NS | 5.06* | 1.51NS |
| 灭活×施肥×飞虱 Sterilization × Fertilization × Planthopper (S × F × P) | 1 | 0.19NS | 1.66NS | 1.52NS | 1.41NS | 1.99NS | 2.53NS | 2.74NS |
| Error | 24 |
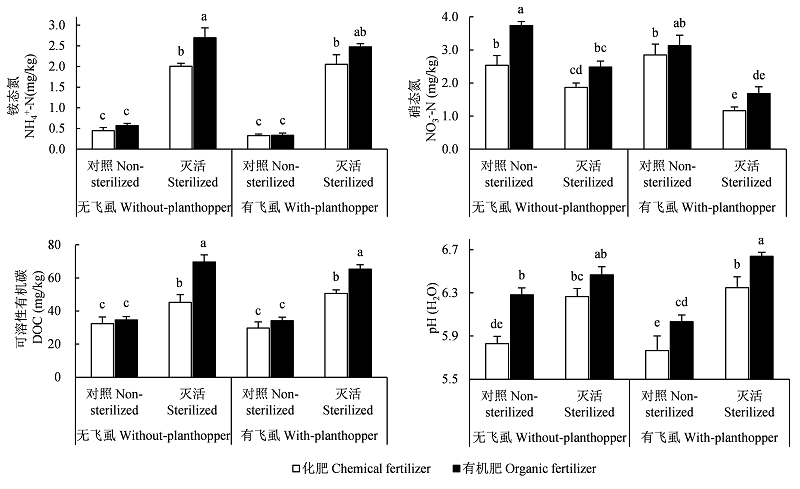
Fig. 1 Effects of soil biological factor (non-sterilized vs. sterilized), fertilization management (chemical vs. organic fertilizer) and brown planthopper (with vs. without planthoppers) on the content of soil NH4+-N、NO3--N、DOC and pH. Different letters among the treatments mean significant differences, P < 0.05.
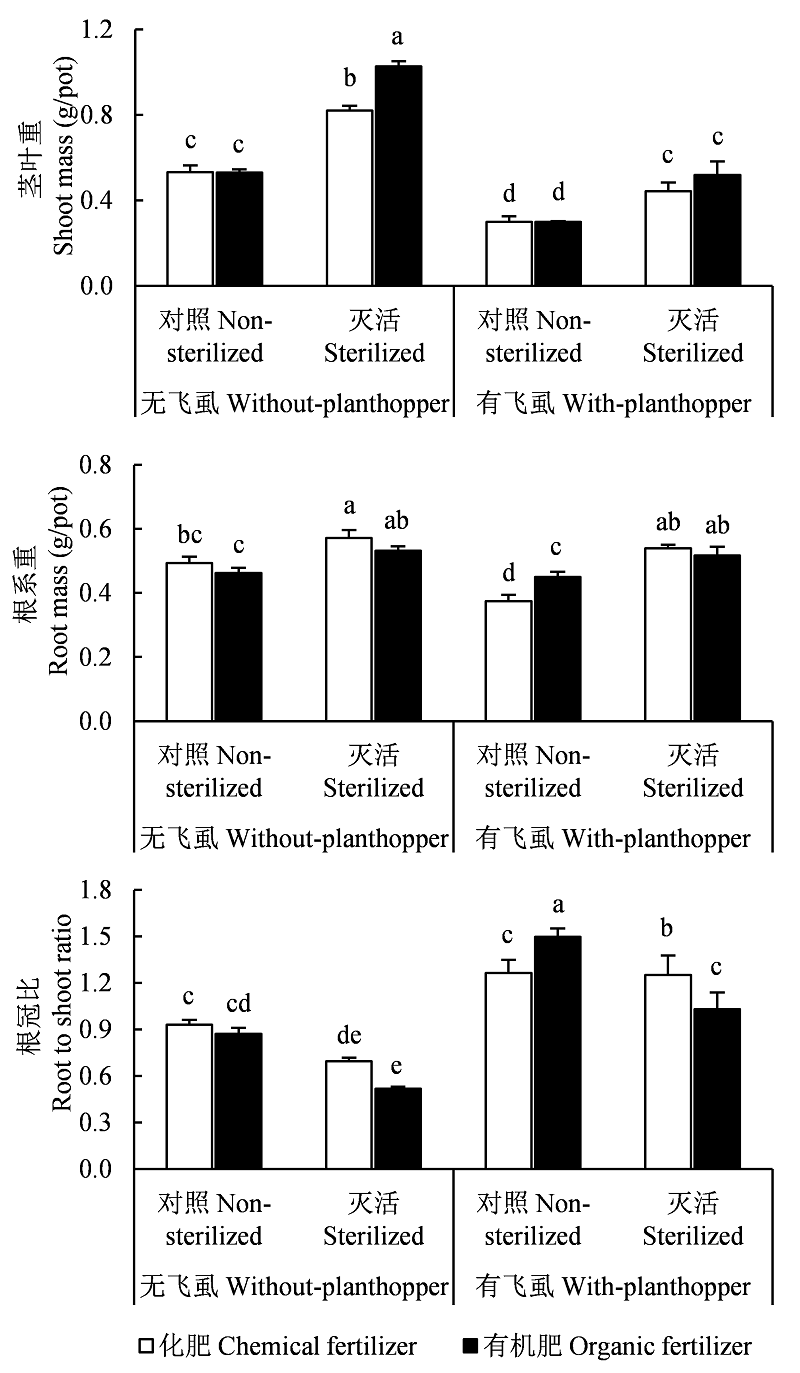
Fig. 2 Effects of soil biological factor (non-sterilized vs. sterilized), fertilization management (chemical vs. organic fertilizer) and brown planthopper (with vs. without planthoppers) on shoot mass, root mass and root to shoot ratio. Different letters among the treatments mean significant differences, P < 0.05.
| 自由度 df | 茎叶氮 Shoot N | 根系氮 Root N | 茎叶糖 Shoot sugar | 根系糖 Root sugar | 茎叶酚 Shoot phenolic | 根系酚 Root phenolic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灭活 Sterilization (S) | 1 | 151.95** | 35.50** | 9.56** | 39.27** | 20.41** | 15.22** |
| 施肥 Fertilization (F) | 1 | 9.28** | 27.93** | 31.76** | 0.39NS | 7.71* | 10.49** |
| 飞虱 Planthopper (P) | 1 | 210.59** | 72.93** | 83.24** | 2.73NS | 1.59NS | 0.57NS |
| 灭活×施肥 Sterilization × Fertilization (S × F) | 1 | 9.44** | 50.35** | 0.02NS | 0.023NS | 0.62NS | 10.82** |
| 灭活×飞虱 Sterilization × Planthopper (S × P) | 1 | 20.62** | 2.00NS | 11.45** | 0.42NS | 5.31* | 0.53NS |
| 施肥×飞虱 Fertilization × Planthopper (F × P) | 1 | 1.89NS | 5.42* | 3.18NS | 2.65NS | 0.30NS | 2.06NS |
| 灭活×施肥×飞虱 Sterilization × Fertilization × Planthopper (S × F × P) | 1 | 1.99NS | 6.18* | 0.06NS | 12.86** | 4.68* | 0.73NS |
| Error | 24 |
Table 3 ANOVA results showing the effects of soil biological factor (non-sterilized vs. sterilized), fertilization management (chemical vs. organic fertilizer) and brown planthopper (with vs. without planthoppers) on the content of nitrogen, soluble sugar, phenolic in shoot and root, respectively.
| 自由度 df | 茎叶氮 Shoot N | 根系氮 Root N | 茎叶糖 Shoot sugar | 根系糖 Root sugar | 茎叶酚 Shoot phenolic | 根系酚 Root phenolic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灭活 Sterilization (S) | 1 | 151.95** | 35.50** | 9.56** | 39.27** | 20.41** | 15.22** |
| 施肥 Fertilization (F) | 1 | 9.28** | 27.93** | 31.76** | 0.39NS | 7.71* | 10.49** |
| 飞虱 Planthopper (P) | 1 | 210.59** | 72.93** | 83.24** | 2.73NS | 1.59NS | 0.57NS |
| 灭活×施肥 Sterilization × Fertilization (S × F) | 1 | 9.44** | 50.35** | 0.02NS | 0.023NS | 0.62NS | 10.82** |
| 灭活×飞虱 Sterilization × Planthopper (S × P) | 1 | 20.62** | 2.00NS | 11.45** | 0.42NS | 5.31* | 0.53NS |
| 施肥×飞虱 Fertilization × Planthopper (F × P) | 1 | 1.89NS | 5.42* | 3.18NS | 2.65NS | 0.30NS | 2.06NS |
| 灭活×施肥×飞虱 Sterilization × Fertilization × Planthopper (S × F × P) | 1 | 1.99NS | 6.18* | 0.06NS | 12.86** | 4.68* | 0.73NS |
| Error | 24 |
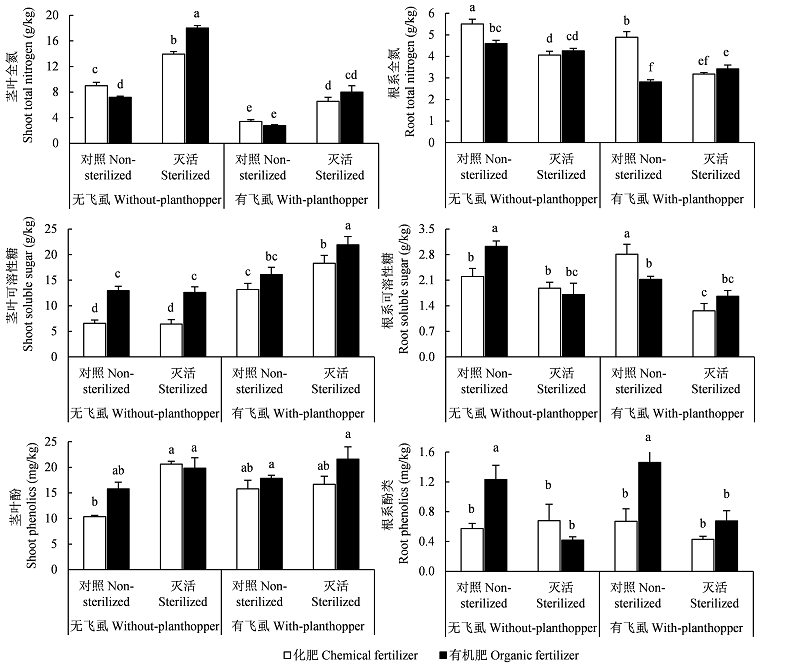
Fig. 3 Effects of soil biological factor (non-sterilized vs. sterilized), fertilization management (chemical vs. organic fertilizer) and brown planthopper (with vs. without planthoppers) on the content of shoot total nitrogen, root total nitrogen, shoot soluble sugar, root soluble sugar, shoot phenolics and root phenolics. Different letters among the treatments mean significant differences, P < 0.05.
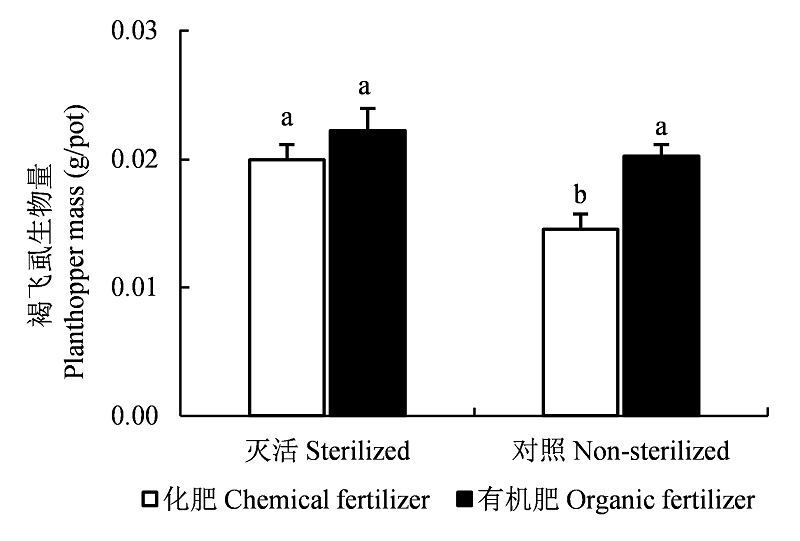
Fig. 4 Effects of soil biological factor (non-sterilized vs. sterilized) and fertilization management (chemical vs. organic fertilizer) on planthopper mass. Different letters among the treatments mean significant differences, P < 0.05.

Fig. 5 Principle component analysis (PCA) of plant and soil properties affected by soil biological factor, fertilization management and planthopper.□ plant metabolome and soil physicochemical property; ● different treatments.
| [1] | Ainsworth EA, Gillespie KM (2007) Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Nature Protocols, 2, 875-877. |
| [2] | Altieri MA, Nicholls CI (2003) Soil fertility management and insect pests: harmonizing soil and plant health in agroecosystems. Soil and Tillage Research, 72, 203-211. |
| [3] | Badri DV, Zolla G, Bakker MG, Manter DK, Vivanco JM (2013) Potential impact of soil microbiomes on the leaf metabolome and on herbivore feeding behavior. New Phytologist, 198, 264-273. |
| [4] | Bakker MG, Manter DK, Sheflin AM, Weir TL, Vivanco JM (2012) Harnessing the rhizosphere microbiome through plant breeding and agricultural management. Plant and Soil, 360, 1-13. |
| [5] | Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2003) Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology, 84, 2258-2268. |
| [6] | Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 515, 505-511. |
| [7] | Bardgett RD, Wardle D (2010) Biotic interactions in soil as drivers of ecosystem properties. In: Aboveground- Belowground Linkages, Biotic Interactions, Ecosystem Processes, and Global Change (eds Bardgett RD, Wardle D), pp.15-61. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [8] | Berendsen RL, Pieterse CM, Bakker PA (2012) The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in Plant Science, 17, 478-486. |
| [9] | Bissett A, Brown MV, Siciliano SD, Thrall PH (2013) Microbial community responses to anthropogenically induced environmental change: towards a systems approach. Ecology Letters, 16, 128-139. |
| [10] | Cohen MB, Alam SN, Medina EB, Bernal CC (1997) Brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, resistance in rice cultivar IR64: mechanism and role in successful N. lugens management in Central Luzon, Philippines. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 85, 221-229. |
| [11] | D’Alessandro M, Erb M, Ton J, Brandenburg A, Karlen D, Zopfi J, Turlings TC (2014) Volatiles produced by soil-borne endophytic bacteria increase plant pathogen resistance and affect tritrophic interactions. Plant Cell & Environment, 37, 813-826. |
| [12] | Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers P, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350-356. |
| [13] | Erb M (2012) The role of roots in plant defence. In: Plant Defence: Biological Control (eds Mérillon JM, Ramawat KG), pp. 291-309. Springer Netherlands Press, Berlin. |
| [14] | Fu SL (2007) A review and perspective on soil biodiversity research. Biodiversity Science, 15, 109-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [傅声雷 (2007) 土壤生物多样性的研究概况与发展趋势. 生物多样性, 15, 109-115.] | |
| [15] | Gu YF, Zhang XP, Tu SH, Sun XF (2008) Effect of long-term fertilization on nitrification and nitrobacteria community in a purple paddy soil under rice-wheat rotations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 2123-2130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [辜运富, 张小平, 涂仕华, 孙锡发 (2008) 长期定位施肥对紫色水稻土硝化作用及硝化细菌群落结构的影响. 生态学报, 28, 2123-2130.] | |
| [16] | Jiang T, Zhao JL, Cheng JJ, Xu S, Su W, Bao SW, Liu F (2011) Effects of rice varieties and nitrogen fertilizer application rates on the occurrence of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens under field conditions. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 48, 1359-1368. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [江涛, 赵俊玲, 程建军, 徐帅, 苏文, 包善微, 刘芳 (2011) 水稻品种与氮肥施用水平对田间褐飞虱发生的影响. 应用昆虫学报, 48, 1359-1368.] | |
| [17] | Jiang ZG, Qin HN, Liu YN, Ji LQ, Ma KP (2015) Protecting biodiversity and promoting sustainable development: in memory of the releasing of Catalogue of Life China 2015 and China Biodiversity Red List on the International Day for Biological Diversity 2015. Biodiversity Science, 23, 433-434. (in Chinese) |
| [蒋志刚, 覃海宁, 刘忆南, 纪力强, 马克平 (2015) 保护生物多样性, 促进可持续发展——纪念《中国生物物种名录》和《中国生物多样性红色名录》发布. 生物多样性, 23, 433-434.] | |
| [18] | Kenmore PE (1980) Ecology and Outbreaks of a Tropical Insects Pest of the Green Revolution, the Rice Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal). PhD dissertation, University of California, Berkeley. |
| [19] | Lazcano C, Gómez-Brandón M, Revilla P, Domínguez J (2013) Short-term effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial community structure and function. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 49, 723-733. |
| [20] | Liu M, Bjørnlund L, Rønn R, Christensen S, Ekelund F (2012) Disturbance promotes non-indigenous bacterial invasion in soil microcosms: analysis of the roles of resource availability and community structure. PLoS ONE, 7, e45306. |
| [21] | Liu MQ, Huang JH, Chen XY, Wang F, Ge C, Su Y, Shao B, Tang Y, Li HX, Hu F (2009) Aboveground herbivory by the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) affects soil nematode communities under different rice varieties. Biodiversity Science, 17, 431-439. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘满强, 黄菁华, 陈小云, 王峰, 葛成, 苏昱, 邵波, 汤英, 李辉信, 胡锋 (2009) 地上部植食者褐飞虱对不同水稻品种土壤线虫群落的影响. 生物多样性, 17, 431-439.] | |
| [22] | Lu RK (2000) Analysis Method of Soil Agricultural Chemistry. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [鲁如坤 (2000) 土壤农业化学分析方法. 中国农业科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [23] | Martinuz A, Schouten A, Menjivar RD, Sikora RA (2012) Effectiveness of systemic resistance toward Aphis gossypii (Hom., Aphididae) as induced by combined applications of the endophytes Fusarium oxysporum Fo162 and Rhizobium etli G12. Biological Control, 62, 206-212. |
| [24] | Megali L, Schlau B, Rasmann S (2015) Soil microbial inoculation increases corn yield and insect attack. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 35, 1511-1519. |
| [25] | Phelan PL, Mason JF, Stinner BR (1995) Soil-fertility management and host preference by European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner), on Zea mays L.: a comparison of organic and conventional chemical farming. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 56, 1-8. |
| [26] | Philippot L, Spor A, Hénault C, Bru D, Bizouard F, Jones CM, Maron PA (2013) Loss in microbial diversity affects nitrogen cycling in soil. The ISME Journal, 7, 1609-1619. |
| [27] | Pineda A, Zheng SJ, van Loon JJA, Dicke M (2012) Rhizobacteria modify plant-aphid interactions: a case of induced systemic susceptibility. Plant Biology, 14, 83-90. |
| [28] | Roger A, Getaz M, Rasmann S, Sanders IR (2013) Identity and combinations of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates influence plant resistance and insect preference. Ecological Entomology, 38, 330-338. |
| [29] | Senthil-Nathan S, Choi MY, Paik CH, Seo HY, Kalaivani K (2009) Toxicity and physiological effects of neem pesticides applied to rice on the Nilaparvata lugens, the brown planthopper. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 1707-1713. |
| [30] | Shavit R, Ofek-Lalzar M, Burdman S, Morin S (2013) Inoculation of tomato plants with rhizobacteria enhances the performance of the phloem-feeding insect Bemisia tabaci. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4, 1-12. |
| [31] | Shi LL, Fu SL (2014) Review of soil biodiversity research: history, current status and future challenges. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 493-509. (in Chinese) |
| [时雷雷, 傅声雷 (2014) 土壤生物多样性研究: 历史, 现状与挑战. 科学通报, 59, 493-509.] | |
| [32] | Soler R, van der Putten WH, Harvey JA, Vet LE, Dicke M, Bezemer TM (2012) Root herbivore effects on aboveground multitrophic interactions: patterns, processes and mechanisms. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 38, 755-767. |
| [33] | Su T, Xu HX, Han HL, Yang YJ, Wang GY, Zheng XS, Lü ZX (2014) Soil microbe quantities and enzyme activities in rhizosphere of different rice varieties fed by brown planthoppers. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 28, 322-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏婷, 徐红星, 韩海亮, 杨亚军, 王桂跃, 郑许松, 吕仲贤 (2014) 褐飞虱胁迫对不同抗性水稻品种根际土壤酶活性和微生物含量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 28, 322-326.] | |
| [34] | Tang Y, Liu MQ, Wang F, Chen FJ, Shao B, Su Y, Ge C, Huang JH, Li HX, Hu F (2010) Herbivory by the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) affects rice seeding growth and belowground soil labile erganic carbon and nitrogen fractions. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 2890-2898. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汤英, 刘满强, 王峰, 陈法军, 邵波, 苏昱, 葛成, 黄菁华, 李辉信, 胡锋 (2010) 褐飞虱对水稻苗期生长及地下部土壤活性碳氮的影响. 生态学报, 30, 2890-2898.] | |
| [35] | Wang J, Zhu B, Zhang J, Müller C, Cai Z (2015) Mechanisms of soil N dynamics following long-term application of organic fertilizers to subtropical rain-fed purple soil in China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 91, 222-231. |
| [36] | Zha Y, Wu XP, Zhang HM, Cai DX, Zhu P, Gao HJ (2015) Effects of long-term organic and inorganic fertilization on enhancing soil organic carbon and basic soil productivity in black soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 48, 4649-4659. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [查燕, 武雪萍, 张会民, 蔡典雄, 朱平, 高洪军 (2015) 长期有机无机配施黑土土壤有机碳对农田基础地力提升的影响. 中国农业科学, 48, 4649-4659.] | |
| [37] | Zhu Q, Riley WJ, Tang J, Koven CD (2016) Multiple soil nutrient competition between plants, microbes, and mineral surfaces: model development, parameterization, and example applications in several tropical forests. Biogeosciences, 13, 341-363. |
| [1] | Ruoyue Li, Xiaochao Yang, Zhanqing Hao, Shihong Jia. The intensity of heat waves and insect herbivory on campus plants and their relationship with leaf functional traits [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24283-. |
| [2] | Lejie Wu, Zekang Liu, Xing Tian, Qun Zhang, Bo Li, Jihua Wu. Effects of genotypic diversity on vegetative growth and reproductive strategies of Scirpus mariqueter population [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23478-. |
| [3] | Xiaodan Tan, Peng Zhang, Sirui Zhu, Xiang Liu, Shurong Zhou, Mu Liu. Effect of shrub encroachment on insect herbivory of Polygonum macrophyllum in alpine meadow of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23417-. |
| [4] | Wenting Wang, Rong Wang, Cuiping Niu, Yang Bai, Xiaodong Yang. Soil multitrophic ecological network structure of agroforestry rubber plantation in Xishuangbanna [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22626-. |
| [5] | Yaochu Sun, Yuanfei Pan, Mu Liu, Xiaoyun Pan. The specialist-to-generalist ratio affects growth and defense strategy of invasive plant Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22632-. |
| [6] | Jiman Li, Nan Jin, Maogang Xu, Jusong Huo, Xiaoyun Chen, Feng Hu, Manqiang Liu. Effects of earthworm on tomato resistance under different drought levels [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| [7] | Huiling Hu, Zhiyuan Yao, Shibin Gao, Bo Zhu. Nematode response to long-term fertilization in purple soil [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22189-. |
| [8] | Yuanli Ouyang, Cancan Zhang, Xiaofan Lin, Lixin Tian, Hanjiao Gu, Fusheng Chen, Wensheng Bu. Growth differences and characteristics of root and leaf morphological traits for different mycorrhizal tree species in the subtropical China: A case study of Xingangshan, Jiangxi Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 746-758. |
| [9] | Wensheng Yu, Yaolin Guo, Jiajia Jiang, Keke Sun, Ruiting Ju. Comparison of the life history of a native insect Laelia coenosa with a native plant Phragmites australis and an invasive plant Spartina alterniflora [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 433-438. |
| [10] | Baijing Zhu, Jingrong Xue, Rong Xia, Miaomiao Jin, You Wu, Shanyi Tian, Xiaoyun Chen, Manqiang Liu, Feng Hu. Effect of soil nematode functional guilds on plant growth and aboveground herbivores [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 409-418. |
| [11] | Zhuang Ping. Progress on the fertility of Rhododendron [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(3): 327-338. |
| [12] | Zhengjun Guan,Shunbao Lu,Yanlin Huo,Haoyong Hao,Jianbin Cao,Wei Wei,Biao Liu. Effects of Bt crops on non-target insect pests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(6): 636-644. |
| [13] | Yu Zhang, Zhenggao Xiao, Linhui Jiang, Lei Qian, Xiaoyun Chen, Fajun Chen, Feng Hu, Manqiang Liu. Nitrogen levels modify earthworm-mediated tomato growth and resistance to pests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(12): 1296-1307. |
| [14] | Jiliang Liu, Fengrui Li. Effects of oasis expansion regimes on ecosystem function and dominant functional groups of soil biota in arid regions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(10): 1116-1126. |
| [15] | Ma Ding, Ju Ruiting, Li Bo. Preference of Laelia coenosa for native and introduced populations of invasive Spartina alterniflora [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(1): 101-108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn