



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 22359. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022359 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022359
• 中国野生脊椎动物鸣声监测与生物声学研究专题 • 上一篇 下一篇
岑渝华1, 王鹏1, 陈庆春2, 张承云2, 余上3, 胡珂1, 刘阳4, 肖荣波1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-29
接受日期:2022-10-14
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2022-11-10
通讯作者:
*肖荣波, E-mail: ecoxiaorb@163.com
基金资助:
Yuhua Cen1, Peng Wang1, Qingchun Chen2, Chengyun Zhang2, Shang Yu3, Ke Hu1, Yang Liu4, Rongbo Xiao1,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-29
Accepted:2022-10-14
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2022-11-10
Contact:
*Rongbo Xiao, E-mail: ecoxiaorb@163.com
摘要:
动物群落是构成城市绿地生态系统的关键要素, 声景作为野生动物重要的生态信息, 掌握其时空变化及其影响因素, 对于指导城市绿地景观设计与生物多样性保护具有重要意义。本文以Web of Science数据库的核心合集2005-2022年收录的67篇研究文献为对象, 综合梳理与分析了城市绿地动物声景的时空模式及其驱动因素。城市绿地动物声景在空间上表现出环境空间梯度和植被空间结构的差异, 动物声音多样性随海拔、纬度、城市化程度的降低以及植被类型和高度的增加呈现升高趋势。时间尺度呈现出昼夜、季节和年度变化差异, 表现为鸟类在黎明和黄昏合唱、昆虫和两栖动物在夜间鸣叫以及季节性和年度性发声规律等。影响城市动物声景模式的因素主要包括植被、环境、人为干扰和动物自身驱动等。动物声景作为当前声景生态学研究的热点之一, 面临大时空尺度演变规律研究不足、动物声景分析有限等挑战, 建议未来着重开展多时空尺度变化规律研究、创新动物声景分析方法、定量解析影响因素及其响应机制、建立全球动物声景数据库等。
岑渝华, 王鹏, 陈庆春, 张承云, 余上, 胡珂, 刘阳, 肖荣波 (2023) 城市绿地动物声景的时空特征及其驱动因素. 生物多样性, 31, 22359. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022359.
Yuhua Cen, Peng Wang, Qingchun Chen, Chengyun Zhang, Shang Yu, Ke Hu, Yang Liu, Rongbo Xiao (2023) Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of animal soundscape in urban green spaces. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22359. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022359.
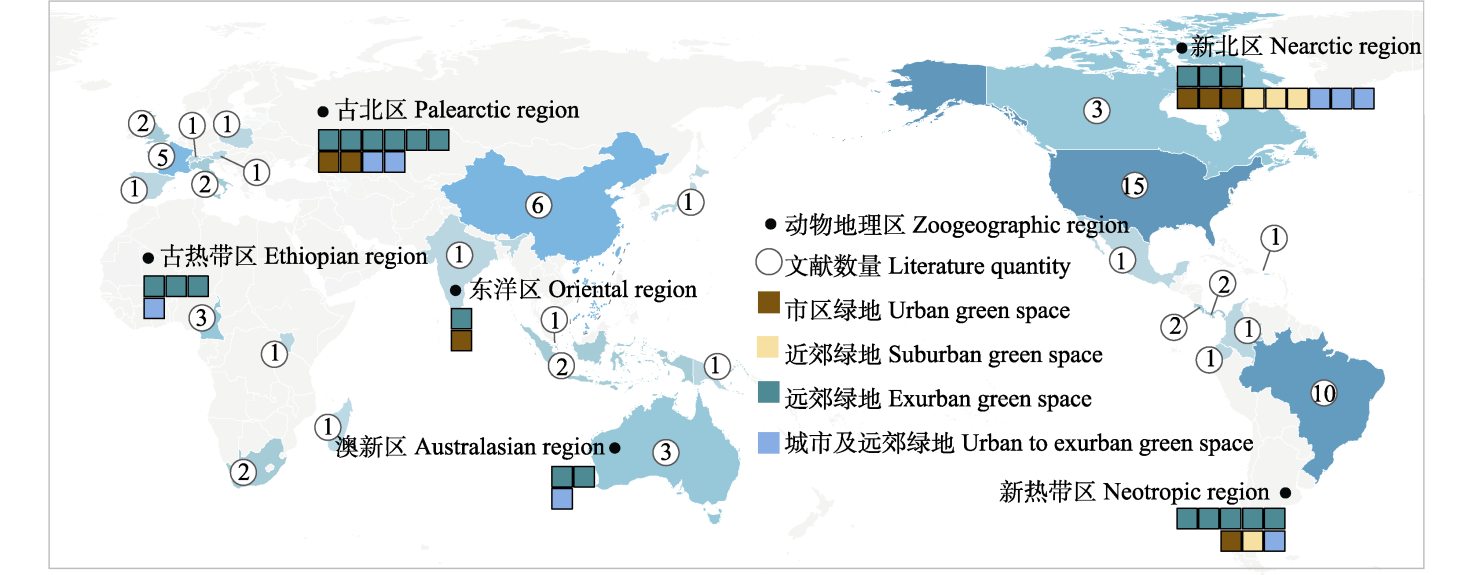
图1 动物声景个例研究的全球分布图。 颜色(蓝色)越深表示发表文献数量越多; 圆点、圆圈及正方形图框分别表示6个动物区系、文献数量和各区内4种城市绿地类型的研究数量。
Fig. 1 Global distribution map of animal soundscape case studies. The deeper color (blue) represents more documents were published; the dots, circle and the square box represent the number of studies on the six major fauna, number of documents and the four types of urban green space in each region.
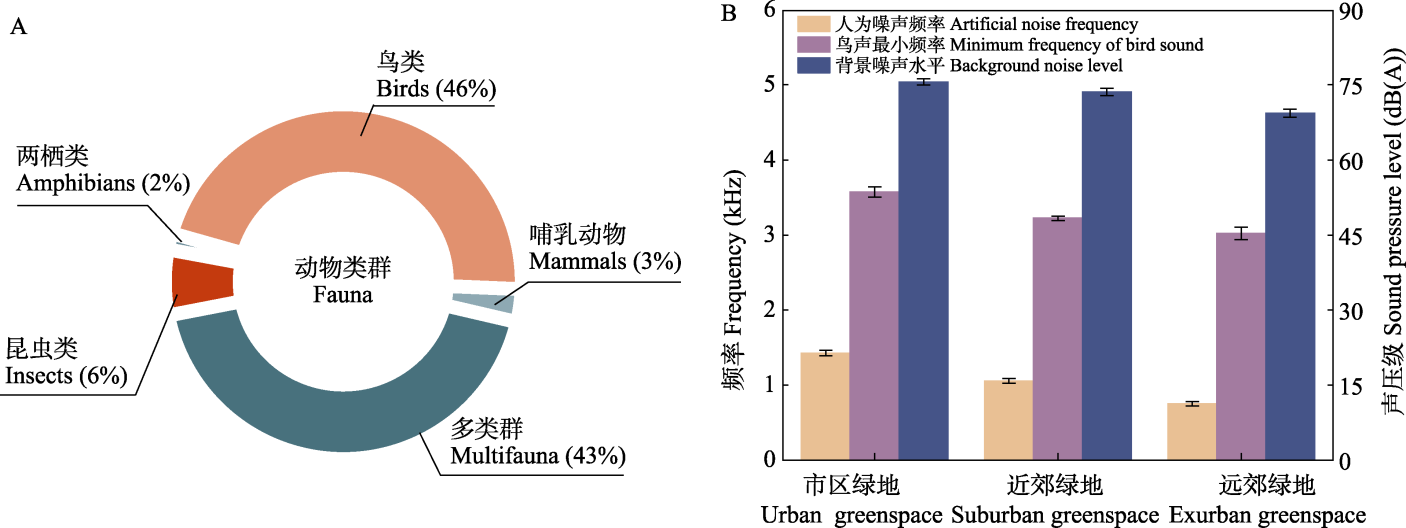
图2 不同城市绿地的研究动物类群分布(A)及声景差异(B)。 %表示文献数量占比。
Fig. 2 Distribution of research animal groups (A) and differences in soundscapes (B) in different urban green spaces. % represents the proportion of the number of documents.
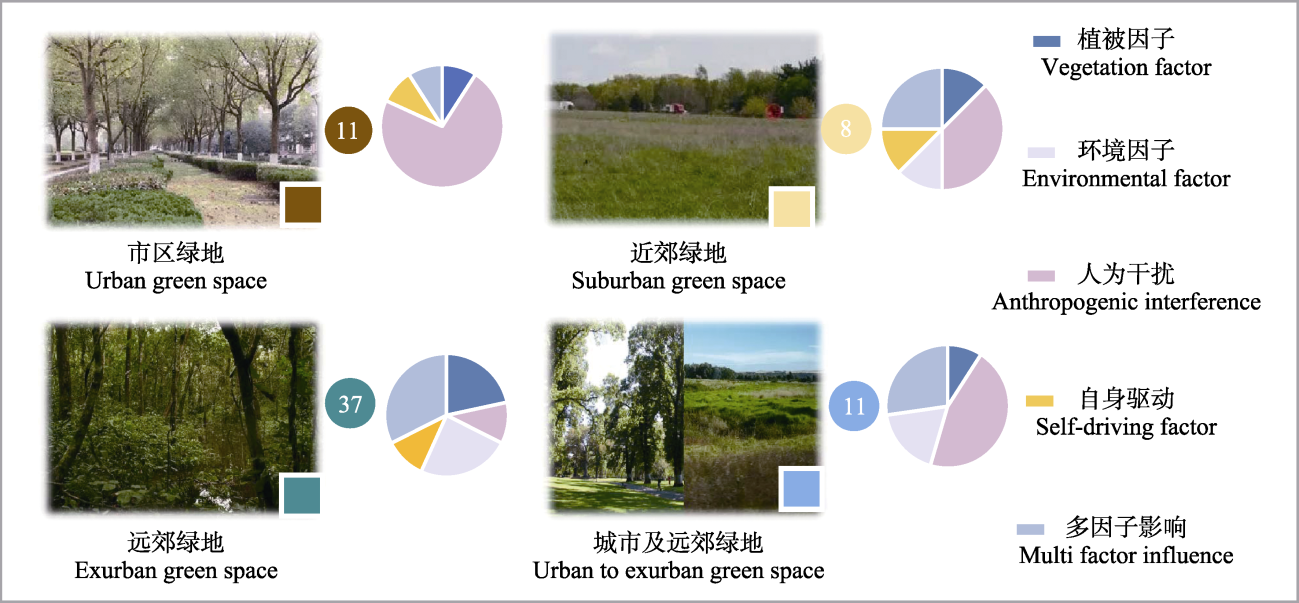
图3 不同城市绿地动物声景的驱动因素。 饼状图表示4种城市绿地类型中5种驱动因素类型的研究比例。数字表示文献数量。
Fig. 3 Drivers of animal soundscapes in different urban green spaces. Pie charts represent the research proportions of five types of driving factors in four types of urban green space. Numbers represent the number of documents.
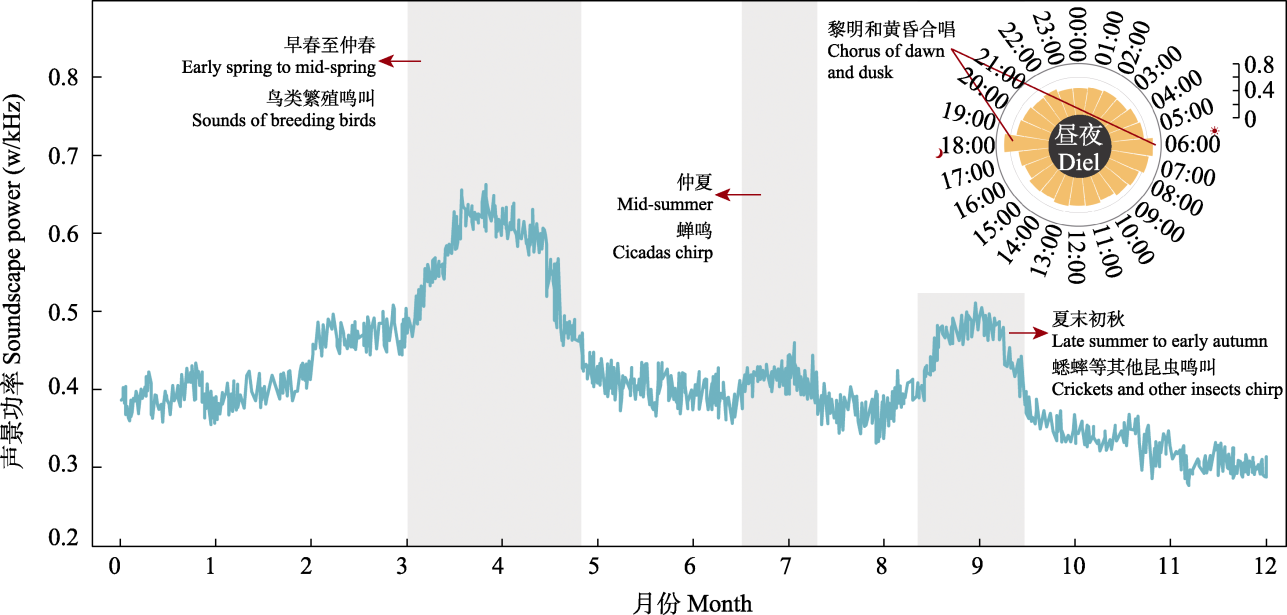
图4 城市绿地动物在一天(玫瑰图)和一年(折线图)中的声景功率变化。 太阳和月亮图标表示日出和日落时间。
Fig. 4 Variation of soundscape power in animals during the day (rose plot) and year (line plot). The sun and moon icons represent the time of sunrise and sunset.
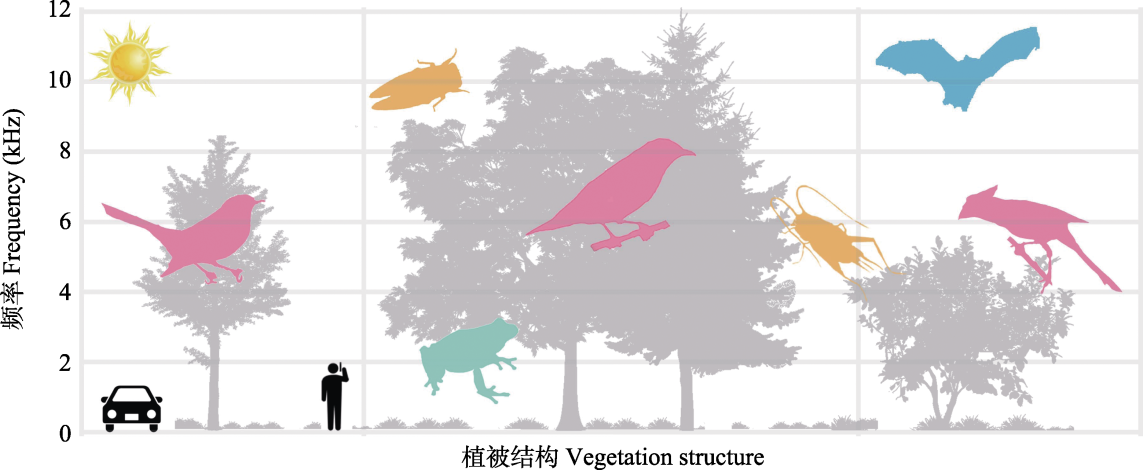
图5 动物声景的驱动因素及部分物种的频率分布概念图。 根据动物的频率分布展示了影响动物声景时空模式的4种驱动因素, 即植被因子(深灰色阴影)、环境因子、人为干扰(黑色阴影)、自身驱动。涉及动物类别包括了城市绿地上常见的鸟类(粉色阴影)、昆虫(黄色阴影)、两栖动物(如蛙类, 绿色阴影)以及哺乳动物(如蝙蝠, 蓝色阴影)。
Fig. 5 Concept map of driving factors of animal soundscapes and frequency distribution of some species. Four driving factors affecting the spatiotemporal patterns of animal soundscapes are shown according to the frequency distribution of animals, i.e. vegetation structure (indicated by dark gray shading), environmental factors, human interference (black shading), and self-driving. The categories of animal include birds (pink shading), insects (yellow shading), amphibians (such as frogs, green shading), and mammals (such as bats, blue shading) that are commonly found in urban green spaces.
| [1] |
Alquezar RD, Macedo RH, Sierro J, Gil D (2020) Lack of consistent responses to aircraft noise in dawn song timing of bird populations near tropical airports. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 74, 88.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Amrhein V, Erne N (2006) Dawn singing reflects past territorial challenges in the winter wren. Animal Behaviour, 71, 1075-1080.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Barber JR, Crooks KR, Fristrup KM (2010) The costs of chronic noise exposure for terrestrial organisms. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 180-189.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Benocci R, Roman HE, Bisceglie A, Angelini F, Brambilla G, Zambon G (2021) Eco-acoustic assessment of an urban park by statistical analysis. Sustainability, 13, 7857.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Benocci R, Roman HE, Bisceglie A, Angelini F, Brambilla G, Zambon G (2022) Auto-correlations and long time memory of environment sound: The case of an urban park in the city of Milan (Italy). Ecological Indicators, 134, 108492. |
| [6] | Berg KS, Brumfield RT, Apanius V (2006) Phylogenetic and ecological determinants of the neotropical dawn chorus. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 273, 999-1005. |
| [7] |
Bian Q, Wang C, Hao ZZ (2021) Application of ecoacoustic monitoring in the field of biodiversity science. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 1119-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[边琦, 王成, 郝泽周 (2021) 生物声音监测研究在生物多样性领域的应用. 应用生态学报, 32, 1119-1128.]
DOI |
|
| [8] | Bradfer-Lawrence T, Bunnefeld N, Gardner N, Willis SG, Dent DH (2020) Rapid assessment of avian species richness and abundance using acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106400. |
| [9] | Buckley EMB, Gottesman BL, Caven AJ, Harner MJ, Pijanowski BC (2021) Assessing ecological and environmental influences on boreal chorus frog (Pseudacris maculata) spring calling phenology using multimodal passive monitoring technologies. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107171. |
| [10] |
Budka M, Skierczyńska A, Antczak M, Osiejuk TS (2021) Nocturnal singing by diurnal birds in Afrotropical highlands. Journal of Ornithology, 162, 435-445.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Burivalova Z, Purnomo, Wahyudi B, Boucher TM, Ellis P, Truskinger A, Towsey M, Roe P, Marthinus D, Griscom B, Game ET (2019) Using soundscapes to investigate homogenization of tropical forest diversity in selectively logged forests. Journal of Applied Ecology, 56, 2493-2504.
DOI |
| [12] |
Burivalova Z, Towsey M, Boucher T, Truskinger A, Apelis C, Roe P, Game ET (2018) Using soundscapes to detect variable degrees of human influence on tropical forests in Papua New Guinea. Conservation Biology, 32, 205-215.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Buxton RT, Brown E, Sharman L, Gabriele CM, McKenna MF (2016) Using bioacoustics to examine shifts in songbird phenology. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 4697-4710.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Chen YF, Luo YH, Mammides C, Cao KF, Zhu SD, Goodale E (2021) The relationship between acoustic indices, elevation, and vegetation, in a forest plot network of southern China. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107942. |
| [15] |
Colino-Rabanal VJ, Mendes S, Peris SJ, Pescador M (2016) Does the song of the Wren Troglodytes troglodytes change with different environmental sounds? Acta Ornithologica, 51, 13-22.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Da Silva A, Samplonius JM, Schlicht E, Valcu M, Kempenaers B (2014) Artificial night lighting rather than traffic noise affects the daily timing of dawn and dusk singing in common European songbirds. Behavioral Ecology, 25, 1037-1047.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
de Andrade AC, Medeiros S, Chiarello AG (2020) City sloths and marmosets in Atlantic forest fragments with contrasting levels of anthropogenic disturbance. Mammal Research, 65, 481-491.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
de Camargo U, Roslin T, Ovaskainen O (2019) Spatio-temporal scaling of biodiversity in acoustic tropical bird communities. Ecography, 42, 1936-1947.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Deoniziak K, Osiejuk TS (2021) Seasonality and social factors, but not noise pollution, influence the song characteristics of two leaf warbler species. PLoS ONE, 16, e0257074. |
| [20] | Derryberry EP, Danner RM, Danner JE, Derryberry GE, Phillips JN, Lipshutz SE, Gentry K, Luther DA (2016) Patterns of song across natural and anthropogenic soundscapes suggest that white-crowned sparrows minimize acoustic masking and maximize signal content. PLoS ONE, 11, e0154456. |
| [21] | Diepstraten J, Willie J (2021) Assessing the structure and drivers of biological sounds along a disturbance gradient. Global Ecology and Conservation, 31, e01819. |
| [22] |
Dominoni DM (2015) The effects of light pollution on biological rhythms of birds: An integrated, mechanistic perspective. Journal of Ornithology, 156, 409-418.
DOI |
| [23] | Doser JW, Finley AO, Kasten EP, Gage SH (2020) Assessing soundscape disturbance through hierarchical models and acoustic indices: A case study on a shelterwood logged northern Michigan forest. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106244. |
| [24] | Dröge S, Martin DA, Andriafanomezantsoa R, Burivalova Z, Fulgence TR, Osen K, Rakotomalala E, Schwab D, Wurz A, Richter T, Kreft H (2021) Listening to a changing landscape: Acoustic indices reflect bird species richness and plot-scale vegetation structure across different land-use types in north-eastern Madagascar. Ecological Indicators, 120, 106929. |
| [25] |
Duarte MHL, Sousa-Lima RS, Young RJ, Farina A, Vasconcelos M, Rodrigues M, Pieretti N (2015) The impact of noise from open-cast mining on Atlantic forest biophony. Biological Conservation, 191, 623-631.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Duarte MHL, Sousa-Lima RS, Young RJ, Vasconcelos MF, Bittencourt E, Scarpelli MDA, Farina A, Pieretti N (2021) Changes on soundscapes reveal impacts of wildfires in the fauna of a Brazilian savanna. Science of the Total Environment, 769, 144988. |
| [27] |
Eldridge A, Guyot P, Moscoso P, Johnston A, Eyre-Walker Y, Peck M (2018) Sounding out ecoacoustic metrics: Avian species richness is predicted by acoustic indices in temperate but not tropical habitats. Ecological Indicators, 95, 939-952.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Farina A, Lattanzi E, Malavasi R, Pieretti N, Piccioli L (2011) Avian soundscapes and cognitive landscapes: Theory, application and ecological perspectives. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1257-1267.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Farina A, Pieretti N (2014) Sonic environment and vegetation structure: A methodological approach for a soundscape analysis of a Mediterranean maqui. Ecological Informatics, 21, 120-132.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Francomano D, Valenzuela AEJ, Gottesman BL, González- Calderón A, Anderson CB, Hardiman BS, Pijanowski BC (2021) Acoustic monitoring shows invasive beavers Castor canadensis increase patch-level avian diversity in Tierra del Fuego. Journal of Applied Ecology, 58, 2987-2998.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Gage SH, Axel AC (2014) Visualization of temporal change in soundscape power of a Michigan lake habitat over a 4-year period. Ecological Informatics, 21, 100-109.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Gage SH, Wimmer J, Tarrant T, Grace PR (2017) Acoustic patterns at the Samford ecological research facility in South East Queensland, Australia: The Peri-Urban SuperSite of the Terrestrial Ecosystem Research Network. Ecological Informatics, 38, 62-75.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Gallo T, Fidino M, Lehrer EW, Magle SB (2017) Mammal diversity and metacommunity dynamics in urban green spaces: Implications for urban wildlife conservation. Ecological Applications, 27, 2330-2341.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Gasc A, Anso J, Sueur J, Jourdan H, Desutter-Grandcolas L (2018) Cricket calling communities as an indicator of the invasive ant Wasmannia auropunctata in an insular biodiversity hotspot. Biological Invasions, 20, 1099-1111.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Gibson M, Maron M, Taws N, Simmonds JS, Walsh JC (2021) Use of citizen science datasets to test effects of grazing exclusion and replanting on Australian woodland birds. Restoration Ecology, 30, e13610. |
| [36] | Gottesman BL, Olson JC, Yang S, Acevedo-Charry O, Francomano D, Martinez FA, Appeldoorn RS, Mason DM, Weil E, Pijanowski BC (2021) What does resilience sound like? Coral reef and dry forest acoustic communities respond differently to Hurricane Maria. Ecological Indicators, 126, 107635. |
| [37] | Grabarczyk EE, Gill SA (2019) Anthropogenic noise affects male house wren response to but not detection of territorial intruders. PLoS ONE, 14, e0220576. |
| [38] |
Grabarczyk EE, Gill SA (2020) Anthropogenic noise masking diminishes house wren (Troglodytes aedon) song transmission in urban natural areas. Bioacoustics, 29, 518-532.
DOI |
| [39] |
Grinfeder E, Haupert S, Ducrettet M, Barlet J, Reynet MP, Sèbe F, Sueur J (2022) Soundscape dynamics of a cold protected forest: Dominance of aircraft noise. Landscape Ecology, 37, 567-582.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Guo FY, Bonebrake TC, Dingle C (2016) Low frequency dove coos vary across noise gradients in an urbanized environment. Behavioural Processes, 129, 86-93.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Hao YY, Kang J, Krijnders JD (2015) Integrated effects of urban morphology on birdsong loudness and visibility of green areas. Landscape and Urban Planning, 137, 149-162.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Hao ZZ, Wang C, Sun ZK, Zhao DX, Sun BQ, Wang HJ, van den Bosch CK (2021) Vegetation structure and temporality influence the dominance, diversity, and composition of forest acoustic communities. Forest Ecology and Management, 482, 118871. |
| [43] |
Haq SMA (2011) Urban green spaces and an integrative approach to sustainable environment. Journal of Environmental Protection, 2, 601-608.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Hedblom M, Knez I, Sang ÅO, Gunnarsson B (2017) Evaluation of natural sounds in urban greenery: Potential impact for urban nature preservation. Royal Society Open Science, 4, 170037. |
| [45] | Hensley CB, Trisos CH, Warren PS, MacFarland J, Blumenshine S, Reece J, Katti M (2019) Effects of urbanization on native bird species in three southwestern US cities. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 71. |
| [46] | Herrera-Montes MI (2018) Protected area zoning as a strategy to preserve natural soundscapes, reduce anthropogenic noise intrusion, and conserve biodiversity. Tropical Conservation Science, 11, 194008291880434. |
| [47] |
Hopson A, de Szalay F (2021) Alteration of above and below-water soundscapes by roads. Wetlands, 41, 2.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Izaguirre MR, Barrantes-Madrigal J, Sequeira DS, Spínola-Parallada M, Ramírez-Alán O (2021) It is not just about birds: What do acoustic indices reveal about a Costa Rican tropical rainforest? Neotropical Biodiverity, 7, 431-442. |
| [49] | Jahani A, Kalantary S, Alitavoli A, Li SN (2022) An application of artificial intelligence techniques in prediction of bird soundscape impact on tourists’ mental restoration in natural urban areas. Urban Planning Forum, (1), 126. (in Chinese) |
| [ Jahani A, Kalantary S, Alitavoli A, 李胜男 (2022) 人工智能技术在预测城市自然地区鸟类声景对游客心理恢复的影响中的应用. 城市规划学刊, (1), 126.] | |
| [50] | Jahn O, Ganchev TD, Marques MI, Schuchmann KL (2017) Automated sound recognition provides insights into the behavioral ecology of a tropical bird. PLoS ONE, 12, e0169041. |
| [51] |
Jordão JM, Fonseca PJ, Amorim MCP (2012) Chorusing behaviour in the lusitanian toadfish: Should I match my neighbours’ calling rate? Ethology, 118, 885-895.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Khanaposhtani MG, Gasc A, Francomano D, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Jung JH, Mossman MJ, Pijanowski BC (2019) Effects of highways on bird distribution and soundscape diversity around Aldo Leopold’s shack in Baraboo, Wisconsin, USA. Landscape and Urban Planning, 192, 103666. |
| [53] |
Kight CR, Swaddle JP (2015) Eastern bluebirds alter their song in response to anthropogenic changes in the acoustic environment. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 55, 418-431.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Kirschel ANG, Blumstein DT, Cohen RE, Buermann W, Smith TB, Slabbekoorn H (2009) Birdsong tuned to the environment: Green hylia song varies with elevation, tree cover, and noise. Behavioral Ecology, 20, 1089-1095.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Kong F, Nakagoshi N (2006) Spatial-temporal gradient analysis of urban green spaces in Jinan, China. Landscape and Urban Planning, 78, 147-164.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Krause B, Farina A (2016) Using ecoacoustic methods to survey the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Biological Conservation, 195, 245-254.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Kułaga K, Budka M (2020) Nocturnal singing by diurnal birds in a temperate region of central Europe. Journal of Ornithology, 161, 1143-1152.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Laverne RJ, Kellogg WA (2019) Loss of urban forest canopy and the effects on neighborhood soundscapes. Urban Ecosystems, 22, 249-270.
DOI |
| [59] |
LaZerte SE, Otter KA, Slabbekoorn H (2015) Relative effects of ambient noise and habitat openness on signal transfer for chickadee vocalizations in rural and urban green-spaces. Bioacoustics, 24, 233-252.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Li H, Xie H, Woodward G (2021) Soundscape components, perceptions, and EEG reactions in typical mountainous urban parks. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 64, 127269. |
| [61] | Lin TH, Tsao Y, Wang YH, Yen HW, Lu SS (2017) Computing biodiversity change via a soundscape monitoring network. In:Proceedings of the 2017 Pacific Neighborhood Consortium Annual Conference and Joint Meetings (PNG), pp. 128-133. IEEE, Taipei, China. |
| [62] |
Liu J, Kang J, Luo T, Behm H, Coppack T (2013) Spatiotemporal variability of soundscapes in a multiple functional urban area. Landscape and Urban Planning, 115, 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Liu J, Wang YJ, Zimmer C, Kang J, Yu TH (2019) Factors associated with soundscape experiences in urban green spaces: A case study in Rostock, Germany. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 37, 135-146. |
| [64] |
Marín-Gómez OH, MacGregor-Fors I (2019) How early do birds start chirping? Dawn chorus onset and peak time in a neotropical city. Ardeola, 66, 327-341.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Marín-Gómez OH, MacGregor-Fors I (2021) A global synthesis of the impacts of urbanization on bird dawn choruses. Ibis, 163, 1133-1154.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Morrison CA, Auniņš A, Benkő Z, Brotons L, Chodkiewicz T, Chylarecki P, Escandell V, Eskildsen DP, Gamero A, Herrando S, Jiguet F, Kålås JA, Kamp J, Klvaňová A, Kmecl P, Lehikoinen A, Lindström Å, Moshøj C, Noble DG, Øien IJ, Paquet JY, Reif J, Sattler T, Seaman BS, Teufelbauer N, Trautmann S, Vořišek P, Butler SJ (2021) Bird population declines and species turnover are changing the acoustic properties of spring soundscapes. Nature Communications, 12, 6217.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Müller S, Mitesser O, Oschwald L, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Potvin C (2022) Temporal soundscape patterns in a Panamanian tree diversity experiment: Polycultures show an increase in high frequency cover. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 808589. |
| [68] |
Mullet TC, Gage SH, Morton JM, Huettmann F (2016) Temporal and spatial variation of a winter soundscape in south-central Alaska. Landscape Ecology, 31, 1117-1137.
DOI URL |
| [69] | Nava-Díaz R, Pineda-López R, Dorantes-Euan A (2020) Drivers of functional composition of bird assemblages in green spaces of a neotropical city: A case study from Merida, Mexico. Tropical Conservation Science, 13, 1940082920923896. |
| [70] | Nawar N, Sorker R, Chowdhury FJ, Mostafizur Rahman M (2022) Present status and historical changes of urban green space in Dhaka City, Bangladesh: A remote sensing driven approach. Environmental Challenges, 6, 100425. |
| [71] | Oliveira EG, Ribeiro MC, Roe P, Sousa-Lima RS (2021) The Caatinga Orchestra: Acoustic indices track temporal changes in a seasonally dry tropical forest. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107897. |
| [72] | Parsons MJG, Lin TH, Mooney TA, Erbe C, Juanes F, Lammers M, Li SH, Linke S, Looby A, Nedelec SL, Van Opzeeland I, Radford C, Rice AN, Sayigh L, Stanley J, Urban E, Di Iorio L (2022) Sounding the call for a global Llibrary of underwater biological sounds. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 810156. |
| [73] |
Pieretti N, Duarte MHL, Sousa-Lima RS, Rodrigues M, Young RJ, Farina A (2015) Determining temporal sampling schemes for passive acoustic studies in different tropical ecosystems. Tropical Conservation Science, 8, 215-234.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Pijanowski BC, Farina A, Gage SH, Dumyahn SL, Krause BL (2011a) What is soundscape ecology? An introduction and overview of an emerging new science. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1213-1232.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Pijanowski BC, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Dumyahn SL, Farina A, Krause BL, Napoletano BM, Gage SH, Pieretti N (2011b) Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience, 61, 203-216.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Proppe DS, Sturdy CB, St Clair CC (2013) Anthropogenic noise decreases urban songbird diversity and may contribute to homogenization. Global Change Biology, 19, 1075-1084.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Puswal SM, Mei JJ, Liu FL (2021) Effects of temperature and season on birds’ dawn singing behavior in a forest of eastern China. Journal of Ornithology, 162, 447-459.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Quiroz-Oliva M, Sosa-López JR (2022) Vocal behaviour of Sclater’s wrens, a duetting Neotropical songbird: Repertoires, dawn chorus variation, and song sharing. Journal of Ornithology, 163, 121-136.
DOI URL |
| [79] | Retamosa Izaguirre MI, Segura Sequeira D, Barrantes Madrigal J, Spínola Parallada M, Ramírez Alán O (2021) Vegetation, bird and soundscape characterization: A case study in Braulio Carrillo National Park, Costa Rica. Biota Colombiana, 22, 57-73. |
| [80] |
Robert A, Lengagne T, Melo M, Gardette V, Julien S, Covas R, Gomez D, Doutrelant C (2019) The theory of island biogeography and soundscapes: Species diversity and the organization of acoustic communities. Journal of Biogeography, 46, 1901-1911.
DOI |
| [81] |
Rodriguez A, Gasc A, Pavoine S, Grandcolas P, Gaucher P, Sueur J (2014) Temporal and spatial variability of animal sound within a neotropical forest. Ecological Informatics, 21, 133-143.
DOI URL |
| [82] | Ross S, Friedman NR, Dudley KL, Yoshimura M, Yoshida T, Economo EP (2018) Listening to ecosystems: Data-rich acoustic monitoring through landscape-scale sensor networks. Ecological Research, 33, 135-147. |
| [83] | Scarpelli MDA, Ribeiro MC, Teixeira CP (2021) What does Atlantic forest soundscapes can tell us about landscape? Ecological Indicators, 121, 107050. |
| [84] | Schafer RM (1993) The Soundscape: Our Sonic Environment and the Tuning of the World. Destiny Books, Rochester. |
| [85] |
Schlicht L, Kempenaers B (2020) The effects of season, sex, age and weather on population-level variation in the timing of activity in Eurasian Blue Tits Cyanistes caeruleus. Ibis, 162, 1146-1162.
DOI URL |
| [86] | Sikuzani YU, Kouagou RS, Maréchal J, Ilunga EIW, Malaisse F, Bogaert J, Kankumbi FM (2018) Changes in the spatial pattern and ecological functionalities of green spaces in Lubumbashi (the Democratic Republic of Congo) in relation with the degree of urbanization. Tropical Conservation Science, 11, 1940082918771325. |
| [87] |
Straka TM, Wolf M, Gras P, Buchholz S, Voigt CC (2019) Tree cover mediates the effect of artificial light on urban bats. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 91.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Suarez-Rubio M, Ille C, Bruckner A (2018) Insectivorous bats respond to vegetation complexity in urban green spaces. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 3240-3253.
DOI PMID |
| [89] |
Suhonen J, Jokimäki J (2019) Temporally stable species occupancy frequency distribution and abundance-occupancy relationship patterns in urban wintering bird assemblages. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 129.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Tan MK (2021) Soundscape of urban-tolerant crickets (Orthoptera: Gryllidae, Trigonidiidae) in a tropical Southeast Asia city, Singapore. Bioacoustics, 30, 469-486.
DOI URL |
| [91] | Tennessen JB, Parks SE, Langkilde T (2014) Traffic noise causes physiological stress and impairs breeding migration behaviour in frogs. Conservation Physiology, 2, cou032. |
| [92] |
To AWY, Dingle C, Collins SA (2021) Multiple constraints on urban bird communication: Both abiotic and biotic noise shape songs in cities. Behavioral Ecology, 32, 1042-1053.
DOI PMID |
| [93] | Turner A, Fischer M, Tzanopoulos J (2018) Sound-mapping a coniferous forest—Perspectives for biodiversity monitoring and noise mitigation. PLoS ONE, 13, e0189843. |
| [94] |
Ulloa JS, Gasc A, Gaucher P, Aubin T, Rejou-Mechain M, Sueur J (2016) Screening large audio datasets to determine the time and space distribution of screaming piha birds in a tropical forest. Ecological Informatics, 31, 91-99.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Van Duyse E, Pinxten R, Snoeijs T, Eens M (2005) Simultaneous treatment with an aromatase inhibitor and an anti-androgen decreases the likelihood of dawn song in free-living male great tits, Parus major. Hormones and Behavior, 48, 243-251.
DOI PMID |
| [96] |
van Niekerk JH, Forcina G (2020) Purpose of crested Francolin Ortygornis sephaena male collective calls at dusk based on livestream audio censusing. Ostrich, 91, 326-337.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Vieira J, Matos P, Mexia T, Silva P, Lopes N, Freitas C, Correia O, Santos-Reis M, Branquinho C, Pinho P (2018) Green spaces are not all the same for the provision of air purification and climate regulation services: The case of urban parks. Environmental Research, 160, 306-313.
DOI PMID |
| [98] |
Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Pijanowski BC, Doucette J, Pekin B (2011) A primer of acoustic analysis for landscape ecologists. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1233-1246.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
Xie J, Towsey M, Zhang J, Roe P (2016) Acoustic classification of Australian frogs based on enhanced features and machine learning algorithms. Applied Acoustics, 113, 193-201.
DOI URL |
| [100] | Xie S, Marzluff JM, Su Y, Wang Y, Meng N, Wu T, Gong C, Lu F, Xian C, Zhang Y, Ouyang Z (2022) The role of urban waterbodies in maintaining bird species diversity within built area of Beijing. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 150430. |
| [101] | Zhan X, Liang D, Lin X, Li LG, Wei CT, Dingle C, Liu Y (2021) Background noise but not urbanization level impacted song frequencies in an urban songbird in the Pearl River Delta, Southern China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 28, e01695. |
| [102] | Zhang Y, Huang TT, Hu Q, Zhu JN (2022) Analysis on the habitat design strategy of community park based on the improvement of bird diversity. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 38(3), 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张颖, 黄婷婷, 胡骞, 朱建宁 (2022) 基于鸟类多样性提升的社区公园生境营造策略探析. 中国园林, 38(3), 106-111.] | |
| [103] |
Zhang YJ, Murray AT, Turner BL (2017) Optimizing green space locations to reduce daytime and nighttime urban heat island effects in Phoenix, Arizona. Landscape and Urban Planning, 165, 162-171.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Zhao Y, Shen XL, Li S, Zhang YY, Peng RH, Ma KP (2020) Progress and outlook for soundscape ecology. Biodiversity Science, 28, 806-820. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[赵莹, 申小莉, 李晟, 张雁云, 彭任华, 马克平 (2020) 声景生态学研究进展和展望. 生物多样性, 28, 806-820.]
DOI |
|
| [105] | Znidersic E, Towsey M, Roy WK, Darling SE, Truskinger A, Roe P, Watson DM (2020) Using visualization and machine learning methods to monitor low detectability species—The least bittern as a case study. Ecological Informatics, 55, 101014. |
| [1] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [2] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [3] | 马尚飞, 龚鑫, 上官华媛, 姚海凤, 王滨, 李志鹏, 孙新. 城市化过程中不同用地类型对土壤真核生物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24540-. |
| [4] | 刘双祺, 华方圆, 夏舫, 闫亮亮, 于方, 叶红, 彭澎, 张东元, 关雪燕, 付建平, 梁烜, 侯笑如, 李晓阳, 赵欣如. 城市绿地作为迁徙陆鸟中途停歇地的栖息地质量及其受留野措施的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24046-. |
| [5] | 吴琼, 赵梓羲, 孙桃柱, 赵雨梦, 于丛, 祝芹, 李忠秋. 城市道路特征及自然景观对动物路杀的影响: 以南京为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24141-. |
| [6] | 王秦韵, 张玉泉, 刘浩, 李明, 刘菲, 赵宁, 陈鹏, 齐敦武, 阙品甲. 成都大熊猫繁育研究基地鸟类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24066-. |
| [7] | 李乐, 张承云, 裴男才, 高丙涛, 王娜, 李嘉睿, 武瑞琛, 郝泽周. 基于被动声学监测技术的城市绿地景观格局与鸟类多样性关联分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24296-. |
| [8] | 唐楚飞, 葛成, 曹烨, 曹弘毅, 宋晓晓, 廖怀建. 城市森林不同林分类型的昆虫多样性: 以南京紫金山南麓为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22357-. |
| [9] | 牛铜钢, 刘为. 双碳战略背景下城市生态系统的碳汇功能与生物多样性可以兼得[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22168-. |
| [10] | 黄越, 顾燚芸, 阳文锐, 闻丞. 如何在北京充分实现受胁鸟类栖息地保护?[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 340-350. |
| [11] | 洪雪萌, 戈昕宇, 李俊兰. 赛罕乌拉自然保护区蝶类多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(6): 590-600. |
| [12] | 王勇, 许洁, 杨刚, 李宏庆, 吴时英, 唐海明, 马波, 王正寰. 城市公共绿地常见木本植物组成对鸟类群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(2): 196-207. |
| [13] | 赵娟娟, 欧阳志云, 郑华, 徐卫华, 王效科, 倪永明. 北京建成区外来植物的种类构成[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(1): 19-28. |
| [14] | 凌琪, 王晏平, 王莉, 舒莹, 陶勇, 鲍立宁. 合肥城区空气真菌浓度的时空分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(2): 175-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()