



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22526. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022526 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022526
孙军1,2,3,*( ), 宋煜尧3, 施义锋3, 翟键3, 燕文卓3
), 宋煜尧3, 施义锋3, 翟键3, 燕文卓3
收稿日期:2022-09-13
接受日期:2022-10-31
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-08
通讯作者:
孙军
作者简介:* E-mail: phytoplankton@163.com基金资助:
Jun Sun1,2,3,*( ), Yuyao Song3, Yifeng Shi3, Jian Zhai3, Wenzhuo Yan3
), Yuyao Song3, Yifeng Shi3, Jian Zhai3, Wenzhuo Yan3
Received:2022-09-13
Accepted:2022-10-31
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-08
Contact:
Jun Sun
摘要:
本文系统地总结了近10年中国研究人员在遗传、物种、生态系统3个层次上对海洋生物多样性研究的重要进展, 并使用VOSviewer软件对近10年中国近海生物多样性的研究成果进行文献计量分析。近年来, 中国研究人员借助新的研究方法和手段, 比如分子生物学和流式细胞术等, 可以在物种多样性水平进行更准确和快速的分类鉴定, 借此在中国近海发现了较多新的物种; 通过多学科交叉融合, 更多的是在生态系统水平探讨海洋生物多样性, 也为今后海洋生态系统的修复提供了科学依据。目前中国的海洋生物多样性研究紧跟国际科技前沿和步伐, 在深海、海山和极端环境生物类群等新兴领域有了长足发展, 新物种的发现不断更新了原有认识, 对典型海洋生态系统的监测和部分入侵物种的整治有了长足的进步。中国近海生物多样性高, 监测数据全, 通过整合空间数据资料和时间序列变化, 进行更广更深的宏观生态模式分析研究十分必要。通过探究生物多样性的多重胁迫因子及其交互作用, 可为优化海洋生物多样性的保护和管理提供帮助。
孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓 (2022) 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22526. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022526.
Jun Sun, Yuyao Song, Yifeng Shi, Jian Zhai, Wenzhuo Yan (2022) Progress of marine biodiversity studies in China seas in the past decade. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22526. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022526.
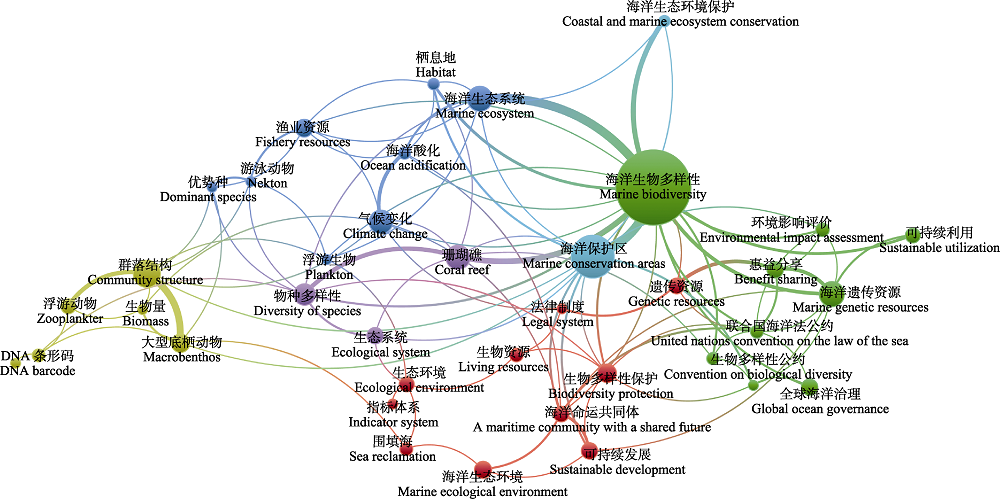
图2 2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性文献中文关键词共现图(数据来源于中国知网数据库)
Fig. 2 Keyword co-occurrence map of Chinese marine biodiversity literatures from 2011 to 2021 (data from CNKI database)
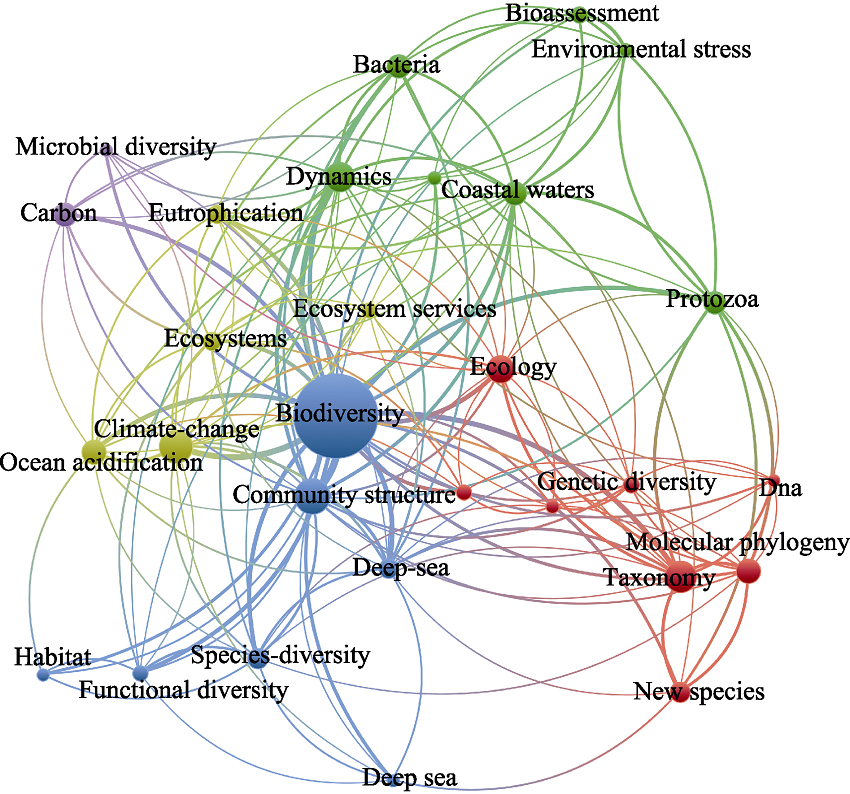
图3 2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性研究英文关键字共现图(数据来源于Web of Science数据库)
Fig. 3 Keyword co-occurrence map for marine biodiversity studies in China from 2011 to 2021 (data from Web of Science database)
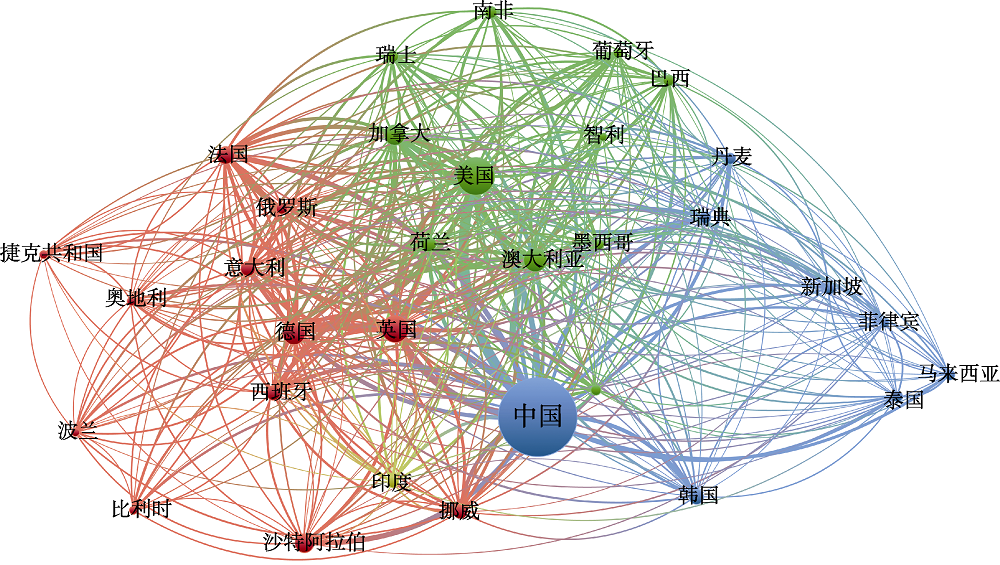
图4 2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性研究国家合作共现图(数据来源于Web of Science数据库)
Fig. 4 International cooperation co-existence map for marine biodiversity studies in China from 2011 to 2021 (data from Web of Science database)
| [1] |
Arbi I, Zhang JP, Liu SL, Wu YC, Huang XP (2017) Benthic habitat health assessment using macrofauna communities of a sub-tropical semi-enclosed bay under excess nutrients. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 119, 39-49.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Chen BZ, Smith SL, Wirtz KW (2018) Effect of phytoplankton size diversity on primary productivity in the North Pacific: Trait distributions under environmental variability. Ecology Letters, 22, 56-66.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chen NS, Wang F (2021) Preface. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52, 261. (in Chinese) |
| [陈楠生, 王凡 (2021) 前言. 海洋与湖沼, 52, 261.] | |
| [4] | Chen QC (1997) Current status and prospects of marine biodiversity in China. Chinese Biodiversity, 5, 142-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈清潮 (1997) 中国海洋生物多样性的现状和展望. 生物多样性, 5, 142-146.] | |
| [5] |
Chen TT, Zhang YX, Song SQ, Liu Y, Sun XX, Li CW (2021) Diversity and seasonal variation of marine phytoplankton in Jiaozhou Bay, China revealed by morphological observation and metabarcoding. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 40, 577-591.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chen XH, Guo L, Li MM, Meng ZN, Lin HR (2014) Analysis of RAPD and mitochondrial Cytb gene sequences of three cultured stocks of Epinephelus coioides from Guangdong Province, China. South China Fisheries Science, 10, 27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈兴汉, 郭梁, 李明明, 蒙子宁, 林浩然 (2014) 广东沿海3个斜带石斑鱼养殖群体的RAPD和线粒体Cytb基因序列变异分析. 南方水产科学, 10, 27-33.] | |
| [7] | Chen Y, Sun DY, Zhang HL, Wang SQ, Qiu ZF, He YJ (2020) Remote-sensing monitoring of green tide and its drifting trajectories in Yellow Sea based on observation data of geostationary ocean color imager, China. Acta Optica Sinica, 40(3), 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈莹, 孙德勇, 张海龙, 王胜强, 丘仲锋, 何宜军 (2020) 结合GOCI数据的黄海绿潮遥感监测及漂移轨迹研究. 光学学报, 40(3), 1-13.] | |
| [8] | Chen Z, Sun J, Zhang GC (2018) Netz-phytoplankton community structure of the tropical Western Pacific Ocean in summer 2016. Marine Sciences, 42(7), 114-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈卓, 孙军, 张桂成 (2018) 2016年秋季热带西太平洋网采浮游植物群落结构. 海洋科学, 42(7), 114-130.] | |
| [9] |
Chen ZQ, Shou L, Liao YB, Gao AG, Zeng JN, Chen QZ (2013) Community structure of benthic algae and its seasonal variation in the rocky intertidal zone of Sanya. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 3370-3382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [陈自强, 寿鹿, 廖一波, 高爱根, 曾江宁, 陈全震 (2013) 三亚岩相潮间带底栖海藻群落结构及其季节变化. 生态学报, 33, 3370-3382.] | |
| [10] | Cheng J, Sha ZL, Sun SE, Hui M (2021) Progress on the origin, evolution and biogeographic pattern of megafauna biodiversity in deep-sea chemosynthetic ecosystems, China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52, 508-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程娇, 沙忠利, 孙邵娥, 惠敏 (2021) 深海化能生态系统大型生物多样性分布格局及其起源演化研究进展. 海洋与湖沼, 52, 508-521.] | |
| [11] |
Cui ZX, Zhang H, Song LS, You F (2011) Genetic diversity of marine animals in China: A summary and prospectiveness, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 815-833. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[崔朝霞, 张峘, 宋林生, 尤锋 (2011) 中国重要海洋动物遗传多样性的研究进展. 生物多样性, 19, 815-833.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Danovaro R, Gambi C, Dell’Anno A, Corinaldesi C, Fraschetti S, Vanreusel A, Vincx M, Gooday AJ (2008) Exponential decline of deep-sea ecosystem functioning linked to benthic biodiversity loss. Current Biology, 18, 1-8.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Ding LP, Huang BX, Xie YQ (2011) Advances and problems with the study of marine macroalgae of China seas, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 798-804. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[丁兰平, 黄冰心, 谢艳齐 (2011) 中国大型海藻的研究现状及其存在的问题. 生物多样性, 19, 798-804.]
DOI |
|
| [14] | Ding LP, Liu MY, Yan PZ, Wang YX, Wang XC, Huang BX (2022) Classification status and prospects of the family Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta, China. Guangxi Sciences, 29, 131-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁兰平, 刘美媛, 闫盼竹, 王艺晓, 王雪聪, 黄冰心 (2022) 红藻门仙菜科Ceramiaceae的分类现状与展望. 广西科学, 29, 131-146.] | |
| [15] | Ding LP, Ma YY, Huang BX (2012) The application and perspective of DNA barcoding technology on the macroalgae China. Marine Sciences, 36, 103-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁兰平, 马元元, 黄冰心 (2012) DNA条形码技术在大型海藻学研究中的应用及前景. 海洋科学, 36, 103-110.] | |
| [16] | Dong D, Li XZ, Yang M, Gong L, Li Y, Sui JX, Gan ZB, Kou Q, Xiao N, Zhang JL (2021) Report of epibenthic macrofauna found from Haima cold seeps and adjacent deep-sea habitats, South China Sea. Marine Life Science & Technology, 3, 1-12. |
| [17] |
Dong ZG, Li XY, Wang PL, Wang WJ, Zhang QQ, Yan BL, Sun XW (2013) Genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) from six geographical populations of China Sea based on mitochondrial D-loop gene, China. Journal of Fisheries of China, 37, 1304-1312. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [董志国, 李晓英, 王普力, 王文进, 张庆起, 阎斌伦, 孙效文 (2013) 基于线粒体D-loop基因的中国海三疣梭子蟹遗传多样性与遗传分化研究. 水产学报, 37, 1304-1312.] | |
| [18] | Dou P, Cui BS, Xie T, Dong DZ, Gu BH (2016) Macrobenthos Diversity response to hydrological connectivity gradient. Wetlands, 36, S45-S55. |
| [19] |
Du GY, Wu FF, Guo H, Xue HF, Mao YX (2015) DNA barcode assessment of Ceramiales (Rhodophyta) in the intertidal zone of the northwestern Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 33, 685-695.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Du JG, Chen B, Zhou QL, Yang SY, Wen Q, Shi HH, Yu WW, Huang H (2011) Strategies for the marine biodiversity conservation based on the integrated coastal zone management, China. Marine Science Bulletin, 30, 456-462. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜建国, 陈彬, 周秋麟, 杨圣云, 温泉, 石洪华, 俞炜炜, 黄浩 (2011) 以海岸带综合管理为工具开展海洋生物多样性保护管理. 海洋通报, 30, 456-462.] | |
| [21] | Flombaum P, Gallegos JL, Gordillo RA, Rincón J, Zabala LL, Jiao N, Karl DM, Li WKW, Lomas MW, Veneziano D, Vera CS, Vrugt JA, Martiny AC (2013) Present and future global distributions of the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 9824-9829. |
| [22] |
Gao DH, Sun ZM, Huang CH, Yao JT, Wang YQ, Tan W, Chen FX (2020) First record of Caulerpa lentillifera J. Agardh (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) from China. Marine Biology Research, 16, 44-49.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Gao F, Huang J, Zhao Y, Li LF, Liu WW, Miao M, Zhang QQ, Li JM, Yi ZZ, El-Serehy HA, Warren A, Song WB (2017) Systematic studies on ciliates (Alveolata, Ciliophora) in China: Progress and achievements based on molecular information. European Journal of Protistology, 61, 409-423.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Gao Y, Lin GH (2018) Algal diversity and their importance in ecological processes in typical mangrove ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1223-1235. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[高宇, 林光辉 (2018) 典型红树林生态系统藻类多样性及其在生态过程中的作用. 生物多样性, 26, 1223-1235.]
DOI |
|
| [25] | Geng GB (2022) Protect and restore mangroves and maintain marine ecosystems. Green China, (3), 26-31. (in Chinese) |
| [耿国彪 (2022) 保护修复红树林维护海洋生态系统. 绿色中国, (3), 26-31.] | |
| [26] |
Gong J, Song YJ, Zhang XL (2013) Phylogenetic and functional diversity of nitrogen cycling microbes in coastal sediments. Biodiversity Science, 21, 433-444. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[龚骏, 宋延静, 张晓黎 (2013) 海岸带沉积物中氮循环功能微生物多样性. 生物多样性, 21, 433-444.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Gu DX, Wang T, Xu YF, Wu N, Wang N, Hao Y, Wang G, Li WW, Liu GS (2021) Genetic diversity of wild populations of mantis shrimp Oratosqilla oratoria in Bohai Bay using microsatellite markers. Fisheries Science, 40, 693-699. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谷德贤, 王婷, 许玉甫, 吴宁, 王娜, 郝郁, 王刚, 李文雯, 刘国山 (2021) 利用微卫星分子标记分析渤海湾的口虾蛄遗传多样性. 水产科学, 40, 693-699.] | |
| [28] | Guo SJ, Li YQ, Zhang CX, Zhai WD, Huang T, Wang LF, Ma W, Jin HL, Sun J (2014) Phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea and its relationship with environmental factors. Marine Science Bulletin, 33, 95-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭术津, 李彦翘, 张翠霞, 翟惟东, 黄韬, 王丽芳, 马威, 谨华龙, 孙军 (2014) 渤海浮游植物群落结构及与环境因子的相关性分析. 海洋通报, 33, 95-105.] | |
| [29] | Guo SJ, Sun J, Zhang H, Zhai WD (2013) Phytoplankton communities in the Northern Yellow Sea in autumn 2011, China. Journal of Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 28(1), 22-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭术津, 孙军, 张辉, 翟惟东 (2013) 2011年秋季北黄海浮游植物群落. 天津科技大学学报, 28(1), 22-29.] | |
| [30] | Han QX, Li BQ, Han QY, Zhang Y, Wang YQ, Wang QC, Liu DY (2011) Preliminary study of the impact of fishery trawling on epifauna community in the coastal water of Weihai Port. Marine Science Bulletin, 30, 121-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩庆喜, 李宝泉, 韩秋影, 张永, 王跃启, 王全超, 刘东艳 (2011) 渔业捕捞对威海港附近海域底上大型底栖群落结构影响的初步研究. 海洋通报, 30, 121-126.] | |
| [31] | Ji YY, Xu L, Li H, Wang LG, Du FY (2019) Genetic structure of Oithona setigera from South China Sea based on 28S rDNA gene. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38, 89-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[季莹莹, 徐磊, 黎红, 王亮根, 杜飞雁 (2019) 基于28S rDNA的南海刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)种群遗传多样性研究. 热带海洋学报, 38, 89-97.]
DOI |
|
| [32] |
Ke ZX, Huang LM, Tan YH, Yin JQ (2011) Plankton community structure and diversity in coral reefs area of Sanya Bay, Hainan Province, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 696-701. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[柯志新, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 尹健强 (2011) 三亚珊瑚礁分布海区浮游生物的群落结构. 生物多样性, 19, 696-701.]
DOI |
|
| [33] | Li CH, Jia XP (2005) Advances and hot topics for the marine biodiversity protection in China. South China Fisheries Science, 1(1), 66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李纯厚, 贾晓平 (2005) 中国海洋生物多样性保护研究进展与几个热点问题. 南方水产, 1(1), 66-70.] | |
| [34] |
Li CL, Wang MX, Cheng FP, Sun S (2011) DNA barcoding and its application to marine zooplankton ecology. Biodiversity Science, 19, 805-814. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李超伦, 王敏晓, 程方平, 孙松 (2011) DNA条形码及其在海洋浮游动物生态学研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 19, 805-814.]
DOI |
|
| [35] |
Li HX, Huang XN, Li SG, Zhan AB (2019) Environmental DNA (eDNA)-metabarcoding-based early monitoring and warning for invasive species in aquatic ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 27, 491-504. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李晗溪, 黄雪娜, 李世国, 战爱斌 (2019) 基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警. 生物多样性, 27, 491-504.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Li XZ (2011) An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: Principally from the Yellow Sea. Biodiversity Science, 19, 676-684. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[李新正 (2011) 我国海洋大型底栖生物多样性研究及展望: 以黄海为例. 生物多样性, 19, 676-684.]
DOI |
|
| [37] | Li Y, Song PQ, Feng J, Zhang N, Zhang R, Lin LS (2019) Complete mitochondrial genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Myoxocephalus scorpius (Linnaeus, 1758). Mitochondrial DNA Part B: Resources, 4, 862-863. |
| [38] | Li Y, Zheng W, Zheng TL (2013) Advances in research of marine microbial diversity and molecular ecology. Microbiology China, 40, 655-668. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李祎, 郑伟, 郑天凌 (2013) 海洋微生物多样性及其分子生态学研究进展. 微生物学通报, 40, 655-668.] | |
| [39] | Li YF, Bi R, Zhao PH, Liu WH, Li P (2022) Research progress on distribution characteristics and environmental behavior of microplastics in mangrove forests. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41, 1835-1844. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李一璠, 毕然, 赵普晖, 刘文华, 李平 (2022) 红树林环境中微塑料污染分布特征及生态风险研究进展. 生态学杂志, 41, 1835-1844.] | |
| [40] | Li YX, Dong Y, Xu QZ, Fan SL, Lin HS, Wang MH, Zhang XL (2020) Genetic differentiation and evolutionary history of the circumpolar species Ophiura sarsii and subspecies Ophiura sarsii vadicola (Ophiurida: Ophiuridae). Continental Shelf Research, 197, 104805. |
| [41] | Liang RS, Tang FS, He HB, Wang J, Li JT, Li QQ, Chen YZ, Lin L, Zhang K (2021) DNA barcoding and molecular phylogenetic relationships of Epinephelus species from western Pacific coastal areas. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 45, 851-860. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁日深, 唐丰寿, 何浩斌, 汪健, 李江涛, 李清清, 陈轶之, 林蠡, 张凯 (2021) 西太平洋沿海石斑鱼属鱼类DNA条形码及分子系统进化研究. 水生生物学报, 45, 851-860.] | |
| [42] |
Lin YJ, Moreno C, Marchetti A, Ducklow H, Schofield O, Delage E, Meredith M, Li ZC, Eveillard D, Chaffron S, Cassar N (2021) Decline in plankton diversity and carbon flux with reduced sea ice extent along the Western Antarctic Peninsula. Nature Communications, 12, 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Liu CZ, Song LS, Wu Q (2002) Application of molecular biotechniques in research on marine microbial diversity: A review. Marine Sciences, 26(8), 27-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [柳承璋, 宋林生, 吴青 (2002) 分子生物学技术在海洋微生物多样性研究中的应用. 海洋科学, 26(8), 27-30.] | |
| [44] | Liu HJ, Fu WC, Sun J (2015) Seasonal variations of netz-phytoplankton community in East China Sea continental shelf from 2009-2011. Haiyang Xuebao, 37, 106-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘海娇, 傅文诚, 孙军 (2015) 2009-2011年东海陆架海域网采浮游植物群落的季节变化. 海洋学报, 37, 106-122.] | |
| [45] |
Liu K, Lin HS, He XB, Huang YQ, Li Z, Lin JH, Mou JF, Zhang SY, Lin LS, Wang JJ, Sun J (2019) Functional trait composition and diversity patterns of marine macrobenthos across the Arctic Bering Sea. Ecological Indicators, 102, 673-685.
DOI |
| [46] |
Liu RY (2011) Progress of marine biodiversity studies in China Seas. Biodiversity Science, 19, 614-626. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[刘瑞玉 (2011) 中国海物种多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 19, 614-626.]
DOI |
|
| [47] |
Liu XS, Wang L, Li S, Huo YZ, He PM, Zhang ZN (2015) Quantitative distribution and functional groups of intertidal macrofaunal assemblages in Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Southern Ocean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 99, 1-2.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Liu XS, Zhao R, Hua E, Lu L, Zhang ZN (2014) Macrofaunal community structure in the Laizhou Bay in summer and the comparison with historical data. Marine Science Bulletin, 33, 283-292. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓收, 赵瑞, 华尔, 路璐, 张志南 (2014) 莱州湾夏季大型底栖动物群落结构特征及其与历史资料的比较. 海洋通报, 33, 283-292.] | |
| [49] | Liu Y, Huang YS (1995) Study on the population structure and pollution ecology of algae in mangrove area in Futian, Shenzhen. China Environmental Science, 15, 171-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘玉, 黄玉山 (1995) 红树林区污水对藻类种群结构的影响. 中国环境科学, 15, 171-176.] | |
| [50] |
Long LJ, Yang FF, Wei ZL (2019) A review on ecological restoration techniques of coral reefs. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(6), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[龙丽娟, 杨芳芳, 韦章良 (2019) 珊瑚礁生态系统修复研究进展. 热带海洋学报, 38(6), 1-8.]
DOI |
|
| [51] |
Lü ZB, Li F, Xu BQ, Wang B (2012) Fish community diversity during spring and autumn in the Yellow Sea off the coast of Shandong. Biodiversity Science, 20, 207-214. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[吕振波, 李凡, 徐炳庆, 王波 (2012) 黄海山东海域春、秋季鱼类群落多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 207-214.]
DOI |
|
| [52] | Luan QS, Sun JQ, Wu Q, Wang J (2012) Phytoplankton community in adjoining water of the Antarctic Peninsula during austral summer 2010. Advances in Marine Science, 30, 508-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [栾青杉, 孙坚强, 吴强, 王俊 (2012) 2010年夏南极半岛邻近海域的浮游植物群落. 海洋科学进展, 30, 508-518.] | |
| [53] |
Luo XL, Ren YP, Xing L, Xu BD (2015) Species composition and diversity of crab assemblage in Haizhou Bay. Biodiversity Science, 23, 210-216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[罗西玲, 任一平, 邢磊, 徐宾铎 (2015) 海州湾蟹类群落种类组成及其多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 210-216.]
DOI |
|
| [54] | Ma CA, Xu LL, Tian W, Lü WW, Zhao YL (2012) The influence of a reclamation project on the macrobenthos of an East Nanhui tidal flat. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 3-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马长安, 徐霖林, 田伟, 吕巍巍, 赵云龙 (2012) 围垦对南汇东滩湿地大型底栖动物的影响. 生态学报, 32, 3-11.] | |
| [55] | Ma QY, Han DY, Liu H, Xue Y, Ji YP, Ren YP (2015) Construction of a continuous trophic spectrum for the food web in Jiaozhou Bay using stable isotope analyses. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 7207-7218. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [麻秋云, 韩东燕, 刘贺, 薛莹, 纪毓鹏, 任一平 (2015) 应用稳定同位素技术构建胶州湾食物网的连续营养谱. 生态学报, 35, 7207-7218.] | |
| [56] | Mou WX, Yang G, Hao Q, Xu ZQ, Li CL (2021) The zooplankton community in Cosmonaut Sea: Community structure and environmental factors. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52, 925-935. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牟文秀, 杨光, 郝锵, 徐志强, 李超伦 (2021) 南极夏季宇航员海浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系. 海洋与湖沼, 52, 925-935.] | |
| [57] |
Qu FY, Yu ZS (2010) The application of taxonomic diversity in macrobenthic ecology: Taking Yellow Sea for example. Biodiversity Science, 18, 150-155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[曲方圆, 于子山 (2010) 分类多样性在大型底栖动物生态学方面的应用: 以黄海底栖动物为例. 生物多样性, 18, 150-155.]
DOI |
|
| [58] | Quan JX, Dai JX, Shang X (1999) Studies on the genetic diversity of marine organisms: A review. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 29, 283-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [权洁霞, 戴继勋, 尚迅 (1999) 海洋生物遗传多样性研究现状. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 29, 283-288.] | |
| [59] |
Shan BB, Liu Y, Yang CP, Zhao Y, Zhang GJ, Wu Q, Sun DR (2021) DNA barcoding of fish in Mischief Reef—Fish diversity of a reef-fish community from Nansha Islands. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 618954.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Shao KT (2011) Ten years accomplishment of Census of Marine Life. Biodiversity Science, 19, 627-634. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[邵广昭 (2011) 十年有成的“海洋生物普查计划”. 生物多样性, 19, 627-634.]
DOI |
|
| [61] | Sikder MNA, Abdullah Al M, Xu GJ, Hu GB, Xu HL (2019) Spatial variations in trophic-functional patterns of periphytic ciliates and indications to water quality in coastal waters of the Yellow Sea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 2592-2602. |
| [62] |
Song L, Wang NB, Yang GJ, Song YG (2013) The stress response of biological communities in China’s Yalu River Estuary and neighboring waters. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 2790-2802. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [宋伦, 王年斌, 杨国军, 宋永刚 (2013) 鸭绿江口及邻近海域生物群落的胁迫响应. 生态学报, 33, 2790-2802.] | |
| [63] |
Sun J (2011) Marine biodiversity: Why so high? Biodiversity Science, 19, 611-613. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[孙军 (2011) 海洋生物多样性: 为什么存在高的多样性? 生物多样性, 19, 611-613.]
DOI |
|
| [64] | Sun J (2018) Protection of marine species diversity in China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37, 1-3. |
| [65] | Sun J, Cai LZ, Chen JF, Shan XJ, Ding LP, Huang LF, Jin XS, Lin M, Liu Y, Shao ZZ, Xu KD, Wang Y, Zhang XH (2019) Progress on marine biological studies in China over the past 70 years. Haiyang Xuebao, 41, 81-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙军, 蔡立哲, 陈建芳, 单秀娟, 丁兰平, 黄凌风, 金显仕, 林茂, 刘洋, 邵宗泽, 徐奎栋, 王雨, 张晓华 (2019) 中国海洋生物研究70年. 海洋学报, 41, 81-98.] | |
| [66] | Sun J, Guo Y, Park GS, Hudson A (2022) Dynamics of ecosystems and anthropogenic drivers in the Yellow Sea large marine ecosystem. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 41, 1-3. |
| [67] |
Sun J, Lin M, Chen MX, Xu KD (2016) Marine biodiversity under global climate change. Biodiversity Science, 24, 737-738. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[孙军, 林茂, 陈孟仙, 徐奎栋 (2016) 全球气候变化下的海洋生物多样性. 生物多样性, 24, 737-738.]
DOI |
|
| [68] | Sun J, Liu DY (2004) The application of diversity indices in marine phytoplankton studies. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 26(1), 62-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙军, 刘东艳 (2004) 多样性指数在海洋浮游植物研究中的应用. 海洋学报, 26(1), 62-75.] | |
| [69] | Sun XW, Sun MC, Zhang S, Zhang H, Liu J, Lu L (2011) Preliminary study on macrobenthos in the second phase artificial reef construction area of Haizhou Gulf. Journal of Biology, 28, 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙习武, 孙满昌, 张硕, 张虎, 刘健, 卢璐 (2011) 海州湾人工鱼礁二期工程海域大型底栖生物初步研究. 生物学杂志, 28, 57-61.] | |
| [70] |
Sun YX, Li XX, Tan Y, Wang J, Dong YW (2022) Microhabitat thermal environment controls community structure of macrobenthos on coastal infrastructures. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 277, 108060.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Tan HJ, Cai RS, Du JG, Hu WJ (2022) Climate change and marine ecosystems: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 45, 489-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭红建, 蔡榕硕, 杜建国, 胡文佳 (2022) 气候变化与海洋生态系统及服务: 影响、适应和脆弱性——IPCC AR6 WGII报告之解读性. 大气科学学报, 45, 489-501.] | |
| [72] |
Tang YJ, Fang ZQ, Zhong YT, Zhang ZW, Chen K, An D, Yang XB, Liao BW (2012) Succession of macrofauna communities in wetlands of Sonneratia apetala artificial mangroves during different ecological restoration stages. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 3160-3169. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [唐以杰, 方展强, 钟燕婷, 张再旺, 陈康, 安东, 杨雄邦, 廖宝文 (2012) 不同生态恢复阶段无瓣海桑人工林湿地中大型底栖动物群落的演替. 生态学报, 32, 3160-3169.] | |
| [73] | Wang AL, Wang WN, Hu JR, Liu BB, Sun RY (2000) Study on marine organism diversity in China. Journal of Hebei University (Natural Science Edition), 20, 204-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王安利, 王维娜, 胡俊荣, 刘彬彬, 孙儒泳 (2000) 中国海洋生物多样性的研究. 河北大学学报: 自然科学版, 20, 204-208.] | |
| [74] | Wang HJ, Sun Y, Wang WQ, Fan QJ, Wang SM, Xie SH (2018) Methodological options for molecular marker technology in marine biology research. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 46(21), 1-6. (in Chinese) |
| [王惠君, 孙妍, 王文泉, 范庆君, 王仕明, 谢诗宏 (2018) 分子标记技术在海洋生物研究中的方法选择. 江苏农业科学, 46(21), 1-6.] | |
| [75] | Wang HS, Jiang H, Chen Z, Yang CJ, Ye L (2022) Evolution analysis of members in family Carassiidae based on mitochondrial genome. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 35(2), 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王海山, 蒋欢, 陈治, 杨超杰, 叶乐 (2022) 基于线粒体基因组的鲹科鱼类进化分析. 水产学杂志, 35(2), 14-20.] | |
| [76] | Wang JJ, He XB, Lin HS, Lin JH, Huang YQ, Zheng CX, Zheng FW, Li RG, Jiang JX (2014) Community structure and spatial distribution of macrobenthos in the shelf area of the Bering Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33, 74-81. |
| [77] | Wang LR, Yu HB, Li CT, Sun N (2018) Progress in marine ecosystem restoration. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 37, 435-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王丽荣, 于红兵, 李翠田, 孙妮 (2018) 海洋生态系统修复研究进展. 应用海洋学学报, 37, 435-446.] | |
| [78] |
Wang XZ, Wang F, Sun J (2022) Distribution and environmental impact factors of picophytoplankton in the Eastern Indian Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10, 628.
DOI URL |
| [79] | Wang Y, Lin M, Chen XQ, Lin GM (2011) Spatial and temporal variation of phytoplankton and impacting factors in Jiulongjiang Estuary of Xiamen, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 3399-3414. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王雨, 林茂, 陈兴群, 林更铭 (2011) 九龙江河口浮游植物的时空变动及主要影响因素. 生态学报, 31, 3399-3414.] | |
| [80] | Wang Y, Lu CY, Tan FY, Tang SM (2010) Phytoplankton diversity and assessment of trophic state in Futian mangroves in Shenzhen. Marine Environmental Science, 29, 17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王雨, 卢昌义, 谭凤仪, 唐森铭 (2010) 深圳红树林水体浮游植物多样性与营养状态评价. 海洋环境科学, 29, 17-21.] | |
| [81] | Wang YS (2011) Research on the diversity of marine ecosystems. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 26, 184-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王友绍 (2011) 海洋生态系统多样性研究. 中国科学院院刊, 26, 184-189.] | |
| [82] | Wu Q, Li ZY, Wang J, Shan XJ, Jin XS (2018) Inter-annual variation in the community structure of crustaceans in the Bohai Sea during summer. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 39(2), 16-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴强, 李忠义, 王俊, 单秀娟, 金显仕 (2018) 渤海夏季甲壳类群落结构的年际变化. 渔业科学进展, 39(2), 16-23.] | |
| [83] | Wu ZL, Zhang SY (2019) Effect of typhoon on the distribution of macroalgae in the seaweed beds of Gouqi Island, Zhejiang Province. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 21, 159-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[吴祖立, 章守宇 (2019) 台风对浙江枸杞岛大型底栖海藻分布的影响分析. 中国农业科技导报, 21, 159-168.]
DOI |
|
| [84] | Xia M (1999) Research progress of genetic diversity. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 18, 59-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏铭 (1999) 遗传多样性研究进展. 生态学杂志, 18, 59-65.] | |
| [85] | Xie W, Yin KD (2019) Development trend of deep-sea ecosystem and marine protected areas. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 21(6), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢伟, 殷克东 (2019) 深海海洋生态系统与海洋生态保护区发展趋势. 中国工程科学, 21, 1-8.] | |
| [86] |
Xu KD (2011) Biodiversity and biogeography of marine microbenthos: Progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 19, 661-675. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[徐奎栋 (2011) 海洋微型底栖生物的多样性与地理分布. 生物多样性, 19, 661-675.]
DOI |
|
| [87] | Xu KD (2020) Preface. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51, 433. (in Chinese) |
| 徐奎栋 2020 前言. 海洋与湖沼, 51, 433. | |
| [88] | Xu KD, Lin M, Wang SQ, Li Y, Wu XW, Wang CG (2020) Marine taxonomy in the China Seas and Western Pacific Ocean: Progress and prospects. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51, 728-739. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐奎栋, 林茂, 王少青, 李阳, 吴旭文, 王春光 (2020) 中国海及西太平洋生物分类研究进展及展望. 海洋与湖沼, 51, 728-739.] | |
| [89] |
Xu WZ, Cheung S, Shin PKS (2014) Structure and taxonomic composition of free-living nematode and macrofaunal assemblages in a eutrophic subtropical harbour, Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 85, 764-773.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Xu ZL (2011) The past and the future of zooplankton diversity studies in China seas. Biodiversity Science, 19, 635-645. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[徐兆礼 (2011) 中国近海浮游动物多样性研究的过去和未来. 生物多样性, 19, 635-645.]
DOI |
|
| [91] | Yang M, Kou Q, Li XZ (2018) Advances in DNA barcoding of macrozoobenthos in coastal waters of China. Marine Sciences, 42, 163-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨梅, 寇琦, 李新正 (2018) 中国近海大型底栖动物DNA条形码的研究进展. 海洋科学, 42, 163-173.] | |
| [92] | Yang W, Sun T, Yang ZF (2016) Effect of activities associated with coastal reclamation on the macrobenthos community in coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China: A literature review and systematic assessment. Ocean & Coastal Management, 129, 1-9. |
| [93] |
Yang XL, Lü HB, Hu CY, Zhang XM (2018) Spatial-temporal variations of benthic macroalgae and their responses to variations in the environment in the artificial reef zones of Laoshan Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 25, 642-653. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [杨晓龙, 吕洪斌, 胡成业, 张秀梅 (2018) 崂山湾人工礁区大型底栖海藻时空格局及对环境变化的响应. 中国水产科学, 25, 642-653.] | |
| [94] |
Yao GY, Zhang H, Xiong PP, Jia HX, Shi Y, He MX (2022) Community characteristics and genetic diversity of macrobenthos in Haima cold seep. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9, 920327.
DOI URL |
| [95] | Yao QX, Song WH, Cai HC, Wang F (2016) Study on the macroalgae based on the ArcGIS in Nanji Islands Marine Nature. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 44(18), 11-15, 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚启学, 宋伟华, 蔡厚才, 王飞 (2016) 基于ArcGIS的南麂列岛潮间带大型底栖藻类研究. 安徽农业科学, 44(18), 11-15, 61.] | |
| [96] | Yao X, Yu D, Wang XM, Liu T (2011) Development and application of DNA barcoding technology for macroalgae. Modern Science, (2), 161-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚雪, 于丹, 王绪敏, 刘涛 (2011) 大型海洋藻类DNA条形码技术的开发与应用. 今日科苑, (2), 161-162.] | |
| [97] | Yu DD, Song JJ, Liu KK, Chi WD, Gai SS, Tang JW, Yuan TZ, Wu HY (2021) An ecosystem perspective on fisheries conservation based on the importance of the big old fish. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 7432-7439. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于道德, 宋静静, 刘凯凯, 迟雯丹, 盖珊珊, 唐君玮, 袁廷柱, 吴海一 (2021) 大型年长鱼类对海洋生态系统生物资源养护的作用. 生态学报, 41, 7432-7439.] | |
| [98] |
Zhang CX, Zhou WN, Sun XL, Song ZG (2020) Seasonal succession of macroalgae community in Naozhou Island. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39, 74-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张才学, 周伟男, 孙省利, 宋之光 (2020) 硇洲岛大型海藻群落的季节演替. 热带海洋学报, 39, 74-84.]
DOI |
|
| [99] | Zhang GQ, Yang JL, Li PY, Liang XY, Liang RS, Lin L, Li QQ (2022) The morphological and molecular phylogenetic studies of a new record Gymnothorax species in the coastal waters of China: Gymnothorax mucifer. Haiyang Xuebao, 44(7), 112-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张国庆, 杨杰銮, 李培源, 梁馨艺, 梁日深, 林蠡, 李清清 (2022) 我国近海裸胸鳝属鱼类新记录种——黏裸胸鳝(Gymnothorax mucifer)形态与分子系统学研究. 海洋学报, 44(7), 112-121.] | |
| [100] | Zhang J, Wang XL, Jiang YE, Chen ZZ, Zhao XY, Gong YY, Ying YP, Li ZY, Kong XL, Chen GB, Zhou M (2019) Species composition and biomass density of mesopelagic nekton of the South China Sea continental slope. Deep-sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 167, 105-120. |
| [101] |
Zhang JH (2014) The variation of biodiversity of macrobenthic fauna with salinity and water depth near the Pearl Estuary of the northern South China Sea. Biodiversity Science, 22, 302-310. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张敬怀 (2014) 珠江口及邻近海域大型底栖动物多样性随盐度、水深的变化趋势. 生物多样性, 22, 302-310.]
DOI |
|
| [102] | Zhang JL, Shi BZ, Zhao F, Xu KD (2016) Progress and prospect in marine benthology in China. Studia Marina Sinica, (1), 194-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张均龙, 史本泽, 赵峰, 徐奎栋 (2016) 中国海洋底栖生物学发展回顾与展望. 海洋科学集刊, (1), 194-204.] | |
| [103] | Zhang QJ, Zhao LB (2018) Overview of China’s ocean satellite development. Satellite Application, (5), 28-31. (in Chinese) |
| [张庆君, 赵良波 (2018) 我国海洋卫星发展综述. 卫星应用, (5), 28-31.] | |
| [104] | Zhang WC, Li HB, Feng MP, Yu Y, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Xiao T, Sun J (2014) Phytoplankton in the deep sea, a review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 3820-3826. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张武昌, 李海波, 丰美萍, 于莹, 赵苑, 赵丽, 肖天, 孙军 (2014) 深层海洋浮游植物研究综述. 生态学报, 34, 3820-3826.] | |
| [105] | Zhang WC, Zhao Y, Dong Y, Li HB, Zhao L, Xiao T (2021) Biogeography of epipelagic marine plankton. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52, 332-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张武昌, 赵苑, 董逸, 李海波, 赵丽, 肖天 (2021) 上层海洋浮游生物地理分布. 海洋与湖沼, 52, 332-345.] | |
| [106] | Zhang Y, Lü ZB, Xu ZF, Liu YH, Jin Y (2011) Ecological characteristics of macrobenthic communities and their relation to water environmental factors in four bays of southern Shandong Peninsula. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 4455-4467. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张莹, 吕振波, 徐宗法, 刘义豪, 靳洋 (2011) 山东半岛南部海湾底栖动物群落生态特征及其与水环境的关系. 生态学报, 31, 4455-4467.] | |
| [107] | Zhang ZW, Chen AH, Yao GX, Wu JP, Wu YP, Xu GP, Cheng HL (2010) SRAP analysis on germplasm of wild Meretrix meretrix off Chinese coasts. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 41, 429-434. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张志伟, 陈爱华, 姚国兴, 吴建平, 吴杨平, 许广平, 程汉良 (2010) 我国沿海不同地理原种文蛤(Meretrix meretrix)的SRAP分析. 海洋与湖沼, 41, 429-434.] | |
| [108] | Zhao S, Liu XD, Zhang AJ, Liu YT, Leng Y (2013) Effects of thermal water discharged from Huangdao power plant on structure of macrozoobenthos. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 25, 18-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵升, 刘旭东, 张爱君, 刘一霆, 冷宇 (2013) 黄岛电厂温排水对大型底栖生物群落的影响. 环境监测管理与技术, 25, 18-23.] | |
| [109] | Zheng TL, Zhang HQ, Zhang XH (2013) Genetic diversity status and conservation strategies of Miichthys miiuy. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 54, 1183-1186. (in Chinese) |
| [郑天伦, 张海琪, 张晓辉 (2013) 鮸鱼的遗传多样性现状及保护策略. 浙江农业科学, 54, 1183-1186.] | |
| [110] | Zhu J, Zhang YR, Yan ZY, Jin YJ, Li ZM (2016) Status of fishery resources near Daishan Island in Zhejiang Province, China. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (14), 252-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱剑, 张玉荣, 严忠雍, 金衍健, 李子孟 (2016) 浙江岱山岛附近海域春秋季渔业资源调查研究. 现代农业科技, (14), 252-254.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn