



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 627-637. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017090 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017090
郑硕理1,2, 田晓玲3, 黄承玲3, 王灵军4, 冯元4, 张敬丽1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-03-22
接受日期:2017-06-28
出版日期:2017-06-20
发布日期:2017-07-10
通讯作者:
张敬丽
基金资助:
Shuoli Zheng1,2, Xiaoling Tian3, Chengling Huang3, Lingjun Wang4, Yuan Feng4, Jingli Zhang1,*( )
)
Received:2017-03-22
Accepted:2017-06-28
Online:2017-06-20
Published:2017-07-10
Contact:
Zhang Jingli
摘要:
中国西南地区是世界杜鹃属(Rhododendron)植物的分布和分化中心, 开展杜鹃属自然杂交研究可为分类修订和新品种选育提供依据。本文以贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区(百里保护区)和云南石宝山分布的大白杜鹃(Rhododendron decorum)、马缨杜鹃(R. delavayi)及两种间疑似自然杂交后代和人工杂交后代个体为研究材料, 通过形态特征比较、核基因间隔序列ITS以及叶绿体基因片段trnL-trnF、rbcL和trnH-psbA测序特征分析, 发现疑似自然杂交后代与人工杂交后代形态特征介于大白杜鹃与马缨杜鹃之间; 4个DNA片段序列均能区分大白杜鹃和马缨杜鹃, 同一物种的不同居群在叶绿体基因片段rbcL、trnH-psbA序列存在差异位点; 所有人工杂交后代个体和1个石宝山疑似杂交个体均以大白杜鹃为母本, 所有百里保护区疑似杂交个体和6个石宝山疑似杂交个体以马缨杜鹃为母本。本研究证实了大白杜鹃与马缨杜鹃在百里保护区和云南石宝山存在自然杂交现象, 杂交为双向且自然杂交后代绝大多数以马缨杜鹃为母本。
郑硕理, 田晓玲, 黄承玲, 王灵军, 冯元, 张敬丽 (2017) 结合分子手段和形态分析验证大白杜鹃与马缨杜鹃的自然杂交. 生物多样性, 25, 627-637. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017090.
Shuoli Zheng, Xiaoling Tian, Chengling Huang, Lingjun Wang, Yuan Feng, Jingli Zhang (2017) Molecular and morphological evidence for natural hybridization between Rhododendron decorum and R. delavayi (Ericaceae). Biodiversity Science, 25, 627-637. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017090.
| 编号 Code | 种类 Taxon | 地点 Site | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 个体数量 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLM (1-10) | 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区 Baili Rhododendron Nature Reserve in Guizhou Province | 27°15′ N 105°58′ E | 1,700-1,800 | 10 |
| BLD (1-10) | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区 Baili Rhododendron Nature Reserve in Guizhou Province | 27°15′ N 105°58′ E | 1,700-1,800 | 10 |
| BLH (1-8) | 疑似杂交后代 Putative hybrids | 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区 Baili Rhododendron Nature Reserve in Guizhou Province | 27°15′ N 105°58′ E | 1,700-1,800 | 8 |
| SBSM (1-5) | 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 云南大理石宝山 Shibao Mountain of Dali, Yunnan | 26°22′ N 99°50′ E | 2,400-2,600 | 5 |
| SBSD (1-5) | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 云南大理石宝山 Shibao Mountain of Dali, Yunnan | 26°22′ N 99°50′ E | 2,400-2,600 | 5 |
| SBSH (2/3/4/5/7/8/9) | 疑似杂交后代 Putative hybrids | 云南大理石宝山 Shibao Mountain of Dali, Yunnan | 26°22′ N 99°50′ E | 2,400-2,600 | 7 |
| AH (1-5) | 人工杂交后代 Artificial hybrids | 昆明植物园 Kunming Botanical Garden | 5 | ||
| 总计 Total | 50 |
表1 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃及疑似杂交后代的来源和数量
Table 1 Sources and sample size of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi, and putative hybrids used in this study
| 编号 Code | 种类 Taxon | 地点 Site | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 个体数量 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLM (1-10) | 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区 Baili Rhododendron Nature Reserve in Guizhou Province | 27°15′ N 105°58′ E | 1,700-1,800 | 10 |
| BLD (1-10) | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区 Baili Rhododendron Nature Reserve in Guizhou Province | 27°15′ N 105°58′ E | 1,700-1,800 | 10 |
| BLH (1-8) | 疑似杂交后代 Putative hybrids | 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区 Baili Rhododendron Nature Reserve in Guizhou Province | 27°15′ N 105°58′ E | 1,700-1,800 | 8 |
| SBSM (1-5) | 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 云南大理石宝山 Shibao Mountain of Dali, Yunnan | 26°22′ N 99°50′ E | 2,400-2,600 | 5 |
| SBSD (1-5) | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 云南大理石宝山 Shibao Mountain of Dali, Yunnan | 26°22′ N 99°50′ E | 2,400-2,600 | 5 |
| SBSH (2/3/4/5/7/8/9) | 疑似杂交后代 Putative hybrids | 云南大理石宝山 Shibao Mountain of Dali, Yunnan | 26°22′ N 99°50′ E | 2,400-2,600 | 7 |
| AH (1-5) | 人工杂交后代 Artificial hybrids | 昆明植物园 Kunming Botanical Garden | 5 | ||
| 总计 Total | 50 |
| 形态特征 Morphological characters | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 疑似自然杂交与人工杂交后代 Putative and artificial hybrids | 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 花冠颜色 Corolla color | 白色 White | 粉红 Pink | 红色 Red |
| 花冠裂片数 No. of corolla lobes | 6-8, 通常7 6-8, usually 7 | 5-6, 无规律 5-6, irregular | 5 |
| 叶片形状 Leaf shape | 长圆形 Oblong | 长圆形至披针形 Oblong to lanceolate | 披针形 Lanceolate |
| 叶片毛被 Ventral leaf suraface indumentum | 无毛 Glabrous | 稀疏毛被 Thin indumentum | 浓密海绵状毛被 Woolly indumentum |
| 果实表面特征 Fruit surface character | 有腺体 Glands | 有腺体或毛被或两者均有 Glands or/and indumentum | 密被棕红色毛被 Continuous brownish red indumentum |
| 花期 Flowering period | 5-6月 May to June | 4月中旬-5月中旬 Mid-April to mid-May | 3月-5月 March to May |
表2 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃、人工杂交后代与疑似杂交后代的形态特征对比
Table 2 Comparison of morphological characters of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi, artificial and putative hybrids
| 形态特征 Morphological characters | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 疑似自然杂交与人工杂交后代 Putative and artificial hybrids | 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 花冠颜色 Corolla color | 白色 White | 粉红 Pink | 红色 Red |
| 花冠裂片数 No. of corolla lobes | 6-8, 通常7 6-8, usually 7 | 5-6, 无规律 5-6, irregular | 5 |
| 叶片形状 Leaf shape | 长圆形 Oblong | 长圆形至披针形 Oblong to lanceolate | 披针形 Lanceolate |
| 叶片毛被 Ventral leaf suraface indumentum | 无毛 Glabrous | 稀疏毛被 Thin indumentum | 浓密海绵状毛被 Woolly indumentum |
| 果实表面特征 Fruit surface character | 有腺体 Glands | 有腺体或毛被或两者均有 Glands or/and indumentum | 密被棕红色毛被 Continuous brownish red indumentum |
| 花期 Flowering period | 5-6月 May to June | 4月中旬-5月中旬 Mid-April to mid-May | 3月-5月 March to May |
| 编号 Code | 克隆数量 Clone numbers | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | 类型 Type | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 94 | 101 | 114 | 203 | 494 | 505 | A1 | A2 | A4 | |||
| 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 0 | A1 | T | G | G | T | T | C | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 0 | A2 | C | C | T | G | C | T | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| AH、BLH、SBSH | A3 | Y | S | K | K | Y | Y | ||||
| 克隆测序 Clone sequences | |||||||||||
| BLH1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| BLH2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| BLH3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| BLH4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| BLH5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| BLH6 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| BLH7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| BLH8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| AH1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| AH2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| AH3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| AH4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| AH5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| SBSH2 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH3 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH7 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH8 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH9 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| 克隆数量总计 Total clone numbers | 53 | 31 | 10 | ||||||||
表3 大白杜鹃与马缨杜鹃的ITS序列差异位点及疑似杂交后代克隆序列
Table 3 The location of variable sites based on ITS and clone sequences of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi and putative hybrids
| 编号 Code | 克隆数量 Clone numbers | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | 类型 Type | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 94 | 101 | 114 | 203 | 494 | 505 | A1 | A2 | A4 | |||
| 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 0 | A1 | T | G | G | T | T | C | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 0 | A2 | C | C | T | G | C | T | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| AH、BLH、SBSH | A3 | Y | S | K | K | Y | Y | ||||
| 克隆测序 Clone sequences | |||||||||||
| BLH1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| BLH2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| BLH3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| BLH4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| BLH5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| BLH6 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| BLH7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| BLH8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| AH1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| AH2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| AH3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| AH4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| AH5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| SBSH2 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH3 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH4 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH7 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH8 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 0 | |||||||
| SBSH9 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |||||||
| 克隆数量总计 Total clone numbers | 53 | 31 | 10 | ||||||||
| 编号 Code | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147 | 622 | 623 | 624 | 626 | 627 | 629 | 646 | 831 | ||
| 大白杜鹃 Rhododendron decorum | B1 | G | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T |
| 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | B2 | T | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | C |
| AH、SBSH5 | B1 | G | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T |
| BLH、SHSH2/3/4/7/8/9 | B2 | T | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | C |
表4 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃及疑似杂交后代的trnL-trnF序列差异位点
Table 4 The location of variable sites based on trnL-trnF sequences of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi and putative hybrids
| 编号 Code | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147 | 622 | 623 | 624 | 626 | 627 | 629 | 646 | 831 | ||
| 大白杜鹃 Rhododendron decorum | B1 | G | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T |
| 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | B2 | T | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | C |
| AH、SBSH5 | B1 | G | T | T | T | T | T | T | C | T |
| BLH、SHSH2/3/4/7/8/9 | B2 | T | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | C |
| 编号 Code | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 30 | 263 | 398 | 407 | ||
| BLD | C1 | C | G | T | C | C |
| BLM | C2 | C | T | A | T | T |
| SBSD | C3 | G | G | T | C | C |
| SBSM | C4 | G | T | A | T | T |
| AH | C1 | C | G | T | C | C |
| BLH | C2 | C | T | A | T | T |
| SBSH5 | C3 | G | G | T | C | C |
| SBSH2/3/4/7/8/9 | C4 | G | T | A | T | T |
表5 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃及疑似杂交后代的rbcL序列差异位点
Table 5 The location of variable sites based on rbcL sequences of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi and putative hybrids
| 编号 Code | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 30 | 263 | 398 | 407 | ||
| BLD | C1 | C | G | T | C | C |
| BLM | C2 | C | T | A | T | T |
| SBSD | C3 | G | G | T | C | C |
| SBSM | C4 | G | T | A | T | T |
| AH | C1 | C | G | T | C | C |
| BLH | C2 | C | T | A | T | T |
| SBSH5 | C3 | G | G | T | C | C |
| SBSH2/3/4/7/8/9 | C4 | G | T | A | T | T |
| 编号 Code | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 128 | 135 | 211 | 214 | 245 | 254 | 254 | 299 | 313 | 333 | 337 | 340 | 344 | 348 | 351 | 358 | 365-369 | ||
| BLD | D1 | G | A | T | C | G | C | G | A | C | A | A | G | T | G | G | T | T | T | AATTC |
| SBSD | D2 | - | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | A | A | A | A | A | G | G | ***** |
| BLM | D3 | * | * | A | G | A | C | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | G---- |
| SBSM | D4 | * | * | A | G | A | A | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | G---- |
| AH | D1 | G | A | T | C | G | C | G | A | C | A | A | G | T | G | G | T | T | T | AATTC |
| SBSH5 | D2 | * | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | A | A | A | A | A | G | G | ***** |
| BLH | D3 | * | * | A | G | A | C | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | G---- |
| SBSH2/3/4/7/8/9 | D4 | * | * | A | G | A | A | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | · | G---- |
表6 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃及疑似杂交后代的trnH-psbA序列差异位点
Table 6 The location of variable sites based on trnH-psbA sequences of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi and putative hybrids
| 编号 Code | 类型 Type | 差异位点 Variable sites (bp) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 128 | 135 | 211 | 214 | 245 | 254 | 254 | 299 | 313 | 333 | 337 | 340 | 344 | 348 | 351 | 358 | 365-369 | ||
| BLD | D1 | G | A | T | C | G | C | G | A | C | A | A | G | T | G | G | T | T | T | AATTC |
| SBSD | D2 | - | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | A | A | A | A | A | G | G | ***** |
| BLM | D3 | * | * | A | G | A | C | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | G---- |
| SBSM | D4 | * | * | A | G | A | A | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | G---- |
| AH | D1 | G | A | T | C | G | C | G | A | C | A | A | G | T | G | G | T | T | T | AATTC |
| SBSH5 | D2 | * | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | A | A | A | A | A | G | G | ***** |
| BLH | D3 | * | * | A | G | A | C | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | G---- |
| SBSH2/3/4/7/8/9 | D4 | * | * | A | G | A | A | T | T | T | T | G | * | * | * | * | * | * | · | G---- |
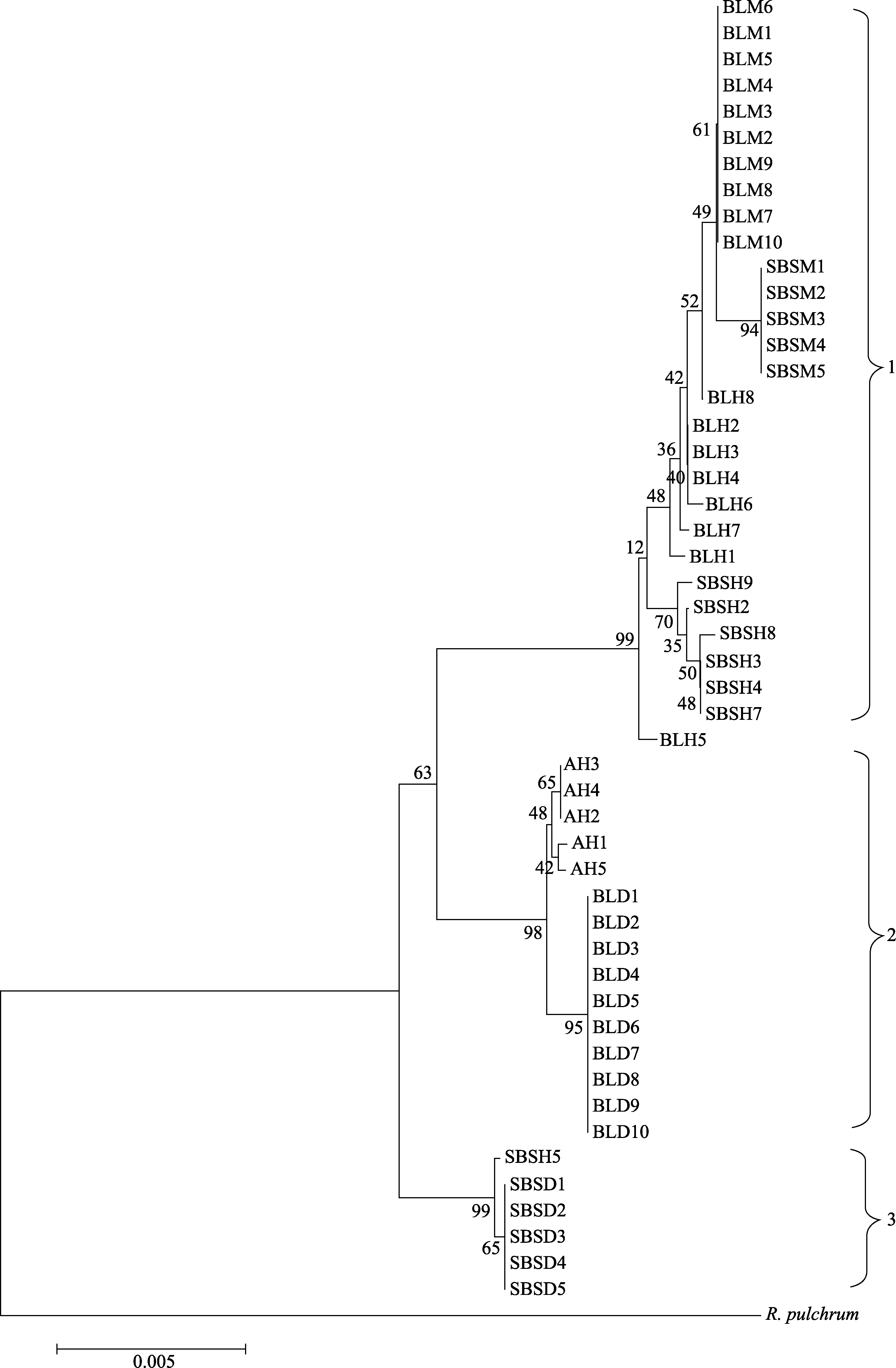
图1 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃及疑似杂交后代的联合ITS、trnL-trnF、rbcL、psbA-trnH序列片段的聚类图。AH、BLH、SBSH、BLM、BLD、SBSM和SBSD含义见表1。
Fig. 1 Clustering chart of combined ITS, trnL-trnF, rbcL, psbA-trnH sequence of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi and putative hybrids. The means of AH, BLH, SBSH, BLM, BLD, SBSM, and SBSD see Table 1.
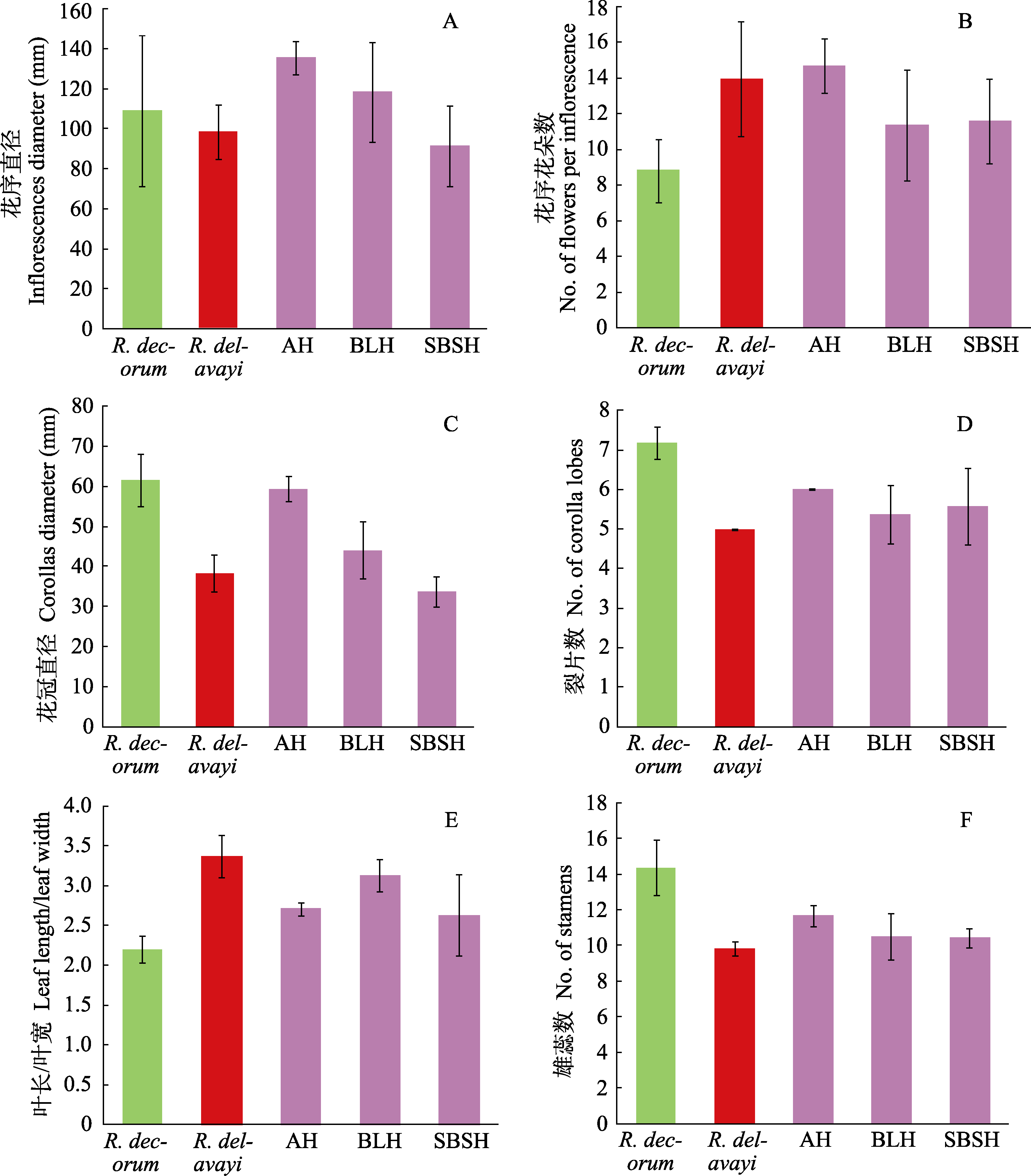
图3 大白杜鹃、马缨杜鹃、疑似杂交后代与人工杂交后代部分数量性状。AH、BLH和SBSH含义见表1。
Fig. 3 Part of quantitative characters of Rhododendron decorum, R. delavayi, putative and artificial hybrid. The means of AH, BLH, and SBSH see Table 1.
| [1] | Arnold ML (1997) Natural Hybridization and Evolution. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [2] | Barton NH (2001) The role of hybridization in evolution. Molecular Ecology, 10, 551-568. |
| [3] | Chamberlain DF (1982) A revision of Rhododendron. II. Subgenus Hyemanthes. Notes from the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh, 39, 209-486. |
| [4] | Chamberlain DF (2003) Rhododendrons in the wild: a taxonomist’s view. In: Rhododendrons in Horticulture and Science (eds Argent G, Mcfralane M), pp. 42-52. The Royal Botanic Garden, Edinburgh. |
| [5] | Chamberlain DF, Hyam R, Argent G, Fairweather G, Walter KS (1996) The Genus Rhododendron, Its Classification and Synonymy. Alden Press, Oxford. |
| [6] | Chase MW, Paun O, Fay MF (2010) Hybridization and speciation in angiosperms: a role for pollinator shifts. BMC Biology, 8, doi:10.1186/1741-7007-8-45. |
| [7] | Cox PA (1995) Note of natural hybrids and intraspecific variation of Rhododendron in China. In: Scientific Investigation of the Plant on Cangshan Mountain (eds Duan CZ, Liao SC, Li QL, Li XW). Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [Cox PA (1995) 中国杜鹃属植物的天然杂交及种内变异. 见: 苍山植物科学考察(段诚忠, 廖士长, 李琼兰, 李锡文). 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [8] | Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf material. Phytochemical Bulletin, 19, 11-15. |
| [9] | Gottlieb LD (1972) Leaves of confidence in the analysis of hybridization in plants. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 59, 435-446. |
| [10] | Grant PR, Grant BR, Petren K (2005) Hybridization in the recent past. The American Naturalist, 166, 56-67. |
| [11] | Kobayashi N, Horikoshi T, Katsuyama H, Handa T, Takayangi K (1998) A simple and efficient DNA extraction method for plants, especially woody plants. Plant Tissue Culture & Biotechnology, 4, 72-80. |
| [12] | Krewss WJ, Erickson DL (2007) A two-locus global DNA barcode for land plant: the coding rbcL gene complements the non-coding trnH-psbA spacer region. PLoS ONE, 2, e508. |
| [13] | Kron KA, Gawen LM, Chase MW (1993) Evidence for introgression in azaleas (Rhododendron; Ericaceae): chloroplast DNA and morphological variation in a hybrid swarm on Georgia. American Journal of Botany, 80, 1095-1099. |
| [14] | Li XJ, Wang LY, Yang HL, Liu JQ (2008) Confirmation of natural hybrid between Gentiana straminea and G. siphonantha (Gentianaceae) based on molecular evidence. Frontiers of Biology in China, 3, 470-476. |
| [15] | Liu YL (2006) The Genetic Structure and Introgression Among Natural Populations of Actinidia. PhD dissertation, Central China Agricultural University, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘亚令 (2006) 猕猴桃属植物自然居群的遗传结构与种间基因渐渗研究. 博士学位论文, 华中农业大学, 武汉.] | |
| [16] | Lu BR, Xia H, Wang W, Yang X (2010) Impact of natural hybridization and introgression on biological in invasion of plant species. Biodiversity Science, 18, 577-589. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢宝荣, 夏辉, 汪魏, 杨箫 (2010) 天然杂交与遗传渐渗对植物入侵性的影响. 生物多样性, 18, 577-589.] | |
| [17] | Ma YP, Zhang CQ, Zhang JL, Yang JB (2010) Natural hybridization between Rhododendron delavayi and R. cyanocarpum (Ericaceae), from morphological, molecular and reproductive evidence. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 52, 844-851. |
| [18] | Ma YP, Xie WJ, Tian XL, Sun WB, Wu ZK, Milne RI (2014) Unidirectional hybridization and reproductive barriers between two heterostylous primrose species in north-west Yunnan, China. Annals of Botany, 113, 763-775. |
| [19] | Ma YP, Xie WJ, Sun WB, Tobias M (2016) Strong reproductive isolation despite occasional hybridization between a widely distributed and a narrow endemic Rhododendron species. Scientific Reports, 6, 19146. |
| [20] | Mallet J (2005) Hybridization as an invasion of the genome. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 20, 229-237. |
| [21] | Mao JF, Wang XR (2011) Distinct niche divergence characterizes the homoploid hybrid speciation of Pinus densata on the Tibetan Plateau. The American Naturalist, 177, 424-439. |
| [22] | Mason HL (1949) Evidence for the Genetic Submergence of Pinus remorata Genetics, Paleontology and Evolution. Princton University Press, Princton. |
| [23] | Milne RI (2004) Phylogeny and biogeography of Rhododendron subsection Pontica, a group with a Tertiary relict distribution. Molecular Phylogenetic & Evolution, 33, 389-401. |
| [24] | Milne RI, Abbott RJ (2008) Reproductive isolation among two interfertile Rhododendron species: low frequency of post-F1 hybrid genotypes in alpine hybrid zones. Molecular Ecology, 17, 1108-1121. |
| [25] | Milne RI, Abbott RJ, Wolff K, Chamberlain DF (1999) Hybridization among sympatric species of Rhododendron (Ericaceae) in Turkey: morphological and molecular evidence. American Journal of Botany, 86, 1776-1785. |
| [26] | Milne RI, Terzioglu S, Abbott RJ (2003) A hybrid zone dominated by fertile F1s: maintenance of species barriers in Rhododendron. Molecular Ecology, 12, 2719-2729. |
| [27] | Min TL (1984) A revision of subgenus Hymenanthes (Rhododendron L.) in Yunnan-Xizang. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 6, 141-171. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闵天禄 (1984) 滇藏常绿杜鹃亚属的修订. 云南植物研究, 6, 141-171.] | |
| [28] | Oberprieler C, Dietz L, Harlander C, Heilmann J (2013) Molecular and phytochemical evidence for the taxonomic integrity of Salix alba, S. fragilis, and their hybrid S. × rubens (Salicaceae) in mixed stands in SE Germany. Plant Systematics & Evolution, 299, 1107-1118. |
| [29] | Rieseberg LH (1997) Hybrid origins of plant species. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics 28, 259-389. |
| [30] | Seehausen O (2004) Hybridization and adaptive radiation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 198-207. |
| [31] | Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2009) The role of hybridization in plant speciation. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 60, 561-588. |
| [32] | Taberlet P, Gielliy L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of the three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Molecular Biology, 17, 1105-1109. |
| [33] | Tagane S, Hiramatsu M, Okubo H (2008) Hybridization and asymmetric introgression between Rhododendron eriocarpum and R. indicum on Yakushima Island, Southwest Japan. Journal of Plant Research, 121, 387-395. |
| [34] | Wang ZF, Peng SL (2003) Plant hybridization and its harmful genetic consequences. Biodiversity Science, 11, 333-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王峥峰, 彭少鳞 (2003) 杂交产生的遗传危害——以植物为例. 生物多样性, 11, 333-339.] | |
| [35] | White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications (eds Innis M, Gelfand D, Sninsky J, White T), pp. 315-322. Academic, San Diego. |
| [36] | Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY (2005) Flora of China, Vol. 14. Science Press, Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [37] | Yan LJ, Gao LM, Li DZ (2013) Molecular evidence for natural hybridization between Rhododendron spiciferum and R. spinuliferum (Ericaceae). Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 51, 426-434. |
| [38] | Yu JJ, Pan L, Pan YZ, Gong X (2014) Natural hybrid between Ligularia vellerea and L. subspicata (Asteravear: Senecioneae). Plant Diversity and Resources, 36, 219-226. |
| [39] | Yuan CC, He XB, Yuan QM, Shi SH (2007) Genetic relationship between a natural hybrid Meconopsis × cookei (Papaveraceae) and its parents based on cpDNA trnL-trnF region sequence. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 29, 103-108. |
| [40] | Zha HG, Milne RI, Sun H (2008) Morphological and molecular evidence of natural hybridization between two distantly related Rhododendron species from the Sino-Himalaya, Botanical Journal of Linnean Society, 156, 119-129. |
| [41] | Zha HG, Milne RI, Sun H (2010) Asymmetric hybridization in Rhododendron agastum: a hybrid taxon comprising mainly F1s in Yunnan, China. Annals of Botany, 105, 89-100. |
| [42] | Zhang JL, Zhang CQ, Gao LM, Yang JB, Li HT (2007) Natural hybridization origin of Rhododendron agastum (Ericaceae) in Yunnan, China: inferred from morphological and molecular evidence. Journal of Plant Research, 120, 457-463. |
| [43] | Zhang JL, Zhang CQ, Wu ZK, Qiao Q (2007) The potential roles of interspecific pollination in natural hybridization of Rhododendron species in Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science, 15, 658-665. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张敬丽, 张长芹, 吴之坤, 乔琴 (2007) 探讨种间传粉在杜鹃花属自然杂交物种形成中的作用. 生物多样性, 15, 658-665.] | |
| [44] | Zhang CQ, Feng BJ, Lü YL (1998) Hybridization study of the genus Rhododendron. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 20, 94-96.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张长芹, 冯宝均, 吕元林 (1998) 杜鹃花属的杂交育种研究. 云南植物研究, 20, 94-96.] | |
| [45] | Zhang CQ, Huang CL, Huang JY, Wang LJ, Zhang JL, Sun WB, Ma YP (2015) Investigation of germplasm resources of the genus Rhododendron in Baili Nature Reserve in Guizhou. Plants Diversity and Resources, 37, 357-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张长芹, 黄承玲, 黄家勇, 王灵军, 张敬丽, 孙卫邦, 马永鹏 (2015) 贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区杜鹃花属种质资源的调查. 植物分类与资源学报, 37, 357-364.] |
| [1] | 陈静, 张丙昌, 刘燕晋, 武杰, 赵康, 明姣. 荒漠生物结皮细鞘丝藻类(Leptolyngbya-like)蓝藻多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24186-. |
| [2] | 王江, 赵一凡, 屈彦福, 张财文, 张亮, 陈传武, 王彦平. 中国蛇类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23126-. |
| [3] | 姚仁秀, 陈燕, 吕晓琴, 王江湖, 杨付军, 王晓月. 海拔及环境因子影响杜鹃属植物的表型特征和化学性状[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [4] | 钟雨茜, 陈传武, 王彦平. 中国蜥蜴类生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 22071-. |
| [5] | 丁晨晨, 梁冬妮, 信文培, 李春旺, 蒋志刚. 中国哺乳动物形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21520-. |
| [6] | 王彦平, 宋云枫, 钟雨茜, 陈传武, 赵郁豪, 曾頔, 吴亦如, 丁平. 中国鸟类的生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1149-1153. |
| [7] | 俞正森, 宋娜, 本村浩之, 高天翔. 中国银口天竺鲷属鱼类的分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 971-979. |
| [8] | 莫日根高娃, 商辉, 刘保东, 康明, 严岳鸿. 一个种还是多个种? 简化基因组及其形态学证据揭示中国白桫椤植物的物种多样性分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(11): 1196-1204. |
| [9] | 商辉, 严岳鸿. 自然杂交与生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(6): 683-688. |
| [10] | 周秋杰, 蔡亚城, 黄伟伦, 吴伟, 代色平, 王峰, 周仁超. 野牡丹属两个海南特有种与同属广布种自然杂交的分子证据[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(6): 638-646. |
| [11] | 王玉国. 自然杂交与物种形成[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(6): 565-576. |
| [12] | 魏宇昆, 黄艳波, 李桂彬. 同域分布共享传粉者的鼠尾草属植物的生殖隔离[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(6): 608-614. |
| [13] | 田代科, 李春, 肖艳, 付乃峰, 童毅, 吴瑞娟. 中国秋海棠属植物的自然杂交发生及其特点[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(6): 654-674. |
| [14] | 王雨, 张会勇, 项鹏, 叶又茵, 林更铭, 杨清良, 林茂. 颗石藻颗石粒形态的原子力显微观测方法: 以赫氏艾密里藻为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(7): 847-854. |
| [15] | 孙华之, 谭敦炎, 曲荣明. 短命植物小疮菊异形瘦果特性及其对荒漠环境的适应[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(4): 353-361. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn