



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (4): 463-469. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07267 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07267
王雪辉1,2,*( ), 杜飞雁1,3, 林昭进1, 孙典荣1, 邱永松1, 黄硕琳2
), 杜飞雁1,3, 林昭进1, 孙典荣1, 邱永松1, 黄硕琳2
收稿日期:2010-11-03
接受日期:2011-01-20
出版日期:2011-07-20
发布日期:2011-07-29
通讯作者:
王雪辉
作者简介:* E-mail: wxhscs@163.com基金资助:
Xuehui Wang1,2,*( ), Feiyan Du1,3, Zhaojin Lin1, Dianrong Sun1, Yongsong Qiu1, Shuolin Huang2
), Feiyan Du1,3, Zhaojin Lin1, Dianrong Sun1, Yongsong Qiu1, Shuolin Huang2
Received:2010-11-03
Accepted:2011-01-20
Online:2011-07-20
Published:2011-07-29
Contact:
Xuehui Wang
摘要:
为了解珊瑚礁海域鱼类物种多样性及其群落特征, 作者2003年5月在西沙群岛7座主要岛礁(北礁、华光礁、金银岛、东岛、浪花礁、玉琢礁和永兴岛)采用底层刺网进行了调查, 运用聚类分析和非度量多维标度(NMDS)等多元统计分析方法, 对7个岛礁鱼类的种类组成、优势种、多样性和群落格局进行了分析。调查海域共记录鱼类146种, 隶属10目31科; 各主要岛礁的鱼类以典型的热带种类为主, 如鹦嘴鱼科、蝴蝶鱼科、笛鲷科等珊瑚礁鱼类; 白边锯鳞鳂(Myripristis murdjan)、四带笛鲷(Lutjanus kasmira)、灰若梅鲷(Paracaesio sordidus)、双带梅鲷(Caesio diagramma)、单板盾尾鱼(Axinurus thynnoides)和灰六鳃鲨(Hexanchus griseus)为主要优势种; 全海域鱼类的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')在1.91-3.33之间, 平均为2.81, 明显高于纬度较高的东海和黄渤海海域; 该海域鱼类可划分为两个群落, 即永乐群岛群落(群落I)和宣德群岛群落(群落II)。ANOSIM和RELATE检验表明, 两个群落间鱼类组成的差异显著(R=0.685, P=0.029<0.05), 且群落格局较为稳定(R=0.958, P=0.003<0.01)。
王雪辉, 杜飞雁, 林昭进, 孙典荣, 邱永松, 黄硕琳 (2011) 西沙群岛主要岛礁鱼类物种多样性及其群落格局. 生物多样性, 19, 463-469. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07267.
Xuehui Wang, Feiyan Du, Zhaojin Lin, Dianrong Sun, Yongsong Qiu, Shuolin Huang (2011) Fish species diversity and community pattern in coral reefs of the Xisha Islands, South China Sea. Biodiversity Science, 19, 463-469. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07267.
| 种名 Species | 分布区域 Distribution region | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRI | 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 东岛 Dongdao Island | 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | |
| 六鳃鲨目 HEXANCHIFORMES | ||||||||
| 六鳃鲨科 Hexanchidae | ||||||||
| 灰六鳃鲨 Hexanchus griseus | 525 | + | + | |||||
| 真鲨目 CARCHARHINIFORMES | ||||||||
| 真鲨科 Carcharhinidae | ||||||||
| 尖头斜齿鲨 Scoliodon sorrakowah | 68 | + | + | |||||
| 侧条真鲨 Carcharhinus pleurotaenia | 8 | + | ||||||
| 灯笼鱼目 MYCTOPHIFORMES | ||||||||
| 狗母鱼科 Synodidae | ||||||||
| 花斑狗母鱼 Synodus jaculum | 21 | + | + | |||||
| 鳗鲡目 ANGUILLIFORMES | ||||||||
| 海鳝科 Muraenidae | ||||||||
| 异纹裸胸鳝 Gymnothorax richardsoni | 10 | + | ||||||
| 白斑裸胸鳝 G. leucostingmus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 花斑裸胸鳝 G. pictus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 金眼鲷目 BERYCIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鳂科 Holocentridae | ||||||||
| 骨鳂 Ostichthys sheni | 1 | + | ||||||
| 少鳞骨鳂 O. kaianus | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 灯眼鱼科 Anomalopidae | ||||||||
| 白边锯鳞鳂 Myripristis murdjan | 4,390 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 纵带锯鳞鳂 M. vittata | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 白纹棘鳞鳂 Sargocentron diadema | 21 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 尾斑棘鳞鳂 S. caudimaculatus | 30 | + | ||||||
| 尖吻棘鳞鳂 S. spiniferum | 1 | + | ||||||
| 条长颏鳂 Flammeo sammara | 29 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 斑尾鳂 Adioryx caudimaculatus | 15 | + | ||||||
| 赤鳂 A. tiere | 3 | + | ||||||
| 黄纹鳂 A. furcatus | 173 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 棘鳂 A. spinifer | 89 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 红双棘鳂 Dispinus ruber | 53 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 刺鱼目 GASTEROSTEIFORMES | ||||||||
| 烟管鱼科 Fistulariidae | ||||||||
| 鳞烟管鱼 Fistularia petimba | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲻形目 MUGILIFORMES | ||||||||
| 魣科 Sphyraenidae | ||||||||
| 大眼魣 Sphyraena forsteri | 252 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 大魣 S. barracuda | 47 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 鲈形目 PERCIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鮨科 Serranidae | ||||||||
| 鳃棘鲈 Plectropomus leopardus | 55 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 线点鳃棘鲈 P. oligacanthus | 57 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 豹纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis leopardus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 尾纹九棘鲈 C. urodelus | 35 | + | + | + | ||||
| 白线光腭鲈 Anyperodon leucogrammicus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 蜂巢石斑鱼 Epinephelus merra | 4 | + | ||||||
| 黑边石斑鱼 E. fasciatus | 140 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 大眼鲷科 Priacanthidae | ||||||||
| 金目大眼鲷 P. hamrur | 468 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 方头鱼科 Branchiostegidae | ||||||||
| 侧条弱棘鱼 Malacanthus latovittatus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲹科 Carangidae | ||||||||
| 星点鲹 Carangoides stellatus | 109 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 散鲹 C. sansun | 4 | + | ||||||
| 长体圆鲹 Decapterus macrosoma | 237 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 脂眼凹肩鲹 Selar crumenophthalmus | 57 | + | + | |||||
| 笛鲷科 Lutjanidae | ||||||||
| 红钻鱼 Etelis carbunculus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 细鳞紫鱼 Pristipomoides microlepis | 5 | + | ||||||
| 黄尾紫鱼 P. auricilla | 284 | + | ||||||
| 黄线紫鱼 P. multidens | 242 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 绿短臂鱼 Aprion virescens | 2 | + | ||||||
| 叉尾鲷 A. furcatus | 149 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 若梅鲷 Paracaesio xanthurus | 366 | + | + | |||||
| 灰若梅鲷 P. sordidus | 1,121 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira | 1,281 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 五带笛鲷 L. spilurus | 6 | + | ||||||
| 千年笛鲷 L. sebae | 1 | + | ||||||
| 双带梅鲷 Caesio diagramma | 949 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 褐梅鲷 C. coerulaureus | 24 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 新月梅鲷 C. lunaris | 46 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 裸颊鲷科 Lethrinidae | ||||||||
| 短吻裸颊鲷 Lethrinus ornatus | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 丽鳍裸颊鲷 L. kalloperus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 纵带裸颊鲷 L. leutjanus | 152 | + | + | |||||
| 杂色裸颊鲷 L. variegatus | 264 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 星斑裸颊鲷 L. nebulosus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 松鲷科 Lobotidae | ||||||||
| 松鲷 Lobotes surinamensis | 7 | + | + | |||||
| 锥齿鲷科 Pentapodidae | ||||||||
| 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aurolineatus | 342 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 灰裸顶鲷 Gymnocranius griseus | 156 | + | + | + | ||||
| 眶棘鲈科 Scolopsidae | ||||||||
| 条纹眶棘鲈 Scolopsis taeniopterus | 7 | + | + | |||||
| 石鲈科 Pomadasyidae | ||||||||
| 条纹胡椒鲷 Plectorhynchus lineatus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 斜纹胡椒鲷 P. goldmanni | 4 | + | + | |||||
| 羊鱼科 Mullidae | ||||||||
| 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 条斑副绯鲤 P. barberinus | 96 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 二带副绯鲤 P. bifasciatus | 6 | + | + | + | ||||
| 侧斑副绯鲤 P. heptacanthus | 188 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 头带副绯鲤 P. chryserdros | 70 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 纵条副绯鲤 P. fraterculus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 黑斑副绯鲤 P. pleurostigma | 2 | + | ||||||
| 金带拟羊鱼 Mulloidichthys suriflamma | 1 | + | ||||||
| 单鳍鱼科 Pempheridae | ||||||||
| 黑边单鳍鱼 Pempheris oualensis | 91 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 蝴蝶鱼科 Chaetodontidae | ||||||||
| 镊口鱼 Forcipiger longirostris | 0 | + | ||||||
| 四带马夫鱼 Heniochus singularius | 1 | + | ||||||
| 三带马夫鱼 H. permutatus | 24 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 马夫鱼 H. acuminatus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 霞蝶鱼 Hemitaurichthys zoster | 1 | + | ||||||
| 双条蝴蝶鱼 Chaetodon bennetti | 1 | + | ||||||
| 点带蝴蝶鱼 C. guttatissimus | 0 | + | ||||||
| 魏氏蝴蝶鱼 C. vagabundus | 2 | + | + | |||||
| 项斑蝴蝶鱼 C. adiergastos | 1 | + | ||||||
| 羽纹蝴蝶鱼 C. strigangulus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 密点蝴蝶鱼 C. citrinellus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 蓝斑蝴蝶鱼 C. plebeius | 1 | + | ||||||
| 橙带蝴蝶鱼 C. ornatissimus | 7 | + | + | |||||
| 川纹蝴蝶鱼 C. trifascialis | 1 | + | ||||||
| 单斑蝴蝶鱼 C. unimaculatus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 斑带蝴蝶鱼 C. punctatofasciatus | 0 | + | ||||||
| 隆头鱼科 Labridae | ||||||||
| 尖头普提鱼 Bodianus oxycephalus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 普提鱼 B. bilunulatus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 尾斑阿南鱼 Anampses melanurus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 黑鳍厚唇鱼 Hemigymnus melapterus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 横带粗唇鱼 H. fasciatus | 11 | + | + | |||||
| 胸斑海猪鱼 Halichoeres melanochir | 1 | + | ||||||
| 云斑海猪鱼 H. nigrescens | 1 | + | ||||||
| 方斑海猪鱼 H. centiquadrus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 狭带细鳞盔鱼 Hologymnosus semidiscus | 12 | + | + | |||||
| 花尾连鳍鱼 Novaculichthys taeniourus | 77 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 伸口鱼 Epibulus insidiator | 47 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 横带唇鱼 Cheilinus fasciatus | 42 | + | + | + | ||||
| 红唇鱼 C. rhodochrous | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 鹦嘴鱼科 Scaridae | ||||||||
| 凹尾绚鹦嘴鱼 Calotomus spinidens | 58 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 二色大鹦嘴鱼 Bolbometopon bicolor | 1 | + | ||||||
| 棕吻鹦嘴鱼 Scarus psittacus | 188 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 新月鹦嘴鱼 S. lunula | 3 | + | ||||||
| 五带鹦嘴鱼 S. venosus | 222 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 条腹鹦嘴鱼 S. aeruginosus | 189 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 带纹鹦嘴鱼 S. fasciatus | 21 | + | ||||||
| 长头鹦嘴鱼 S. longiceps | 15 | + | + | |||||
| 弧带鹦嘴鱼 S. dimidiatus | 9 | + | + | |||||
| 灰鹦嘴鱼 S. sordidus | 79 | + | + | + | ||||
| 黄鞍鹦嘴鱼 S. oviceps | 53 | + | ||||||
| 截尾鹦嘴鱼 S. rivulatus | 22 | + | + | + | ||||
| 蓝颊鹦嘴鱼 S. janthochir | 103 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 绿唇鹦嘴鱼 S. forsteri | 108 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 绿牙鹦嘴鱼 S. chlorodon | 129 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 三色鹦嘴鱼 S. tricolor | 233 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 青点鹦嘴鱼 S. ghobban | 15 | + | + | |||||
| 黑斑鹦嘴鱼 S. globiceps | 2 | + | ||||||
| 雀鲷科 Pomacentridae | ||||||||
| 三斑宅泥鱼 Dascyllus trimaculatus | 8 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 金豆娘鱼 Abudefduf aureus | 5 | + | + | |||||
| 弧带豆娘鱼 A. dickii | 1 | + | ||||||
| 蓝子鱼科 Siganidae | ||||||||
| 狐蓝子鱼 Siganus vulpinus | 9 | + | + | |||||
| 褐蓝子鱼 S. fuscescens | 34 | + | + | + | ||||
| 带蓝子鱼 S. virgatus | 16 | + | + | + | ||||
| 点蓝子鱼 S. guttatus | 105 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 镰鱼科 Zanclidae | ||||||||
| 镰鱼 Zanclus cornutus | 2 | + | + | |||||
| 刺尾鱼科 Acanthuridae | ||||||||
| 黄高鳍刺尾鱼 Zebrasoma flavescens | 1 | + | ||||||
| 橙斑刺尾鱼 Acanthurus olivaceus | 14 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 灰额刺尾鱼 A. glaucopareius | 28 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 双斑刺尾鱼 A. nigrofuscus | 225 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 双板盾尾鱼 Prionurus scalprus | 4 | + | ||||||
| 单板盾尾鱼 Axinurus thynnoides | 655 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 剑角鼻鱼 Naso herrei | 9 | + | ||||||
| 短吻鼻鱼 N. brevirostris | 4 | + | + | |||||
| 丝尾鼻鱼 N. vlamingi | 3 | + | ||||||
| 颊纹双板盾尾鱼 Callicanthus lituratus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 小齿双板盾尾鱼 C. hexacanthus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 蛇鲭科 Gempylidae | ||||||||
| 棘鳞蛇鲭 Ruvettus tydemani | 15 | + | ||||||
| 黑鳍蛇鲭 Thyrsitoides marleyi | 124 | + | ||||||
| 短蛇鲭 Rexea prometheoides | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲅科 Cybiidae | ||||||||
| 双线鲅 Grammatorcynus bicarinatus | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 鲉形目 SCORPAENIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鲉科 Scorpaenidae | ||||||||
| 斑鳍鲉 Scorpaena neglecta | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 须拟鲉 Scorpaenopsis cirrhosa | 2 | + | ||||||
| 翱翔衰鲉 Pterois volitans | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲀形目 TETRAODONTIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鳞鲀科 Balistidae | ||||||||
| 褐副鳞鲀 Pseudobalistes fuscus | 43 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 黑边角鳞鲀 Melischthys vidua | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 宽尾鳞鲀 Abalistes stellatus | 9 | + | ||||||
附录I 西沙群岛主要岛礁鱼类分布
Appendix I Distribution of fish in the coral islands/reefs of the Xisha Islands, South China Sea
| 种名 Species | 分布区域 Distribution region | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRI | 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 东岛 Dongdao Island | 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | |
| 六鳃鲨目 HEXANCHIFORMES | ||||||||
| 六鳃鲨科 Hexanchidae | ||||||||
| 灰六鳃鲨 Hexanchus griseus | 525 | + | + | |||||
| 真鲨目 CARCHARHINIFORMES | ||||||||
| 真鲨科 Carcharhinidae | ||||||||
| 尖头斜齿鲨 Scoliodon sorrakowah | 68 | + | + | |||||
| 侧条真鲨 Carcharhinus pleurotaenia | 8 | + | ||||||
| 灯笼鱼目 MYCTOPHIFORMES | ||||||||
| 狗母鱼科 Synodidae | ||||||||
| 花斑狗母鱼 Synodus jaculum | 21 | + | + | |||||
| 鳗鲡目 ANGUILLIFORMES | ||||||||
| 海鳝科 Muraenidae | ||||||||
| 异纹裸胸鳝 Gymnothorax richardsoni | 10 | + | ||||||
| 白斑裸胸鳝 G. leucostingmus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 花斑裸胸鳝 G. pictus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 金眼鲷目 BERYCIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鳂科 Holocentridae | ||||||||
| 骨鳂 Ostichthys sheni | 1 | + | ||||||
| 少鳞骨鳂 O. kaianus | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 灯眼鱼科 Anomalopidae | ||||||||
| 白边锯鳞鳂 Myripristis murdjan | 4,390 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 纵带锯鳞鳂 M. vittata | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 白纹棘鳞鳂 Sargocentron diadema | 21 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 尾斑棘鳞鳂 S. caudimaculatus | 30 | + | ||||||
| 尖吻棘鳞鳂 S. spiniferum | 1 | + | ||||||
| 条长颏鳂 Flammeo sammara | 29 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 斑尾鳂 Adioryx caudimaculatus | 15 | + | ||||||
| 赤鳂 A. tiere | 3 | + | ||||||
| 黄纹鳂 A. furcatus | 173 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 棘鳂 A. spinifer | 89 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 红双棘鳂 Dispinus ruber | 53 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 刺鱼目 GASTEROSTEIFORMES | ||||||||
| 烟管鱼科 Fistulariidae | ||||||||
| 鳞烟管鱼 Fistularia petimba | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲻形目 MUGILIFORMES | ||||||||
| 魣科 Sphyraenidae | ||||||||
| 大眼魣 Sphyraena forsteri | 252 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 大魣 S. barracuda | 47 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 鲈形目 PERCIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鮨科 Serranidae | ||||||||
| 鳃棘鲈 Plectropomus leopardus | 55 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 线点鳃棘鲈 P. oligacanthus | 57 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 豹纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis leopardus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 尾纹九棘鲈 C. urodelus | 35 | + | + | + | ||||
| 白线光腭鲈 Anyperodon leucogrammicus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 蜂巢石斑鱼 Epinephelus merra | 4 | + | ||||||
| 黑边石斑鱼 E. fasciatus | 140 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 大眼鲷科 Priacanthidae | ||||||||
| 金目大眼鲷 P. hamrur | 468 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 方头鱼科 Branchiostegidae | ||||||||
| 侧条弱棘鱼 Malacanthus latovittatus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲹科 Carangidae | ||||||||
| 星点鲹 Carangoides stellatus | 109 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 散鲹 C. sansun | 4 | + | ||||||
| 长体圆鲹 Decapterus macrosoma | 237 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 脂眼凹肩鲹 Selar crumenophthalmus | 57 | + | + | |||||
| 笛鲷科 Lutjanidae | ||||||||
| 红钻鱼 Etelis carbunculus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 细鳞紫鱼 Pristipomoides microlepis | 5 | + | ||||||
| 黄尾紫鱼 P. auricilla | 284 | + | ||||||
| 黄线紫鱼 P. multidens | 242 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 绿短臂鱼 Aprion virescens | 2 | + | ||||||
| 叉尾鲷 A. furcatus | 149 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 若梅鲷 Paracaesio xanthurus | 366 | + | + | |||||
| 灰若梅鲷 P. sordidus | 1,121 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira | 1,281 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 五带笛鲷 L. spilurus | 6 | + | ||||||
| 千年笛鲷 L. sebae | 1 | + | ||||||
| 双带梅鲷 Caesio diagramma | 949 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 褐梅鲷 C. coerulaureus | 24 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 新月梅鲷 C. lunaris | 46 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 裸颊鲷科 Lethrinidae | ||||||||
| 短吻裸颊鲷 Lethrinus ornatus | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 丽鳍裸颊鲷 L. kalloperus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 纵带裸颊鲷 L. leutjanus | 152 | + | + | |||||
| 杂色裸颊鲷 L. variegatus | 264 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 星斑裸颊鲷 L. nebulosus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 松鲷科 Lobotidae | ||||||||
| 松鲷 Lobotes surinamensis | 7 | + | + | |||||
| 锥齿鲷科 Pentapodidae | ||||||||
| 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aurolineatus | 342 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 灰裸顶鲷 Gymnocranius griseus | 156 | + | + | + | ||||
| 眶棘鲈科 Scolopsidae | ||||||||
| 条纹眶棘鲈 Scolopsis taeniopterus | 7 | + | + | |||||
| 石鲈科 Pomadasyidae | ||||||||
| 条纹胡椒鲷 Plectorhynchus lineatus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 斜纹胡椒鲷 P. goldmanni | 4 | + | + | |||||
| 羊鱼科 Mullidae | ||||||||
| 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 条斑副绯鲤 P. barberinus | 96 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 二带副绯鲤 P. bifasciatus | 6 | + | + | + | ||||
| 侧斑副绯鲤 P. heptacanthus | 188 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 头带副绯鲤 P. chryserdros | 70 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 纵条副绯鲤 P. fraterculus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 黑斑副绯鲤 P. pleurostigma | 2 | + | ||||||
| 金带拟羊鱼 Mulloidichthys suriflamma | 1 | + | ||||||
| 单鳍鱼科 Pempheridae | ||||||||
| 黑边单鳍鱼 Pempheris oualensis | 91 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 蝴蝶鱼科 Chaetodontidae | ||||||||
| 镊口鱼 Forcipiger longirostris | 0 | + | ||||||
| 四带马夫鱼 Heniochus singularius | 1 | + | ||||||
| 三带马夫鱼 H. permutatus | 24 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 马夫鱼 H. acuminatus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 霞蝶鱼 Hemitaurichthys zoster | 1 | + | ||||||
| 双条蝴蝶鱼 Chaetodon bennetti | 1 | + | ||||||
| 点带蝴蝶鱼 C. guttatissimus | 0 | + | ||||||
| 魏氏蝴蝶鱼 C. vagabundus | 2 | + | + | |||||
| 项斑蝴蝶鱼 C. adiergastos | 1 | + | ||||||
| 羽纹蝴蝶鱼 C. strigangulus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 密点蝴蝶鱼 C. citrinellus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 蓝斑蝴蝶鱼 C. plebeius | 1 | + | ||||||
| 橙带蝴蝶鱼 C. ornatissimus | 7 | + | + | |||||
| 川纹蝴蝶鱼 C. trifascialis | 1 | + | ||||||
| 单斑蝴蝶鱼 C. unimaculatus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 斑带蝴蝶鱼 C. punctatofasciatus | 0 | + | ||||||
| 隆头鱼科 Labridae | ||||||||
| 尖头普提鱼 Bodianus oxycephalus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 普提鱼 B. bilunulatus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 尾斑阿南鱼 Anampses melanurus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 黑鳍厚唇鱼 Hemigymnus melapterus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 横带粗唇鱼 H. fasciatus | 11 | + | + | |||||
| 胸斑海猪鱼 Halichoeres melanochir | 1 | + | ||||||
| 云斑海猪鱼 H. nigrescens | 1 | + | ||||||
| 方斑海猪鱼 H. centiquadrus | 1 | + | ||||||
| 狭带细鳞盔鱼 Hologymnosus semidiscus | 12 | + | + | |||||
| 花尾连鳍鱼 Novaculichthys taeniourus | 77 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 伸口鱼 Epibulus insidiator | 47 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 横带唇鱼 Cheilinus fasciatus | 42 | + | + | + | ||||
| 红唇鱼 C. rhodochrous | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 鹦嘴鱼科 Scaridae | ||||||||
| 凹尾绚鹦嘴鱼 Calotomus spinidens | 58 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 二色大鹦嘴鱼 Bolbometopon bicolor | 1 | + | ||||||
| 棕吻鹦嘴鱼 Scarus psittacus | 188 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 新月鹦嘴鱼 S. lunula | 3 | + | ||||||
| 五带鹦嘴鱼 S. venosus | 222 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 条腹鹦嘴鱼 S. aeruginosus | 189 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 带纹鹦嘴鱼 S. fasciatus | 21 | + | ||||||
| 长头鹦嘴鱼 S. longiceps | 15 | + | + | |||||
| 弧带鹦嘴鱼 S. dimidiatus | 9 | + | + | |||||
| 灰鹦嘴鱼 S. sordidus | 79 | + | + | + | ||||
| 黄鞍鹦嘴鱼 S. oviceps | 53 | + | ||||||
| 截尾鹦嘴鱼 S. rivulatus | 22 | + | + | + | ||||
| 蓝颊鹦嘴鱼 S. janthochir | 103 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 绿唇鹦嘴鱼 S. forsteri | 108 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 绿牙鹦嘴鱼 S. chlorodon | 129 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 三色鹦嘴鱼 S. tricolor | 233 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 青点鹦嘴鱼 S. ghobban | 15 | + | + | |||||
| 黑斑鹦嘴鱼 S. globiceps | 2 | + | ||||||
| 雀鲷科 Pomacentridae | ||||||||
| 三斑宅泥鱼 Dascyllus trimaculatus | 8 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 金豆娘鱼 Abudefduf aureus | 5 | + | + | |||||
| 弧带豆娘鱼 A. dickii | 1 | + | ||||||
| 蓝子鱼科 Siganidae | ||||||||
| 狐蓝子鱼 Siganus vulpinus | 9 | + | + | |||||
| 褐蓝子鱼 S. fuscescens | 34 | + | + | + | ||||
| 带蓝子鱼 S. virgatus | 16 | + | + | + | ||||
| 点蓝子鱼 S. guttatus | 105 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 镰鱼科 Zanclidae | ||||||||
| 镰鱼 Zanclus cornutus | 2 | + | + | |||||
| 刺尾鱼科 Acanthuridae | ||||||||
| 黄高鳍刺尾鱼 Zebrasoma flavescens | 1 | + | ||||||
| 橙斑刺尾鱼 Acanthurus olivaceus | 14 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 灰额刺尾鱼 A. glaucopareius | 28 | + | + | + | + | |||
| 双斑刺尾鱼 A. nigrofuscus | 225 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 双板盾尾鱼 Prionurus scalprus | 4 | + | ||||||
| 单板盾尾鱼 Axinurus thynnoides | 655 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 剑角鼻鱼 Naso herrei | 9 | + | ||||||
| 短吻鼻鱼 N. brevirostris | 4 | + | + | |||||
| 丝尾鼻鱼 N. vlamingi | 3 | + | ||||||
| 颊纹双板盾尾鱼 Callicanthus lituratus | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 小齿双板盾尾鱼 C. hexacanthus | 2 | + | ||||||
| 蛇鲭科 Gempylidae | ||||||||
| 棘鳞蛇鲭 Ruvettus tydemani | 15 | + | ||||||
| 黑鳍蛇鲭 Thyrsitoides marleyi | 124 | + | ||||||
| 短蛇鲭 Rexea prometheoides | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲅科 Cybiidae | ||||||||
| 双线鲅 Grammatorcynus bicarinatus | 6 | + | + | |||||
| 鲉形目 SCORPAENIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鲉科 Scorpaenidae | ||||||||
| 斑鳍鲉 Scorpaena neglecta | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 须拟鲉 Scorpaenopsis cirrhosa | 2 | + | ||||||
| 翱翔衰鲉 Pterois volitans | 1 | + | ||||||
| 鲀形目 TETRAODONTIFORMES | ||||||||
| 鳞鲀科 Balistidae | ||||||||
| 褐副鳞鲀 Pseudobalistes fuscus | 43 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 黑边角鳞鲀 Melischthys vidua | 3 | + | + | |||||
| 宽尾鳞鲀 Abalistes stellatus | 9 | + | ||||||
| 岛礁 Island/Reef | 目 Order | 科 Family | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 6 | 20 | 45 |
| 东岛 Dongdao Island | 7 | 22 | 50 |
| 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 6 | 20 | 48 |
| 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 3 | 18 | 51 |
| 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 4 | 19 | 63 |
| 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 5 | 19 | 50 |
| 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | 7 | 24 | 74 |
| 合计 Total | 10 | 31 | 146 |
表1 西沙群岛主要岛礁鱼类的目/科/种类组成
Table 1 Composition of the fish species/family/order of the major coral reefs in Xisha Islands
| 岛礁 Island/Reef | 目 Order | 科 Family | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 6 | 20 | 45 |
| 东岛 Dongdao Island | 7 | 22 | 50 |
| 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 6 | 20 | 48 |
| 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 3 | 18 | 51 |
| 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 4 | 19 | 63 |
| 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 5 | 19 | 50 |
| 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | 7 | 24 | 74 |
| 合计 Total | 10 | 31 | 146 |
| 种名 Species | 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 东岛 Dongdao Island | 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰六鳃鲨 Hexanchus griseus | 0.0 | 18.3 | 0.0 | 425.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 443.3 |
| 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira | 205.5 | 7.5 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 5.2 | 223.7 |
| 白边锯鳞鳂 Myripristis murdjan | 22.9 | 17.7 | 5.5 | 12.3 | 2.6 | 9.3 | 103.4 | 173.6 |
| 灰若梅鲷 Paracaesio sordidus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 14.7 | 15.3 | 30.4 | 0.0 | 50.1 | 110.4 |
| 双带梅鲷 Caesio diagramma | 45.3 | 0.0 | 13.7 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 26.0 | 88.0 |
| 黄尾紫鱼 Pristipomoides multidens | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 86.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 86.5 |
| 若梅鲷 Paracaesio xanthurus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 65.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 10.4 | 75.7 |
| 金目大眼鲷 Priacanthus hamru | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 6.0 | 39.0 | 63.9 |
| 黑鳍蛇鲭 Thyrsitoides marleyi | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 56.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 56.8 |
| 单板盾尾鱼 Axinurus thynnoides | 9.9 | 2.4 | 6.2 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 20.8 | 45.5 |
| 尖头斜齿鲨 Scoliodon sorrakowah | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 17.7 | 25.0 | 0.0 | 42.7 |
| 大眼魣 Sphyraena forsteri | 5.0 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 23.4 | 35.8 |
| 黄线紫鱼 Pristipomoides multidens | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 0.0 | 14.2 | 30.7 |
| 棕吻鹦嘴鱼 Scarus psittacus | 0.1 | 4.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 25.7 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 30.6 |
| 三色鹦嘴鱼 S. tricolor | 0.0 | 14.6 | 8.2 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 27.0 |
| 长体圆鲹 Decapterus macrosoma | 5.5 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 26.0 |
| 条斑副绯鲤 Parupeneus barberinus | 3.1 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 16.9 | 25.5 |
| 杂色裸颊鲷 Lethrinus variegatus | 10.1 | 3.2 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 0.0 | 25.1 |
| 棘鳞蛇鲭 Ruvettus tydemani | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.3 |
| 五带鹦嘴鱼 Scarus venosus | 6.1 | 1.5 | 5.8 | 0.3 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 4.2 | 23.1 |
| 叉尾鲷 Aphareus furcatus | 4.1 | 0.0 | 4.1 | 0.5 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 7.3 | 21.4 |
| 蓝颊鹦嘴鱼 Scarus janthochir | 0.0 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 15.8 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 20.7 |
| 条腹鹦嘴鱼 S. aeruginosus | 1.2 | 7.5 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 5.4 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 20.4 |
| 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aurolineatus | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 11.5 | 3.3 | 18.9 |
| 纵带裸颊鲷 Lethrinus leutjanus | 3.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.1 | 16.0 |
| 灰裸顶鲷 Gymnocranius griseus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 15.4 |
| 宽尾鳞鲀 Abalistes stellatus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.9 | 0.0 | 13.9 |
| 侧斑副绯鲤 Parupeneus heptacanthus | 5.6 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 3.4 | 13.5 |
| 侧条真鲨 Carcharhinus pleurotaenia | 0.0 | 13.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.0 |
| 大魣 Sphyraena barracuda | 0.0 | 0.7 | 10.3 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 13.0 |
| 绿牙鹦嘴鱼 Scarus chlorodon | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 12.9 |
| 黄纹鳂 Adioryx furcatus | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 6.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 12.4 |
| 灰鹦嘴鱼 Scarus sordidus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 9.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 11.7 |
| 黄鞍鹦嘴鱼 S. oviceps | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 11.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 11.6 |
| 新月梅鲷 Caesio lunaris | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 5.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 8.1 |
| 脂眼凹肩鲹 Selar crumenophthalmus | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 0.0 | 7.5 |
| 双板盾尾鱼 Prionurus scalprus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.8 |
| 散鲹 Carangoides sansun | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.5 |
| 小齿双板盾尾鱼 Callicanthus hexacanthus | 0.0 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| 合计 Total | 334.0 | 105.7 | 106.2 | 733.1 | 156.0 | 112.4 | 357.1 | 1,904.4 |
表2 西沙群岛主要岛礁单位捕捞努力量渔获量(CPUE)前10位的鱼类
Table 2 Top 10 fish species in catch per unit effort (g/km) of the major coral reefs in Xisha Islands
| 种名 Species | 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 东岛 Dongdao Island | 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰六鳃鲨 Hexanchus griseus | 0.0 | 18.3 | 0.0 | 425.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 443.3 |
| 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira | 205.5 | 7.5 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 5.2 | 223.7 |
| 白边锯鳞鳂 Myripristis murdjan | 22.9 | 17.7 | 5.5 | 12.3 | 2.6 | 9.3 | 103.4 | 173.6 |
| 灰若梅鲷 Paracaesio sordidus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 14.7 | 15.3 | 30.4 | 0.0 | 50.1 | 110.4 |
| 双带梅鲷 Caesio diagramma | 45.3 | 0.0 | 13.7 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 26.0 | 88.0 |
| 黄尾紫鱼 Pristipomoides multidens | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 86.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 86.5 |
| 若梅鲷 Paracaesio xanthurus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 65.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 10.4 | 75.7 |
| 金目大眼鲷 Priacanthus hamru | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 6.0 | 39.0 | 63.9 |
| 黑鳍蛇鲭 Thyrsitoides marleyi | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 56.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 56.8 |
| 单板盾尾鱼 Axinurus thynnoides | 9.9 | 2.4 | 6.2 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 20.8 | 45.5 |
| 尖头斜齿鲨 Scoliodon sorrakowah | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 17.7 | 25.0 | 0.0 | 42.7 |
| 大眼魣 Sphyraena forsteri | 5.0 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 23.4 | 35.8 |
| 黄线紫鱼 Pristipomoides multidens | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 0.0 | 14.2 | 30.7 |
| 棕吻鹦嘴鱼 Scarus psittacus | 0.1 | 4.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 25.7 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 30.6 |
| 三色鹦嘴鱼 S. tricolor | 0.0 | 14.6 | 8.2 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 27.0 |
| 长体圆鲹 Decapterus macrosoma | 5.5 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 26.0 |
| 条斑副绯鲤 Parupeneus barberinus | 3.1 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 16.9 | 25.5 |
| 杂色裸颊鲷 Lethrinus variegatus | 10.1 | 3.2 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 0.0 | 25.1 |
| 棘鳞蛇鲭 Ruvettus tydemani | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 24.3 |
| 五带鹦嘴鱼 Scarus venosus | 6.1 | 1.5 | 5.8 | 0.3 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 4.2 | 23.1 |
| 叉尾鲷 Aphareus furcatus | 4.1 | 0.0 | 4.1 | 0.5 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 7.3 | 21.4 |
| 蓝颊鹦嘴鱼 Scarus janthochir | 0.0 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 15.8 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 20.7 |
| 条腹鹦嘴鱼 S. aeruginosus | 1.2 | 7.5 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 5.4 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 20.4 |
| 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aurolineatus | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 11.5 | 3.3 | 18.9 |
| 纵带裸颊鲷 Lethrinus leutjanus | 3.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.1 | 16.0 |
| 灰裸顶鲷 Gymnocranius griseus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 15.4 |
| 宽尾鳞鲀 Abalistes stellatus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.9 | 0.0 | 13.9 |
| 侧斑副绯鲤 Parupeneus heptacanthus | 5.6 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 3.4 | 13.5 |
| 侧条真鲨 Carcharhinus pleurotaenia | 0.0 | 13.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.0 |
| 大魣 Sphyraena barracuda | 0.0 | 0.7 | 10.3 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 13.0 |
| 绿牙鹦嘴鱼 Scarus chlorodon | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 12.9 |
| 黄纹鳂 Adioryx furcatus | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 6.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 12.4 |
| 灰鹦嘴鱼 Scarus sordidus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 9.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 11.7 |
| 黄鞍鹦嘴鱼 S. oviceps | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 11.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 11.6 |
| 新月梅鲷 Caesio lunaris | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 5.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 8.1 |
| 脂眼凹肩鲹 Selar crumenophthalmus | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 0.0 | 7.5 |
| 双板盾尾鱼 Prionurus scalprus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.8 |
| 散鲹 Carangoides sansun | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.5 |
| 小齿双板盾尾鱼 Callicanthus hexacanthus | 0.0 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| 合计 Total | 334.0 | 105.7 | 106.2 | 733.1 | 156.0 | 112.4 | 357.1 | 1,904.4 |
| 岛礁 Island/Reef | 丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index (J') | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H' W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 3.67 | 0.53 | 2.00 |
| 东岛 Dongdao Island | 4.58 | 0.79 | 3.11 |
| 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 4.32 | 0.86 | 3.33 |
| 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 4.03 | 0.48 | 1.91 |
| 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 5.51 | 0.79 | 3.28 |
| 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 4.41 | 0.80 | 3.13 |
| 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | 5.93 | 0.67 | 2.89 |
| 平均 Mean | 4.63 | 0.70 | 2.81 |
表3 西沙群岛主要岛礁的鱼类多样性指数
Table 3 Fish diversity indices of the coral reefs in the Xisha Islands
| 岛礁 Island/Reef | 丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index (J') | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H' W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 北礁 Beijiao Reef | 3.67 | 0.53 | 2.00 |
| 东岛 Dongdao Island | 4.58 | 0.79 | 3.11 |
| 华光礁 Huaguang Reef | 4.32 | 0.86 | 3.33 |
| 金银岛 Jinyin Island | 4.03 | 0.48 | 1.91 |
| 浪花礁 Langhua Reef | 5.51 | 0.79 | 3.28 |
| 永兴岛 Yongxing Island | 4.41 | 0.80 | 3.13 |
| 玉琢礁 Yuzhuo Reef | 5.93 | 0.67 | 2.89 |
| 平均 Mean | 4.63 | 0.70 | 2.81 |
| 区域 Region | H'N | H'W | 文献 Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | ||
| 大堡礁 Great Barrier Reef | 1.56-2.98 | 2.31 | |||
| 墨西哥湾 Gulf of Mexico | 1.31-1.86 | 1.56 | |||
| 地中海沿岸水域 Coastal waters of Mediterranean | 1.00-2.40 | ||||
| 黄海南部 Southern Yellow Sea | 0.36-2.14 | 1.29 | 0.82-1.99 | 1.45 | |
| 黄海 Yellow Sea | 0.40-2.34 | 1.58 | |||
| 莱州湾 Laizhou Bay | 1.32-2.27 | 1.93 | |||
| 东海北部 Northern East China Sea | 0.55-2.33 | 1.81 | 0.54-2.74 | 1.84 | |
| 东海中部 Central East China Sea | 0.34-2.75 | 1.56 | 0.31-2.78 | 1.88 | |
| 东海 East China Sea | 0.31-3.15 | 1.79 | |||
| 西沙群岛 Xisha Islands, South China Sea | 2.18-3.51 | 2.94 | 1.91-3.33 | 2.81 | 本文 |
表4 不同区域鱼类多样性指数的比较
Table 4 Comparison of the fish diversity index among different regions
| 区域 Region | H'N | H'W | 文献 Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | ||
| 大堡礁 Great Barrier Reef | 1.56-2.98 | 2.31 | |||
| 墨西哥湾 Gulf of Mexico | 1.31-1.86 | 1.56 | |||
| 地中海沿岸水域 Coastal waters of Mediterranean | 1.00-2.40 | ||||
| 黄海南部 Southern Yellow Sea | 0.36-2.14 | 1.29 | 0.82-1.99 | 1.45 | |
| 黄海 Yellow Sea | 0.40-2.34 | 1.58 | |||
| 莱州湾 Laizhou Bay | 1.32-2.27 | 1.93 | |||
| 东海北部 Northern East China Sea | 0.55-2.33 | 1.81 | 0.54-2.74 | 1.84 | |
| 东海中部 Central East China Sea | 0.34-2.75 | 1.56 | 0.31-2.78 | 1.88 | |
| 东海 East China Sea | 0.31-3.15 | 1.79 | |||
| 西沙群岛 Xisha Islands, South China Sea | 2.18-3.51 | 2.94 | 1.91-3.33 | 2.81 | 本文 |
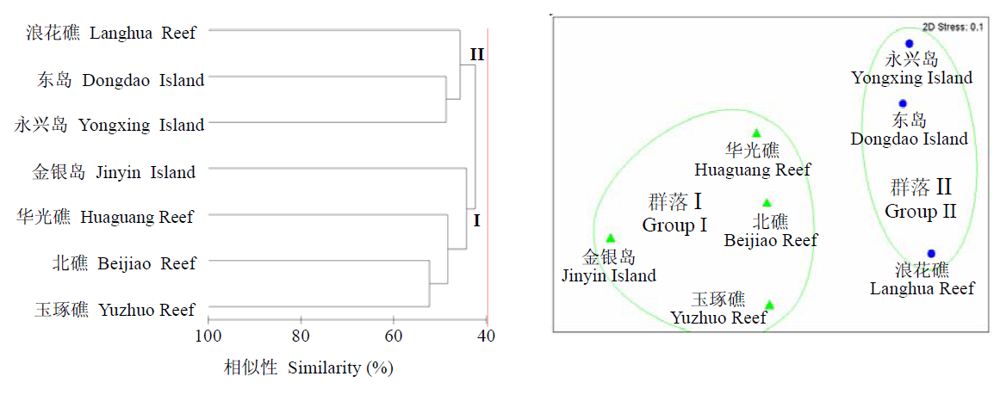
图2 西沙群岛各采样岛礁鱼类群落的等级聚类分析图(左)和NMDS排序图(右)
Fig. 2 Group average clustering (left) and NMDS ordination (right) of sampling coral islands/reefs in the Xisha Islands
| [1] | Brazner JC, Beals EW (1997) Patterns in fish assemblages from coastal wetland and beach habitats in Green Bay, Lake Michigan: a multivariate analysis of abiotic and biotic forcing factors. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 54, 1743-1761. |
| [2] | Chen GB (陈国宝), Li YZ (李永振), Chen XJ (陈新军) (2007) Species diversity of fishes in the coral reefs of South China Sea. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15, 373-381. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen QC (陈清潮) (1997) Current status and prospects of marine biodiversity in China. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 5, 142-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Cheng JS (程济生), Yu LF (俞连福) (2004) The change of structure and diversity of demersal fish communities in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in winter. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 28, 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMPER-E Ltd, Plymouth. |
| [6] | Field JG, Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1982) A practical strategy for analysing multispecies distribution patterns. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 8, 37-52. |
| [7] | George DD, Thomas JB (1988) Reef fish assemblages on hard banks in the northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Bulletin of Marine Science, 43, 280-307. |
| [8] | Jin XS (金显仕), Deng JY (邓景耀) (2000) Variations in community structure of fishery resources and biodiversity in the Laizhou Bay, Shandong. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 8, 65-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Khalaf MA, Kochzius M (2002) Changes in trophic community structure of shore fishes at an industrial site in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 239, 287-299. |
| [10] | Li SF (李圣法), Cheng JH (程家骅), Yan LP (严利萍) (2005) The spatial pattern of the fish assemblage structure in the mid-southern East China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (海洋学报), 27(3), 110-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Li XZ (李新正), Li BQ (李宝泉), Wang HF (王洪法), Wang SQ (王少青), Wang JB (王金宝), Zhang BL (张宝琳) (2007) Macrobenthic community characters of Zhubi Reef, Nansha Islands, South China Sea. Acta Zoologica Sinica (动物学报), 53, 83-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Li YH (李颖虹), Huang XP (黄小平), Yue WZ (岳维忠), Lin YT (林燕棠), Zou RL (邹仁林), Huang H (黄晖) (2004) Ecological study on coral reef and intertidal benthos around Yongxing Island, South China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 35, 176-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Liu Y (刘勇), Li SF (李圣法), Chen XG (陈学刚), Cheng JH (程家骅) (2007) The structure and diversity of demersal fish communities in winter 2000 in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Marine Sciences (海洋科学), 31(10), 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Ma ZY (马藏允), Liu H (刘海), Wang HQ (王惠卿), Wang SQ (王世权) (1997) Multivariate analysis of community structure on macrobenthos. China Environmental Science (中国环境科学), 17, 297-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Margalef R (1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [16] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [17] | Pinkas L, Oliphant MS, Iverson ILK (1971) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. California Department of Fish and Game, Fish Bulletin, 152, 1-105. |
| [18] | Shen GY (沈国英), Huang LF (黄凌风), Guo F (郭丰), Shi BZ (施并章) (2010) Marine Ecology (海洋生态学), 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | Shi XJ (时小军), Liu YB (刘元兵), Chen TG (陈特固), Yu KF (余克服) (2008) The potential threats of global warming on corals living in the Xisha Islands and Nansha Islands. Tropical Geography (热带地理), 28, 342-368. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Sun DR (孙典荣), Lin ZJ (林昭进), Qiu YS (邱永松) (2005a) Survey of coral reef fish resources of the Xisha Islands. Periodical of Ocean University of China (中国海洋大学学报 (自然科学版)), 35, 225-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Sun DR (孙典荣), Lin ZJ (林昭进), Qiu YS (邱永松), Wang XH (王雪辉) (2005b) Fish fauna of coral reef waters of the Xisha Islands. South China Fisheries Science (南方水产), 1(5), 18-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Wang GZ (王国忠), Lü BQ (吕炳全), Quan SQ (全松青) (1986) The sedimentary environments and characteristics of the coral reef of the Yongxing Island. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 17, 36-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Wang XH (王雪辉), Qiu YS (邱永松), Du FY (杜飞雁), Lin ZJ (林昭进), Sun DR (孙典荣), Huang SL (黄硕琳) (2010) Fish community pattern and its relation to environmental factor in the Beibu Gulf. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 34, 1579-1586. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Wilhm JL (1968) Use of biomass units in Shannon’s formula. Ecology, 49, 153-156. |
| [25] | Williams DM, Hatcher AI (1983) Structure of fish communities on out slopes of inshore, mid-shelf and outer shelf reefs of the Great Barrier Reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 10, 239-250. |
| [26] | Zou RL (邹仁林) (1980) Further analysis on the community structure of the hermatypic corals of the Xisha Qundao (Hsisha Islands), Guangdong Sheng (Kwangtung Province), China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (海洋学报), 2(3), 98-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 孙智闲, 田晨, 王鑫, 方雨田, 李博, 赵亚辉. 热带沿海城市土著鱼类面临的威胁: 以海南省三亚市为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24165-. |
| [12] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [13] | 李雪原, 孙智闲, 王凤震, 席蕊, 方雨田, 郝浚源, 盛冬, 孙书雅, 赵亚辉. 城市发展对鱼类功能多样性的影响: 以超大城市北京为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24150-. |
| [14] | 张作鹏, 要晨阳, 吴玲, 罗遵兰, 孙光, 郭宗勇, 李晓思, 林峰, 陈小勇. 怒江云南段鱼类多样性现状与威胁因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24076-. |
| [15] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()