



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 1358-1368. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021082 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021082
收稿日期:2021-03-07
接受日期:2021-06-30
出版日期:2021-10-20
发布日期:2021-10-20
通讯作者:
谢屹
作者简介:* E-mail: yixie@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xinyu Zhang, Yuxuan Hu, Zhongyi Zhang, Yuhan Fu, Yi Xie( )
)
Received:2021-03-07
Accepted:2021-06-30
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-10-20
Contact:
Yi Xie
摘要:
我国高度重视野生动物保护事业, 认真履行野生动物保护国际义务, 积极鼓励公众参与, 以扩大野生动物保护事业的公众基础。已有文献多关注了公众的国内野生动物保护意愿, 鲜有文献关注公众对国际野生动物的保护意愿, 难以为促进公众参与国际野生动物保护事业提供决策参考。本研究以全球旗舰物种非洲象(Loxodonta africana)为例, 结合非洲象保护的相关研究与实践, 构建拓展的计划行为理论框架, 通过线下和线上调研获取数据, 运用结构方程模型, 从态度、规范、知觉行为控制、过去经验及个体特征五个方面, 分析了我国公众的非洲象保护意愿及影响因素。结果表明: (1) 68.5%的公众具有非洲象保护愿意; (2)公众规范(系数为0.422)、过去经验(系数为0.253)、知觉行为控制(系数为0.160)、保护态度(系数为0.156)对保护意愿存在显著的正向影响; 男性公众(系数为-0.054)的保护意愿低于女性公众; 居住在西部地区的公众(系数为0.066)保护意愿更高; (3)模型整体通过了拟合检验, 表明研究结果具有稳健性。本研究的政策建议如下: (1)明确政策导向作用, 提升公众的道德义务感和社会责任感; (2)加强宣传教育, 丰富公众知识经验, 培育公众积极的保护态度; (3)拓宽保护参与渠道, 提高公众知觉行为控制; (4)制定合理方案, 提升保护宣教等实践活动成效。
张馨予, 胡宇轩, 张忠义, 傅钰涵, 谢屹 (2021) 中国公众的国际野生动物保护意愿调查: 以非洲象为例. 生物多样性, 29, 1358-1368. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021082.
Xinyu Zhang, Yuxuan Hu, Zhongyi Zhang, Yuhan Fu, Yi Xie (2021) Chinese public willingness of international wildlife conservation: A case study of African elephant. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1358-1368. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021082.
| 统计变量 Demographic variables | 频数 Frequency | 占比 % | 2010年人口普查占比 Percent in the census data in 2010 (%) | 文献占比(Wang et al, Percent in the literatures (Wang et al, | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 Gender | 男 Male | 503 | 52.9 | 51.1 | 46.45 |
| 女 Female | 447 | 47.1 | 48.9 | 53.55 | |
| 年龄 Age | 0-18岁 0-18 years old | 62 | 6.5 | 13.7 | 5.69 |
| 19-28岁 19-28 years old | 359 | 37.8 | 25.3 | 44.31 | |
| 29-40岁 29-40 years old | 286 | 30.1 | 22.4 | 36.36 | |
| 41-64岁 41-64 years old | 202 | 21.3 | 30.9 | 11.85 | |
| ≥ 65岁 Above 65 years old | 41 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 1.9 | |
| 受教育程度 Education level | 小学及以下 Below primary school | 23 | 2.5 | 18.0 | 0.47 |
| 初中 Middle school | 133 | 14.0 | 36.1 | 3.79 | |
| 大专及高中 High school | 313 | 32.9 | 35.8 | 23.93 | |
| 本科 Undergraduate | 366 | 38.5 | 9.1 | 60.19 | |
| 硕士及以上 Master and higher academic degree | 104 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 10.66 | |
| 居住地区 Residence | 东部地区 Eastern regions | 510 | 53.7 | 59.0 | ? |
| 中部地区 Central regions | 268 | 28.2 | 26.0 | ? | |
| 西部地区 Western regions | 172 | 18.1 | 15.0 | ? | |
表1 本研究样本人口统计信息与人口普查和现有文献数据的比较
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of the samples in this study compared with the data of census and literatures
| 统计变量 Demographic variables | 频数 Frequency | 占比 % | 2010年人口普查占比 Percent in the census data in 2010 (%) | 文献占比(Wang et al, Percent in the literatures (Wang et al, | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 Gender | 男 Male | 503 | 52.9 | 51.1 | 46.45 |
| 女 Female | 447 | 47.1 | 48.9 | 53.55 | |
| 年龄 Age | 0-18岁 0-18 years old | 62 | 6.5 | 13.7 | 5.69 |
| 19-28岁 19-28 years old | 359 | 37.8 | 25.3 | 44.31 | |
| 29-40岁 29-40 years old | 286 | 30.1 | 22.4 | 36.36 | |
| 41-64岁 41-64 years old | 202 | 21.3 | 30.9 | 11.85 | |
| ≥ 65岁 Above 65 years old | 41 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 1.9 | |
| 受教育程度 Education level | 小学及以下 Below primary school | 23 | 2.5 | 18.0 | 0.47 |
| 初中 Middle school | 133 | 14.0 | 36.1 | 3.79 | |
| 大专及高中 High school | 313 | 32.9 | 35.8 | 23.93 | |
| 本科 Undergraduate | 366 | 38.5 | 9.1 | 60.19 | |
| 硕士及以上 Master and higher academic degree | 104 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 10.66 | |
| 居住地区 Residence | 东部地区 Eastern regions | 510 | 53.7 | 59.0 | ? |
| 中部地区 Central regions | 268 | 28.2 | 26.0 | ? | |
| 西部地区 Western regions | 172 | 18.1 | 15.0 | ? | |
| 拟合指标 Fit indices | 绝对适配度指标 Absolute fit measurement | 增值适配度指标 Incremental fit measurement | 简约适配度指标 Parsimonious fit measurement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSEA | SRMR | GFI | TLI | CFI | NFI | IFI | PNFI | χ2/DF | |
| 评价标准 Norms | <0.08 | <0.08 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.50 | 1<χ2/DF<5 |
| 模型结果 Results | 0.050 | 0.060 | 0.920 | 0.929 | 0.938 | 0.914 | 0.938 | 0.799 | 3.373 |
表2 我国公众非洲象保护意愿结构方程模型拟合检验结果
Table 2 Confirmatory analysis fitting indicators of the structural equation model to predict Chinese public willingness of African elephant conservation
| 拟合指标 Fit indices | 绝对适配度指标 Absolute fit measurement | 增值适配度指标 Incremental fit measurement | 简约适配度指标 Parsimonious fit measurement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSEA | SRMR | GFI | TLI | CFI | NFI | IFI | PNFI | χ2/DF | |
| 评价标准 Norms | <0.08 | <0.08 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.90 | >0.50 | 1<χ2/DF<5 |
| 模型结果 Results | 0.050 | 0.060 | 0.920 | 0.929 | 0.938 | 0.914 | 0.938 | 0.799 | 3.373 |
| 估算系数 Estimate | 标准误 S.E. | 临界值 C.R. | 假设检验结果 Evaluation of hypotheses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 态度 Attitude | 0.156*** | 0.083 | 3.914 | H1 | 接受 Supported |
| 规范 Norm | 0.422*** | 0.058 | 7.889 | H2 | 接受 Supported |
| 知觉行为控制 Perceived behavior control | 0.160*** | 0.036 | 4.218 | H3 | 接受 Supported |
| 过去经验 Past experience | 0.253*** | 0.161 | 5.074 | H4 | 接受 Supported |
| 性别 Gender | -0.054* | 0.059 | -2.258 | H5 | 部分接受 Partially supported |
| 东部地区 Eastern regions | 0.058 | 0.080 | 1.858 | ||
| 西部地区 Western regions | 0.066* | 0.103 | 2.084 | ||
表3 我国公众非洲象保护意愿结构方程模型假设检验结果
Table 3 Hypotheses testing results of the structural equation model to predict Chinese public willingness of African elephant conservation
| 估算系数 Estimate | 标准误 S.E. | 临界值 C.R. | 假设检验结果 Evaluation of hypotheses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 态度 Attitude | 0.156*** | 0.083 | 3.914 | H1 | 接受 Supported |
| 规范 Norm | 0.422*** | 0.058 | 7.889 | H2 | 接受 Supported |
| 知觉行为控制 Perceived behavior control | 0.160*** | 0.036 | 4.218 | H3 | 接受 Supported |
| 过去经验 Past experience | 0.253*** | 0.161 | 5.074 | H4 | 接受 Supported |
| 性别 Gender | -0.054* | 0.059 | -2.258 | H5 | 部分接受 Partially supported |
| 东部地区 Eastern regions | 0.058 | 0.080 | 1.858 | ||
| 西部地区 Western regions | 0.066* | 0.103 | 2.084 | ||
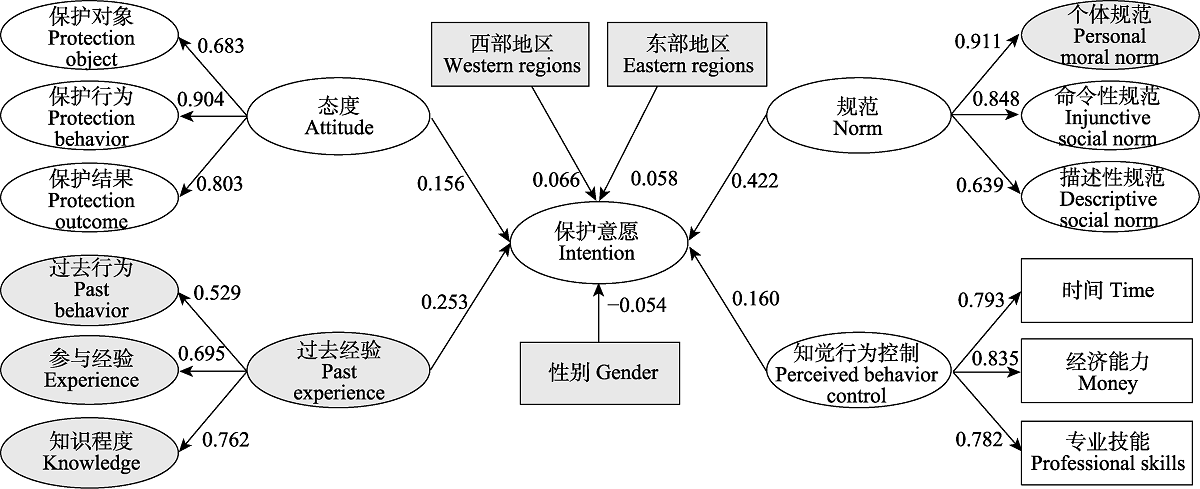
图1 我国公众的非洲象保护意愿结构方程模型路径图。灰色为拓展变量。
Fig. 1 Structural equation model, used to predict Chinese public willingness of African elephant conservation. Grey areas are expanded variable.
| [1] |
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179-211.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Ajzen I (2011) The theory of planned behaviour: Reactions and reflections. Psychology & Health, 26, 1113-1127. |
| [3] | Ajzen I (2019) Constructing a theory of planned behavior questionnaire. http://people.umass.edu/aizen/pdf/tpb.measurement.pdf. (accessed on 2021-09-01) |
| [4] |
Ajzen I, Fishbein M (2008) Scaling and testing multiplicative combinations in the expectancy-value model of attitudes. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 38, 2222-2247.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Armitage CJ, Conner M (2001) Efficacy of the theory of planned behavior: A meta-analytic review. The British Journal of Social Psychology, 40, 471-499. |
| [6] |
Bandara R, Tisdell C (2005) Changing abundance of elephants and willingness to pay for their conservation. Journal of Environmental Management, 76, 47-59.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Bentler PM, Chou CP (1987) Practical issues in structural modeling. Sociological Methods & Research, 16, 78-117. |
| [8] |
Brockington D, Scholfield K (2010) The conservationist mode of production and conservation NGOs in sub-Saharan Africa. Antipode, 42, 551-575.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Browne-Nuñez C, Jacobson SK, Vaske JJ (2013) Beliefs, attitudes, and intentions for allowing elephants in group ranches around Amboseli National Park, Kenya. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 37, 639-648. |
| [10] | Caughley G, Dublin H, Parker I (1990) Projected decline of the African elephant. Biodiversity Conservation, 54, 157-164. |
| [11] | Cheng KM (2006) Characteristics and application of structural equation model. Statistics and Decision, (10), 22-25. (in Chinese) |
| [程开明 (2006) 结构方程模型的特点及应用. 统计与决策, (10), 22-25.] | |
| [12] | Cialdini RB, Kallgren CA, Reno RR (1991) A focus theory of normative conduct, a theoretical refinement and reevaluation of the role of norms in human behavior. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 24, 201-234. |
| [13] | CITES (2019) Report on Monitoring the Illegal Killing of Elephants. https://cites.org/sites/default/files/eng/cop/18/doc/E-CoP18-069-02-Add.pdf. (accessed on 2020-09-01) |
| [14] |
Cronbach LJ (1951) Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16, 297-334.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Dalrymple CJ, Peterson MN, Cobb DT, Sills EO, Bondell HD, Dalrymple DJ (2012) Estimating public willingness to fund nongame conservation through state tax initiatives. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 36, 483-491.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Davies J, Foxall GR, Pallister J (2002) Beyond the intention- behaviour mythology: An integrated model of recycling. Marketing Theory, 2, 29-113.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Dawes J (2008) Do data characteristics change according to the number of scale points used? An experiment using 5-point, 7-point and 10-point scales. International Journal of Market Research, 50, 61-104.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Du FZ (2017) Study on wild animal protection in public participation. Forest Investigation Design, (3), 70-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 杜芳芝 (2017) 野生动物保护中的公众参与研究. 林业勘查设计, 3, 70-71.] | |
| [19] | Duan WT, Jiang GR (2008) A review of the theory of planned behavior. Advances in Psychological Science, 16, 315-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [段文婷, 江光荣 (2008) 计划行为理论述评. 心理科学进展, 16, 315-320.] | |
| [20] | EPI (2018) Stop Talking. Please Stop Talking. It is Now Time for Action. https://www.elephantprotectioninitiative.org/post/inaugural-meeting-of-the-epi-consultative-group. (accessed on 2020-09-01) |
| [21] | Gray TNE, Gauntlett S (2017) Scale up elephant anti-poaching funds. Nature, 541, 157. |
| [22] |
Haefele MA, Loomis JB, Lien AM, Dubovsky JA, Merideth RW, Bagstad KJ, Huang TK, Mattsson BJ, Semmens DJ, Thogmartin WE, Wiederholt R, Diffendorfer JE, López- Hoffman L (2019) Multi-country willingness to pay for transborder migratory species conservation: A case study of Northern Pintails. Ecological Economics, 157, 321-331.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Halkos GE, Jones N (2012) Modeling the effect of social factors on improving biodiversity protection. Ecological Economics, 78, 90-99.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Heiny J, Ajzen I, Leonhäuser IU, Schmidt P (2019) Intentions to enhance tourism in private households: Explanation and mediated effects of entrepreneurial experience. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Emerging Economies, 5, 128-148.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Kideghesho JR (2016) Reversing the trend of wildlife crime in Tanzania: Challenges and opportunities. Biodiversity and Conservation, 25, 427-449.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Landis RS, Edwards BD, Cortina JM (2009) On the practice of allowing correlated residuals among indicators in structural equation models. In: Statistical and Methodological Myths and Urban Legends: Doctrine, Verity and Fable in the Organizational and Social Sciences (eds Lance CE, Vandenberg RJ), pp. 193-215. Routledge, New York. |
| [27] |
Langin C, Jacobson SK (2012) Risk and residency influences on public support for Florida panther recovery. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 36, 713-721.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Liu JZ (2020) Chinese plan for anti-poaching in Africa. Man and the Biosphere, (4), 67. (in Chinese) |
| [刘建周 (2020) 为非洲反盗猎提供“中国方案”. 人与生物圈, (4), 67.] | |
| [29] | Liu P, Zhang YJ (2020) The regulation of wildlife trade in China: Current status, problems and policy suggestions. Nanjing Journal of Social Sciences, (5), 68-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘鹏, 张伊静 (2020) 中国野生动物市场监管: 现状、问题与优化对策. 南京社会科学, (5), 68-75.] | |
| [30] |
Loyau A, Schmeller DS (2017) Positive sentiment and knowledge increase tolerance towards conservation actions. Biodiversity and Conservation, 26, 461-478.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Mai YJ, Wen ZL (2013) Exploratory structural equation modeling (ESEM): An integration of EFA and CFA. Advances in Psychological Science, 21, 934-939. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [麦玉娇, 温忠麟 (2013) 探索性结构方程建模(ESEM): EFA和CFA的整合. 心理科学进展, 21, 934-939.] | |
| [32] |
Martín-López B, Montes C, Benayas J (2007) The non- economic motives behind the willingness to pay for biodiversity conservation. Biological Conservation, 139, 67-82.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Meng M, Xie Y (2013) Analysis of public participation in wild animal conservation. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 34, 249-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梦梦, 谢屹 (2013) 浅析野生动物保护中的公众参与. 野生动物, 34, 249-252.] | |
| [34] |
Miller ZD (2017) The enduring use of the theory of planned behavior. Human Dimensions of Wildlife, 22, 583-590.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Morse-Jones S, Bateman IJ, Kontoleon A, Ferrini S, Burgess ND, Turner RK (2012) Stated preferences for tropical wildlife conservation amongst distant beneficiaries: Charisma, endemism, scope and substitution effects. Ecological Economics, 78, 9-18.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Neupane D, Kunwar S, Bohara AK, Risch TS, Johnson RL (2017) Willingness to pay for mitigating human-elephant conflict by residents of Nepal. Journal for Nature Conservation, 36, 65-76.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Ojea E, Loureiro ML (2007) Altruistic, egoistic and biospheric values in willingness to pay (WTP) for wildlife. Ecological Economics, 63, 807-814.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Phang SC, Failler P, Bridgewater P (2020) Addressing the implementation challenge of the global biodiversity framework. Biodiversity and Conservation, 29, 3061-3066.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Qi X, Ploeger A (2019) Explaining consumers' intentions towards purchasing green food in Qingdao, China: The amendment and extension of the theory of planned behavior. Appetite, 133, 414-422.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Qin TB, Yuan X (2021) China's practice to promote the biodiversity conservation in transboundary areas. Biodiversity Science, 29, 220-230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [秦天宝, 袁昕 (2021) 推进生物多样性跨境区域保护的中国实践. 生物多样性, 29, 220-230.] | |
| [41] | Qiu HZ, Lin BF (2009) Principle and Application of Structural Equation Model. China Light Industry Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [邱皓政, 林碧芳 (2009) 结构方程模型的原理与应用. 中国轻工业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] |
Raines-Eudy R (2000) Using structural equation modeling to test for differential reliability and validity: An empirical demonstration. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 7, 124-141.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Ru XJ, Qin HB, Wang SY (2019) Young people's behaviour intentions towards reducing PM2.5 in China: Extending the theory of planned behaviour. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 141, 99-108.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Sakurai R, Enari H, Matsuda T (2014) Testing social- psychological theories to predict residents' behavioral intentions regarding wildlife issues. Honyurui Kagaku, 54, 219-230. |
| [45] | Schwartz SH (1977) Normative influences on altruism. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 10, 221-279. |
| [46] | Shi HT, Wang ZY, Yan L (2019) The influence of ecological cognition on farmers' grain for green behavior: Based on theory of planned behavior and multi-group SEM. China Land Science, (3), 42-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [史恒通, 王铮钰, 阎亮 (2019) 生态认知对农户退耕还林行为的影响--基于计划行为理论与多群组结构方程模型. 中国土地科学, (3), 42-49.] | |
| [47] |
Shi XY, Zhang XC, Xiao LY, Li BB, Liu JM, Yang FY, Zhao X, Cheng C, Lv Z (2020) Public perception of wildlife consumption and trade during the COVID-19 outbreak. Biodiversity Science, 28, 630-643. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[史湘莹, 张晓川, 肖凌云, 李彬彬, 刘金梅, 杨方义, 赵翔, 程琛, 吕植 (2020) 新冠肺炎时期公众对野生动物消费和贸易意愿的调查. 生物多样性, 28, 630-643.]
DOI |
|
| [48] | Steger MAE, Witt SL (1989) Gender differences in environmental orientations: A comparison of publics and activists in Canada and the U. S. Political Research Quarterly, 42, 627-649. |
| [49] |
Subroy V, Rogers AA, Kragt ME (2018) To bait or not to bait: A discrete choice experiment on public preferences for native wildlife and conservation management in western Australia. Ecological Economics, 147, 114-122.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Tonglet M, Phillips PS, Read AD (2004) Using the theory of planned behaviour to investigate the determinants of recycling behavior: A case study from Brixworth, UK. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 41, 191-214.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Turpie JK (2003) The existence value of biodiversity in South Africa: How interest, experience, knowledge, income and perceived level of threat influence local willingness to pay. Ecological Economics, 46, 199-216.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Wang C (2020) Research on the external communication of international NGOs. Journalism Communication, (18), 105-106. (in Chinese) |
| [王翀 (2020) 国际非政府组织对外传播研究--以美国非政府组织“野生救援(WILDAID)”为例. 新闻传播, (18), 105-106.] | |
| [53] | Wang GZ (2019) 70 years of China: The changes of population age structure and the trend of population aging. Chinese Journal of Population Science, (3), 2-15, 126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王广州 (2019) 新中国70年: 人口年龄结构变化与老龄化发展趋势. 中国人口科学, (3), 2-15, 126.] | |
| [54] |
Wang SK, Cai Z, Hu YX, Cirella GT, Xie Y (2020) Chinese resident preferences for African elephant conservation: Choice experiment. Diversity, 12, 453.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Wang ZZ, Gong YZ, Mao XQ (2018) Exploring the value of overseas biodiversity to Chinese netizens based on willingness to pay for the African elephants' protection. Science of the Total Environment, 637- 638, 600-608. |
| [56] | Wen ZL, Hou JT, Marsh HW (2004) Structural equation model testing: Cutoff criteria for goodness of fit indices and chi-square test. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 36, 186-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [温忠麟, 侯杰泰, 马什赫伯特 (2004) 结构方程模型检验: 拟合指数与卡方准则. 心理学报, 36, 186-194.] | |
| [57] |
Wilbur RC, Lischka SA, Young JR, Johnson HE (2018) Experience, attitudes, and demographic factors influence the probability of reporting human-black bear interactions. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 42, 22-31.
DOI URL |
| [58] | Wu ML (2010) Structural Equation Modeling:Operation and Application of AMOS. Chongqing University Press, Chongqing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴明隆 (2010) 结构方程模型:AMOS的操作与应用. 重庆大学出版社, 重庆.] | |
| [59] |
Xie Y (2020) Ecological labeling and wildlife conservation: Citizens' perceptions of the elephant ivory-labeling system in China. Science of the Total Environment, 702, 134709.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Yuan DD (2018) Global ivory trade and elephant protection. Ecological Economy, 34(3), 2-5. (in Chinese) |
| [袁丹丹 (2018) 全球象牙贸易与大象保护. 生态经济, 34(3), 2-5.] | |
| [61] | Zhang LR, Meng R, Jin SC, Pan Z, Zhou J, Dong JC, Wang XH, Wang JN, Chang JW (2020) Protecting wildlife by the strictest instruments: China's current situation and reform direction. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, (2), 5-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张丽荣, 孟锐, 金世超, 潘哲, 周佳, 董金池, 王夏晖, 王金南, 常纪文 (2020) 实施最严格的野生动物保护: 中国现状与改革方向. 中国环境管理, (2), 5-19.] | |
| [62] | Zhou XH, Ma JZ, Zhang W, Wang Q (2009) Evaluating the economic value and its reliability analysis of endangered species conservation with contigent method-A case study on the willingness to pay of the citizens in Harbin on Amur. Journal of Natural Resources, 24, 276-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周学红, 马建章, 张伟, 王强 (2009) 运用CVM评估濒危物种保护的经济价值及其可靠性分析--以哈尔滨市区居民对东北虎保护的支付意愿为例. 自然资源学报, 24, 276-285.] | |
| [63] | Zhou XH, Wang Q, Zhang W, Jin Y, Wang Z, Chai Z, Zhou ZQ, Cui XF, MacMillan DC (2018) Elephant poaching and the ivory trade: The impact of demand reduction and enforcement efforts by China from 2005-2017. Global Ecology & Conservation, 16, e00486. |
| [1] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [2] | 顾燚芸, 薛嘉祈, 高金会, 谢心仪, 韦铭, 雷进宇, 闻丞. 一种基于公众科学数据的区域性鸟类多样性评价方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [3] | 杜宇晨, 刘蓓萌, 陈俊峰, 王浩, 谢屹. 基于结构方程模型的农户保护意愿影响因素分析: 以东北虎豹国家公园珲春片区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23155-. |
| [4] | 宋蕊, 邓晶, 秦涛. 野生动物肇事公众责任保险发展困境与优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22291-. |
| [5] | 刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 夏凡, 陈月龙, 王一晴, 黄巧雯. 中国猫科动物红外相机监测平台介绍: 民间环保机构的数据整合[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1067-1074. |
| [6] | 张健. 大数据时代的生物多样性科学与宏生态学[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(4): 355-363. |
| [7] | 张婧雅, 张玉钧. 论国家公园建设的公众参与[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 80-87. |
| [8] | 吕植, 顾垒, 闻丞, 王昊, 钟嘉. 中国自然观察2014: 一份关于中国生物多样性保护的独立报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(5): 570-574. |
| [9] | 严海, 陈进, 贺赫. 公众对植物园功能定位和形象认知的初步调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(5): 516-522. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()