



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 1251-1259. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019177 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019177
所属专题: 数据论文
收稿日期:2019-05-27
接受日期:2019-09-10
出版日期:2019-11-20
发布日期:2020-01-17
通讯作者:
詹选怀
基金资助:
Hongli Ji,Xuanhuai Zhan( ),Li Zhang,Yansong Peng,Saixia Zhou,Wan Hu
),Li Zhang,Yansong Peng,Saixia Zhou,Wan Hu
Received:2019-05-27
Accepted:2019-09-10
Online:2019-11-20
Published:2020-01-17
Contact:
Zhan Xuanhuai
摘要:
通过资料收集及野外调查, 得出幕阜山脉地区共有石松类和蕨类植物26科72属261种, 具有一定的东西过渡性, 为鳞毛蕨-铁角蕨植物区系, 最大属为鳞毛蕨属(Dryopteris) (29种)。其中, 庐山的物种丰富度较高(224种), 以铁角蕨属(Asplenium)为主; 幕阜山的物种密度较大(2.09种/km 2), 以卷柏属(Selaginella)为主; 九宫山以瓦韦属(Lepisorus)为主; 三者共通种有95种, 新特有现象较丰富。该区属种分化限制明显, 表现在单种科、属及寡种科、属占总科数的60%及总属数的80%。从区系成分看, 该区科、属以热带成分为主, 科和属的热带性成分与温带性成分比值(R/T值)分别为2.6和2.3。与同纬度带山地石松类和蕨类植物属的R/T值比较, 中亚热带与北亚热带交界带的蕨类植物属的R/T值在2.18-2.36之间; 种的R/T值为0.2, 为热带成分的5倍, 表现出明显的温带性质, 是罗霄山脉植物区系温带成分的重要组成部分。该区石松类和蕨类植物区系与华东、华南植物区系联系比较紧密, 表现出华东与华南两区系成分的交汇。
姬红利, 詹选怀, 张丽, 彭焱松, 周赛霞, 胡菀 (2019) 幕阜山脉石松类和蕨类植物多样性及生物地理学特征. 生物多样性, 27, 1251-1259. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019177.
Hongli Ji, Xuanhuai Zhan, Li Zhang, Yansong Peng, Saixia Zhou, Wan Hu (2019) Diversity and biogeographical characteristics of lycophytes and ferns in Mufu Mountains, China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1251-1259. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019177.
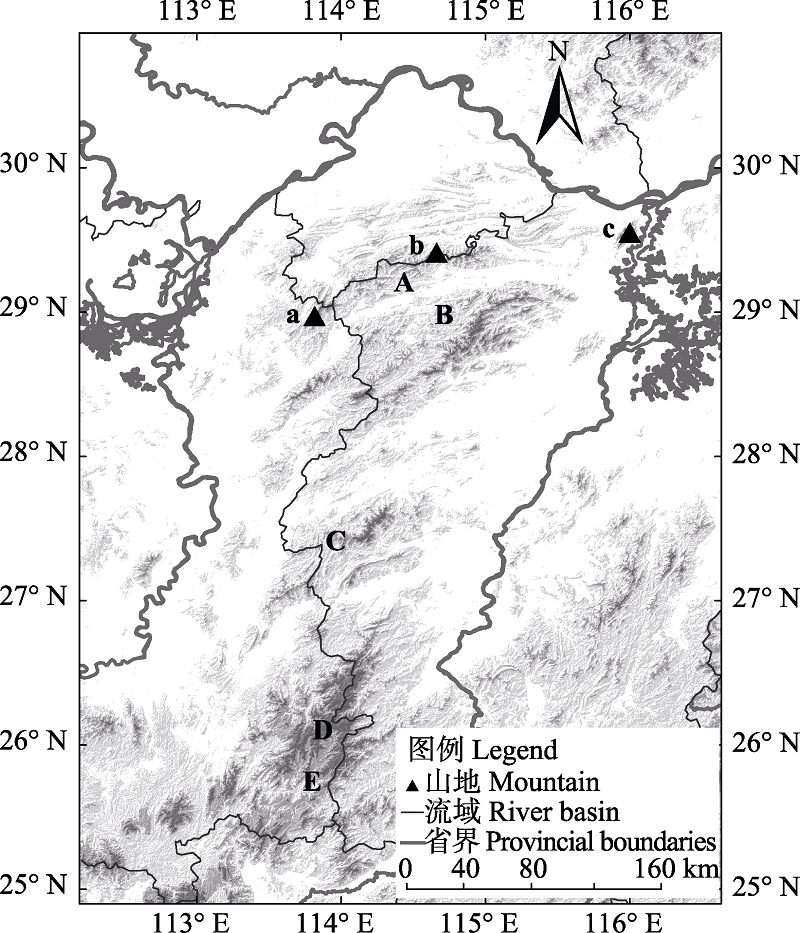
图1 研究区域地理位置。 a: 湖南幕阜山; b: 湖北九宫山; c: 江西庐山; A: 幕阜山脉; B: 九岭山脉; C: 武功山脉; D: 万洋山脉; E: 诸广山脉。
Fig. 1 Location of Mufu Mountains. a, Mount Mufu in Hunan Province; b, Mount Jiugong in Hubei Province; c, Mount Lushan in Jiangxi Province; A, Mufu Mountains; B, Jiuling Mountains; C, Wugong Mountains; D, Wanyang Mountains; E, Zhuguang Mountains.
| 等级 Grade | 科数 No. of family (%) | 所含属数 No.of genera in the family (%) | 所含种数 No.of species in the family (%) | 等级 Grade | 属数 No. of genus (%) | 所含种数 No. of species in the genus (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大科( ≥ 20种) Large family ( ≥ 20 species) | 5 (19.2) | 39 (54.2) | 179 (68.6) | 大属( ≥ 20种) Large genus ( ≥ 20 species) | 1 (1.4) | 29 (11.1) |
| 较大科(10-19种) Secondary family (10-19 species) | 3 (11.5) | 7 (9.7) | 41 (15.7) | 较大属(10-19种) Secondary genus (10-19 species) | 6 (8.3) | 73 (28.0) |
| 中等科(5-9种) Medium family (5-9 species) | 2 (7.7) | 5 (6.9) | 11 (4.2) | 中等属(5-9种) Medium genus (5-9 species) | 8 (11.1) | 49 (18.8) |
| 寡种科(2-4种) Depauperate family (2-4 species) | 8 (30.8) | 13 (18.1) | 22 (8.4) | 寡种属(2-4种) Depauperate genus (2-4 species) | 31 (43.1) | 84 (32.2) |
| 单种科(1种) Monotypic family (1 species) | 8 (30.8) | 8 (11.1) | 8 (3.1) | 单种属(1种) Monotypic genus (1 species) | 26 (36.1) | 26 (9.9) |
| 合计 Total | 26 (100) | 72 (100) | 261 (100) | 合计 Total | 72 (100) | 261 (100) |
表1 幕阜山脉石松类与蕨类植物区系科和属的分级统计
Table 1 Statistics on families and genera of lycophytes and ferns in Mufu Mountains
| 等级 Grade | 科数 No. of family (%) | 所含属数 No.of genera in the family (%) | 所含种数 No.of species in the family (%) | 等级 Grade | 属数 No. of genus (%) | 所含种数 No. of species in the genus (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大科( ≥ 20种) Large family ( ≥ 20 species) | 5 (19.2) | 39 (54.2) | 179 (68.6) | 大属( ≥ 20种) Large genus ( ≥ 20 species) | 1 (1.4) | 29 (11.1) |
| 较大科(10-19种) Secondary family (10-19 species) | 3 (11.5) | 7 (9.7) | 41 (15.7) | 较大属(10-19种) Secondary genus (10-19 species) | 6 (8.3) | 73 (28.0) |
| 中等科(5-9种) Medium family (5-9 species) | 2 (7.7) | 5 (6.9) | 11 (4.2) | 中等属(5-9种) Medium genus (5-9 species) | 8 (11.1) | 49 (18.8) |
| 寡种科(2-4种) Depauperate family (2-4 species) | 8 (30.8) | 13 (18.1) | 22 (8.4) | 寡种属(2-4种) Depauperate genus (2-4 species) | 31 (43.1) | 84 (32.2) |
| 单种科(1种) Monotypic family (1 species) | 8 (30.8) | 8 (11.1) | 8 (3.1) | 单种属(1种) Monotypic genus (1 species) | 26 (36.1) | 26 (9.9) |
| 合计 Total | 26 (100) | 72 (100) | 261 (100) | 合计 Total | 72 (100) | 261 (100) |
| 分布区类型 Areal type | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 Number | % | 数量 Number | % | 数量 Number | % | |
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 8 | - | 19 | - | 6 | - |
| 热带分布 Tropical Distribution | ||||||
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 9 | 50.0 | 19 | 35.8 | 4 | 1.6 |
| 3. 旧大陆热带分布 Old World Tropics | 1 | 5.6 | 6 | 11.3 | 3 | 1.2 |
| 4. 热带亚洲和热带美洲分布 Trop. Asia & Trop. Amer. Disjuncted | 1 | 5.6 | 1 | 1.9 | 2 | 0.8 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Trop. Asia to Trop. Australasia | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.8 | 13 | 5.1 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Trop. Asia to Trop. Africa | 1 | 5.6 | 6 | 11.3 | 2 | 0.8 |
| 7. 热带亚洲分布 Trop. Asia | 1 | 5.6 | 3 | 5.7 | 18 | 7.1 |
| 热带成分小计 Subtotal | 13 | 72.2 | 37 | 69.8 | 42 | 16.5 |
| 温带分布 Temperate Distribution | ||||||
| 8. 北温带分布 North temperate | 4 | 22.2 | 5 | 9.4 | 4 | 1.6 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 E. Asia & N. Amer. Disjuncted | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10. 旧大陆温带分布 Old World Temperate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 |
| 11. 温带亚洲分布 Temperate Asia | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.8 | 32 | 12.5 |
| 12. 东亚分布 East Asia | (1) | (5.6) | (9) | (17.0) | (136) | (53.3) |
| 12-1. 东亚广布(H-S-J) | 1 | 5.6 | 6 | 11.3 | 46 | 18.0 |
| 12-2. 中国-喜马拉雅(S-H) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.9 | 18 | 7.1 |
| 12-3. 中国-日本(S-J) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.8 | 72 | 28.2 |
| 13. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 15.7 |
| 温带成分小计 Subtotal | 5 | 27.8 | 16 | 30.2 | 213 | 83.5 |
| 总计 Total | 26 | 100 | 72 | 100 | 261 | 100 |
表2 幕阜山脉石松类与蕨类植物分布区类型统计
Table 2 Areal types at families, genera and species of lycophytes and ferns in Mufu Mountains
| 分布区类型 Areal type | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 Number | % | 数量 Number | % | 数量 Number | % | |
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 8 | - | 19 | - | 6 | - |
| 热带分布 Tropical Distribution | ||||||
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 9 | 50.0 | 19 | 35.8 | 4 | 1.6 |
| 3. 旧大陆热带分布 Old World Tropics | 1 | 5.6 | 6 | 11.3 | 3 | 1.2 |
| 4. 热带亚洲和热带美洲分布 Trop. Asia & Trop. Amer. Disjuncted | 1 | 5.6 | 1 | 1.9 | 2 | 0.8 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Trop. Asia to Trop. Australasia | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.8 | 13 | 5.1 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Trop. Asia to Trop. Africa | 1 | 5.6 | 6 | 11.3 | 2 | 0.8 |
| 7. 热带亚洲分布 Trop. Asia | 1 | 5.6 | 3 | 5.7 | 18 | 7.1 |
| 热带成分小计 Subtotal | 13 | 72.2 | 37 | 69.8 | 42 | 16.5 |
| 温带分布 Temperate Distribution | ||||||
| 8. 北温带分布 North temperate | 4 | 22.2 | 5 | 9.4 | 4 | 1.6 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 E. Asia & N. Amer. Disjuncted | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10. 旧大陆温带分布 Old World Temperate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 |
| 11. 温带亚洲分布 Temperate Asia | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.8 | 32 | 12.5 |
| 12. 东亚分布 East Asia | (1) | (5.6) | (9) | (17.0) | (136) | (53.3) |
| 12-1. 东亚广布(H-S-J) | 1 | 5.6 | 6 | 11.3 | 46 | 18.0 |
| 12-2. 中国-喜马拉雅(S-H) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.9 | 18 | 7.1 |
| 12-3. 中国-日本(S-J) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3.8 | 72 | 28.2 |
| 13. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 15.7 |
| 温带成分小计 Subtotal | 5 | 27.8 | 16 | 30.2 | 213 | 83.5 |
| 总计 Total | 26 | 100 | 72 | 100 | 261 | 100 |
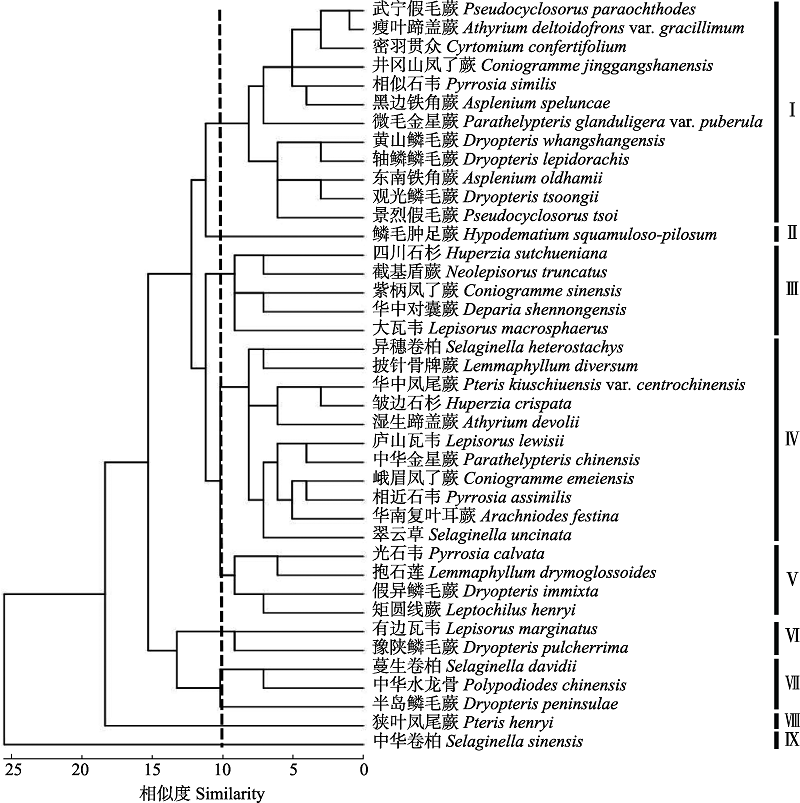
图2 幕阜山脉石松类与蕨类植物中国特有种分布聚类图。 I-IX表示不同地理分布格局。(I)华东南部-华中南部-华南分布; (II)华东-华北分布; (III)西南-华中分布; (IV)秦淮以南广布; (V)沿长江流域分布; (VI)西南-西北-华北分布; (VII)南北广布; (VIII)西南-西北分布; (IX)长江以北分布。
Fig. 2 Cluster analysis of Chinese endemic lycophytes and ferns in Mufu Mountains. I-IX indicate different geographical distribution patterns. (I) Southern East China-Southern Central China-Southern China distribution; (II) Easten China-Northern China distribution; (III) Southwestern China-Central China distribution; (IV) South of Qinling Mountains-Huaihe River distribution; (V) Along the Yangtze River Basin distribution; (VI) Southwestern China-Northwestern China-Northern China distribution; (VII) South- North distribution; (VIII) Southwestern China-Northwestern China distribution; (IX) North of the Yangtze River distribution.
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 科相似性 Similarity at family level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.94 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.87 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
| 属相似性 Similarity at genus level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.96 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.80 | 0.82 | 1.00 |
| 种相似性 Similarity at species level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.72 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.68 | 0.65 | 1.00 |
| 特有种相似性 Similarity at endemism level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.53 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.59 | 0.39 | 1.00 |
| 种相似性 Similarity at species level | |||
| 幕阜山脉 Mufu Mountains | |||
| 东侧: 怀玉山脉 East: Huaiyu Mountains | 0.42 | ||
| 西侧: 武陵山脉 West: Wuling Mountains | 0.26 | ||
| 南侧: 武功山脉 South: Wugong Mountains | 0.60 | ||
| 北侧: 大别山脉 North: Dabie Mountains | 0.40 | ||
表3 幕阜山脉与毗邻山脉石松类和蕨类植物相似性比较
Table 3 Comparison of floristic similarity coefficients of lycophytes and ferns between Mufu Mountains and adjacent mountains
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 科相似性 Similarity at family level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.94 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.87 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
| 属相似性 Similarity at genus level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.96 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.80 | 0.82 | 1.00 |
| 种相似性 Similarity at species level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.72 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.68 | 0.65 | 1.00 |
| 特有种相似性 Similarity at endemism level | |||
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 1.00 | ||
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 0.53 | 1.00 | |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 0.59 | 0.39 | 1.00 |
| 种相似性 Similarity at species level | |||
| 幕阜山脉 Mufu Mountains | |||
| 东侧: 怀玉山脉 East: Huaiyu Mountains | 0.42 | ||
| 西侧: 武陵山脉 West: Wuling Mountains | 0.26 | ||
| 南侧: 武功山脉 South: Wugong Mountains | 0.60 | ||
| 北侧: 大别山脉 North: Dabie Mountains | 0.40 | ||
| 山脉 Mountain | 经纬度 Location | 热带性属/温带性属 R/T value of genus | 热带性种/温带性种 R/T value of species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大别山脉 Dabie Mountains | 31.42°-32.50° N; 114.92°-115.92° E | 1.70 | 0.12 |
| 幕阜山脉 Mufu Mountains | 28.88°-29.68° N; 113.78°-116.13° E | 2.31 | 0.20 |
| 武功山脉 Wugong Mountains | 26.78°-28.20° N; 113.35°-114.62° E | 2.61 | 0.29 |
| 诸广山脉 Zhuguang Mountains | 25.70°-25.85° N; 112.50°-113.07° E | 3.47 | 0.35 |
| 南岭山脉 Nanling Mountains | 24.62°-24.95° N; 113.90°-113.98° E | 3.86 | 0.81 |
| 峨眉山 Mount Emei | 29.27°-29.73° N; 103.17°-103.62° E | 2.34 | - |
| 武陵山 Mount Wuling | 28.47°-30.08° N; 107.03°-111.58° E | 2.19 | - |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 28.88°-29.10° N; 113.78°-113.90° E | 2.31 | - |
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 29.32°-29.45° N; 114.38°-114.72° E | 2.19 | - |
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 29.43°-29.68° N; 115.87°-116.13° E | 2.25 | - |
| 齐云山 Mount Qiyun | 29.78°-29.83° N; 117.95°-118.12° E | 2.36 | - |
| 黄山 Mount Huang | 29.22°-30.37° N; 118.02°-118.98° E | 2.18 | - |
| 三清山 Mount Sanqing | 28.88°-28.92° N; 118.05°-118.07° E | 2.33 | - |
| 天目山 Mount Tianmu | 29.87°-30.92° N; 119.40°-119.45° E | 2.20 | - |
表4 幕阜山脉与毗邻山脉石松类和蕨类植物热带性与温带性属、种比值
Table 4 Ratios of tropical elements to temperate elements of genera and species of lycophytes and ferns in Mufu Mountains and adjacent mountains
| 山脉 Mountain | 经纬度 Location | 热带性属/温带性属 R/T value of genus | 热带性种/温带性种 R/T value of species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大别山脉 Dabie Mountains | 31.42°-32.50° N; 114.92°-115.92° E | 1.70 | 0.12 |
| 幕阜山脉 Mufu Mountains | 28.88°-29.68° N; 113.78°-116.13° E | 2.31 | 0.20 |
| 武功山脉 Wugong Mountains | 26.78°-28.20° N; 113.35°-114.62° E | 2.61 | 0.29 |
| 诸广山脉 Zhuguang Mountains | 25.70°-25.85° N; 112.50°-113.07° E | 3.47 | 0.35 |
| 南岭山脉 Nanling Mountains | 24.62°-24.95° N; 113.90°-113.98° E | 3.86 | 0.81 |
| 峨眉山 Mount Emei | 29.27°-29.73° N; 103.17°-103.62° E | 2.34 | - |
| 武陵山 Mount Wuling | 28.47°-30.08° N; 107.03°-111.58° E | 2.19 | - |
| 幕阜山 Mount Mufu | 28.88°-29.10° N; 113.78°-113.90° E | 2.31 | - |
| 九宫山 Mount Jiugong | 29.32°-29.45° N; 114.38°-114.72° E | 2.19 | - |
| 庐山 Mount Lushan | 29.43°-29.68° N; 115.87°-116.13° E | 2.25 | - |
| 齐云山 Mount Qiyun | 29.78°-29.83° N; 117.95°-118.12° E | 2.36 | - |
| 黄山 Mount Huang | 29.22°-30.37° N; 118.02°-118.98° E | 2.18 | - |
| 三清山 Mount Sanqing | 28.88°-28.92° N; 118.05°-118.07° E | 2.33 | - |
| 天目山 Mount Tianmu | 29.87°-30.92° N; 119.40°-119.45° E | 2.20 | - |
| 1 | Anderson S ( 1994) Area and endemism. Quarterly Review of Biology, 69, 451-471. |
| 2 | Chen GX, Ao CQ, Liao WB, Zhu JY, Xiang CM ( 2003) Comparative analysis on the pteridophyte floral relationships between Wulingshan region and its neighboring florae. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 23, 120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈功锡, 敖成奇, 廖文波, 朱杰英, 向春明 ( 2003) 武陵山地区蕨类植物区系与邻近区系关系的比较研究. 西北植物学报, 23, 120-126.] | |
| 3 | Chen GX, Yang B, Deng T, Xia ST ( 2014) Progress in understanding several issues of the floristic geography of the pteridophytes in China.Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34, 2130-2136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈功锡, 杨斌, 邓涛, 夏石头 ( 2014) 中国蕨类植物区系地理若干问题研究进展. 西北植物学报, 34, 2130-2136.] | |
| 4 | Cheng JF, Zhu GF ( 1993) Flora of Jiangxi (Vol.1). Jiangxi Science and Technology Press, Nanchang . (in Chinese) |
| [ 程景福, 朱国芳 ( 1993) 江西植物志(第一卷).江西科学技术出版社, 南昌.] | |
| 5 | Ching RC, Wu SG ( 1980) The floristic characteristics of the Xizang (Tibet) ptheridophyte flora in relation to the upheaval of the Himalayas. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 2, 382-389. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦仁昌, 武素功 ( 1980) 西藏蕨类植物区系的特点及其与喜马拉雅隆升的关系. 云南植物研究, 2, 382-389.] | |
| 6 | Ding BY, Li GY, Fu CX, Yang SZ ( 2010) Flora of Tianmushan,Vol. 1. Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 丁炳扬, 李根有, 傅承新, 杨淑贞 ( 2010) 天目山植物志:第1卷. 浙江大学出版社,杭州.] | |
| 7 | Dong SY, Zuo ZY, Yan YH, Xiang JY ( 2017) Red list assessment of lycophytes and ferns in China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 765-773. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 董仕勇, 左政裕, 严岳鸿, 向建英 ( 2017) 中国石松类和蕨类植物的红色名录评估. 生物多样性, 25, 765-773.] | |
| 8 | Feng JM, Xu CD ( 2008) Floristic equilibrium point and its biogeographic significance. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 30, 400-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯建孟, 徐成东 ( 2008) 植物区系平衡点及其生物地理意义. 云南植物研究, 30, 400-404.] | |
| 9 | Gu HY, Li CH ( 2008) Preliminary study on the pteridophytes flora of Emei Mountain. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 28, 2381-2387. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谷海燕, 李策宏 ( 2008) 峨眉山蕨类植物区系的初步研究. 西北植物学报, 28, 2381-2387.] | |
| 10 | Guo CY, Liu DY ( 2002) Studies on the pteridophyte flora of Qiyun Mountainous region in Anhui Province. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 22, 1115-1121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭传友, 刘登义 ( 2002) 安徽齐云山区蕨类植物区系研究. 西北植物学报, 22, 1115-1121.] | |
| 11 | Hu JQ, Liang SW ( 1996) Plants of Huangshan Mountain.Fudan University Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 胡嘉琪, 梁师文 ( 1996) 黄山植物. 复旦大学出版社, 上海.] | |
| 12 | Huang S, Huang W, Qin L, Huang BH, Liu Y ( 2019) Studies on characteristics of pteridophyte flora of the Enshi region in Hubei Province, China. Plant Science Journal, 37, 28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄升, 黄伟, 覃磊, 黄毕华, 刘毅 ( 2019) 湖北恩施地区蕨类植物区系研究. 植物科学学报, 37, 28-36.] | |
| 13 | Ji HL, Zhan XH, Peng YS, Gui ZM, Zhang L ( 2018) Resources and flora of pteridophytes in Mt. Zhuguangshan of Jiangxi, China. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 37(5), 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姬红利, 詹选怀, 彭焱松, 桂忠明, 张丽 ( 2018) 诸广山地区石松类和蕨类植物资源及区系研究. 中国野生植物资源, 37(5), 49-55.] | |
| 14 | Jin YX, Wu JQ, Jiang MX, Shen ZH ( 1996) A preliminary study on types and exploitation of the terrestrial plant resources in the Yangtze valley. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Valley, 5, 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 金义兴, 吴金清, 江明喜, 沈泽昊 ( 1996) 长江流域陆生植物资源的类型与开发利用. 长江流域资源与环境, 5, 16-21.] | |
| 15 | Kung HS ( 1984) The phytogeographical features of pteridophytes of Sichuan, China with some remarks on the “Polysticho-Dryopteris flora”. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 6, 27-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孔宪需 ( 1984) 四川蕨类植物地理特点兼论“耳蕨-鳞毛蕨类植物区系”. 云南植物研究, 6, 27-38.] | |
| 16 | Lamoreux JF, Morrison JC, Ricketts TH, Olson DM, Dinerstein E, McKnight MW, Shugart HH ( 2006) Global tests of biodiversity concordance and the importance of endemism. Nature, 440, 212-214. |
| 17 | Li JZ, Chen SM, Lin QZ (2004)Flora of Hunan (Vol.1).Hunan Science & Technology Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李建宗, 陈三茂, 林亲众 (2004)湖南植物志(第一卷). 湖南科学技术出版社, 长沙.] | |
| 18 | Lu SG (2004) Advances in Plant Science (Vol.6). igher Education Press,Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陆树刚 ( 2004) 植物科学进展(第六卷). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| 19 | Ma KP, Qian YQ, Wang C ( 1995) Present state and future of biodiversity studies. Science and Technology Review, 13(1), 27-30. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平, 钱迎倩, 王晨 ( 1995) 生物多样性研究的现状与发展趋势. 科技导报, 13(1), 27-30.] | |
| 20 | Ni J, Chen ZX, Dong M, Chen XD, Zhang XS ( 1998) An ecogeographical regionalization for biodiversity in China. Acta Botanica Sinica, 40, 83-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 倪健, 陈仲新, 董鸣, 陈旭东, 张新时 ( 1998) 中国生物多样性的生态地理区划. 植物学报, 40, 83-95.] | |
| 21 | Schneider H, He LJ, Hennequin S, Zhang XC ( 2013) Towards a natural classification of Pteridaceae: Inferring the relationships of enigmatic pteridoid fern species occurring in the Sino-Himalaya and Afro-Madagascar. Phytotaxa, 77, 49-60. |
| 22 | Shen ZH, Yang MZ, Feng JM, Li XH, Peng PH, Zheng Z ( 2017) Geographic patterns of alpine flora in China in relation to environmental and spatial factors. Biodiversity Science, 25, 182-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈泽昊, 杨明正, 冯建孟, 李新辉, 彭培好, 郑智 ( 2017) 中国高山植物区系地理格局与环境和空间因素的关系. 生物多样性, 25, 182-194.] | |
| 23 | Sun H, Deng T, Chen YS, Zhou Z ( 2017) Current research and development trends in floristic geography. Biodiversity Science, 25, 111-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙航, 邓涛, 陈永生, 周卓 ( 2017) 植物区系地理研究现状及发展趋势. 生物多样性, 25, 111-122.] | |
| 24 | Sun L, Xiao JW, Chen GX ( 2016) Study on the pteridophyte flora in Wugong Mountain. Central South Forest Inventory and Planning, 35(2), 63-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙林, 肖佳伟, 陈功锡 ( 2016) 武功山地区蕨类植物区系研究. 中南林业调查规划, 35(2), 63-67.] | |
| 25 | Wu ZY ( 1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 13(S4), 1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴征镒 ( 1991) 中国种子植物属的分布区类型. 云南植物研究, 13(S4), 1-139.] | |
| 26 | Wu ZY, Raven P, Hong DY ( 2013) Flora of China,Vol.2-3(Pteridophytes). Science Press, Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| 27 | Xie GW, Wang HY, Lai XR, Tan CM ( 1996) Diversity and conservation of Chinese endemic genera of the flora in Jiuling- Mufu Mountain. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Valley, 5, 128-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢国文, 汪红燕, 赖小荣, 谭策铭 ( 1996) 九岭幕阜山植物特有属的生物多样性保护研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 5, 128-132.] | |
| 28 | Xu SX, Guo HH, Cheng JF ( 1996) On pteridophyta in Sanqingshan Mountain of northeast Jiangxi. Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science), 20, 61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐声修, 郭惠红, 程景福 ( 1996) 赣东北三清山风景名胜区的蕨类植物. 南昌大学学报(理科版), 20, 61-66.] | |
| 29 | Yan YH, Zhang XC, Ma KP ( 2013) Pteridophytes in China:Diversity and Distribution. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 严岳鸿, 张宪春, 马克平 ( 2013) 中国蕨类植物多样性与地理分布.科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 30 | Yan YH, Zhang XC, Zhou XL, Sun JQ ( 2016) Species Catalogue of China, Vol.1:Pteridophytes .Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 严岳鸿, 张宪春, 周喜乐, 孙久琼 ( 2016) (第一卷):蕨类植物.科学出版社,北京.] | |
| 31 | Yan YH, Zhou XL ( 2018) Pteridophytes of Hainan. China Forestry Publishing House,Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 严岳鸿, 周喜乐 ( 2018) 海南蕨类植物. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 32 | Yang XF, Li JY, Wang TX, Li FQ, Han SL ( 1999) Study on the pteridophytic flora of Mountain Dabie, Henan. Wuhan Botanical Research, 17, 153-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨相甫, 李景原, 王太霞, 李发启, 韩书亮 ( 1999) 河南大别山蕨类植物区系的研究. 武汉植物学研究, 17, 153-157.] | |
| 33 | Zhang XC, Wei R, Liu HM, He LJ, Wang L, Zhang GM ( 2013) Phylogeny and classification of the extant lycophytes and ferns from China. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 48, 119-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张宪春, 卫然, 刘红梅, 何丽娟, 王丽, 张钢民 ( 2013) 中国现代石松类和蕨类的系统发育与分类系统. 植物学报, 48, 119-120.] | |
| 34 | Zhang YL ( 1998) Coefficient of similarity—An important parameter in floristic geography. Geographical Research, 17, 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张镱锂 (1998) 植物区系地理研究中的重要参数——相似性系数. 地理研究, 17, 94-99.] | |
| 35 | Zhao WY (2017) The Floristic Phytogeography of Spermatophyte Flora in Luoxiao Range. PhD dissertation, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵万义 (2017) 罗霄山脉种子植物区系地理学研究. 博士学位论文, 中山大学, 广州.] | |
| 36 | Zheng JY, Yin YH, Li BY (2010) A new scheme for climate regionalization in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65, 3-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑景云, 尹云鹤, 李炳元 (2010) 中国气候区划新方案. 地理学报, 65, 3-12.] | |
| 37 | Zhou XL, Zhang XC, Sun JQ, Yan YH (2016) Diversity and distribution of lycophytes and ferns in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周喜乐, 张宪春, 孙久琼, 严岳鸿 (2016) 中国石松类和蕨类植物的多样性与地理分布. 生物多样性, 24, 102-107.] |
| [1] | 赵一凡, 王彦平. 全球蛇类生活史、生态学和生物地理特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24476-. |
| [2] | 董云伟, 鲍梦幻, 程娇, 陈义永, 杜建国, 高养春, 胡利莎, 李心诚, 刘春龙, 秦耿, 孙进, 王信, 杨光, 张崇良, 张雄, 张宇洋, 张志新, 战爱斌, 贺强, 孙军, 陈彬, 沙忠利, 林强. 中国海洋生物地理学研究进展和热点: 物种分布模型及其应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23453-. |
| [3] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [4] | 高德, 王彦平. 小岛屿效应检测方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [5] | 王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修. 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法、影响机制及保护应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [6] | 商晓凡, 张健, 高浩杰, 库伟鹏, 毕玉科, 李修鹏, 阎恩荣. 岛屿面积与气候共同影响舟山群岛种子植物丰富度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [7] | 孟宏虎, 宋以刚. 东南亚生物地理格局: 回溯与思考[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23261-. |
| [8] | 孙亚君. 为何要信达尔文的演化论——论《物种起源》的二十五重简约美[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22243-. |
| [9] | 梁伟诺, 胡亮. 中国新石器时代以来淡水及河口鱼类考古遗存的地理分布及其生物地理学意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21471-. |
| [10] | 付飞, 魏慧玉, 常育腾, 王备新, 陈凯. 澜沧江中游水生昆虫生活史和生态学性状多样性的海拔格局: 气候和土地利用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21332-. |
| [11] | 王梦霞, 陈心怡, 张洁, 宋宇航, 杨娟. 菲律宾海脊索动物多样性评估: 基于OBIS数据库[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1481-1489. |
| [12] | 魏慧玉,陈凯,王备新. 澜沧江流域水生昆虫群落分类多样性和功能多样性海拔格局的空间尺度依赖性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 504-514. |
| [13] | 王波, 黄勇, 李家堂, 戴强, 王跃招, 杨道德. 西南喀斯特地貌区两栖动物丰富度分布格局与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 941-950. |
| [14] | 张凤麟, 王昕, 张健. 生物多样性信息资源.II.环境类型数据[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 53-65. |
| [15] | 朱华. 探讨海南岛生物地理起源上有意义的一些种子植物科和属[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(8): 816-822. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()