



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1364-1378. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019138 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019138
收稿日期:2019-04-22
接受日期:2019-07-29
出版日期:2019-12-20
发布日期:2019-12-24
通讯作者:
施春华
基金资助:
Guanghua Xu1,Xiaoyu Li2,Chunhua Shi1,*( )
)
Received:2019-04-22
Accepted:2019-07-29
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2019-12-24
Contact:
Shi Chunhua
摘要:
对自然生态系统的观察给人们以复杂的群落更稳定的直观印象, 但数学模型却得出了截然相反的结论。这一“悖论”使得复杂性-稳定性研究自20世纪70年代以来成为长期的热点。本文对这一领域的数学模型研究进行简要综述。首先对这一论题进行概念剖析, 然后将各类模型分为线性和非线性两大类, 前者即群落矩阵法, 后者包括相互作用矩阵法、复杂网络数值模拟法和食物网构件动力学法。它们分别基于不同的群落构建方法和稳定性判断标准, 探求各物种是如何相互作用并实现共存的。总体而言, 在随机构建的群落模型中, 多样性和连接度的增长不利于系统稳定; 而在更接近真实自然群落的模型中, 相互作用方式、网络拓扑结构、相互作用强度分布等方面的机制提供了稳定效应, 按此组织的生态网络可达到很高的复杂度。然而, 复杂性-稳定性的研究还远未结束, 当前的模型仍不足以反映自然群落中的复杂相互作用, 稳定性的概念也有待拓展。对这一议题的深入研究在生态学理论和生态系统管理实践方面都具有重大价值。
徐光华,李小玉,施春华 (2019) 复杂性-稳定性研究: 数学模型的进展. 生物多样性, 27, 1364-1378. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019138.
Guanghua Xu,Xiaoyu Li,Chunhua Shi (2019) The complexity-stability relationship: Progress in mathematical models. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1364-1378. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019138.
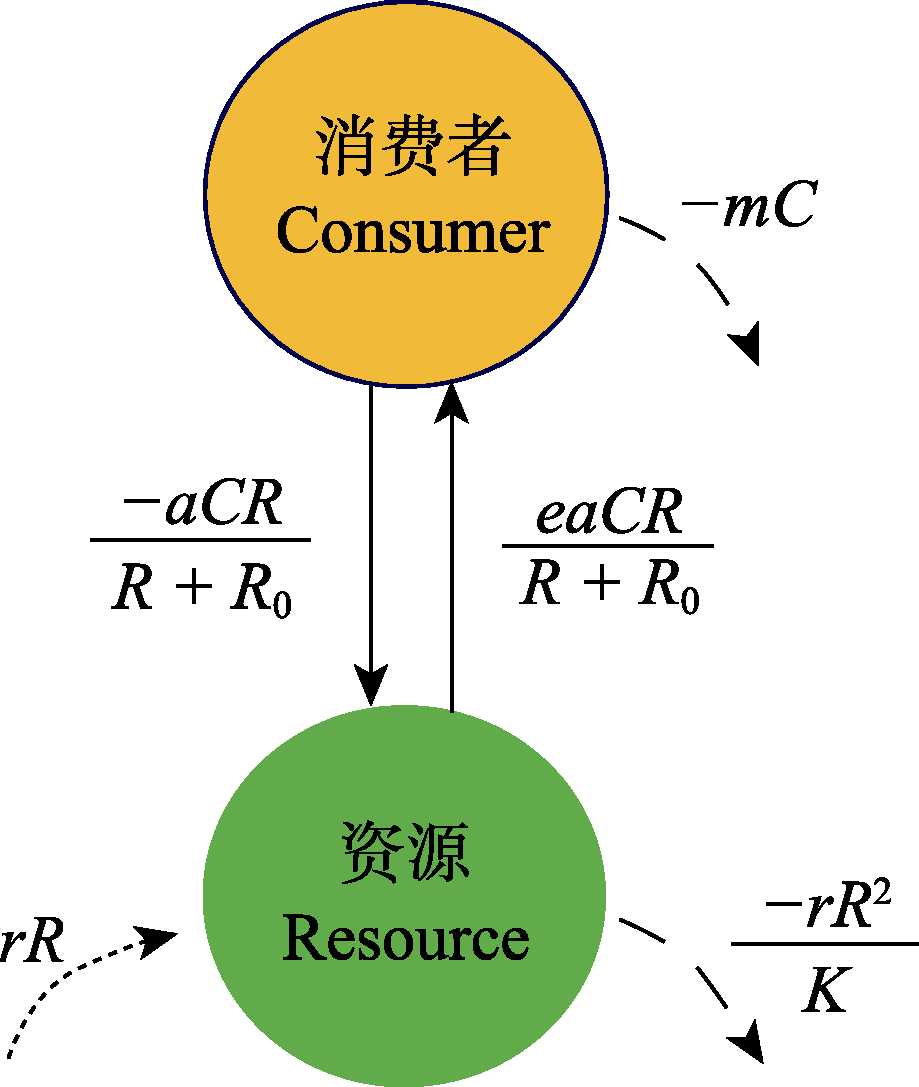
图2 消费者-资源相互作用(改绘自McCann, 2010)。其中R和C分别表示资源和消费者种群密度, r为资源内禀增长率, K为承载力, a为攻击率, R0是资源的半饱和密度, e是转化为消费者生物量的比例, m为消费者的个体死亡率。
Fig. 2 Consumer-resource interaction (redrawing from McCann, 2010). Where R and C are population density of the resource and consumer, respectively, r is intrinsic growth rate of resource, K is the carrying capacity, a is the attack rate, R0 is the semi-saturation density of resource, e is the proportion converted to the consumer biomass, and m is mortality rate of consumer.
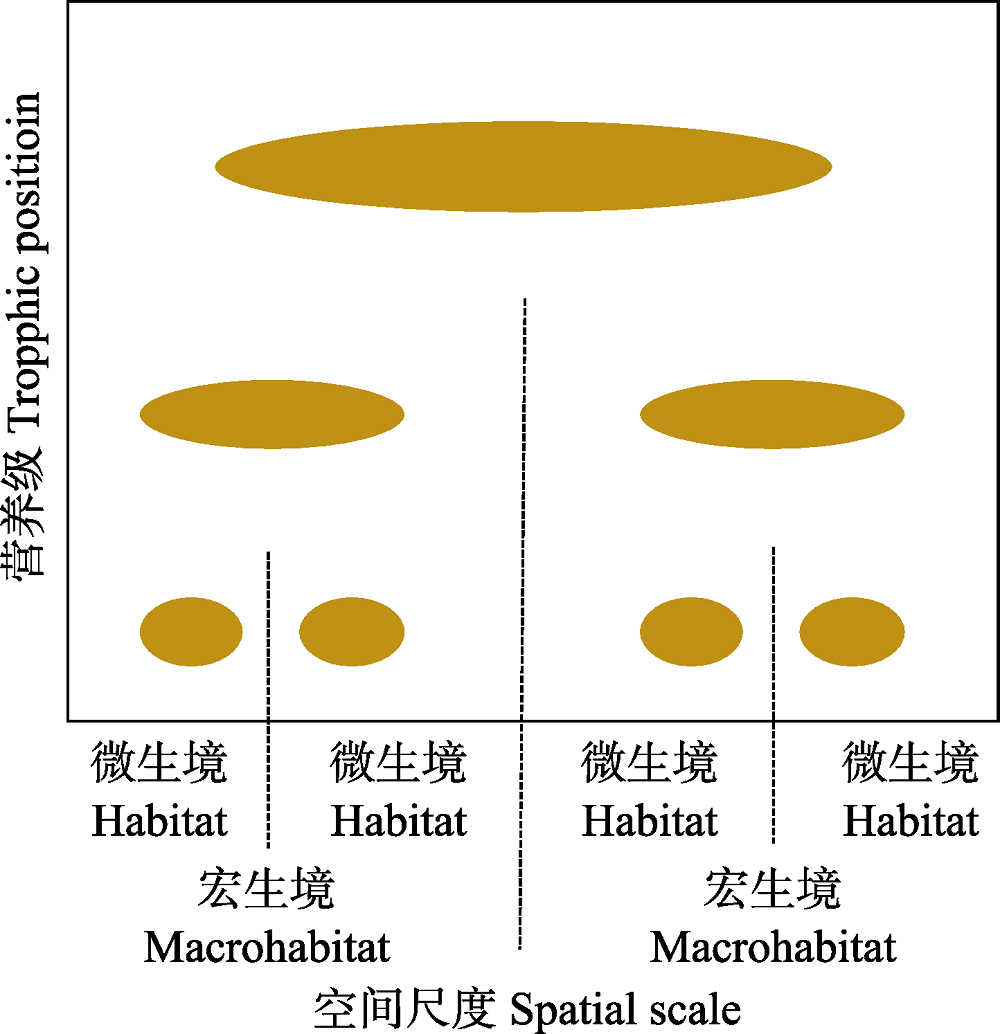
图3 食物网的空间等级结构。椭圆表示各营养级物种的空间尺度及其所覆盖的栖息地(改绘自McCann, 2010)。
Fig. 3 The spatial hierarchy structure of food web. Ellipses indicate the spatial scale of each trophic level and the habitat it covers (redrawing from McCann, 2010).
| 方法名称 Approach name | 群落构建方法 Community construction method | 群落规模 Community size | 稳定性衡量 Stability measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 群落矩阵法 Community matrix approach | 指定物种数、连接度、平均相互作用强度, 随机给出或指定网络结构和相互作用分布 Species number, connectivity, average interaction intensities are designated; web structure and interaction distribution rule are random or designated | 适用大型生态网络 Suitable for large ecological networks | 局部稳定性, 稳定网络的百分比(PSW) Local stability, percentage of stable webs (PSW) |
| 相互作用矩阵法 Interaction matrix approach | 指定物种数, 网络结构可随机给出或指定, 随机给出每单位相互作用强度 Species number is designated, web structure can be designated or random, per unit interaction intensities are random | 适用大中型生态网络 Suitable for large and middle-sized ecological networks | 局部稳定性+可行性, 稳定网络的百分比(PSW) Local stability and feasibility, percentage of stable webs (PSW) |
| 复杂网络的数值模拟法 Numerical simulation of complex network | 指定物种数, 网络结构由专门模型生成, 相互作用强度参数通过与体型比给出, 或在一定范围内变动 Species number is designated, web structure is generated by model, parameters of interaction intensity are given by the ratio to body size, or vary within a certain range | 适用中型生态网络 Suitable for middle-sized ecological networks | 持久性(共存的物种数占比) Persistence (the proportion of coexisting species) |
| 食物网构件动力学法 Food web module dynamics approach | 所有参数都直接指定 All parameters are designated | 适用小型构件, 但可通过构件组合推测大型食物网的稳定性 Suitable for small web module, but could be used to infer the stability of large food webs | 永久性+波动程度 Permanence and variability |
表1 复杂性?稳定性研究模型方法
Table 1 Modeling approaches of complexity?stability research
| 方法名称 Approach name | 群落构建方法 Community construction method | 群落规模 Community size | 稳定性衡量 Stability measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 群落矩阵法 Community matrix approach | 指定物种数、连接度、平均相互作用强度, 随机给出或指定网络结构和相互作用分布 Species number, connectivity, average interaction intensities are designated; web structure and interaction distribution rule are random or designated | 适用大型生态网络 Suitable for large ecological networks | 局部稳定性, 稳定网络的百分比(PSW) Local stability, percentage of stable webs (PSW) |
| 相互作用矩阵法 Interaction matrix approach | 指定物种数, 网络结构可随机给出或指定, 随机给出每单位相互作用强度 Species number is designated, web structure can be designated or random, per unit interaction intensities are random | 适用大中型生态网络 Suitable for large and middle-sized ecological networks | 局部稳定性+可行性, 稳定网络的百分比(PSW) Local stability and feasibility, percentage of stable webs (PSW) |
| 复杂网络的数值模拟法 Numerical simulation of complex network | 指定物种数, 网络结构由专门模型生成, 相互作用强度参数通过与体型比给出, 或在一定范围内变动 Species number is designated, web structure is generated by model, parameters of interaction intensity are given by the ratio to body size, or vary within a certain range | 适用中型生态网络 Suitable for middle-sized ecological networks | 持久性(共存的物种数占比) Persistence (the proportion of coexisting species) |
| 食物网构件动力学法 Food web module dynamics approach | 所有参数都直接指定 All parameters are designated | 适用小型构件, 但可通过构件组合推测大型食物网的稳定性 Suitable for small web module, but could be used to infer the stability of large food webs | 永久性+波动程度 Permanence and variability |
| [1] | Allesina S, Pascual M ( 2010) Food web models: A plea for groups. Ecology Letters, 12, 652-662. |
| [2] | Allesina S, Levine JM ( 2011) A competitive network theory of species diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 5638-5642. |
| [3] | Allesina S, Tang S ( 2012) Stability criteria for complex ecosystems. Nature, 483, 205-208. |
| [4] | Allesina S, Tang S ( 2015) The stability‒complexity relationship at age 40: A random matrix perspective. Population Ecology, 57, 63-75. |
| [5] | Anderson GW, Guionnet A, Zeitouni O ( 2010) An Introduction to Random Matrices. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [6] | Anderson HM, Hutson V, Law R ( 1992) On the conditions for permanence of species in ecological communities. The American Naturalist, 139, 663-668. |
| [7] | Bachelot B, Uriarte M, Mcguire K ( 2015) Interactions among mutualism, competition, and predation foster species coexistence in diverse communities. Theoretical Ecology, 8, 297-312. |
| [8] | Bai ZD, Silverstein JW ( 2012) Spectral analysis of large dimensional random matrices. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 175, 822-823. |
| [9] | Bairey E, Kelsic ED, Kishony R ( 2016) High-order species interactions shape ecosystem diversity. Nature Communications, 7, 12285. |
| [10] | Bascompte J ( 2009) Disentangling the web of life. Science, 325, 416-419. |
| [11] | Bascompte J, Jordano P, Melián CJ, Olesen JM ( 2003) The nested assembly of plant-animal mutualistic networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 9383-9387. |
| [12] | Bastolla U, Lässig M, Manrubia SC, Valleriani A ( 2005) Biodiversity in model ecosystems. I. Coexistence conditions for competing species. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 235, 521-530. |
| [13] | Berlow EL, Neutel A-M, Cohen JE, de Ruiter PC, Ebenman B, Emmerson M, Fox JW, Vincent AA, Jones JI, Kokkoris GD, Logofet DO ( 2004) Interaction strengths in food webs: Issues and opportunities. Journal of Animal Ecology, 73, 585-598. |
| [14] | Bersier LF ( 2007) A history of the study of ecological networks. In: Biological Networks (ed. Kepes F), pp. 365-421. World Scientific Pub Co. Inc., New Jersey. |
| [15] | Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND ( 2003) Comment on “Foraging adaptation and the relationship between food-web complexity and stability”. Science, 301, 918. |
| [16] | Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND ( 2006) Allometric scaling enhances stability in complex food webs. Ecology Letters, 9, 1228-1236. |
| [17] | Cattin MF, Bersier LF, Banasek-Richter C, Baltensperger R, Gabriel JP ( 2004) Phylogenetic constraints and adaptation explain food-web structure. Nature, 427, 835-839. |
| [18] | Chen LS, Liu PZ, Xiao Z ( 1988) Permanence in ecosystems. Journal of Biomath, 3(1), 18-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈兰荪, 刘平舟, 肖藻 ( 1988) 种群生态系统的持续生存. 生物数学学报, 3(1), 18-32.] | |
| [19] | Chen X, Cohen JE ( 2001) Global stability, local stability and permanence in model food webs. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 212, 223-235. |
| [20] | Chen YF, Tang Z, Li H, Han XM, Li YF, Hu C ( 2014) Research progress on ecosystem complexity-stability relationships based on soil food web. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 2173-2186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈云峰, 唐政, 李慧, 韩雪梅, 李钰飞, 胡诚 ( 2014) 基于土壤食物网的生态系统复杂性‒稳定性关系研究进展. 生态学报, 34, 2173-2186.] | |
| [21] | Christianou M, Kokkoris GD ( 2008) Complexity does not affect stability in feasible model communities. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 253, 162-169. |
| [22] | Cohen JE ( 1989) Food webs and community structure. In: Perspectives on Ecological Theory (eds Roughgarden J, May RM, Levin S), pp. 181-202. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [23] | Cohen JE, Briand F, Newman CM ( 1990) Community Food Webs: Data and theory. Biomathematics Vol. 20. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg and New York. |
| [24] | Cohen JE, Pimm SL, Yodzis P, Saldana J ( 1993) Body sizes of animal predators and animal prey in food webs. Journal of Animal Ecology, 62, 67-78. |
| [25] | Connell JH, Sousa WP ( 1983) On the evidence needed to judge ecological stability or persistence. The American Naturalist, 121, 789-824. |
| [26] | Dambacher JM, Luh HK, Li HW, Rossignol PA ( 2003) Qualitative stability and ambiguity in model ecosystems. The American Naturalist, 161, 876-888. |
| [27] | de Angelis DL ( 1975) Stability and connectance in food web models. Ecology, 56, 238-243. |
| [28] | de Ruiter PC, Neutel AM, Moore JC ( 1995) Energetics, patterns of interaction strengths, and stability in real ecosystems. Science, 269, 1257-1260. |
| [29] | Delmas E, Besson M, Brice M-H, Burkle LA, Dalla Riva GV, Fortin M-J, Gravel D, Guimaraes PR, Hembry DH, Newman EA, Olesen JM, Pires MM, Yeakel JD, Poisot T ( 2019) Analysing ecological networks of species interactions. Biological Reviews, 94, 16-36. |
| [30] | Donohue I, Hillebrand H, Montoya JM, Petchey OL, Pimm SL, Fowler MS, Healy K, Jackson AL, Lurgi M, McClean D, O’Connor NE, O’Gorman EJ, Yang Q ( 2016) Navigating the complexity of ecological stability. Ecology Letters, 19, 1172-1185. |
| [31] | Dougoud M, Vinckenbosch L, Rohr RP, Bersier LF, Mazza C ( 2018) The feasibility of equilibria in large ecosystems: A primary but neglected concept in the complexity-stability debate. PLoS Computational Biology, 14, e1005988. |
| [32] | Dunne JA, Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND ( 2005) Modeling food-web dynamics: Complexity-stability implications. In: Aquatic Food Webs: An Ecosystem Approach (eds Belgrano A, Scharler SU, Dunne J, Ulanowicz RE), pp. 117-129. Oxford University Press Inc., New York. |
| [33] | Dunne JA, Williams RJ, Martinez ND ( 2002) Food-web structure and network theory: The role of connectance and size. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 99, 12917-12922. |
| [34] | Elton CS ( 1958) Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants. Chapman & Hall, London. |
| [35] | Emmerson MC, Yearsley JM ( 2004) Weak interactions, omnivory and emergent food-web properties. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 271, 397-405. |
| [36] | Emmerson MC, Raffaelli D ( 2004) Predator-prey body size, interaction strength and the stability of a real food web. Journal of Animal Ecology, 73, 399-409. |
| [37] | Fagan WF ( 1997) Omnivory as a stabilizing feature of natural communities. The American Naturalist, 150, 554-567. |
| [38] | Fath BD, Cabezas H, Pawlowski CW ( 2003) Regime changes in ecological systems: An information theory approach. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 222, 517-530. |
| [39] | Gao D, He HX ( 2010) Research advances on biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29, 2507-2513. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高东, 何霞红 ( 2010) 生物多样性与生态系统稳定性研究进展. 生态学杂志, 29, 2507-2513.] | |
| [40] | Gardner MR, Ashby WR ( 1970) Connectance of large dynamical (cybernetic) systems: Critical values for stability. Nature, 228, 784. |
| [41] | Gibbs T, Grilli J, Rogers T, Allesina S ( 2017) The effect of population abundances on the stability of large random ecosystems. Physical Review E, 98, 022410. |
| [42] | Gilpin ME ( 1975) Stability of feasible predator-prey systems. Nature, 254, 137-139. |
| [43] | Goh BS, Jennings LS ( 1977) Feasibility and stability in randomly assembled Lotka-Volterra models. Ecological Modelling, 3, 63-71. |
| [44] | Goldwasser L, Roughgarden J ( 1993) Construction and analysis of a large Caribbean food web. Ecology, 74, 1216-1233. |
| [45] | Goodman D ( 1975) The theory of diversity-stability relationships in ecology. Quarterly Review of Biology, 50, 237-266. |
| [46] | Gravel D, Massol F, Leibold MA ( 2016) Stability and complexity in model meta-ecosystems. Nature Communications, 7, 12457. |
| [47] | Grimm V ( 1996) A down-to-earth assessment of stability concepts in ecology: Dreams, demands, and the real problems. Senckenbergiana Maritima, 27, 215-226. |
| [48] | Grimm V, Wissel C ( 1997) Babel, or the ecological stability discussions: An inventory and analysis of terminology and a guide for avoiding confusion. Oecologia, 109, 323-334. |
| [49] | Harte J, Kinzig A, Green J ( 1999) Self-similarity in the distribution and abundance of species. Science, 284, 334-336. |
| [50] | Haydon DT ( 2000) Maximally stable model ecosystems can be highly connected. Ecology, 81, 2631-2636. |
| [51] | Haydon DT, Lloyd AL ( 1999) On the origins of the Lotka- Volterra equations. Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America, 80, 205-206. |
| [52] | Holling CS ( 1996) Engineering resilience versus ecological resilience. In: Engineering Within Ecological Constraints (ed. National Academy of Engineering), pp. 31-44. National Academy Press, Washington, DC. |
| [53] | Huang JH, Han XG ( 1995) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 31-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄建辉, 韩兴国 ( 1995) 生物多样性和生态系统稳定性. 生物多样性, 3, 31-37.] | |
| [54] | Hutson V, Schmitt K ( 1992) Permanence and the dynamics of biological systems. Mathematical Biosciences, 111, 1-71. |
| [55] | Ives AR, Carpenter SR ( 2007) Stability and diversity of ecosystems. Science, 317, 58-62. |
| [56] | Jacquet C, Moritz C, Morissette L, Legagneux P, Massol F, Archambault P, Gravel D ( 2016) No complexity-stability relationship in empirical ecosystems. Nature Communications, 7, 12573. |
| [57] | Jansen VAA, Kokkoris GD ( 2003) Complexity and stability revisited. Ecology Letters, 6, 498-502. |
| [58] | Jansen VAA, Sigmund K ( 1998) Shaken not stirred: On permanence in ecological communities. Theoretical Population Biology, 54, 195-201. |
| [59] | Johnson S, Dominguez-Garcia V, Donetti L, Munoz MA ( 2014) Trophic coherence determines food-web stability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 17923-17928. |
| [60] | Johnson S, Jones NS ( 2017) Looplessness in networks is linked to trophic coherence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 5618-5623. |
| [61] | Jonsson T, Ebenman B ( 1998) Effects of predator-prey body size ratios on the stability of food chains. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 193, 407-417. |
| [62] | Kendall BE, Briggs CJ, Murdoch WW, Turchin P, Ellner SP, Mccauley E, Nisbet RM, Wood SN ( 1999) Why do populations cycle? A synthesis of statistical and mechanistic modeling approaches. Ecology, 80, 1789-1805. |
| [63] | Kokkoris GD, Jansen VAA, Loreau M, Troumbis AY ( 2002) Variability in interaction strength and implications for biodiversity. Journal of Animal Ecology, 71, 362-371. |
| [64] | Krause AE, Frank KA, Mason DM, Ulanowicz RE, Taylor WW ( 2003) Compartments revealed in food-web structure. Nature, 426, 282-285. |
| [65] | Landi P, Minoarivelo HO, Brannstrom A, Hui C, Dieckmann U ( 2018) Complexity and stability of ecological networks: A review of the theory. Population Ecology, 60, 319-345. |
| [66] | Law R, Blackford JC ( 1992) Self-assembling food webs: A global viewpoint of coexistence of species in Lotka-Volterra communities. Ecology, 73, 567-578. |
| [67] | Law R, Morton RD ( 1993) Alternative permanent states of ecological communities. Ecology, 74, 1347-1361. |
| [68] | Lawlor LR ( 1978) A comment on randomly constructed ecosystem models. The American Naturalist, 112, 445-447. |
| [69] | Levin SA ( 2005) Self-organization and the emergence of complexity in ecological systems. BioScience, 55, 1075-1079. |
| [70] | Levine JM, Bascompte J, Adler PB, Allesina S ( 2017) Beyond pairwise mechanisms of species coexistence in complex communities. Nature, 546, 56-64. |
| [71] | Lewontin RC ( 1969) The meaning of stability. Brookhaven Symposium in Biology, 22, 13-24. |
| [72] | Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B ( 2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 294, 804-808. |
| [73] | Lotka AJ ( 1925) Elements of Physical Biology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore. |
| [74] | Ma FY ( 2002) Research advances on ecosystem stability. Journal of Desert Research, 22, 401-407. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马风云 ( 2002) 生态系统稳定性若干问题研究评述. 中国沙漠, 22, 401-407.] | |
| [75] | MacArthur RH ( 1955) Fluctuations of animal populations and a measure of community stability. Ecology, 36, 533-536. |
| [76] | Margalef R ( 1975) Diversity, stability and maturity in natural ecosystems. In: Unifying Concepts in Ecology (eds van Dobben WH, Lowe-McConnell RH), pp. 151-160. Junk, The Hague. |
| [77] | May RM ( 1972 a) Limit cycles in predator-prey communities. Science, 177, 900-902. |
| [78] | May RM ( 1972 b) Will a large complex system be stable? Nature, 238, 413-414. |
| [79] | May RM ( 1973) Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [80] | May RM, Leonard WJ ( 1975) Nonlinear aspects of competition between three species. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 29, 243-253. |
| [81] | Mayfield M, Stouffer D ( 2017) Data from higher-order interactions capture unexplained complexity in diverse communities. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 0062. |
| [82] | McCann KS, Hastings A, Huxel GR ( 1998) Weak trophic interactions and the balance of nature. Nature, 395, 794-798. |
| [83] | McCann KS ( 2000) The diversity-stability debate. Nature, 405, 228-233. |
| [84] | McCann KS ( 2010) Food Webs. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [85] | McCann KS, Rasmussen JB, Umbanhowar J ( 2005) The dynamics of spatially coupled food webs. Ecology Letters, 8, 513-523. |
| [86] | McNaughton SJ ( 1977) Diversity and stability of ecological communities: A comment on the role of empiricism in ecology. The American Naturalist, 111, 515-525. |
| [87] | Michio K ( 2008) Building trophic modules into a persistent food web. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 16631-16635. |
| [88] | Moore JC, Hunt WH ( 1988) Resource compartmentation and the stability of real ecosystems. Nature, 333, 261-263. |
| [89] | Morton RD, Law R, Pimm SL, Drake JA ( 1996) On models for assembling ecological communities. Oikos, 75, 493-499. |
| [90] | Mougi A, Kondoh M ( 2012) Diversity of interaction types and ecological community stability. Science, 337, 349-351. |
| [91] | Neutel AM, Heesterbeek JAP, de Ruiter PC ( 2002) Stability in real food webs: Weak links in long loops. Science, 296, 1120-1123. |
| [92] | Neutel AM, Thorne MAS ( 2014) Interaction strengths in balanced carbon cycles and the absence of a relation between ecosystem complexity and stability. Ecology Letters, 17, 651-661. |
| [93] | Odum EP ( 1953) Fundamentals of Ecology. Saunders, Philadelphia. |
| [94] | Oksanen L, Fretwell SD, Arruda J, Niemala P ( 1981) Exploitation ecosystems in gradients of primary productivity. The American Naturalist, 118, 240-261. |
| [95] | Olesen JM, Jordi B, Dupont YL, Pedro J ( 2007) The modularity of pollination networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 19891-19896. |
| [96] | Orians GH ( 1975) Diversity, stability and maturity in natural ecosystems. In: Unifying Concepts in Ecology (eds van Dobben WH, Lowe-McConnell RH), pp. 139-150. Junk, The Hague. |
| [97] | Paine RT ( 1980) Food webs: Linkage, interaction strength and community infrastructure. Journal of Animal Ecology, 49, 667-686. |
| [98] | Paine RT ( 1992) Food-web analysis through field measurement of per capita interaction strength. Nature, 355, 73-75. |
| [99] | Pimentel D ( 1961) Species diversity and insect population outbreaks. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 54, 76-86. |
| [100] | Pimm SL ( 1980) Bounds on food web connectance. Nature, 284, 591. |
| [101] | Pimm SL ( 1982) Food Webs. Chapman and Hall, London, New York. |
| [102] | Pimm SL ( 1984) The complexity and stability of ecosystems. Nature, 307, 321-326. |
| [103] | Pimm SL, Lawton JH ( 1977) Number of trophic levels in ecological communities. Nature, 268, 329-331. |
| [104] | Pimm SL, Lawton JH ( 1978) On feeding on more than one trophic level. Nature, 275, 542-544. |
| [105] | Pimm SL, Lawton JH ( 1980) Are food webs divided into compartments? Journal of Animal Ecology, 49, 879-898. |
| [106] | Raffaelli D ( 2002) From Elton to mathematics and back again. Science, 296, 1035-1037. |
| [107] | Raffaelli D, Hall SJ ( 1992) Compartments and predation in an estuarine food web. Journal of Animal Ecology, 61, 551-560. |
| [108] | Rezende EL, Albert EM, Fortuna MA, Bascompte J ( 2009) Compartments in a marine food web associated with phylogeny, body mass, and habitat structure. Ecology Letters, 12, 779-788. |
| [109] | Roberts A ( 1974) The stability of a feasible random ecosystem. Nature, 251, 607-608. |
| [110] | Rohr RP, Saavedra S, Bascompte J ( 2014) On the structural stability of mutualistic systems. Science, 345, 1253497. |
| [111] | Rosenzweig ML, MacArthur RH ( 1963) Graphical representation and stability conditions of predator-prey interactions. The American Naturalist, 97, 209-223. |
| [112] | Saavedra S, Rohr RP, Bascompte J, Godoy O, Kraft NJB, Levine JM ( 2017) A structural approach for understanding multispecies coexistence. Ecological Monographs, 87, 470-486. |
| [113] | Scheffer M, Carpenter S, Foley JA, Folke C, Walker B ( 2001) Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature, 413, 591-596. |
| [114] | Schoener TW ( 1968) Size of feeding territories among birds. Ecology, 49, 123-141. |
| [115] | Schuster P, Sigmund K, Wolff R ( 1979) Dynamical systems under constant organization. III. Cooperative and competitive behavior of hypercycles. Journal of Differential Equations, 32, 357-368. |
| [116] | Solow AR, Beet AR ( 1998) On lumping species in food webs. Ecology, 79, 2013-2018. |
| [117] | Solow AR, Costello C, Beet AR ( 1999) On an early result on stability and complexity. The American Naturalist, 154, 587-588. |
| [118] | Song C, Saavedra S ( 2018) Will a small randomly assembled community be feasible and stable? Ecology, 99, 743-751. |
| [119] | Stone L ( 2018) The feasibility and stability of large complex biological networks: A random matrix approach. Scientific Reports, 8, 8246. |
| [120] | Stouffer DB, Bascompte J ( 2011) Compartmentalization increases food-web persistence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 3648-3652. |
| [121] | Stouffer DB, Camacho J, Amaral LAN ( 2006) A robust measure of food web intervality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 19015-19020. |
| [122] | Tang S, Pawar S, Allesina S ( 2014) Correlation between interaction strengths drives stability in large ecological networks. Ecology Letters, 17, 1094-1100. |
| [123] | Teng J, McCann KS ( 2004) Dynamics of compartmented and reticulate food webs in relation to energetic flows. The American Naturalist, 164, 85-100. |
| [124] | Thébault E, Fontaine C ( 2010) Stability of ecological communities and the architecture of mutualistic and trophic networks. Science, 329, 853-856. |
| [125] | Townsend S, Haydon D, Matthews L ( 2010) On the generality of stability-complexity relationships in Lotka-Volterra ecosystems. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 267, 243-251. |
| [126] | Townsend SE ( 2009) The Stability of Model Ecosystems. PhD dissertation, University of Glasgow, Glasgow. |
| [127] | Vandermeer J H ( 1975) Interspecific competition: A new approach to the classical theory. Science, 188, 253-255. |
| [128] | Volterra V ( 1926) Fluctuations in the abundance of a species considered mathematically. Nature, 118, 558-560. |
| [129] | Wang GH ( 2002) Further thoughts on diversity and stability in ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 10, 126-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王国宏 ( 2002) 再论生物多样性与生态系统的稳定性. 生物多样性, 10, 126-134.] | |
| [130] | Warren CP, Pascual M, Lafferty KD, Kuris AM ( 2010) The inverse niche model for food webs with parasites. Theoretical Ecology, 3, 285. |
| [131] | West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ ( 1997) A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science, 276, 122-126. |
| [132] | Williams RJ, Martinez ND ( 2000) Simple rules yield complex food webs. Nature, 404, 180-183. |
| [133] | Williams RJ, Martinez ND ( 2007) Dynamic network models of ecological diversity, complexity, and nonlinear persistence. In: Biological Networks (ed. Kepes F), pp. 423-447. World Scientific Pub Co. Inc., New Jersey. |
| [134] | Wootton JT ( 1997) Estimates and tests of per capita interaction strength: Diet, abundance, and impact of intertidally for aging birds. Ecological Monographs, 67, 45-64. |
| [135] | Yodzis P ( 1981) The stability of real ecosystems. Nature, 289, 674-676. |
| [136] | Yodzis P, Innes S ( 1992) Body size and consumer-resource dynamics. The American Naturalist, 139, 1151-1175. |
| [137] | Zhang XA, Deng HL ( 1996) Ecosystem organization: Food chain dynamics and mutualism‒cybernetics. Zoological Research, 17, 429-436. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张晓爱, 邓合黎 ( 1996) 生态系统的组织理论: 食物链动态论与互惠共生‒控制论. 动物学研究, 17, 429-436.] | |
| [138] | Zhao L, Zhang HY, Tian W, Xu X ( 2017) Identifying compartments in ecological networks based on energy channels. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 309-318. |
| [1] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [2] | 赵榕江, 吴纪华, 何维明, 赵彩云, 周波, 李博, 杨强. 土壤生物多样性与外来植物入侵: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24243-. |
| [3] | 牛永杰, 马全会, 朱玉, 刘海荣, 吕佳乐, 邹元春, 姜明. 氮沉降对草地昆虫多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23130-. |
| [4] | 姚海凤, 张赛超, 上官华媛, 李志鹏, 孙新. 城市化对土壤动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22547-. |
| [5] | 姚保民, 曾青, 张丽梅. 土壤原生生物多样性及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22353-. |
| [6] | 胡惠玲, 姚致远, 高世斌, 朱波. 紫色土线虫对长期不同施肥措施的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22189-. |
| [7] | 宋博,陈琳琳,闫朗,姜少玉,刘春云,李秉钧,李宝泉. 山东东营和烟台潮间带海草床食物网结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(9): 984-992. |
| [8] | 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙. |
| [9] | 刘继亮, 李锋瑞. 干旱区绿洲扩张方式对土壤生物优势类群及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(10): 1116-1126. |
| [10] | 廖建基, 郑新庆, 杜建国, 陈彬, 马志远, 胡文佳. 厦门同安湾定置网捕获鱼类的多样性及营养级特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 624-629. |
| [11] | 杜建国, 叶观琼, 陈彬, 郑新庆. 中国海域海洋生物的营养级指数变化特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(4): 532-538. |
| [12] | 王思凯, 盛强, 储忝江, 李博, 陈家宽, 吴纪华. 植物入侵对食物网的影响及其途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(3): 249-259. |
| [13] | 邵元虎, 傅声雷. 试论土壤线虫多样性在生态系统中的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(2): 116-123. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn