



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1065-1074. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017095 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017095
何增丽1, 许涵2, 秦新生1,*( ), 唐光大1, 李意德2
), 唐光大1, 李意德2
收稿日期:2017-03-23
接受日期:2017-07-01
出版日期:2017-10-20
发布日期:2018-05-05
通讯作者:
秦新生
基金资助:
Zengli He1, Han Xu2, Xinsheng Qin1,*( ), Guangda Tang1, Yide Li2
), Guangda Tang1, Yide Li2
Received:2017-03-23
Accepted:2017-07-01
Online:2017-10-20
Published:2018-05-05
Contact:
Qin Xinsheng
摘要:
根类药用植物在生产栽培过程中常产生连作障碍, 原因之一是其容易产生化感作用, 而化感作用是密度制约产生的主要原因之一。夹竹桃科植物是重要的药用植物, 也是热带植物区系的主要科。为探究自然条件下密度制约是否存在于根类药用植物中, 本文以海南尖峰岭60 ha森林动态监测样地中两种常见的夹竹桃科根类药用植物盆架树(Alstonia rostrata)和尖蕾狗牙花(Tabernaemontana bufalina)为研究对象, 采用点格局分析的成对相关函数Ripley’s g(r), 结合完全随机零模型和异质泊松零模型, 分析了它们的空间分布格局、种内和种间空间关联, 并采用Berman-test方法分析了地形因子对其种群分布的影响。结果表明: (1)盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花在0-100 m的研究尺度上主要表现为聚集分布, 但随着尺度的增大, 聚集程度降低, 逐渐变为随机分布。(2)盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花各龄级的分布特征类似: 幼树和中龄树个体在较大尺度范围内为聚集分布, 而成年树个体在0-100 m尺度上为随机分布或均匀分布。(3)在小尺度上, 盆架树的幼树与中龄树呈空间正关联, 与成年树呈空间负关联, 而中龄树与成年树空间无关联。尖蕾狗牙花各龄级间在0-65 m的尺度范围内以空间正关联为主。(4)在0-49 m尺度内盆架树与尖蕾狗牙花呈显著空间正相关。盆架树的中龄树和成年树与同龄级的尖蕾狗牙花都表现为空间无显著关联, 而幼树与尖蕾狗牙花幼树存在明显的空间正关联。(5)盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花幼树的分布与海拔、凹凸度显著正相关, 中龄树的分布与凹凸度显著正相关, 而成年树中只有盆架树的分布与海拔正相关。从现有格局推断: 生境异质性和扩散限制影响盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花空间格局的形成, 相对于尖蕾狗牙花, 密度制约对盆架树空间格局形成的影响更显著。
何增丽, 许涵, 秦新生, 唐光大, 李意德 (2017) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林2种夹竹桃科植物的空间分布格局与关联性. 生物多样性, 25, 1065-1074. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017095.
Zengli He, Han Xu, Xinsheng Qin, Guangda Tang, Yide Li (2017) Spatial distribution patterns and association of two Apocynaceae plants in the tropical mountain rainforests of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1065-1074. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017095.
| 树种 Tree species | 幼树 Young trees (%) | 中龄树 Middle-aged trees (%) | 成年树 Adult trees (%) | 总数 Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盆架树 Alstonia rostrata | 1,098 (56.25) | 296 (15.16) | 558 (28.59) | 1,952 (100) |
| 尖蕾狗牙花 Tabernaemontana bufalina | 2,459 (74.05) | 751 (22.61) | 111 (3.34) | 3,321 (100) |
表1 海南尖峰岭60 ha森林动态监测样地中盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花种群各龄级株数
Table 1 Number of Alstonia rostrata and Tabernaemontana bufalina with different ages in the 60 ha forest dynamics plot in Jianfengling, Hainan Island.
| 树种 Tree species | 幼树 Young trees (%) | 中龄树 Middle-aged trees (%) | 成年树 Adult trees (%) | 总数 Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盆架树 Alstonia rostrata | 1,098 (56.25) | 296 (15.16) | 558 (28.59) | 1,952 (100) |
| 尖蕾狗牙花 Tabernaemontana bufalina | 2,459 (74.05) | 751 (22.61) | 111 (3.34) | 3,321 (100) |
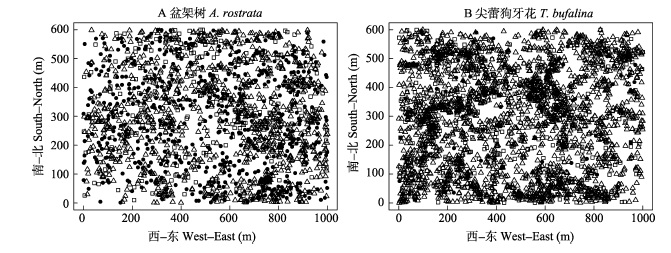
图1 海南尖峰岭60 ha森林动态监测样地中盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花各龄级的散点分布图。△ 幼树; □ 中龄树; ● 成年树。
Fig. 1 Scatter distribution patterns of Alstonia rostrata and Tabernaemontana bufalina with different ages in the 60 ha forest dynamics plot in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. △ Young trees; □ Middle-aged trees; ● Adult trees.
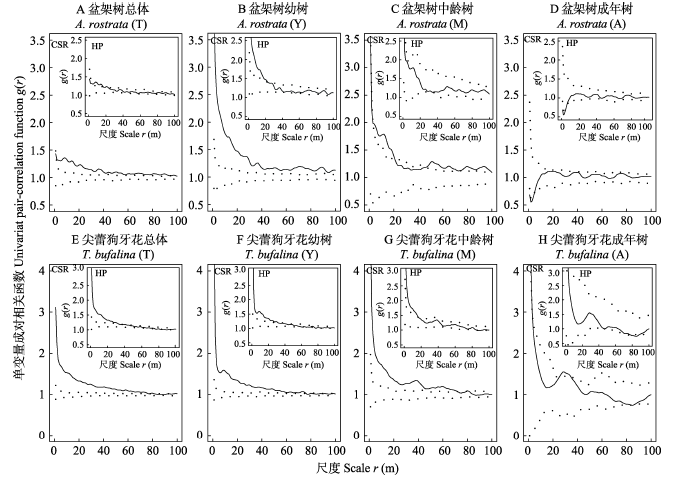
图2 海南尖峰岭60 ha森林动态监测样地中盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花各龄级的点格局分析。实线表示成对相关函数, 虚线表示99%包迹线。零模型为完全空间随机模型(CSR)和sigma = 15 m的异质泊松模型(HP)。
Fig. 2 Point pattern analysis of Alstonia rostrata and Tabernaemontana bufalina with different ages in the 60 ha forest dynamics plot in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. (T), (Y), (M), (A) represent the total, young trees, middle-aged trees and adult trees, respectively. Solid lines are pair-correlation functions, and dotted lines are 99% confidence envelopes. Null models: complete spatial randomness (CSR) model and Heterogeneous Poission (HP) model with sigma = 15 m.
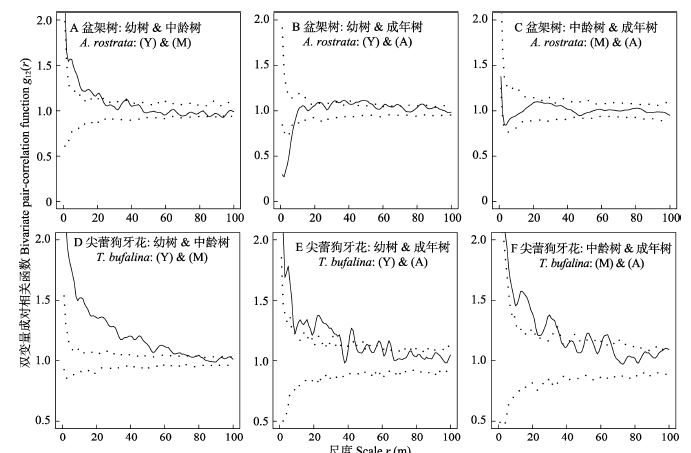
图3 海南尖峰岭60 ha森林动态监测样地中盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花各龄级的种内空间关联。实线表示成对相关函数, 虚线表示99%包迹线。零模型为完全空间随机模型(CSR)。
Fig. 3 Spatial association of intraspecific individuals of Alstonia rostrata and Tabernaemontana bufalina with different ages in the 60 ha forest dynamics plot in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. (T), (Y), (M), (A) represent the total, young trees, middle-aged trees and adult trees, respectively. Solid lines are pair-correlation functions, and dotted lines are 99% confidence envelopes. Null model: complete spatial randomness (CSR) model.
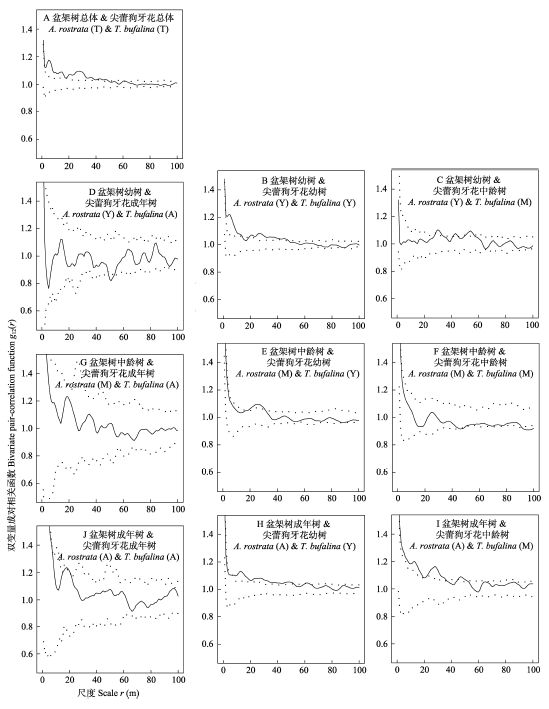
图4 海南尖峰岭60 ha 森林动态监测样地中盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花各龄级的种间关联。实线表示成对相关函数, 虚线表示99%包迹线。零模型为完全空间随机模型(CSR)。
Fig. 4 Spatial association of interspecific individuals of Alstonia rostrate and Tabernaemontana bufalina with different ages in the 60 ha forest dynamics plot in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. (T), (Y), (M), (A) represent the total, young trees, middle-aged trees and adult trees, respectively. Solid lines are pair-correlation functions, and dotted lines are 99% confidence envelopes. Null model: complete spatial randomness (CSR) model.
| 地形因子 Topographic factors | 盆架树 Alstonia rostrata | 尖蕾狗牙花 Tabernaemontana bufalina | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 Total | 幼树 Young tree | 中龄树 Middle-aged tree | 成年树 Adult tree | 总体 Total | 幼树 Young tree | 中龄树 Middle-aged tree | 成年树 Adult tree | |
| 坡度 Slope | + | n | n | + | n | n | n | n |
| 海拔 Elevation | + | + | n | n | + | + | n | n |
| 凹凸度 Convex | + | + | + | n | + | + | + | n |
表2 地形因子对海南尖峰岭60 ha森林动态监测样地中盆架树和尖蕾狗牙花各龄级个体分布格局的影响
Table 2 Influences of topographic factors on the distribution of the individuals of Alstonia rostrata and Tabernaemontana bufalina with different ages in the 60 ha forest dynamics plot in Jianfengling, Hainan Island
| 地形因子 Topographic factors | 盆架树 Alstonia rostrata | 尖蕾狗牙花 Tabernaemontana bufalina | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 Total | 幼树 Young tree | 中龄树 Middle-aged tree | 成年树 Adult tree | 总体 Total | 幼树 Young tree | 中龄树 Middle-aged tree | 成年树 Adult tree | |
| 坡度 Slope | + | n | n | + | n | n | n | n |
| 海拔 Elevation | + | + | n | n | + | + | n | n |
| 凹凸度 Convex | + | + | + | n | + | + | + | n |
| [9] | Illian J, Penttinen A, Stoyan H, Stoyan D (2008) Statistical Analysis and Modelling of Spatial Point Patterns. John Wiley & Sons, London. |
| [10] | Jiang YX, Lu JP (1991) Tropical Forest Ecosystem of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [蒋有绪, 卢俊培 (1991) 中国海南岛尖峰岭热带林生态系统. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] | Li HT (1995) Introduction to studies of the pattern of plant population. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 12(2), 19-26. (in Chinese) |
| [李海涛 (1995) 植物种群分布格局研究概况. 植物学通报, 12(2), 19-26.] | |
| [12] | Li YD, Chen BF, Zhou GY (2002) Research and Conservation of Tropical Forest and the Biodiversity—A Special Reference to Hainan Island, China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李意德, 陈步峰, 周光益 (2002) 中国海南岛热带森林及其生物多样性保护研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Li YD, Xu H, Luo TS, Chen DX, Lin MX (2012) Data Set of China Ecosystem Positioning Observation and Research, Volume of Forest Ecosystem, Jianfengling, Hainan Station (Data Set of Biological Species). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李意德, 许涵, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 林明献 (2012) 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集, 森林生态系统卷, 海南尖峰岭站(生物物种数据集). 中国农业出版社,北京 .] | |
| [14] | Li YP, Xu H, Li YD, Luo TS, Chen DX, Zhou Z, Lin MX, Yang H (2016) Scale-dependent spatial patterns of species diversity in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 861-870. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李艳朋, 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 周璋, 林明献, 杨怀 (2016) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林物种多样性空间分布格局的尺度效应. 植物生态学报, 40, 861-870.] | |
| [15] | Liang S, Xu H, Lin JY, Li YD, Lin MX (2014) Spatial distribution pattern of the dominant species Gironniera subaequalis in tropical montane rainforest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 1273-1282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁爽, 许涵, 林家怡, 李意德, 林明献 (2014) 尖峰岭热带山地雨林优势树种白颜树空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 38, 1273-1282.] | |
| [16] | Long C, Yang XB, Long WX, Li DH (2015) Population structure and spatial patterns of five Syzygium species in tropical evergreen monsoon elfin forest, Tongguling. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 51(2), 18-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龙成, 杨小波, 龙文兴, 李东海 (2015) 铜鼓岭热带常绿季雨矮林5种蒲桃属植物的种群结构及空间格局. 林业科学, 51(2), 18-27.] | |
| [17] | Ma JM, Liang Q, Liu JF, Chen ZF, Zheng SQ (2013) Spatial distribution pattern of Eurya nectar plant and environmental factor in Daiyun Mountain. Apiculture of China, 64(4), 26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马建梅, 梁勤, 刘金福, 陈志芳, 郑世群 (2013) 戴云山柃属蜜源植物空间分布及其环境因子研究. 中国蜂业, 64(4), 26-30.] | |
| [18] | Mcintire EJ, Fajardo A (2009) Beyond description: the active and effective way to infer processes from spatial patterns. Ecology, 90, 46-56. |
| [19] | Nong Y, Zheng L, Jia HY, Lu LH, Huang DW, Huang BH, Lei LQ (2015) Community characteristics and spatial distribution of dominant tree species in a secondary forest of Daqing Mountains, southwestern Guangxi, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 321-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [农友, 郑路, 贾宏炎, 卢立华, 黄德卫, 黄柏华, 雷丽群 (2015) 广西大青山次生林的群落特征及主要乔木种群的空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 23, 321-331.] | |
| [20] | Ou YD, Su ZY, Li ZK, Lin YH (2011) Effects of topographic factors on the distribution patterns of ground plants with different growth forms in montane forests in north Guangdong, China.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22, 1107-1113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [区余端, 苏志尧, 李镇魁, 林义辉 (2011) 地形因子对粤北山地森林不同生长型地表植物分布格局的影响. 应用生态学报, 22, 1107-1113.] | |
| [1] | Chen Y, Wang T, Li PK, Yao CL, Yuan ZL, Ye YZ (2016) Community characteristics and spatial distribution of dominant tree species in a deciduous broad-leaved forest of Muzhaling, Henan, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 1179-1188. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈云, 王婷, 李培坤, 姚成亮, 袁志良, 叶永忠 (2016) 河南木札岭温带落叶阔叶林群落特征及主要乔木空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 40, 1179-1188.] | |
| [21] | Ripley BD (1976) The second-order analysis of stationary point processes. Journal of Applied Probability, 13, 255-266. |
| [22] | Wang XG, Ye J, Li BH, Zhang J, Lin F, Hao ZQ (2010) Spatial distributions of species in an old-growth temperate forest, northeastern China. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 40, 1011-1019. |
| [2] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and A Comparison with Other Plots. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [3] | Connell JH (1971) On the role of natural enemies in preventing competitive exclusion in some marine animals and in rain forest trees. Dynamics of Populations, 86, 298-312. |
| [23] | Wang TT, Wang Q, Wang HZ, Zhang EH (2012) Autotoxicity of Angelica sinensis and allelopathy on tested plants. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 20, 1132-1138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王田涛, 王琦, 王惠珍, 张恩和 (2012) 当归自毒作用和其对不同作物的化感效应. 草地学报, 20, 1132-1138.] | |
| [4] | Diggle PJ (2003) Statistical Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns, 2nd edn. Hodder Education Publishers, London. |
| [5] | Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Huang FZ, Li DX, Wen SJ, He YL, Li XK (2015a) Dynamics of density-dependent effects of tree species in a 15 ha seasonal rain forest plot in northern tropical karst in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60, 1602-1611. (in Chinese) |
| [24] | Wright SJ (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: a review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia, 130, 1-14. |
| [25] | Xu H, Li YD, Lin MX, Wu JH, Luo TS, Zhou Z, Chen DX, Yang H, Li GJ, Liu SR (2015a) Community characteristics of a 60 ha dynamics plot in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 23, 192-201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | [郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 文淑均, 何运林, 李先琨 (2015b) 弄岗喀斯特季节性雨林15 ha样地密度制约效应分析. 科学通报, 60, 1602-1611.] |
| [6] | Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Huang YS, Huang FZ, Li DX, Li XK (2015b) Spatial distribution of tree species in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 183-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | [许涵, 李意德, 林明献, 吴建辉, 骆土寿, 周璋, 陈德祥, 杨怀, 李广建, 刘世荣 (2015) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha动态监测样地群落结构特征. 生物多样性, 23, 192-201.] |
| [26] | Yamakura T (1995) Topography of a large-scale research plot established within a tropical rain forest at Lambir, Sarawak. Tropics, 5, 41-56. |
| [6] | [郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄俞淞, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 李先琨 (2015a) 广西弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林监测样地种群空间点格局分析. 生物多样性, 23, 183-191.] |
| [7] | GuoYL, Lu JM, Franklin SB, Wang QG, Xu YZ, Zhang KH, Bao DC, Qiao XJ, Huang HD, Lu ZJ, Jiang MX (2013) Spatial distribution of tree species in a species-rich subtropical mountain forest in central China. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 43, 826-835. |
| [27] | Yang ML, Chen J, Sun M, Zhang DB, Gao K (2016) Antifungal indole alkaloids from Winchia calophylla. Planta Medica, 82, 712-716. |
| [28] | Zeng QB, Li YD, Chen BF, Wu ZM, Zhou GY (1997) Research and Management of Tropical Forest Ecosystem. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [曾庆波, 李意德, 陈步峰, 吴仲民, 周光益 (1997) 热带森林生态系统研究与管理. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] | Zhang AH, Gao YG, Xu YH, Lei FJ, Zhang LX (2011) Advances in studies on allelopathy of medicinal plants in China. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 42, 1885-1890. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Huang MC, Shi YC, Wei X, Wu LF, Wu RH, Pan ZP, Cao HL (2013) Point pattern analysis of rare and endangered plant Camellia nitidissima Chi. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 1127-1134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄明钗, 史艳财, 韦霄, 吴林芳, 吴儒华, 潘子平, 曹洪麟 (2013) 珍稀濒危植物金花茶的点格局分析. 生态学杂志, 32, 1127-1134.] | |
| [29] | [张爱华, 郜玉钢, 许永华, 雷锋杰, 张连学 (2011) 我国药用植物化感作用研究进展. 中草药, 42, 1885-1890.] |
| [30] | Zhang DB, Yu DG, Sun M, Zhu XX, Yao XJ, Zhou SY (2015) Ervatamines A-I, anti-inflammatory monoterpenoid indole alkaloids with diverse skeletons from Ervatamia hainanensis. Journal of Natural Products, 78, 1253-1261. |
| [31] | Zhang JT (1998) Analysis of spatial point pattern for plant species. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 22, 344-349. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张金屯 (1998) 植物种群空间分布的点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 22, 344-349.] | |
| [32] | Zhang QJ, Zhang AH, Sun JB, Zhang LX (2012) Advances of research on allelopathic potencial of terpenoids in plants. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21, 187-193. |
| [张秋菊, 张爱华, 孙晶波, 张连学 (2012) 植物体中萜类物质化感作用的研究进展. 生态环境学报, 21, 187-193.] | |
| [33] | Zhang CS, Xie GD, Chen L, Pei S, Fan N (2012) Effects of topography and tree structure on the distribution patterns of understory plants in the transitional area between China’s southern subtropical zone and the northern edge of the tropical zone. Resources Science, 34, 1232-1239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张昌顺, 谢高地, 陈龙, 裴厦, 范娜 (2012) 地形和乔木结构对热带北缘与南亚热带过渡带林下植被分布的影响. 资源科学, 34, 1232-1239.] | |
| [34] | Zhang XH, An SZ, Wang XR, Xiong ZY (2012) Spatial distribution patterns of Aconitum leucostomum. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 20, 428-433. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张鲜花, 安沙舟, 王显瑞, 熊增艳 (2012) 白喉乌头种群空间分布格局初步研究. 草地学报, 20, 428-433.] | |
| [35] | Zhu Y (2009) The prevalence of density dependence in Gutianshan subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest, China. PhD dissertation, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕 (2009) 古田山亚热带常绿阔叶林密度制约普遍性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院植物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [36] | Zhu Y, Bai F, Liu HF, Li WC, Li L, Li GQ, Wang SZ, Sang WG (2011) Population distribution patterns and interspecific spatial associations in warm temperate secondary forests, Beijing. Biodiversity Science, 19, 252-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕, 白帆, 刘海丰, 李文超, 李亮, 李广起, 王顺忠, 桑卫国 (2011) 北京暖温带次生林种群分布格局与种间空间关联性. 生物多样性, 19, 252-259.] | |
| [37] | Zhu Y, Getzin S, Wiegand T, Ren HB, Ma KP (2013) The relative importance of Janzen-Connell effects in influencing the spatial patterns at the Gutianshan subtropical forest. PLoS ONE, 8(9), e74560. |
| [1] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [2] | 颜文博, 莫燕妮, 曾治高, 薛少亮, 王琦, 梁春生, 黄祝礼, 罗文, 刘大业, 莫世琴, 李晓光, 梁路, 杜鹍鹏. 海南尖峰岭中华穿山甲的分布与保护现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 22106-. |
| [3] | 郭朝丹, 赵彩云, 李飞飞, 李俊生. 天然林和人工林外来入侵和本地植物对比研究: 以弄岗国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21356-. |
| [4] | 李帅锋, 郎学东, 黄小波, 刘万德, 苏建荣, 徐崇华, 李智宏, 徐凡迪. 藤枣生境地木本植物种间关联性与群落稳定性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 350-357. |
| [5] | 江焕, 张辉, 龙文兴, 方燕山, 符明期, 朱孔新. 金钟藤入侵群落的种间联结及生态位特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 388-399. |
| [6] | 许格希, 史作民, 唐敬超, 许涵, 杨怀, 刘世荣, 李意德, 林明献. 物种多度和径级尺度对于评价群落系统发育结构的影响: 以尖峰岭热带山地雨林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(6): 617-628. |
| [7] | 许涵, 李意德, 林明献, 吴建辉, 骆土寿, 周璋, 陈德祥, 杨怀, 李广建, 刘世荣. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 192-201. |
| [8] | 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 林明献, 杨怀. 森林采伐对尖峰岭海南特有种子植物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(2): 168-176. |
| [9] | 田中平, 庄丽, 李建贵, 程模香. 伊犁河谷北坡野果林木本植物种间关系 及环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3): 335-342. |
| [10] | 陶冶, 王丹, 刘彤, 蒋成国, 翟伟, 李勇冠, 唐诚. 天山北部拟南芥生存群落特征及其与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(1): 51-61. |
| [11] | 李渊博, 徐晗, 石雷, 李振宇. 紫茎泽兰对五种苦苣苔科植物化感作用的初步研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(5): 486-491. |
| [12] | 欧芷阳, 杨小波, 吴庆书. 尖峰岭自然保护区扩大区域植物多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(4): 437-444. |
| [13] | 王文进, 张明, 刘福德, 郑建伟, 王中生, 张世挺, 杨文杰, 安树青. 海南岛吊罗山热带山地雨林两个演替阶段的种间联结性[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(3): 257-263. |
| [14] | 朱圣潮. 中华水韭松阳居群的群落结构与种间联结性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(3): 258-264. |
| [15] | 张开梅, 石雷, 李振宇. 蕨类植物的化感作用及其对生物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(4): 466-471. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn