



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 109-115. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014128 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014128
田园1, 冯永军1, 张春兰1, 遇宝成2, 唐小平2, 胡慧建1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-06-17
接受日期:2015-01-04
出版日期:2015-01-20
发布日期:2015-05-04
通讯作者:
胡慧建
作者简介:E-mail: 13922339577@139.com基金资助:
Yuan Tian1, Yongjun Feng1, Chunlan Zhang1, Baocheng Yu2, Xiaoping Tang2, Huijian Hu1,*( )
)
Received:2014-06-17
Accepted:2015-01-04
Online:2015-01-20
Published:2015-05-04
Contact:
Huijian Hu
摘要:
样线法是全国第二次陆生野生动物资源调查中的首选方法, 但已有文献表明该方法在南方山地森林中应用时存在诸多问题。为此, 我们于2010年4月19-24日在广东车八岭国家级自然保护区对样线法的实际调查效果进行试点, 在保护区中心区域划定5 km × 10 km的范围, 布设6条3 km长的理论样线。实际调查时, 使用GPS轨迹记录功能精确标记调查样线和时间。调查时有2条样线未能达到理论长度, 平均每条样线耗时5.3 ± 1.4 h, 调查速度小于600 m/h。该方法针对常规调查物种的发现概率偏低, 调查到的物种总数占保护区常规调查物种总数的比例(0.22)小于调查到的总物种数占保护区总物种数的比例(0.37); 在调查强度为0.75%时, 可对区域内物种进行有效抽样, 但在有效评估一个区域的具体物种数量上可能存在缺陷。为此, 我们对比了全国第一次陆生野生动物调查及试点工作的结果, 针对南方山地森林生态系统调查提出以下建议: (1)应用GPS轨迹记录功能进行实际样线的设置和记录; (2)调查速度从2-3 km/h适当降低至600 m/h左右; 样线长度控制在3-5 km, 确保1天内可完成2条样线调查; (3)在现有的财力和人力条件下, 样区内各类群调查强度略高于1%是较为适宜的; (4)采用多种辅助手段来提升常规调查物种的发现概率; (5)在地形复杂的位置可考虑使用样方或样点法辅助调查, 增加物种发现概率, 但不宜限制其调查强度。
田园, 冯永军, 张春兰, 遇宝成, 唐小平, 胡慧建 (2015) 样线法在南方山地生态系统野生动物调查中的试点效果评价. 生物多样性, 23, 109-115. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014128.
Yuan Tian, Yongjun Feng, Chunlan Zhang, Baocheng Yu, Xiaoping Tang, Huijian Hu (2015) Effectiveness of line transects during wild animal surveys in mountain forests of South China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 109-115. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014128.
| 类群 Classes | 保护区物种数 Number of species in the reserve | 调查到物种数 Number of recorded species | 调查到个体数 Number of recorded individuals | 花费时间 Time (h) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总物种 Total | 常规调查物种 General survey species | 总物种 Total | 常规调查物种 General survey species | 总个体 Total | 常规调查个体 Individual | 总时间 Total time | 平均时间 Average time | ||||
| 两栖类 Amphibia | 16 | 6 | 13 | 3 | 73 | 32 | 32.9 | 5.5±1.4 | |||
| 爬行类 Reptile | 36 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 32.9 | 5.5±1.4 | |||
| 鸟类 Aves | 170 | 30 | 65 | 7 | 726 | 52 | 30.4 | 5.1±1.7 | |||
| 兽类 Mammal | 38 | 18 | 14 | 5 | 38 | 6 | 30.4 | 5.1±1.7 | |||
| 总计 Total | 260 | 68 | 96 | 15 | 844 | 90 | 126.6 | 5.3±1.4 | |||
表1 各类群样线调查信息表
Table 1 Data of line transect survey of each class
| 类群 Classes | 保护区物种数 Number of species in the reserve | 调查到物种数 Number of recorded species | 调查到个体数 Number of recorded individuals | 花费时间 Time (h) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总物种 Total | 常规调查物种 General survey species | 总物种 Total | 常规调查物种 General survey species | 总个体 Total | 常规调查个体 Individual | 总时间 Total time | 平均时间 Average time | ||||
| 两栖类 Amphibia | 16 | 6 | 13 | 3 | 73 | 32 | 32.9 | 5.5±1.4 | |||
| 爬行类 Reptile | 36 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 32.9 | 5.5±1.4 | |||
| 鸟类 Aves | 170 | 30 | 65 | 7 | 726 | 52 | 30.4 | 5.1±1.7 | |||
| 兽类 Mammal | 38 | 18 | 14 | 5 | 38 | 6 | 30.4 | 5.1±1.7 | |||
| 总计 Total | 260 | 68 | 96 | 15 | 844 | 90 | 126.6 | 5.3±1.4 | |||
| 类群 Classes | 基于多度的 物种估计量 Abundance -based coverage estimator (ACE) | 基于盖度的 物种估计量 Incidence- based coverage estimator (ICE) | 非参数估计丰富度 Richness with nonparametric estimation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jack knife 1 | Jack knife 2 | |||
| 两栖类 Amphibia | 16.68 | 17.55 | 18.17 | 18.30 |
| 爬行类 Reptile | 9.56 | 8.96 | 7.50 | 8.97 |
| 鸟类 Aves | 74.58 | 92.28 | 87.50 | 95.37 |
| 兽类 Mammal | 18.15 | 32.50 | 21.50 | 27.50 |
表2 各类群的实际物种丰富度和非参数估计丰富度
Table 2 Non-parametric estimated and recorded species richness of each class
| 类群 Classes | 基于多度的 物种估计量 Abundance -based coverage estimator (ACE) | 基于盖度的 物种估计量 Incidence- based coverage estimator (ICE) | 非参数估计丰富度 Richness with nonparametric estimation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jack knife 1 | Jack knife 2 | |||
| 两栖类 Amphibia | 16.68 | 17.55 | 18.17 | 18.30 |
| 爬行类 Reptile | 9.56 | 8.96 | 7.50 | 8.97 |
| 鸟类 Aves | 74.58 | 92.28 | 87.50 | 95.37 |
| 兽类 Mammal | 18.15 | 32.50 | 21.50 | 27.50 |
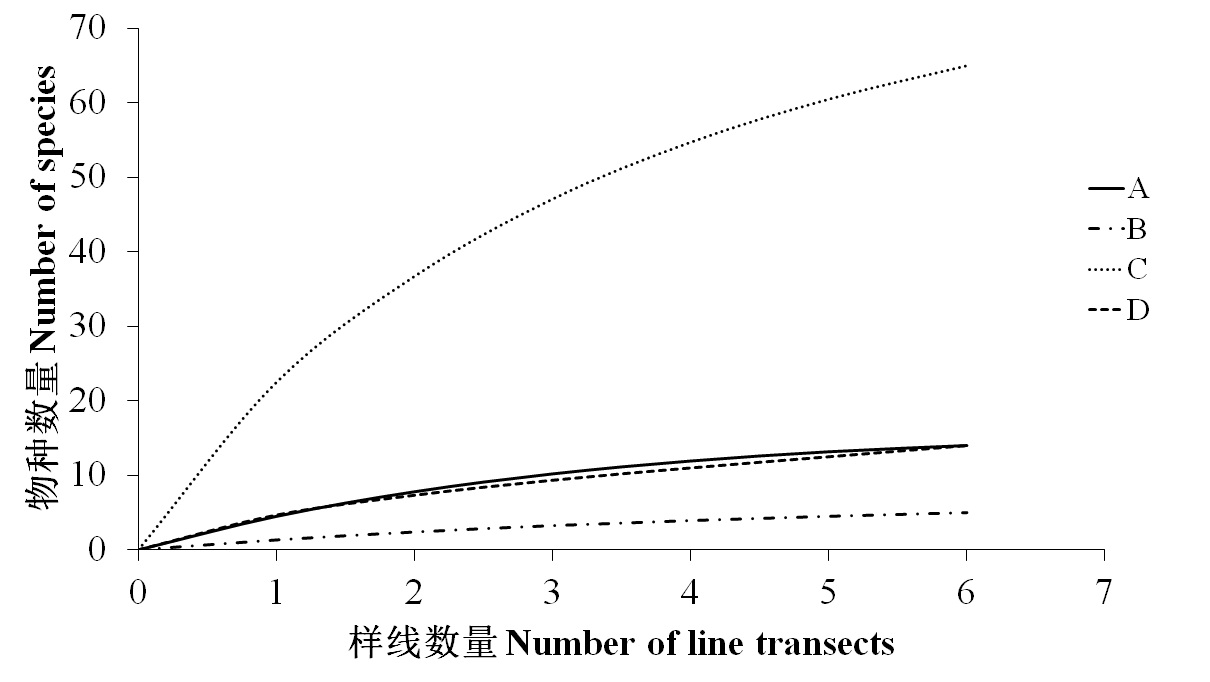
图2 各类群物种累积曲线变化图。A: 两栖类; B: 爬行类; C: 鸟类; D: 兽类。
Fig. 2 Species accumulation curves of each groups in six line transects. A, Amphibia; B, Reptile; C, Aves; D, Mammal
| 1 | Acharya BK, Vijayan L, Chettri B ( 2010) The bird community of Shingba Rhododendron Wildlife Sanctuary, Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya, India. Tropical Ecology, 51, 149-159. |
| 2 | Andrew TS, Xie Y ( 解焱) ( 2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China (中国兽类野外手册). Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| 3 | Bibby CJ, Burgesss ND, Hill DA ( 2000) Bird Census Techniques. Academic Press, London. |
| 4 | Buckland ST, Anderson DR, Burnham KP, Laake JL ( 1993) Distance Sampling: Estimating Abundance of Biological Populations. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| 5 |
Cai YT ( 蔡音亭), Gan XJ ( 干晓静), Ma ZJ ( 马志军 ) ( 2010) A comparison of line transect and point count surveys: a case study of spring salt marsh birds at Chongming Dongtan. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 18, 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Chao A, Chazdon RL, Colwell RK, Shen TJ ( 2005) A new statistical approach for assessing similarity of species composition with incidence and abundance data. Ecology Letters, 8, 148-159.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Chao A, Colwell RK, Lin CW, Gotelli NJ ( 2009) Sufficient sampling for asymptotic minimum species richness estimators. Ecology, 90, 1125-1133.
DOI URL PMID |
| 8 | China Wildlife Conservation Association (中国野生动物保护协会) ( 2002) Atlas of Reptiles of China (中国爬行动物图鉴). Henan Science and Technology Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| 9 | Colwell RK ( 2004) EstimateS: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from Samples. (2015-01-10). |
| 10 |
Colwell RK, Coddington JA ( 1994) Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B:Biological Sciences, 345, 101-118.
DOI URL PMID |
| 11 | David SD, Adam CR ( 1998) Comparison of line-transect, spot-map, and point-count surveys for birds in riparian habitats of the Great Basin. Journal of Field Ornithology, 69, 430-443. |
| 12 | Editor Committee of the Collected Papers for Investigation in National Chebaling Nature Reserve ( 车八岭国家级自然保护区调查研究论文集编委会) ( 1993) Collected Papers for Investigation in National Chebaling Nature Reserve (车八岭国家级自然保护区调查研究论文集), pp. 237-260. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| 13 | Fei L ( 费梁), Ye CY ( 叶昌媛), Huang YZ ( 黄永昭) ( 2005) An Illustrated Key to Chinese Amphibian (中国两栖动物检索及图解). Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| 14 | John M ( 约翰·马敬能), Karen P ( 卡伦·菲利普斯), He FQ ( 何芬奇) ( 2000) A Field Guide to the Birds of China (中国鸟类野外手册). Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| 15 | Li K ( 李昆), Luo CW ( 罗长维), Chen Y ( 陈友), Sun YY ( 孙永玉), He QJ ( 和秋菊 ) ( 2006) Insect species diversity in ecologically restored area of Yuanmou dry and hot valley. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 25, 417-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Li Q ( 李巧 ) ( 2011) Species accumulation curves and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology (应用昆虫学报), 48, 1882-1888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 |
Moreno CE, Halffter G ( 2001) On the measure of sampling effort used in species accumulation curves. Journal of Applied Ecology, 38, 487-490.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Reynolds RT, Scott JM, Nussbaum RA ( 1980) A variable circular plot method for estimating bird numbers. The Condor, 82, 309-311.
DOI URL |
| 19 | Richard BH, Kenneth PB ( 2002) On estimating wild life densities from line-transect data. Acta Zoologica Sinica (动物学报), 48, 812-818. |
| 20 |
Rowe RJ, Lidgard S ( 2009) Elevational gradients and species richness: do methods change pattern perception? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 163-177.
DOI URL |
| 21 | Sun HY ( 孙海义), Tang XP ( 唐小平), Zhou SC ( 周绍春), Wang ZC ( 王志臣), Lu XD ( 卢向东 ) ( 2011) Monitoring technique of big plot sample method for ungulate and other species, mammal. Forestry Science and Technology (林业科技), 36(6), 33-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 22 | Sun WT ( 孙文婷), Zhao SQ ( 赵思琪), Ma LL ( 马莉丽), Liu Y ( 刘垚), Li ZQ ( 李忠秋 ) ( 2012) Different results in using distance in line transect and point count method. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science (安徽农业科学), 40, 13383-13384, 13436. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 23 |
Ugland KI, Gray JS, Ellingsen KE ( 2003) The species-accumulation curve and estimation of species richness. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 888-897.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Walther BA, Moore JL ( 2005) The concepts of bias, precision and accuracy, and their use in testing the performance of species richness estimators, with a literature review of estimator performance. Ecography, 28, 815-829.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Wilson RR, Twedt DJ, Elliott AB ( 2000) Comparison of line transects and point counts for monitoring spring migration in forested wetlands. Journal of Field Ornithology, 71, 345-355.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Xing KX ( 邢开雄), Kang MY ( 康慕谊), Wang Q ( 王强), Duan J ( 段锦), Dai C ( 戴诚 ) ( 2011) Rarefaction approach to analyzing distribution patterns of species richness along altitudinal gradients: a case study with arborous species data. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 581-588. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 27 | Zhang RZ ( 张荣祖 ) ( 2011) Zoogeography of China (中国动物地理). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 28 | Zhao EM ( 赵尔宓 ) ( 2006) Snakes of China (中国蛇类). Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House, Hefei. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [2] | 何欣怡, 潘玉梅, 祝燕, 陈佳仪, 张思榕, 张乃莉. 暖温带森林外生菌根树种优势和植物多样性对土壤氮素周转的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24173-. |
| [3] | 白皓天, 余上, 潘新园, 凌嘉乐, 吴娟, 谢恺琪, 刘阳, 陈学业. AI辅助识别的鸟类被动声学监测在城市湿地公园中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24188-. |
| [4] | 江南, 徐卫华, 赵娟娟, 肖燚. 生态系统原真性概念及评价方法: 以长白山地区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1288-1294. |
| [5] | 魏鑫磊, 李姝, 窦文俊, 亓宝, 王琦, 李玉. 甘肃省祁连山国家级自然保护区的黏菌物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 65-71. |
| [6] | 孙晶琦, 陈泉, 李航宇, 常艳芬, 巩合德, 宋亮, 卢华正. 附生蕨类植物的克隆性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(11): 1184-1195. |
| [7] | 张倩雯, 龚粤宁, 宋相金, 王新财, 杨昌腾, 束祖飞, 邹发生. 红外相机技术与其他几种森林鸟类多样性调查方法的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 229-237. |
| [8] | 袁志忠, 崔洋, 颜绍馗. 叶凋落物数量和类型对森林土壤动物及其生物学质量的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(2): 206-213. |
| [9] | 蔡音亭, 干晓静, 马志军. 鸟类调查的样线法和样点法比较:以崇明东滩春季盐沼鸟类调查为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(1): 44-49. |
| [10] | 王淯, 王小明. 矮岩羊种群生态的初步研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2003, 11(1): 59-62. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()