



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 25166. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025166 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025166
卜凡玉1( ), 丁雨1(
), 丁雨1( ), 程晓兰2(
), 程晓兰2( ), 李昕峪1(
), 李昕峪1( ), 张雅璇1(
), 张雅璇1( ), 何巧巧1,*(
), 何巧巧1,*( )(
)( ), 姚志远1,*(
), 姚志远1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-06
接受日期:2025-07-23
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-11-20
通讯作者:
* 共同通讯作者 E-mail: heqq@synu.edu.cn;
yaozy@synu.edu.cn基金资助:
Fanyu Bu1( ), Yu Ding1(
), Yu Ding1( ), Xiaolan Cheng2(
), Xiaolan Cheng2( ), Xinyu Li1(
), Xinyu Li1( ), Yaxuan Zhang1(
), Yaxuan Zhang1( ), Qiaoqiao He1,*(
), Qiaoqiao He1,*( )(
)( ), Zhiyuan Yao1,*(
), Zhiyuan Yao1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-05-06
Accepted:2025-07-23
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-11-20
Contact:
* Co-authors for correspondence. E-mail: Supported by:摘要:
生物多样性是支撑人类可持续发展和生态系统稳定的重要基础。发现并描述新的生物物种, 定期梳理并更新物种名录, 是生物多样性研究、保护及可持续利用的重要途经。本文总结了2024年全世界发表的蜘蛛目新分类单元。394位学者发表了83个国家或地区的1,048个新分类单元, 隶属68科54新属994新种。这些新分类单元发表在65种刊物的329篇文献中, 其中科和属水平的修订、地区志或专著类的文献共有57篇, 占文献总数的17.3%; 运用DNA分子数据分析方法的论文共计49篇, 占文献总数的14.9%; 643个新种是基于雌雄两性标本发表, 占新种总数的64.7%; 351个新种仅基于雄性或雌性标本发表, 占新种总数的35.3%。中国是2024年发现蜘蛛目新种最多的国家, 共309种, 占世界新种总数的31.1%。中国学者李枢强是2024年命名蜘蛛目新分类单元数量最多的学者, 共命名144个, 占世界新分类单元总数的13.7%。此外, 无论是命名蜘蛛目新分类单元数量还是参与命名新分类单元的学者数量, 均是中国学者位列第一。中国共有92位学者参与命名, 占世界新分类单元命名学者总数的23.4%; 这92位学者命名了中国和越南等8个国家或地区的18新属326新种, 合计344个新分类单元, 命名新分类单元数量占世界新分类单元总数的32.8%。该贡献率高于2016-2020年的平均贡献率28.1%, 但较2021年的33.8%、2022年的37.0%和2023年的41.2%有所下降。
卜凡玉, 丁雨, 程晓兰, 李昕峪, 张雅璇, 何巧巧, 姚志远 (2025) 2024年世界蜘蛛目新分类单元. 生物多样性, 33, 25166. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025166.
Fanyu Bu, Yu Ding, Xiaolan Cheng, Xinyu Li, Yaxuan Zhang, Qiaoqiao He, Zhiyuan Yao (2025) New taxa of spiders (Araneae) from the world in 2024. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25166. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025166.
| 序号 No. | 科名 Family name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa | 序号 No. | 科名 Family name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 漏斗蛛科 Agelenidae | 0 | 24 | 24 | 35 | 线蛛科 Nemesiidae | 0 | 33 | 33 |
| 2 | 暗蛛科 Amaurobiidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 36 | 类球蛛科 Nesticidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 安蛛科 Anapidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 37 | 花洞蛛科 Ochyroceratidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 近管蛛科 Anyphaenidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 38 | 拟壁钱科 Oecobiidae | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 5 | 园蛛科 Araneidae | 6 | 29 | 35 | 39 | 卵形蛛科 Oonopidae | 0 | 25 | 25 |
| 6 | 古蛛科 Archaeidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 猫蛛科 Oxyopidae | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| 7 | 开普蛛科 Caponiidae | 0 | 11 | 11 | 41 | 二纺蛛科 Palpimanidae | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 8 | 红螯蛛科 Cheiracanthiidae | 2 | 11 | 13 | 42 | 鳞毛蛛科 Paratropididae | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| 9 | 洞叶蛛科 Cicurinidae | 1 | 5 | 6 | 43 | 逍遥蛛科 Philodromidae | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 10 | 管巢蛛科 Clubionidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 44 | 幽灵蛛科 Pholcidae | 0 | 78 | 78 |
| 11 | 圆颚蛛科 Corinnidae | 0 | 24 | 24 | 45 | 刺足蛛科 Phrurolithidae | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 12 | 栉足蛛科 Ctenidae | 1 | 17 | 18 | 46 | 粗螯蛛科 Prodidomidae | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 13 | 弓蛛科 Cyrtaucheniidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 47 | 密疣蛛科 Pycnothelidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | 卷叶蛛科 Dictynidae | 1 | 3 | 4 | 48 | 皱栖蛛科 Rhytidicolidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 15 | 长尾蛛科 Dipluridae | 1 | 6 | 7 | 49 | 跳蛛科 Salticidae | 9 | 195 | 204 |
| 16 | 狡蛛科 Dolomedidae | 0 | 4 | 4 | 50 | 类石蛛科 Segestriidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 17 | 石蛛科 Dysderidae | 0 | 14 | 14 | 51 | 拟扁蛛科 Selenopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | 佳螲蟷科 Euctenizidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 52 | 刺客蛛科 Sicariidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 19 | 管网蛛科 Filistatidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 53 | 巨蟹蛛科 Sparassidae | 0 | 45 | 45 |
| 20 | 平腹蛛科 Gnaphosidae | 2 | 22 | 24 | 54 | 合螯蛛科 Symphytognathidae | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 21 | 格拉蛛科 Gradungulidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 55 | 合蛛科 Synotaxidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 22 | 栅蛛科 Hahniidae | 4 | 18 | 22 | 56 | 四盾蛛科 Tetrablemmidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 23 | 盘腹蛛科 Halonoproctidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 57 | 肖蛸蛛科 Tetragnathidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 24 | 异蛛科 Idiopidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 58 | 捕鸟蛛科 Theraphosidae | 5 | 52 | 57 |
| 25 | 弱蛛科 Leptonetidae | 0 | 14 | 14 | 59 | 球蛛科 Theridiidae | 7 | 51 | 58 |
| 26 | 皿蛛科 Linyphiidae | 1 | 29 | 30 | 60 | 球体蛛科 Theridiosomatidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 27 | 光盔蛛科 Liocranidae | 0 | 15 | 15 | 61 | 蟹蛛科 Thomisidae | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 28 | 节板蛛科 Liphistiidae | 0 | 11 | 11 | 62 | 隐石蛛科 Titanoecidae | 0 | 9 | 9 |
| 29 | 狼蛛科 Lycosidae | 1 | 35 | 36 | 63 | 管蛛科 Trachelidae | 5 | 24 | 29 |
| 30 | 巨眼蛛科 Macrobunidae | 1 | 4 | 5 | 64 | 行蛛科 Trechaleidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 31 | 大疣蛛科 Macrothelidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 65 | 雨蛛科 Udubidae | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| 32 | 四纺蛛科 Migidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 66 | 异栉蛛科 Xenoctenidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 33 | 拟态蛛科 Mimetidae | 0 | 5 | 5 | 67 | 拟平腹蛛科 Zodariidae | 0 | 27 | 27 |
| 34 | 米图蛛科 Miturgidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 68 | 逸蛛科 Zoropsidae | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 合计 Total | 54 | 994 | 1,048 |
表1 2024年世界蜘蛛目新分类单元数
Table 1 Number of new spider taxa globally in 2024
| 序号 No. | 科名 Family name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa | 序号 No. | 科名 Family name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 漏斗蛛科 Agelenidae | 0 | 24 | 24 | 35 | 线蛛科 Nemesiidae | 0 | 33 | 33 |
| 2 | 暗蛛科 Amaurobiidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 36 | 类球蛛科 Nesticidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 安蛛科 Anapidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 37 | 花洞蛛科 Ochyroceratidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 近管蛛科 Anyphaenidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 38 | 拟壁钱科 Oecobiidae | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 5 | 园蛛科 Araneidae | 6 | 29 | 35 | 39 | 卵形蛛科 Oonopidae | 0 | 25 | 25 |
| 6 | 古蛛科 Archaeidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 猫蛛科 Oxyopidae | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| 7 | 开普蛛科 Caponiidae | 0 | 11 | 11 | 41 | 二纺蛛科 Palpimanidae | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 8 | 红螯蛛科 Cheiracanthiidae | 2 | 11 | 13 | 42 | 鳞毛蛛科 Paratropididae | 0 | 7 | 7 |
| 9 | 洞叶蛛科 Cicurinidae | 1 | 5 | 6 | 43 | 逍遥蛛科 Philodromidae | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 10 | 管巢蛛科 Clubionidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 44 | 幽灵蛛科 Pholcidae | 0 | 78 | 78 |
| 11 | 圆颚蛛科 Corinnidae | 0 | 24 | 24 | 45 | 刺足蛛科 Phrurolithidae | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 12 | 栉足蛛科 Ctenidae | 1 | 17 | 18 | 46 | 粗螯蛛科 Prodidomidae | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 13 | 弓蛛科 Cyrtaucheniidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 47 | 密疣蛛科 Pycnothelidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | 卷叶蛛科 Dictynidae | 1 | 3 | 4 | 48 | 皱栖蛛科 Rhytidicolidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 15 | 长尾蛛科 Dipluridae | 1 | 6 | 7 | 49 | 跳蛛科 Salticidae | 9 | 195 | 204 |
| 16 | 狡蛛科 Dolomedidae | 0 | 4 | 4 | 50 | 类石蛛科 Segestriidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 17 | 石蛛科 Dysderidae | 0 | 14 | 14 | 51 | 拟扁蛛科 Selenopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | 佳螲蟷科 Euctenizidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 52 | 刺客蛛科 Sicariidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 19 | 管网蛛科 Filistatidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 53 | 巨蟹蛛科 Sparassidae | 0 | 45 | 45 |
| 20 | 平腹蛛科 Gnaphosidae | 2 | 22 | 24 | 54 | 合螯蛛科 Symphytognathidae | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 21 | 格拉蛛科 Gradungulidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 55 | 合蛛科 Synotaxidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 22 | 栅蛛科 Hahniidae | 4 | 18 | 22 | 56 | 四盾蛛科 Tetrablemmidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 23 | 盘腹蛛科 Halonoproctidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 57 | 肖蛸蛛科 Tetragnathidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 24 | 异蛛科 Idiopidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 58 | 捕鸟蛛科 Theraphosidae | 5 | 52 | 57 |
| 25 | 弱蛛科 Leptonetidae | 0 | 14 | 14 | 59 | 球蛛科 Theridiidae | 7 | 51 | 58 |
| 26 | 皿蛛科 Linyphiidae | 1 | 29 | 30 | 60 | 球体蛛科 Theridiosomatidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 27 | 光盔蛛科 Liocranidae | 0 | 15 | 15 | 61 | 蟹蛛科 Thomisidae | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 28 | 节板蛛科 Liphistiidae | 0 | 11 | 11 | 62 | 隐石蛛科 Titanoecidae | 0 | 9 | 9 |
| 29 | 狼蛛科 Lycosidae | 1 | 35 | 36 | 63 | 管蛛科 Trachelidae | 5 | 24 | 29 |
| 30 | 巨眼蛛科 Macrobunidae | 1 | 4 | 5 | 64 | 行蛛科 Trechaleidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 31 | 大疣蛛科 Macrothelidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 65 | 雨蛛科 Udubidae | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| 32 | 四纺蛛科 Migidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 66 | 异栉蛛科 Xenoctenidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 33 | 拟态蛛科 Mimetidae | 0 | 5 | 5 | 67 | 拟平腹蛛科 Zodariidae | 0 | 27 | 27 |
| 34 | 米图蛛科 Miturgidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 68 | 逸蛛科 Zoropsidae | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 合计 Total | 54 | 994 | 1,048 |
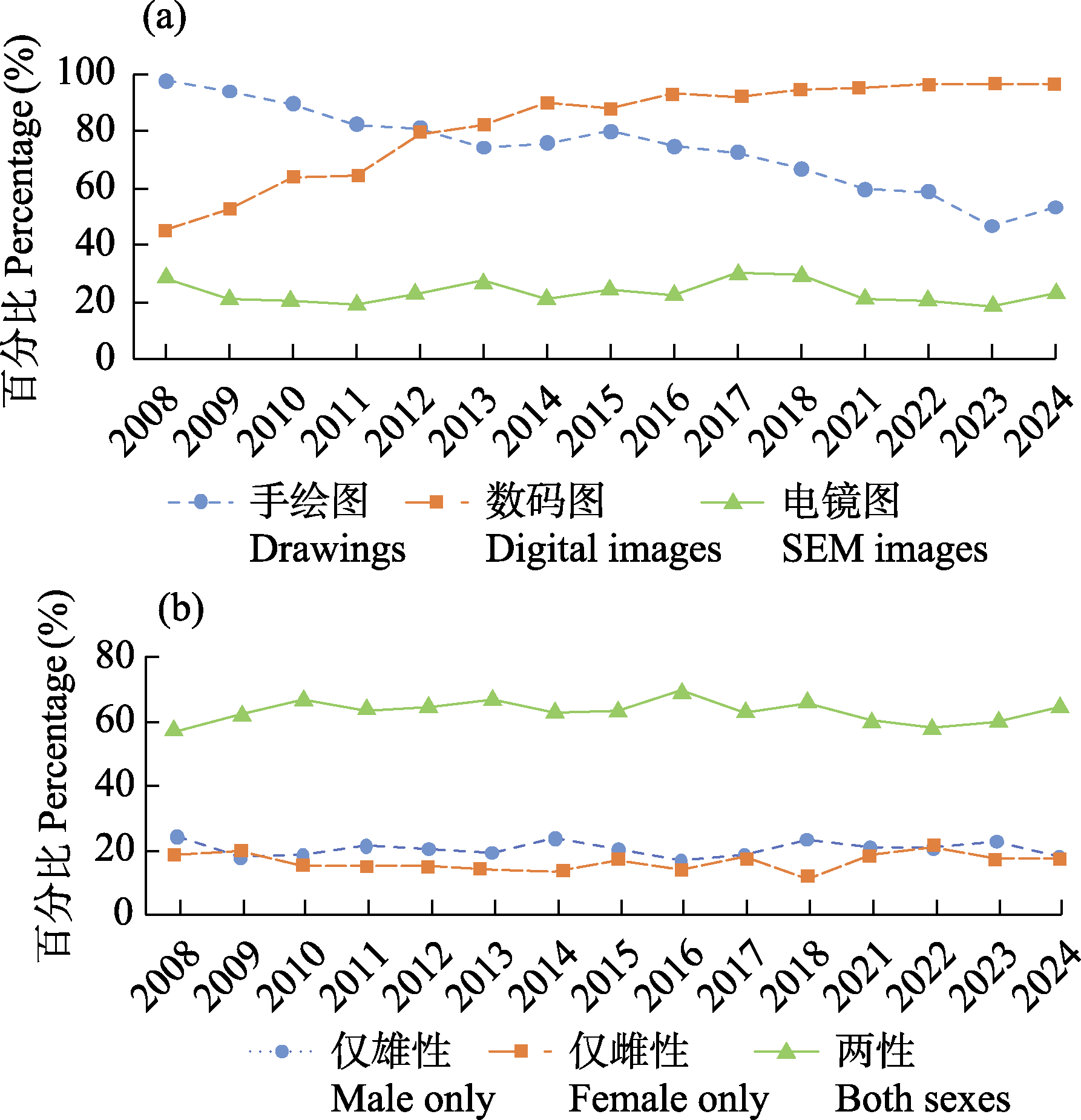
图2 2008-2018年和2021-2024年世界蜘蛛目特征图类型和物种性别。(a)手绘图、数码图和电镜图类型论文数量的百分比; (b)单性和两性新种数量的百分比。2008-2018年、2021年、2022年和2023年的特征图类型和物种性别数据分别来自Bond等(2022)、张露丹等(2022)、杨蕊含等(2023)和李昕峪等(2024)。
Fig. 2 Illustration techniques and sexes featured in the descriptions of Araneae in 2008-2018 and 2021-2024. (a) Percentage of publications based on illustration techniques; (b) Percentage of new species described based on sex. Data on illustration techniques and species sexes for the years 2008-2018, 2021, 2022, and 2023 are derived from Bond et al (2022), Zhang et al (2022), Yang et al (2023) and Li et al (2024), respectively.
| 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total | 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Li/S.Q. Li/S. Li | 李枢强 Shuqiang Li | 10 | 134 | 144 | 32 | Benjamin | Suresh Benjamin | 1 | 17 | 18 |
| 2 | Mi | 米小其 Xiaoqi Mi | 6 | 60 | 66 | 32 | do Prado | André do Prado | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 3 | Wang | 王成 Cheng Wang | 6 | 59 | 65 | 34 | Liu | 刘科科 Keke Liu | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| 4 | Marusik | Yuri Marusik | 6 | 46 | 52 | 34 | Yao | 姚彦彬 Yanbin Yao | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| 4 | Lin | 林业杰 Yejie Lin | 4 | 48 | 52 | 34 | Logunov | Dmitri Logunov | 0 | 17 | 17 |
| 4 | Wesołowska | Wanda Wesołowska | 2 | 50 | 52 | 37 | Lyle | Robin Lyle | 3 | 13 | 16 |
| 7 | Wiśniewski | Konrad Wiśniewski | 2 | 47 | 49 | 37 | Pett | Brogan Pett | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 8 | Jocqué | Rudy Jocqué | 4 | 35 | 39 | 39 | Lu | 陆千乐 Qianle Lu/陆锋 Feng Lu | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| 9 | Brescovit | Antonio Brescovit | 2 | 36 | 38 | 39 | Mu | 母炎楠 Yannan Mu | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| 9 | Yao | 姚志远 Zhiyuan Yao | 0 | 38 | 38 | 41 | Framenau | Volker Framenau | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 11 | Zhang/Z.S. Zhang | 张志升 Zhisheng Zhang | 2 | 34 | 36 | 41 | Yang | 杨澜 Lan Yang | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 11 | Zamani | Alireza Zamani | 1 | 35 | 36 | 43 | Peñaherrera-R | Pedro Peñaherrera-R | 2 | 11 | 13 |
| 13 | Haddad | Charles Haddad | 3 | 32 | 35 | 43 | Yu | 于影 Ying Yu | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 13 | Wang | 王露雨 Luyu Wang | 2 | 33 | 35 | 43 | Liu/J. Liu | 刘杰 Jie Liu | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 13 | Huber | Bernhard Huber | 0 | 35 | 35 | 43 | Zhang/L. Zhang | 张露丹 Ludan Zhang | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 16 | Dupérré | Nadine Dupérré | 3 | 29 | 32 | 47 | Caleb | John Caleb | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 17 | Fomichev | Alexander Fomichev | 3 | 27 | 30 | 47 | Gabriel | Ray Gabriel | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 18 | Jäger | Peter Jäger | 0 | 29 | 29 | 47 | Yang | 杨智勇 Zhiyong Yang | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 19 | Tapia | Elicio Tapia | 3 | 25 | 28 | 50 | Osorio | Luis Osorio | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 19 | Tong | 佟艳丰 Yanfeng Tong | 0 | 28 | 28 | 50 | Wunderlich | Joerg Wunderlich | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 19 | Xu | 徐湘 Xiang Xu | 0 | 28 | 28 | 50 | Rheims | Cristina Rheims | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 22 | Zhang | 张俊霞 Junxia Zhang | 2 | 25 | 27 | 50 | Silva-Junior | Cláudio Silva-Junior | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 23 | Sherwood | Danniella Sherwood | 3 | 23 | 26 | 54 | Benavides | Léiner Benavides | 1 | 9 | 10 |
| 24 | Baptista | Renner Baptista | 1 | 22 | 23 | 54 | Omelko | Mikhail Omelko | 1 | 9 | 10 |
| 24 | Zonstein | Sergei Zonstein | 0 | 23 | 23 | 54 | Korai | Shakal Korai | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 26 | Zhang/F. Zhang | 张锋 Feng Zhang | 3 | 19 | 22 | 54 | Nobre | Welington Nobre | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 27 | Deeleman- Reinhold | Christa Deeleman-Reinhold | 2 | 19 | 21 | 54 | Ponomarev | Alexander Ponomarev | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 28 | Vanuytven | Herman Vanuytven | 2 | 18 | 20 | 54 | Ruiz | Gustavo Ruiz | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 29 | Henrard | Arnaud Henrard | 2 | 17 | 19 | 54 | Tripathi | Rishikesh Tripathi | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 29 | Wang | 王苇杭 Weihang Wang | 2 | 17 | 19 | 54 | Wang | 王冰 Bing Wang | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 29 | Bonaldo | Alexandre Bonaldo | 0 | 19 | 19 |
表2 2024年世界命名蜘蛛目新分类单元10个及以上的学者
Table 2 Arachnologists who published 10 and more new taxa of Araneae in 2024
| 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total | 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Li/S.Q. Li/S. Li | 李枢强 Shuqiang Li | 10 | 134 | 144 | 32 | Benjamin | Suresh Benjamin | 1 | 17 | 18 |
| 2 | Mi | 米小其 Xiaoqi Mi | 6 | 60 | 66 | 32 | do Prado | André do Prado | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 3 | Wang | 王成 Cheng Wang | 6 | 59 | 65 | 34 | Liu | 刘科科 Keke Liu | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| 4 | Marusik | Yuri Marusik | 6 | 46 | 52 | 34 | Yao | 姚彦彬 Yanbin Yao | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| 4 | Lin | 林业杰 Yejie Lin | 4 | 48 | 52 | 34 | Logunov | Dmitri Logunov | 0 | 17 | 17 |
| 4 | Wesołowska | Wanda Wesołowska | 2 | 50 | 52 | 37 | Lyle | Robin Lyle | 3 | 13 | 16 |
| 7 | Wiśniewski | Konrad Wiśniewski | 2 | 47 | 49 | 37 | Pett | Brogan Pett | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 8 | Jocqué | Rudy Jocqué | 4 | 35 | 39 | 39 | Lu | 陆千乐 Qianle Lu/陆锋 Feng Lu | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| 9 | Brescovit | Antonio Brescovit | 2 | 36 | 38 | 39 | Mu | 母炎楠 Yannan Mu | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| 9 | Yao | 姚志远 Zhiyuan Yao | 0 | 38 | 38 | 41 | Framenau | Volker Framenau | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 11 | Zhang/Z.S. Zhang | 张志升 Zhisheng Zhang | 2 | 34 | 36 | 41 | Yang | 杨澜 Lan Yang | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 11 | Zamani | Alireza Zamani | 1 | 35 | 36 | 43 | Peñaherrera-R | Pedro Peñaherrera-R | 2 | 11 | 13 |
| 13 | Haddad | Charles Haddad | 3 | 32 | 35 | 43 | Yu | 于影 Ying Yu | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 13 | Wang | 王露雨 Luyu Wang | 2 | 33 | 35 | 43 | Liu/J. Liu | 刘杰 Jie Liu | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 13 | Huber | Bernhard Huber | 0 | 35 | 35 | 43 | Zhang/L. Zhang | 张露丹 Ludan Zhang | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 16 | Dupérré | Nadine Dupérré | 3 | 29 | 32 | 47 | Caleb | John Caleb | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 17 | Fomichev | Alexander Fomichev | 3 | 27 | 30 | 47 | Gabriel | Ray Gabriel | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 18 | Jäger | Peter Jäger | 0 | 29 | 29 | 47 | Yang | 杨智勇 Zhiyong Yang | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 19 | Tapia | Elicio Tapia | 3 | 25 | 28 | 50 | Osorio | Luis Osorio | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 19 | Tong | 佟艳丰 Yanfeng Tong | 0 | 28 | 28 | 50 | Wunderlich | Joerg Wunderlich | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 19 | Xu | 徐湘 Xiang Xu | 0 | 28 | 28 | 50 | Rheims | Cristina Rheims | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 22 | Zhang | 张俊霞 Junxia Zhang | 2 | 25 | 27 | 50 | Silva-Junior | Cláudio Silva-Junior | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 23 | Sherwood | Danniella Sherwood | 3 | 23 | 26 | 54 | Benavides | Léiner Benavides | 1 | 9 | 10 |
| 24 | Baptista | Renner Baptista | 1 | 22 | 23 | 54 | Omelko | Mikhail Omelko | 1 | 9 | 10 |
| 24 | Zonstein | Sergei Zonstein | 0 | 23 | 23 | 54 | Korai | Shakal Korai | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 26 | Zhang/F. Zhang | 张锋 Feng Zhang | 3 | 19 | 22 | 54 | Nobre | Welington Nobre | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 27 | Deeleman- Reinhold | Christa Deeleman-Reinhold | 2 | 19 | 21 | 54 | Ponomarev | Alexander Ponomarev | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 28 | Vanuytven | Herman Vanuytven | 2 | 18 | 20 | 54 | Ruiz | Gustavo Ruiz | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 29 | Henrard | Arnaud Henrard | 2 | 17 | 19 | 54 | Tripathi | Rishikesh Tripathi | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 29 | Wang | 王苇杭 Weihang Wang | 2 | 17 | 19 | 54 | Wang | 王冰 Bing Wang | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 29 | Bonaldo | Alexandre Bonaldo | 0 | 19 | 19 |
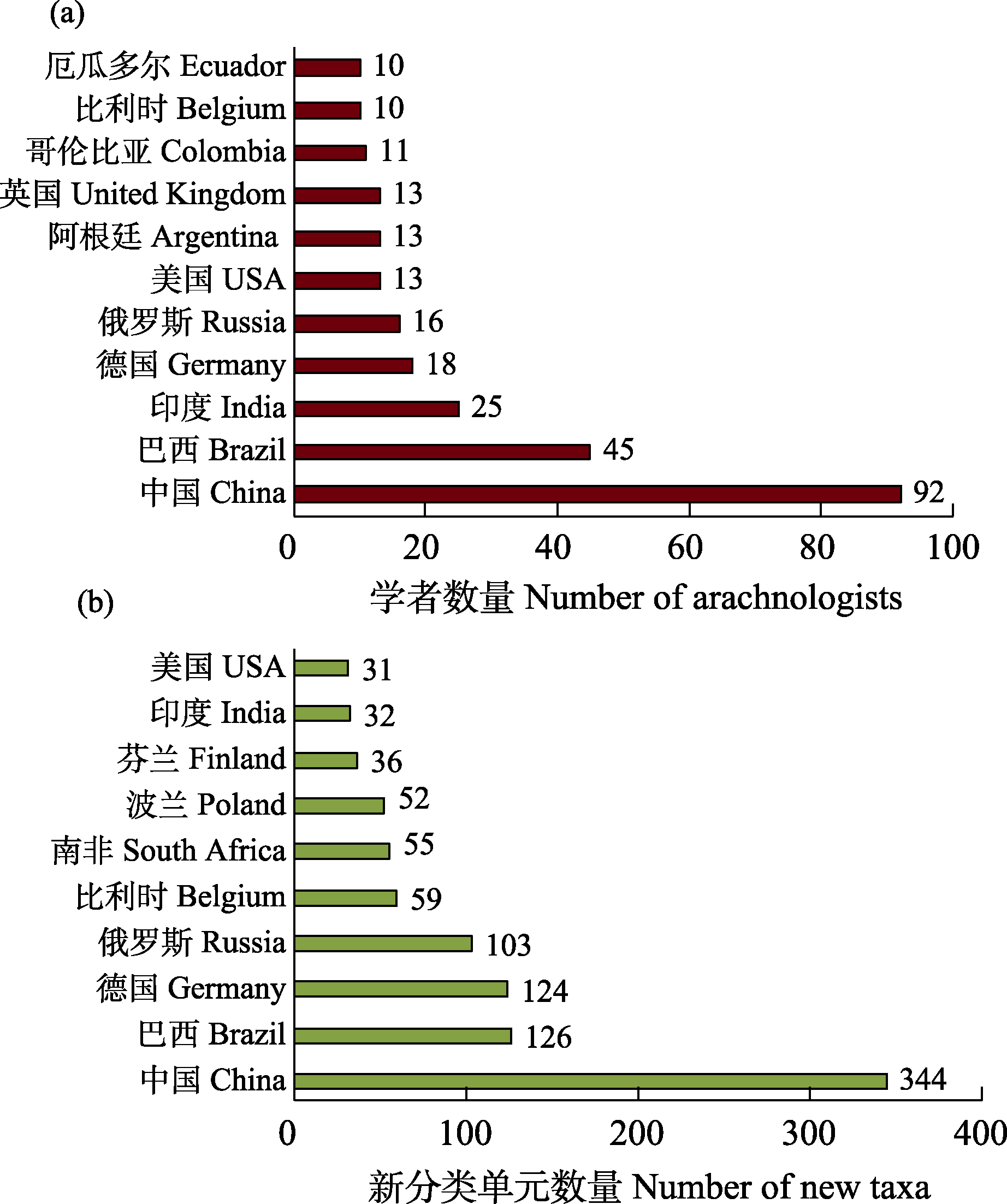
图3 2024年参与蜘蛛目新分类单元命名的学者数量和学者国籍。(a) 2024年参与蜘蛛目新分类单元命名的学者数量在10个及以上的国家; (b) 2024年各国学者命名蜘蛛目新分类单元数量位于前10位的国家。
Fig. 3 Number of arachnologists describing new taxa in 2024 and their nationalities. (a) Countries with 10 and more arachnologists describing new taxa in 2024; (b) Top 10 countries of origin of the most prolific arachnologists describing new taxa in 2024.
| [1] |
Almeida-Silva LM, Brescovit AD (2024) Unraveling the mysteries of Goeldia Keyserling, 1891: Revision, description of seven new species and first record from USA (Araneae: Titanoecidae). Zootaxa, 5428, 151-193.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bond JE, Garrison NL, Hamilton CA, Godwin RL, Hedin M, Agnarsson I (2014) Phylogenomics resolves a spider backbone phylogeny and rejects a prevailing paradigm for orb web evolution. Current Biology, 24, 1765-1771.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Bond JE, Godwin RL, Colby JD, Newton LG, Zahnle XJ, Agnarsson I, Hamilton CA, Kuntner M (2022) Improving taxonomic practices and enhancing its extensibility—An example from araneology. Diversity, 14, 5.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Chen LY, Gai HY, Jiang LL, Ma N, Liu XM, Zhou YC (2025) Research on the impact evaluation of scientific data papers. Chinese Journal of Scientific and Technical Periodicals, 36, 391-399. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈莉玥, 盖虹羽, 姜璐璐, 马娜, 刘筱敏, 周园春 (2025) 科学数据论文影响力评价研究. 中国科技期刊研究, 36, 391-399.]
DOI |
|
| [5] |
Haddad CR, Lyle R (2024) Three new genera of arboreal dark sac spiders from southern Africa (Araneae: Trachelidae). Zootaxa, 5399, 451-504.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Hamilton CA, Hendrixson BE, Bringas KS (2024) Discovery of a new tarantula species from the Madrean Sky Islands and the first documented instance of syntopy between two montane endemics (Araneae, Theraphosidae, Aphonopelma): A case of prior mistaken identity. ZooKeys, 1210, 61-98.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Huber BA, Meng GL, Král J, Ávila Herrera IM, Carvalho LS (2024) Diamonds in the rough: Ibotyporanga (Araneae, Pholcidae) spiders in semi-arid Neotropical environments. European Journal of Taxonomy, 963, 1-169.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Hughes AC (2023) The Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework: How did we get here, and where do we go next? Integrative Conservation, 2, 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Jocqué R, Henrard A (2024) A revision of Afrotropical Asceua (Araneae, Zodariidae), ant-eating spiders with puzzling distributions. African Invertebrates, 65, 161-198.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Li XY, Zhang YX, Yan MC, Yang RH, Zhang XQ, Yao ZY (2024) New taxa of extant spiders (Araneae) from the world in 2023. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李昕峪, 张雅璇, 闫美辰, 杨蕊含, 张小庆, 姚志远 (2024) 2023年世界现生蜘蛛目新分类单元. 生物多样性, 32, 24181.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Lin YJ, Li SQ, Mo HL, Wang XH (2024) Thirty-eight spider species (Arachnida: Araneae) from China, Indonesia, Japan and Vietnam. Zoological Systematics, 49, 4-98.
DOI |
| [12] | Ma KP (2015) Species Catalogue of China: A remarkable achievement in the field of biodiversity science in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 137-138. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性编目取得重要进展. 生物多样性, 23, 137-138.] | |
| [13] |
Ma KP (2023) Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: An important global agenda for biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23133. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[马克平 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》是重要的全球生物多样性保护议程. 生物多样性, 31, 23133.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Mi XQ, Wang C, Li SQ (2024) Description of six new genera and twenty species of the orb-weaver spider family Araneidae (Araneae, Araneoidea) from Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China. Zoological Research: Diversity and Conservation, 1, 290-342.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Prete PH, Brescovit AD (2024) Taxonomic revision of the orb weaving spider genus Plato Coddington, 1986 (Araneae: Theridiosomatidae) with the description of three new species. Zootaxa, 5471, 1-32.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Satkunanathan A, Benjamin SP (2024) Multilocus genetic and morphological phylogenetic analysis: Unveiling a new genus and species in the Tribe Nannenini of jumping spiders (Araneae, Salticidae). Zoologica Scripta, 53, 688-711.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Silva-Junior CJ, Bonaldo AB (2024) A revision of the South American species of the ant-mimicking spider genus Myrmecotypus O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1894 (Araneae: Corinnidae: Castianeirinae). Zootaxa, 5555, 451-496.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Vanuytven H, Jocqué R, Deeleman-Reinhold C (2024) Two new theridiid genera from Southeast Asia (Araneae: Theridiidae, Argyrodinae): Males with a nose for courtship. Journal of the Belgian Arachnological Society, 39, 1-96. |
| [19] |
Wiśniewski K, Wesołowska W (2024) Jumping spiders (Salticidae) of Uganda—Revised list, new species and distributional data. European Journal of Taxonomy, 952, 1-171.
DOI URL |
| [20] | WSC (2025) World Spider Catalog, Version 26.0. Natural History Museum Bern. http://wsc.nmbe.ch. (accessed on 2025-05-06) |
| [21] |
Yang L, Fu C, Zhang YX, He QQ, Yao ZY (2024a) A survey of Pholcus spiders (Araneae, Pholcidae) from the Qinling Mountains of central China, with descriptions of seven new species. Zoosystematics and Evolution, 100, 199-221.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Yang L, He QQ, Yao ZY (2024b) Taxonomic study of four closely-related species of the Pholcus yichengicus species group (Araneae, Pholcidae) from China’s Qinling Mountains: An integrated morphological and molecular approach. Zoosystematics and Evolution, 100, 279-289.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Yang RH, Yan MC, Zhang LD, Liu HX, Koh JKH, He QQ, Yao ZY (2023) New taxa of spiders (Araneae) from the world in 2022. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杨蕊含, 闫美辰, 张露丹, 刘宏鑫, 许国丰, 何巧巧, 姚志远 (2023) 2022年世界蜘蛛目新分类单元. 生物多样性, 31, 23175.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Yao ZY, Li SQ (2021) Annual report of Chinese spider taxonomy in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1058-1063. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚志远, 李枢强 (2021) 2020年中国蜘蛛分类年报. 生物多样性, 29, 1058-1063.] | |
| [25] |
Zhang LD, Lu Y, Chu C, He QQ, Yao ZY (2022) New spider taxa of the world in 2021. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张露丹, 卢影, 褚畅, 何巧巧, 姚志远 (2022) 2021年世界蜘蛛新分类单元. 生物多样性, 30, 22163.]
DOI |
|
| [26] |
Zhang LD, Wu Z, Li SQ, Yao ZY (2024) Eight new spider species of Belisana Thorell, 1898 (Araneae, Pholcidae), with an updated overview of Belisana species from Yunnan, China. ZooKeys, 1202, 255-286.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Zonstein SL (2024) A revision of the spider genus Raveniola (Araneae, Nemesiidae). II. Species from Central Asia. European Journal of Taxonomy, 967, 1-185.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 韩群力. 关于联合国教科文组织人与生物圈计划及世界生物圈保护区网络未来优先行动的建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(9): 25144-. |
| [2] | 李彬彬, 葛蕴丰, 吴舒尧, 华方圆, 米湘成, 曾玉红. 中国长江流域生态恢复回顾与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(9): 25291-. |
| [3] | 岳可欣, 牛钟辉, 刘念, 徐琳, 吕韦韦, 徐茂宏, 崔绍朋. 山西历山三种同域分布食肉动物昼夜活动节律及与月光周期的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(9): 25084-. |
| [4] | 武慧, 俞乐, 赵剑桥, 郑诗军, 刘涛, 戚文超, 赵强, 朱丽, 申小莉, 马克平. 世界生物圈保护区网络生态代表性与保护成效的南北差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(9): 25267-. |
| [5] | 王凤英, 吴增源, 崔涵, 李垠蕾, 邓莉娟, 王红, 刘杰. 第三极荨麻属麻叶荨麻分支的物种界限[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25138-. |
| [6] | 范平, 王欢, 温知新, 宋刚, 雷富民. 气候因子对鸟类遗传多样性与物种分布面积关系的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25072-. |
| [7] | 王儒晓, 史博洋, 潘达, 孙红英. 中国特有华溪蟹属淡水蟹多样性格局及其保护空缺[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25123-. |
| [8] | 彭欣, 刘传, 黄晓磊. 基于GenBank数据库的真核生物遗传数据时空格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25184-. |
| [9] | 冯缨, 宋凤, 金光照, 葛学军. 中亚荒漠区沙拐枣属的分布格局与物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25086-. |
| [10] | 李基才, 邵长亮, 高帅帅, 李佳. 新疆卡拉麦里国家公园候选区蒙古野驴夏季水源利用规律、活动范围和适宜生境分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24509-. |
| [11] | 钱嘉宁. 履行就地保护义务的投资仲裁风险及应对[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24333-. |
| [12] | 时永强, 单秀娟, 赵杰, 王一诺, 栾青杉, 卞晓东, 陈云龙, 金显仕. 1958-2020年黄河口及其邻近海域浮游动物群落组成及多样性演变[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24437-. |
| [13] | 陈耀辉, 周梓华, 邱洪, 张敬怀. 广东省海岸带牡蛎礁的分布特征、主要威胁及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24414-. |
| [14] | 蓝贤娜, 李亦欣, 海路瑶, 骆正伟, 金学林, 秦兴虎, 胡德夫, 刘刚. 华北区野生麝类的分子鉴定及分布现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24505-. |
| [15] | 董雪云, 夏富才, 周繇, 张立秋, 何怀江, 刘冰, 姜润华, 王洪峰. 吉林省野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 25120-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn