



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 25149. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025149 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025149
李慧霞1,2, 李玉1, 宁馨1, 李晓晨1, 王天瑞1, 宋以刚1, 戴锡玲2, 郑斯斯1,*( ), 钟鑫1,*(
), 钟鑫1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-27
接受日期:2025-08-12
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-09-30
通讯作者:
*共同通讯作者E-mail: zhengsisi1228@163.com;zhongxin@csnbgsh.cn
基金资助:
Huixia Li1,2, Yu Li1, Xin Ning1, Xiaochen Li1, Tianrui Wang1, Yigang Song1, Xiling Dai2, Sisi Zheng1,*( ), Xin Zhong1,*(
), Xin Zhong1,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-27
Accepted:2025-08-12
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-30
Contact:
*Co-authors for correspondence. E-mail: zhengsisi1228@163.com;zhongxin@csnbgsh.cn
Supported by:摘要:
江南牡丹草(Gymnospermium kiangnanense)是分布于安徽和浙江的中国特有濒危植物, 已被纳入当地的珍稀濒危植物名录, 然而对其种群间遗传结构的相关研究较少。为了加强对江南牡丹草的保护, 本研究通过组装6个种群39个个体的叶绿体基因组序列并对其进行比较基因组学分析和种群遗传结构分析, 探讨了对江南牡丹草的保护策略。结果表明: (1)江南牡丹草叶绿体基因组在序列组成、基因结构和基因含量等方面都高度保守, 其中简单重复序列(simple sequence repeats, SSRs)类型表现出明显的种群特征; (2)叶绿体基因组中3个非编码区域: psbZ与trnG-GCC的间隔区(psbZ-trnG-GCC)、trnT-UGU与trnL-UAA的间隔区(trnT-UGU-trnL-UAA)以及ycf1与ndhF的间隔区(ycf1-ndhF), 均表现出较高的变异性, 同时ndhF具有较高的核苷酸多样性, 可作为潜在的分子标记; (3)叶绿体基因组具有较高的遗传多样性, 且种群间具有较高的遗传分化; (4) 6个种群39个个体的叶绿体基因组序列计算得出14个单倍型, 经过Network分析和Beast分析可以划分为3个支系; (5)江南牡丹草种群间的变异大, 且具有明显的谱系地理结构; (6)通过种群历史动态分析发现, 江南牡丹草种群未发生扩张, 一直处于平衡状态。江南牡丹草以异交的繁殖方式增加遗传变异、减少近交衰退, 再加上在中国东部存在的第四纪冰期避难所为其提供了稳定的生存环境, 因而其种群的遗传多样性较高。结实率低、种子扩散能力弱以及过度的人为活动可能是导致其濒危的主要原因, 因此通过对江南牡丹草叶绿体基因组的分析结合保护遗传学提出如下保护建议: (1)按支系划分3个保护单元, 重点保护浙江诸暨凤林下村种群, 设立保护小区; (2)在其花期进行人工放蜂, 增加传粉率和结实率; (3)降低群落的种群密度以改善光照, 促进幼苗生长; (4)在就地保护基础上, 于适宜植物园开展迁地保护与人工繁育; (5)加强科普宣传, 减少人为破坏; (6)合理利用其药用价值, 促进人工繁育与保护。
李慧霞, 李玉, 宁馨, 李晓晨, 王天瑞, 宋以刚, 戴锡玲, 郑斯斯, 钟鑫 (2025) 基于叶绿体基因组的江南牡丹草遗传多样性与遗传结构. 生物多样性, 33, 25149. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025149.
Huixia Li, Yu Li, Xin Ning, Xiaochen Li, Tianrui Wang, Yigang Song, Xiling Dai, Sisi Zheng, Xin Zhong (2025) Genetic diversity and genetic structure of Gymnospermium kiangnanense based on chloroplast genome. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25149. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025149.
| 采集地 Locality | 种群代码 Population code | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 个体数量 Number of individuals | 单倍型(个体数) Haplotype (number of individuals) | h | π |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安徽池州贵池石门村 Shimen Village, Guichi, Chizhou, Anhui | AGS | 117.75° E | 30.33° N | 253.67 | 4 | H1 (3), H2 (1) | 0.50 | 0.003 |
| 浙江杭州淳安菖蒲村 Changpu Village, Chun’an, Hangzhou, Zhejiang | ZCC | 119.13° E | 29.95° N | 124.00 | 8 | H3 (8) | 0 | 0 |
| 浙江杭州西湖仙桥洞 Xianqiao Cave, West Lake, Hangzhou, Zhejiang | ZHL | 120.03° E | 30.11° N | 708.24 | 8 | H4 (8) | 0 | 0 |
| 浙江临安河桥陆平下村 Lupingxia Village, Heqiao, Lin’an, Zhejiang | ZLH | 119.27° E | 30.11° N | 557.88 | 3 | H5 (1), H6 (2) | 0.67 | 0.0026 |
| 浙江诸暨半丘村 Banqiu Village, Zhuji, Zhejiang | ZZB | 120.29° E | 29.45° N | 524.58 | 8 | H7 (3), H8 (1), H9 (4) | 0.68 | 0.0023 |
| 浙江诸暨凤林下村 Fenglinxia Village, Zhuji, Zhejiang | ZZF | 120.25° E | 29.51° N | 155.47 | 8 | H10 (1), H11 (2), H12 (2), H13 (1), H14 (2) | 0.89 | 0.0049 |
表1 江南牡丹草样品采集信息和遗传多样性
Table 1 Collection information and genetic diversity of Gymnospermium kiangnanense
| 采集地 Locality | 种群代码 Population code | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 个体数量 Number of individuals | 单倍型(个体数) Haplotype (number of individuals) | h | π |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安徽池州贵池石门村 Shimen Village, Guichi, Chizhou, Anhui | AGS | 117.75° E | 30.33° N | 253.67 | 4 | H1 (3), H2 (1) | 0.50 | 0.003 |
| 浙江杭州淳安菖蒲村 Changpu Village, Chun’an, Hangzhou, Zhejiang | ZCC | 119.13° E | 29.95° N | 124.00 | 8 | H3 (8) | 0 | 0 |
| 浙江杭州西湖仙桥洞 Xianqiao Cave, West Lake, Hangzhou, Zhejiang | ZHL | 120.03° E | 30.11° N | 708.24 | 8 | H4 (8) | 0 | 0 |
| 浙江临安河桥陆平下村 Lupingxia Village, Heqiao, Lin’an, Zhejiang | ZLH | 119.27° E | 30.11° N | 557.88 | 3 | H5 (1), H6 (2) | 0.67 | 0.0026 |
| 浙江诸暨半丘村 Banqiu Village, Zhuji, Zhejiang | ZZB | 120.29° E | 29.45° N | 524.58 | 8 | H7 (3), H8 (1), H9 (4) | 0.68 | 0.0023 |
| 浙江诸暨凤林下村 Fenglinxia Village, Zhuji, Zhejiang | ZZF | 120.25° E | 29.51° N | 155.47 | 8 | H10 (1), H11 (2), H12 (2), H13 (1), H14 (2) | 0.89 | 0.0049 |
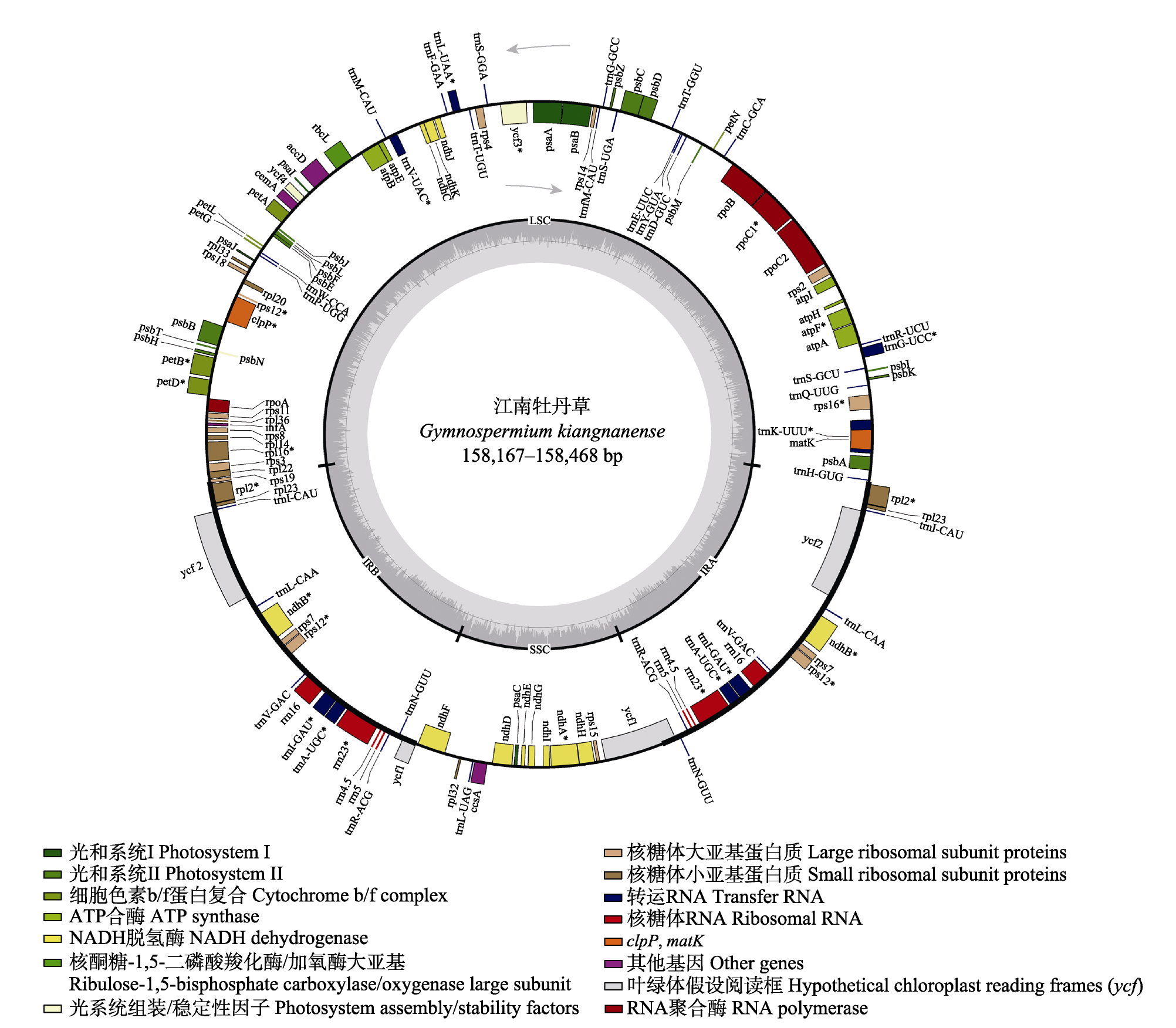
图1 江南牡丹草叶绿体基因组的基因图谱。箭头表示转录方向, 外环基因沿逆时针转录, 内环基因沿顺时针转录。*表示基因含有内含子。内部浅色区域表示GC含量, 深色区域表示AT含量。
Fig. 1 Gene map of Gymnospermium kiangnanense chloroplast genome. The arrow indicates the transcription direction, with outer loop genes transcribed counterclockwise and inner loop genes transcribed clockwise. * denotes that the gene contains introns. The light colored areas inside indicate GC content, while the dark colored areas indicate AT content.
| 基因分类 Genetic classification | 基因分组 Group of gene | 基因名称 Name of genes |
|---|---|---|
| 光合作用相关基因 Photosynthesis-related genes | 光合系统I Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| 光合系统II Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| NADH脱氢酶 NADPH dehydrogenase | ndhA*, ndhB*(2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| 细胞色素b/f蛋白复合体 Cytochrome b/f protein complex | petA, petB*, petD*, petG, petL, petN | |
| ATP合酶 ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF*, atpH, atpI | |
| 核糖体大亚基 Large ribosomal subunit | rbcL | |
| 转录翻译相关基因 Transcription- and translation-related genes | 核糖体大亚基蛋白质 Large ribosomal subunit proteins | rpl14, rpl16*, rpl2*(2), rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| 核糖体小亚基蛋白质 Small ribosomal subunit proteins | rps11, rps12**(2), rps14, rps15, rps16*, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8 | |
| RNA聚合酶亚基 RNA polymerase subunit | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1*, rpoC2 | |
| 核糖体RNA Ribosomal RNA | rrn16(2), rrn23(2), rrn4.5(2), rrn5(2) | |
| 转运RNA Transfer RNA | trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC*, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnK-UUU*, trnL-CAA(2), trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(2), trnV-UAC*, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU | |
| 物质合成相关基因 Biosynthesis-related genes | 成熟酶 Maturase | matK |
| 蛋白酶 Protease | clpP** | |
| 包裹膜蛋白 Envelop membrane protein | cemA | |
| 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | |
| c型细胞色素合成基因 c-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA | |
| 转录起始因子 Transcription initiation factors | infA | |
| 未知功能基因 Uncharacterized genes | 保守的叶绿体假设开放阅读框 Conserved hypothetical chloroplast open reading frames | ycf1(2), ycf2(2), ycf3**, ycf4 |
表2 江南牡丹草叶绿体基因组注释基因
Table 2 Annotation genes of Gymnospermium kiangnanense chloroplast genome
| 基因分类 Genetic classification | 基因分组 Group of gene | 基因名称 Name of genes |
|---|---|---|
| 光合作用相关基因 Photosynthesis-related genes | 光合系统I Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| 光合系统II Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| NADH脱氢酶 NADPH dehydrogenase | ndhA*, ndhB*(2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| 细胞色素b/f蛋白复合体 Cytochrome b/f protein complex | petA, petB*, petD*, petG, petL, petN | |
| ATP合酶 ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF*, atpH, atpI | |
| 核糖体大亚基 Large ribosomal subunit | rbcL | |
| 转录翻译相关基因 Transcription- and translation-related genes | 核糖体大亚基蛋白质 Large ribosomal subunit proteins | rpl14, rpl16*, rpl2*(2), rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| 核糖体小亚基蛋白质 Small ribosomal subunit proteins | rps11, rps12**(2), rps14, rps15, rps16*, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8 | |
| RNA聚合酶亚基 RNA polymerase subunit | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1*, rpoC2 | |
| 核糖体RNA Ribosomal RNA | rrn16(2), rrn23(2), rrn4.5(2), rrn5(2) | |
| 转运RNA Transfer RNA | trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC*, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnK-UUU*, trnL-CAA(2), trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(2), trnV-UAC*, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU | |
| 物质合成相关基因 Biosynthesis-related genes | 成熟酶 Maturase | matK |
| 蛋白酶 Protease | clpP** | |
| 包裹膜蛋白 Envelop membrane protein | cemA | |
| 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | |
| c型细胞色素合成基因 c-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA | |
| 转录起始因子 Transcription initiation factors | infA | |
| 未知功能基因 Uncharacterized genes | 保守的叶绿体假设开放阅读框 Conserved hypothetical chloroplast open reading frames | ycf1(2), ycf2(2), ycf3**, ycf4 |
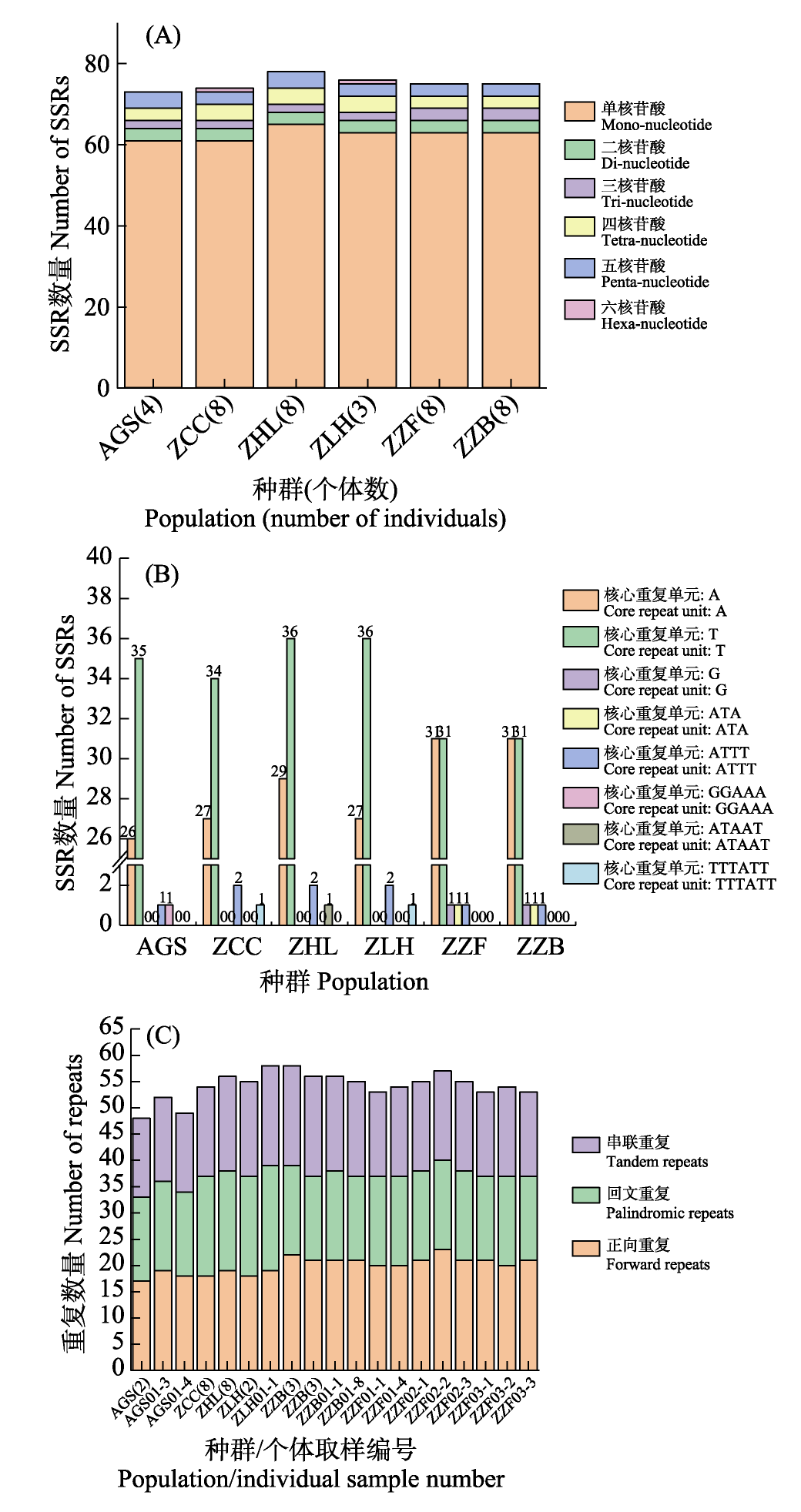
图2 江南牡丹草叶绿体基因组重复序列分析。(A)不同核心重复单元的核苷酸数量的SSRs数量; (B)不同核心重复单元的SSRs数量; (C)正向重复、回文重复和串联重复数量。种群代码见表1。
Fig. 2 Analysis of chloroplast genome repeat sequences in Gymnospermium kiangnanense. (A) Number of SSRs by nucleotide count of the core repeat unit; (B) Number of SSRs by type of core repeat motif; (C) Number of forward, palindromic, and tandem repeats. The population codes see Table 1.
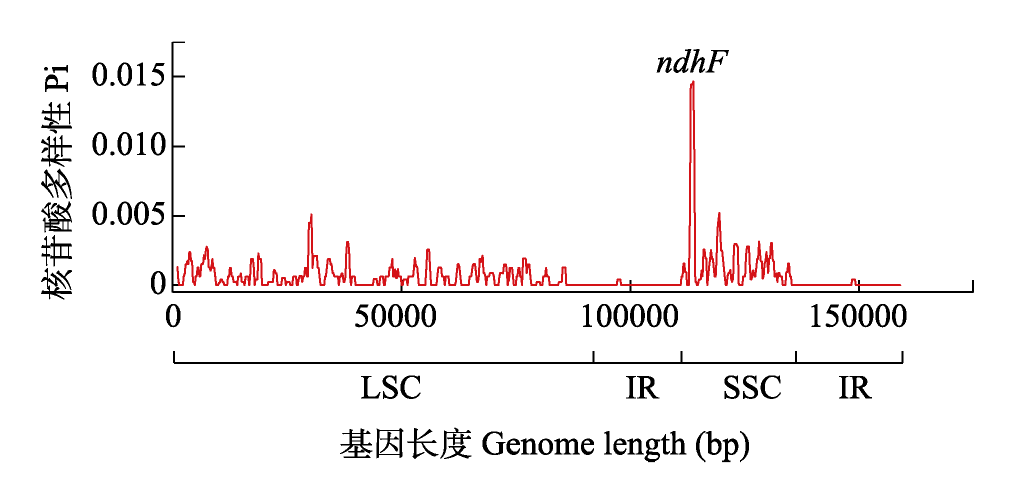
图3 江南牡丹草叶绿体基因组的核苷酸多样性(Pi)。LSC: 大单拷贝区; SSC: 小单拷贝区; IR: 反向重复区。
Fig. 3 Nucleotide diversity (Pi) of Gymnospermium kiangnanense chloroplast genome. LSC, Large single copy; SSC, Small single copy; IR, Inverted repeat.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 Sum of squares | 变异成分 Variance components | 变异率 Percentage of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种群间 Among populations | 5 | 2,430.279 | 76.38595 | 99.58 |
| 种群内 Within populations | 33 | 10.542 | 0.31944 | 0.42 |
| FST | 0.99584 | |||
表3 江南牡丹草种群的分子方差分析
Table 3 Molecular variance analysis of Gymnospermium kiangnanense populations
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 平方和 Sum of squares | 变异成分 Variance components | 变异率 Percentage of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种群间 Among populations | 5 | 2,430.279 | 76.38595 | 99.58 |
| 种群内 Within populations | 33 | 10.542 | 0.31944 | 0.42 |
| FST | 0.99584 | |||
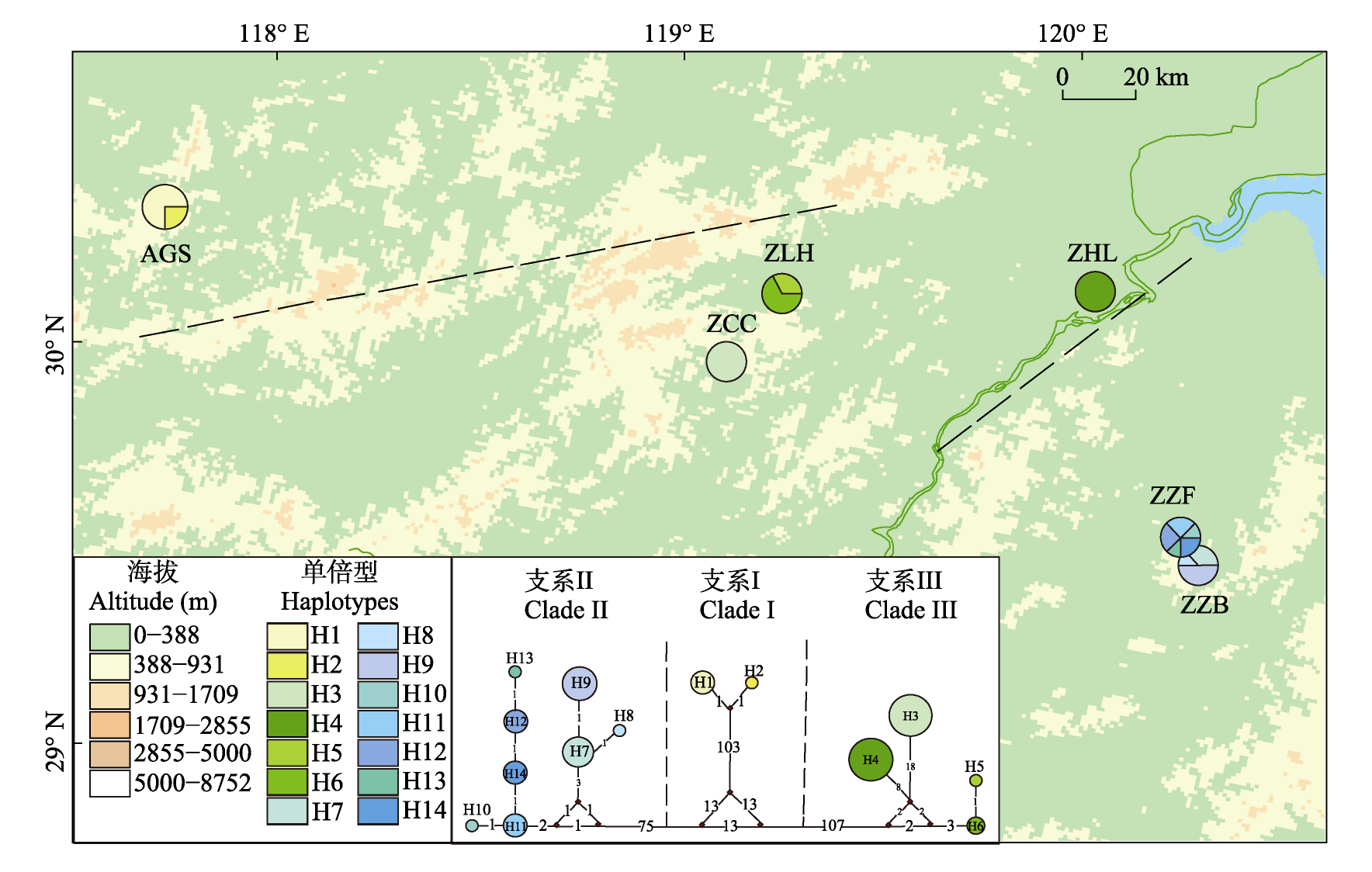
图4 江南牡丹草14个叶绿体单倍型支系关系与地理分布。彩色饼图对应各单倍型及其比例; 虚线表示地理屏障。种群代码见表1。
Fig. 4 Geographical distribution and network of 14 cpDNA haplotypes detected from Gymnospermium kiangnanense. The colored pie charts representing the frequency of haplotype occurrence of each sampling site. The dashed line represents a geographical barrier. Population code see Table 1.
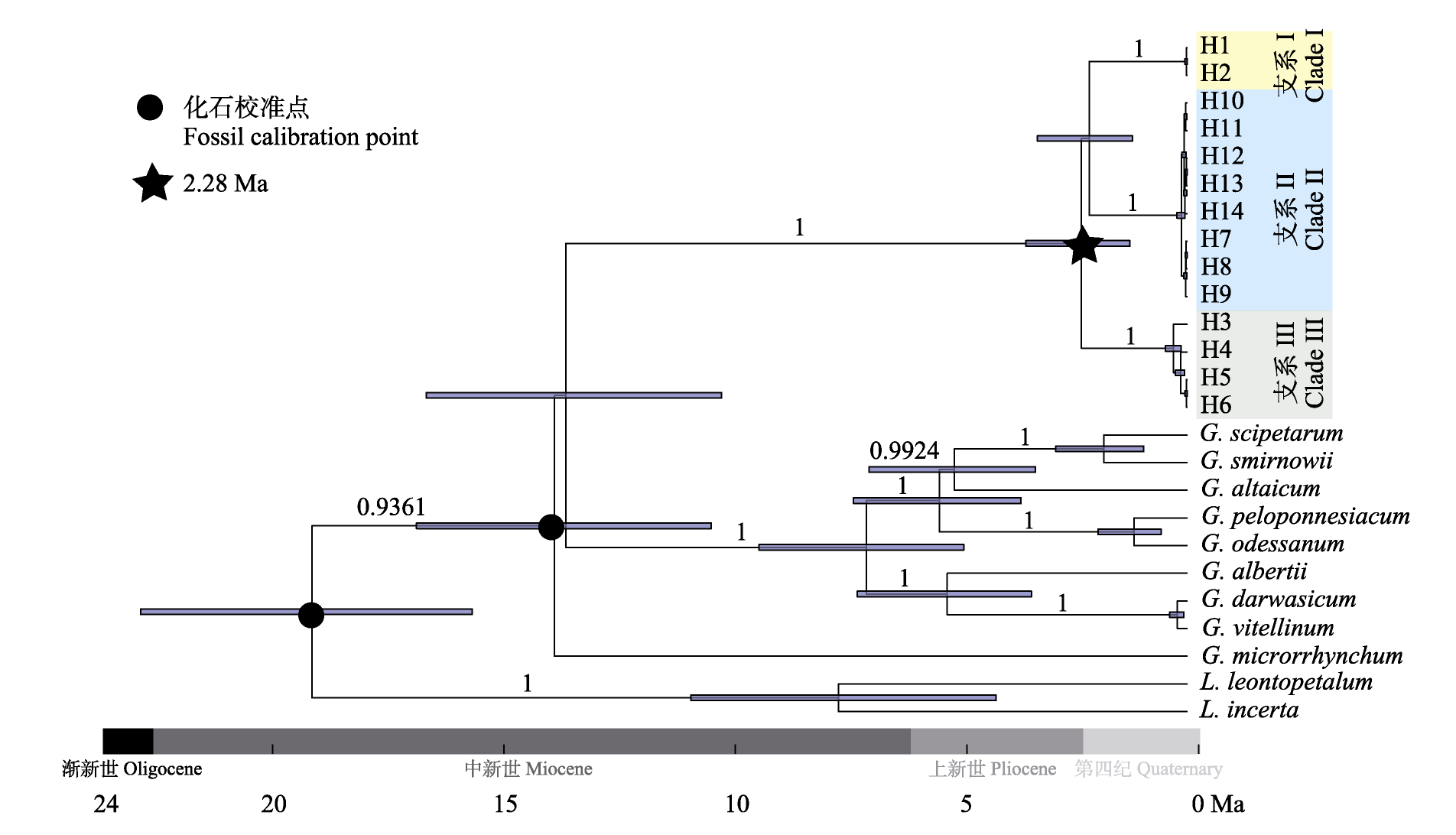
图5 江南牡丹草叶绿体单倍型的系统发育分析。不同颜色的区块表示不同的支系。分化支上标注的数字表示支持率(%)。
Fig. 5 Phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast haplotypes in Gymnospermium kianganese. Different colors of blocks represent different lineages. Support values (%) are shown on the clades.
| [1] |
Abdullah, Shahzadi I, Mehmood F, Ali Z, Malik MS, Waseem S, Mirza B, Ahmed I, Waheed MT (2019) Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes among three Firmiana species: Identification of mutational hotspots and phylogenetic relationship with other species of Malvaceae. Plant Gene, 19, 100199.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Amiryousefi A, Hyvönen J, Poczai P (2018) IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics, 34, 3030-3031.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
An ZS, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature, 411, 62-66.
DOI |
| [4] |
Antil S, Abraham JS, Sripoorna S, Maurya S, Dagar J, Makhija S, Bhagat P, Gupta R, Sood U, Lal R, Toteja R (2023) DNA barcoding, an effective tool for species identification: A review. Molecular Biology Reports, 50, 761-775.
DOI |
| [5] | Axelrod D, Al Shenbaz I, Raven PH (1998) History of the modern flora of China. In: Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants: Proceedings of the First International Symposium of Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants (eds Zhang AL, Wu SG), pp. 43-55. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [6] |
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl AA (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 27, 573-580.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Breslauer KJ, Frank R, Blcker H, Marky LA (1986) Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 83, 3746-3750. |
| [9] |
Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT (2004) Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Research, 14, 1394-1403.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Darriba D, Taboada G, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 9, 772.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
De Kort H, Prunier JG, Ducatez S, Honnay O, Baguette M, Stevens VM, Blanchet S (2021) Life history, climate and biogeography interactively affect worldwide genetic diversity of plant and animal populations. Nature Communications, 12, 516.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Deng M, Jiang XL, Hipp AL, Manos PS, Hahn M (2018) Phylogeny and biogeography of East Asian evergreen oaks (Quercus section Cyclobalanopsis; Fagaceae): Insights into the Cenozoic history of evergreen broad-leaved forests in subtropical Asia. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 119, 170-181.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Dobrogojski J, Adamiec M, Luciński R (2020) The chloroplast genome: A review. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 42, 98.
DOI |
| [14] | Dong WP, Liu J, Yu J, Wang L, Zhou SL (2012) Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE, 7, e35071. |
| [15] |
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 1969-1973.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Excoffier L, Lischer H (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10, 564-567.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Finger A, Kettle CJ, Kaiser-Bunbury CN, Valentin T, Doudee D, Matatiken D, Ghazoul J (2011) Back from the brink: Potential for genetic rescue in a critically endangered tree. Molecular Ecology, 20, 3773-3784. |
| [18] | Frankham R, Ballou JD, Briscoe DA (2002) Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [19] | Frazer KA, Pachter L, Poliakov A, Rubin EM, Dubchak I (2004) VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, W273-W279. |
| [20] |
Fu YX (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics, 147, 915-925.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Gao YW, Liu KJ, Li EZ, Wang YS, Xu C, Zhao LC, Dong WP (2022) Dynamic evolution of the plastome in the Elm family (Ulmaceae). Planta, 257, 14.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Gong W, Chen C, Dobeš C, Fu CX, Koch MA (2008) Phylogeography of a living fossil: Pleistocene glaciations forced Ginkgo biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae) into two refuge areas in China with limited subsequent postglacial expansion. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48, 1094-1105.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
González-Astorga J, Castillo-Campos G (2004) Genetic variability of the narrow endemic tree Antirhea aromatica Castillo-Campos & Lorence, (Rubiaceae, Guettardeae) in a tropical forest of Mexico. Annals of Botany, 93, 521-528.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Goulding SE, Wolfe KH, Olmstead RG, Morden CW (1996) Ebb and flow of the chloroplast inverted repeat. Molecular and General Genetics, 252, 195-206.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Harpending HC (1994) Signature of ancient population growth in a low-resolution mitochondrial DNA mismatch distribution. Human Biology, 66, 591-600.
PMID |
| [26] |
Heber U (1962) Protein synthesis in chloroplasts during photosynthesis. Nature, 195, 91-92.
DOI |
| [27] |
Hewitt GM (2004) Genetic consequences of climatic oscillations in the quaternary. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 359, 183-195.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Jiang FC, Wu XH (1993) Fundamental characteristics of the stepped landform in China continent. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 13, 15-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋复初, 吴锡浩 (1993) 中国大陆阶梯地貌的基本特征. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 13, 15-24.] | |
| [29] |
Jin JJ, Yu WB, Yang JB, Song Y, DePamphilis CW, Yi TS, Li DZ (2020) GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biology, 21, 241.
DOI |
| [30] |
Kim KJ, Lee HL (2004) Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Research, 11, 247-261.
PMID |
| [31] |
Kou Y, Cheng S, Tian S, Li B, Fan D, Chen Y, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Zhang Z (2016) The antiquity of Cyclocarya paliurus (Juglandaceae) provides new insights into the evolution of relict plants in subtropical China since the late Early Miocene. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 351-360.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 7, 1870-1874. |
| [33] |
Kusnetsov VV (2018) Chloroplasts: Structure and expression of the plastid genome. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 65, 465-476.
DOI |
| [34] |
Lande R (1988) Genetics and demography in biological conservation. Science, 241, 1455-1460.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Li EZ, Liu KJ, Deng RY, Gao YW, Liu XY, Dong WP, Zhang ZX (2023) Insights into the phylogeny and chloroplast genome evolution of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae). BMC Plant Biology, 8, 23, 32.
DOI |
| [36] |
Li YY, Guan SM, Yang SZ, Luo Y, Chen XY (2012) Genetic decline and inbreeding depression in an extremely rare tree. Conservation Genetics, 13, 343-347.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Liu X, Wang M, Song S, Ma Q, Yang Z (2024) Population structure and diversification of Gymnospermium kiangnanense, a plant species with extremely small populations endemic to eastern China. PeerJ, 12, e17554. |
| [38] |
López-Pujol J, Zhang F, Sun H, Ying TS, Ge S (2011) Centres of plant endemism in China: Places for survival or for speciation? Journal of Biogeography, 38, 1267-1280.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Lu L, Mao L, Yang T, Ye J, Liu B, Li H, Sun M, Miller JT, Mathews S, Hu H, Niu Y, Peng D, Chen Y, Smith SA, Chen M, Xiang K, Le CT, Dang V, Lu A, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Li J, Chen Z (2018) Evolutionary history of the angiosperm flora of China. Nature, 554, 234-238.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Lu ZH, Liao MC, Wang LJ (2010) Effect of Leontice kiangnanensis total alkaloids on swelling and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Traumatology & Orthopedics, 18(11), 4-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢振华, 廖矛川, 王丽君 (2010) 江南牡丹草总生物碱对大白鼠佐剂关节炎继发肿胀及血沉升高治疗作用的实验研究. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 18(11), 4-6.] | |
| [41] |
Lyttleton JW (1962) Isolation of ribosomes from spinach chloroplasts. Experimental Cell Research, 26, 312-317.
PMID |
| [42] | Mahadani P, Dasgupta M, Vijayan J, Kar CS, Ray S (2022) DNA barcoding in plants:Past, present, and future. In: Plant Genomics for Sustainable Agriculture (eds Singh RL, Mondal S, Parihar A, Singh PK), pp.331-350. Springer, Singapore. |
| [43] |
Ohsawa T, Ide Y (2008) Global patterns of genetic variation in plant species along vertical and horizontal gradients on mountains. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 17, 152-163.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Ottewell K, Bickerton D, Byrne M, Lowe AJ (2015) Bridging the gap: A genetic assessment framework for population- level threatened plant conservation prioritization and decision-making. Diversity and Distributions, 22, 174-188.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Palsbøll PJ, Bérubé M, Allendorf FW (2007) Identification of management units using population genetic data. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22, 11-16.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GenALEx 6: Genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Molecular Ecology Notes, 6, 288-295.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Petit RJ, PineauE, Demesure B, Bacilieri R, Ducousso A, Kremer A (1997) Chloroplast DNA footprints of postglacial recolonization by oaks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 94, 9996-10001. |
| [48] |
Pons O, Petit RJ (1996) Measuring and testing genetic differentiation with ordered versus unordered alleles. Genetics, 144, 1237-1245.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Qiu BL (1980) Plantae Novae ex Provincia Zhejiang (Chekiang). Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 18, 96-97. (in Chinese) |
| [裘宝林 (1980) 浙江的新植物. 植物分类学报, 18, 96-97.] | |
| [50] | Qiu YX, Lu QX, Zhang YH, Cao YN (2017) Phylogeography of East Asia’s Tertiary relict plants: Current progress and future prospects. Biodiversity Science, 25, 136-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[邱英雄, 鹿启祥, 张永华, 曹亚男 (2017) 东亚第三纪孑遗植物的亲缘地理学: 现状与趋势. 生物多样性, 25, 136-146.]
DOI |
|
| [51] |
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwisegenetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9, 552.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A (2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 3299-3302.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Sexton JP, Hufford MB, Bateman AC, Lowry DB, Meimberg H, Strauss SY, Rice KJ (2016) Climate structures genetic variation across a species’ elevation range: A test of range limits hypotheses. Molecular Ecology, 25, 911-928. |
| [54] | Shi C, Liu Y, Huang H, Xia EH, Zhang HB, Gao LZ (2013) Contradiction between plastid gene transcription and function due to complex posttranscriptional splicing: An exemplary study of ycf15 function and evolution in angiosperms. PLoS ONE, 8, e59620. |
| [55] |
Shu JW, Wang WM (2012) A unique Middle Pleistocene beech (Fagus)-rich deciduous broad-leaved forest in the Yangtze Delta Plain, East China: Its climatic and stratigraphic implication. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 56, 180-190.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Song SQ, Zubov D, Comes HP, Li HW, Liu XL, Zhong X, Lee JK, Yang ZP, Li P (2022) Plastid phylogenomics and plastome evolution of Nandinoideae (Berberidaceae). Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 913011.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Suchard M, Lemey P, Baele G, Ayres D, Drummond A, Rambaut A (2018) Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evolution, 4, vey016. |
| [58] |
Sun XJ, Wang PX (2005) How old is the Asian monsoon system? Palaeobotanical records from China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 222, 181-222.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Sun ZS (2016) Studies of Phylogeny and Phylogeography of Smilax china Complex in East Asia. PhD dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙中帅 (2016) 东亚菝葜复合种(Smilax china complex)系统发育及谱系地理研究. 博士学位论文, 浙江大学, 杭州.] | |
| [60] |
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics, 123, 585-595.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Tillich M, Lehwark P, Pellizzer T, Ulbricht-Jones ES, Fischer A, Bock R, Greiner S (2017) GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, W6-W11. |
| [62] | Wen YF, Han WJ, Wu S (2010) Plant genetic diversity and its influencing factors. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 30(12), 80-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [文亚峰, 韩文军, 吴顺 (2010) 植物遗传多样性及其影响因素. 中南林业科技大学学报, 30(12), 80-87.] | |
| [63] |
Willi Y, Van Buskirk J, Hoffmann AA (2006) Limits to the adaptive potential of small populations. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 37, 433-458.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Xu L, Wang H, La Q, Lu F, Sun K, Fang Y, Yang M, Zhong Y, Wu QH, Chen JK, Birks J, Zhang WJ (2014) Microrefugia and shifts of Hippophae tibetana (Elaeagnaceae) on the north side of Mt. Qomolangma (Mt. Everest) during the last 25000 years. PLoS ONE, 9, e97601. |
| [65] |
Yang JX, Hu GX, Hu GW (2022) Comparative genomics and phylogenetic relationships of two endemic and endangered species (Handeliodendron bodinieri and Eurycorymbus cavaleriei) of two monotypic genera within Sapindales. BMC Genomics, 23, 27.
DOI |
| [66] | Yang YC, Zhou T, Duan D, Yang J, Feng L, Zhao GF (2016) Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of five Quercus species. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 959. |
| [67] | Yu QL, Liu SZ, Xu RXM, Pan CH, Yan YM, Wang YY, Xia GH (2021) Population structure and breeding systems of rare and endangered Gymnospermium kiangnanense (Berberidaceae). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48, 539-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[虞钦岚, 刘守赞, 徐韧析谋, 潘晨航, 颜忆铭, 王义英, 夏国华 (2021) 珍稀濒危植物江南牡丹草种群结构和繁育系统研究. 园艺学报, 48, 539-552.]
DOI |
|
| [68] |
Yu XQ, Gao LM, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Yang JB, Fang L, Yang SX, Li DZ (2017) Insights into the historical assembly of East Asian subtropical evergreen broadleaved forests revealed by the temporal history of the tea family. New Phytologist, 215, 1235-1248.
DOI URL |
| [69] | Yuan N (2015) Comparative Studies of the Genetic Effects of Habitat Fragmentation on Three Different Plant Species. PhD dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁娜 (2015) 生境片断化对三种不同植物种群遗传学影响的比较研究. 博士学位论文, 浙江大学, 杭州.] | |
| [70] |
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Sodmergen (2003) Examination of the cytoplasmic DNA in male reproductive cells to determine the potential for cytoplasmic inheritance in 295 angiosperm species. Plant and Cell Physiology, 44, 941-951.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Zhang X, Sun Y, Landis JB, Zhang J, Yang L, Lin N, Zhang H, Guo R, Li L, Zhang Y, Deng T, Sun H, Wang H (2020) Genomic insights into adaptation to heterogeneous environments for the ancient relictual Circaeaster agrestis (Circaeasteraceae, Ranunculales). New Phytologist, 228, 285-301.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Zhang YJ, Du LW, Liu A, Chen JJ, Wu L, Hu WM, Zhang W, Kim K, Lee SC, Yang TJ, Wang Y (2016) The complete chloroplast genome sequences of five Epimedium species: Lights into phylogenetic and taxonomic analyses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 306. |
| [73] |
Zhang ZY, Wu R, Wang Q, Zhang ZR, López-Pujol J, Fan DM, Li DZ (2013) Comparative phylogeography of two sympatric beeches in subtropical China: Species-specific geographic mosaic of lineages. Ecology and Evolution, 3, 4461-4472.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Zhao R, He Q, Chu X, He A, Zhang Y, Zhu Z (2024) Regional environmental differences significantly affect the genetic structure and genetic differentiation of Carpinus tientaiensis Cheng, an endemic and extremely endangered species from China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 15, 1277173.
DOI URL |
| [75] | Zhou S, Li J, Zhao J, Wang J, Zheng J (2011) Quaternary glaciations: Extent and chronology in China. Developments in Quaternary Sciences, 15, 981-1002. |
| [1] | 旦增尼玛, 孙伟, 李聪, 张纾意, 赵竹楠, 许永强, 普布卓玛, 罗诗琦, 达娃, 周欣. 西藏吉隆沟地区开花植物叶绿体基因组数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(9): 25270-. |
| [2] | 梁思琪, 张宪春, 卫然. 利用整合分类学方法进行蕨类植物复合体的物种划分: 以线裂铁角蕨复合体为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(11): 1205-1220. |
| [3] | 刘铁燕, 陈明生. 稻属植物的基因组进化[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(1): 51-65. |
| [4] | 徐刚标, 梁艳, 蒋燚, 刘雄盛, 胡尚力, 肖玉菲, 郝博搏. 伯乐树种群遗传多样性及遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(6): 723-731. |
| [5] | 傅洪拓, 乔慧, 姚建华, 龚永生, 吴滟, 蒋速飞, 熊贻伟. 基于SRAP分子标记的海南沼虾种群遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(2): 145-149. |
| [6] | 邱芳, 伏健民, 金德敏, 王斌. 遗传多样性的分子检测[J]. 生物多样性, 1998, 06(2): 143-150. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn