



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 698-703. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019089 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019089
• 保护论坛 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2019-03-19
接受日期:2019-06-08
出版日期:2019-06-20
发布日期:2019-07-08
通讯作者:
蒋志刚
基金资助:Received:2019-03-19
Accepted:2019-06-08
Online:2019-06-20
Published:2019-07-08
Contact:
Jiang Zhigang
摘要:
中国野生动物保护名录包括《国家重点保护野生动物名录》(简称《国家重点保护名录》)、《具有重要生态、科学和社会价值的陆生野生动物名录》》(简称《三有名录》)和地方重点保护野生动物名录(简称地方重点保护名录)。2017年《中华人民共和国野生动物保护法》修订实施后, 《国家重点保护名录》修订工作提上日程。修订《国家重点保护名录》应明确该名录与《三有名录》之间的关系, 前者要突出重点, 体现保护优先和方便管理的原则, 划分中央和地方的保护责任。建议依据物种的濒危属性、特有属性、稀有属性、珍贵属性以及管理属性来确定重点保护野生动物物种的级别。保护名录可以采取将整个属、整个科等较高的分类阶元集体列入原则(Principle of Clump Listing)。当一个亚种、一个种群有显著的进化潜力和确定的分布区时, 也可以应用拆分列入原则(Principle of Splitting Listing), 将其作为管理单位列入物种保护名单。此外, 还应密切跟踪并及时更新物种分类法的变化、制订保护级别的判定标准、编写物种恢复计划指南、制定《国家重点保护名录》修订程序。建议为每一个重点保护物种制定相应的种群和生境恢复计划。根据珍稀濒危野生动物动态管理的需要, 通过定期评估, 及时对列入名录的物种进行升级、降级、删除或维持现有保护等级等处理。
蒋志刚 (2019) 中国重点保护物种名录、标准与管理. 生物多样性, 27, 698-703. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019089.
Jiang Zhigang (2019) China’s key protected species lists, their criteria and management. Biodiversity Science, 27, 698-703. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019089.
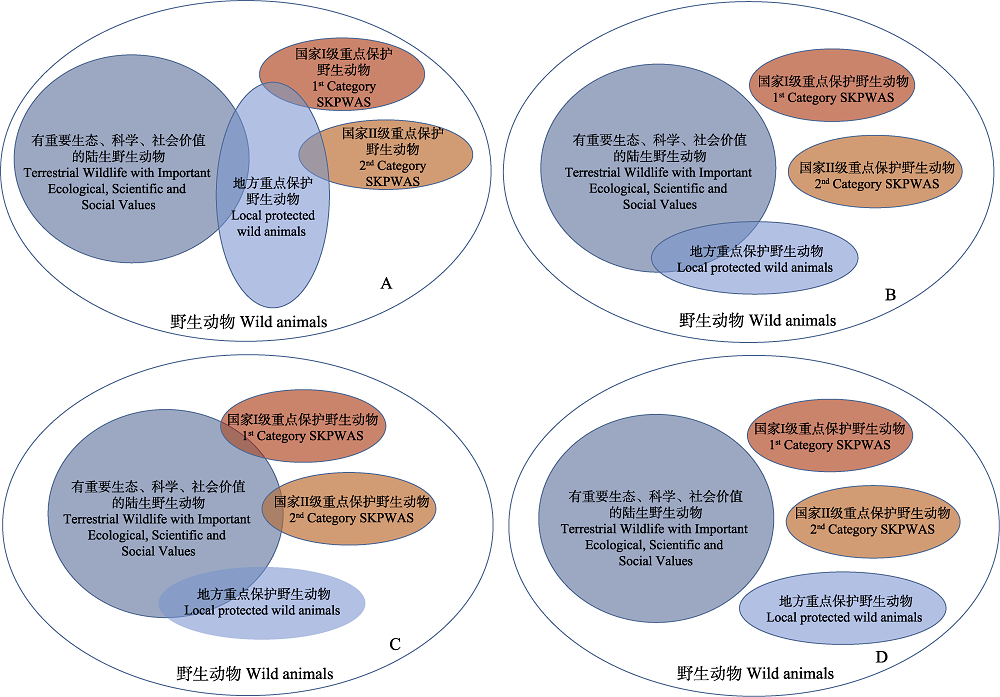
图1 《国家重点保护名录》、地方重点保护名录和《三有名录》的集合关系。图中用集合表示保护名录。部分省级重点保护名录与《国家重点保护名录》、《三有名录》有重叠(A), 多数省级重点保护名录仅与《三有名录》有重叠(B)。事实上, 有重要生态、科学、社会价值是陆生野生动物的共同属性, 三个名录存在着一定的交集(C)。《国家重点保护名录》、《三有名录》和地方重点保护名录应是不同的集合(D)。
Fig. 1 The set relations of the List of State Key Protected Wild Animal Species (SKPWAS), lists of local protected wild animals, and List of Terrestrial Wildlife with Important Ecological, Scientific and Social Values. Different protected species lists are represented as different sets. The lists of local key protected species of some provinces overlap with the List of State Key Protected Species and the List of Terrestrial Wildlife with Important Ecological, Scientific and Social Values (A), while lists of local key protected species in most provinces overlap only with the List of Terrestrial Wildlife with Important Ecological, Scientific and Social Values (B). As a matter of fact, important ecological, scientific and social values are the common attributes of terrestrial wildlife, and the intersection of the three lists exists (C), despite that the three lists should be different sets (D).
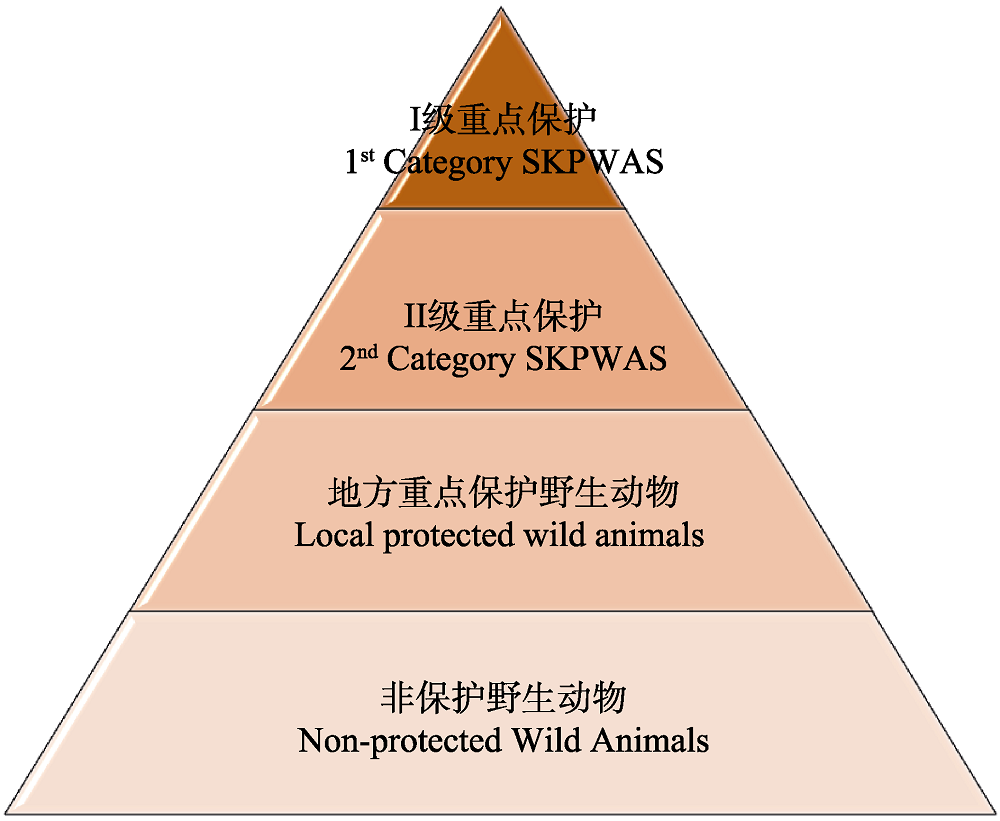
图2 国家与地方重点保护名录之间的集合关系。重要生态、科学、社会价值是陆生野生动物的共同属性, 国家与地方重点保护名录足以区分保护重点。图中三角形的顶点指向保护重要性增加方向。
Fig. 2 The set relationship between the state and local key protection lists. Considering that important ecological, scientific and social values are common attributes of terrestrial wildlife, the lists of state and local key protected species are sufficient to distinguish the key protected species. The top point of the triangle in the figure points to the direction of increasing importance of protection.
| [1] | Apagow PM ( 2007) Species: Demarcation and diversity. In: Phylogeny and Conservation (eds Purvis A, Gittleman JL, Brooks T), pp. 19-56. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [2] |
Apagow PM, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Crandall KA, Gittleman JL, Mace GM, Marshall JC, Purvis A ( 2004) The impact of species concept on biodiversity studies. Quarterly Review of Biology, 79, 161-179.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chu C ( Zhu J ) ( 1974) On the systematic position of the giant panda, Ailuropoda melanoleuca (David). Acta Zoologica Sinica, 20, 174-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱靖 ( 1974) 关于大熊猫分类地位的讨论. 动物学报, 20, 174-183.] | |
| [4] |
Frank EG, Wilcove DS ( 2019) Long delays in banning trade in threatened species. Science, 363, 686-688.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG ( 2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 ( 2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.] | |
| [6] | Jiang ZG, Liu SY, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Zhou KY ( 2017) China’s Mammal Diversity (2nd edn.) Biodiversity Science, 25, 886-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 刘少英, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 周开亚 ( 2017) 中国哺乳动物多样性(第2版). 生物多样性, 25 , 886-895.] | |
| [7] | Jiang ZG ( 2016) On the similarity and dissimilarity of “Endangered Species” and “Protected Species”. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1082-1083. (in Chinese) |
| [ 蒋志刚 ( 2016) 论“濒危物种”与“保护物种”概念的异同. 生物多样性, 24, 1082-1083.] | |
| [8] | Liu DM, Cai L, Wang K, Li JS, Wei TZ, Yao YJ ( 2018) Threat assessments, problems and countermeasures of China’s macrofungi. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1236-1242. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘冬梅, 蔡蕾, 王科, 李俊生, 魏铁铮, 姚一建 ( 2018) 中国野生大型真菌受威胁程度评估、问题和对策. 生物多样性, 26, 1236-1242.] | |
| [9] | Liu J, Que PJ, Zhang ZW ( 2019) Species diversity and suggestions for adjustment of the national protection level of waterbirds in China. Wetland Science, 17, 123-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘金, 阙品甲, 张正旺 ( 2019) 中国水鸟的物种多样性及其国家重点保护等级调整的建议. 湿地科学, 17, 123-136.] | |
| [10] | Ma KP ( 2016) On key issues and possible solutions related to nature reserve management in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 249-251. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平 ( 2016) 当前我国自然保护区管理中存在的问题与对策思考. 生物多样性, 24, 249-251.] | |
| [11] | Mayr E ( 1997) This is Biology: The Science of the Living World. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. |
| [12] | Qin HN, Zhao LN, Yu SX, Liu HY, Liu B, Xia NH, Peng H, Li ZY, Zhang ZX, He XJ, Yin LK, Lin YL, Liu QR, Hou YT, Liu Y, Liu QX, Cao W, Li JQ, Chen SL, Jin XH, Gao TG, Chen WL, Ma HY, Geng YY, Jin XF, Chang CY, Jiang H, Cai L, Zang CX, Wu JY, Ye JF, Lai YJ, Liu B, Lin QW, Xue NX ( 2017) Evaluating the endangerment status of China’s angiosperms through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 25, 745-757. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 覃海宁, 赵莉娜, 于胜祥, 刘慧圆, 刘博, 夏念和, 彭华, 李振宇, 张志翔, 何兴金, 尹林克, 林余霖, 刘全儒, 侯元同, 刘演, 刘启新, 曹伟, 李建强, 陈世龙, 金效华, 高天刚, 陈文俐, 马海英, 耿玉英, 金孝锋, 常朝阳, 蒋宏, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 武建勇, 叶建飞, 赖阳均, 刘冰, 林秦文, 薛纳新 ( 2017) 中国被子植物濒危等级的评估. 生物多样性, 25, 745-757.] | |
| [13] | Wang YX ( 2003) A Complete Checklist of Mammal Species and Subspecies in China: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王应祥 ( 2003) 中国哺乳动物种与亚种分类名录与分布大全. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] | Wilson DE, Reeder DM ( 2005) Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd edn. John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MA. |
| [1] | 易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静. 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [2] | 李沫潼, 何拓, 李薇, 廖菁, 曾岩. 从CITES的术语看野生动植物国际贸易监管规则[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [3] | 何拓, 曾岩, 殷亚方, 张坤, 袁良琛, 董晖, 周志华. 为野生植物保护和可持续贸易奠定科学基础——CITES植物委员会第27次会议评述[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24390-. |
| [4] | 陈金锋, 吴欣静, 林海, 崔国发. 《国家重点保护野生动物名录》和其他保护名录对比分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22639-. |
| [5] | 魏辰, 佟一杰, 曾岩, 白明, 万霞. 警惕物种致危和生物入侵的风险: 我国主要电商平台的甲虫贸易调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22541-. |
| [6] | 牛晓锋, 王晓梅, 张研, 赵志鹏, 樊恩源. 鲟鱼分子鉴定方法的整合应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 22034-. |
| [7] | 刘艳艳, 刘畅, 魏晓新. 我国及周边地区松属白松亚组系统学研究进展和保护现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21344-. |
| [8] | 王文婷, 杨婷婷, 金磊, 蒋家民. 未来气候变化下两种红景天植物的脆弱性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1620-1628. |
| [9] | 李飞, 郑玺, 张华荣, 杨剑焕, 陈辈乐. 广东省珠海市近海诸岛水獭现状与保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(8): 840-846. |
| [10] | 褚建民, 李毅夫, 张雷, 李斌, 高明远, 唐晓倩, 倪建伟, 许新桥. 濒危物种长柄扁桃的潜在分布与保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(8): 799-806. |
| [11] | 董仕勇, 左政裕, 严岳鸿, 向建英. 中国石松类和蕨类植物的红色名录评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(7): 765-773. |
| [12] | 陈军. 实物凭证标本作为命名动物新种必要性条件的挑战:《国际动物命名法规》、物种保护与数码时代[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(11): 1239-1245. |
| [13] | 杨文忠, 向振勇, 张珊珊, 康洪梅, 史富强. 极小种群野生植物的概念及其对我国野生植物保护的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 419-425. |
| [14] | 张大勇, 雷光春, ILKKA HANKI. 集合种群动态:理论与应用[J]. 生物多样性, 1999, 07(2): 81-90. |
| [15] | 贺金生, 林洁, 陈伟烈. 我国珍稀特有植物珙桐的现状及其保护[J]. 生物多样性, 1995, 03(4): 213-221. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
