



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 358-365. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13202 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13202
Special Issue: 生物多样性与生态系统功能
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuanjie Xu1,2( ), Dunmei Lin2, Xiangcheng Mi2, Haibao Ren2, Keping Ma2
), Dunmei Lin2, Xiangcheng Mi2, Haibao Ren2, Keping Ma2
Received:2013-09-17
Accepted:2014-02-22
Online:2014-05-20
Published:2014-06-04
Yuanjie Xu, Dunmei Lin, Xiangcheng Mi, Haibao Ren, Keping Ma. Recovery dynamics of secondary forests with different disturbance intensity in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(3): 358-365.
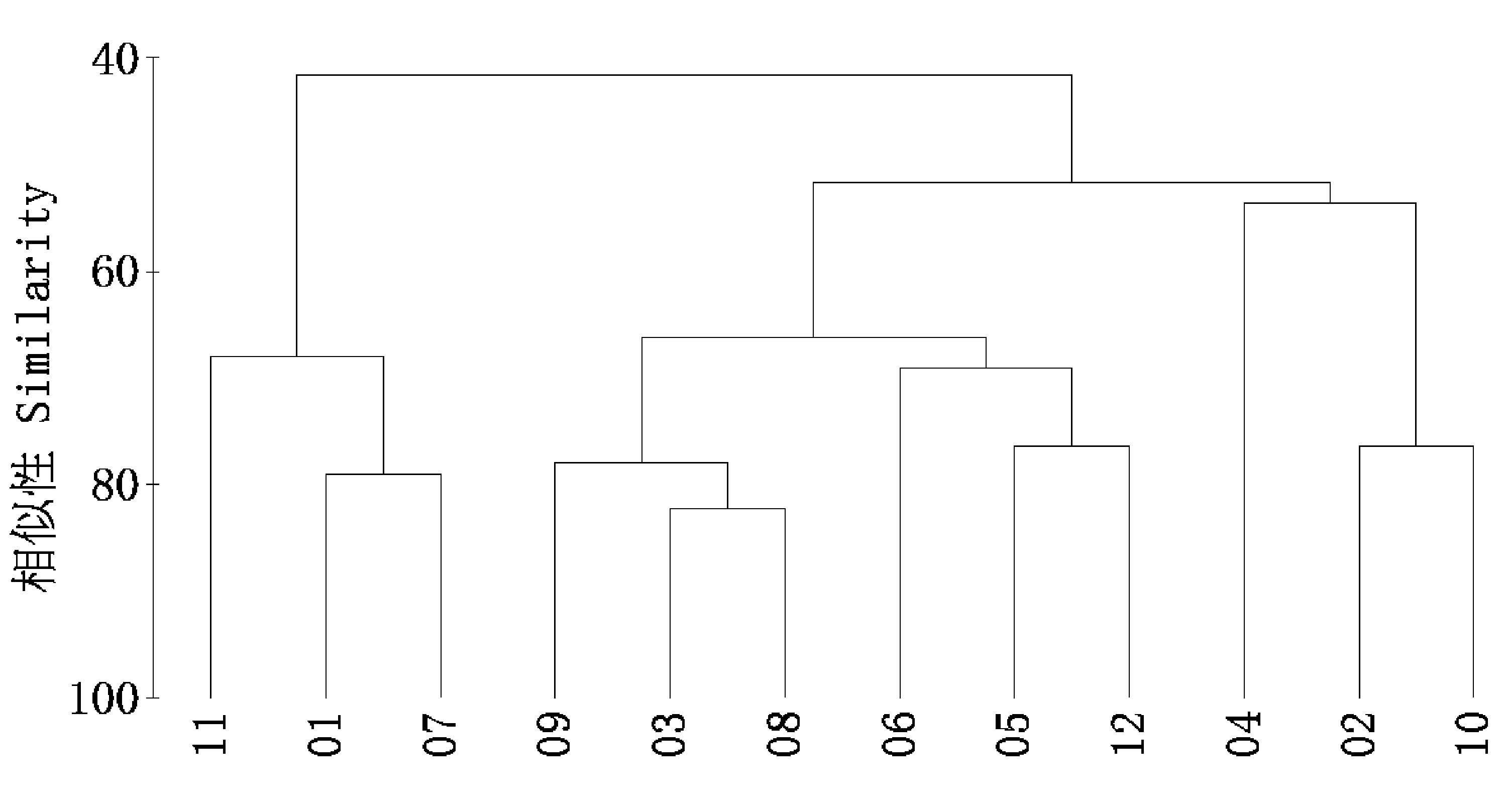
Fig. 1 Hierarchical clustering of 12 forest plots during four recovery phases in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. Chinese fir forest plots include 01, 07, 11; Young secondary forest plots include 03, 08, 09; Old secondary forest plots include 05, 06, 12; Old-growth forest plots include 02, 04, 10.
| 物种名 Species name | 人工林 Chinese fir forests (CFF) | 幼龄次生林 Young secondary forests (YSF) | 老次生林 Old secondary forests (OSF) | 老龄林 Old-growth forests (OGF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 71.27 (25.85) | |||
| 檵木 Loropetalum chinensis | 3.06 (4.69) | 2.70 (2.89) | 6.17 (4.74) | |
| 隔药柃 Eurya muricata | 3.02 (4.68) | 2.78 (3.04) | 2.80 (3.77) | |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 1.71 (3.79) | 7.37 (4.92) | 14.33 (7.55) | |
| 石栎 Lithocarpus glaber | 1.90 (3.54) | 5.32 (3.89) | 7.98 (5.36) | |
| 山合欢 Albizia kalkora | 0.81 (2.82) | |||
| 黄瑞木 Adinandra millettii | 0.77 (2.34) | |||
| 柳叶蜡梅 Chimonanthus salicifolius | 3.05 (2.08) | |||
| 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana | 0.64 (1.98) | |||
| 拟赤杨 Alniphyllum fortunei | 0.59 (1.95) | |||
| 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 23.76 (9.03) | 5.89 (4.31) | 15.69 (8.73) | |
| 米槠 C. carlesii | 9.04 (5.27) | 8.32 (3.43) | ||
| 木荷 Schima superba | 4.56 (3.51) | 11.30 (6.61) | 10.95 (6.25) | |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 3.11 (3.26) | 5.44 (4.86) | ||
| 麂角杜鹃 R. latoucheae | 2.95 (3.18) | 5.36 (5.26) | ||
| 短尾越橘 Vaccinium carlesii | 3.30 (3.04) | |||
| 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 2.52 (2.80) | 5.39 (4.02) | 5.12 (2.53) | |
| 栲 Castanopsis fargesii | 2.18 (2.94 | |||
| 杨梅 Myrica rubra | 2.04 (2.82) | |||
| 浙江红山茶 Camellia chekiangoleosa | 2.43 (2.94) | |||
| 浙江新木姜子 Neolitsea aurata var. chekiangensis | 1.47 (2.81) | |||
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 2.74 (2.46) | |||
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 2.38 (2.49) | |||
Table 1 Average importance values (%) of dominant species and their contributions (%) to within-group similarity
| 物种名 Species name | 人工林 Chinese fir forests (CFF) | 幼龄次生林 Young secondary forests (YSF) | 老次生林 Old secondary forests (OSF) | 老龄林 Old-growth forests (OGF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 71.27 (25.85) | |||
| 檵木 Loropetalum chinensis | 3.06 (4.69) | 2.70 (2.89) | 6.17 (4.74) | |
| 隔药柃 Eurya muricata | 3.02 (4.68) | 2.78 (3.04) | 2.80 (3.77) | |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 1.71 (3.79) | 7.37 (4.92) | 14.33 (7.55) | |
| 石栎 Lithocarpus glaber | 1.90 (3.54) | 5.32 (3.89) | 7.98 (5.36) | |
| 山合欢 Albizia kalkora | 0.81 (2.82) | |||
| 黄瑞木 Adinandra millettii | 0.77 (2.34) | |||
| 柳叶蜡梅 Chimonanthus salicifolius | 3.05 (2.08) | |||
| 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana | 0.64 (1.98) | |||
| 拟赤杨 Alniphyllum fortunei | 0.59 (1.95) | |||
| 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 23.76 (9.03) | 5.89 (4.31) | 15.69 (8.73) | |
| 米槠 C. carlesii | 9.04 (5.27) | 8.32 (3.43) | ||
| 木荷 Schima superba | 4.56 (3.51) | 11.30 (6.61) | 10.95 (6.25) | |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 3.11 (3.26) | 5.44 (4.86) | ||
| 麂角杜鹃 R. latoucheae | 2.95 (3.18) | 5.36 (5.26) | ||
| 短尾越橘 Vaccinium carlesii | 3.30 (3.04) | |||
| 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 2.52 (2.80) | 5.39 (4.02) | 5.12 (2.53) | |
| 栲 Castanopsis fargesii | 2.18 (2.94 | |||
| 杨梅 Myrica rubra | 2.04 (2.82) | |||
| 浙江红山茶 Camellia chekiangoleosa | 2.43 (2.94) | |||
| 浙江新木姜子 Neolitsea aurata var. chekiangensis | 1.47 (2.81) | |||
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 2.74 (2.46) | |||
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 2.38 (2.49) | |||
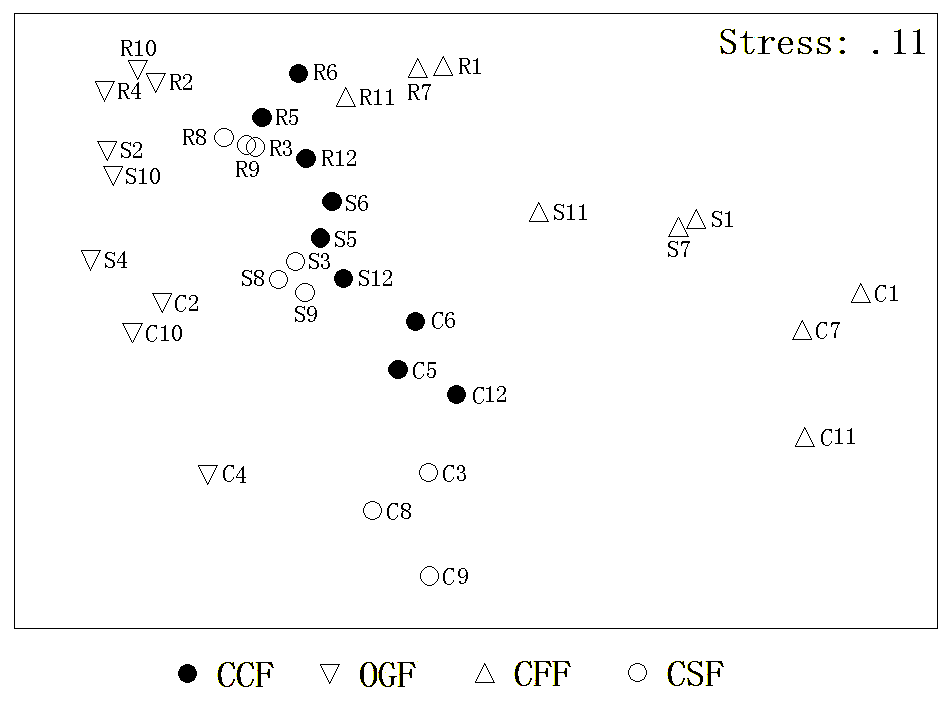
Fig. 2 Non-metric multidimensional scale (NMS) ordination of canopy, sub-canopy, and shrub and regeneration layers of 12 forest plots during four recovery phases in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. C, S, R represent canopy layer, sub-canopy layer, shrub and regeneration layer, respectively. Numbers are plot codes. CFF, OGF, OSF, YSF, see Table 1.
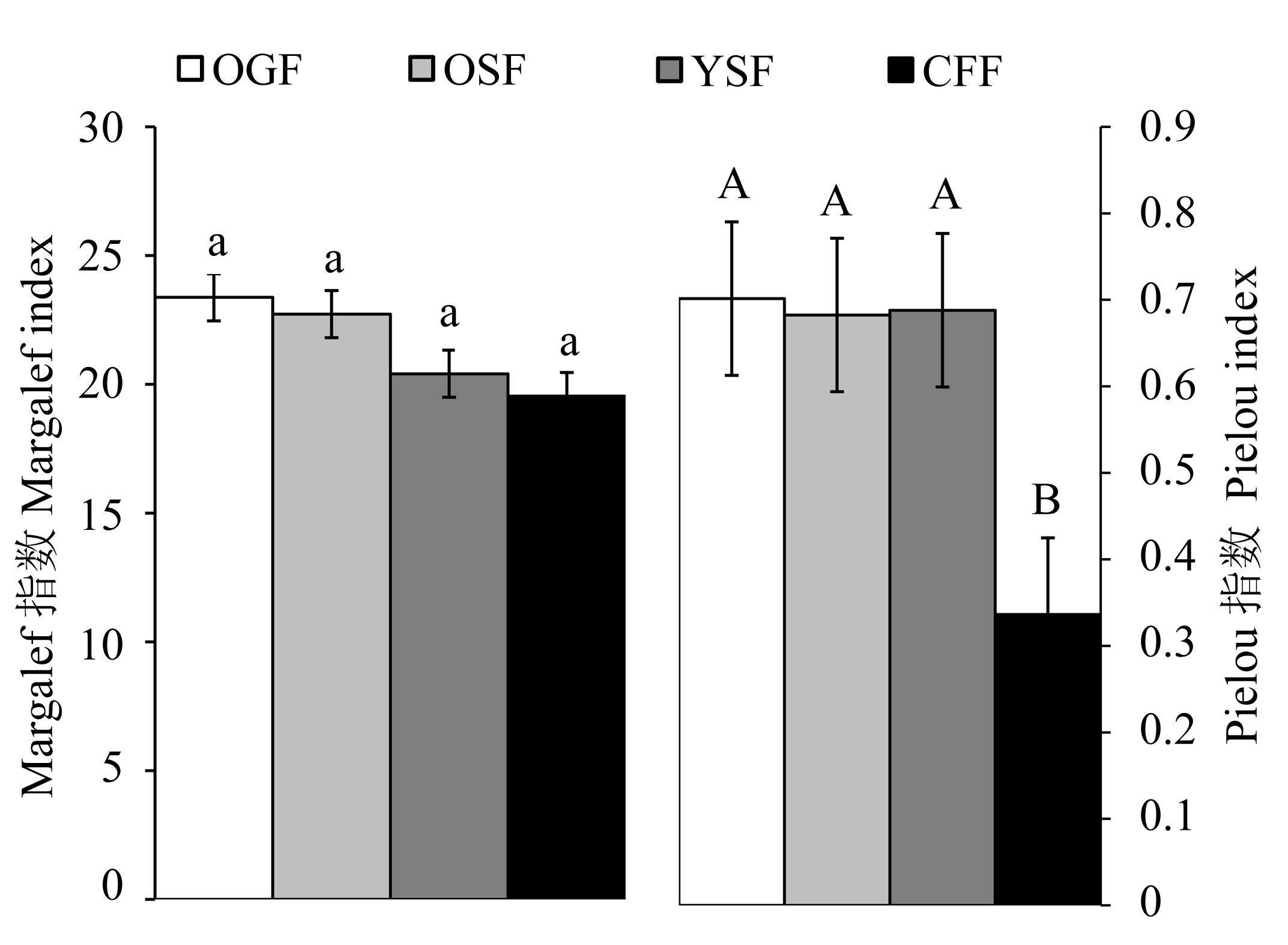
Fig. 3 Species diversity indices of 12 forest plots during four recovery phases in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. CFF, OGF, OSF, YSF, see Table 1.
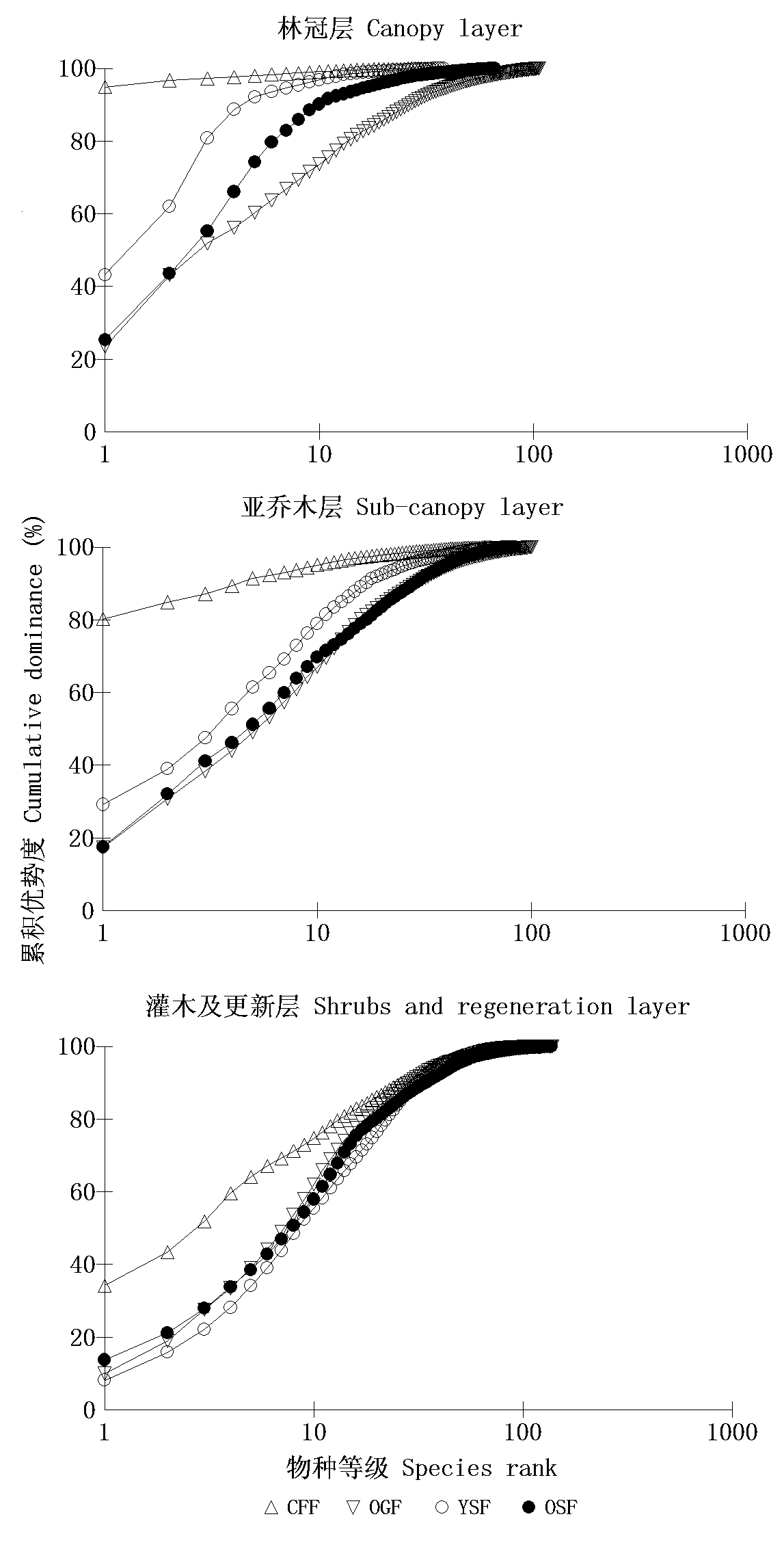
Fig. 4 K-dominance plot of canopy, sub-canopy, shrubs and regeneration layers of 12 forest plots during four recovery phases in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. CFF, OGF, OSF, YSF, see Table 1.
| 树种 Tree species | 组别 Group | 指示值 Value | P值 P<0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 山合欢 Albizia kalkora | CFF | 84.3 | 0.0188 |
| 拟赤杨 Alniphyllum fortunei | CFF | 59.7 | 0.0346 |
| 楤木 Aralia chinensis | CFF | 80.4 | 0.0188 |
| 紫珠 Callicarpa bodinieri | CFF | 69.0 | 0.0412 |
| 大青 Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum | CFF | 62.3 | 0.0346 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | CFF | 98.6 | 0.0188 |
| 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana | CFF | 79.7 | 0.0188 |
| 小果冬青 Ilex micrococca | CFF | 93.5 | 0.0188 |
| 山胡椒 Lindera glauca | CFF | 85.0 | 0.0188 |
| 山鸡椒 Litsea cubeba | CFF | 89.2 | 0.0188 |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | CFF | 66.2 | 0.0188 |
| 化香 Platycarya strobilacea | CFF | 86.3 | 0.0354 |
| 豆腐柴 Premna microphylla | CFF | 68.4 | 0.0168 |
| 水马桑 Weigela japonica var. sinica | CFF | 86.2 | 0.0188 |
| 栀子 Gardenia jasminoides | CSF | 45.0 | 0.0486 |
| 野漆 Toxicodendron succedaneum | YSF | 74.6 | 0.0496 |
| 短尾越桔 Vaccinium carlesii | YSF | 48.8 | 0.0456 |
| 厚叶冬青 Ilex elmerriliana | YSF | 67.9 | 0.0128 |
| 宁波木犀 Osmanthus cooperi | YSF | 74.7 | 0.0160 |
| 石斑木 Rhaphiolepis indica | YSF | 65.7 | 0.0160 |
| 赤楠 Syzygium buxifolium | YSF | 75.7 | 0.0088 |
| 冬青 Ilex chinensis | OSF | 67.1 | 0.0190 |
| 浙闽樱 Prunus schneideriana | OSF | 51.4 | 0.0130 |
| 檵木 Loropetalum chinensis | OSF | 49.9 | 0.0166 |
| 乳源木莲 Manglietia yuyuanensis | OSF | 91.6 | 0.0376 |
| 刨花楠 Machilus pauhoi | OSF | 100.0 | 0.0190 |
| 浙江红山茶 Camellia chekiangoleosa | OGF | 94.0 | 0.0146 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | OGF | 64.6 | 0.0332 |
| 麂角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | OGF | 55.1 | 0.0162 |
| 秀丽槭 Acer elegantulum | OGF | 100.0 | 0.0162 |
| 钩栲 Castanopsis tibetana | OGF | 96.9 | 0.0446 |
| 浙江樟 Cinnamomum japonicum | OGF | 97.8 | 0.0162 |
| 灰白蜡瓣花 Corylopsis glandulifera | OGF | 99.3 | 0.0162 |
| 小叶青冈 Cyclobalanopsis gracilis | OGF | 97.5 | 0.0162 |
| 细叶青冈 C. myrsinaefolia | OGF | 100.0 | 0.0162 |
| 尾叶冬青 Ilex wilsonii | OGF | 96.5 | 0.0066 |
| 马醉木 Pieris japonica | OGF | 74.7 | 0.0334 |
Table 2 Indicator species of shrubs and regeneration layer of 12 forest plots during four recovery phases in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve
| 树种 Tree species | 组别 Group | 指示值 Value | P值 P<0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 山合欢 Albizia kalkora | CFF | 84.3 | 0.0188 |
| 拟赤杨 Alniphyllum fortunei | CFF | 59.7 | 0.0346 |
| 楤木 Aralia chinensis | CFF | 80.4 | 0.0188 |
| 紫珠 Callicarpa bodinieri | CFF | 69.0 | 0.0412 |
| 大青 Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum | CFF | 62.3 | 0.0346 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | CFF | 98.6 | 0.0188 |
| 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana | CFF | 79.7 | 0.0188 |
| 小果冬青 Ilex micrococca | CFF | 93.5 | 0.0188 |
| 山胡椒 Lindera glauca | CFF | 85.0 | 0.0188 |
| 山鸡椒 Litsea cubeba | CFF | 89.2 | 0.0188 |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | CFF | 66.2 | 0.0188 |
| 化香 Platycarya strobilacea | CFF | 86.3 | 0.0354 |
| 豆腐柴 Premna microphylla | CFF | 68.4 | 0.0168 |
| 水马桑 Weigela japonica var. sinica | CFF | 86.2 | 0.0188 |
| 栀子 Gardenia jasminoides | CSF | 45.0 | 0.0486 |
| 野漆 Toxicodendron succedaneum | YSF | 74.6 | 0.0496 |
| 短尾越桔 Vaccinium carlesii | YSF | 48.8 | 0.0456 |
| 厚叶冬青 Ilex elmerriliana | YSF | 67.9 | 0.0128 |
| 宁波木犀 Osmanthus cooperi | YSF | 74.7 | 0.0160 |
| 石斑木 Rhaphiolepis indica | YSF | 65.7 | 0.0160 |
| 赤楠 Syzygium buxifolium | YSF | 75.7 | 0.0088 |
| 冬青 Ilex chinensis | OSF | 67.1 | 0.0190 |
| 浙闽樱 Prunus schneideriana | OSF | 51.4 | 0.0130 |
| 檵木 Loropetalum chinensis | OSF | 49.9 | 0.0166 |
| 乳源木莲 Manglietia yuyuanensis | OSF | 91.6 | 0.0376 |
| 刨花楠 Machilus pauhoi | OSF | 100.0 | 0.0190 |
| 浙江红山茶 Camellia chekiangoleosa | OGF | 94.0 | 0.0146 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | OGF | 64.6 | 0.0332 |
| 麂角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | OGF | 55.1 | 0.0162 |
| 秀丽槭 Acer elegantulum | OGF | 100.0 | 0.0162 |
| 钩栲 Castanopsis tibetana | OGF | 96.9 | 0.0446 |
| 浙江樟 Cinnamomum japonicum | OGF | 97.8 | 0.0162 |
| 灰白蜡瓣花 Corylopsis glandulifera | OGF | 99.3 | 0.0162 |
| 小叶青冈 Cyclobalanopsis gracilis | OGF | 97.5 | 0.0162 |
| 细叶青冈 C. myrsinaefolia | OGF | 100.0 | 0.0162 |
| 尾叶冬青 Ilex wilsonii | OGF | 96.5 | 0.0066 |
| 马醉木 Pieris japonica | OGF | 74.7 | 0.0334 |
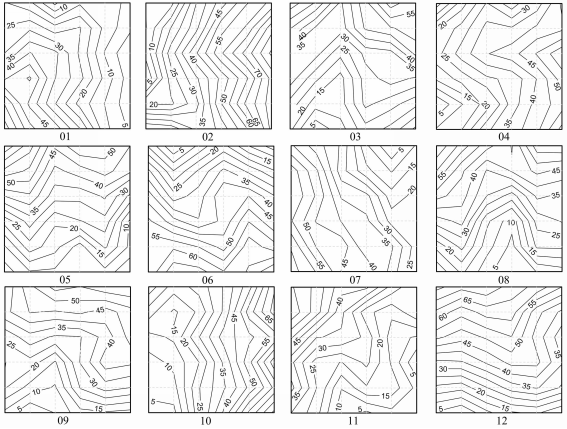

Fig. S1 Topographical maps of 12 forest plots during four recovery phases in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. The figures in the map refer to relative elevations of forest plots; Chinese fir forest plots include 01, 07, 11; Young secondary forest plots include 03, 08, 09; Old secondary forest plots include 05, 06, 12; Old-growth forest plots include 02, 04, 10. http://www.biodiversity-science.net/fileup/PDF/w2013-202-1.pdf
| [1] | Baker PJ, Bunyavejchewin S, Oliver CD, Ashton PS (2005) Disturbance history and historical stand dynamics of a seasonal tropical forest in western Thailand.Ecological Monographs, 75, 317-343. |
| [2] | Bengtsson J, Nilsson SG, Franc A, Menozzi P (2000) Biodiversity, disturbances, ecosystem function and management of European forests.Forest Ecology and Management, 132, 39-50. |
| [3] | Bruelheide H, Böhnke M, Both S, Fang T, Assmann T, Baruffol M, Bauhus J, Buscot F, Chen XY, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fischer M, Geißler C, Guo DL, Guo LD, Härdtle W, He JS, Hector A, Kröber W, Kühn P, Lang A, Nadrowski K, Pei KQ, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Shi XZ, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Welk E, Wirth C, Wu YT, Yang XF, Zeng XQ, Zhang SR, Zhou HZ, Ma KP, Schmid B (2011) Community assembly during secondary forest succession in a Chinese subtropical forest.Ecological Monographs, 81, 25-41. |
| [4] | Cannon C, Peart DR, Leighton M, Kartawinata K (1994) The structure of lowland rainforest after selective logging in West Kalimantan, Indonesia.Forest Ecology and Management, 67, 49-68. |
| [5] | Capers RS, Chazdon RL, Brenes AR, Alvarado BV (2005) Successional dynamics of woody seedling communities in wet tropical secondary forests.Journal of Ecology, 93, 1071-1084. |
| [6] | Carignan V, Villard MA (2001) Selecting indicator species to monitor ecological integrity: a review.Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 78, 45-61. |
| [7] | Chazdon RL (2003) Tropical forest recovery: legacies of human impact and natural disturbances.Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 6, 51-71. |
| [8] | Chazdon RL, Letcher SG, Van Breugel M, Martínez-Ramos M, Bongers F, Bryan F (2007) Rates of change in tree communities of secondary Neotropical forests following major disturbances.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 362, 273-289. |
| [9] | Dent DH, DeWalt SJ, Denslow JS (2012) Secondary forests of central Panama increase in similarity to old-growth forest over time in shade tolerance but not species composition.Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 530-542. |
| [10] | DeWalt SJ, Maliakal SK, Denslow JS (2003) Changes in vegetation structure and composition along a tropical forest chronosequence: implications for wildlife.Forest Ecology and Management, 182, 139-151. |
| [11] | Diekmann M (2003) Species indicator values as an important tool in applied plant ecology—a review.Basic and Applied Ecology, 4, 493-506. |
| [12] | Ding SY (丁圣彦), Song YC (宋永昌) (1998) Declining causes of Pinus massoniana in the processes of succession of evergreen broad-leaved forest.Acta Botanica Sinica(植物学报), 40, 755-760. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Dupuy JM, Chazdon RL (2008) Interacting effects of canopy gap, understory vegetation and leaf litter on tree seedling recruitment and composition in tropical secondary forests.Forest Ecology and Management, 255, 3716-3725. |
| [14] | Finegan B (1996) Pattern and process in neotropical secondary rain forests: the first 100 years of succession.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 119-124. |
| [15] | Fornwalt PJ, Kaufmann MR, Huckaby LS, Stohlgrenvon TJ (2009) Effects of past logging and grazing on understory plant communities in a montane Colorado forest.Plant Ecology, 203, 99-109. |
| [16] | Guariguata MR, Ostertag R (2001) Neotropical secondary forest succession: changes in structural and functional characteristics.Forest Ecology and Management, 148, 185-206. |
| [17] | Hu ZH (胡正华), Yu MJ (于明坚), Ding BY (丁炳扬), Fang T (方腾), Qian HY (钱海源), Chen QC (陈启瑺) (2003) Types of evergreen broad-leaved forests and their species diversity in Gutian Mountain National Nature Reserve.Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology(应用与环境生物学报), 9, 341-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Kassi NK, Decocq G (2008) Successional patterns of plant species and community diversity in a semi-deciduous tropical forest under shifting cultivation.Journal of Vegetation Science, 19, 809-820. |
| [19] | Klanderud K, Mbolatiana HZH, Vololomboahangy MN, Radimbison MA, Roger E, Totland Ø, Rajeriarison C (2010) Recovery of plant species richness and composition after slash-and-burn agriculture in a tropical rainforest in Madagascar.Biodiversity and Conservation, 19, 187-204. |
| [20] | Kubota Y, Katsuda K, Kikuzawa K (2005) Secondary succession and effects of clear-logging on diversity in the subtropical forests on Okinawa Island, southern Japan.Biodiversity and Conservation, 14, 879-901. |
| [21] | McDonald RI, Motzkin G, Foster DR (2008) The effect of logging on vegetation composition in Western Massachusetts.Forest Ecology and Management, 255, 4021-4031. |
| [22] | Mishra BP, Tripathi OP, Tripathi RS, Pandey HN (2004) Effects of anthropogenic disturbance on plant diversity and community structure of a sacred grove in Meghalaya, northeast India.Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 421-436. |
| [23] | Norden N, Chazdon RL, Chao A, Jiang YH, Vilchez-Alvarado B (2009) Resilience of tropical rain forests: tree community reassembly in secondary forests.Ecology Letters, 12, 385-394. |
| [24] | Peña-Claros M (2003) Changes in forest structure and species composition during secondary forest succession in the Bolivian Amazon.Biotropica, 35, 450-461. |
| [25] | Sagar R, Raghubanshi AS, Singh JS (2003) Tree species composition, dispersion and diversity along a disturbance gradient in a dry tropical forest region of India.Forest Ecology and Management, 186, 61-71. |
| [26] | Saldarriaga JG, West DC, Tharp ML, Uhl C (1988) Long-term chronosequence of forest succession in the Upper Rio Negro of Colombia and Venezuela.Journal of Ecology, 76, 938-958. |
| [27] | Smith RGB, Nichols JD, Vanclay JK (2005) Dynamics of tree diversity in undisturbed and logged subtropical rainforest in Australia.Biodiversity and Conservation, 14, 2447-2463. |
| [28] | Verburg R, van Eijk-Bos C (2003) Effects of selective logging on tree diversity, composition and plant functional type patterns in a Bornean rain forest.Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 99-110. |
| [29] | Villela DM, Nascimento MT, Aragão LE, Gama DM (2006) Effect of selective logging on forest structure and nutrient cycling in a seasonally dry Brazilian Atlantic forest.Journal of Biogeography, 33, 506-516. |
| [30] | von Oheimb G, Härdtle W (2009) Selection harvest in temperate deciduous forests: impact on herb layer richness and composition.Biodiversity and Conservation, 18, 271-287. |
| [31] | Wang XH, Kent M, Fang XF (2007) Evergreen broad-leaved forest in Eastern China: its ecology and conservation and the importance of resprouting in forest restoration.Forest Ecology and Management, 245, 76-87. |
| [32] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of a Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China.Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [5] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | Li Hualiang, Zhang Mingjun, Zhang Xibin, Tan Rong, Li Shichuan, Feng Erhui, Lin Xueyun, Chen Min, Yan enbo, Zeng Zhigao. Composition and influencing factors of the amphibian community in Hainan Dongzhaigang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [8] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [9] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [10] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [11] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()