



Biodiv Sci ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (3): 288-295. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08251 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08251
• Editorial • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ming Luo1,*( ), Jian Han1, Pingan Jiang2, Hongqi Wu2
), Jian Han1, Pingan Jiang2, Hongqi Wu2
Received:2008-09-27
Accepted:2009-05-15
Online:2009-05-20
Published:2009-05-20
Contact:
Ming Luo
Ming Luo, Jian Han, Pingan Jiang, Hongqi Wu. Diversity of culturable halophilic bacteria isolated from Lop Nur region in Xinjiang[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 288-295.
| 操作分类单元 OTUs | 代表性菌株Representative strains | 参考物种(登录号) Reference taxa (accession number) | 序列相似性 Similarity (%) | 菌株数(个) No. of strains | 比例 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU1 | LY036 | Brevibacterium sp.CNJ737 PL04 (DQ448693) | 99.30 | 1 | 0.92 |
| OTU2 | LY054 | Halomonassp.69 (AM409192) | 99.50 | 33 | 30.55 |
| OTU3 | LY096 | Bacillus baekryungensis(AY505507) | 99.70 | 5 | 4.62 |
| OTU4 | LY007 | Salinicoccus sp.RM11R (EF675622) | 99.70 | 2 | 1.85 |
| OTU5 | LY106 | Kocuria sp.4_O_59 (EF540518) | 97.00 | 4 | 3.70 |
| OTU6 | LY060 | Halobacillussp. IS-Hb6 (AB189300) | 99.40 | 20 | 18.51 |
| OTU7 | LY108 | Bacillussp. M31 (AB116125) | 98.20 | 3 | 2.78 |
| OTU8 | LY008 | Kocuriasp.JL-33 (AY745865) | 97.90 | 1 | 0.92 |
| OTU9 | LY076 | Micrococcus antarcticus(AJ005932) | 99.50 | 2 | 1.85 |
| OTU10 | LY004 | Chromohalobacter sp. NT N29 (AB166979) | 99.70 | 22 | 20.37 |
| OTU11 | LY048 | Bacillus subtili(EF563825) | 93.70 | 10 | 9.26 |
| OTU12 | LY100 | Staphylococcussp.(X86642) | 96.60 | 5 | 4.64 |
Table 1 16S rDNA sequence similarity between the representative strains from each OTU and reference taxa
| 操作分类单元 OTUs | 代表性菌株Representative strains | 参考物种(登录号) Reference taxa (accession number) | 序列相似性 Similarity (%) | 菌株数(个) No. of strains | 比例 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU1 | LY036 | Brevibacterium sp.CNJ737 PL04 (DQ448693) | 99.30 | 1 | 0.92 |
| OTU2 | LY054 | Halomonassp.69 (AM409192) | 99.50 | 33 | 30.55 |
| OTU3 | LY096 | Bacillus baekryungensis(AY505507) | 99.70 | 5 | 4.62 |
| OTU4 | LY007 | Salinicoccus sp.RM11R (EF675622) | 99.70 | 2 | 1.85 |
| OTU5 | LY106 | Kocuria sp.4_O_59 (EF540518) | 97.00 | 4 | 3.70 |
| OTU6 | LY060 | Halobacillussp. IS-Hb6 (AB189300) | 99.40 | 20 | 18.51 |
| OTU7 | LY108 | Bacillussp. M31 (AB116125) | 98.20 | 3 | 2.78 |
| OTU8 | LY008 | Kocuriasp.JL-33 (AY745865) | 97.90 | 1 | 0.92 |
| OTU9 | LY076 | Micrococcus antarcticus(AJ005932) | 99.50 | 2 | 1.85 |
| OTU10 | LY004 | Chromohalobacter sp. NT N29 (AB166979) | 99.70 | 22 | 20.37 |
| OTU11 | LY048 | Bacillus subtili(EF563825) | 93.70 | 10 | 9.26 |
| OTU12 | LY100 | Staphylococcussp.(X86642) | 96.60 | 5 | 4.64 |
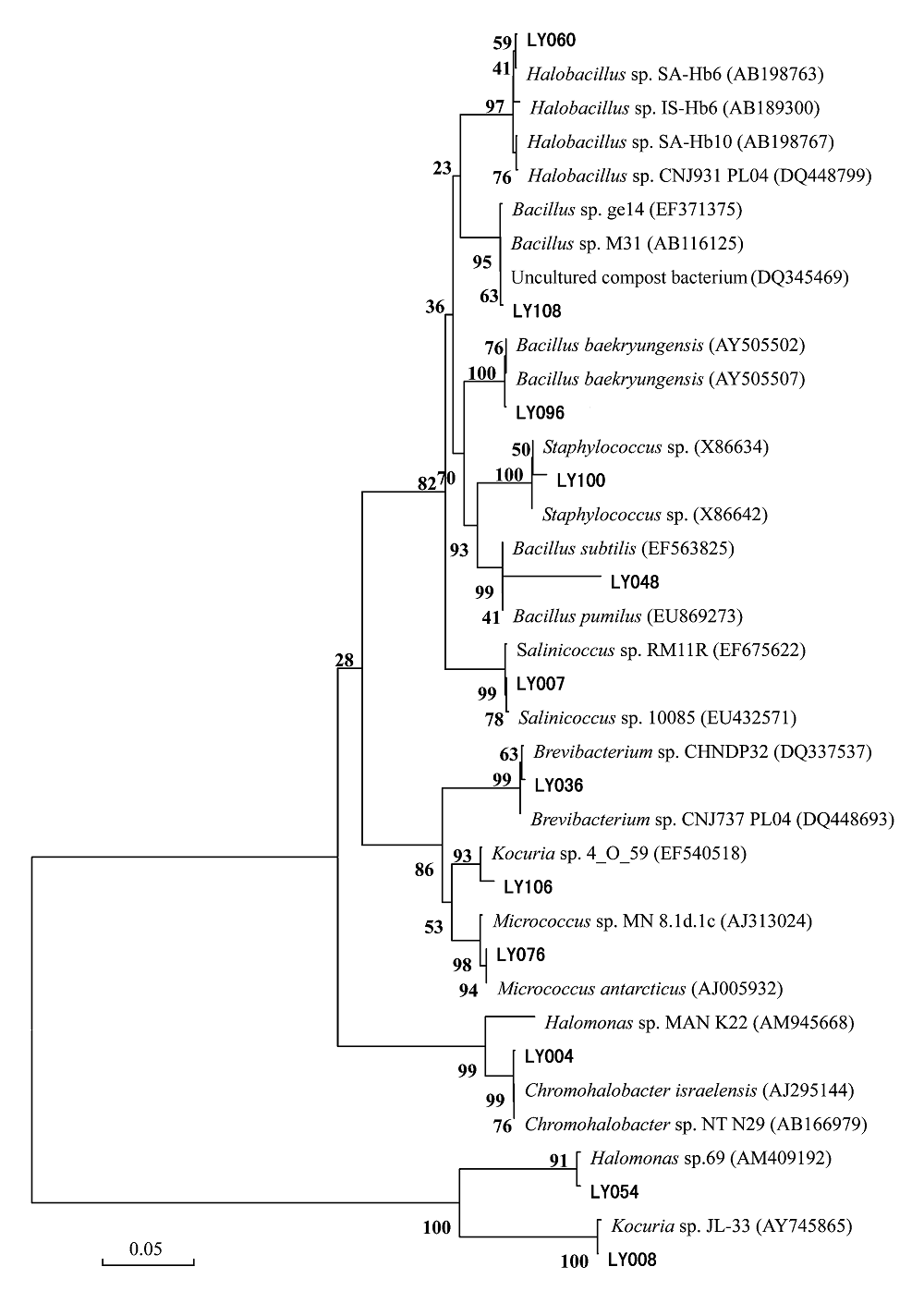
Fig. 1 A neighbor-joining dendrogram based on 16S rDNA sequences of the halophilic bacteria isolated from Lop Nur. GenBank accession numbers are in the parentheses. The boldfaces are strains for 16S rDNA sequencing.
| | 代表性菌株 Representative isolates | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY036 | LY054 | LY096 | LY007 | LY106 | LY060 | LY108 | LY008 | LY076 | LY004 | LY048 | LY100 | |
| 菌体形状 Shape | 杆状 Rod | 杆状 Rod | 杆状 Rod | 球状 Spherical | 球状 Spherical | 杆状 Rod | 球状 Spherical | 球状 Spherical | 球状 Spherical | 杆状 Rod | 杆状 Rod | 球状 Spherical |
| 菌落颜色 Colony color | 乳黄 Cream | 乳白 Milky white | 桔黄 Orange | 红色 Red | 灰白 Greyish white | 粉红 Pink | 灰白 Greyish white | 灰色 Grey | 乳白 Milky white | 粉红 Pink | 红色 Red | 乳白 Milky white |
| 芽孢 Endospore | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| 最适NaCl浓度(w/v) Optimal NaCl concentration (%) | 0 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 10 | 25 | 5 |
| 最适温度 Optimum temperature (℃) | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 |
| 最适pH Optimum pH | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 |
| 革兰氏染色 Gram staining | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + |
| 淀粉酶 Amylase | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | + |
| 蛋白酶 Protease | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + |
| 纤维素酶 Cellulase | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 脂肪酶 Lipase | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 接触酶 Catalase | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 氧化酶 Oxidase | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + |
| 甲基红 Methyl red | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| V.P. Voges-Prokauer | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| 葡萄糖氧化发酵 Glucose oxidase | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + |
Table 2 Morphological and physiological properties of the representative halophilic bacteria isolated from Lop Nur, Xinjiang
| | 代表性菌株 Representative isolates | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY036 | LY054 | LY096 | LY007 | LY106 | LY060 | LY108 | LY008 | LY076 | LY004 | LY048 | LY100 | |
| 菌体形状 Shape | 杆状 Rod | 杆状 Rod | 杆状 Rod | 球状 Spherical | 球状 Spherical | 杆状 Rod | 球状 Spherical | 球状 Spherical | 球状 Spherical | 杆状 Rod | 杆状 Rod | 球状 Spherical |
| 菌落颜色 Colony color | 乳黄 Cream | 乳白 Milky white | 桔黄 Orange | 红色 Red | 灰白 Greyish white | 粉红 Pink | 灰白 Greyish white | 灰色 Grey | 乳白 Milky white | 粉红 Pink | 红色 Red | 乳白 Milky white |
| 芽孢 Endospore | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| 最适NaCl浓度(w/v) Optimal NaCl concentration (%) | 0 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 10 | 25 | 5 |
| 最适温度 Optimum temperature (℃) | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 |
| 最适pH Optimum pH | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 |
| 革兰氏染色 Gram staining | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + |
| 淀粉酶 Amylase | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | + |
| 蛋白酶 Protease | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + |
| 纤维素酶 Cellulase | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 脂肪酶 Lipase | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 接触酶 Catalase | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 氧化酶 Oxidase | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + |
| 甲基红 Methyl red | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| V.P. Voges-Prokauer | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - |
| 葡萄糖氧化发酵 Glucose oxidase | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + |
| [1] |
Cabrera A, Aguilera M, Fuentes S, Incerti C, Russell NJ, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Monteoliva-Sanchez M (2007) Halomonas indalinina sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a solar saltern in Cabo de Gata, Almeria, southern Spain. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57,376-380.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Chai LH (柴丽红), Wang T (王涛), Cui XL (崔晓龙), Peng Q (彭谦), Xu LH (徐丽华), Jiang CL (姜成林) (2003) A primary study of 16 strains in Keke Salt Lake by ARDRA and phylogenetic analysis. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences) (云南大学学报(自然科学版)), 25,541-544. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen M (陈敏), Zhao LP (赵立平) (2003) Biodiversity of bacterial isolates on three different media from coking wastewater treatment system. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 43,366-371. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Chen M (陈敏), Fang X (方序) (2006) Isolation and ARDRA analysis of cucumber entophytic antagonists against Ralstonia solanacearum. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 46,984-987. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Chen YG (陈义光), Li HM (李汇明), Li QY (李沁元), Chen W (陈维), Cui XL (崔晓龙) (2007) Phylogenetic diversity of culturable bacteria in the ancient salt deposits of the Yipinglang Salt Mine, P. R. China. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 47,571-577. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Chmielewsli R, Wieliczko A, Kuczkowski M, Mazurkiewicz M, Ugorski M (2002) Comparison of ITS profiling, REP- and ERIC-PCR of Salmonella enteritidis isolates from Poland. Journal of Veterinary Medicine, Series B, 49,63-168. |
| [7] | Devereux R, He SH, Doyle CL, Orkland S, Stahl DA, LeGall J Whitman WB (1990) Diversity and origin of Desulfovibrio species: phylogenetic definition of a family. Journal of Bacteriology, 7,3609-3619. |
| [8] | Dong XZ (东秀珠), Cai MY (蔡妙英) (2001) Identification Manual of Common Bacteria (常见细菌系统鉴定手册). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [9] |
Eichler J (2001) Biotechnological uses of archaeal extremoz- ymes. Biotechnology Advances, 19,261-278.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Fu YN (傅英楠), Chen ZL (陈志亮), Jiang WY (姜蔚宇), Chen RZ (陈荣忠) (2007) Characterization of the ectABC gene and the ectA gene expression product in Chromhalobacter sp. NJS-2 from Antarctica deep-sea sediment. China Biotechnology (中国生物工程杂志), 27 (12),36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] |
Ghozlan H, Deif H, Kandil RA, Sabry S (2006) Biodiversity of moderately halophilic bacteria in hypersaline habitats in Egypt. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 52,63-71.
URL PMID |
| [12] |
Gochnauer MB, Kushner DJ (1969) Growth and nutrition of extremely halophilic bacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 15,1157-1165.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Gu XY (顾晓颖), Li G (李冠), Wu M (吴敏) (2007) Isolation and enzyme screening of halophiles from Barkol Lake and Manasi Lake. Biotechnology (生物技术), 17(3),26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Han J (韩剑), Luo M (罗明), Jiang PA (蒋平安), Wu HQ (武红旗) (2008) Isolation halophilic bacteria from Lop Nur region and their growth for selectivity to positive ions. Arid Land Geography (干旱区地理), 31,878-884. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Heyndrickx M, Vandamme P, Kersters K (1996) Application of combined ribosomal and restriction analysis (ARDRA) patterns in bacterial phylogeny and taxonomy. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 3,247-259. |
| [16] | Hu DS (胡东生), Zhang HJ (张华京) (2004) Lake-evaporated salt resources and the environmental evolution in the Lop Nur region. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology (冰川冻土), 26,212-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Liu HQ (刘会强), Lü JJ (吕建江) (2008) The 16S rDNA sequence research of moderately halophilic bacteria from Dabancheng Saline Lake in Xinjiang. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition) (新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 27(4),46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Luo C (罗超), Peng ZC (彭子成), Yang D (杨东), Liu WG (刘卫国), He JF (贺剑峰), Liu GJ (刘桂建) (2005) Research on the environmental evolution of Lop Nur in Xinjiang, China. Nature Magazine (自然杂志), 28,37-41. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | Noel RK (1984) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, pp.170-171. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [20] | Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the Order Halobacterials. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 47,233-238. |
| [21] |
Priem A, Braker G, Tiedje JM (2002) Diversity of nitrite reductase (nirK and nirS ) gene fragments in forested upland and wetland soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68,1893-1900.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Pan HL (潘海莲), Zhou C (周成), Wang HL (王红蕾), Xue YF (薛燕芬), Ma YH (马延和) (2006) Diversity of halophilic archaea in hypersaline lakes of Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 46,1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Ren PG (任培根), Zhou PJ (周培瑾) (2003) Research progress of moderately halophilic eubacteria. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 43,427-431. (in Chinese) |
| [24] | Ross HNM, Collins MD, Tindall BJ, Grant WD (1981) A rapid procedure for the detection of archaebacterial lipids in halophilic bacteria. Journal of General Microbiology, 123,75-80. |
| [25] |
Sehgal SN, Gibbons NE (1960) Effect of metal ions on the growth of halobacterium cutirubrum. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 6,165-169.
URL PMID |
| [26] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24,1596-1599.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Tian MJ (田美娟), Shao ZZ (邵宗泽) (2006) Isolation and cha- racterization of manganese resistant bacteria from deep sea sediments. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报(自然科学版)), 45(Suppl.),272-276. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] |
Uphoff HU, Felske A, Fehr W, Wagner-Döbler I (2001) The microbial diversity in picoplankton enrichment cultures: a molecular screening of marine isolates. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 35,249-258.
URL PMID |
| [29] | Vaneechoutte M, Rossau R, De Vos P, Gillis M, Janssens D, Paepe N, De Rouck A, Fiers T, Claeys G, Kersters K (1992) Rapid identification of bacteria of the Comamonadaceae with amplified ribosomal DNA-restriction analysis (ARDRA). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 93,227-233. |
| [30] | Xu XW (许学伟), Wu M (吴敏), Dilbar T (迪丽拜尔·托乎提), Ababaikeli G (古丽巴哈尔·阿巴拜克利) (2006) Halophilic archaea diversity of Aibi Lake and Yiwu Lake in Xinjiang. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14,359-362. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Yang RX (杨瑞先), Sun GY (孙广宇), Zhang R (张荣), Chen LJ (陈立军) (2005) 16S rDNA RFLP analysis of endophytic bacteria from Brassica napus. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 45,606-609. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Zhao LP (赵立平), Xiao H (肖虹), Li YQ (李艳琴), Zhang F (张峰) (1999) ERIC-PCR as a new tool for quick identification of environmental bacteria. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (应用与环境生物学报), 15(Suppl.),30-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Zhao YJ (赵元杰), Xia XC (夏训诚), Wang FB (王富葆), Cao QY (曹琼英), Gao WM (高伟明), You GY (游广永) (2006) Features and causes of formation on ring-shaped salt crust in Lop Nur region of Xinjiang, China. Arid Land Geography (干旱区地理), 29,779-783. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Zhong JP (钟骏平), Ma LC (马黎春), Li BG (李保国), Jiang PA (蒋平安), Qiu HL (邱宏烈), Wu HQ (武红旗) (2008) Rediscussion on the latest drying up of the “Great Ear” in the Lop Nor area. Arid Land Geography (干旱区地理), 31,10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()