



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 260-270. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.11279 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.11279
所属专题: 中国的森林生物多样性监测
王利伟1,2, 李步杭1,2, 叶吉1,2, 白雪娇1,2, 原作强1,2, 邢丁亮1,2, 蔺菲1,2, 师帅1, 王绪高1, 郝占庆1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2010-11-22
接受日期:2011-02-26
出版日期:2011-03-20
发布日期:2011-06-01
通讯作者:
郝占庆
作者简介:*E-mail: hzq@iae.ac.cn基金资助:
Liwei Wang1,2, Buhang Li1,2, Ji Ye1,2, Xuejiao Bai1,2, Zuoqiang Yuan1,2, Dingliang Xing1,2, Fei Lin1,2, Shuai Shi1, Xugao Wang1, Zhanqing Hao1,*( )
)
Received:2010-11-22
Accepted:2011-02-26
Online:2011-03-20
Published:2011-06-01
Contact:
Zhanqing Hao
摘要:
树木死亡是森林群落动态的重要过程, 是多种因素共同作用的结果。本文基于长白山阔叶红松林25 ha样地2004年和2009年两次调查数据, 从物种组成、数量特征、径级结构和空间分布等方面分析了5年间样地中死亡树木的特征。结果表明: 5年间样地DBH ≥ 1 cm的独立个体树种数由52变为51, 3个树种因仅有的1个个体死亡而消失, 新增2个树种; 独立个体数从36,908变为34,926, 死亡个体数为4,030, 死亡个体数占2004年个体总数的10.9%, 新增个体数为2,048, 独立个体数净减少1,982; 死亡量大的树种其新增量也较大, 灌木树种的死亡量和新增量均多于乔木树种; 有5个树种的平均胸径减小, 44个树种平均胸径增加; 从死亡个体的径级结构来看, 小径级个体死亡较多, 大径级个体死亡少, 5 cm以下的死亡个体占总死亡量的81.5%, 不同林层的优势树种死亡个体的径级分布与2004年该树种的径级分布基本相同; 不同树种死亡个体的空间分布具有较大差异, 不同林层的优势树种死亡个体空间格局主要以聚集分布为主, 小径级死亡个体在小尺度呈聚集分布, 在其他尺度呈随机分布, 中径级和大径级死亡个体在各尺度上都呈不同程度的随机分布。
王利伟, 李步杭, 叶吉, 白雪娇, 原作强, 邢丁亮, 蔺菲, 师帅, 王绪高, 郝占庆 (2011) 长白山阔叶红松林树木短期死亡动态. 生物多样性, 19, 260-270. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.11279.
Liwei Wang, Buhang Li, Ji Ye, Xuejiao Bai, Zuoqiang Yuan, Dingliang Xing, Fei Lin, Shuai Shi, Xugao Wang, Zhanqing Hao (2011) Dynamics of short-term tree mortality in broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest in the Changbai Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 19, 260-270. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.11279.
| 物种 Species | 拉丁名 Latin name | 2004年多度 Abundance 04 | 2009年多度 Abundance 09 | 多度变化 Abundance variation | 死亡量 Death number | 新增量 Recruit number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毛榛 | Corylus mandshurica | 7,700 | 6,925 | -775 | 1,480 | 705 |
| 假色槭 | Acer pseudo-sieboldianum | 4,891 | 4,690 | -201 | 308 | 107 |
| 簇毛槭 | A. barbinerve | 3,709 | 3,562 | -147 | 365 | 218 |
| 紫椴 | Tilia amurensis | 2,644 | 2,504 | -140 | 149 | 9 |
| 暴马丁香 | Syringa reticulata | 1,544 | 1,405 | -139 | 234 | 95 |
| 怀槐 | Maackia amurensis | 748 | 642 | -106 | 118 | 12 |
| 红松 | Pinus koraiensis | 2,450 | 2,351 | -99 | 100 | 1 |
| 色木槭 | Acer mono | 6,569 | 6,479 | -90 | 474 | 384 |
| 糠椴 | Tilia mandshurica | 423 | 336 | -87 | 91 | 4 |
| 东北山梅花 | Philadelphus schrenkii | 466 | 422 | -44 | 177 | 133 |
| 春榆 | Ulmus japonica | 1,101 | 1,065 | -36 | 96 | 60 |
| 稠李 | Prunus padus | 485 | 452 | -33 | 85 | 52 |
| 水曲柳 | Fraxinus mandshurica | 694 | 667 | -27 | 28 | 1 |
| 蒙古栎 | Quercus mongolica | 926 | 905 | -21 | 34 | 13 |
| 拧筋槭 | Acer triflorum | 278 | 267 | -11 | 17 | 6 |
| 接骨木 | Sambucus williamsii | 19 | 10 | -9 | 13 | 4 |
| 乌苏里鼠李 | Rhamnus ussuriensis | 102 | 95 | -7 | 13 | 6 |
| 山杨 | Populus davidiana | 31 | 25 | -6 | 6 | 0 |
| 辽东楤木 | Aralia elata | 12 | 6 | -6 | 6 | 0 |
| 山梨 | Pyrus ussuriensis | 67 | 62 | -5 | 7 | 2 |
| 白桦 | Betula platyphylla | 97 | 92 | -5 | 5 | 0 |
| 裂叶榆 | Ulmus laciniata | 171 | 167 | -4 | 12 | 8 |
| 白牛槭 | Acer mandshuricum | 236 | 233 | -3 | 16 | 13 |
| 鼠李 | Rhamnus davarica | 21 | 18 | -3 | 4 | 1 |
| 黄檗 | Phellodendron amurense | 60 | 57 | -3 | 3 | 0 |
| 大青杨 | Populus ussuriensis | 38 | 35 | -3 | 3 | 0 |
| 茶条槭 | Acer ginnala | 137 | 135 | -2 | 12 | 10 |
| 珍珠梅 | Sorbaria sorbifolia | 4 | 3 | -1 | 3 | 2 |
| 水榆花楸 | Sorbus alnifolia | 25 | 24 | -1 | 2 | 1 |
| 翅卫矛 | Euonymus macropterus | 8 | 7 | -1 | 2 | 1 |
| 风桦 | Betula costata | 16 | 15 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 东北茶藨子 | Ribes mandshuricum | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 花楸 | Sorbus pohuashanensis | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 山刺玫 | Rosa davurica | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 青楷槭 | Acer tegmentosum | 687 | 687 | 0 | 54 | 54 |
| 刺五加 | Acanthopanax senticosus | 36 | 36 | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 金花忍冬 | Lonicera chrysantha | 26 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 香杨 | Populus koreana | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 臭冷杉 | Abies nephrolepis | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 松杉冷杉 | A. holophylla | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 金刚鼠李 | Rhamnus diamantiaca | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 山葡萄 | Vitis amurensis | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 东北溲疏 | Deutzia parviflora | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 崖柳 | Salix floderusii | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 毛山楂 | Crataegus maximouwiczii | 125 | 126 | 1 | 26 | 27 |
| 黑樱桃 | Cerasus maximowiczii | 50 | 51 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 长白忍冬 | Lonicera ruprechtiana | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 单花忍冬 | L. monantha | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 山荆子 | Malus baccata | 150 | 152 | 2 | 22 | 24 |
| 鸡树条荚蒾 | Viburnum sargenti | 45 | 48 | 3 | 11 | 14 |
| 瘤枝卫矛 | Euonymus pauciflorus | 43 | 48 | 5 | 9 | 14 |
| 狗枣猕猴桃 | Actinidia kolomikta | 1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 6 |
| 卫矛 | Euonymus alatus | 33 | 39 | 6 | 9 | 15 |
| 暖木条荚蒾 | Viburnum burejaeticum | 19 | 31 | 12 | 6 | 18 |
| 总计 | Total | 36,908 | 34,926 | -1,982 | 4,030 | 2,048 |
表1 5年间样地树种的多度变化、死亡量和新增量
Table 1 Abundance variation, death number and recruitment number of species during five years in the plot
| 物种 Species | 拉丁名 Latin name | 2004年多度 Abundance 04 | 2009年多度 Abundance 09 | 多度变化 Abundance variation | 死亡量 Death number | 新增量 Recruit number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毛榛 | Corylus mandshurica | 7,700 | 6,925 | -775 | 1,480 | 705 |
| 假色槭 | Acer pseudo-sieboldianum | 4,891 | 4,690 | -201 | 308 | 107 |
| 簇毛槭 | A. barbinerve | 3,709 | 3,562 | -147 | 365 | 218 |
| 紫椴 | Tilia amurensis | 2,644 | 2,504 | -140 | 149 | 9 |
| 暴马丁香 | Syringa reticulata | 1,544 | 1,405 | -139 | 234 | 95 |
| 怀槐 | Maackia amurensis | 748 | 642 | -106 | 118 | 12 |
| 红松 | Pinus koraiensis | 2,450 | 2,351 | -99 | 100 | 1 |
| 色木槭 | Acer mono | 6,569 | 6,479 | -90 | 474 | 384 |
| 糠椴 | Tilia mandshurica | 423 | 336 | -87 | 91 | 4 |
| 东北山梅花 | Philadelphus schrenkii | 466 | 422 | -44 | 177 | 133 |
| 春榆 | Ulmus japonica | 1,101 | 1,065 | -36 | 96 | 60 |
| 稠李 | Prunus padus | 485 | 452 | -33 | 85 | 52 |
| 水曲柳 | Fraxinus mandshurica | 694 | 667 | -27 | 28 | 1 |
| 蒙古栎 | Quercus mongolica | 926 | 905 | -21 | 34 | 13 |
| 拧筋槭 | Acer triflorum | 278 | 267 | -11 | 17 | 6 |
| 接骨木 | Sambucus williamsii | 19 | 10 | -9 | 13 | 4 |
| 乌苏里鼠李 | Rhamnus ussuriensis | 102 | 95 | -7 | 13 | 6 |
| 山杨 | Populus davidiana | 31 | 25 | -6 | 6 | 0 |
| 辽东楤木 | Aralia elata | 12 | 6 | -6 | 6 | 0 |
| 山梨 | Pyrus ussuriensis | 67 | 62 | -5 | 7 | 2 |
| 白桦 | Betula platyphylla | 97 | 92 | -5 | 5 | 0 |
| 裂叶榆 | Ulmus laciniata | 171 | 167 | -4 | 12 | 8 |
| 白牛槭 | Acer mandshuricum | 236 | 233 | -3 | 16 | 13 |
| 鼠李 | Rhamnus davarica | 21 | 18 | -3 | 4 | 1 |
| 黄檗 | Phellodendron amurense | 60 | 57 | -3 | 3 | 0 |
| 大青杨 | Populus ussuriensis | 38 | 35 | -3 | 3 | 0 |
| 茶条槭 | Acer ginnala | 137 | 135 | -2 | 12 | 10 |
| 珍珠梅 | Sorbaria sorbifolia | 4 | 3 | -1 | 3 | 2 |
| 水榆花楸 | Sorbus alnifolia | 25 | 24 | -1 | 2 | 1 |
| 翅卫矛 | Euonymus macropterus | 8 | 7 | -1 | 2 | 1 |
| 风桦 | Betula costata | 16 | 15 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 东北茶藨子 | Ribes mandshuricum | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 花楸 | Sorbus pohuashanensis | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 山刺玫 | Rosa davurica | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 |
| 青楷槭 | Acer tegmentosum | 687 | 687 | 0 | 54 | 54 |
| 刺五加 | Acanthopanax senticosus | 36 | 36 | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 金花忍冬 | Lonicera chrysantha | 26 | 26 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 香杨 | Populus koreana | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 臭冷杉 | Abies nephrolepis | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 松杉冷杉 | A. holophylla | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 金刚鼠李 | Rhamnus diamantiaca | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 山葡萄 | Vitis amurensis | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 东北溲疏 | Deutzia parviflora | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 崖柳 | Salix floderusii | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 毛山楂 | Crataegus maximouwiczii | 125 | 126 | 1 | 26 | 27 |
| 黑樱桃 | Cerasus maximowiczii | 50 | 51 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 长白忍冬 | Lonicera ruprechtiana | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 单花忍冬 | L. monantha | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 山荆子 | Malus baccata | 150 | 152 | 2 | 22 | 24 |
| 鸡树条荚蒾 | Viburnum sargenti | 45 | 48 | 3 | 11 | 14 |
| 瘤枝卫矛 | Euonymus pauciflorus | 43 | 48 | 5 | 9 | 14 |
| 狗枣猕猴桃 | Actinidia kolomikta | 1 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 6 |
| 卫矛 | Euonymus alatus | 33 | 39 | 6 | 9 | 15 |
| 暖木条荚蒾 | Viburnum burejaeticum | 19 | 31 | 12 | 6 | 18 |
| 总计 | Total | 36,908 | 34,926 | -1,982 | 4,030 | 2,048 |
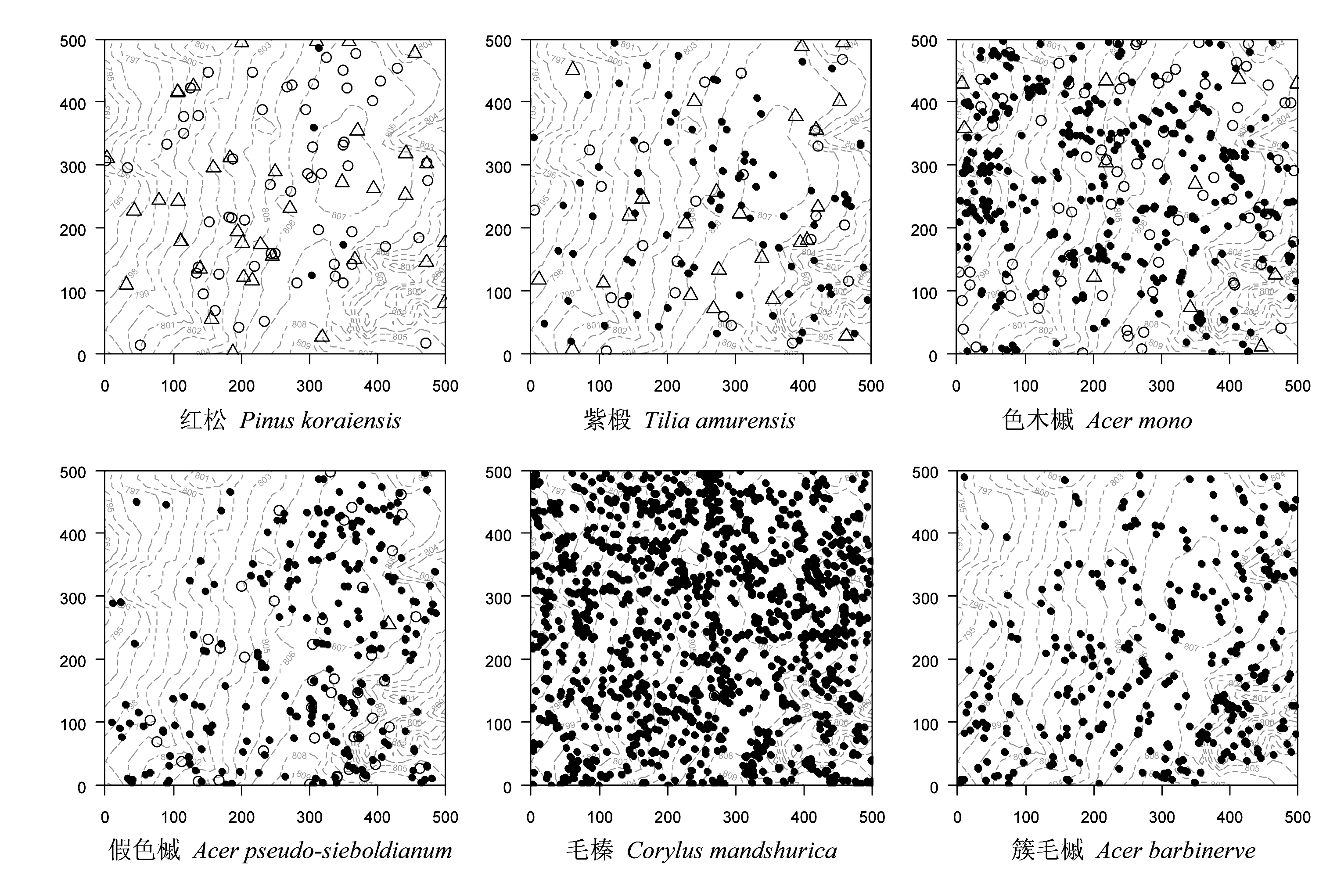
图3 6个树种死亡个体空间分布。 ●代表小径级(1-10 cm)死亡个体, ○代表中径级(10-30 cm)死亡个体, △代表大径级(≥30 cm)死亡个体。
Fig. 3 Scatter plots of dead individuals of six species. ● ○ △represent 1-10 cm, 10-30 cm, ≥30 cm size class dead individuals respectively.
| [1] |
Bai XJ (白雪娇), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang LW (王利伟), Yuan ZQ (原作强), Lin F (蔺菲), Hao ZQ (郝占庆) (2010) Species composition, structure, and spatial distribution of shrubs in broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest in Changbai Mountains. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 21, 1899-1906. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| [2] | Ban Y (班勇), Xu HC (徐化成), Li ZD (李湛东) (1997) Mortality patterns of Larix gmelini and effect of fallen dead wood on regeneration of old Larix gmelini forest. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 8, 449-454. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Carmona MR, Armesto JJ, Aravena JC, Pérez CA (2002) Coarse woody debris biomass in successional and primary temperate forests in Chiloé Island, Chile. Forest Ecology and Management, 164, 265-275. |
| [4] | Chen H (陈华), Xu ZB (徐振邦) (1991) Preliminary study on tree death of Korean pine deciduous mixed forest of Changbai Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 2, 89-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Coomes DA, Duncan RP, Allen RB, Truscott J (2003) Disturbances prevent stem size-density distributions in natural forests from following scaling relationships. Ecology Letters, 6, 980-989. |
| [6] | Dai LM (代力民), Xu ZB (徐振邦), Yang LY (杨丽韫), Cao YM (曹玉明) (1999) Storage dynamics of fallen trees in Korean pine broad-leaved forest. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 10, 513-517. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Diggle PJ (1983) Statistical Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns. Academic Press, New York. |
| [8] | Franklin JF, Shugart HH, Harmon ME (1987) Tree death as an ecological process. BioScience, 37, 550-556. |
| [9] | Gray L, He F (2009) Spatial point-pattern analysis for detecting density-dependent competition in a boreal chronosequence of Alberta. Forest Ecology and Management, 259, 98-106. |
| [10] | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Guo SL (郭水良), Cao T (曹同) (2002) Plant Biodiversity and Distribution Patterns in Changbai Mountain (长白山植物多样性及其格局). Liaoning Science and Technology Publishing House, Shenyang. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang XG (王绪高), Ye J (叶吉), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2008) Broad- leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest plot in Changbaishan of China: community composition and structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 32, 238-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Hao Z, Zhang J, Song B, Ye J, Li B (2007) Vertical structure and spatial associations of dominant tree species in an old-growth temperate forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 252, 1-11. |
| [13] | Harmon ME, Franklin JF, Swanson FJ, Sollins P, Gregory SV, Lattin JD, Anderson NH, Cline SP, Aumen NG, Sedell JR, Lienkaemper GW, Cromack K Jr, Cummins KW (1986) Ecology of coarse woody debris in temperate ecosystems. Advances in Ecological Research, 15, 133-302. |
| [14] | Hibbs DE (1983) Forty years of forest succession in central New England. Ecology, 64, 1394-1401. |
| [15] | Hubbell SP (2004) Two decades of research on the BCI Forest Dynamic Plot: where we have been and where we are going. In: Tropical Forest Diversity and Dynamism: Findings from a Large-scale Plot Network (eds Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr), pp. 8-30. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [16] | Liu CL (刘翠玲), Pan CD (潘存德), Liang Y (梁瀛) (2009) Storage and decomposition dynamics of coarse woody debris in Picea schrenkiana-Dryopteris filix-mas stand. Arid Land Geography (干旱区地理), 32, 175-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Liu D, Kelly M, Gong P, Guo Q (2007) Characterizing spatial-temporal tree mortality patterns associated with a new forest disease. Forest Ecology and Management, 253, 220-231. |
| [18] | Lutz JA, Halpern CB (2006) Tree mortality during early forest development: a long-term study of rates, causes, and consequences. Ecological Monographs, 76, 257-275. |
| [19] | Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Large scale permanent plots: important platform for long term research on biodiversity in forest ecosystem. Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 32, 237. (in Chinese) |
| [20] |
Menges ES (2000) Population viability analyses in plants: challenges and opportunities. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15, 51-56.
URL PMID |
| [21] |
Metcalf CJE, Horvitz CC, Tuljapurkar S, Clark DA (2009) A time to grow and a time to die: a new way to analyze the dynamics of size, light, age, and death of tropical trees. Ecology, 90, 2766-2778.
URL PMID |
| [22] | Ripley BD (1981) Spatial Statistics. Wiley, New York. |
| [23] | Rouvinen S, Kuuluvainen T, Siitonen J (2002) Tree mortality in a Pinus sylvestris dominated boreal forest landscape in Vienansalo wilderness, eastern Fennoscandia. Silva Fennica, 36, 127-145. |
| [24] | Runkle JR (2000) Canopy tree turnover in old-growth mesic forests of eastern North America. Ecology, 81, 554-567. |
| [25] | Schmitt CL, Filip GM (2007) Understanding and defining mortality in western conifer forests. Western Journal of Applied Forestry, 22, 105-115. |
| [26] | Siitonen J (2001) Forest management, coarse woody debris and saproxylic organisms: fennoscandian boreal forests as an example. Ecological Bulletins, 49, 11-41. |
| [27] | Tang XL (唐旭利), Zhou GY (周国逸) (2005) Coarse woody debris biomass and its potential contribution to carbon cycle in successional subtropical forests of southern China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 29, 559-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Wang X, Hao Z, Zhang J, Lian J, Li B, Ye J, Yao X (2009) Tree size distributions in an old-growth temperate forest. Oikos, 118, 25-36. |
| [29] | Wang X, Ye J, Li B, Zhang J, Lin F, Hao Z (2010) Spatial distributions of species in an old-growth temperate forest, northeastern China. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 40, 1011-1019. |
| [30] | Xu GS (许广山), Ding GF (丁桂芳), Zhang YH (张玉华), Cheng BR (程伯容) (1980) A primary study on soil humus and its characteristics in the main forests on northern slope of Changbai Mountain. Research of Forest Ecosystem (森林生态系统研究), 1, 215-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Xu HC (徐化成) (2001) Natural Forests of Pinus koraiensis in China (中国红松天然林). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [32] | Yang HX (阳含熙), Wu YG (伍业钢) (1988) Tree composition, age structure and regeneration strategy of the mixed broadleaf Korean pine forest in Changbaishan Biosphere Reserve, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 24, 18-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Zhang C (张池), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Shi JH (史军辉), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Li J (李炯) (2006) Dynamics and causes of woody plant death in the monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Dinghushan Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 26, 2457-2462. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] |
Zhang J (张健), Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Song B (宋波), Ye J (叶吉), Li BH (李步杭), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2007) Spatial distribution patterns and associations of Pinus koraiensis and Tilia amurensis in broad-leaved Korean pine mixed forest in Changbai Mountains. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 18, 1681-1687. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| [35] | Zhou XY (周小勇), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Shi JH (史军辉), Ouyang XJ (欧阳学军), Li J (李炯), Zhang C (张池) (2004) Short-term dynamics of community composition and structure during succession of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest in Dinghushan. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany (热带亚热带植物学报), 12, 323-330. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 廖雅晴, 黄泽锋, 王晓云, 张礼标, 吴毅, 余文华. 广东省翼手目物种名录更新及分子条形码数据库[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [3] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [4] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [5] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [6] | 曲文杰, 王磊, 康文岩, 杨新国, 屈建军, 张雪. 腾格里沙漠东南缘不同年限固沙植被区种子雨和土壤种子库动态与植被更新潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24254-. |
| [7] | 郑博瀚, 陈鑫瑶, 倪健. 中国维管植物生长型和生活型数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23468-. |
| [8] | 舒为杰, 何花, 曾罗, 谷志容, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 雌雄异株物种一把伞南星雌雄株空间分布及性别二态性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [9] | 丁扬, 冯英群, 张金羽, 王博. 动物对濒危特有种大别山五针松种子的捕食和散布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23401-. |
| [10] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [11] | 陈明苗, 张楚然, 邓云, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 魏兆喆, 张彩彩, 林露湘. 地形因子对亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物萌生特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24282-. |
| [12] | 谭晓丹, 张鹏, 朱思睿, 刘向, 周淑荣, 刘木. 青藏高原高寒草甸灌丛化对圆穗蓼昆虫植食作用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23417-. |
| [13] | 冯尔辉, 梁伟诺, 胡亮, 张旭. 海南东寨港国家级自然保护区潮间带蟹类(十足目: 短尾下目)物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23030-. |
| [14] | 梁伟诺, 张旭, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛潮间带蟹类(十足目: 短尾下目)物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23086-. |
| [15] | 苏荣菲, 陈睿山, 郭晓娜. 城市社区更新中生物多样性的保护策略: 以上海市长宁区生境花园为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23118-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn