



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 167-173. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13131 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13131
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yinbo Zhang1, Xiaolong Zhang1, Hu Yuan2,*( )
)
Received:2013-05-29
Accepted:2013-12-20
Online:2014-03-20
Published:2014-04-03
Contact:
Yuan Hu
Yinbo Zhang,Xiaolong Zhang,Hu Yuan. Assessing the in situ conservation status of key protected wild plants in Shanxi Province[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(2): 167-173.
| 类群 Group | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | I级保护物种 Category I | II级保护物种 Category II | 省级保护物种 Provincial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Pteridophyta | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 裸子植物 Gymnospermae | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 被子植物 Angiospermae | 33 | 40 | 51 | 0 | 6 | 45 |
| 总计 Total | 38 | 45 | 57 | 2 | 6 | 49 |
Table 1 Composition and protection categories of the key protected wild plants in Shanxi
| 类群 Group | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | I级保护物种 Category I | II级保护物种 Category II | 省级保护物种 Provincial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Pteridophyta | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 裸子植物 Gymnospermae | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 被子植物 Angiospermae | 33 | 40 | 51 | 0 | 6 | 45 |
| 总计 Total | 38 | 45 | 57 | 2 | 6 | 49 |
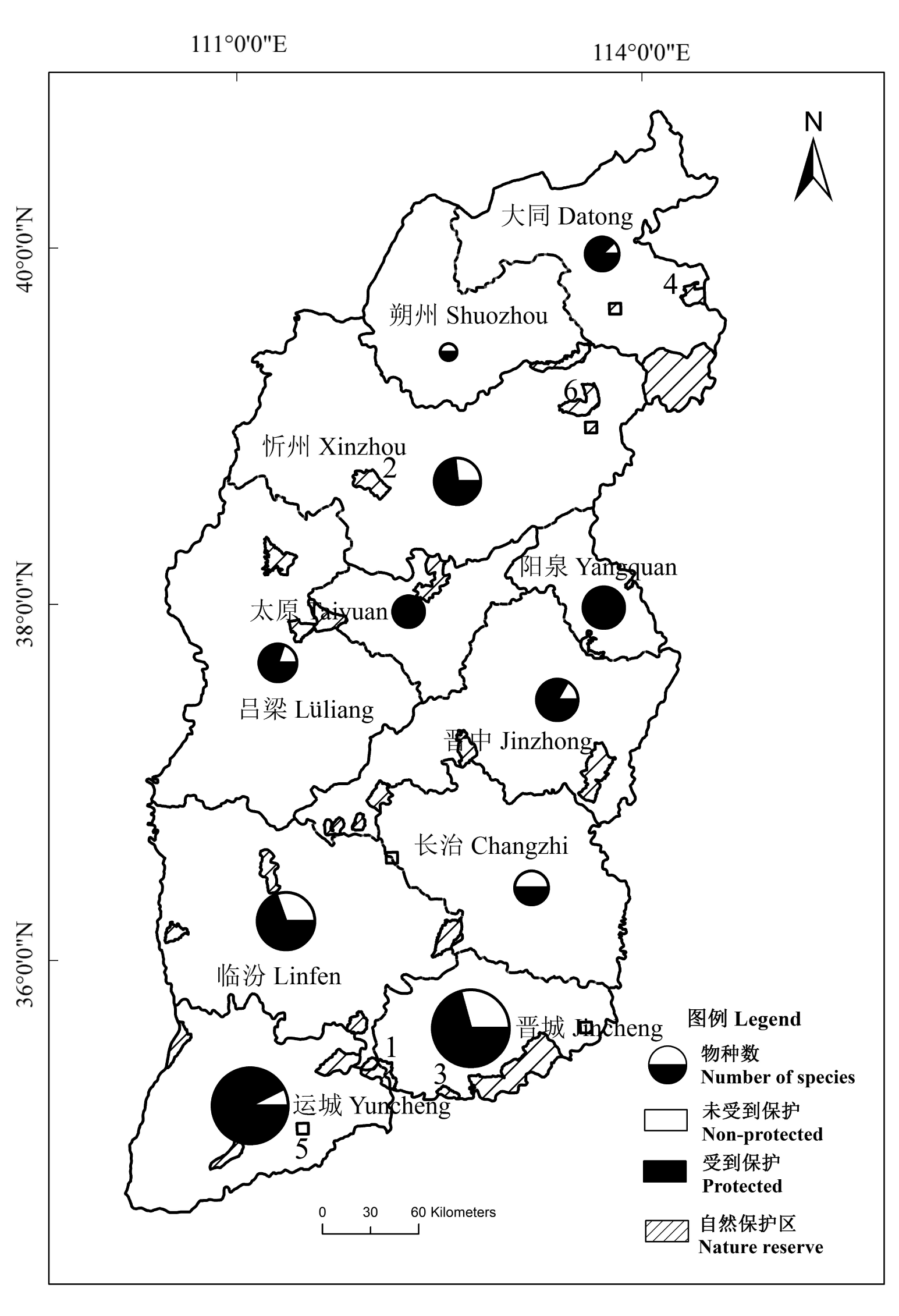
Fig. 1 The distribution and in situ conservation status of the key protected wild plants in Shanxi. 1. Lishan National Nature Reserve; 2. Luyashan National Nature Reserve; 3. Yangcheng Manghe Macaque National Nature Reserve; 4. Huliuhe Provincial Nature Reserve; 5. Taikuanhe Provincial Nature Reserve; 6. Fanshi Abies nephrolepis Provincial Nature Reserve.
| 分布保护区数 No. of reserves | 物种 Species |
|---|---|
| 1 | 臭冷杉、山橿、血皮槭、山桐子、红豆杉 Abies nephrolepis, Lindera reflexa, Acer griseum, Idesia polycarpa, Taxus wallichiana var. chinensis |
| 2 | 连香树、冬瓜杨、匙叶栎、泡花树、暖木、狗枣猕猴桃、四照花、迎红杜鹃 Cercidiphyllum japonicum, Populus purdomii, Quercus dolicholepis, Meliosma cuneifolia, Meliosma vertchiorum, Actinidia kolomikta, Cornus kousa subsp. chinensis, Rhododendron mucronulatum |
| 3 | 南方红豆杉、翅果油树、铁木、领春木、楔裂美花草、野茉莉、芬芳安息香 Taxus wallichiana var. mairei, Elaeagnus mollis, Ostrya japonica, Euptelea pleiosperma, Callianthemum cuneilobum, Styrax japonicus, Styrax odoratissimus |
| 4 | 水曲柳、异叶榕、宁武乌头、山西乌头、山胡椒、木姜子、山白树、软枣猕猴桃 Fraxinus mandschurica, Ficus heteromorpha, Aconitum ningwuense, Aconitum smithii, Lindera glauca, Litsea pungens, Sinowilsonia henryi, Actinidia arguta |
| 5 | 木贼麻黄、青檀、竹叶花椒、膀胱果、刺楸、角柱花、老鸹铃、络石、蝟实 Ephedra equisetina, Pteroceltis tatarinowii, Zanthoxylum armatum, Staphylea holocarpa, Kalopanax septemlobus, Ceratostigma plumbaginoides, Styrax hemsleyanus, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Kolkwitzia amabilis |
| 6 | 脱皮榆、省沽油、山茱萸 Ulmus lamellosa, Staphylea bumalda, Cornus officinalis |
| 7 | 红景天、窄叶紫珠 Rhodiola rosea, Callicarpa membranacea |
| 8 | 紫椴、漆树 Tilia amurensis, Toxicodendron vernicifluum |
| >8 | 野大豆、流苏树、文冠果、党参、桔梗 Glycine soja, Chionanthus retusus, Xanthoceras sorbifolia, Codonopsis pilosula, Platycodon grandiflorus |
Table 2 Number of nature reserves with distribution of the key protected wild plants in Shanxi
| 分布保护区数 No. of reserves | 物种 Species |
|---|---|
| 1 | 臭冷杉、山橿、血皮槭、山桐子、红豆杉 Abies nephrolepis, Lindera reflexa, Acer griseum, Idesia polycarpa, Taxus wallichiana var. chinensis |
| 2 | 连香树、冬瓜杨、匙叶栎、泡花树、暖木、狗枣猕猴桃、四照花、迎红杜鹃 Cercidiphyllum japonicum, Populus purdomii, Quercus dolicholepis, Meliosma cuneifolia, Meliosma vertchiorum, Actinidia kolomikta, Cornus kousa subsp. chinensis, Rhododendron mucronulatum |
| 3 | 南方红豆杉、翅果油树、铁木、领春木、楔裂美花草、野茉莉、芬芳安息香 Taxus wallichiana var. mairei, Elaeagnus mollis, Ostrya japonica, Euptelea pleiosperma, Callianthemum cuneilobum, Styrax japonicus, Styrax odoratissimus |
| 4 | 水曲柳、异叶榕、宁武乌头、山西乌头、山胡椒、木姜子、山白树、软枣猕猴桃 Fraxinus mandschurica, Ficus heteromorpha, Aconitum ningwuense, Aconitum smithii, Lindera glauca, Litsea pungens, Sinowilsonia henryi, Actinidia arguta |
| 5 | 木贼麻黄、青檀、竹叶花椒、膀胱果、刺楸、角柱花、老鸹铃、络石、蝟实 Ephedra equisetina, Pteroceltis tatarinowii, Zanthoxylum armatum, Staphylea holocarpa, Kalopanax septemlobus, Ceratostigma plumbaginoides, Styrax hemsleyanus, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Kolkwitzia amabilis |
| 6 | 脱皮榆、省沽油、山茱萸 Ulmus lamellosa, Staphylea bumalda, Cornus officinalis |
| 7 | 红景天、窄叶紫珠 Rhodiola rosea, Callicarpa membranacea |
| 8 | 紫椴、漆树 Tilia amurensis, Toxicodendron vernicifluum |
| >8 | 野大豆、流苏树、文冠果、党参、桔梗 Glycine soja, Chionanthus retusus, Xanthoceras sorbifolia, Codonopsis pilosula, Platycodon grandiflorus |
| [1] | Bi RC (毕润成) (2009) Scientific Research Report of Wulushan Nature Reserve in Shanxi (山西省五鹿山自然保护区科学考察报告). China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Brooks TM, da Fonseca GAB, Rodrigues ASL (2004) Protected areas and species. Conservation Biology, 18, 616–618. |
| [3] | Chen YH (陈雅涵), Tang ZY (唐志尧), Fang JY (方精云) (2009) Distribution of nature reserves and status of biodiversity protection in China. Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 17, 664–674. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Cui GF (崔国发) (2004) Special research fields and hot spots in science of nature reserves. Journal of Beijing Forestry University(北京林业大学学报), 26, 102–105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Ge JW (葛继稳), Wu JQ (吴金清), Zhu ZQ (朱兆泉), Yang JY (杨敬元), Lei Y (雷耘) (1998) The present status and in-situ conservation of the rare and endangered plants in Hubei Province. Chinese Biodiversity(生物多样性), 6, 220–228. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Jenkins CN, Joppa L (2009) Expansion of the global terrestrial protected area system. Biological Conservation, 142, 2166–2174. |
| [7] | Jiang MK (蒋明康), Wang Z (王智), Qin WH (秦卫华), He ZH (贺昭和) (2006) Effectiveness of national priority wildlife protection in nature reserves. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment(生态与农村环境学报), 22, 35–38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Jiang MK (蒋明康), Wang Z (王智), Zhu GQ (朱广庆), Tao SM (陶思明), Zhou HL (周海丽) (2004) Chinese nature reserve classification standard based on IUCN protected area categories. Rural Eco-Environment(农村生态环境), 20(2), 1–6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Joppa LN, Loarie SR, Pimm SL (2008) On the protection of “protected areas”. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences,USA, 105, 6673–6678. |
| [10] | Lu JL (卢景龙) (2009) Rare and endangered plants in Lishan Nature Reserve, Shanxi and their conservation. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition) (山西大学学报(自然科学版)), 32, 483–486. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Luan XF (栾晓峰), Zhou JH (周建华), Zhou N (周楠), Wu B (吴波), Li DQ (李迪强) (2009a) Preliminary assessment on management effectiveness of protected area in Northeast China. Journal of Natural Resources(自然资源学报), 24, 567–576. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Luan XF (栾晓峰), Huang WN (黄维妮), Wang XL (王秀磊), Liu MC (刘敏超), Liu SR (刘世荣), Wu B (吴波), Li DQ (李迪强) (2009b) Identification of hotspots and gaps for biodiversity conservation in Northeast China based on a systematic conservation planning methodology. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 29, 144–150. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Ministry of Environmental Protection, PRC (中华人民共和国环境保护部) (2012) Checklist of Nature Reserves of China (全国自然保护区名录).. (accessed August, 2012) (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Olson DM, Dinerstein E (1998) The global 200: a representation approach to conserving the Earth’s most biologically valuable ecoregions. Conservation Biology, 12, 502–515. |
| [15] | Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云), Wang XK (王效科), Miao H (苗鸿), Han NY (韩念勇) (2002) Problems of management system of China’s nature preservation zones. Science and Technology Review(科技导报), 20(1), 49–52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Pawar S, Koo MS, Kelley C, Ahmed MF, Chaudhuri S, Sarkar S (2007) Conservation assessment and prioritization of areas in Northeast India: priorities for amphibians and reptiles. Biological Conservation, 136, 346–361. |
| [17] | Qin WH (秦卫华), Jiang MK (蒋明康), Xu WG (徐网谷), He ZH (贺昭和) (2012) Assessment of in situ conservation of 1,334 native orchids in China. Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 20, 177–183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Sang WG, Ma KP, Axmacher JC (2011) Securing a future for China's wild plant resources. BioScience, 61, 720–725. |
| [19] | Shanxi Provincial People’s Government (山西省人民政府) (2004) List of Wild Plants under Provincial Protection in Shanxi (First Batch)(山西省重点保护野生植物名录第一批). Shanxi Province People's Government Documents, Jin Zheng Fa [2004] No. 45. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | State Forestry AdministrationMinistry of Agriculture, PRC (国家林业局和农业部) (1999) List of Wild Plants Under State Protection (First Batch) (国家重点保护野生植物名录第一批). Decree No. 4.(in Chinese) |
| [21] | Stem C, Margoluis R, Salafsky N, Brown M (2005) Monitoring and evaluation in conservation: a review of trends and approaches. Conservation Biology, 19, 295–309. |
| [22] | Tang ZY, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Fang JY (2006) Biodiversity in China’s mountains. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 4, 347–352. |
| [23] | Turner WR, Wilcove DS, Swain HM (2006) Assessing the effectiveness of reserve acquisition programs in protecting rare and threatened species. Conservation Biology, 20, 1657–1669. |
| [24] | Wang S (汪松), Xie Y (解焱) (2004) China Species Red List (中国物种红色名录). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | Wang Z (王智), Jiang MK (蒋明康), Qin WH (秦卫华) (2007) Criteria for evaluation of priority biodiversity nature reserves of China. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment(生态与农村环境学报), 23, 93–96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Xue DY (薛达元), Jiang MK (蒋明康) (1995) Contribution of nature reserves of China to biodiversity conservation. Journal of Natural Resources(自然资源学报), 10, 286–292. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Yu H (喻泓), Zhang XS (张学顺), Yang XH (杨晓晖), Xiao SG (肖曙光), Luo JC (罗菊春), Cui GF (崔国发) (2007) A new category system of China nature reserves based on their attributes. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 18, 2289–2294. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Yuan H (苑虎), Zhang YB (张殷波), Qin HN (覃海宁), Liu Y (刘燕), Yu M (喻梅) (2009) The in situ conservation of state key protected wild plants in national nature reserves in China. Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 17, 280–287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Zhang J (张军), Tian SW (田随味), Wei QH (魏清华), Zhang R (张蕊) (2004) Investigation and analysis of wild plants in Manghe Nature Reserve. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology(山西林业科技), 4, 27–29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Zhang YB (张殷波), Yan RF (闫瑞峰), Yuan H (苑虎), Li M (李明) (2010) Construction and management measures of nature reserves in Shanxi. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition) (山西大学学报(自然科学版)), 33, 625–630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Zhang YB (张殷波), Zhang XL (张晓龙), Lu YM (卢怡萌), Li M (李明) (2013) Resource and floristic characteristics of the key protection wild plants in Shanxi. Bulletin of Botanical Research(植物研究), 33(1), 18–23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Zhao SQ, Fang JY (2006) Patterns of species richness for vascular plants in China’s nature reserves. Diversity and Distributions, 12, 364–372. |
| [1] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [3] | Xuemeng Li, Jibao Jiang, Zenglu Zhang, Xiaojing Liu, Yali Wang, Yizhao Wu, Yinsheng Li, Jiangping Qiu, Qi Zhao. Earthworm biodiversity and its influencing factors in Baotianman National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [4] | Qifan Wang, Xiaohui Liu, Ziwei Zhu, Lei Liu, Xinxue Wang, Xuyang Ji, Shaochun Zhou, Zidong Zhang, Hongyu Dong, Minghai Zhang. Mammal and avian diversity in Beijicun National Nature Reserve, Heilongjiang Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [5] | Di Suo, Ruoxi Yu, Yuanhui Li, Jiliang Xu. Problem review and optimization path of local legislation in nature reserves in China based on empirical analysis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [6] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [7] | Xiaolong Huang, Bingshun Meng, Haibo Li, Wei Ran, Wei Yang, Cheng Wang, Bo Xie, Xu Zhang, Jingcheng Ran, Mingming Zhang. Interspecific associations between Rhinopithecus brelichi and its sympatric species using infrared cameras [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [8] | Xianglin Yang, Caiyun Zhao, Junsheng Li, Fangfang Chong, Wenjin Li. Invasive plant species lead to a more clustered community phylogenetic structure: An analysis of herbaceous plants in Guangxi’s national nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [9] | Ruirui Mao, Tuo Shen, Hui Li, Linchu Tian, Hairong Tan, Lirong Lu, Xiaogang Wu, Zongji Fan, Guoyi Wu, Jie Li, Yong Wu, Bicheng Zhu, Zhishu Xiao. A dataset of call characteristics of anuran from the Chebaling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [10] | Guofa Cui. Discussion and suggestions on several key issues in the integration and optimization of protected areas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [11] | Chao Xing, Yi Lin, Zhiqiang Zhou, Lianjun Zhao, Shiwei Jiang, Zhenzhen Lin, Jiliang Xu, Xiangjiang Zhan. The establishment of terrestrial vertebrate genetic resource bank and species identification based on DNA barcoding in Wanglang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [12] | Benping Chen, Jianwu Chen, Zhengwen Ling, Xu Yang, Xin Chen, Shengqiang Li, Biao Yang. Developing a dataset on the diversity and dynamic changes of mammals and birds recorded using camera traps in Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| [13] | Xue Yao, Xing Chen, Zun Dai, Kun Song, Shichen Xing, Hongyu Cao, Lu Zou, Jian Wang. Importance of collection strategy on detection probability and species diversity of epiphyllous liverworts [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| [14] | Lisong Wang, Qingqing Zhan, Jingping Liao, Hongwen Huang. Vascular plant diversity of National Key Protected Wild Plants, threatened species, and endemic species ex situ conserved in botanic gardens of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22495-. |
| [15] | Mengqiao Zhao, You Chen, Zhenghui Xu, Xubo Wang, Zhongliang Zhao, Wenchuan Xu, Zonghui He, Wenhua Wang. Ant species diversity along the vertical zones of the east slope of Ailao Mountain National Nature Reserve, Yunnan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23168-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn