



Biodiv Sci ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 22029. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022029 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022029
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mengjun Qu1, Nueryila·Ababaike 2, Xuge Zou1, Hang Zhao1, Weilin Zhu1, Jianming Wang1, Jingwen Li1,*( )
)
Received:2022-01-15
Accepted:2022-04-22
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-06-23
Contact:
Jingwen Li
Mengjun Qu, Nueryila·Ababaike , Xuge Zou, Hang Zhao, Weilin Zhu, Jianming Wang, Jingwen Li. Influence of geographic distance and environmental factors on beta diversity of plants in the Alxa gobi region in northern China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22029.
| 变量 Variables | 范围 Range | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 经度 Longitude | 98.06°-106.33° E | 102.82 | 2.38 |
| 纬度 Latitude | 37.47°-42.49° N | 40.54 | 1.36 |
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 855.00-1,937.67 | 1,228.55 | 245.82 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (%) | 0.05-7.87 | 1.93 | 1.79 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (mg/g) | 0.06-1.47 | 0.34 | 0.24 |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (mg/g) | 0.99-12.46 | 4.02 | 2.13 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 7.65-9.55 | 8.45 | 0.42 |
| 地表砾石盖度 Surface gravel coverage (%) | 0.00-0.95 | 0.46 | 0.26 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 5.18-9.14 | 7.85 | 1.07 |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month (℃) | -12.40 to -7.60 | -10.29 | 1.12 |
| 最热月均温 Mean temperature of warmest month (℃) | 20.00-26.50 | 24.00 | 1.57 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (℃) | 12.80-15.00 | 14.32 | 0.57 |
| 气温年较差 Temperature annual range (℃) | 42.90-51.50 | 48.18 | 2.11 |
| 年降水量 Annual precipitation (mm) | 29.00-223.00 | 90.20 | 53.73 |
| 湿润指数 Moisture index | -97.48 to -75.73 | -91.57 | 5.18 |
| 实际蒸散量 Actual evapotranspiration (mm) | 32.00-202.00 | 86.14 | 45.67 |
| 潜在蒸散量 Potential evapotranspiration (mm) | 919.00-1,157.00 | 1,086.26 | 54.99 |
Table 1 Descriptive statistics of geographic and environmental variables in Alxa gobi region
| 变量 Variables | 范围 Range | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 经度 Longitude | 98.06°-106.33° E | 102.82 | 2.38 |
| 纬度 Latitude | 37.47°-42.49° N | 40.54 | 1.36 |
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 855.00-1,937.67 | 1,228.55 | 245.82 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (%) | 0.05-7.87 | 1.93 | 1.79 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (mg/g) | 0.06-1.47 | 0.34 | 0.24 |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (mg/g) | 0.99-12.46 | 4.02 | 2.13 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 7.65-9.55 | 8.45 | 0.42 |
| 地表砾石盖度 Surface gravel coverage (%) | 0.00-0.95 | 0.46 | 0.26 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 5.18-9.14 | 7.85 | 1.07 |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month (℃) | -12.40 to -7.60 | -10.29 | 1.12 |
| 最热月均温 Mean temperature of warmest month (℃) | 20.00-26.50 | 24.00 | 1.57 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (℃) | 12.80-15.00 | 14.32 | 0.57 |
| 气温年较差 Temperature annual range (℃) | 42.90-51.50 | 48.18 | 2.11 |
| 年降水量 Annual precipitation (mm) | 29.00-223.00 | 90.20 | 53.73 |
| 湿润指数 Moisture index | -97.48 to -75.73 | -91.57 | 5.18 |
| 实际蒸散量 Actual evapotranspiration (mm) | 32.00-202.00 | 86.14 | 45.67 |
| 潜在蒸散量 Potential evapotranspiration (mm) | 919.00-1,157.00 | 1,086.26 | 54.99 |
| 影响因素 Variables | 控制因素 Control variables | Bray-Curtis | S?rensen | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | ||
| 环境距离 Environmental distance | - | 0.3063** | 0.2790** | -0.2198 | 0.3715** | 0.3052** | -0.1239 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | - | 0.2461** | 0.2006** | -0.1110 | 0.2706** | 0.2427** | -0.1333 |
| 环境距离 Environmental distance | 地理距离 Geographic distance | 0.2251** | 0.2151** | -0.1913 | 0.2896** | 0.2254** | -0.0717 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | 环境距离 Environmental distance | 0.1257** | 0.0860* | -0.0125 | 0.1226** | 0.1222** | -0.0870 |
Table 2 The correlation between β diversity and environmental distance or geographic distance using Mantel and partial Mantel tests (r value)
| 影响因素 Variables | 控制因素 Control variables | Bray-Curtis | S?rensen | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | ||
| 环境距离 Environmental distance | - | 0.3063** | 0.2790** | -0.2198 | 0.3715** | 0.3052** | -0.1239 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | - | 0.2461** | 0.2006** | -0.1110 | 0.2706** | 0.2427** | -0.1333 |
| 环境距离 Environmental distance | 地理距离 Geographic distance | 0.2251** | 0.2151** | -0.1913 | 0.2896** | 0.2254** | -0.0717 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | 环境距离 Environmental distance | 0.1257** | 0.0860* | -0.0125 | 0.1226** | 0.1222** | -0.0870 |
| Bray-Curtis指数 Bray-Curtis index | S?rensen指数 S?rensen index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 = 0.167 | R2 = 0.099 | R2 = 0.236 | R2 = 0.138 | |
| 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | |
| ln(地理距离) ln(Geographic distance) | 4.60 | 2.98 | 8.19 | 5.32 |
| 海拔 Altitude | 2.16 | - | 4.35 | - |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content | 2.21 | 1.55 | 3.56 | 2.21 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen | - | - | - | - |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | - | - | - | - |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 1.59 | - | - | - |
| 地表砾石盖度 Surface gravel coverage | 1.96 | 1.20 | 2.57 | 1.85 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | 1.85 | 1.89 | - | - |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month | - | - | - | - |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range | 2.33 | 2.31 | 4.93 | 4.43 |
| 气温年较差 Temperature annual range | - | - | - | - |
Table 3 Results of multiple regression analysis on matrices for β diversity
| Bray-Curtis指数 Bray-Curtis index | S?rensen指数 S?rensen index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 = 0.167 | R2 = 0.099 | R2 = 0.236 | R2 = 0.138 | |
| 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | |
| ln(地理距离) ln(Geographic distance) | 4.60 | 2.98 | 8.19 | 5.32 |
| 海拔 Altitude | 2.16 | - | 4.35 | - |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content | 2.21 | 1.55 | 3.56 | 2.21 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen | - | - | - | - |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | - | - | - | - |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 1.59 | - | - | - |
| 地表砾石盖度 Surface gravel coverage | 1.96 | 1.20 | 2.57 | 1.85 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | 1.85 | 1.89 | - | - |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month | - | - | - | - |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range | 2.33 | 2.31 | 4.93 | 4.43 |
| 气温年较差 Temperature annual range | - | - | - | - |
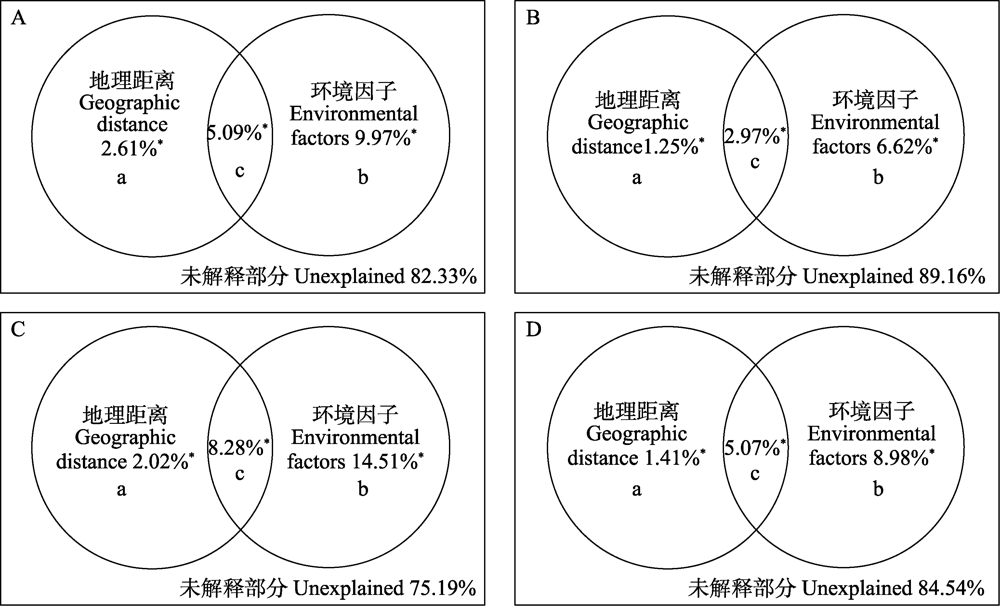
Fig. 3 The explanation of geographic distance and environmental factors to β diversity and its turnover components. A and B are the explanations of geographical distance and environmental factors to Bray-Curtis diversity and its turnover component; C and D are the explanations of geographical distance and environmental factors to S?rensen diversity and its turnover component. a, The independent influence of geographic distance; b, The independent influence of environmental factors; c, The combined influence of geographic distance and environmental factors. * P < 0.05.
| [1] |
Adler PB, HilleRisLambers J, Levine JM (2007) A niche for neutrality. Ecology Letters, 10, 95-104.
PMID |
| [2] | Arekhi S, Heydari M, Pourbabaei H (2010) Vegetation-environmental relationships and ecological species groups of the Ilam oak forest landscape, Iran. Caspian Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8, 115-125. |
| [3] | Baselga A (2007) Disentangling distance decay of similarity from richness gradients: Response to Soininen et al, 2007. Ecography, 30, 838-841. |
| [4] | Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143. |
| [5] | Baselga A, Orme D, Villeger S, De Bortoli JB, Leprieur F, Logez M, Henriques-Silva R (2021) betapart: Partitioning Beta Diversity into Turnover and Nestedness Components. R package version 1.5.4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=betapart. (accessed on 2022-03-07) |
| [6] | Blundo C, González-Espinosa M, Malizia LR (2016) Relative contribution of niche and neutral processes on tree species turnover across scales in seasonal forests of NW Argentina. Plant Ecology, 217, 359-368. |
| [7] | Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Gomes P (2012) Determining the relative roles of species replacement and species richness differences in generating beta-diversity patterns. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 760-771. |
| [8] |
Chase JM (2003) Community assembly: When should history matter? Oecologia, 136, 489-498.
PMID |
| [9] | Chen C, Wang Y, Wang JM, Yang H, Wang YC, Xu C, Li JW, Chu JM (2020) Species diversity of plant communities and its main influencing factors in Horqin Sandy Land, Inner Mongolia of northern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 42(5), 106-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈晨, 王寅, 王健铭, 杨欢, 王雨辰, 徐超, 李景文, 褚建民 (2020) 科尔沁沙地植物群落物种多样性及其主要影响因素. 北京林业大学学报, 42(5), 106-114.] | |
| [10] |
Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.]
DOI |
|
| [11] | Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 31, 343-366. |
| [12] |
Condit R, Pitman N, Leigh EG Jr, Chave J, Terborgh J, Foster RB, Núñez P, Aguilar S, Valencia R, Villa G, Muller-Landau HC, Losos E, Hubbell SP (2002) Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees. Science, 295, 666-669.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Cottenie K (2005) Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecology Letters, 8, 1175-1182.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | De Bello F, Lavergne S, Meynard CN, Lepš J, Thuiller W (2010) The partitioning of diversity: Showing Theseus a way out of the labyrinth. Journal of Vegetation Science, 21, 992-1000. |
| [15] | De Cáceres M, Legendre P, Valencia R, Cao M, Chang LW, Chuyong G, Condit R, Hao ZQ, Hsieh CF, Hubbell S, Kenfack D, Ma KP, Mi XC, Supardi Noor MN, Kassim AR, Ren HB, Su SH, Sun IF, Thomas D, Ye WH, He FL (2012) The variation of tree beta diversity across a global network of forest plots. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1191-1202. |
| [16] | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Gallardo A, Bowker MA, Wallenstein MD, Quero JL, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, García-Gómez M, Soliveres S, García-Palacios P, Berdugo M, Valencia E, Escolar C, Arredondo T, Barraza-Zepeda C, Bran D, Carreira JA, Chaieb M, Conceição AA, Derak M, Eldridge DJ, Escudero A, Espinosa CI, Gaitán J, Gatica MG, Gómez-González S, Guzman E, Gutiérrez JR, Florentino A, Hepper E, Hernández RM, Huber-Sannwald E, Jankju M, Liu JS, Mau RL, Miriti M, Monerris J, Naseri K, Noumi Z, Polo V, Prina A, Pucheta E, Ramírez E, Ramírez-Collantes DA, Romáo R, Tighe M, Torres D, Torres-Díaz C, Ungar ED, Val J, Wamiti W, Wang DL, Zaady EL (2013) Decoupling of soil nutrient cycles as a function of aridity in global drylands. Nature, 502, 672-676. |
| [17] | Dobrovolski R, Melo AS, Cassemiro FAS, Diniz-Filho JAF (2012) Climatic history and dispersal ability explain the relative importance of turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 191-197. |
| [18] | Goslee S, Urban D (2021) ecodist: Dissimilarity-Based Functions for Ecological Analysis. R package version 2.0.7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ecodist. (accessed on 2022-03-07) |
| [19] |
Gravel D, Canham CD, Beaudet M, Messier C (2006) Reconciling niche and neutrality: The continuum hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 9, 399-409.
PMID |
| [20] | Gundale MJ, Fajardo A, Lucas RW, Nilsson MC, Wardle DA (2011) Resource heterogeneity does not explain the diversity-productivity relationship across a boreal island fertility gradient. Ecography, 34, 887-896. |
| [21] |
Guo YL, Xiang WS, Wang B, Li DX, Mallik AU, Chen HYH, Huang FZ, Ding T, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Li XK (2018) Partitioning beta diversity in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Southern China. Scientific Reports, 8, 17408.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Harrell JFE, Dupont C (2021) Hmisc: Harrell Miscellaneous. R package version 4.6-0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package= Hmisc. (accessed on 2022-03-07) |
| [23] | Hijmans RJ, Karney C, Williams E, Vennes C (2021) Geosphere: Spherical Trigonometry. R package version 1.5-14. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=geosphere. (accessed on 2022-03-07) |
| [24] | Hubbell SP (2001) A Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [25] | Jia ZT, Yang JY, Sun YX, Chen Q, Yan RL, Li NN (2021) Analysis of species diversity and regulation factors of Salsola passerina community in Alxa Plateau. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 43(6), 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾喆亭, 杨九艳, 孙艳霞, 陈琪, 闫瑞玲, 李娜娜 (2021) 阿拉善高原珍珠猪毛菜群落物种多样性及与环境因子的相关性. 中国草地学报, 43(6), 1-9.] | |
| [26] | Jones MM, Tuomisto H, Borcard D, Legendre P, Clark DB, Olivas PC (2008) Explaining variation in tropical plant community composition: Influence of environmental and spatial data quality. Oecologia, 155, 593-604. |
| [27] | Legendre P (2007) Studying beta diversity: Ecological variation partitioning by multiple regression and canonical analysis. Journal of Plant Ecology, 1, 3-8. |
| [28] |
Legendre P, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP, Yu MJ, Sun IF, He FL (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. Ecology, 90, 663-674.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Leprieur F, Oikonomou A (2014) The need for richness-independent measures of turnover when delineating biogeographical regions. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 417-420. |
| [30] | Li XR, Tan HJ, He MZ, Wang XP, Li XJ (2009) Response of shrub species richness and abundance patterns to changes in environmental factors in Alxa Plateau: A precondition for shrub diversity conservation in extreme arid desert region. Science in China (Series D: Earth Science), 39, 504-515. (in Chinese) |
| [李新荣, 谭会娟, 何明珠, 王新平, 李小军 (2009) 阿拉善高原灌木种的丰富度和多度格局对环境因子变化的响应: 极端干旱荒漠地区灌木多样性保育的前提. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 39, 504-515.] | |
| [31] | Luo N, Liu ZC, Yu H, Liu T (2016) Regional differences in plant diversity in the southern Gurbantonggut Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 3572-3581. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗宁, 刘尊驰, 于航, 刘彤 (2016) 古尔班通古特沙漠南部植物多样性的区域差异. 生态学报, 36, 3572-3581.] | |
| [32] | Maestre FT, Salguero-Gómez R, Quero JL (2012) It is getting hotter in here: Determining and projecting the impacts of global environmental change on drylands. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 367, 3062-3075. |
| [33] |
Niu KC, Liu YN, Shen ZH, He FL, Fang JY (2009) Community assembly: The relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 579-593. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[牛克昌, 刘怿宁, 沈泽昊, 何芳良, 方精云 (2009) 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论. 生物多样性, 17, 579-593.]
DOI |
|
| [34] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2020) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.5-7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. (accessed on 2022-03-07) |
| [35] |
Qiao XJ, Li QX, Jiang QH, Lu JM, Franklin S, Tang ZY, Wang QG, Zhang JX, Lu ZJ, Bao DC, Guo YL, Liu HB, Xu YZ, Jiang MX (2015) Beta diversity determinants in Badagongshan, a subtropical forest in Central China. Scientific Reports, 5, 17043.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Si XF, Baselga A, Ding P (2015) Revealing beta-diversity patterns of breeding bird and lizard communities on inundated land-bridge islands by separating the turnover and nestedness components. PLoS ONE., 10, e0127692. |
| [37] | Soininen J, Heino J, Wang JJ (2018) A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 96-109. |
| [38] | Svenning JC, Fløjgaard C, Baselga A (2011) Climate, history and neutrality as drivers of mammal beta diversity in Europe: Insights from multiscale deconstruction. Journal of Animal Ecology, 80, 393-402. |
| [39] | Tang Z, Fang J, Chi X, Yang Y, Ma W, Mohhamot A, Guo Z, Liu Y, Gaston KJ (2012) Geography, environment, and spatial turnover of species in China’s grasslands. Ecography, 35, 1103-1109. |
| [40] | Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geographical Review, 38, 55-94. |
| [41] |
Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M (2003) Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science, 299, 241-244.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | Tuomisto H (2010a) A diversity of beta diversities: Straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 1. Defining beta diversity as a function of alpha and gamma diversity. Ecography, 33, 2-22. |
| [43] | Tuomisto H (2010b) A diversity of beta diversities: Straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 2. Quantifying beta diversity and related phenomena. Ecography, 33, 23-45. |
| [44] | Unger PW (1971) Soil profile gravel layers. II. Effect on growth and water use by a hybrid forage sorghum. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 35, 980-983. |
| [45] | Wang JM (2019) Biogeographical Patterns and Its Environmental Interpretation of Plant and Soil Microbial Diversity in Temperate Desert Regions of China. PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 王健铭 (2019) 中国温带荒漠区植物与土壤微生物多样性地理格局及其环境解释. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| [46] | Wang JM, Chen C, Li JW, Feng YM, Lu Q (2019) Different ecological processes determined the alpha and beta components of taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic diversity for plant communities in dryland regions of Northwest China. PeerJ, 6, e6220. |
| [47] | Wang JM, Cui PJ, Zhong YM, Li JW, Chu JM (2019) Biogeographic patterns and environmental interpretation of plant regional species richness in Alxa Plateau of northern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 41(3), 14-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王健铭, 崔盼杰, 钟悦鸣, 李景文, 褚建民 (2019) 阿拉善高原植物区域物种丰富度格局及其环境解释. 北京林业大学学报, 41(3), 14-23.] | |
| [48] |
Wang JM, Wang WJ, Li JW, Feng YM, Wu B, Lu Q (2017) Biogeographic patterns and environmental interpretation of plant species richness in desert regions of Northwest China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1192-1201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王健铭, 王文娟, 李景文, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦 (2017) 中国西北荒漠区植物物种丰富度分布格局及其环境解释. 生物多样性, 25, 1192-1201.]
DOI |
|
| [49] | Wang XG, Wiegand T, Anderson-Teixeira KJ, Bourg NA, Hao ZQ, Howe R, Jin GZ, Orwig DA, Spasojevic MJ, Wang SZ, Wolf A, Myers JA (2018) Ecological drivers of spatial community dissimilarity, species replacement and species nestedness across temperate forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 581-592. |
| [50] |
Weng CL, Zhang TT, Wu DH, Chen SW, Jin Y, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Luo YY (2019) Drivers and patterns of α- and β-diversity in ten main forest community types in Gutianshan, Eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 33-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[翁昌露, 张田田, 巫东豪, 陈声文, 金毅, 任海保, 于明坚, 罗媛媛 (2019) 古田山10种主要森林群落类型的α和β多样性格局及影响因素. 生物多样性, 27, 33-41.]
DOI |
|
| [51] | Williams PH (1996) Mapping variations in the strength and breadth of biogeographic transition zones using species turnover. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 263, 579-588. |
| [52] | Williams PH, de Klerk HM, Crowe TM (1999) Interpreting biogeographical boundaries among Afrotropical birds: Spatial patterns in richness gradients and species replacement. Journal of Biogeography, 26, 459-474. |
| [53] | Xia YG, Ning Y, Li JW, Li JQ, Feng YM, Wu B, Lu Q (2013) Plant species diversity and floral characters in the black gobi desert of China. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 33, 1906-1915. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏延国, 宁宇, 李景文, 李俊清, 冯益民, 吴波, 卢琦 (2013) 中国黑戈壁地区植物区系及其物种多样性研究. 西北植物学报, 33, 1906-1915.] | |
| [54] | Yang H, Wang Y, Wang JM, Xia YG, Li JW, Jia XH, Wu B (2021) Effects of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on the β-diversity of plant communities in the south fringe of Kumtag Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 41, 147-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨欢, 王寅, 王健铭, 夏延国, 李景文, 贾晓红, 吴波 (2021) 环境过滤和扩散限制对库姆塔格沙漠南缘植物群落β-多样性的影响. 中国沙漠, 41, 147-154.] | |
| [55] |
Yao ZL, Wen HD, Deng Y, Cao M, Lin LX (2020) Driving forces underlying the beta diversity of tree species in subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forests in Ailao Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 28, 445-454. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[姚志良, 温韩东, 邓云, 曹敏, 林露湘 (2020) 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林树种beta多样性格局形成的驱动力. 生物多样性, 28, 445-454.]
DOI |
|
| [56] |
Zhang PP, Shao MA, Zhang XC (2017) Spatial pattern of plant species diversity and the influencing factors in a Gobi Desert within the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Journal of Arid Land, 9, 379-393.
DOI |
| [57] | Zhang XS (2007) Vegetation Map of China (1:1 million) (Vol. I). Geological Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张新时 (2007) 中国植被及其地理格局中华人民共和国植被图集(1:100 万)说明书(上卷). 地质出版社, 北京.] | |
| [58] | Zhu JT, Yu JJ, Wang P, Yu Q, Eamus D (2013) Distribution patterns of groundwater-dependent vegetation species diversity and their relationship to groundwater attributes in northwestern China. Ecohydrology, 6, 191-200. |
| [59] | Zhu ZD (1994) Sandy Desertification of Land in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [朱震达 (1994) 中国土地沙质荒漠化. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | Guoshan Shi, Feng Liu, Guanghong Cao, Dian Chen, Shangwen Xia, Yun Deng, Bin Wang, Xiaodong Yang, Luxiang Lin. Beta diversity of woody plants in a tropical seasonal rainforest at Xishuangbanna: Roles of space, environment, and forest stand structure [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [2] | Weiwei Wang, Xiangcheng Mi, Ningning Wang, Haibao Ren, Zhixi Tang, Zhuning Zhang, Keping Ma, Lei Chen. Plant diversity dataset of the 24-ha Zhejiang Gutianshan subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest dynamics plot (2005-2020) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24417-. |
| [3] | Yue Chen, Zikun Mao, Xugao Wang. Research advances and prospects on β diversity based on ecological uniqueness [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24199-. |
| [4] | Qing Yang, Xiaodong Li, Shengxian Yang, Xin Chao, Huiqiu Liu, Sang Ba. Protozoan community diversity and its impact factor in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River in the wet season [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22500-. |
| [5] | Xiaofeng Wang, Jiesheng Rao, Tao Yang, Wencong Liu, Xi Tian, Xi Chen, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Qiuyu Zhang, Hongqiang Zhang, Xu Zhang, Xiaokun Ou, Zehao Shen. Spatial variation and determinants of woody plant species diversity in a semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [6] | Yanhui Li, Tianyuan Lan, Yue Wang, Yang Yu, Changming Zhao, Lihua Li, Wenting Xu, Guozhen Shen. Driving factors of spatial turnover of plant species in Shennongjia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21377-. |
| [7] | Danqi She, Xiting Zhang, Lu Xiao, Zhaoliang Zhong, Huimei Wang, Wenjie Wang. Plant beta diversity and its influence factors in the Liangshui National Nature Reserve in the central region of the Xiaoxing’an Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(3): 21274-. |
| [8] | Xiangcheng Mi, Xugao Wang, Guochun Shen, Xubin Liu, Xiaoyang Song, Xiujuan Qiao, Gang Feng, Jie Yang, Zikun Mao, Xuehong Xu, Keping Ma. Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network (CForBio): Twenty years of exploring community assembly mechanisms and prospects for future research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22504-. |
| [9] | Zhiliang Yao,Handong Wen,Yun Deng,Min Cao,Luxiang Lin. Driving forces underlying the beta diversity of tree species in subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forests in Ailao Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(4): 445-454. |
| [10] | Mingjia Li, Kaiyuan Wu, Fanfan Meng, Ji Shen, Yongqin Liu, Nengwen Xiao, Jianjun Wang. Beta diversity of stream bacteria in Hengduan Mountains: The effects of climatic and environmental variables [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(12): 1570-1580. |
| [11] | Gui Xujun, Lian Juyu, Zhang Ruyun, Li Yanpeng, Shen Hao, Ni Yunlong, Ye Wanhui. Vertical structure and its biodiversity in a subtropical evergreen broad- leaved forest at Dinghushan in Guangdong Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(6): 619-629. |
| [12] | Xiangyu Liu, Ciliang Zhao, Mingshan Xu, Qiming Liang, Xiaotong Zhu, Liang Li, Enrong Yan. Beta diversity of vascular plants and its drivers in sea-islands of eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 380-387. |
| [13] | Haonan Zhou, Yuhao Zhao, Di Zeng, Juan Liu, Tinghao Jin, Ping Ding. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of ground ant species diversity on the land-bridge islands in the Thousand Island Lake, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(10): 1101-1111. |
| [14] | Tiantian Zhang, Xuan Wang, Haibao Ren, Jianping Yu, Yi Jin, Haiyuan Qian, Xiaoyou Song, Keping Ma, Mingjian Yu. A comparative study on the community characteristics of secondary and old-growth evergreen broad-leaved forests in Gutianshan, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(10): 1069-1080. |
| [15] | Weng Changlu,Zhang Tiantian,Wu Donghao,Chen Shengwen,Jin Yi,Ren Haibao,Yu Mingjian,Luo Yuanyuan. Drivers and patterns of α- and β-diversity in ten main forest community types in Gutianshan, eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(1): 33-41. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()