



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1313-1320. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017076 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017076
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yang Meng1,2, Yue Qiu1,2, Liang Zhang1,3, Cuiling Wang1,2, Zhenhua Zang1,4, Xueyao Zhang1,2, Guozhen Shen1, Caifeng Yan1, Quansheng Chen1,3,*( )
)
Received:2017-11-23
Accepted:2017-11-26
Online:2017-12-20
Published:2017-12-10
Contact:
Chen Quansheng
Yang Meng, Yue Qiu, Liang Zhang, Cuiling Wang, Zhenhua Zang, Xueyao Zhang, Guozhen Shen, Caifeng Yan, Quansheng Chen. Effects of geographical distance and differences in climate and altitude on species dissimilarity of vascular plant communities in the Dulongjiang River Watershed Area[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(12): 1313-1320.
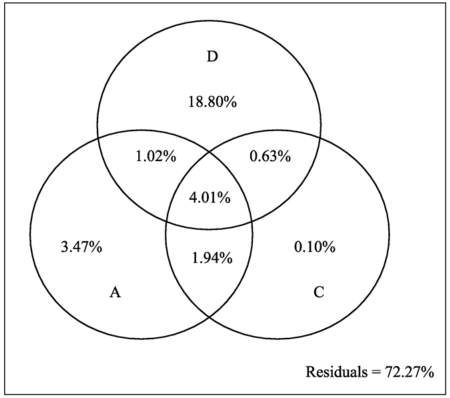
Fig. 4 Partitional effects of Ln-transformed geographic distance (D), altitude difference (A) and climatic difference (C) on species turnover of plants.
| [1] | Aiello-Lammens ME, Slingsby JA, Merow C, Mollmann HK, Euston-Brown D, Jones CS, Silander JA (2016) Processes of community assembly in an environmentally heterogeneous, high biodiversity region. Ecography, 39, 1-16. |
| [2] | Blundo C, Gonzalez-Espinosa M, Malizia LR (2016) Relative contribution of niche and neutral processes on tree species turnover across scales in seasonal forests of NW Argentina. Plant Ecology, 217, 359-368. |
| [3] | Chave J, Muller-Landau HC, Levin SA (2002) Comparing classical community models: theoretical consequences for patterns of diversity. The American Naturalist, 159, 1-23. |
| [4] | Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.] | |
| [5] | Chen Y, Yuan ZL, Li PK, Cao RF, Jia HR, Ye YZ (2016) Effects of environment and space on species turnover of woody plants across multiple forest dynamic plots in East Asia. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1-11. |
| [6] | Cheng JJ, Mi XC, Ma KP, Zhang JT (2011) Responses of species-abundance distribution to varying sampling scales in a subtropical broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science, 19, 168-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程佳佳, 米湘成, 马克平, 张金屯 (2011) 亚热带常绿阔叶林群落物种多度分布格局对取样尺度的响应. 生物多样性, 19, 168-177.] | |
| [7] | Dodson R, Marks D (1997) Daily air temperature interpolated at high spatial resolution over a large mountainous region. Climate Research, 8, 1-20. |
| [8] | Fahrig L, Baudry J, Brotons L, Burel FG, Crist TO, Fuller RJ, Sirami C, Siriwardena GM, Martin JL (2011) Functional landscape heterogeneity and animal biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Ecology Letters, 14, 101-112. |
| [9] | Feng JM, Wang XP, Fang JY (2006) Altitudinal pattern of species richness and test of the Rapoport’s rules in the Drung River Area, Southwest China. Acta Scientiarum Na¬tu¬ralium Universitatis Pekinensis, 42, 515-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯建孟, 王襄平, 方精云 (2006) 云南独龙江地区种子植物物种多样性垂直分布格局和 Rapoport法则的验证. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 42, 515-520.] | |
| [10] | Freestone AL, Inouye BD (2006) Dispersal limitation and environmental heterogeneity shape scale-dependent diversity patterns in plant communities. Ecology, 87, 2425-2432. |
| [11] | Gueze M, Paneque-Galvez J, Luz AC, Pino J, Orta-Martinez M, Reyes-Garcia V, Macia MJ (2013) Determinants of tree species turnover in a southern Amazonian rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 284-295. |
| [12] | Hager A (2010) The effect of climate and soil conditions on tree species turnover in a tropical montane cloud forest in Costa Rica. Revista De Biologia Tropical, 58, 1489-1506. |
| [13] | Hardy OJ, Couteron P, Munoz F, Ramesh BR, Pelissier R (2012) Phylogenetic turnover in tropical tree communities: impact of environmental filtering, biogeography and mesoclimatic niche conservatism. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1007-1016. |
| [14] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [15] | Jones MM, Gibson N, Yates C, Ferrier S, Mokany K, Williams KJ, Manion G, Svenning JC (2016) Underestimated effects of climate on plant species turnover in the Southwest Australian Floristic Region. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 289-300. |
| [16] | Jones MM, Tuomisto H, Clark DB, Olivas P (2006) Effects of mesoscale environmental heterogeneity and dispersal limitation on floristic variation in rain forest ferns. Journal of Ecology, 94, 181-195. |
| [17] | Leps J, de Bello F, Smilauer P, Dolezal J (2011) Community trait response to environment: disentangling species turnover vs. intraspecific trait variability effects. Ecography, 34, 856-863. |
| [18] | Li H (1996) Investigation on the overwintering of Dulongjiang Plant. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 8, 93-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李恒 (1996) 独龙江植物越冬考察记实. 云南地理环境研究, 8, 93-96.] | |
| [19] | Li XH, Liu YH, Liu Y, Xu Y, Yang Y, Shen ZH (2016) Impacts of geographical distances and environmental differences on the beta diversity of plant communities in the dry-hot valley of the Yuanjiang River. Biodiversity Science, 24, 399-406. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李新辉, 刘延虹, 刘晔, 许玥, 杨阳, 沈泽昊 (2016) 地理距离及环境差异对云南元江干热河谷植物群落beta多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 399-406.] | |
| [20] | Li XZ (1996) Landforms in Drang River Basin. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 8, 59-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李先之 (1996) 独龙江流域地貌. 云南地理环境研究, 8, 59-72.] | |
| [21] | Liu WL, Yang J, Sun J, Li XZ (2016) Species turnover of wetland vegetation in northeastern China: disentangling the relative effects of geographic distance, climate, and hydro-geomorphology. Flora, 220, 1-7. |
| [22] | Loke LH, Bouma TJ, Todd PA (2017) The effects of manipulating microhabitat size and variability on tropical seawall biodiversity: field and flume experiments. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 492, 113-120. |
| [23] | Ma KP (2016) Conservation biology, conservation ecology and biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 24, 125-126. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2016) 保护生物学, 保护生态学与生物多样性科学. 生物多样性, 24, 125-126.] | |
| [24] | Ma KP, Qian YQ, Wang C (1995) Present state and future of biodiversity studies. Science and Technology Review, 13, 27-30. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 钱迎倩, 王晨 (1995) 生物多样性研究的现状与发展趋势. 科技导报, 13, 27-30.] | |
| [25] | Ma KP, Ye WH, Yu SL, Ma KM, Wang W, Guan WB (1997) Studies on plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 17, 593-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 叶万辉, 于顺利, 马克明, 王巍, 关文彬 (1997) 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性研究. 生态学报, 17, 593-600.] | |
| [26] | Marion ZH, Fordyce JA, Fitzpatrick BM (2017) Pairwise beta diversity resolves an underappreciated source of confusion in calculating species turnover. Ecology, 98, 933-939. |
| [27] | McCain CM, Beck J (2016) Species turnover in vertebrate communities along elevational gradients is idiosyncratic and unrelated to species richness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 299-310. |
| [28] | McGlinn DJ, Palmer MW (2011) Quantifying the influence of environmental texture on the rate of species turnover: evidence from two habitats. Plant Ecology, 212, 495-506. |
| [29] | Mena JL, Vazquez-Dominguez E (2005) Species turnover on elevational gradients in small rodents. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 14, 539-547. |
| [30] | Michel AK, Winter S (2009) Tree microhabitat structures as indicators of biodiversity in Douglas-fir forests of different stand ages and management histories in the Pacific Northwest, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 257, 1453-1464. |
| [31] | Murphy SJ, Salpeter K, Comita LS (2016) Higher beta-di¬versity observed for herbs over woody plants is driven by stronger habitat filtering in a tropical understory. Ecology, 97, 2074-2084. |
| [32] | Niu KC, Liu YN, Shen ZH, He FL, Fang JY (2009) Community assembly: the relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 579-593. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛克昌, 刘怿宁, 沈泽昊, 何芳良, 方精云 (2009) 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论. 生物多样性, 17, 579-593.] | |
| [33] | Oksanen J, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara B, Stevens MHH, Oksanen MJ, Suggests M (2007) The vegan package. Community Ecology Package. R Package version 2.0-4.0.2007) The vegan package. Community Ecology Package. R Package version 2.0-4.0. |
| [34] | Pandit SN, Kolasa J (2012) Opposite effects of environmental variability and species richness on temporal turnover of species in a complex habitat mosaic. Hydrobiologia, 685, 145-154. |
| [35] | Qian H, Badgley C, Fox DL (2009) The latitudinal gradient of beta diversity in relation to climate and topography for mammals in North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 111-122. |
| [36] | Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2012) Disentangling the effects of geographic distance and environmental dissimilarity on global patterns of species turnover. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 341-351. |
| [37] | Qian H, Shimono A (2012) Effects of geographic distance and climatic dissimilarity on species turnover in alpine meadow communities across a broad spatial extent on the Tibetan Plateau. Plant Ecology, 213, 1357-1364. |
| [38] | Ruokolainen K, Tuomisto H (2002) Beta-diversity in tropical forests. Science, 297, 1439. |
| [39] | Tian H (1994) The soil type and distribution regular of Dulongjiang River basin. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 2, 17-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田宏 (1994) 独龙江流域土壤类型及分布规律. 云南地理环境研究, 2, 17-26.] | |
| [40] | Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M (2003) Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science, 299, 241-244. |
| [41] | Ulrich W, Jabot F, Gotelli NJ (2017) Competitive interactions change the pattern of species co-occurrences under neutral dispersal. Oikos, 126, 91-100. |
| [42] | Wang CY, He ZR, Peng MC (2013) Studies on Vegetation and Plants in Dulongjiang (Upper Irrawaddy River) Watershed and Adjacent Area. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王崇云, 和兆荣, 彭明春 (2013) 独龙江流域及邻近区域植被与植物研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Wang S, Wang X, Guo H, Fan W, Lü H, Duan R (2013) Distinguishing the importance between habitat specialization and dispersal limitation on species turnover. Ecology and Evolution, 3, 3545-3553. |
| [44] | Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 280-338. |
| [45] | Zemunik G, Turner BL, Lambers H, Laliberte E (2016) Increasing plant species diversity and extreme species turnover accompany declining soil fertility along a long-term chronosequence in a biodiversity hotspot. Journal of Ecology, 104, 792-805. |
| [46] | Zhao MF, Wang GY, Xing KX, Wang GY, Wang YH, Xue F, Kang MY, Luo K (2017) Patterns and determinants of species similarity decay of forest communities in the western Qinling Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 25, 3-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵鸣飞, 王国义, 邢开雄, 王宇航, 薛峰, 康慕谊, 罗开 (2017) 秦岭西部森林群落相似性递减格局及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 25, 3-10.] |
| [1] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [2] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [3] | Gu Jingjing, Liu Yizhuo, Su Yang. The functions and challenges of grass-roots local governments in fulfilling the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework—A comparative analysis with the objectives of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [4] | Lei Liu, Zhiming Hao, Leshan Du, Haiou Liu. Mainstreaming gender in China’s biodiversity actions under Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24235-. |
| [5] | Yuan Liu, Jianqing Du, Liyuan Ma, Gang Yang, Jianqing Tian. Diversity and distribution of methanogen communities in the riparian wetlands of the Nam Co basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24247-. |
| [6] | Yongjin Han, Yongliang Liang, Yijie Tong, Qiang Ding, Zhehao Tian, Lulu Li, Xiaojuan Li, Hao Shen, Yachao Zhu, Ning Liu, Xinpu Wang, Ming Bai. Dataset of beetle specimen images based on three passive acquisition methods in Mt. Helanshan, Ningxia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24054-. |
| [7] | Mengyao Zheng, Yuan Li, Xuerong Wang, Yue Zhang, Tong Jia. Soil protozoa community assembly mechanism in different vegetation types of Luya Mountain [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| [8] | Rui Qu, Zhenjun Zuo, Youxin Wang, Liangjian Zhang, Zhigang Wu, Xiujuan Qiao, Zhong Wang. The biogeochemical niche based on elementome and its applications in different ecosystems [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [9] | Haiou Liu, Leshan Du, Wenhui Liu, Ziyuan Li, Libo Pan, Lei Liu. Analysis and enlightenment on Global Biodiversity Framework Fund management policy [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23334-. |
| [10] | Guoshan Shi, Feng Liu, Guanghong Cao, Dian Chen, Shangwen Xia, Yun Deng, Bin Wang, Xiaodong Yang, Luxiang Lin. Beta diversity of woody plants in a tropical seasonal rainforest at Xishuangbanna: Roles of space, environment, and forest stand structure [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [11] | Kailun Xu, Xiaorong Chen, Minhua Zhang, Wanwan Yu, Sumei Wu, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Rongguang Lan, Shu Dong, Yu Liu. Succession and topography jointly influence the diversity of plant sexual systems in the Baishanzu forest community [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| [12] | Yijia Geng, Yu Tian, Junsheng Li, Ziyuan Li, Yuxue Pan. The global progress, ongoing challenges, and future prospects of invasive alien species under the framework of Convention on Biological Diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24275-. |
| [13] | Hao Shen, Yijie Tong, Shuzhe Zhao, Yongjin Han, Xiaoxu Shi, Bei Teng, Xinpu Wang, Ming Bai. A photographic dataset of the beetle specimens by three passive acquisition methods in Ma On Shan, Hong Kong [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23021-. |
| [14] | Shengxian Yang, Qing Yang, Xiaodong Li, Xin Chao, Huiqiu Liu, Lanruoxue Wei, Sang Ba. Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [15] | Yijia Geng, Ziyuan Li, Yu Tian. Convention on Biological Diversity: The current status, ongoing challenges, and future prospects of marine biodiversity conservation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22645-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn