



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 24121. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024121 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024121
• Technology and Methodologies • Next Articles
Wanjun Hu1, Zezhou Hao2( ), Canwei Xia3(
), Canwei Xia3( ), Jiangjian Xie1,4,5,*(
), Jiangjian Xie1,4,5,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-03-30
Accepted:2024-05-28
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-16
Contact:
*E-mail: shyneforce@bjfu.edu.cn
Supported by:Wanjun Hu, Zezhou Hao, Canwei Xia, Jiangjian Xie. Wetland soundscape recording scheme and feature selection for soundscape classification[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24121.
| 声学指数 Acoustic indices | 计算公式 Computing formula | 描述 Description | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 声学复杂度指数 Acoustic complexity index (ACI) | 相邻频段窗口音量的变化; D为相邻频段音量差的累积; Ik为各频段的音量 Difference in amplitude among samples; D is summary of intensity difference among adjacent frequency bands ; Ik is intensity in a single frequency band | Pieretti et al, | |
| 声学多样性指数 Acoustic diversity index (ADI) | 基于Shannon指数量化音量在不同频段的分布; pi是每个频率区间的相对强度 Spectral complexity based on Shannon index; pi is relative intensity in each frequency band | Villanueva-Rivera et al, | |
| 声学均匀度指数 Acoustic evenness index (AEI) | 基于Gini指数量化音量在不同频段的分布; I是音量 Gini coefficient with intensity at each frequency band; I is intensity | Villanueva-Rivera et al, | |
| 生物声学指数 Bioacoustic index (BIO) | 特定频段音量的汇总; Ik为各频段的音量 Sum of intensity in particular frequency band; Ik is intensity in a single frequency band | Boelman et al, | |
| 声熵指数 Acoustic entropy index (H) | 时间熵(Ht)和频谱熵(Hf)的乘积 Product of time entropy (Ht) and spectral entropy (Hf) | Sueur et al, | |
| 振幅包络线中值 Median of the amplitude envelope (M) | 声音振幅包络值的中值; Ak是振幅包络值 Median of the amplitude envelope value; Ak is amplitude envelope value | Depraetere et al, | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 Normalized difference sound index (NDSI) | 生物产生音量(b)与人类产生音量(a)的比率 Ratio of amplitude in biophony (b) and anthrophony (a) | Kasten et al, |
Table 1 Seven acoustic indices used in this study
| 声学指数 Acoustic indices | 计算公式 Computing formula | 描述 Description | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 声学复杂度指数 Acoustic complexity index (ACI) | 相邻频段窗口音量的变化; D为相邻频段音量差的累积; Ik为各频段的音量 Difference in amplitude among samples; D is summary of intensity difference among adjacent frequency bands ; Ik is intensity in a single frequency band | Pieretti et al, | |
| 声学多样性指数 Acoustic diversity index (ADI) | 基于Shannon指数量化音量在不同频段的分布; pi是每个频率区间的相对强度 Spectral complexity based on Shannon index; pi is relative intensity in each frequency band | Villanueva-Rivera et al, | |
| 声学均匀度指数 Acoustic evenness index (AEI) | 基于Gini指数量化音量在不同频段的分布; I是音量 Gini coefficient with intensity at each frequency band; I is intensity | Villanueva-Rivera et al, | |
| 生物声学指数 Bioacoustic index (BIO) | 特定频段音量的汇总; Ik为各频段的音量 Sum of intensity in particular frequency band; Ik is intensity in a single frequency band | Boelman et al, | |
| 声熵指数 Acoustic entropy index (H) | 时间熵(Ht)和频谱熵(Hf)的乘积 Product of time entropy (Ht) and spectral entropy (Hf) | Sueur et al, | |
| 振幅包络线中值 Median of the amplitude envelope (M) | 声音振幅包络值的中值; Ak是振幅包络值 Median of the amplitude envelope value; Ak is amplitude envelope value | Depraetere et al, | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 Normalized difference sound index (NDSI) | 生物产生音量(b)与人类产生音量(a)的比率 Ratio of amplitude in biophony (b) and anthrophony (a) | Kasten et al, |
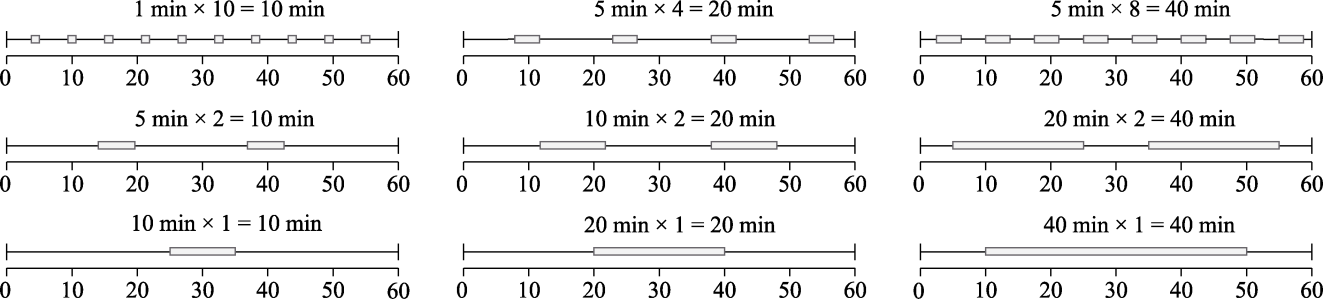
Fig. 3 Sub-samples recording schemes. Taking samples of 10 min, 20 min, and 40 min in length as examples, three different sub-samples recording schemes are listed.
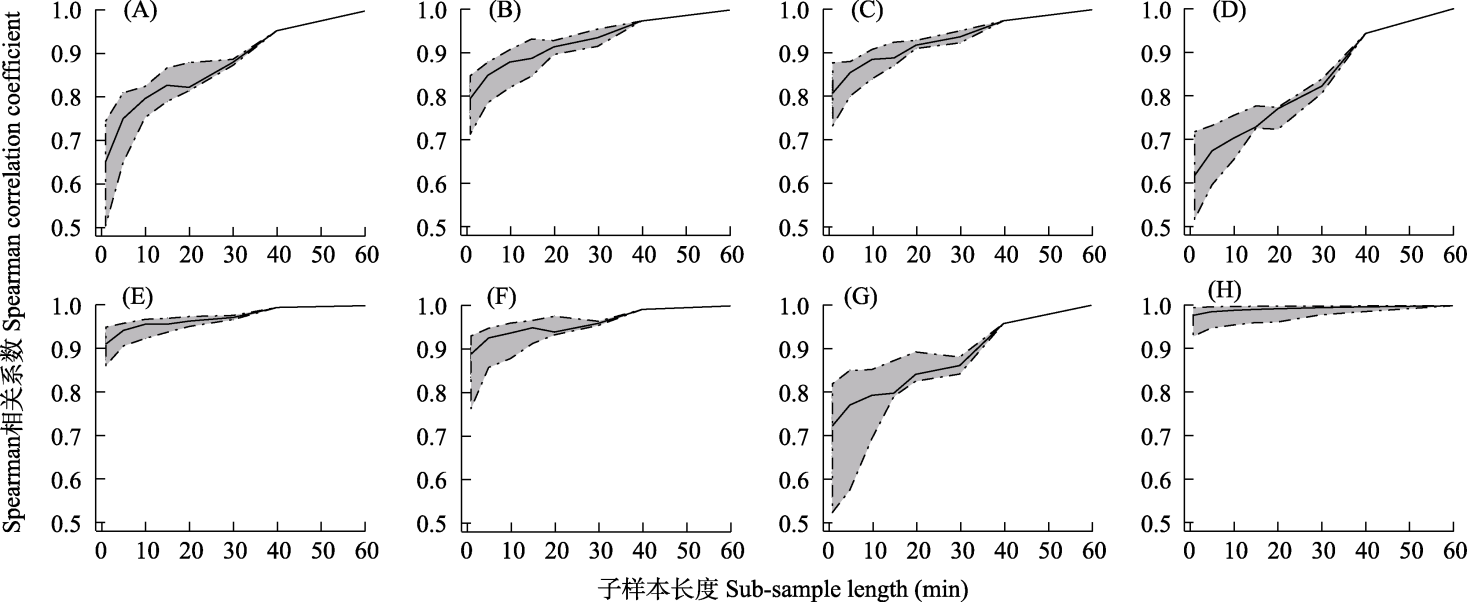
Fig. 4 The correlation of the acoustic index features and BYOL-A feature (H) between sub-sample length and total sample. The black line in the graph represents the median of the correlation coefficients, and the shaded area represents the range of values for the correlation coefficients. (A) ACI; (B) ADI; (C) AEI; (D) BIO; (E) H; (F) M; (G) NDSI. Abbreviations of acoustic indices are the same as denoted in Table 1, BYOL-A, Bootstrap your own latent for audio.
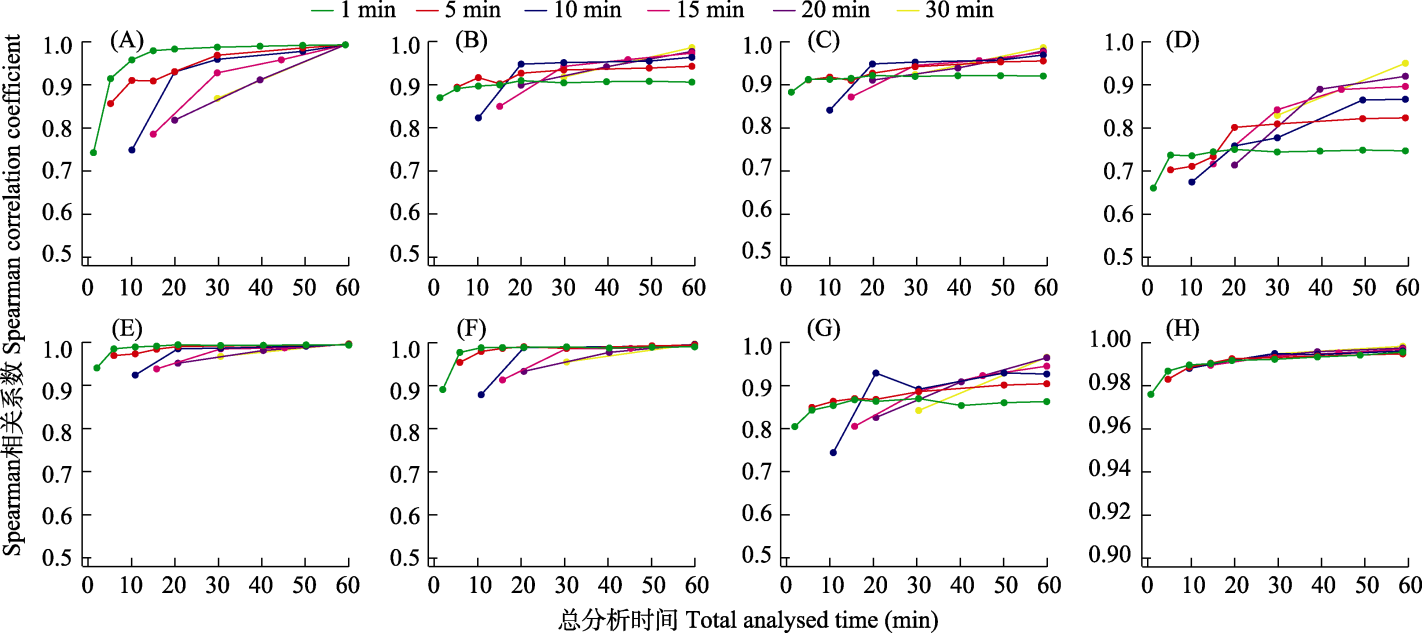
Fig. 5 The correlation of the acoustic index features and BYOL-A (H) between sub-samples by different recording schemes and total sample.(A) ACI; (B) ADI; (C) AEI; (D) BIO; (E) H; (F) M; (G) NDSI. Abbreviations of acoustic indices are the same as denoted in Table 1, BYOL-A, Bootstrap your own latent for audio.
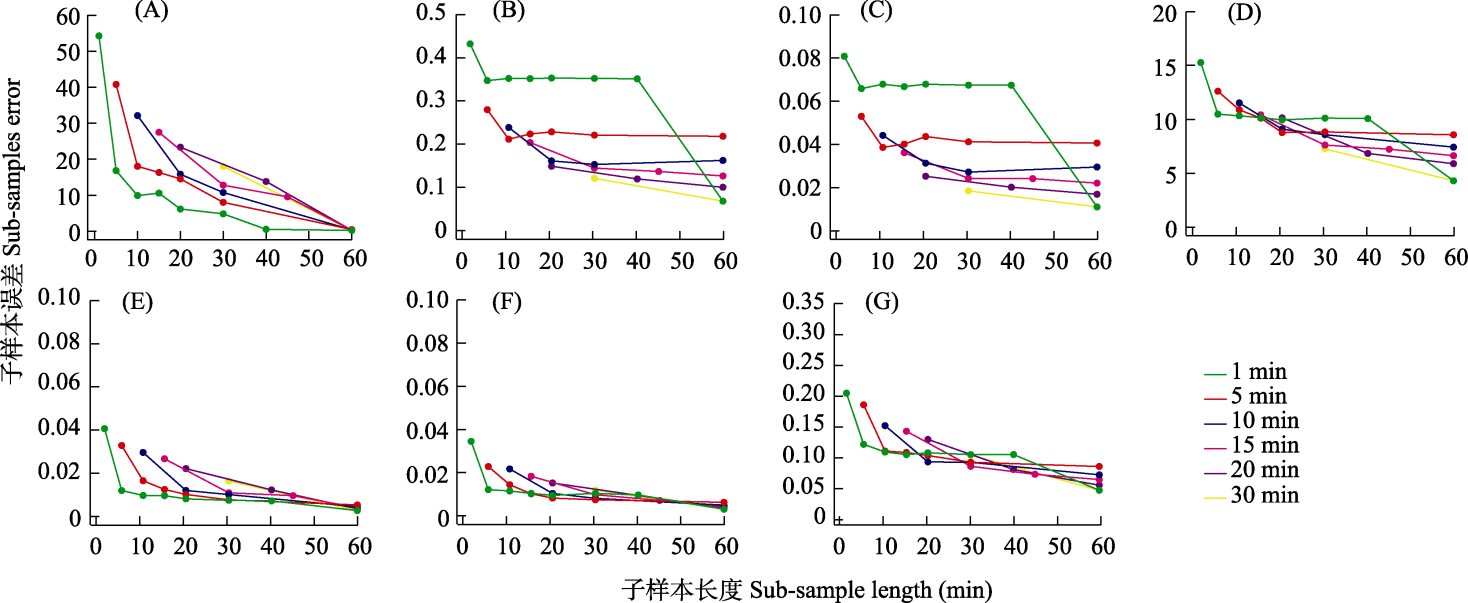
Fig. 6 The error of the acoustic index features between sub-samples by different recording schemes and total sample. (A) ACI; (B) ADI; (C) AEI; (D) BIO; (E) H; (F) M; (G) NDSI. Abbreviations of acoustic indices are the same as denoted in Table 1.
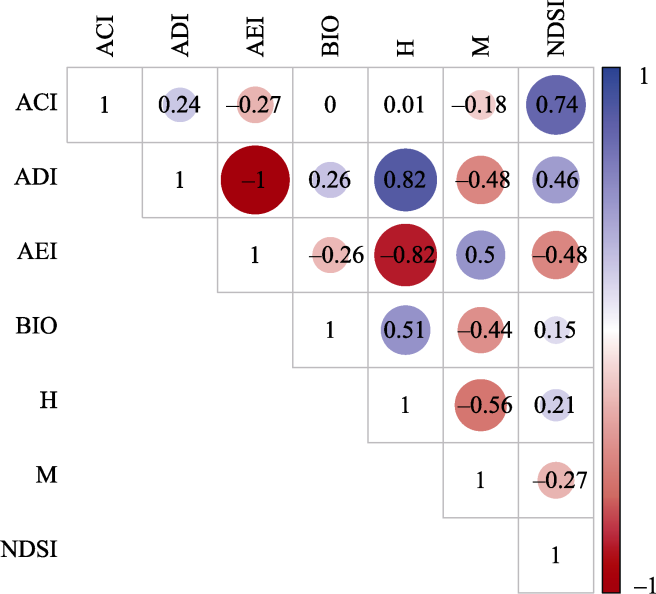
Fig. 7 The correlation between acoustic indices ACI, ADI, AEI, BIO, H, M, and NDSI. Abbreviations of acoustic indices are the same as denoted in Table 1.
| 袋外误差 Out-of-bag error | Kappa值 Kappa value | 准确率 Accuracy | 精确率 Precision | 召回率 Recall | F1分数 F1 score | 运算时间 Calculating time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 声学指数 Acoustic indices | 3% | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 121.57 s |
| BYOL-A特征 Bootstrap your own latent for audio feature | 0.88% | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 36.42 s |
Table 2 Comparison of the effectiveness of soundscape classification based on acoustic indices (ACI, ADI, AEI, BIO, H, M, NDSI) and BYOL-A feature. Abbreviations of acoustic indices are the same as denoted in Table 1, BYOL-A, Bootstrap your own latent for audio.
| 袋外误差 Out-of-bag error | Kappa值 Kappa value | 准确率 Accuracy | 精确率 Precision | 召回率 Recall | F1分数 F1 score | 运算时间 Calculating time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 声学指数 Acoustic indices | 3% | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 121.57 s |
| BYOL-A特征 Bootstrap your own latent for audio feature | 0.88% | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 36.42 s |
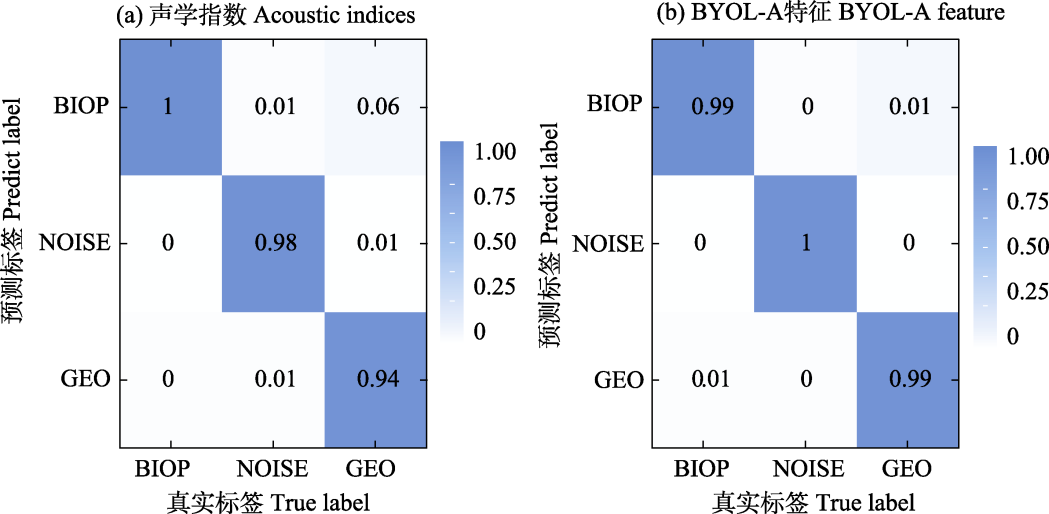
Fig. 8 Confusion matrix of soundscape classification based on acoustic indices (ACI, ADI, AEI, BIO, H, M, NDSI) and BYOL-A feature. BIOP, Biophony; NOISE, Anthrophony; GEO, Geophony. Abbreviations of acoustic indices are the same as in Table 1, BYOL-A, Bootstrap your own latent for audio.
| [1] | Aide TM, Corrada-Bravo C, Campos-Cerqueira M, Milan C, Vega G, Alvarez R (2013) Real-time bioacoustics monitoring and automated species identification. PeerJ, 1, e103. |
| [2] | Anunciação PR, Sugai LSM, Martello F, Ribeiro MC (2022) Estimating the diversity of tropical anurans in fragmented landscapes with acoustic monitoring: Lessons from a sampling sufficiency perspective. Biodiversity and Conservation, 31, 3055-3074. |
| [3] | Blumstein DT, Mennill DJ, Clemins P, Girod L, Yao K, Patricelli G, Hanser SF (2011) Acoustic monitoring in terrestrial environments using microphone arrays: Applications, technological considerations and prospectus. Journal of Applied Ecology, 48, 758-767. |
| [4] |
Boelman N, Asner G, Hart P, Martin R (2007) Multi-trophic invasion resistance in Hawaii: Bioacoustics, field surveys, and airborne remote sensing. Ecological Applications, 17, 2137-2144.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Bradfer-Lawrence T, Gardner N, Bunnefeld L, Bunnefeld N, Willis SG, Dent DH (2019) Guidelines for the use of acoustic indices in environmental research. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1796-1807.
DOI |
| [6] |
Buxton R, McKenna M, Clapp M, Meyer E, Stabenau E, Angeloni L, Crooks K, Wittemyer G (2018) Efficacy of extracting indices from large-scale acoustic recordings to monitor biodiversity. Conservation Biology, 32, 1174-1184.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Cifuentes E, Vélez Gómez J, Butler SJ (2021) Relación entre índices acústicos, duración de las grabaciones y tiempo de procesamiento: Una prueba metodológica. Biota Colombiana, 22, 26-35. |
| [8] | Cook A, Hartley S (2018) Efficient sampling of avian acoustic recordings: Intermittent subsamples improve estimates of single species prevalence and total species richness. Avian Conservation and Ecology, 13, 21. |
| [9] | Depraetere M, Pavoine S, Jiguet F, Gasc A, Duvail S, Sueur J (2012) Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecological Indicators, 13, 46-54. |
| [10] | Digby A, Towsey M, Bell BD, Teal PD (2013) A practical comparison of manual and autonomous methods for acoustic monitoring. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 4, 675-683. |
| [11] |
Fairbrass AJ, Firman M, Williams C, Brostow GJ, Titheridge H, Jones KE (2019) CityNet—Deep learning tools for urban ecoacoustic assessment. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 186-197.
DOI |
| [12] | Fairbrass AJ, Rennert P, Williams C, Titheridge H, Jones KE (2017) Biases of acoustic indices measuring biodiversity in urban areas. Ecological Indicators, 83, 169-177. |
| [13] | Farina A, Pieretti N, Piccioli L (2011) The soundscape methodology for long-term bird monitoring: A Mediterranean Europe case-study. Ecological Informatics, 6, 354-363. |
| [14] | Gasc A, Francomano D, Dunning JB, Pijanowski BC (2017) Future directions for soundscape ecology: The importance of ornithological contributions. The Auk, 134, 215-228. |
| [15] | Gasc A, Sueur J, Jiguet F, Devictor V, Grandcolas P, Burrow C, Depraetere M, Pavoine S (2013) Assessing biodiversity with sound: Do acoustic diversity indices reflect phylogenetic and functional diversities of bird communities? Ecological Indicators, 25, 279-287. |
| [16] | Grill JB, Strub F, Altché F, Tallec C (2020) Bootstrap your own latent: A new approach to self-supervised learning. Neural Information Processing Systems. arXiv, 2006.07733. |
| [17] |
Heath BE, Sethi SS, Orme CDL, Ewers RM, Picinali L (2021) How index selection, compression, and recording schedule impact the description of ecological soundscapes. Ecology and Evolution, 11, 13206-13217.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Hutto RL, Stutzman RJ (2009) Humans versus autonomous recording units: A comparison of point-count results. Journal of Ornithology, 80, 387-398. |
| [19] | Jorge FC, Machado CG, da Cunha Nogueira SS, Nogueira-Filho SLG (2018) The effectiveness of acoustic indices for forest monitoring in Atlantic rainforest fragments. Ecological Indicators, 91, 71-76. |
| [20] | Kasten E, Gage S, Fox J, Joo W (2012) The remote environmental assessment laboratory’s acoustic library: An archive for studying soundscape ecology. Ecological Informatics, 12, 50-67. |
| [21] | Laiolo P (2010) The emerging significance of bioacoustics in animal species conservation. Biological Conservation, 143, 1635-1645. |
| [22] | Li CH, Lei T (2014) Effects of anthropogenic disturbance on plant diversity in Yeyahu Municipal Nature Reserve of Beijing. Journal of Fujian Forestry University, 34, 309-315. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李聪慧, 雷霆 (2014) 人为干扰对北京野鸭湖市级自然保护区植物多样性的影响. 福建林学院学报, 34, 309-315.] | |
| [23] | Mullet TC, Gage SH, Morton JM, Huettmann F (2016) Temporal and spatial variation of a winter soundscape in south-central Alaska. Landscape Ecology, 31, 1117-1137. |
| [24] | Niizumi D, Takeuchi D, Ohishi Y, Harada N, Kashino K (2021) BYOL for audio: Self-supervised learning for general-purpose audio representation. 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1-8. Shenzhen, China. |
| [25] | Pieretti N, Duarte MHL, Sousa-Lima RS, Rodrigues M, Young RJ, Farina A (2015) Determining temporal sampling schemes for passive acoustic studies in different tropical ecosystems. Tropical Conservation Science, 8, 215-234. |
| [26] | Pieretti N, Farina A, Morri D (2011) A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The acoustic complexity index (ACI). Ecological Indicators, 11, 868-873. |
| [27] | Pijanowski BC, Farina A, Gage SH, Dumyahn SL, Krause BL (2011a) What is soundscape ecology? An introduction and overview of an emerging new science. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1213-1232. |
| [28] | Pijanowski BC, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Dumyahn SL, Farina A, Krause BL, Napoletano BM, Gage SH, Pieretti N (2011b) Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience, 61, 203-216. |
| [29] | Priyadarshani N, Marsland S, Castro I (2018) Automated birdsong recognition in complex acoustic environments: A review. Journal of Avian Biology, 49, e01447. |
| [30] | Rempel RS, Hobson KA, Holborn G, Wilgenburg SLV, Elliott J (2005) Bioacoustic monitoring of forest songbirds: Interpreter variability and effects of configuration and digital processing methods in the laboratory. Journal of Field Ornithology, 76, 1-11. |
| [31] | Rodrigues M (1996) Song activity in the chiffchaff: Territorial defence or mate guarding? Animal Behaviour, 51, 709-716. |
| [32] | Ruff ZJ, Lesmeister DB, Appel CL, Sullivan CM (2021) Workflow and convolutional neural network for automated identification of animal sounds. Ecological Indicators, 124, 107419. |
| [33] | Sethi SS, Jones NS, Fulcher BD, Picinali L, Clink DJ, Klinck H, Orme CDL, Wrege PH, Ewers RM (2020) Characterizing soundscapes across diverse ecosystems using a universal acoustic feature set. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 17049-17055. |
| [34] | Stevenson BC, Borchers DL, Altwegg R, Swift RJ, Gillespie DM, Measey GJ (2015) A general framework for animal density estimation from acoustic detections across a fixed microphone array. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 38-48. |
| [35] |
Stowell D, Wood MD, Pamuła H, Stylianou Y, Glotin H (2019) Automatic acoustic detection of birds through deep learning: The first Bird Audio Detection Challenge. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 368-380.
DOI |
| [36] | Sueur J, Farina A (2015) Ecoacoustics: The ecological investigation and interpretation of environmental sound. Biosemiotics, 8, 493-502. |
| [37] | Sueur J, Farina A, Gasc A, Pieretti N, Pavoine S (2014) Acoustic indices for biodiversity assessment and landscape investigation. Acta Acustica United with Acustica, 100, 772-781. |
| [38] | Sueur J, Pavoine S, Hamerlynck O, Duvail S (2008) Rapid acoustic survey for biodiversity appraisal. PLoS ONE, 3, e4065. |
| [39] |
Sugai LSM, Silva TSF, Llusia D, Siqueira T (2021) Drivers of assemblage-wide calling activity in tropical anurans and the role of temporal resolution. Journal of Animal Ecology, 90, 673-684.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Swiston KA, Mennill DJ (2009) Comparison of manual and automated methods for identifying target sounds in audio recordings of Pileated, Pale-Billed, and Putative Ivory- Billed Woodpeckers. Journal of Field Ornithology, 80, 42-50. |
| [41] | Takeuchi D, Koizumi Y, Ohishi Y, Harada N, Kashino K (2020) Effects of word-frequency based pre- and post- processings for audio captioning. In:International Workshop on Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events. arXiv, 2009.11436. |
| [42] | Towsey M, Parsons S, Sueur J (2014) Ecology and acoustics at a large scale. Ecological Informatics, 21, 1-3. |
| [43] |
Ulloa JS, Aubin T, Llusia D, Courtois ÉA, Fouquet A, Gaucher P, Pavoine S, Sueur J (2019) Explosive breeding in tropical anurans: Environmental triggers, community composition and acoustic structure. BMC Ecology, 19, 28.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Villanueva-Rivera L, Pijanowski B, Doucette J, Pekin B (2011) A primer of acoustic analysis forlandscape ecologists. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1233-1246. |
| [45] |
Wang Y, Gao GC, Fu BQ, Wu Z (2009) Composition and spatial distribution pattern of ground-dwelling beetle communities in Yeyahu Wetland, Beijing. Biodiversity Science, 17, 30-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王玉, 高光彩, 付必谦, 吴专 (2009) 北京野鸭湖湿地地表甲虫群落组成与空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 17, 30-42.]
DOI |
|
| [46] | Wilkins MR, Seddon N, Safran RJ (2013) Evolutionary divergence in acoustic signals: Causes and consequences. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 156-166. |
| [47] | Wrege PH, Rowland ED, Keen S, Shiu Y (2017) Acoustic monitoring for conservation in tropical forests: Examples from forest elephants. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 1292-1301. |
| [48] | Zwart MC, Baker A, McGowan PJ, Whittingham MJ (2014) The use of automated bioacoustic recorders to replace human wildlife surveys: An example using nightjars. PLoS ONE, 9, e102770. |
| [1] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [2] | Song Yuanhao, Gong Lü, Li Ben, Hu Yang, Li Xiuzhen. Impacts of different pond-to-wetland restoration methods on macrofauna in the Liao River Estuary, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | Yuan Liu, Jianqing Du, Liyuan Ma, Gang Yang, Jianqing Tian. Diversity and distribution of methanogen communities in the riparian wetlands of the Nam Co basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24247-. |
| [4] | Haotian Bai, Shang Yu, Xinyuan Pan, Jiale Ling, Juan Wu, Kaiqi Xie, Yang Liu, Xueye Chen. AI-assisted recognition for passive acoustic monitoring of birds in urban wetland parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24188-. |
| [5] | Naipeng Zhang, Hongru Liang, Yan Zhang, Chao Sun, Yong Chen, Lulu Wang, Jiangbao Xia, FangLei Gao. Effects of soil type and groundwater depth on spatial differentiation of typical salt marsh plant communities in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [6] | Zezhou Hao, Chengyun Zhang, Le Li, Bingtao Gao, Wei Zeng, Chun Wang, Zixuan Wang, Wantao Huang, Yue Zhang, Nancai Pei, Zhishu Xiao. Applications of passive acoustic monitoring and evaluation in urban bird research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24123-. |
| [7] | Le Li, Chengyun Zhang, Nancai Pei, Bingtao Gao, Na Wang, Jiarui Li, Ruichen Wu, Zezhou Hao. Correlation analysis of urban green landscape patterns and bird diversity based on passive acoustic monitoring technology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24296-. |
| [8] | Wantao Huang, Zezhou Hao, Zixin Zhang, Zhishu Xiao, Chengyun Zhang. A comparison of bird sound recognition performance among acoustic recorders [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24273-. |
| [9] | Yingying Liu, Lixin Gong, Hao Zeng, Jiang Feng, Yongjun Dong, Lei Wang, Tinglei Jiang. Application of passive acoustic monitoring in Chiropteran research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24233-. |
| [10] | Lei Chen, Zhiyong Xu, Pukun Su, Xiaotian Lai, Zhao Zhao. Exploring the application of frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index in human-dominated areas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [11] | Xiaoyuan Li, Wenli Zhang, Shuliao Tian, Zhenlong Wang, Zhishu Xiao. Advances in bioacoustic monitoring and animal welfare assessment in zoos [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24297-. |
| [12] | Qianrong Guo, Shufei Duan, Jie Xie, Xueyan Dong, Zhishu Xiao. Advances in bird sound annotation methods for passive acoustic monitoring [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24313-. |
| [13] | Jiangjian Xie, Chen Shen, Feiyu Zhang, Zhishu Xiao. Cross-regional bird species recognition method integrating audio and ecological niche information [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [14] | Yufei Huang, Chunyan Lu, Mingming Jia, Zili Wang, Yue Su, Yanlin Su. Plant species classification of coastal wetlands based on UAV images and object- oriented deep learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22411-. |
| [15] | Zhishu Xiao, Jianguo Cui, Daiping Wang, Zhitao Wang, Jinhong Luo, Jie Xie. Interdisciplinary development trends of contemporary bioacoustics and the opportunities for China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22423-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()