



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 825-842. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020370 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020370
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaofeng Yang1, Xiaomeng Li2,*( ), Wanjin Liao1
), Wanjin Liao1
Received:2020-09-21
Accepted:2020-11-30
Online:2021-06-20
Published:2021-02-01
Contact:
Xiaomeng Li
Xiaofeng Yang, Xiaomeng Li, Wanjin Liao. Advances in the genetic regulating pathways of plant flowering time[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 825-842.
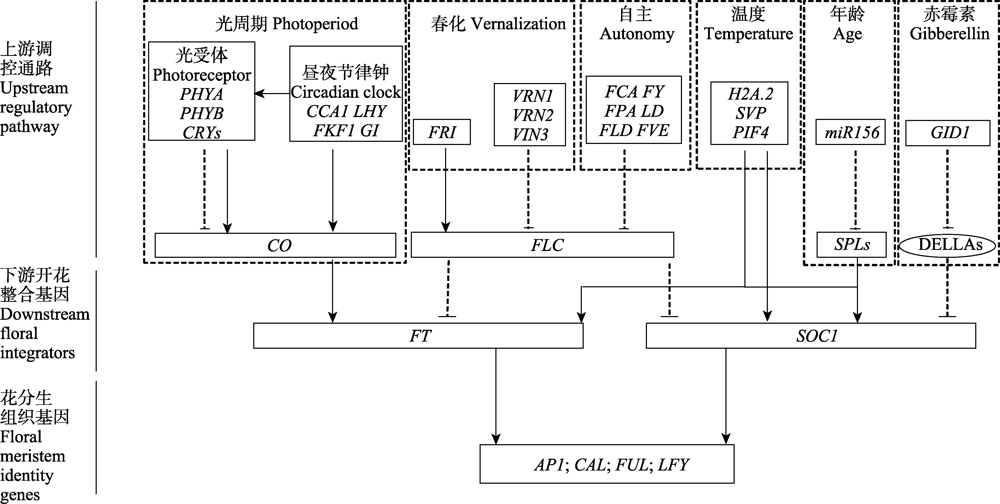
Fig. 1 The genetic pathways regulating flowering (take Arabidopsis thaliana as an example). The figure includes three parts from top to bottom: upstream regulatory pathway, downstream floral integrators and floral meristem identity genes. Six pathways and related genes that regulate flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana are enclosed in the dashed boxes separately. The letters in the boxes stand for abbreviation of genes, and the letters in the ovals stand for abbreviation of proteins. Lines with arrows indicate activation, and broken lines with blunt ends indicate repression. Modified from Banta & Purugganan ( 2011).
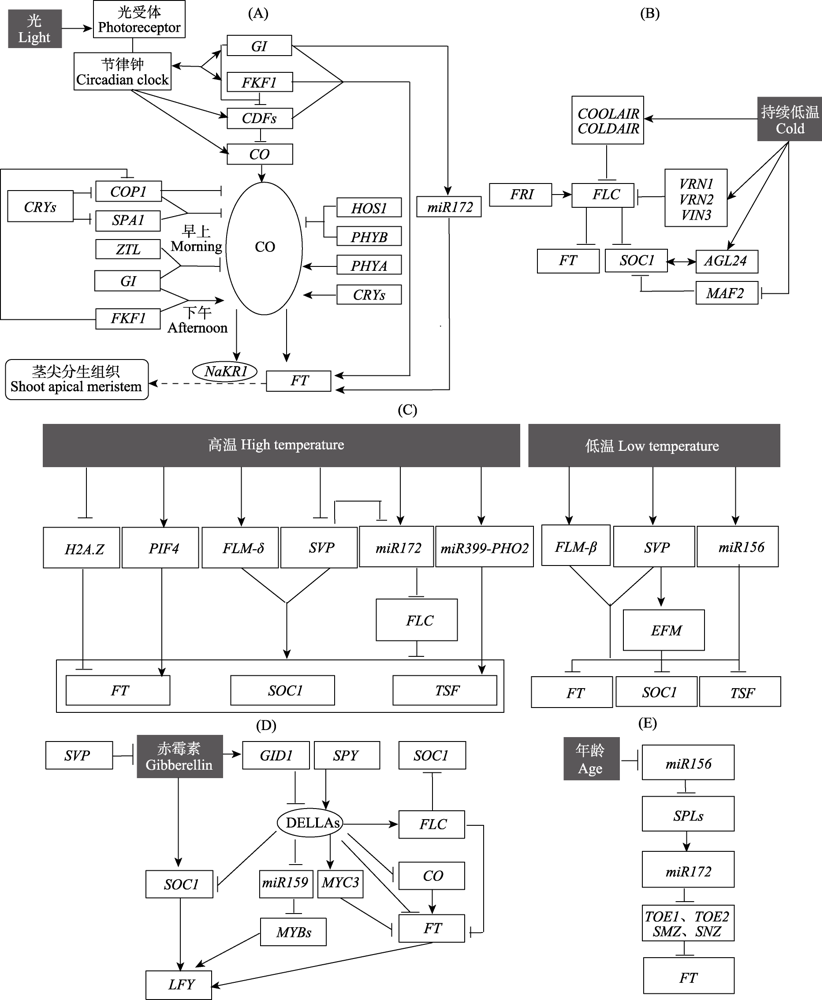
Fig. 2 Detailed diagrams of the regulation pathways of flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. (A) The photoperiodic pathway; (B) The vernalization pathway; (C) The temperature pathway; (D) The gibberellin pathway; (E) The age pathway. The black-filled box represents external regulating factors. The letters in the boxes stand for abbreviation of genes, and the letters in the ovals stand for abbreviation of proteins. Lines with arrows and blunt ends indicate activation and repression, respectively. The two-way arrows represent interactions. In figure (A), rectangle with rounded corners indicates the position where the florigen to be transferred, and the broken lines with arrows represent the transport process.
| [1] | Abe M, Kosaka S, Shibuta M, Nagata K, Uemura T, Nakano A, Kaya H (2019) Transient activity of the florigen complex during the floral transition in Arabidopsis thaliana . Development, 146, dev171504. |
| [2] |
Abou-Elwafa SF, Büttner B, Chia T, Schulze-Buxloh G, Hohmann U, Mutasa-Göttgens E, Jung C, Müller AE (2011) Conservation and divergence of autonomous pathway genes in the flowering regulatory network of Beta vulgaris . Journal of Experimental Botany, 62,3359-3374.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Achard P, Herr A, Baulcombe DC, Harberd NP (2004) Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development, 131,3357-3365.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Alexandre CM, Hennig L (2008) FLC or not FLC: The other side of vernalization . Journal of Experimental Botany, 59,1127-1135.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Alonso-Blanco C, Aarts MGM, Bentsink L, Keurentjes JJB, Reymond M, Vreugdenhil D, Koornneef M (2009) What has natural variation taught us about plant development, physiology, and adaptation? The Plant Cell, 21,1877-1896.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Andrés F, Coupland G (2012) The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues. Nature Reviews Genetics, 13,627-639.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Andrés F, Porri A, Torti S, Mateos J, Romera-Branchat M, Garcia-Martinez JL, Fornara F, Gregis V, Kater MM, Coupland G (2014) SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE reduces gibberellin biosynthesis at the Arabidopsis shoot apex to regulate the floral transition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111,E2760-E2769. |
| [8] |
Balasubramanian S, Sureshkumar S, Lempe J, Weigel D (2006) Potent induction of Arabidopsis thaliana flowering by elevated growth temperature . PLoS Genetics, 2,e106.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Banta S,and Heyland MD. (2011) The genetics and evolution of flowering time variation in plants: Identifying genes that control a key life history transition. In: Mechanisms of life history evolution (eds Flatt T, Heyland A), pp. 114-126. Oxford University Press Inc., New York. |
| [10] |
Bao SJ, Hua CM, Huang GQ, Cheng P, Gong XM, Shen LS, Yu H (2019) Molecular basis of natural variation in photoperiodic flowering responses. Developmental Cell, 50,90-101.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Barrett SCH, Colautti RI, Eckert CG (2008) Plant reproductive systems and evolution during biological invasion. Molecular Ecology, 17,373-383.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Bäurle I, Dean C (2008) Differential interactions of the autonomous pathway RRM proteins and chromatin regulators in the silencing of Arabidopsis targets . PLoS ONE, 3,e2733.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Bernler G, Havelange A, Houssa C, Petitjean A, Lejeune P (1993) Physiological signals that induce flowering. The Plant Cell, 5,1147-1155.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Busch MA, Bomblies K, Weigel D (1999) Activation of a floral homeotic gene in Arabidopsis . Science, 285,585-587.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Campos-Rivero G, Osorio-Montalvo P, Sánchez-Borges R, Us-Camas R, Duarte-Aké F, De-La-Peña C (2017) Plant hormone signaling in flowering: An epigenetic point of view. Journal of Plant Physiology, 214,16-27.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Cheng JZ, Zhou YP, Lv TX, Xie CP, Tian CE (2017) Research progress on the autonomous flowering time pathway in Arabidopsis . Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 23,477-485.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Corbesier L, Vincent C, Jang S, Fornara F, Fan QZ, Searle I, Giakountis A, Farrona S, Gissot L, Turnbull C, Coupland G (2007) FT protein movement contributes to long-distance signaling in floral induction of Arabidopsis . Science, 316,1030-1033.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
de Lucas M, Davière JM, Rodríguez-Falcón M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blázquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S (2008) A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature, 451,480-484.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Doi K, Izawa T, Fuse T, Yamanouchi U, Kubo T, Shimatani Z, Yano M, Yoshimura A (2004) Ehd1, a B-type response regulator in rice, confers short-day promotion of flowering and controls FT-like gene expression independently of Hd1. Genes & Development. 18,926-936.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Elzinga JA, Atlan A, Biere A, Gigord L, Weis AE, Bernasconi G (2007) Time after time: Flowering phenology and biotic interactions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22,432-439.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Fernández V, Takahashi Y, Le Gourrierec J, Coupland G (2016) Photoperiodic and thermosensory pathways interact through CONSTANS to promote flowering at high temperature under short days. The Plant Journal, 86,426-440.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Fornara F, de Montaigu A, Coupland G (2010) SnapShot: Control of flowering in Arabidopsis . Cell, 141,550-550.e2.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Fornara F, Panigrahi KCS, Gissot L, Sauerbrunn N, Rühl M, Jarillo JA, Coupland G (2009) Arabidopsis DOF transcription factors act redundantly to reduce CONSTANS expression and are essential for a photoperiodic flowering response . Developmental Cell, 17,75-86.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Gendall AR, Levy YY, Wilson A, Dean C (2001) The VERNALIZATION 2 gene mediates the epigenetic regulation of vernalization in Arabidopsis . Cell, 107,525-535.
PMID |
| [25] | Golicz AA, Steinfort U, Arya H, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2020) Analysis of the quinoa genome reveals conservation and divergence of the flowering pathways. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 20,245-258. |
| [26] |
Gou JQ, Tang CR, Chen NC, Wang H, Debnath S, Sun L, Flanagan A, Tang YH, Jiang QZ, Allen RD, Wang ZY (2019) SPL7 and SPL8 represent a novel flowering regulation mechanism in switchgrass . New Phytologist, 222,1610-1623.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Guo TT, Mu Q, Wang JY, Vanous AE, Onogi A, Iwata H, Li XR, Yu JM (2020) Dynamic effects of interacting genes underlying rice flowering-time phenotypic plasticity and global adaptation. Genome Research, 30,673-683.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Halliday KJ, Salter MG, Thingnaes E, Whitelam GC (2003) Phytochrome control of flowering is temperature sensitive and correlates with expression of the floral integrator FT . The Plant Journal, 33,875-885.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Hayama R, Agashe B, Luley E, King R, Coupland G (2007) A circadian rhythm set by dusk determines the expression of FT homologs and the short-day photoperiodic flowering response in Pharbitis . The Plant Cell, 19,2988-3000.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Hayama R, Mizoguchi T, Coupland G (2018) Differential effects of light-to-dark transitions on phase setting in circadian expression among clock-controlled genes in Pharbitis nil . Plant Signaling & Behavior, 13,e1473686. |
| [31] |
He J, Xu ML, Willmann MR, McCormick K, Hu TQ, Yang L, Starker CG, Voytas DF, Meyers BC, Poethig RS (2018) Threshold-dependent repression of SPL gene expression by miR156/miR157 controls vegetative phase change in Arabidopsis thaliana . PLoS Genetics, 14,e1007337.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Heidari B, Nemie-Feyissa D, Kangasjärvi S, Lillo C (2013) Antagonistic regulation of flowering time through distinct regulatory subunits of protein phosphatase 2A. PLoS ONE, 8,e67987.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Hemming MN, Walford SA, Fieg S, Dennis ES, Trevaskis B (2012) Identification of high-temperature-responsive genes in cereals. Plant Physiology, 158,1439-1450.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Heo JB, Sung S (2011) Vernalization-mediated epigenetic silencing by a long intronic noncoding RNA. Science, 331,76-79.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Hirakawa H, Sumitomo K, Hisamatsu T, Nagano S, Shirasawa K, Higuchi Y, Kusaba M, Koshioka M, Nakano Y, Yagi M, Yamaguchi H, Taniguchi K, Nakano M, Isobe SN (2019) De novo whole-genome assembly in Chrysanthemum seticuspe, a model species of Chrysanthemums, and its application to genetic and gene discovery analysis . DNA Research, 26,195-203.
DOI |
| [36] |
Huang FY, Liu TK, Tang J, Duan WK, Hou XL (2019) BcMAF2 activates BcTEM1 and represses flowering in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis). Plant Molecular Biology, 100,19-32.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Hyun Y, Richter R, Coupland G (2017) Competence to flower: Age-controlled sensitivity to environmental cues. Plant Physiology, 173,36-46.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Hyun Y, Richter R, Vincent C, Martinez-Gallegos R, Porri A, Coupland G (2016) Multi-layered regulation of SPL15 and cooperation with SOC1integrate endogenous flowering pathways at the Arabidopsis shoot meristem . Developmental Cell, 37,254-266.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Harmon FG, Ho LA, Kay SA (2005) FKF1 F-box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science, 309,293-297.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Ito S, Song YH, Josephson-Day AR, Miller RJ, Breton G, Olmstead RG, Imaizumi T (2012) FLOWERING BHLH transcriptional activators control expression of the photoperiodic flowering regulator CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA. 109,3582-3587. |
| [41] |
Itoh H, Nonoue Y, Yano M, Izawa T (2010) A pair of floral regulators sets critical day length for Hd3a florigen expression in rice . Nature Genetics, 42,635-638.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Jacobsen SE, Olszewski NE, Meyerowitz EM (1998) SPINDLY's role in the gibberellin response pathway. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology, 51,73-78.
PMID |
| [43] |
Jagadish SVK, Bahuguna RN, Djanaguiraman M, Gamuyao R, Prasad PVV, Craufurd PQ (2016) Implications of high temperature and elevated CO 2 on flowering time in plants . Frontiers in Plant Science, 7,913.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Jang S, Marchal V, Panigrahi KCS, Wenkel S, Soppe W, Deng XW, Valverde F, Coupland G (2008) Arabidopsis COP1 shapes the temporal pattern of CO accumulation conferring a photoperiodic flowering response . The EMBO Journal, 27,1277-1288.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Johanson U, West J, Lister C, Michaels S, Amasino R, Dean C (2000) Molecular analysis of FRIGIDA, a major determinant of natural variation in Arabidopsis flowering time . Science, 290,344-347.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Kim JJ, Lee JH, Kim W, Jung HS, Huijser P, Ahn JH (2012) The microRNA156-SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE3 module regulates ambient temperature-responsive flowering via FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis . Plant Physiology, 159,461-478.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Kim MY, Kang YJ, Lee T, Lee SH (2013) Divergence of flowering-related genes in three legume species. The Plant Genome, 6, plantgenome2013. 03.0008. |
| [48] |
Kim S, Soltis PS, Wall K, Soltis DE (2006) Phylogeny and domain evolution in the APETALA2-like gene family . Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23,107-120.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Kim W, Ahn HJ, Chiou TJ, Ahn JH (2011) The role of the miR399-PHO2 module in the regulation of flowering time in response to different ambient temperatures in Arabidopsis thaliana . Molecules and Cells, 32,83-88.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Kinmonth-Schultz HA, Tong XR, Lee J, Song YH, Ito S, Kim SH, Imaizumi T (2016) Cool night-time temperatures induce the expression of CONSTANS and FLOWERING LOCUS T to regulate flowering in Arabidopsis . New Phytologist, 211,208-224.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Kinoshita A, Richter R (2020) Genetic and molecular basis of floral induction in Arabidopsis thaliana . Journal of Experimental Botany, 71,2490-2504.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Kitamoto N, Ueno S, Takenaka A, Tsumura Y, Washitani I, Ohsawa R (2006) Effect of flowering phenology on pollen flow distance and the consequences for spatial genetic structure within a population of Primula sieboldii (Primulaceae). American Journal of Botany, 93,226-233.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Kobayashi Y, Weigel D (2007) Move on up, it's time for change—Mobile signals controlling photoperiod-dependent flowering. Genes & Development, 21,2371-2384.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi Y, Monna L, Sasaki T, Araki T, Yano M (2002) Hd3a, a rice ortholog of the Arabidopsis FT gene, promotes transition to flowering downstream of Hd1under short-day conditions . Plant and Cell Physiology, 43,1096-1105.
PMID |
| [55] |
Komiya R, Ikegami A, Tamaki S, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K (2008) Hd3a and RFT1 are essential for flowering in rice . Development, 135,767-774.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Kralemann LEM, Scalone R, Andersson L, Hennig L (2018) North European invasion by common ragweed is associated with early flowering and dominant changes in FT/TFL1expression . Journal of Experimental Botany, 69,2647-2658.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
Kubota A, Ito S, Shim JS, Johnson RS, Song YH, Breton G, Goralogia GS, Kwon MS, Laboy Cintrón D, Koyama T, Ohme-Takagi M, Pruneda-Paz JL, Kay SA, MacCoss MJ, Imaizumi T (2017) TCP4-dependent induction of CONSTANS transcription requires GIGANTEA in photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis . PLoS Genetics. 13,e1006856.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Kumar SV, Lucyshyn D, Jaeger KE, Alós E, Alvey E, Harberd NP, Wigge PA (2012) Transcription factor PIF4 controls the thermosensory activation of flowering . Nature, 484,242-245.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Lazaro A, Mouriz A, Piñeiro M, Jarillo JA (2015) Red light-mediated degradation of CONSTANS by the E 3 ubiquitin ligase HOS1 regulates photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis . The Plant Cell, 27,2437-2454.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Lee BD, Kim MR, Kang MY, Cha JY, Han SH, Nawkar GM, Sakuraba Y, Lee SY, Imaizumi T, McClung CR, Kim WY, Paek NC (2017) The F-box protein FKF1 inhibits dimerization of COP1in the control of photoperiodic flowering . Nature Communications, 8,2259.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Lee H, Yoo SJ, Lee JH, Kim W, Yoo SK, Fitzgerald H, Carrington JC, Ahn JH (2010) Genetic framework for flowering-time regulation by ambient temperature-responsive miRNAs in Arabidopsis . Nucleic Acids Research, 38,3081-3093.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Leeggangers HACF, Rosilio-Brami T, Bigas-Nadal J, Rubin N, van Dijk ADJ, Gonzalez FFNC, Saadon-Shitrit S, Nijveen H, Hilhorst HWM, Immink RGH, Zaccai M (2018) Tulipa gesneriana and Lilium longiflorum PEBP genes and their putative roles in flowering time control . Plant and Cell Physiology, 59,90-106.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Lemoine NP, Doublet D, Salminen JP, Burkepile DE, Parker JD (2017) Responses of plant phenology, growth, defense, and reproduction to interactive effects of warming and insect herbivory. Ecology, 98,1817-1828.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Li C, Li YH, Li YF, Lu HF, Hong HL, Tian Y, Li HY, Zhao T, Zhou XW, Liu J, Zhou XN, Jackson SA, Liu B, Qiu LJ (2020) A domestication-associated gene GmPRR3b regulates the circadian clock and flowering time in soybean . Molecular Plant, 13,745-759.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Li D, Liu C, Shen LS, Wu Y, Chen HY, Robertson M, Helliwell CA, Ito T, Meyerowitz E, Yu H (2008) A repressor complex governs the integration of flowering signals in Arabidopsis . Developmental Cell, 15,110-120.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Li MZ, An FY, Li WY, Ma MD, Feng Y, Zhang X, Guo HW (2016) DELLA proteins interact with FLC to repress flowering transition . Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 58,642-655.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Li XF, Jia LY, Xu J, Deng XJ, Wang Y, Zhang W, Zhang XP, Fang Q, Zhang DM, Sun Y, Xu L (2013) FT-like NFT1 gene may play a role in flower transition induced by heat accumulation in Narcissus tazetta var. chinensis . Plant and Cell Physiology, 54,270-281.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Li XM, Zhang DY, Liao WJ (2015) The rhythmic expression of genes controlling flowering time in southern and northern populations of invasive Ambrosia artemisiifolia . Journal of Plant Ecology, 8,207-212.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Li ZC, Jiang DH, He YH (2018) FRIGIDA establishes a local chromosomal environment for FLOWERING LOCUS C mRNA production . Nature Plants, 4,836-846.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Liljegren SJ, Gustafson-Brown C, Pinyopich A, Ditta GS, Yanofsky MF (1999) Interactions among APETALA1, LEAFY, and TERMINAL FLOWER1 specify meristem fate . The Plant Cell, 11,1007-1018.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Liu FQ, Quesada V, Crevillén P, Bäurle I, Swiezewski S, Dean C (2007) The Arabidopsis RNA-binding protein FCA requires a lysine-specific demethylase 1 homolog to downregulate FLC . Molecular Cell, 28,398-407.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Liu KD, Feng SX, Pan YL, Zhong JD, Chen Y, Yuan CC, Li HL (2016) Transcriptome analysis and identification of genes associated with floral transition and flower development in sugar apple ( Annona squamosa L.) . Frontiers in Plant Science, 7,1695. |
| [73] |
Liu KP, Yu Y, Dong AW, Shen WH (2017) SET DOMAIN GROUP701encodes a H3K4-methytransferase and regulates multiple key processes of rice plant development . New Phytologist, 215,609-623.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Liu L, Liu C, Hou XL, Xi WY, Shen LS, Tao Z, Wang Y, Yu H (2012) FTIP1is an essential regulator required for florigen transport . PLoS Biology, 10,e1001313.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Liu Y, Hao XY, Lu QH, Zhang WF, Zhang HJ, Wang L, Yang YJ, Xiao B, Wang XC (2020) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of flowering-related genes reveal putative floral induction and differentiation mechanisms in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Genomics, 112,2318-2326.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Liu YY, Yang KZ, Wei XX, Wang XQ (2016) Revisiting the phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein (PEBP) gene family reveals cryptic FLOWERING LOCUS T gene homologs in gymnosperms and sheds new light on functional evolution . New Phytologist, 212,730-744.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Luo M, Tai R, Yu CW, Yang SG, Chen CY, Lin WD, Schmidt W, Wu KQ (2015) Regulation of flowering time by the histone deacetylase HDA5 in Arabidopsis . The Plant Journal, 82,925-936.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Mathieu J, Yant LJ, Mürdter F, Küttner F, Schmid M (2009) Repression of flowering by the miR172 target SMZ . PLoS Biology, 7,e1000148.
DOI URL |
| [79] | Mátyás KK, Hegedűs G, Taller J, Farkas E, Decsi K, Kutasy B, Kálmán N, Nagy E, Kolics B, Virág E (2019) Different expression pattern of flowering pathway genes contribute to male or female organ development during floral transition in the monoecious weed Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. (Asteraceae). PeerJ, 7,e7421. |
| [80] |
Mawphlang OIL, Kharshiing EV (2017) Photoreceptor mediated plant growth responses: Implications for photoreceptor engineering toward improved performance in crops. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8,1181.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Méndez-Vigo B, Ausín I, Zhu WS, Mollá-Morales A, Balasubramanian S, Alonso-Blanco C (2019) Genetic interactions and molecular evolution of the duplicated genes ICARUS2 and ICARUS1 help Arabidopsis plants adapt to different ambient temperatures . The Plant Cell, 31,1222-1237.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Méndez-Vigo B, Martínez-Zapater JM, Alonso-Blanco C (2013) The flowering repressor SVP underlies a novel Arabidopsis thaliana QTL interacting with the genetic background . PLoS Genetics, 9,e1003289.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Michaels SD, Amasino RM (2001) Loss of FLOWERING LOCUS C activity eliminates the late-flowering phenotype of FRIGIDA and autonomous pathway mutations but not responsiveness to vernalization . The Plant Cell, 13,935-941.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Michaels SD, Ditta G, Gustafson-Brown C, Pelaz S, Yanofsky M, Amasino RM (2003) AGL24 acts as a promoter of flowering in Arabidopsis and is positively regulated by vernalization . The Plant Journal, 33,867-874.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Mitchum MG, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, Kuwahara A, Yoshioka Y, Kato T, Tabata S, Kamiya Y, Sun TP (2006) Distinct and overlapping roles of two gibberellin 3-oxidases in Arabidopsis development . The Plant Journal, 45,804-818.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Moon J, Suh SS, Lee H, Choi KR, Hong CB, Paek NC, Kim SG, Lee I (2003) The SOC1 MADS-box gene integrates vernalization and gibberellin signals for flowering in Arabidopsis . The Plant Journal, 35,613-623.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Mulekar JJ, Huq E (2015) Arabidopsis casein kinase 2 α 4 subunit regulates various developmental pathways in a functionally overlapping manner . Plant Science, 236,295-303.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Mutasa-Göttgens E, Hedden P (2009) Gibberellin as a factor in floral regulatory networks. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60,1979-1989.
DOI PMID |
| [89] |
Nie SS, Li C, Xu L, Wang Y, Huang DQ, Muleke EM, Sun XC, Xie Y, Liu LW (2016) De novo transcriptome analysis in radish ( Raphanus sativus L.) and identification of critical genes involved in bolting and flowering . BMC Genomics, 17,389.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Niu LF, Lu FL, Pei YX, Liu CY, Cao XF (2007) Regulation of flowering time by the protein arginine methyltransferase AtPRMT10 . EMBO Reports, 8,1190-1195.
DOI URL |
| [91] | Niu XM, Xu YC, Li ZW, Bian YT, Hou XH, Chen JF, Zou YP, Jiang J, Wu Q, Ge S, Balasubramanian S, Guo YL (2019) Transposable elements drive rapid phenotypic variation in Capsella rubella. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116,6908-6913. |
| [92] |
Oda A, Higuchi Y, Hisamatsu T (2020) Constitutive expression of CsGI alters critical night length for flowering by changing the photo-sensitive phase of anti-florigen induction in Chrysanthemum . Plant Science, 293,110417.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Perrella G, Vellutini E, Zioutopoulou A, Patitaki E, Headland LR, Kaiserli E (2020) Let it bloom: Cross-talk between light and flowering signaling in Arabidopsis . Physiologia Plantarum, 169,301-311.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Pin PA, Benlloch R, Bonnet D, Wremerth-Weich E, Kraft T, Gielen JJL, Nilsson O (2010) An antagonistic pair of FT homologs mediates the control of flowering time in sugar beet . Science, 330,1397-1400.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Pin PA, Zhang WY, Vogt SH, Dally N, Büttner B, Schulze-Buxloh G, Jelly NS, Chia TYP, Mutasa-Göttgens ES, Dohm JC, Himmelbauer H, Weisshaar B, Kraus J, Gielen JJL, Lommel M, Weyens G, Wahl B, Schechert A, Müller AE (2012) The role of a pseudo-response regulator gene in life cycle adaptation and domestication of beet. Current Biology, 22,1095-1101.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Porri A, Torti S, Romera-Branchat M, Coupland G (2012) Spatially distinct regulatory roles for gibberellins in the promotion of flowering of Arabidopsis under long photoperiods . Development, 139,2198-2209.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Posé D, Verhage L, Ott F, Yant L, Mathieu J, Angenent GC, Immink RGH, Schmid M (2013) Temperature-dependent regulation of flowering by antagonistic FLM variants. Nature, 503,414-417.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
Putterill J, Laurie R, MacKnight R (2004) It's time to flower: The genetic control of flowering time. BioEssays, 26,363-373.
PMID |
| [99] |
Reeves PA, He YH, Schmitz RJ, Amasino RM, Panella LW, Richards CM (2007) Evolutionary conservation of the FLOWERING LOCUS C-mediated vernalization response: Evidence from the sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Genetics, 176,295-307.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Ripoll JJ, Rodríguez-Cazorla E, González-Reig S, Andújar A, Alonso-Cantabrana H, Perez-Amador MA, Carbonell J, Martínez-Laborda A, Vera A (2009) Antagonistic interactions between Arabidopsis K-homology domain genes uncover PEPPER as a positive regulator of the central floral repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C . Developmental Biology, 333,251-262.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Rosloski SM, Jali SS, Balasubramanian S, Weigel D, Grbic V (2010) Natural diversity in flowering responses of Arabidopsis thaliana caused by variation in a tandem gene array . Genetics, 186,263-276.
DOI PMID |
| [102] |
Ruelens P, de Maagd RA, Proost S, Theißen G, Geuten K, Kaufmann K (2013) FLOWERING LOCUS C in monocots and the tandem origin of angiosperm-specific MADS-box genes . Nature Communications, 4,2280.
DOI PMID |
| [103] |
Sanchez SE, Rugnone ML, Kay SA (2020) Light perception: A matter of time. Molecular Plant, 13,363-385.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Sasani S, Hemming MN, Oliver SN, Greenup A, Tavakkol-Afshari R, Mahfoozi S, Poustini K, Sharifi HR, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ, Trevaskis B (2009) The influence of vernalization and daylength on expression of flowering-time genes in the shoot apex and leaves of barley(Hordeum vulgare). Journal of Experimental Botany, 60,2169-2178.
DOI URL |
| [105] | Sawa M, Kay SA (2011) GIGANTEA directly activates Flowering Locus T in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108,11698-11703. |
| [106] |
Sawa M, Nusinow DA, Kay SA, Imaizumi T (2007) FKF1 and GIGANTEA complex formation is required for day-length measurement in Arabidopsis. Science, 318,261-265.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Schiessl SV, Huettel B, Kuehn D, Reinhardt R, Snowdon RJ (2017) Flowering time gene variation in Brassica species shows evolutionary principles . Frontiers in Plant Science, 8,1742.
DOI PMID |
| [108] |
Shaw LM, Li CX, Woods DP, Alvarez MA, Lin HQ, Lau MY, Chen A, Dubcovsky J (2020) Epistatic interactions between PHOTOPERIOD1, CONSTANS1and CONSTANS2 modulate the photoperiodic response in wheat . PLoS Genetics, 16,e1008812.
DOI URL |
| [109] | Sheldon CC, Rouse DT, Finnegan EJ, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES (2000) The molecular basis of vernalization: The central role of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 97,3753-3758. |
| [110] |
Shibaya T, Hori K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Yamanouchi U, Shu K, Kitazawa N, Shomura A, Ando T, Ebana K, Wu JZ, Yamazaki T, Yano M (2016) Hd18, encoding histone acetylase related to Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS D, is involved in the control of flowering time in rice . Plant and Cell Physiology, 57,1828-1838.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Shim JS, Jang G (2020) Environmental signal-dependent regulation of flowering time in rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21,6155.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Shim JS, Kubota A, Imaizumi T (2017) Circadian clock and photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis: CONSTANS is a hub for signal integration . Plant Physiology, 173,5-15.
DOI URL |
| [113] |
Shindo C, Aranzana MJ, Lister C, Baxter C, Nicholls C, Nordborg M, Dean C (2005) Role of FRIGIDA and FLOWERING LOCUS C in determining variation in flowering time of Arabidopsis . Plant Physiology, 138,1163-1173.
DOI URL |
| [114] |
Simpson GG (2004) The autonomous pathway: Epigenetic and post-transcriptional gene regulation in the control of Arabidopsis flowering time . Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 7,570-574.
DOI URL |
| [115] | Simpson GG, Dean C (2002) Arabidopsis, the Rosetta stone of flowering time? Science, 296,285-289. |
| [116] | Song YH, Estrada DA, Johnson RS, Kim SK, Lee SY, MacCoss MJ, Imaizumi T (2014) Distinct roles of FKF1, GIGANTEA, and ZEITLUPE proteins in the regulation of CONSTANS stability in Arabidopsis photoperiodic flowering. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111,17672-17677. |
| [117] |
Song YH, Ito S, Imaizumi T (2013) Flowering time regulation: Photoperiod- and temperature-sensing in leaves. Trends in Plant Science, 18,575-583.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
Spanudakis E, Jackson S (2014) The role of microRNAs in the control of flowering time. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65,365-380.
DOI PMID |
| [119] |
Srikanth A, Schmid M (2011) Regulation of flowering time: All roads lead to Rome. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 68,2013-2037.
DOI URL |
| [120] |
Steffen A, Elgner M, Staiger D (2019) Regulation of flowering time by the RNA-binding proteins AtGRP7 and AtGRP8. Plant and Cell Physiology, 60,2040-2050.
DOI URL |
| [121] | Sugano S, Andronis C, Ong MS, Green RM, Tobin EM (1999) The protein kinase CK2 is involved in regulation of circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 96,12362-12366. |
| [122] |
Sun H, Zhang WP, Wu YZ, Gao LF, Cui F, Zhao CH, Guo ZA, Jia JZ (2020) The circadian clock gene, TaPRR1, is associated with yield-related traits in wheat ( Triticum aestivum L.) . Frontiers in Plant Science, 11,285.
DOI URL |
| [123] |
Sun TP (2010) Gibberellin- GID1- DELLA: A pivotal regulatory module for plant growth and development . Plant Physiology, 154,567-570.
DOI URL |
| [124] |
Sung S, Amasino RM (2004) Vernalization in Arabidopsis thaliana is mediated by the PHD finger protein VIN3 . Nature, 427,159-164.
DOI URL |
| [125] |
Swiezewski S, Liu FQ, Magusin A, Dean C (2009) Cold-induced silencing by long antisense transcripts of an Arabidopsis polycomb target . Nature, 462,799-802.
DOI PMID |
| [126] |
Takada S, Goto K (2003) TERMINAL FLOWER2, an Arabidopsis homolog of HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1, counteracts the activation of FLOWERING LOCUS T by CONSTANS in the vascular tissues of leaves to regulate flowering time . The Plant Cell, 15,2856-2865.
DOI URL |
| [127] | Tamaki S, Tsuji H, Matsumoto A, Fujita A, Shimatani Z, Terada R, Sakamoto T, Kurata T, Shimamoto K (2015) FT-like proteins induce transposon silencing in the shoot apex during floral induction in rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112,E901-E910. |
| [128] |
Turner A, Beales J, Faure S, Dunford RP, Laurie DA (2005) The pseudo-response regulator Ppd-H1 provides adaptation to photoperiod in barley . Science, 310,1031-1034.
DOI URL |
| [129] |
Valverde F, Mouradov A, Soppe W, Ravenscroft D, Samach A, Coupland G (2004) Photoreceptor regulation of CONSTANS protein in photoperiodic flowering . Science, 303,1003-1006.
DOI URL |
| [130] |
Verhage L, Angenent GC, Immink RGH (2014) Research on floral timing by ambient temperature comes into blossom. Trends in Plant Science, 19,583-591.
DOI PMID |
| [131] |
Vermeulen PJ (2015) On selection for flowering time plasticity in response to density. New Phytologist, 205,429-439.
DOI URL |
| [132] |
Wang FF, Nan HY, Chen LY, Fang C, Zhang HY, Su T, Li SC, Cheng Q, Dong LD, Liu BH, Kong FJ, Lu SJ (2019) A new dominant locus, E11, controls early flowering time and maturity in soybean. Molecular Breeding, 39,70.
DOI URL |
| [133] |
Wang HP, Pan JJ, Li Y, Lou DJ, Hu YR, Yu DQ (2016) The DELLA-CONSTANS transcription factor cascade integrates gibberellic acid and photoperiod signaling to regulate flowering . Plant Physiology, 172,479-488.
DOI URL |
| [134] |
Wang LW, Sun S, Wu TT, Liu LP, Sun XG, Cai YP, Li JC, Jia HC, Yuan S, Chen L, Jiang BJ, Wu CX, Hou WS, Han TF (2020) Natural variation and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation in GmPRR37 affect photoperiodic flowering and contribute to regional adaptation of soybean . Plant Biotechnology Journal, 18,1869-1881.
DOI URL |
| [135] |
Wang P, Gong R, Yang Y, Yu SB (2019) Ghd8 controls rice photoperiod sensitivity by forming a complex that interacts with Ghd7 . BMC Plant Biology, 19,462.
DOI URL |
| [136] |
Wang SL, Gao J, Xue JQ, Xue YQ, Li DD, Guan YR, Zhang XX (2019) De novo sequencing of tree peony ( Paeonia suffruticosa) transcriptome to identify critical genes involved in flowering and floral organ development . BMC Genomics, 20,572.
DOI URL |
| [137] | Wang YY, Xiong F, Ren QP, Wang XL (2020) Regulation of flowering transition by alternative splicing: The role of the U 2 auxiliary factor. Journal of Experimental Botany, 71,751-758. |
| [138] |
Wei JH, Choi H, Jin P, Wu YF, Yoon J, Lee YS, Quan TY, An G (2016) GL2-type homeobox gene Roc4 in rice promotes flowering time preferentially under long days by repressing Ghd7 . Plant Science, 252,133-143.
DOI URL |
| [139] |
Weigel D (2012) Natural variation in Arabidopsis: From molecular genetics to ecological genomics . Plant Physiology, 158,2-22.
DOI URL |
| [140] |
Xia W, Liu R, Zhang J, Mason AS, Li ZY, Gong SF, Zhong YZ, Dou YJ, Sun XW, Fan HK, Xiao Y (2020) Alternative splicing of flowering time gene FT is associated with halving of time to flowering in coconut . Scientific Reports, 10,11640.
DOI URL |
| [141] |
Xing DH, Zhao HW, Xu RQ, Li QQ (2008) Arabidopsis PCFS4, a homologue of yeast polyadenylation factor Pcf11p, regulates FCA alternative processing and promotes flowering time . The Plant Journal, 54,899-910.
DOI URL |
| [142] |
Xu F, Li T, Xu PB, Li L, Du SS, Lian HL, Yang HQ (2016) DELLA proteins physically interact with CONSTANS to regulate flowering under long days in Arabidopsis . FEBS Letters, 590,541-549.
DOI URL |
| [143] |
Xu ML, Hu TQ, Zhao JF, Park MY, Earley KW, Wu G, Yang L, Poethig RS (2016) Developmental functions of miR156-regulated SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE ( SPL) genes in Arabidopsis thaliana . PLoS Genetics, 12,e1006263.
DOI URL |
| [144] |
Yadav A, Jayaswal PK, Venkat Raman K, Singh B, Singh NK, Usha K (2020) Transcriptome analysis of flowering genes in mango ( Mangifera indica L.) in relation to floral malformation . Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 29,193-212.
DOI URL |
| [145] |
Yamaguchi A, Abe M (2012) Regulation of reproductive development by non-coding RNA in Arabidopsis: To flower or not to flower . Journal of Plant Research, 125,693-704.
DOI PMID |
| [146] | Yan L, Fu D, Li C, Blechl A, Tranquilli G, Bonafede M, Sanchez A, Valarik M, Yasuda S, Dubcovsky J (2006) The wheat and barley vernalization gene VRN3 is an orthologue of FT. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103,19581-19586. |
| [147] | Yan L, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2003) Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100,6263-6268. |
| [148] |
Yan LL, Loukoianov A, Blechl A, Tranquilli G, Ramakrishna W, SanMiguel P, Bennetzen JL, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2004) The wheat VRN2 gene is a flowering repressor down-regulated by vernalization . Science, 303,1640-1644.
DOI URL |
| [149] |
Yan YY, Shen LS, Chen Y, Bao SJ, Thong ZH, Yu H (2014) A MYB-domain protein EFM mediates flowering responses to environmental cues in Arabidopsis . Developmental Cell, 30,437-448.
DOI URL |
| [150] |
Yang FX, Zhu GF, Wei YL, Gao J, Liang G, Peng LY, Lu CQ, Jin JP (2019) Low-temperature-induced changes in the transcriptome reveal a major role of CgSVP genes in regulating flowering of Cymbidium goeringii . BMC Genomics, 20,53.
DOI URL |
| [151] |
Yang L, Wang HN, Hou XH, Zou YP, Han TS, Niu XM, Zhang J, Zhao Z, Todesco M, Balasubramanian S, Guo YL (2018) Parallel evolution of common allelic variants confers flowering diversity in Capsella rubella . The Plant Cell, 30,1322-1336.
DOI PMID |
| [152] |
Yano K, Aya K, Hirano K, Ordonio RL, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M (2015) Comprehensive gene expression analysis of rice aleurone cells: Probing the existence of an alternative gibberellin receptor. Plant Physiology, 167,531-544.
DOI URL |
| [153] |
Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T (2000) Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. The Plant Cell, 12,2473-2484.
DOI URL |
| [154] |
Yanovsky MJ, Kay SA (2001) Signaling networks in the plant circadian system. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 4,429-435.
DOI URL |
| [155] |
Yi H, Li XN, Lee SH, Nou IS, Lim YP, Hur Y (2017) Natural variation in CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 is associated with flowering time in Brassica rapa . Genome, 60,402-413.
DOI URL |
| [156] |
Yun H, Hyun Y, Kang MJ, Noh YS, Noh B, Choi Y (2011) Identification of regulators required for the reactivation of FLOWERING LOCUS C during Arabidopsis reproduction . Planta, 234,1237-1250.
DOI URL |
| [157] |
Zentella R, Sui N, Barnhill B, Hsieh WP, Hu JH, Shabanowitz J, Boyce M, Olszewski NE, Zhou P, Hunt DF, Sun TP (2017) The Arabidopsis O-fucosyltransferase SPINDLY activates nuclear growth repressor DELLA . Nature Chemical Biology, 13,479-485.
DOI PMID |
| [158] |
Zhang L, Jiang YY, Zhu YM, Su WB, Long T, Huang TQ, Peng JR, Yu H, Lin SQ, Gao YS (2019) Functional characterization of GI and CO homologs from Eriobotrya deflexa Nakai forma koshunensis . Plant Cell Reports, 38,533-543.
DOI PMID |
| [159] |
Zhang SW, Gottschalk C, Nocker S (2019) Genetic mechanisms in the repression of flowering by gibberellins in apple ( Malus × domestica Borkh.) . BMC Genomics, 20,747.
DOI URL |
| [160] |
Zhao ML, Ni J, Chen MS, Xu ZF (2019) Ectopic expression of Jatropha curcas TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE PHOSPHATASE J causes late-flowering and heterostylous phenotypes in Arabidopsis but not in Jatropha . International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20,2165.
DOI URL |
| [161] |
Zhong XH, Du JM, Hale CJ, Gallego-Bartolome J, Feng SH, Vashisht AA, Chory J, Wohlschlegel JA, Patel DJ, Jacobsen SE (2014) Molecular mechanism of action of plant DRM de novo DNA methyltransferases. Cell, 157,1050-1060.
DOI URL |
| [162] |
Zhu QH, Helliwell CA (2011) Regulation of flowering time and floral patterning by miR172 . Journal of Experimental Botany, 62,487-495.
DOI URL |
| [163] |
Zhu Y, Liu L, Shen LS, Yu H (2016) NaKR1 regulates long-distance movement of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis . Nature Plants, 2,16075.
DOI URL |
| [164] |
Zicola J, Liu LY, Tänzler P, Turck F (2019) Targeted DNA methylation represses two enhancers of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis thaliana . Nature Plants, 5,300-307.
DOI PMID |
| [165] |
Zuo ZC, Liu HT, Liu B, Liu XM, Lin CT (2011) Blue light-dependent interaction of CRY2with SPA1 regulates COP1 activity and floral initiation in Arabidopsis . Current Biology, 21,841-847.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Shunyu Wang, Yang Li, Xiaoqin Lü, Xin Li, Quanxiu Fan, Xiaoyue Wang. The color preference of bumblebee nectar robbing and its impact on the reproductive fitness of Lonicera calcarata [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24554-. |
| [2] | Nan Chen, Quan-Guo Zhang. The experimental evolution approach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [3] | Ruiwu Wang, Minlan Li, Jiaxu Han, Chao Wang. Fitness relativity and path-dependent selection [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21323-. |
| [4] | Ningna Lu, Zhenheng Liu, Yan Ma, Guangmei Lu, Xiuxiang Meng. Phenotypic selection analysis of flower traits in Delphinium kamaonense var. glabrescens (Ranunculaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(7): 772-777. |
| [5] | Wenzhao Hu, Jimin Zhao, Yanwen Zhang. Fitness advantage and maintenance mechanisms of dimorphic mixed- mating plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 468-474. |
| [6] | Wensheng Yu, Yaolin Guo, Jiajia Jiang, Keke Sun, Ruiting Ju. Comparison of the life history of a native insect Laelia coenosa with a native plant Phragmites australis and an invasive plant Spartina alterniflora [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 433-438. |
| [7] | Chengjin Chu, Youshi Wang, Yu Liu, Lin Jiang, Fangliang He. Advances in species coexistence theory [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(4): 345-354. |
| [8] | Lin Li, Ningna Lu, Baoli Fan, Zhigang Zhao. Effect of flowering time on floral sexual durations and phenotypic gender in dichogamous Aconitum gymnandrum [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 665-671. |
| [9] | Chan Zhang, Shaoqin Zha, Yongping Yang, Yuanwen Duan. Effects of the yellow barbs of the staminodes on reproductive success of Delphinium caeruleum (Ranunculaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(3): 348-353. |
| [10] | Lele Liu, Zuojun Liu, Guozhen Du, Zhigang Zhao. Floral traits, pollinator assemblages, and phenotypic selection at different flowering time for Trollius ranunculoides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(3): 317-323. |
| [11] | Bao-Rong Lu, Hui Xia, Wei Wang, Xiao Yang. Impacts of natural hybridization and introgression on biological invasion of plant species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(6): 577-589. |
| [12] | Bao-Rong Lu, Hui Xia, Xiao Yang, Xin Jin, Ping Liu, Wei Wang. [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(4): 362-377. |
| [13] | Jingli Zhang, Changqin Zhang, Zhikun Wu, Qin Qiao. The potential roles of interspecific pollination in natural hybridization of Rhododendron species in Yunnan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2007, 15(6): 658-665. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()