



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 1122-1131. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019180 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019180
• Original Papers:Ecosystem Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ying Zhao1, Rong Ma1, Yongxiang Yin2, Zhidong Zhang3, Chengming Tian4,*( )
)
Received:2019-05-29
Accepted:2019-08-09
Online:2019-10-20
Published:2019-10-20
Contact:
Chengming Tian
Ying Zhao, Rong Ma, Yongxiang Yin, Zhidong Zhang, Chengming Tian. Diversity of Cytospora chrysosperma from different hosts in Xinjiang[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(10): 1122-1131.
| 菌株 Isolate | 寄主 Host | 采集时间 Collecting time | 采集地点 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 319-1 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2011/8/7 | 昌吉吉木萨尔县 Jimusar County, Changji Prefecture |
| 790-2 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2015/6/28 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 908 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 936 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2015/8/4 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 701 | 榆树 Ulmus sp. | 2015/4/18 | 吐鲁番市鄯善县 Shanshan County, Turpan City |
| 1155 | 榆树 Ulmus sp. | 2015/8/20 | 昌吉州奇台县 Qitai County, Changji Prefecture |
| 600-2 | 胡杨 Populus euphratica | 2012/8/20 | 喀什地区泽普县 Zepu County, Kashgar Prefecture |
| 626 | 新疆杨 Populus alba | 2012/8/20 | 喀什地区喀什市 Kashgar City, Kashgar Prefecture |
| 686-1 | 山杨 Populus davidiana | 2014/8/31 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 686-2 | 山杨 Populus davidiana | 2014/9/1 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 702 | 小叶杨 Populus simonii | 2015/4/18 | 吐鲁番市鄯善县 Shanshan County, Turpan City |
| 737 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 739 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 740 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 742 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 793 | 俄罗斯杨 Populus russkii | 2015/6/29 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 882 | 北京杨 Populus beijingensis | 2015/7/22 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 891-1 | 俄罗斯杨 Populus russkii | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 891-3 | 俄罗斯杨 Populus russkii | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 904 | 大叶杨 Populus lasiocarpa | 2015/7/16 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 914-1 | 杨树 Populus sp. | 2015/7/21 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 934 | 新疆杨 Populus alba | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 1074-2 | 胡杨 Populus euphratica | 2015/8/26 | 吐鲁番市托克逊县 Toxon County, Turpan City |
| 1076 | 胡杨 Populus euphratica | 2015/8/26 | 吐鲁番市托克逊县 Toxon County, Turpan City |
| 812-1 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/1 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 835-1 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/11 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 839-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/2 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 839-3 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/2 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 847 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/6 | 塔城地区裕民县 Yumin County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 856-1 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/7/29 | 塔城地区沙湾县 Shawan County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 755-2 | 红瑞木 Swida alba | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 874-2 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/7/26 | 塔城地区沙湾县 Shawan County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 895-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 896 | 灰柳 Salix cinerea | 2015/7/14 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 897 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/14 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 901 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/7/14 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 919-1 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/7/22 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 933 | 金丝垂柳 Salix × aureo-pendula | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 935 | 金丝垂柳 Salix × aureo-pendula | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 942 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/8/4 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 944-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/8/10 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 976-1 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/8/10 | 五家渠市 Wujiaqu City |
| 976-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/8/10 | 五家渠市 Wujiaqu City |
| 863 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/7/29 | 塔城地区沙湾县 Shawan County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 921 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/31 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 922 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/7/31 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 930-1 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
Table 1 Related information of the isolates in this study
| 菌株 Isolate | 寄主 Host | 采集时间 Collecting time | 采集地点 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 319-1 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2011/8/7 | 昌吉吉木萨尔县 Jimusar County, Changji Prefecture |
| 790-2 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2015/6/28 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 908 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 936 | 苹果 Malus sp. | 2015/8/4 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 701 | 榆树 Ulmus sp. | 2015/4/18 | 吐鲁番市鄯善县 Shanshan County, Turpan City |
| 1155 | 榆树 Ulmus sp. | 2015/8/20 | 昌吉州奇台县 Qitai County, Changji Prefecture |
| 600-2 | 胡杨 Populus euphratica | 2012/8/20 | 喀什地区泽普县 Zepu County, Kashgar Prefecture |
| 626 | 新疆杨 Populus alba | 2012/8/20 | 喀什地区喀什市 Kashgar City, Kashgar Prefecture |
| 686-1 | 山杨 Populus davidiana | 2014/8/31 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 686-2 | 山杨 Populus davidiana | 2014/9/1 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 702 | 小叶杨 Populus simonii | 2015/4/18 | 吐鲁番市鄯善县 Shanshan County, Turpan City |
| 737 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 739 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 740 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 742 | 钻天杨 Populus nigra | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 793 | 俄罗斯杨 Populus russkii | 2015/6/29 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 882 | 北京杨 Populus beijingensis | 2015/7/22 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 891-1 | 俄罗斯杨 Populus russkii | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 891-3 | 俄罗斯杨 Populus russkii | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 904 | 大叶杨 Populus lasiocarpa | 2015/7/16 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 914-1 | 杨树 Populus sp. | 2015/7/21 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 934 | 新疆杨 Populus alba | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 1074-2 | 胡杨 Populus euphratica | 2015/8/26 | 吐鲁番市托克逊县 Toxon County, Turpan City |
| 1076 | 胡杨 Populus euphratica | 2015/8/26 | 吐鲁番市托克逊县 Toxon County, Turpan City |
| 812-1 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/1 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 835-1 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/11 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 839-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/2 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 839-3 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/2 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 847 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/6 | 塔城地区裕民县 Yumin County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 856-1 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/7/29 | 塔城地区沙湾县 Shawan County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 755-2 | 红瑞木 Swida alba | 2015/6/4 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 874-2 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/7/26 | 塔城地区沙湾县 Shawan County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 895-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/17 | 塔城地区乌苏市 Wusu City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 896 | 灰柳 Salix cinerea | 2015/7/14 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 897 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/14 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 901 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/7/14 | 塔城地区托里县 Tori County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 919-1 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/7/22 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 933 | 金丝垂柳 Salix × aureo-pendula | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 935 | 金丝垂柳 Salix × aureo-pendula | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 942 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/8/4 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 944-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/8/10 | 哈密地区哈密市 Hami City, Hami Prefecture |
| 976-1 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/8/10 | 五家渠市 Wujiaqu City |
| 976-2 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/8/10 | 五家渠市 Wujiaqu City |
| 863 | 旱柳 Salix matsudana | 2015/7/29 | 塔城地区沙湾县 Shawan County, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 921 | 柳树 Salix sp. | 2015/7/31 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 922 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/7/31 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 930-1 | 疏锯齿柳 Salix serrulatifolia | 2015/8/3 | 塔城地区塔城市 Tacheng City, Tacheng Prefecture |
| 编号 No. | 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 退火温度 Annealing temp. (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IJ-5 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGATG | 52 |
| 2 | IL-7 | ACAACACACACACACAC | 52 |
| 3 | IJ-7 | GGGTGGGGTGGGGTG | 52 |
| 4 | IJ-9 | AGATGTGTGTGTGTGTG | 52 |
| 5 | IJ-8 | ATAAGAGAGAGAGAGAG | 52 |
| 6 | ID-8 | GTGCGTGCGTGCGTGC | 52 |
| 7 | IL-3 | CACGAGAGAGAGAGAGA | 52 |
| 8 | IQ-2 | CCAAACCACCACCACCACCA | 53 |
| 9 | IJ-3 | AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGTC | 53 |
| 10 | IJ-4 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGATC | 53 |
Table 2 The sequence of ISSR primers used in this study
| 编号 No. | 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 退火温度 Annealing temp. (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IJ-5 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGATG | 52 |
| 2 | IL-7 | ACAACACACACACACAC | 52 |
| 3 | IJ-7 | GGGTGGGGTGGGGTG | 52 |
| 4 | IJ-9 | AGATGTGTGTGTGTGTG | 52 |
| 5 | IJ-8 | ATAAGAGAGAGAGAGAG | 52 |
| 6 | ID-8 | GTGCGTGCGTGCGTGC | 52 |
| 7 | IL-3 | CACGAGAGAGAGAGAGA | 52 |
| 8 | IQ-2 | CCAAACCACCACCACCACCA | 53 |
| 9 | IJ-3 | AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGTC | 53 |
| 10 | IJ-4 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGATC | 53 |
| 观察项 Item | 代表值 Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 菌落颜色 Colony color | 白色 White | 米黄色 Light yellow | 土黄色 Khaki | 灰色 Gray | 深灰色 Dark gray | 桔红色 Orange |
| 菌落形状 Colony shape | 圆形生长 Circular growth | 辐射状生长 Radial growth | - | - | - | - |
| 表面形态 Surface morphology | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稀疏 Hyphae sparse |
| 平伏 Flat exhibition | 轻微凸起 Slight raised | 轻微凸起 Slight raised | 凸起 Raised | 凸起 Raised | 轻微凸起 Slight raised | |
| 无轮纹 No concentric ring | 无轮纹 No concentric ring | 有轮纹 Concentric ring | 无轮纹 No concentric ring | 有轮纹 Concentric ring | 无轮纹 No concentric ring | |
| 有/无子实体 Sporulation | 子实体小 Small sporophore | 子实体小 Small sporophore | 子实体大 Larger sporophore | 子实体大 Larger sporophore | - | - |
| 密集型 Intensive | 稀疏型 Sparse | 稀疏型 Sparse | 聚生型 Concentrated | - | - | |
| 色素分泌 Pigment secretion | 米白色 Creamy-white | 米黄色 Light yellow | 土黄色 Khaki | 灰色 Gray | 黑色 Black | 桔红色 Orange |
Table 3 Observation items and assignment of morphological characteristics of Cytospora chrysosperma on PDA in this study.
| 观察项 Item | 代表值 Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 菌落颜色 Colony color | 白色 White | 米黄色 Light yellow | 土黄色 Khaki | 灰色 Gray | 深灰色 Dark gray | 桔红色 Orange |
| 菌落形状 Colony shape | 圆形生长 Circular growth | 辐射状生长 Radial growth | - | - | - | - |
| 表面形态 Surface morphology | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稠密 Hyphae dense | 菌丝稀疏 Hyphae sparse |
| 平伏 Flat exhibition | 轻微凸起 Slight raised | 轻微凸起 Slight raised | 凸起 Raised | 凸起 Raised | 轻微凸起 Slight raised | |
| 无轮纹 No concentric ring | 无轮纹 No concentric ring | 有轮纹 Concentric ring | 无轮纹 No concentric ring | 有轮纹 Concentric ring | 无轮纹 No concentric ring | |
| 有/无子实体 Sporulation | 子实体小 Small sporophore | 子实体小 Small sporophore | 子实体大 Larger sporophore | 子实体大 Larger sporophore | - | - |
| 密集型 Intensive | 稀疏型 Sparse | 稀疏型 Sparse | 聚生型 Concentrated | - | - | |
| 色素分泌 Pigment secretion | 米白色 Creamy-white | 米黄色 Light yellow | 土黄色 Khaki | 灰色 Gray | 黑色 Black | 桔红色 Orange |
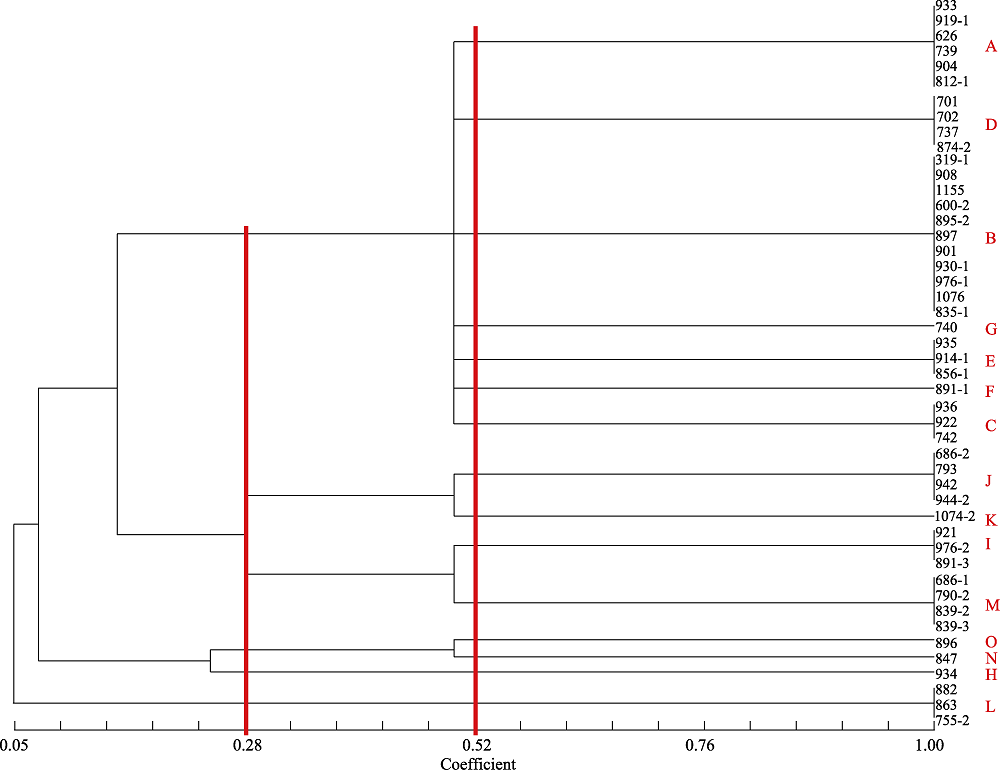
Fig. 1 The UPGMA dendrogram of 47 Cytospora chrysosperma isolates based on morphological characteristics. A-O, Branches with different culture traits. The numbers represent strain numbers, which correspond to those in Table 1.
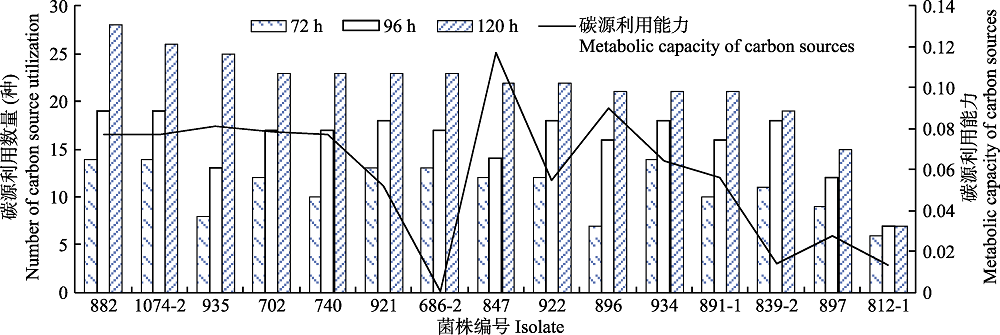
Fig. 2 Changes in the amount of Cytospora chersosperma carbon source utilization and metabolic activity over time. The strain numbers are the same to Table 1.
| 碳源种类 Carbon source type | 吸光度值 Absorbance value (Ci-R) | 平均吸光 度值 Average absorbance value | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 812-1 | 897 | 1074-2 | 686-2 | 921 | 922 | 839-2 | 847 | 934 | 882 | 702 | 891-1 | 896 | 740 | 935 | ||
| 吐温80 Tween 80 | 0.735 | 0.715 | 0.296 | 0.525 | 0.334 | 0.472 | 0.332 | 0.305 | 0.349 | 0.290 | 0.598 | 0.458 | 0.401 | 0.812 | 0.700 | 0.488 |
| 苦杏仁苷 Amygdalin | - | 0.282 | 0.274 | 0.322 | 0.276 | 0.583 | 0.653 | 0.254 | 0.418 | 0.284 | 0.396 | 0.475 | 0.493 | 0.313 | 0.330 | 0.357 |
| D-阿拉伯糖 D-Arabinose | 0.685 | 0.632 | 0.821 | 0.521 | 0.266 | 0.709 | 0.624 | 0.250 | 0.419 | 0.272 | 0.499 | 0.557 | 0.425 | 0.426 | 0.307 | 0.494 |
| L-阿拉伯糖 L-Arabinose | 0.688 | 0.627 | 0.670 | 0.568 | 0.285 | 0.724 | 0.453 | 0.375 | 0.582 | 0.266 | 0.629 | 0.496 | 0.285 | 0.259 | 0.304 | 0.481 |
| 糊精 Dextrin | 0.392 | 0.686 | 0.661 | 0.782 | 0.503 | 0.447 | 0.438 | 0.345 | 0.414 | 0.264 | 0.543 | 0.522 | 0.469 | 0.479 | 0.369 | 0.488 |
| D-果糖 D-Fructose | - | 0.678 | 0.891 | 0.669 | 0.401 | 0.404 | 0.471 | 0.303 | 0.503 | 0.282 | 0.616 | 0.578 | 0.406 | 0.259 | 0.726 | 0.479 |
| α-D-葡萄糖 α-D-glucose | 0.385 | 0.669 | 0.500 | 0.766 | 0.334 | 0.379 | 0.572 | 0.301 | 0.347 | 0.464 | 0.618 | 0.689 | 0.535 | 0.287 | 0.551 | 0.493 |
| D-甘露糖 D-Mannitol | - | 0.899 | 0.563 | 0.741 | 0.336 | 0.312 | 0.314 | 0.510 | 0.992 | 0.610 | 0.297 | 0.508 | 0.314 | 0.251 | 0.416 | 0.471 |
| D-核糖 D-ribose | 0.658 | 0.691 | 0.451 | 0.613 | 0.541 | 0.892 | 0.562 | 0.510 | 0.349 | 0.554 | 0.432 | 0.401 | 0.526 | 0.276 | 0.353 | 0.521 |
| 水杨苷 Salicin | - | 0.394 | 0.534 | 0.323 | 0.342 | 0.359 | 0.335 | 0.523 | 0.318 | 0.282 | 0.463 | 0.579 | 0.551 | 0.331 | 0.334 | 0.378 |
| 蔗糖 Sucrose | - | 0.28 | 0.430 | 0.255 | 0.349 | 0.498 | - | 0.305 | 0.349 | - | 0.356 | 0.252 | - | 0.343 | 0.518 | 0.262 |
| D-木糖 D-xylose | 0.756 | 0.686 | 0.270 | 0.592 | 0.336 | 0.518 | 0.423 | 0.347 | 0.319 | 0.666 | 0.293 | 0.592 | 0.406 | 0.356 | 0.514 | 0.472 |
| 富马酸 Fumaric acid | - | 0.354 | 0.361 | 0.378 | 0.436 | 0.381 | - | 1.522 | 0.314 | 0.595 | 0.280 | 0.625 | - | 0.294 | 0.517 | 0.404 |
| 琥珀酸 Butanedioic acid | - | 0.371 | 0.360 | 0.255 | 0.348 | 0.331 | - | 0.400 | 0.279 | 0.346 | 0.649 | 0.535 | - | 0.284 | 0.326 | 0.299 |
| L-天门冬酰 L-asparagine | - | 1.246 | 0.460 | 0.578 | 0.436 | 0.304 | 0.306 | 0.453 | 0.258 | 0.329 | 0.284 | 0.410 | 0.260 | 0.265 | 0.954 | 0.436 |
| 平均吸光度值 Average absorbance value | 0.287 | 0.614 | 0.503 | 0.526 | 0.368 | 0.488 | 0.366 | 0.447 | 0.414 | 0.367 | 0.464 | 0.512 | 0.338 | 0.349 | 0.481 | |
Table 4 The utilization of carbon type by Cytospora chrysosperma in this study.The strain numbers are the same to Table 1.
| 碳源种类 Carbon source type | 吸光度值 Absorbance value (Ci-R) | 平均吸光 度值 Average absorbance value | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 812-1 | 897 | 1074-2 | 686-2 | 921 | 922 | 839-2 | 847 | 934 | 882 | 702 | 891-1 | 896 | 740 | 935 | ||
| 吐温80 Tween 80 | 0.735 | 0.715 | 0.296 | 0.525 | 0.334 | 0.472 | 0.332 | 0.305 | 0.349 | 0.290 | 0.598 | 0.458 | 0.401 | 0.812 | 0.700 | 0.488 |
| 苦杏仁苷 Amygdalin | - | 0.282 | 0.274 | 0.322 | 0.276 | 0.583 | 0.653 | 0.254 | 0.418 | 0.284 | 0.396 | 0.475 | 0.493 | 0.313 | 0.330 | 0.357 |
| D-阿拉伯糖 D-Arabinose | 0.685 | 0.632 | 0.821 | 0.521 | 0.266 | 0.709 | 0.624 | 0.250 | 0.419 | 0.272 | 0.499 | 0.557 | 0.425 | 0.426 | 0.307 | 0.494 |
| L-阿拉伯糖 L-Arabinose | 0.688 | 0.627 | 0.670 | 0.568 | 0.285 | 0.724 | 0.453 | 0.375 | 0.582 | 0.266 | 0.629 | 0.496 | 0.285 | 0.259 | 0.304 | 0.481 |
| 糊精 Dextrin | 0.392 | 0.686 | 0.661 | 0.782 | 0.503 | 0.447 | 0.438 | 0.345 | 0.414 | 0.264 | 0.543 | 0.522 | 0.469 | 0.479 | 0.369 | 0.488 |
| D-果糖 D-Fructose | - | 0.678 | 0.891 | 0.669 | 0.401 | 0.404 | 0.471 | 0.303 | 0.503 | 0.282 | 0.616 | 0.578 | 0.406 | 0.259 | 0.726 | 0.479 |
| α-D-葡萄糖 α-D-glucose | 0.385 | 0.669 | 0.500 | 0.766 | 0.334 | 0.379 | 0.572 | 0.301 | 0.347 | 0.464 | 0.618 | 0.689 | 0.535 | 0.287 | 0.551 | 0.493 |
| D-甘露糖 D-Mannitol | - | 0.899 | 0.563 | 0.741 | 0.336 | 0.312 | 0.314 | 0.510 | 0.992 | 0.610 | 0.297 | 0.508 | 0.314 | 0.251 | 0.416 | 0.471 |
| D-核糖 D-ribose | 0.658 | 0.691 | 0.451 | 0.613 | 0.541 | 0.892 | 0.562 | 0.510 | 0.349 | 0.554 | 0.432 | 0.401 | 0.526 | 0.276 | 0.353 | 0.521 |
| 水杨苷 Salicin | - | 0.394 | 0.534 | 0.323 | 0.342 | 0.359 | 0.335 | 0.523 | 0.318 | 0.282 | 0.463 | 0.579 | 0.551 | 0.331 | 0.334 | 0.378 |
| 蔗糖 Sucrose | - | 0.28 | 0.430 | 0.255 | 0.349 | 0.498 | - | 0.305 | 0.349 | - | 0.356 | 0.252 | - | 0.343 | 0.518 | 0.262 |
| D-木糖 D-xylose | 0.756 | 0.686 | 0.270 | 0.592 | 0.336 | 0.518 | 0.423 | 0.347 | 0.319 | 0.666 | 0.293 | 0.592 | 0.406 | 0.356 | 0.514 | 0.472 |
| 富马酸 Fumaric acid | - | 0.354 | 0.361 | 0.378 | 0.436 | 0.381 | - | 1.522 | 0.314 | 0.595 | 0.280 | 0.625 | - | 0.294 | 0.517 | 0.404 |
| 琥珀酸 Butanedioic acid | - | 0.371 | 0.360 | 0.255 | 0.348 | 0.331 | - | 0.400 | 0.279 | 0.346 | 0.649 | 0.535 | - | 0.284 | 0.326 | 0.299 |
| L-天门冬酰 L-asparagine | - | 1.246 | 0.460 | 0.578 | 0.436 | 0.304 | 0.306 | 0.453 | 0.258 | 0.329 | 0.284 | 0.410 | 0.260 | 0.265 | 0.954 | 0.436 |
| 平均吸光度值 Average absorbance value | 0.287 | 0.614 | 0.503 | 0.526 | 0.368 | 0.488 | 0.366 | 0.447 | 0.414 | 0.367 | 0.464 | 0.512 | 0.338 | 0.349 | 0.481 | |
| 菌株 Strain | 碳水化合物 Carbohydrate | 羧酸及其衍生物 Carboxylic acids and derivatives | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 磷酸盐类 Phosphates | 胺类 Amine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1074-2 | - | - | L-谷氨酸 L- glutamate | L-丙胺酰胺 L-alamide | - |
| 847 | - | 溴代丁二酸 Bromosuccinic acid | - | - | - |
| 934 | - | - | - | - | 腺苷 Adenosin |
| 891-1 | - | L-乳酸 L-lactic acid | L-苯丙氨酸 L- phenylalanine | - | - |
| 896 | L-海藻糖 L-trehalose | - | - | - | - |
| 740 | - | ρ-羟基苯乙酸 ρ-hydroxy acid | 琥珀酰胺酸 Succinamic acid | - | - |
| L-天门冬氨酸 L-aspartic acid |
Table 5 Strains and types of carbon sources that used carbon sources alone in this study
| 菌株 Strain | 碳水化合物 Carbohydrate | 羧酸及其衍生物 Carboxylic acids and derivatives | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 磷酸盐类 Phosphates | 胺类 Amine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1074-2 | - | - | L-谷氨酸 L- glutamate | L-丙胺酰胺 L-alamide | - |
| 847 | - | 溴代丁二酸 Bromosuccinic acid | - | - | - |
| 934 | - | - | - | - | 腺苷 Adenosin |
| 891-1 | - | L-乳酸 L-lactic acid | L-苯丙氨酸 L- phenylalanine | - | - |
| 896 | L-海藻糖 L-trehalose | - | - | - | - |
| 740 | - | ρ-羟基苯乙酸 ρ-hydroxy acid | 琥珀酰胺酸 Succinamic acid | - | - |
| L-天门冬氨酸 L-aspartic acid |
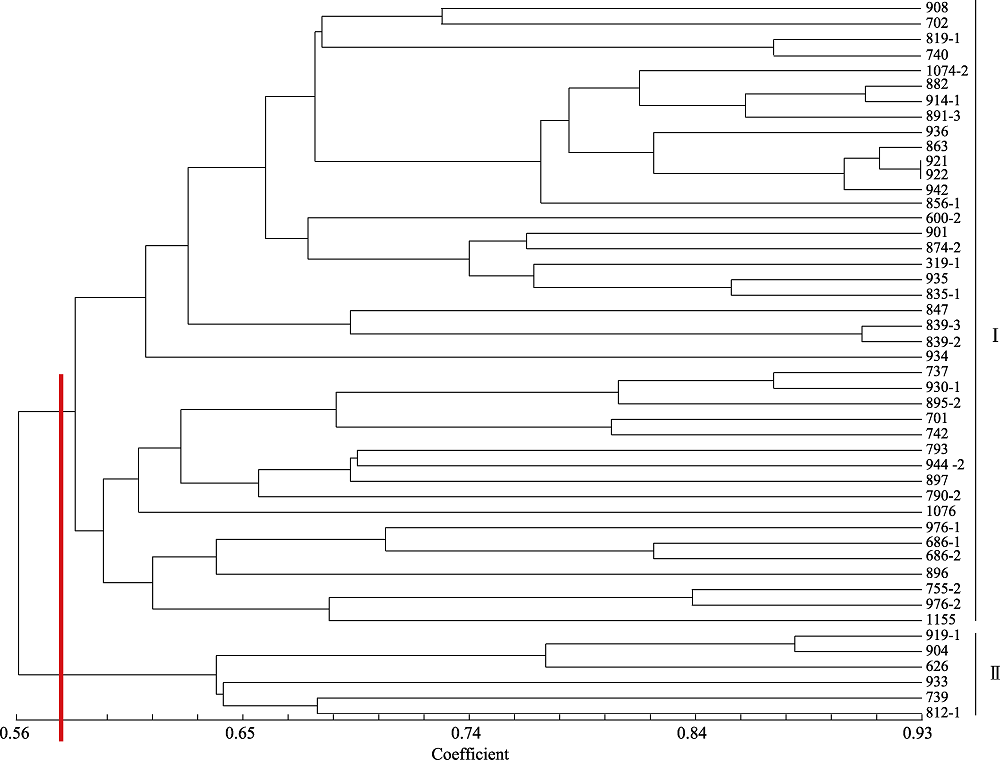
Fig. 3 The UPGMA dendrogram of 47 Crtospora chrysosperma isolates with PCR-ISSR. The 47 strains were divided into group II and group II when genetic similarity coefficient was 0.58. Strain numbers see Table 1.
| [1] | Abbasi K, Abbasi S, Fotouhifar KB, Zebarjabi AR ( 2015) Study of genetic diversity in Cytospora chrysosperma isolates obtained from walnut trees in Iran using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 48, 327-335. |
| [2] | Abbasi K, Abbasi S, Fotouhifar KB, Zebarjabi AR, Cheghamirza K ( 2011) Genetic diversity of Cytospora chrysosperma isolates obtained from Iranian walnut trees using molecular markers. African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 15710-15716. |
| [3] | Du P, Liu JJ, Shen LD, Hu BL, Zeng JN, Chen QZ, Shou L, Liao YB ( 2012) Diversity of microorganisms in sediments of the Jiaojiang estuary as estimated by Biolog and PCR- DGGE. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32, 1436-1444. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜萍, 刘晶晶, 沈李东, 胡宝兰, 曾江宁, 陈全震, 寿鹿, 廖一波 ( 2012) Biolog和PCR-DGGE技术解析椒江口沉积物微生物多样性. 环境科学学报, 32, 1436-1444.] | |
| [4] | Fan XL ( 2016) Phylogeny and Taxonomy of Cytospora in Yellow River Region of China. PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 范鑫磊 ( 2016) 中国黄河流域壳囊孢属的分类和系统学研究. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Ji RQ, Li Y, Song RQ, Wang YJ ( 2010) Cultural characteristics and rDNA ITS sequence analysis of Cytospora chrysosperma. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 32, 483-487. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冀瑞卿, 李玉, 宋瑞清, 王月杰 ( 2010) 金黄壳囊孢菌rDNA ITS序列测定及生理学特性. 吉林农业大学学报, 32, 483-487.] | |
| [6] | Jia X, Dong SM, Zhou CJ ( 2013) Effects of Biolog Eco-plates incubation time on analysis results in microbial ecology researches. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 21, 10-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贾夏, 董岁明, 周春娟 ( 2013) 微生物生态研究中Biolog Eco微平板培养时间对分析结果的影响. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 21, 10-19.] | |
| [7] | Khalil S, Alsanius BW ( 2009) Utilisation of carbon sources by Pythium, Phytophthora and Fusarium species as determined by Biolog® microplate assay. Open Microbiology Journal, 3, 9. |
| [8] | Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW ( 2008) Dictionary of the Fungi. CABI, Wallingford |
| [9] | Li ZL, Huang LL, Kang ZS, Zang R ( 2011) Polymorphism of Valsa mali collected in Yangling Shaanxi using SRAP markers. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 20, 190-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李正力, 黄丽丽, 康振生, 臧睿 ( 2011) 陕西杨凌地区苹果树腐烂病菌 (Valsa mali)基因多态性的SRAP分析. 西北农业学报, 20, 190-195.] | |
| [10] | Liu XL, Liu Y, Ma R, Liang YM, Chen BJ, Yan J ( 2015) Identification and biological characteristics of the pathogen causing Jujube black spot in Xinjiang. Journal of Northwest Forestry, 30, 132-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘晓琳, 刘玉, 马荣, 梁英梅, 陈宝军, 闫军 ( 2015) 新疆枣果黑斑病病原菌鉴定及生物学特性. 西北林学院学报, 30, 132-138.] | |
| [11] | Liu YJ, Wang J, Wang ST, Wang YN, Hu TL, Cao KQ ( 2014) RAPD analysis of genetic diversity of apple tree rot pathogens in Hebei Province. China Fruits, ( 5), 20-24. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘钰娇, 王娟, 王树桐, 王亚南, 胡同乐, 曹克强 ( 2014) 河北省苹果树腐烂病病菌遗传多样性的RAPD分析. 中国果树, ( 5), 20-24.] | |
| [12] | Ma R ( 2017) Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Cytospora in Xinjiang, Northwest of China. PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马荣 ( 2017) 新疆壳囊孢属真菌的分类及系统学研究. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Ma R, Zhao Y, Yin YX, Li Y, Tian CM ( 2018) Study on the culture characteristics of Cytospora chrysosperma from different sources and the pathogenicity to three poplar species. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 41, 339-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马荣, 赵颖, 尹永香, 李瑜, 田呈明 ( 2018) 不同来源金黄壳囊孢菌的培养性状及对3个品种杨树的致病性研究. 新疆农业大学学报, 41, 339-345.] | |
| [14] | Nei M ( 1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 70, 3321-3323. |
| [15] | Rohlf FJ ( 1987) NTSYS-pc: Microcomputer Programs for Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis. American Statistician, 41, 330. |
| [16] | Tian CM, Kang ZS, Li ZQ, Zhao YX, Zhang H ( 2000) Analysis of the genetic specialization of Melampsora larici-Populina with RAPD markers. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 36(5), 54-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 田呈明, 康振生, 李振岐, 赵彦修, 张慧 ( 2000) 落叶松-杨栅锈菌遗传分化的RAPD分析. 林业科学, 36(5), 54-58.] | |
| [17] | Wang Q, Dai JL, Wu DQ, Yu Y, Shen TL, Wang RQ ( 2010) Statistical analysis of data from BIOLOG method in the study of microbial ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 817-823. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王强, 戴九兰, 吴大千, 余悦, 申天琳, 王仁卿 ( 2010) 微生物生态研究中基于BIOLOG方法的数据分析. 生态学报, 30, 817-823] | |
| [18] | Wu ZX, Hao ZP, Chen YL, Zeng Y, Guo LP, Huang LQ, Wang Y, Chen BD ( 2015) Characterization of fungal community composition and carbon source utilization in the rhizosphere soil of Panax notoginseng suffering from root-rot disease. Mycosystema, 34, 65-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴照祥, 郝志鹏, 陈永亮, 曾燕, 郭兰萍, 黄璐琦, 王勇, 陈保冬 ( 2015) 三七根腐病株根际土壤真菌群落组成与碳源利用特征研究. 菌物学报, 34, 65-74.] | |
| [19] | Xiang YY ( 1987) The Disease and Prevention of Poplar. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 向玉英 ( 1987) 杨树病害及其防治. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Yang MX ( 2014) The Genetic Diversity of Cytospora chrysosperma and the Defense Mechanisms of Poplar. PhD dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨明秀 ( 2014) 中国金黄壳囊孢菌遗传多样性及杨树防御机制研究. 博士学位论文, 东北林业大学, 哈尔滨.] | |
| [21] | Zang R, Huang LL, Li ZL, Gao XN, Kang ZS ( 2012) Polymorphism analysis of Valsa mali isolated from Shaanxi Province using ISSR markers. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 39, 51-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 臧睿, 黄丽丽, 李正力, 高小宁, 康振生 ( 2012) 陕西省苹果树腐烂病菌基因多态性的ISSR分析. 植物保护学报, 39, 51-57.] | |
| [22] | Zhang HY, Li YJ, Gu JG, Dong XX, Shang P ( 2015) On carbon metabolism of fungi in chlortetracycline degradation based on Biolog-FF system. Microbiology China, 42, 1241-1247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张惠艳, 李艳菊, 顾金刚, 董晓霞, 尚攀 ( 2015) 基于Biolog-FF技术的金霉素降解真菌的碳代谢特征研究. 微生物学通报, 42 , 1241-1247.] | |
| [23] | Zhang JE, Fan XL, Liang YM, Tian CM ( 2017) Analysis of appearance features and genetic diversity of Cytospora chrysosperma causing poplar canker. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 39, 76-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张俊娥, 范鑫磊, 梁英梅, 田呈明 ( 2017) 杨树腐烂病菌表观特征及遗传多样性分析. 北京林业大学学报, 39, 76-86.] | |
| [24] | Zhang XY, Chen HY, Liang J, Tian CM, Lü Q ( 2007) Cultural morphology and vegetative compatibility of Cytospora chrysosperma isolate. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 35, 99-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张星耀, 陈海燕, 梁军, 田呈明, 吕全 ( 2007) 金黄壳囊孢菌(Cytospora chrysosperma)的培养性状和营养体亲和性. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 35, 99-105.] | |
| [25] | Zhou ZM ( 1990) Forest Pathology. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周仲民 ( 1990) 林木病理学. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()