



Biodiv Sci ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (2): 182-187. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.195 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.195
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lin Liu1, Lei Sun1,*( ), Ruiying Zhang1, Na Yao2, Lubin Li2,*
), Ruiying Zhang1, Na Yao2, Lubin Li2,*
Received:2009-09-15
Accepted:2009-12-16
Online:2010-03-20
Published:2010-03-20
Contact:
Lei Sun, Lubin Li
Lin Liu, Lei Sun, Ruiying Zhang, Na Yao, Lubin Li. Diversity of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria isolated from the roots of Cymbidium goeringii[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(2): 182-187.
| 类群 Group | 分型测序菌株Isolate | 菌株数 No.of strains | IAA分泌量 IAA production (mg·L-1· (OD600)-1) | 最相近菌种(登录号) Nearest strain (accession no.) | 序列相似性Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-变形菌纲Alphaproteobacteria (35.1%) | R209 | 7 | 1.0#-26.3# | Rhizobium miluonense (EF061096) | 100.0 |
| R128-2 | 1 | 5.8# | R. huautlense (AF025852) | 97.1 | |
| R141 | 1 | 3.6# | R. giardinii (U86344) | 97.3 | |
| R224-3 | 4 | 10.0#-43.1# | Skermanella aerolata (DQ672568) | 90.1 | |
| R120 | 2 | 23.9*-47.1# | Devosia insulae (EF012357) | 97.8 | |
| R90 | 2 | 0.5*-1.7# | Sphingopyxis macrogoltabida (AB372254) | 99.8 | |
| R83-1 | 1 | 2.3# | Altererythrobacter epoxidivorans (DQ304436) | 96.3 | |
| R178 | 1 | 14.9# | Mesorhizobium opportunistum (AY601515) | 97.5 | |
| R191 | 1 | 25.8* | Agrobacterium tumefaciens (EU445236) | 100.0 | |
| β-变形菌纲Betaproteobacteria (8.8%) | R94 | 2 | 0.7#-5.3# | Variovorax paradoxus (AJ420329) | 99.0 |
| R199 | 1 | 1.9# | V. soli (DQ432053) | 98.4 | |
| R163 | 1 | 18.9# | Burkholderia caribensis (Y17009) | 99.1 | |
| R235-1 | 1 | 13.1* | Herbaspirillum chlorophenolicum (NR_024804) | 99.4 | |
| γ-变形菌纲 Gammaproteobacteria (14.0%) | R215-2 | 7 | 10.1*-14.6# | Dyella yeojuensis (DQ181549) | 100.0 |
| R192 | 1 | 3.3* | Pseudoxanthomonas japonensis (AB008507) | 99.7 | |
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes (33.33%) | R138 | 11 | 1.1*-114.8# | Paenibacillus agaridevorans (NR_025490) | 98.0 |
| R172 | 4 | 37.6#-44.0# | P. contaminans (EF626690) | 94.6 | |
| R12-2 | 2 | 26.3#-26.4# | P. alkaliterrae (AY960748) | 96.3 | |
| R59 | 1 | 7.7# | Bacillus aerophilus (AJ831844) | 100.0 | |
| R95 | 1 | 11.6# | B. niabensis (DQ176422) | 99.8 | |
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria (7.0%) | R73-1 | 1 | 1.7# | Nocardioides aquiterrae (AF529063) | 98.3 |
| R100 | 1 | 15.3# | Brachybacterium paraconglomeratum (AJ415377) | 100.0 | |
| R152 | 1 | 9.6# | Arthrobacter niigatensis (AB248526) | 100.0 | |
| R205 | 1 | 1.6# | Streptomyces albaduncus (AY999757) | 98.7 | |
| 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes (1.8%) | R156-1 | 1 | 2.1* | Chitinophaga terrae (AB267724) | 97.4 |
Table 1 Identity analysis of the 16S rDNA partial sequences of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria fromCymbidium goeringii roots
| 类群 Group | 分型测序菌株Isolate | 菌株数 No.of strains | IAA分泌量 IAA production (mg·L-1· (OD600)-1) | 最相近菌种(登录号) Nearest strain (accession no.) | 序列相似性Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-变形菌纲Alphaproteobacteria (35.1%) | R209 | 7 | 1.0#-26.3# | Rhizobium miluonense (EF061096) | 100.0 |
| R128-2 | 1 | 5.8# | R. huautlense (AF025852) | 97.1 | |
| R141 | 1 | 3.6# | R. giardinii (U86344) | 97.3 | |
| R224-3 | 4 | 10.0#-43.1# | Skermanella aerolata (DQ672568) | 90.1 | |
| R120 | 2 | 23.9*-47.1# | Devosia insulae (EF012357) | 97.8 | |
| R90 | 2 | 0.5*-1.7# | Sphingopyxis macrogoltabida (AB372254) | 99.8 | |
| R83-1 | 1 | 2.3# | Altererythrobacter epoxidivorans (DQ304436) | 96.3 | |
| R178 | 1 | 14.9# | Mesorhizobium opportunistum (AY601515) | 97.5 | |
| R191 | 1 | 25.8* | Agrobacterium tumefaciens (EU445236) | 100.0 | |
| β-变形菌纲Betaproteobacteria (8.8%) | R94 | 2 | 0.7#-5.3# | Variovorax paradoxus (AJ420329) | 99.0 |
| R199 | 1 | 1.9# | V. soli (DQ432053) | 98.4 | |
| R163 | 1 | 18.9# | Burkholderia caribensis (Y17009) | 99.1 | |
| R235-1 | 1 | 13.1* | Herbaspirillum chlorophenolicum (NR_024804) | 99.4 | |
| γ-变形菌纲 Gammaproteobacteria (14.0%) | R215-2 | 7 | 10.1*-14.6# | Dyella yeojuensis (DQ181549) | 100.0 |
| R192 | 1 | 3.3* | Pseudoxanthomonas japonensis (AB008507) | 99.7 | |
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes (33.33%) | R138 | 11 | 1.1*-114.8# | Paenibacillus agaridevorans (NR_025490) | 98.0 |
| R172 | 4 | 37.6#-44.0# | P. contaminans (EF626690) | 94.6 | |
| R12-2 | 2 | 26.3#-26.4# | P. alkaliterrae (AY960748) | 96.3 | |
| R59 | 1 | 7.7# | Bacillus aerophilus (AJ831844) | 100.0 | |
| R95 | 1 | 11.6# | B. niabensis (DQ176422) | 99.8 | |
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria (7.0%) | R73-1 | 1 | 1.7# | Nocardioides aquiterrae (AF529063) | 98.3 |
| R100 | 1 | 15.3# | Brachybacterium paraconglomeratum (AJ415377) | 100.0 | |
| R152 | 1 | 9.6# | Arthrobacter niigatensis (AB248526) | 100.0 | |
| R205 | 1 | 1.6# | Streptomyces albaduncus (AY999757) | 98.7 | |
| 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes (1.8%) | R156-1 | 1 | 2.1* | Chitinophaga terrae (AB267724) | 97.4 |
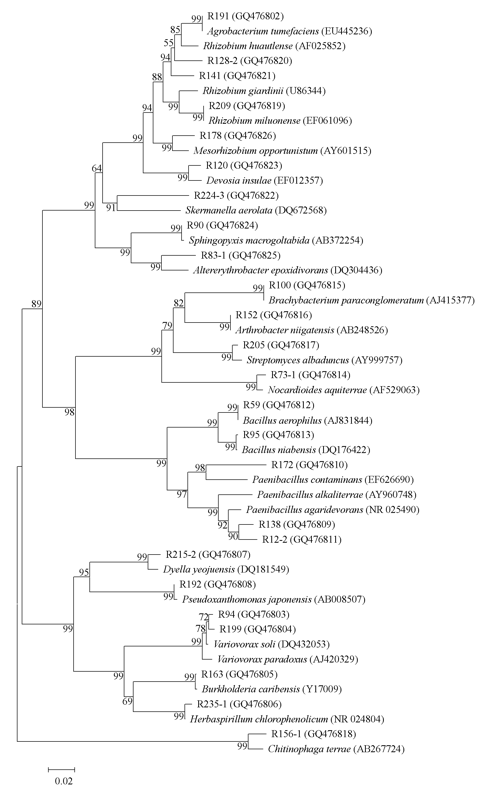
Fig. 1 A dendrogram based on the 16S rDNA partial sequences of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria from the roots of Cymbidium goeringii. Bootstrap values (percent) calculated from 1,000 resamplings are shown at branch nodes. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses.
| [1] |
Aagot N, Nybroe O, Nielsen P, Johnsen K (2001) An altered Pseudomonas diversity is recovered from soil by using nutrient-poor Pseudomonas-selective soil extract media . Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67,5233-5239.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Arshad M, Frankenberger WT (1991) Microbial production of plant hormones. Plant and Soil, 133,1-8. |
| [3] |
Berge O, Guinebretière MH, Achouak W, Normand P, Heulin T (2002) Paenibacillus graminis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus odorifer sp. nov., isolated from plant roots, soil and food . International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 52,607-616.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | Currah RS, Zelmer CD, Hambleton S, Richardson KA (1997) Fungi from orchid mycorrhizas. In: Orchid Biology: Reviews and Perspectives. VII (eds Arditti J, Pridgeon AM),pp.117-170. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. |
| [5] | Da Mota FF, Gomes EA, Seldin L (2008) Auxin production and detection of the gene coding for the Auxin Efflux Carrier (AEC) protein in Paenibacillus polymyxa. Journal of Microbiology, 46,257-264. |
| [6] | Dias ACF, Costa FEC, Andreote FD, Lacava PT, Teixeira MA, Assumpção LC, Araújo WL, João L, Azevedo JL, Melo IS (2008) Isolation of micropropagated strawberry endophytic bacteria and assessment of their potential for plant growth promotion. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 25,189-195. |
| [7] | Du RQ (杜荣骞) (1999) Biostatistics (生物统计学). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [8] |
Edwards U, Rogall T, Blöker H, Emde M, Böttger EC (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes: characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 17,7843-7853.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2,793-796. |
| [10] | Kado CI (1991) Plant pathogenic bacteria. In: The Prokaryotes (eds Balows A, Truper HG, Dworkin M, Schleifer KH)pp.659-674. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [11] | Kamneva SV, Muronets EM (1999) Genetic control of the processes of interaction of bacteria with plants in associations. Genetika, 35,1480-1494. |
| [12] |
Kawai M, Matsutera E, Kanda H, Yamaguchi N, Tani K, Nasu M (2002) 16S ribosomal DNA-based analysis of bacterial diversity in purified water used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes by PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68,699-704.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araujo WL, Mendes R, Geraldi IO, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Azevedo JL (2004) Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environmental Microbiology, 6,1244-1251.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] | Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics (eds Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M),pp.115-175. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, United Kingdom. |
| [15] | Li JH, Wang ET, Chen WF, Chen WX (2008) Genetic diversity and potential for promotion of plant growth detected in nodule endophytic bacteria of soybean grown in Heilongjiang Province of China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40,238-246. |
| [16] | Libbert E, Risch H (1969) Interactions between plants and epiphytic bacteria regarding their auxin metabolism.V. Isolation and identification of the IAA-producing and destroying bacteria from pea plants. Physiologia Plantarum, 22,51-58. |
| [17] | Lodewyckx C, Vangronsveld J, Porteous F, Moore ERB, Taghavi S, Mezgeay M, van der Lelie D (2002) Endophytic bacteria and their potential application. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 86,583-606. |
| [18] |
Long HH, Schmidt DD, Baldwin IT (2008) Native bacterial endophytes promote host growth in a species-specific manner; phytohormone manipulations do not result in common growth responses. PLoS ONE, 3,e2702.
URL PMID |
| [19] |
Mendes R, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Araujo WL, Raaijmakers JM (2007) Diversity of cultivated endophytic bacteria from sugarcane: genetic and biochemical characterization of Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates . Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73,7259-7267.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Rasmussen HN (2002) Recent developments in the study of orchid mycorrhiza. Plant and Soil, 244,149-163. |
| [21] | Sarwar M, Frankenberger WT (1994) Tryptophan dependent biosynthesis of auxins in soil. Plant and Soil, 160,97-104. |
| [22] | Selim S, Negrel J, Govaerts C, Gianinazzi S, Tuinen DV (2005) Isolation and partial characterization of antagonistic peptides produced by Paenibacillus sp. strain B2 isolated from the sorghum mycorrhizosphere . Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,6501-6507. |
| [23] | Sun L (孙磊), Bi XB (毕晓宝), Li LB (李潞滨), Liu L (刘琳), Han JG (韩继刚), Yang K (杨凯) (2009) Primary research on the isolation method of root endophytic bacteria of Cymbidium goeringii. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei (河北农业大学学报), 32,42-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] |
Taghavi B, Garafola C, Monchy S, Newman L, Hoffman A, Weyens N, Barac T, Vangronsveld J,van der Lelie D (2009) Genome survey and characterization of endophytic bacteria exhibiting a beneficial effect on growth and development of poplar trees. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75,748-757.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24,1596-1599.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Tsavkelova EA, Cherdyntseva TA, Netrusov AI (2005) Auxin production by bacteria associated with orchid roots. Microbiology, 74,46-53. |
| [27] |
Tsavkelova EA, Cherdyntseva TA, Botina SG, Netrusov AI (2007) Bacteria associated with orchid roots and microbial production of auxin. Microbiological Research, 162,69-76.
URL PMID |
| [1] | Jianyu He,Xuezhu Liu,Rongtao Zhao,Fangwei Wu,Jianxin Wang. Diversity of cultured and uncultured bacteria in surface layer sediment from the East China Sea [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(1): 28-37. |
| [2] | Derui Zhu, Jian Liu, Rui Han, Guoping Shen, Fang Yang, Qifu Long, Deli Liu. Population diversity and phylogeny of halophiles in the Qinghai Lake [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(4): 495-504. |
| [3] | Ming Luo, Jian Han, Pingan Jiang, Hongqi Wu. Diversity of culturable halophilic bacteria isolated from Lop Nur region in Xinjiang [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 288-295. |
| [4] | Lin Xu, Jiajie Xu, Qiaoli Liu, Ruimei Xie, Gehong Wei. Genetic diversity in rhizobia isolated from Sphaerophysa salsula in several regions of northwestern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(1): 69-75. |
| [5] | Jianping Zhang, Naiyuan Dong, Haobin Yu, Yongjun Zhou, Yongliang Lu, Ruimei Geng, Liuqing Yu. Bacteria diversity in paddy field soil by 16S rDNA-RFLP analysis in Ningxia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(6): 586-592. |
| [6] | Qihui Teng, Hui Cao, Zhongli Cui, Ying Wang, Bo Sun, Hongtao Hao, Shunpeng Li. PCR-RFLP analysis of bacterial 16S rDNA from a typical garden soil in Taihu region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(4): 345-351. |
| [7] | Haoxin Fan, Derek J. Fairley, Christopher Rensing, Ian L. Pepper, Gejiao Wang. Identification of similar non-thermophilic Crenarchaeota in four Chinese and American pristine soils [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(3): 181-187. |
| [8] | HAN Ru-Yang, MIN Hang, CHENG Zhi-Qiang, LIU Liang-Hao. Phenotypic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of crude oil degrading bacteria [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2002, 10(2): 202-207. |
| [9] | DONG Xiu-Zhu, SHEN De-Long, XIN Yu-Hua. Phylogenetic relationship between the genus Bifidobacterium and related bacteria based on 16S rDNA homology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2000, 08(2): 146-152. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()