



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (1): 40-50. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13144 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13144
Special Issue: 基因组和生物多样性
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2013-06-24
Accepted:2013-12-25
Online:2014-01-20
Published:2014-02-10
Contact:
Luo Shu-Jin
Lin Miao,Shu-Jin Luo. Diversification of Southeast Asian mammals during the Quaternary glaciation: insights from the genomic era[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(1): 40-50.
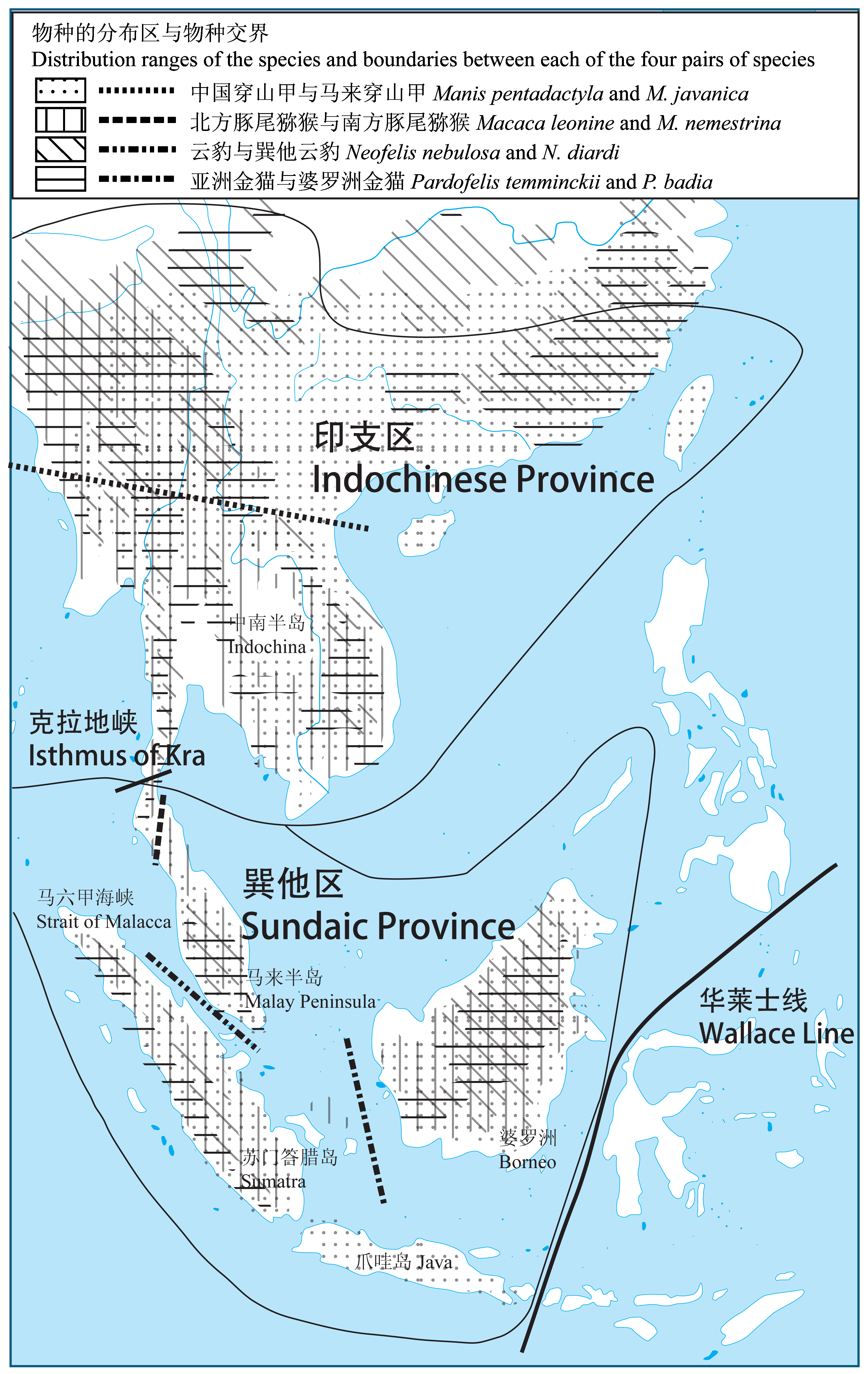
Fig. 1 Major biogeographic divisions and speciation events in Southeast (SE) Asia. The Wallace Line and Isthmus of Kra divide SE Asia into Indochinese and Sundaic provinces (Tougard, 2001). Distribution ranges of the species and boundaries between the congeneric species are shown (data from IUCN, 2013): Manis pentadactyla and M. javanica, Macaca leonine and M. nemestrina, Neofelis nebulosa and N. diardi, and Pardofelis temminckii and P. badia. Ancestral populations of each of these pairs of species retracted into remanent refugia during dramatic geological or geographic events (e.g., glacial periods), leading to subsequent allopatric speciation. When suitable climate and habitats returned (e.g., interglacial periods), such populations (species) expanded out of fragmented refugia in the south and north and converged on current range boundaries, although the exact location of such boundaries varied by species.
| 中文名 | 拉丁名 | 分布区域 | 研究概况 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马来貘 | Tapirus indicus | 缅甸、泰国、马来半岛、苏门答腊岛 | 目前无亚种划分。另外3种貘均分布于美洲, 与马来貘分化时间超过20 Ma。 | Lynam et al., 2008; Steiner & Ryder, 2011 |
| 苏门答腊犀牛 | Dicerorhinus sumatrensis | 历史上曾经分布于印度半岛、中南半岛和巽他群岛, 目前仅分布于婆罗洲、苏门答腊岛和马来半岛南部 | 共3个亚种, D. s. lasiotis分布于印度半岛和缅甸, D. s. sumatrensis分布于泰国、马来半岛和苏门答腊岛, D. s. harrissoni分布于婆罗洲。 | van Strien et al., 2008b |
| 爪哇犀牛 | Rhinoceros sondaicus | 历史上曾经分布于印度半岛、中南半岛和巽他群岛, 目前仅分布于越南和爪哇岛 | 共3个亚种, R. s. inermis分布于印度半岛和缅甸, R. s. annamiticus分布于越南、老挝、柬埔寨和泰国东部, R. s. sondaicus分布于泰国、马来半岛、苏门答腊岛和爪哇岛。 | van Strien et al., 2008a |
| Capricornis milneedwardsii Capricornis sumatraensis | C. milneedwardsii分布于中国南部及克拉地峡以北的中南半岛; C. sumatraensis分布于克拉地峡以南的马来半岛及苏门答腊岛 | Capricornis的分类尚不是很清楚, 目前分为6个种, 此处列出的2个种分布于印支区和巽他区, 并且其物种的分布以克拉地峡为分界线。 | Duckworth et al., 2008a, b | |
| Rusa unicolor | 印度半岛、斯里兰卡、中国南部、中南半岛、巽他群岛 | Rusa unicolor分为7个亚种, 其中R. u. unicolor分布于印度半岛与斯里兰卡, R. u. cambojensis分布于中南半岛, R. u. equina分布于苏门答腊岛, R. u. brookei分布于婆罗洲。 | Timmins et al., 2008b; Leslie, 2011 | |
| 印度野牛 | Bos gaurus | 印度半岛、中南半岛 | 传统上分为3个亚种, B. g. gaurus分布于印度半岛, B. g. readei分布于克拉地峡以北的中南半岛, B. g. hubbacki分布于克拉地峡以南的马来半岛。基于形态学的最新研究认为B. g. readei与B. g. hubbacki应合并为1个亚种B. g. laosiensis, 基于核基因估算亚种间分化时间约为1.85 Ma。 | Duckworth et al., 2008d; Hassanin et al., 2012 |
| 爪哇野牛 | Bos javanicus | 中南半岛、巽他群岛 | 传统上分为3个亚种, B. j. javanicus分布于爪哇岛和巴厘岛, B. j. lowi分布于婆罗洲, B. j. birmanicus分布于中南半岛, 但B. j. lowi亚种的存在受到质疑。染色体研究发现B. j. birmanicus 2n=56, B. j. birmanicus 2n=60, 基于核基因估算亚种间分化时间约为0.75 Ma。 | Ropiquet et al., 2008; Timmins et al., 2008a; Hassanin et al., 2012 |
| Maxomys surifer | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 通过线粒体控制区与细胞色素B基因建树, 印支区种群为一支、克拉地峡以南的马来半岛与苏门答腊岛种群为一支、婆罗洲种群为一支, 估算其分化时间为数百万年(使用不同的突变速率结果差异较大)。 | Gorog et al., 2004 | |
| Maxomys whiteheadi | 巽他群岛和克拉地峡以南的马来半岛 | 通过线粒体控制区与细胞色素B基因建树, 克拉地峡以南的马来半岛与苏门答腊岛种群为一支、婆罗洲种群为一支, 估算其分化时间为数十万年到数百万年(使用不同的突变速率结果差异较大)。 | Gorog et al., 2004 | |
| Leopoldamys sabanus | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 通过线粒体控制区与细胞色素B基因建树, 印支区种群为一支、克拉地峡以南的马来半岛与苏门答腊岛种群为一支、婆罗洲种群为一支, 估算其分化时间为数百万年(使用不同的突变速率结果差异较大)。 | Gorog et al., 2004 | |
| 亚洲象 | Elephas maximus | 印度半岛、斯里兰卡、中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 存在两组线粒体单倍型, 巽他区仅分布β单倍型组, 其他地区α和β两组单倍型均有分布, α组和β组分化时间约1.88 Ma。 | Fernando et al., 2000; Fleischer et al., 2001; Vidya et al., 2009 |
| 巽他鼯猴 | Galeopterus variegatus | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 线粒体与核基因分析显示马来半岛和爪哇岛的鼯猴分化时间分别为约5.4 Ma和约3.9 Ma。 | Janecka et al., 2008 |
| 小毛猬 | Hylomys suillus | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 使用细胞色素B基因建树, 印支区和巽他区的单倍型分为两组, 巽他区的苏门答腊岛和马来半岛分在一起, 爪哇岛和婆罗洲分在一起。印支区和巽他区单倍型分化时间为数百万年(不同校准点结果不同, 分别为3.9 Ma、5.0 Ma、18.1 Ma)。 | Ruedi & Fumagalli, 1996 |
| 中国穿山甲 马来穿山甲 | Manis pentadactyla Manis javanica | 中国穿山甲分布于中国南部地区, 马来穿山甲分布于中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 已知不同物种。 | IUCN, 2013 |
| 北方豚尾猕猴 南方豚尾猕猴 | Macaca leonine Macaca nemestrina | 北方豚尾猕猴分布于印支区, 南方豚尾猕猴分布于巽他区 | 两种豚尾猕猴原先为M. nemestrina的2个亚种, 后分为2个独立的种, 两种豚尾猕猴在素叻他尼–甲米(Surat Thani-Krabi)区带内同域分布并且有杂交, 两种豚尾猕猴具有明显的形态学差异, 使用线粒体与核基因多位点序列估算分化时间大于1 Ma。 | Fabre et al., 2009; Malaivijitnond et al., 2012 |
| 食蟹猴 普通猕猴 | Macaca fascicularis Macaca mulatta | 普通猕猴分布于中国南部、中南半岛北部、印度半岛北部, 食蟹猴分布于中南半岛、巽他群岛和菲律宾群岛 | 两种猕猴在中南半岛北部同域分布, Y染色体和线粒体遗传标记显示两种猕猴存在基因交流, 尽管使用线粒体与核基因多位点序列估算分化时间约2 Ma, 但结果很可能受到个体来源的影响。食蟹猴本身至少存在10个亚种, 使用线粒体D-loop区建树, 食蟹猴按样品来源分为中南半岛、巽他群岛和菲律宾群岛三组。 | Tosi et al., 2002; Smith et al., 2007; Street et al., 2007; Shiina et al., 2010 |
| 戴帽长臂猿 白掌长臂猿 | Hylobates pileatus Hylobates lar | 戴帽长臂猿主要分布于泰国东南及柬埔寨西部, 白掌长臂猿主要分布于泰国中西部、缅甸东部和整个马来半岛及苏门答腊岛北部 | 在泰国中部两物种同域分布并存在杂交, 线粒体基因组估算两物种分化时间约2.9 Ma。白掌长臂猿根据形态差异划分为5个亚种, 但需要进一步的研究。 | Brockelman & Geissmann, 2008; Brockelman et al., 2008; Chan et al., 2010 |
| 苏门答腊红毛猩猩 婆罗洲红毛猩猩 | Pongo abelii Pongo pygmaeus | 苏门答腊猩猩分布于苏门答腊岛, 婆罗洲猩猩分布于婆罗洲 | 两种猩猩原先为P. pygmaeus的2个亚种, 后分为2个独立的种, 全基因组DNA序列估算两种猩猩分化时间约为40 Ma。 | Zhi et al., 1996; Locke et al., 2011; Mailund et al., 2011 |
| 云豹 巽他云豹 | Neofelis nebulosa Neofelis diardi | 云豹分布于喜马拉雅山南麓、中国南部、中南半岛; 巽他云豹分布于苏门答腊岛和婆罗洲 | 两种云豹原先为N. nebulosa的2个亚种, 后分为2个独立的种, 基于线粒体、核基因和微卫星遗传学标记的研究显示两种云豹存在较大遗传差异, 估算分化时间为1.41 Ma。对巽他云豹的进一步研究显示苏门答腊岛和婆罗洲的种群存在明显的形态学和遗传学差异, 并分为2个亚种, 估算分化时间为120-400 ka。 | Buckley-Beason et al., 2006; Kitchener et al., 2006; Wilting et al., 2007, 2011 |
| 虎 | Panthera tigris | 虎历史上曾经广泛分布于亚洲, 现分布于东南亚的有3个亚种: 印支虎(P. t. corbetti, 分布于印支区)、马来虎(P. t. jacksoni, 分布于克拉地峡以南的马来半岛)和苏门答腊虎(P. t. sumatrae, 分布于苏门答腊岛) | 线粒体基因估算所有现存亚种最近共同祖先的时间为72-108 ka, 东南亚分布的不同亚种间体现出明显的遗传学差异。 | Luo et al., 2004 |
| 豹 | Panthera pardus | 广泛分布于旧大陆 | 豹没有体现出从印支区到巽他区明显的遗传差异。 | Uphyrkina et al., 2001 |
| 渔猫 | Prionailurus viverrinus | 印度半岛、斯里兰卡、中南半岛、巽他群岛 | 地理分布呈不连续性, 马来半岛上无分布, 可能体现了南北种群的历史隔离。 | |
| 亚洲金猫 婆罗洲金猫 | Pardofelis temminckii Pardofelis badia | 亚洲金猫分布于中国南部、中南半岛、苏门答腊岛; 婆罗洲金猫分布于婆罗洲 | 婆罗洲金猫被认为是金猫在婆罗洲的特化种, 二者分化时间大约4.3 Ma。 | Johnson et al., 2006 |
| 豺 | Cuon alpinus | 印度半岛、中南半岛、巽他群岛 | 基于线粒体序列的系统发生分析显示, 印度恒河以南的单倍型聚为一支, 印度恒河以北以及缅甸、泰国、马来西亚的单倍型聚为一支, 苏门答腊岛和爪哇岛的单倍型聚为一支。 | Iyengar et al., 2005; Durbin et al., 2008 |
| 马来熊 | Helarctos malayanus | 印度半岛北部、中南半岛及巽他群岛 | 基于形态学的研究发现婆罗洲的个体与其他分布区的差异较大, 故分为2个亚种, H. m. euryspilus(婆罗洲)与H. m. malayanus(其他地区)。 | Meijaard, 2004; Fredriksson et al., 2008 |
| 果子狸 | Paguma larvata | 喜马拉雅山脉南麓、中国南部、中南半岛、巽他群岛、日本 | 基于线粒体控制区和细胞色素B的序列分析表明果子狸遗传多样性较低, 但可以大致分为3个单倍型组: 中国组、印支组和巽他组。 | Duckworth et al., 2008c; Patou et al., 2009 |
Appendix I Case studies of population genetics and biogeography research of Southeast Asian mammals
| 中文名 | 拉丁名 | 分布区域 | 研究概况 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马来貘 | Tapirus indicus | 缅甸、泰国、马来半岛、苏门答腊岛 | 目前无亚种划分。另外3种貘均分布于美洲, 与马来貘分化时间超过20 Ma。 | Lynam et al., 2008; Steiner & Ryder, 2011 |
| 苏门答腊犀牛 | Dicerorhinus sumatrensis | 历史上曾经分布于印度半岛、中南半岛和巽他群岛, 目前仅分布于婆罗洲、苏门答腊岛和马来半岛南部 | 共3个亚种, D. s. lasiotis分布于印度半岛和缅甸, D. s. sumatrensis分布于泰国、马来半岛和苏门答腊岛, D. s. harrissoni分布于婆罗洲。 | van Strien et al., 2008b |
| 爪哇犀牛 | Rhinoceros sondaicus | 历史上曾经分布于印度半岛、中南半岛和巽他群岛, 目前仅分布于越南和爪哇岛 | 共3个亚种, R. s. inermis分布于印度半岛和缅甸, R. s. annamiticus分布于越南、老挝、柬埔寨和泰国东部, R. s. sondaicus分布于泰国、马来半岛、苏门答腊岛和爪哇岛。 | van Strien et al., 2008a |
| Capricornis milneedwardsii Capricornis sumatraensis | C. milneedwardsii分布于中国南部及克拉地峡以北的中南半岛; C. sumatraensis分布于克拉地峡以南的马来半岛及苏门答腊岛 | Capricornis的分类尚不是很清楚, 目前分为6个种, 此处列出的2个种分布于印支区和巽他区, 并且其物种的分布以克拉地峡为分界线。 | Duckworth et al., 2008a, b | |
| Rusa unicolor | 印度半岛、斯里兰卡、中国南部、中南半岛、巽他群岛 | Rusa unicolor分为7个亚种, 其中R. u. unicolor分布于印度半岛与斯里兰卡, R. u. cambojensis分布于中南半岛, R. u. equina分布于苏门答腊岛, R. u. brookei分布于婆罗洲。 | Timmins et al., 2008b; Leslie, 2011 | |
| 印度野牛 | Bos gaurus | 印度半岛、中南半岛 | 传统上分为3个亚种, B. g. gaurus分布于印度半岛, B. g. readei分布于克拉地峡以北的中南半岛, B. g. hubbacki分布于克拉地峡以南的马来半岛。基于形态学的最新研究认为B. g. readei与B. g. hubbacki应合并为1个亚种B. g. laosiensis, 基于核基因估算亚种间分化时间约为1.85 Ma。 | Duckworth et al., 2008d; Hassanin et al., 2012 |
| 爪哇野牛 | Bos javanicus | 中南半岛、巽他群岛 | 传统上分为3个亚种, B. j. javanicus分布于爪哇岛和巴厘岛, B. j. lowi分布于婆罗洲, B. j. birmanicus分布于中南半岛, 但B. j. lowi亚种的存在受到质疑。染色体研究发现B. j. birmanicus 2n=56, B. j. birmanicus 2n=60, 基于核基因估算亚种间分化时间约为0.75 Ma。 | Ropiquet et al., 2008; Timmins et al., 2008a; Hassanin et al., 2012 |
| Maxomys surifer | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 通过线粒体控制区与细胞色素B基因建树, 印支区种群为一支、克拉地峡以南的马来半岛与苏门答腊岛种群为一支、婆罗洲种群为一支, 估算其分化时间为数百万年(使用不同的突变速率结果差异较大)。 | Gorog et al., 2004 | |
| Maxomys whiteheadi | 巽他群岛和克拉地峡以南的马来半岛 | 通过线粒体控制区与细胞色素B基因建树, 克拉地峡以南的马来半岛与苏门答腊岛种群为一支、婆罗洲种群为一支, 估算其分化时间为数十万年到数百万年(使用不同的突变速率结果差异较大)。 | Gorog et al., 2004 | |
| Leopoldamys sabanus | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 通过线粒体控制区与细胞色素B基因建树, 印支区种群为一支、克拉地峡以南的马来半岛与苏门答腊岛种群为一支、婆罗洲种群为一支, 估算其分化时间为数百万年(使用不同的突变速率结果差异较大)。 | Gorog et al., 2004 | |
| 亚洲象 | Elephas maximus | 印度半岛、斯里兰卡、中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 存在两组线粒体单倍型, 巽他区仅分布β单倍型组, 其他地区α和β两组单倍型均有分布, α组和β组分化时间约1.88 Ma。 | Fernando et al., 2000; Fleischer et al., 2001; Vidya et al., 2009 |
| 巽他鼯猴 | Galeopterus variegatus | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 线粒体与核基因分析显示马来半岛和爪哇岛的鼯猴分化时间分别为约5.4 Ma和约3.9 Ma。 | Janecka et al., 2008 |
| 小毛猬 | Hylomys suillus | 中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 使用细胞色素B基因建树, 印支区和巽他区的单倍型分为两组, 巽他区的苏门答腊岛和马来半岛分在一起, 爪哇岛和婆罗洲分在一起。印支区和巽他区单倍型分化时间为数百万年(不同校准点结果不同, 分别为3.9 Ma、5.0 Ma、18.1 Ma)。 | Ruedi & Fumagalli, 1996 |
| 中国穿山甲 马来穿山甲 | Manis pentadactyla Manis javanica | 中国穿山甲分布于中国南部地区, 马来穿山甲分布于中南半岛和巽他群岛 | 已知不同物种。 | IUCN, 2013 |
| 北方豚尾猕猴 南方豚尾猕猴 | Macaca leonine Macaca nemestrina | 北方豚尾猕猴分布于印支区, 南方豚尾猕猴分布于巽他区 | 两种豚尾猕猴原先为M. nemestrina的2个亚种, 后分为2个独立的种, 两种豚尾猕猴在素叻他尼–甲米(Surat Thani-Krabi)区带内同域分布并且有杂交, 两种豚尾猕猴具有明显的形态学差异, 使用线粒体与核基因多位点序列估算分化时间大于1 Ma。 | Fabre et al., 2009; Malaivijitnond et al., 2012 |
| 食蟹猴 普通猕猴 | Macaca fascicularis Macaca mulatta | 普通猕猴分布于中国南部、中南半岛北部、印度半岛北部, 食蟹猴分布于中南半岛、巽他群岛和菲律宾群岛 | 两种猕猴在中南半岛北部同域分布, Y染色体和线粒体遗传标记显示两种猕猴存在基因交流, 尽管使用线粒体与核基因多位点序列估算分化时间约2 Ma, 但结果很可能受到个体来源的影响。食蟹猴本身至少存在10个亚种, 使用线粒体D-loop区建树, 食蟹猴按样品来源分为中南半岛、巽他群岛和菲律宾群岛三组。 | Tosi et al., 2002; Smith et al., 2007; Street et al., 2007; Shiina et al., 2010 |
| 戴帽长臂猿 白掌长臂猿 | Hylobates pileatus Hylobates lar | 戴帽长臂猿主要分布于泰国东南及柬埔寨西部, 白掌长臂猿主要分布于泰国中西部、缅甸东部和整个马来半岛及苏门答腊岛北部 | 在泰国中部两物种同域分布并存在杂交, 线粒体基因组估算两物种分化时间约2.9 Ma。白掌长臂猿根据形态差异划分为5个亚种, 但需要进一步的研究。 | Brockelman & Geissmann, 2008; Brockelman et al., 2008; Chan et al., 2010 |
| 苏门答腊红毛猩猩 婆罗洲红毛猩猩 | Pongo abelii Pongo pygmaeus | 苏门答腊猩猩分布于苏门答腊岛, 婆罗洲猩猩分布于婆罗洲 | 两种猩猩原先为P. pygmaeus的2个亚种, 后分为2个独立的种, 全基因组DNA序列估算两种猩猩分化时间约为40 Ma。 | Zhi et al., 1996; Locke et al., 2011; Mailund et al., 2011 |
| 云豹 巽他云豹 | Neofelis nebulosa Neofelis diardi | 云豹分布于喜马拉雅山南麓、中国南部、中南半岛; 巽他云豹分布于苏门答腊岛和婆罗洲 | 两种云豹原先为N. nebulosa的2个亚种, 后分为2个独立的种, 基于线粒体、核基因和微卫星遗传学标记的研究显示两种云豹存在较大遗传差异, 估算分化时间为1.41 Ma。对巽他云豹的进一步研究显示苏门答腊岛和婆罗洲的种群存在明显的形态学和遗传学差异, 并分为2个亚种, 估算分化时间为120-400 ka。 | Buckley-Beason et al., 2006; Kitchener et al., 2006; Wilting et al., 2007, 2011 |
| 虎 | Panthera tigris | 虎历史上曾经广泛分布于亚洲, 现分布于东南亚的有3个亚种: 印支虎(P. t. corbetti, 分布于印支区)、马来虎(P. t. jacksoni, 分布于克拉地峡以南的马来半岛)和苏门答腊虎(P. t. sumatrae, 分布于苏门答腊岛) | 线粒体基因估算所有现存亚种最近共同祖先的时间为72-108 ka, 东南亚分布的不同亚种间体现出明显的遗传学差异。 | Luo et al., 2004 |
| 豹 | Panthera pardus | 广泛分布于旧大陆 | 豹没有体现出从印支区到巽他区明显的遗传差异。 | Uphyrkina et al., 2001 |
| 渔猫 | Prionailurus viverrinus | 印度半岛、斯里兰卡、中南半岛、巽他群岛 | 地理分布呈不连续性, 马来半岛上无分布, 可能体现了南北种群的历史隔离。 | |
| 亚洲金猫 婆罗洲金猫 | Pardofelis temminckii Pardofelis badia | 亚洲金猫分布于中国南部、中南半岛、苏门答腊岛; 婆罗洲金猫分布于婆罗洲 | 婆罗洲金猫被认为是金猫在婆罗洲的特化种, 二者分化时间大约4.3 Ma。 | Johnson et al., 2006 |
| 豺 | Cuon alpinus | 印度半岛、中南半岛、巽他群岛 | 基于线粒体序列的系统发生分析显示, 印度恒河以南的单倍型聚为一支, 印度恒河以北以及缅甸、泰国、马来西亚的单倍型聚为一支, 苏门答腊岛和爪哇岛的单倍型聚为一支。 | Iyengar et al., 2005; Durbin et al., 2008 |
| 马来熊 | Helarctos malayanus | 印度半岛北部、中南半岛及巽他群岛 | 基于形态学的研究发现婆罗洲的个体与其他分布区的差异较大, 故分为2个亚种, H. m. euryspilus(婆罗洲)与H. m. malayanus(其他地区)。 | Meijaard, 2004; Fredriksson et al., 2008 |
| 果子狸 | Paguma larvata | 喜马拉雅山脉南麓、中国南部、中南半岛、巽他群岛、日本 | 基于线粒体控制区和细胞色素B的序列分析表明果子狸遗传多样性较低, 但可以大致分为3个单倍型组: 中国组、印支组和巽他组。 | Duckworth et al., 2008c; Patou et al., 2009 |
| [1] | Ambrose SH (1998) Late Pleistocene human population bottlenecks, volcanic winter, and differentiation of modern humans.Journal of Human Evolution, 34, 623-651. |
| [2] | Avise JC (2000) Phylogeography: the History and Formation of Species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. |
| [3] | Banks E (1949)Bornean Mammals. Kuching Press, Kuching. |
| [4] | Bird MI, Taylor D, Hunt C (2005) Environments of insular Southeast Asia during the last glacial period: a savanna corridor in Sundaland?Quaternary Science Reviews, 24, 2228-2242. |
| [5] | Brandon-Jones D, Eudey A, Geissmann T, Groves CP, Melnick DJ, Morales JC, Shekelle M, Stewart C-B (2004) Asian primate classification.International Journal of Primatology, 25, 97-164. |
| [6] | Buckley-Beason VA, Johnson WE, Nash WG, Stanyon R, Menninger JC, Driscoll CA, Howard J, Bush M, Page JE, Roelke ME, Stone G, Martelli PP, Wen C, Ling L, Duraisingam RK, Lam PV, O’Brien SJ (2006) Molecular evidence for species-level distinctions in clouded leopards.Current Biology, 16, 2371-2376. |
| [7] | Cannon CH, Morley RJ, Bush AB (2009) The current refugial rainforests of Sundaland are unrepresentative of their biogeographic past and highly vulnerable to disturbance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,USA, 106, 11188-11193. |
| [8] | de Bruyn M, Nugroho E, Hossain MM, Wilson JC, Mather PB (2005) Phylogeographic evidence for the existence of an ancient biogeographic barrier: the Isthmus of Kra Seaway.Heredity, 94, 370-378. |
| [9] | Duckworth JW, Steinmetz R, Pattanavibool A (2008a) Capricornis milneedwardsii. In: IUCN Red List of Thre-atened Species. Version 2012.2. http://www. iucnredlist.org. (2013.04.05) |
| [10] | Duckworth JW, Steinmetz R, MacKinnon J (2008b) Capricornis sumatraensis. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. (2013). 04.05) |
| [11] | Duckworth JW, Steinmetz R, Timmins RJ, Pattanavibool A, Than Zaw DT, Hedges S (2008c) Bos gaurus. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . (2013.04.05) |
| [12] | Durand EY, Patterson N, Reich D, Slatkin M (2011) Testing for ancient admixture between closely related populations.Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2239-2252. |
| [13] | Dwyer GS, Chandler MA (2009) Mid-Pliocene sea level and continental ice volume based on coupled benthic Mg/Ca palaeotemperatures and oxygen isotopes.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 367, 157-168. |
| [14] | Fabre PH, Rodrigues A, Douzery EJ (2009) Patterns of macroevolution among primates inferred from a supermatrix of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA.Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 53, 808-825. |
| [15] | Feder JL, Flaxman SM, Egan SP, Comeault AA, Nosil P (2013) Geographic mode of speciation and genomic divergence.Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 44, 73-97. |
| [16] | Fernando P, Pfrender ME, Encalada SE, Lande R (2000) Mitochondrial DNA variation, phylogeography and population structure of the Asian elephant.Heredity, 84, 362-372. |
| [17] | Fleischer RC, Perry EA, Muralidharan K, Stevens EE, Wemmer CM (2001) Phylogeography of the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) based on mitochondrial DNA.Evolution, 55, 1882-1892. |
| [18] | Fredriksson G, Steinmetz R, Wong S, Garshelis DL (2008) Helarctos malayanus. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . (2013. 04.05) |
| [19] | Gagnaire P-A, Pavey SA, Normandeau E, Bernatchez L (2013) The genetic architecture of reproductive isolation during speciation-with-gene-flow in lake whitefish species pairs assessed by rad sequencing.Evolution, 67, 2483-2497. |
| [20] | Gathorne-Hardy FJ, Syaukani, Davies RG, Eggleton P, Jones DT (2002) Quaternary rainforest refugia in south-east Asia: using termites (Isoptera) as indicators.Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 75, 453-466. |
| [21] | Gautier M, Vitalis R (2013) Inferring population histories using genome-wide allele frequency data.Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 654-668. |
| [22] | Gorog AJ, Sinaga MH, Engstrom MD (2004) Vicariance or dispersal? Historical biogeography of three Sunda shelf murine rodents (Maxomys surifer, Leopoldamys sabanus and Maxomys whiteheadi).Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 81, 91-109. |
| [23] | Groenen MA, Archibald AL, Uenishi H, Tuggle CK, Takeuchi Y, Rothschild MF, Rogel-Gaillard C, Park C, Milan D, Megens HJ, Li S, Larkin DM, Kim H, Frantz LA, Caccamo M, Ahn H, Aken BL, Anselmo A, Anthon C, Auvil L, Badaoui B, Beattie CW, Bendixen C, Berman D, Blecha F, Blomberg J, Bolund L, Bosse M, Botti S, Bujie Z, Bystrom M, Capitanu B, Carvalho-Silva D, Chardon P, Chen C, Cheng R, Choi SH, Chow W, Clark RC, Clee C, Crooijmans RP, Dawson HD, Dehais P, De Sapio F, Dibbits B, Drou N, Du ZQ, Eversole K, Fadista J, Fairley S, Faraut T, Faulkner GJ, Fowler KE, Fredholm M, Fritz E, Gilbert JG, Giuffra E, Gorodkin J, Griffin DK, Harrow JL, Hayward A, Howe K, Hu ZL, Humphray SJ, Hunt T, Hornshoj H, Jeon JT, Jern P, Jones M, Jurka J, Kanamori H, Kapetanovic R, Kim J, Kim JH, Kim KW, Kim TH, Larson G, Lee K, Lee KT, Leggett R, Lewin HA, Li Y, Liu W, Loveland JE, Lu Y, Lunney JK, Ma J, Madsen O, Mann K, Matthews L, McLaren S, Morozumi T, Murtaugh MP, Narayan J, Nguyen DT, Ni P, Oh SJ, Onteru S, Panitz F, Park EW, Park HS, Pascal G, Paudel Y, Perez-Enciso M, Ramirez-Gonzalez R, Reecy JM, Rodriguez-Zas S, Rohrer GA, Rund L, Sang Y, Schachtschneider K, Schraiber JG, Schwartz J, Scobie L, Scott C, Searle S, Servin B, Southey BR, Sperber G, Stadler P, Sweedler JV, Tafer H, Thomsen B, Wali R, Wang J, Wang J, White S, Xu X, Yerle M, Zhang G, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhao S, Rogers J, Churcher C, Schook LB (2012) Analyses of pig genomes provide insight into porcine demography and evolution.Nature, 491, 393-398. |
| [24] | Gronau I, Hubisz MJ, Gulko B, Danko CG, Siepel A (2011) Bayesian inference of ancient human demography from individual genome sequences.Nature Genetics, 43, 1031-1034. |
| [25] | Groves C (2001) Primate Taxonomy. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC. |
| [26] | Gutenkunst RN, Hernandez RD, Williamson SH, Bustamante CD (2009) Inferring the joint demographic history of multiple populations from multidimensional SNP frequency data.PLoS Genetics, 5, e1000695. |
| [27] | Hall R (1998) The plate tectonics of Cenozoic SE Asia and the distribution of land and sea. In: Biogeography and Geological Evolution of SE Asia (eds Hall R, Hollway JD), pp. 99-131. Backhuys, Leiden. |
| [28] | Hassanin A, An J, Ropiquet A, Nguyen TT, Couloux A (2012) Combining multiple autosomal introns for studying shallow phylogeny and taxonomy of Laurasiatherian mammals: application to the tribe Bovini (Cetartiodactyla, Bovidae).Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 66, 766-775. |
| [29] | Heaney LR (1986) Biogeography of mammals in Southeast Asia estimates of rates of colonization extinction and speciation.Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 28, 127-166. |
| [30] | Hewitt G (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages.Nature, 405, 907-913. |
| [31] | Hughes JB, Round PD, Woodruff DS (2003) The Indochinese-Sundaic faunal transition at the Isthmus of Kra: an analysis of resident forest bird species distributions.Journal of Biogeography, 30, 569-580. |
| [32] | IUCN (2013) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. (2013.04.05) |
| [33] | Iyengar A, Babu VN, Hedges S, Venkataraman AB, Maclean N, Morin PA (2005) Phylogeography, genetic structure, and diversity in the dhole (Cuon alpinus).Molecular Ecology, 14, 2281-2297. |
| [34] | Janecka JE, Helgen KM, Lim NT, Baba M, Izawa M, Boeadi, Murphy WJ (2008) Evidence for multiple species of Sunda colugo.Current Biology, 18, R1001-R1002. |
| [35] | Johnson WE, Eizirik E, Pecon-Slattery J, Murphy WJ, Antunes A, Teeling E, O’Brien SJ (2006) The late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: a genetic assessment.Science, 311, 73-77. |
| [36] | Kitchener AC, Beaumont MA, Richardson D (2006) Geographical variation in the clouded leopard, Neofelis nebulosa, reveals two species.Current Biology, 16, 2377-2383. |
| [37] | Koopman KF (1989) Distributional patterns of Indo-Malayan bats (Mammalia, Chiroptera).American Museum Novitates, 2942, 1-19. |
| [38] | Lemmon EM, Lemmon AR (2013) High-throughput genomic data in systematics and phylogenetics.Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 44, 99-121. |
| [39] | Leslie DM (2011) Rusa unicolor (Artiodactyla: Cervidae).Mammalian Species, 43, 1-30. |
| [40] | Li H, Durbin R (2011) Inference of human population history from individual whole-genome sequences.Nature, 475, 493-496. |
| [41] | Lipson M, Loh PR, Levin A, Reich D, Patterson N, Berger B (2013) Efficient moment-based inference of admixture parameters and sources of gene flow.Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 1788-1802. |
| [42] | Locke DP, Hillier LW, Warren WC, Worley KC, Nazareth LV, Muzny DM, Yang SP, Wang Z, Chinwalla AT, Minx P, Mitreva M, Cook L, Delehaunty KD, Fronick C, Schmidt H, Fulton LA, Fulton RS, Nelson JO, Magrini V, Pohl C, Graves TA, Markovic C, Cree A, Dinh HH, Hume J, Kovar CL, Fowler GR, Lunter G, Meader S, Heger A, Ponting CP, Marques-Bonet T, Alkan C, Chen L, Cheng Z, Kidd JM, Eichler EE, White S, Searle S, Vilella AJ, Chen Y, Flicek P, Ma J, Raney B, Suh B, Burhans R, Herrero J, Haussler D, Faria R, Fernando O, Darre F, Farre D, Gazave E, Oliva M, Navarro A, Roberto R, Capozzi O, Archidiacono N, Della Valle G, Purgato S, Rocchi M, Konkel MK, Walker JA, Ullmer B, Batzer MA, Smit AF, Hubley R, Casola C, Schrider DR, Hahn MW, Quesada V, Puente XS, Ordonez GR, Lopez-Otin C, Vinar T, Brejova B, Ratan A, Harris RS, Miller W, Kosiol C, Lawson HA, Taliwal V, Martins AL, Siepel A, Roychoudhury A, Ma X, Degenhardt J, Bustamante CD, Gutenkunst RN, Mailund T, Dutheil JY, Hobolth A, Schierup MH, Ryder OA, Yoshinaga Y, de Jong PJ, Weinstock GM, Rogers J, Mardis ER, Gibbs RA, Wilson RK (2011) Comparative and demographic analysis of orang-utan genomes.Nature, 469, 529-533. |
| [43] | Louys J, Curnoe D, Haowen T (2007) Characteristics of Pleistocene megafauna extinctions in Southeast Asia.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 243, 152-173. |
| [44] | Luo SJ, Kim JH, Johnson WE, van der Walt J, Martenson J, Yuhki N, Miquelle DG, Uphyrkina O, Goodrich JM, Quigley HB, Tilson R, Brady G, Martelli P, Subramaniam V, McDougal C, Hean S, Huang SQ, Pan W, Karanth UK, Sunquist M, Smith JLD, O’Brien SJ (2004) Phylogeography and genetic ancestry of tigers (Panthera tigris).PLoS Biology, 2, e442. |
| [45] | Mailund T, Dutheil JY, Hobolth A, Lunter G, Schierup MH (2011) Estimating divergence time and ancestral effective population size of Bornean and Sumatran orangutan subspecies using a coalescent hidden Markov model.PLoS Genetics, 7, e1001319. |
| [46] | Meijaard E (2003) Mammals of south-east Asian islands and their Late Pleistocene environments.Journal of Biogeography, 30, 1245-1257. |
| [47] | Meijaard E (2004) Craniometric differences among Malayan sun bears (Ursus malayanus); evolutionary and taxonomic implications.Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 52, 665-672. |
| [48] | Miller W, Schuster SC, Welch AJ, Ratan A, Bedoya-Reina OC, Zhao F, Kim HL, Burhans RC, Drautz DI, Wittekindt NE, Tomsho LP, Ibarra-Laclette E, Herrera-Estrella L, Peacock E, Farley S, Sage GK, Rode K, Obbard M, Montiel R, Bachmann L, Ingólfsson Ó, Aars J, Mailund T, Wiig Ø, Talbot SL, Lindqvist C (2012) Polar and brown bear genomes reveal ancient admixture and demographic footprints of past climate change.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, E2382-E2390. |
| [49] | Morley RJ (2000) Origin and Evolution of Tropical Rain Forests. Wiley, Chichester. |
| [50] | Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities.Nature, 403, 853-858. |
| [51] | O’Brien S, Johnson W (2007) The evolution of cats.Scientific American Magazine, 297, 68-75. |
| [52] | Oppenheimer C (2002) Limited global change due to the largest known Quaternary eruption, Toba ~74 kyr BP?Quaternary Science Reviews, 21, 1593-1609. |
| [53] | Patou ML, Chen J, Cosson L, Andersen DH, Cruaud C, Couloux A, Randi E, Zhang S, Veron G (2009) Low genetic diversity in the masked palm civet Paguma larvata (Viverridae).Journal of Zoology, 278, 218-230. |
| [54] | Rampino MR, Self S (1992) Volcanic winter and accelerated glaciation following the Toba super-eruption.Nature, 359, 50-52. |
| [55] | Robinson MM, Dowsett HJ, Chandler MA (2008) Pliocene role in assessing future climate impacts.Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 89, 501-502. |
| [56] | Roos C, Thanh VN, Walter L, Nadler T (2007) Molecular systematics of Indochinese primates.Vietnamese Journal of Primatology, 1, 41-53. |
| [57] | Round PD, Hughes JB, Woodruff DS (2003) Latitudinal range limits of resident forest birds in Thailand and the Indochinese-Sundaic zoogeographic transition.Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society, 51, 69-96. |
| [58] | Ruedi M, Fumagalli L (1996) Genetic structure of gymnures (genus Hylomys; Erinaceidae) on continental islands of Southeast Asia: historical effects of fragmentation.Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research, 34, 153-162. |
| [59] | Scally A, Durbin R (2012) Revising the human mutation rate: implications for understanding human evolution.Nature Reviews: Genetics, 13, 745-753. |
| [60] | Scally A, Dutheil JY, Hillier LW, Jordan GE, Goodhead I, Herrero J, Hobolth A, Lappalainen T, Mailund T, Marques-Bonet T, McCarthy S, Montgomery SH, Schwalie PC, Tang YA, Ward MC, Xue Y, Yngvadottir B, Alkan C, Andersen LN, Ayub Q, Ball EV, Beal K, Bradley BJ, Chen Y, Clee CM, Fitzgerald S, Graves TA, Gu Y, Heath P, Heger A, Karakoc E, Kolb-Kokocinski A, Laird GK, Lunter G, Meader S, Mort M, Mullikin JC, Munch K, O’Connor TD, Phillips AD, Prado-Martinez J, Rogers AS, Sajjadian S, Schmidt D, Shaw K, Simpson JT, Stenson PD, Turner DJ, Vigilant L, Vilella AJ, Whitener W, Zhu B, Cooper DN, de Jong P, Dermitzakis ET, Eichler EE, Flicek P, Goldman N, Mundy NI, Ning Z, Odom DT, Ponting CP, Quail MA, Ryder OA, Searle SM, Warren WC, Wilson RK, Schierup MH, Rogers J, Tyler-Smith C, Durbin R (2012) Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence.Nature, 483, 169-175. |
| [61] | Shiina T, Tanaka K, Katsuyama Y, Otabe K, Sakamoto K, Kurata M, Nomura M, Yamanka H, Nakagawa H, Inoko H, Ota M (2010) Mitochondrial DNA diversity among three subpopulations of cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis) originating from the Indochinese region.Experimental Animals, 59, 567-578. |
| [62] | Siren J, Hanage WP, Corander J (2013) Inference on popula-tion histories by approximating infinite alleles diffusion.Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 457-468. |
| [63] | Smith DG, McDonough JW, George DA (2007) Mitochondrial DNA variation within and among regional populations of longtail macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in relation to other species of the fascicularis group of macaques.American Journal of Primatology, 69, 182-198. |
| [64] | Sousa V, Hey J (2013) Understanding the origin of species with genome-scale data: modelling gene flow.Nature Reviews: Genetics, 14, 404-414. |
| [65] | Steiner CC, Putnam AS, Hoeck PEA, Ryder OA (2013) Conservation genomics of threatened animal species.Annual Review of Animal Biosciences, 1, 261-281. |
| [66] | Steiper ME (2006) Population history, biogeography, and taxonomy of orangutans (Genus: Pongo) based on a population genetic meta-analysis of multiple loci.Journal of Human Evolution, 50, 509-522. |
| [67] | Street SL, Kyes RC, Grant R, Ferguson B (2007) Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are highly conserved in rhesus (Macaca mulatta) and cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) macaques.BMC Genomics, 8, 480. |
| [68] | Surridge AK, Timmins RJ, Hewitt GM, Bell DJ (1999) Striped rabbits in Southeast Asia.Nature, 400, 726. |
| [69] | Timmins RJ, Duckworth JW, Hedges S, Steinmetz R, Pattanavibool A (2008a) Bos javanicus. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . (2013.04.05) |
| [70] | Timmins RJ, Steinmetz R, Sagar Baral H, Samba Kumar N, Duckworth JW, Anwarul Islam M, Giman B, Hedges S, Lynam AJ, Fellowes J, Chan BPL, Evans T (2008b) Rusa unicolor. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . (2013.04.05) |
| [71] | Tosi AJ, Morales JC, Melnick DJ (2002) Y-chromosome and mitochondrial markers in Macaca fascicularis indicate introgression with Indochinese M. mulatta and a biogeographic barrier in the Isthmus of Kra.International Journal of Primatology, 23, 161-178. |
| [72] | Tougard C (2001) Biogeography and migration routes of large mammal faunas in South-East Asia during the Late Middle Pleistocene: focus on the fossil and extant faunas from Thailand.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoec- ology, 168, 337-358. |
| [73] | Tougard C, Montuire S (2006) Pleistocene paleoenvironmental reconstructions and mammalian evolution in South-East Asia: focus on fossil faunas from Thailand.Quaternary Science Reviews, 25, 126-141. |
| [74] | Uphyrkina O, Johnson WE, Quigley H, Miquelle D, Marker L, Bush M, O’Brien SJ (2001) Phylogenetics, genome diversity and origin of modern leopard, Panthera pardus.Molecular Ecology, 10, 2617-2633. |
| [75] | van den Bergh GD, de Vos J, Sondaar PY (2001) The Late Quaternary palaeogeography of mammal evolution in the Indonesian Archipelago.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatol- ogy, Palaeoecology, 171, 385-408. |
| [76] | van Strien NJ, Steinmetz R, Manullang B, Sectionov, Han KH, Isnan W, Rookmaaker K, Sumardja E, Khan MKM, Ellis S(2008a) Rhinoceros sondaicus. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2.. (2013.04.05) |
| [77] | van Strien NJ, Manullang B, Sectionov, Isnan W, Khan MKM, Sumardja E, Ellis S, Han KH, Boeadi, Payne J, Bradley Martin E(2008b) Dicerorhinus sumatrensis. In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . (2013.04.05) |
| [78] | Vidya T, Sukumar R, Melnick DJ (2009) Range-wide mtDNA phylogeography yields insights into the origins of Asian elephants.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 276, 893-902. |
| [79] | Voris HK (2000) Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time durations.Journal of Biogeography, 27, 1153-1167. |
| [80] | Weetman D, Wilding CS, Steen K, Pinto J, Donnelly MJ (2012) Gene flow-dependent genomic divergence between Anopheles gambiae M and S forms.Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29, 279-291. |
| [81] | Whitmore TC (1984) Tropical Rain Forests of the Far East. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [82] | Wikramanayake E, Dinerstein E, Loucks CJ (2001) Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: A Conservation Assessment. Island Press, Washington, D.C. |
| [83] | Williams M (2011) The ~73 ka Toba super-eruption and its impact: history of a debate.Quaternary International, 258, 19-29. |
| [84] | Williams MA, Ambrose SH, van der Kaars S, Ruehlemann C, Chattopadhyaya U, Pal J, Chauhan PR (2009) Environmental impact of the 73ka Toba super-eruption in South Asia.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 284, 295-314. |
| [85] | Wilting A, Buckley-Beason VA, Feldhaar H, Gadau J, O’Brien SJ, Linsenmair KE (2007) Clouded leopard phylogeny revisited: support for species recognition and population division between Borneo and Sumatra.Frontiers in Zoology, 4, 15. |
| [86] | Woodruff DS (2003) The location of the Indochinese-Sundaic biogeographic transition in plants and birds.Natural History Bulletin of the Siam Society, 51, 97-108. |
| [87] | Woodruff DS (2010) Biogeography and conservation in Southeast Asia: how 2.7 million years of repeated environmental fluctuations affect today’s patterns and the future of the remaining refugial-phase biodiversity.Biodiversity and Conservation, 19, 919-941. |
| [88] | Woodruff DS, Turner LM (2009) The Indochinese-Sundaic zoogeographic transition: a description and analysis of terrestrial mammal species distributions.Journal of Biogeography, 36, 803-821. |
| [89] | Yang Z (2010) A likelihood ratio test of speciation with gene flow using genomic sequence data.Genome Biology and Evolution, 2, 200-211. |
| [90] | Zhao S, Zheng P, Dong S, Zhan X, Wu Q, Guo X, Hu Y, He W, Zhang S, Fan W, Zhu L, Li D, Zhang X, Chen Q, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Jin X, Zhang J, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J, Wei F (2013) Whole-genome sequencing of giant pandas provides insights into demographic history and local adaptation.Nature Genetics, 45, 67-71. |
| [91] | Zhi L, Karesh WB, Janczewski DN, Frazier-Taylor H, Sajuthi D, Gombek F, Andau M, Martenson JS, O’Brien SJ (1996) Genomic differentiation among natural populations of orang-utan (Pongo pygmaeus).Current Biology, 6, 1326-1336. |
| [1] | Jiayu Lu, Xiaoyi Shi, Li’an Duo, Tianming Wang, Zhilin Li. Circadian rhythms of urban terrestrial mammals in Tianjin based on camera trapping method [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [2] | Qiong Wu, Zixi Zhao, Taozhu Sun, Yumeng Zhao, Cong Yu, Qin Zhu, Zhongqiu Li. Impact of urban road characteristics and natural landscapes on animal vehicle collisions: A case study in Nanjing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24141-. |
| [3] | Yunwei Dong, Menghuan Bao, Jiao Cheng, Yiyong Chen, Jianguo Du, Yangchun Gao, Lisha Hu, Xincheng Li, Chunlong Liu, Geng Qin, Jin Sun, Xin Wang, Guang Yang, Chongliang Zhang, Xiong Zhang, Yuyang Zhang, Zhixin Zhang, Aibin Zhan, Qiang He, Jun Sun, Bin Chen, Zhongli Sha, Qiang Lin. Advances of marine biogeography in China: Species distribution model and its applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23453-. |
| [4] | Liyuan Wang, Huijian Hu, Jie Jiang, Yiming Hu. Species richness patterns of mammals and birds and their drivers in the Nanling Mountain Range [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [5] | Benping Chen, Jianwu Chen, Zhengwen Ling, Xu Yang, Xin Chen, Shengqiang Li, Biao Yang. Developing a dataset on the diversity and dynamic changes of mammals and birds recorded using camera traps in Laojun Mountain National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| [6] | Yanqiu Xie, Hui Huang, Chunxiao Wang, Yaqin He, Yixuan Jiang, Zilin Liu, Chuanyuan Deng, Yushan Zheng. Determinants of species-area relationship and species richness of coastal endemic plants in the Fujian islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [7] | Min Kang. Wallace’s anthropological thought and its contemporary value [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23304-. |
| [8] | Honghu Meng, Yigang Song. Biogeographic patterns in Southeast Asia: Retrospectives and perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23261-. |
| [9] | Xiaofan Shang, Jian Zhang, Haojie Gao, Weipeng Ku, Yuke Bi, Xiupeng Li, Enrong Yan. Island area and climate jointly impact seed plant richness patterns across the Zhoushan Archipelago [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [10] | Yanping Wang, Minchu Zhang, Chengxiu Zhan. A review on the nested distribution pattern (nestedness): Analysis methods, mechanisms and conservation implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [11] | Wenhong Xiao, Xueyou Li, Ruichang Quan, Xinming Lian, Ming Li, Yonggang Nie, Zuofu Xiang, Weikang Yang, Feng Xu, Jie Wang, Qihai Zhou, Pengfei Fan, Xifu Yang, Wei Liu, Yuehua Sun, Libiao Zhang, Zhipang Huang, Hua Huang, Zongji Fan, Zhishu Xiao. Construction of Sino BON Mammal Diversity Monitoring Network (Sino BON- Mammal): A 10-year review and future outlook [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23326-. |
| [12] | De Gao, Yanping Wang. A review of the small-island effect detection methods and method advancement [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [13] | Jinyu Yang, Wanlong Zhu. Impact of habitat variation and human activities on small mammal community structure and diversity in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23246-. |
| [14] | Yajun Sun. Why do we believe in Darwin’s theory of evolution—On the 25 folds of aesthetic parsimony of On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(9): 22243-. |
| [15] | Weinuo Liang, Liang Hu. Geographical distribution of freshwater and estuarial fish archaeological remains since the Neolithic Age in China and its biogeographical implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 21471-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()
