



Biodiv Sci ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 482-489. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09074 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.09074
• Editorial • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lichuan Dai, Minglong Zhang, Jiye Liu, Xiaobai Li, Hairui Cui( )
)
Received:2009-03-31
Accepted:2009-07-02
Online:2009-09-20
Published:2009-09-20
Contact:
Hairui Cui
Lichuan Dai, Minglong Zhang, Jiye Liu, Xiaobai Li, Hairui Cui. Genetic diversity in Chinese rapeseed (Brassica napus) cultivars based on EST-SSR markers[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(5): 482-489.
| 编号 Code | EST-SSR 引物序列 Sequences | 退火温度 Annealing temp. (℃) | 重复基元 Repeat motif | 目标片段 Target fragment(bp) | 扩增条 带数 Bands amplified | 多态性条 带数 Polymorphic bands | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 预期大小Expected size | 实际大小 Actual size | ||||||
| P1 | CTGGGAAAGGGAAAGTGGC | 60 | (TC)31 | 131 | 130-200 | 3 | 3 |
| TGGCTGAATCCTGCGGAC | |||||||
| P2 | TTCTTCGTCTTCTCCACTCTTATTC | 60 | (CA)15 | 150 | 150-190 | 4 | 3 |
| TGATCTTCTGCTCGACATATCTTTA | |||||||
| P6 | ACTCCGTCATCACCGTCCTT | 50 | (AG)11 | 212 | 210-230 | 3 | 3 |
| CCTATTCAACGCTGCGTCTTA | |||||||
| P7 | TATCCATCGTCTGGTTTTGTTC | 55 | (TG)9(T)11 | 217 | 220-310 | 5 | 4 |
| TTTTCAGATTTACCGTTCACCT | |||||||
| P11 | CTACTCGCATGGAAACGCC | 60 | (TG)10 | 302 | 308-580 | 8 | 7 |
| GCAGCAAGAAGCATTATCGC | |||||||
| P13 | ACCCCAGATATTTTGTTAGCCG | 50 | (AG)17 | 341 | 700-1000 | 8 | 8 |
| CAGGTCTTGCCCATTTTGTCA | |||||||
| P14 | AGAACTAATCCGAAGGAGACCG | 65 | (GAT)14 | 343 | 505-800 | 8 | 6 |
| GGCTAAGCCGCAAACGAC | |||||||
| P16 | TCATATCCATCCATGTCTCAACG | 65 | (TCA)10 | 365 | 365-900 | 10 | 8 |
| CAACAGAAACTCGGTGCAAATC | |||||||
| P17 | CTGGAATACTTGTTTCAATGGGT | 65 | (GGTCTA)6 | 384 | 380-520 | 7 | 3 |
| GCTCACTTTCAGTCTGGGTGTC | |||||||
| P19 | AGTGTTGGAAGCGGAAAAGG | 60 | (TCA)11 | 390 | 220-570 | 6 | 5 |
| GCGTAGGCAGGAAAATAGGG | |||||||
| P20 | TTATCTCAGAACGCTCCGACG | 60 | (GAT)10 | 412 | 405-750 | 8 | 8 |
| CCTCATCCTCCTCTTTCCTCAG | |||||||
| P21 | ATTACCCTGAACCACCACCC | 55 | (GCT)18 | 320 | 320, 680-980 | 6 | 4 |
| TGCTTGTCCAAATAGCTCTTGA | |||||||
| P22 | TTCATTTTGCTTGATGTGATTCTC | 50 | (CT)21 | 267 | 260-340 | 5 | 5 |
| GCTTGGCGTAAAAGGATTCTACT | |||||||
| P23 | GAAGTTGGGTTGAAGAGCAGTT | 50 | (TC)23 | 232 | 232-480 | 9 | 8 |
| TCTGTAAAGTGTCCAGGAGCAAC | |||||||
| P24 | TGGTCTTGATTTTATTGCGAGC | 60 | (GAT)14 | 223 | 170-250 | 6 | 6 |
| TTTGGGCGTGATACCTTGAG | |||||||
| P25 | GCTCTAACCACTGACCACCGA | 60 | (TC)19 | 390 | 390-680 | 4 | 3 |
| ACATCCTGCTCTGGGAAACAT | |||||||
Table 1 Information about 16 EST-SSR primer pairs and their amplification in oilseed rape tested
| 编号 Code | EST-SSR 引物序列 Sequences | 退火温度 Annealing temp. (℃) | 重复基元 Repeat motif | 目标片段 Target fragment(bp) | 扩增条 带数 Bands amplified | 多态性条 带数 Polymorphic bands | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 预期大小Expected size | 实际大小 Actual size | ||||||
| P1 | CTGGGAAAGGGAAAGTGGC | 60 | (TC)31 | 131 | 130-200 | 3 | 3 |
| TGGCTGAATCCTGCGGAC | |||||||
| P2 | TTCTTCGTCTTCTCCACTCTTATTC | 60 | (CA)15 | 150 | 150-190 | 4 | 3 |
| TGATCTTCTGCTCGACATATCTTTA | |||||||
| P6 | ACTCCGTCATCACCGTCCTT | 50 | (AG)11 | 212 | 210-230 | 3 | 3 |
| CCTATTCAACGCTGCGTCTTA | |||||||
| P7 | TATCCATCGTCTGGTTTTGTTC | 55 | (TG)9(T)11 | 217 | 220-310 | 5 | 4 |
| TTTTCAGATTTACCGTTCACCT | |||||||
| P11 | CTACTCGCATGGAAACGCC | 60 | (TG)10 | 302 | 308-580 | 8 | 7 |
| GCAGCAAGAAGCATTATCGC | |||||||
| P13 | ACCCCAGATATTTTGTTAGCCG | 50 | (AG)17 | 341 | 700-1000 | 8 | 8 |
| CAGGTCTTGCCCATTTTGTCA | |||||||
| P14 | AGAACTAATCCGAAGGAGACCG | 65 | (GAT)14 | 343 | 505-800 | 8 | 6 |
| GGCTAAGCCGCAAACGAC | |||||||
| P16 | TCATATCCATCCATGTCTCAACG | 65 | (TCA)10 | 365 | 365-900 | 10 | 8 |
| CAACAGAAACTCGGTGCAAATC | |||||||
| P17 | CTGGAATACTTGTTTCAATGGGT | 65 | (GGTCTA)6 | 384 | 380-520 | 7 | 3 |
| GCTCACTTTCAGTCTGGGTGTC | |||||||
| P19 | AGTGTTGGAAGCGGAAAAGG | 60 | (TCA)11 | 390 | 220-570 | 6 | 5 |
| GCGTAGGCAGGAAAATAGGG | |||||||
| P20 | TTATCTCAGAACGCTCCGACG | 60 | (GAT)10 | 412 | 405-750 | 8 | 8 |
| CCTCATCCTCCTCTTTCCTCAG | |||||||
| P21 | ATTACCCTGAACCACCACCC | 55 | (GCT)18 | 320 | 320, 680-980 | 6 | 4 |
| TGCTTGTCCAAATAGCTCTTGA | |||||||
| P22 | TTCATTTTGCTTGATGTGATTCTC | 50 | (CT)21 | 267 | 260-340 | 5 | 5 |
| GCTTGGCGTAAAAGGATTCTACT | |||||||
| P23 | GAAGTTGGGTTGAAGAGCAGTT | 50 | (TC)23 | 232 | 232-480 | 9 | 8 |
| TCTGTAAAGTGTCCAGGAGCAAC | |||||||
| P24 | TGGTCTTGATTTTATTGCGAGC | 60 | (GAT)14 | 223 | 170-250 | 6 | 6 |
| TTTGGGCGTGATACCTTGAG | |||||||
| P25 | GCTCTAACCACTGACCACCGA | 60 | (TC)19 | 390 | 390-680 | 4 | 3 |
| ACATCCTGCTCTGGGAAACAT | |||||||
| 标记编号 Marker code | 多态性信息含量 PIC | 基因型数 No. of genotypes |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.468 | 3 |
| P2 | 0.296 | 7 |
| P6 | 0.728 | 6 |
| P7 | 0.514 | 8 |
| P11 | 0.851 | 24 |
| P13 | 0.842 | 23 |
| P14 | 0.886 | 15 |
| P16 | 0.891 | 24 |
| P17 | 0.022 | 2 |
| P19 | 0.552 | 10 |
| P20 | 0.926 | 15 |
| P21 | 0.788 | 12 |
| P22 | 0.639 | 7 |
| P23 | 0.829 | 13 |
| P24 | 0.910 | 24 |
| P25 | 0.696 | 6 |
Table 2 Polymorphism information content (PIC) and genotypes revealed by different EST-SSR markers
| 标记编号 Marker code | 多态性信息含量 PIC | 基因型数 No. of genotypes |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.468 | 3 |
| P2 | 0.296 | 7 |
| P6 | 0.728 | 6 |
| P7 | 0.514 | 8 |
| P11 | 0.851 | 24 |
| P13 | 0.842 | 23 |
| P14 | 0.886 | 15 |
| P16 | 0.891 | 24 |
| P17 | 0.022 | 2 |
| P19 | 0.552 | 10 |
| P20 | 0.926 | 15 |
| P21 | 0.788 | 12 |
| P22 | 0.639 | 7 |
| P23 | 0.829 | 13 |
| P24 | 0.910 | 24 |
| P25 | 0.696 | 6 |
| 材料 Accession | 数目 Number | 遗传距离 Genetic distance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 Range | 变异系数 CV (%) | 标准差 SD | 平均 Average | ||
| 常规品种 Open-pollinated variety | 28 | 0.0921-0.4208 | 24.83 | 0.0563 | 0.2383a |
| 杂交品种 Hybrid variety | 63 | 0.0530-0.6336 | 31.59 | 0.0808 | 0.2474b |
Table 3 Parameters of genetic distance among open-pollinated varieties and hybrid varieties
| 材料 Accession | 数目 Number | 遗传距离 Genetic distance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 Range | 变异系数 CV (%) | 标准差 SD | 平均 Average | ||
| 常规品种 Open-pollinated variety | 28 | 0.0921-0.4208 | 24.83 | 0.0563 | 0.2383a |
| 杂交品种 Hybrid variety | 63 | 0.0530-0.6336 | 31.59 | 0.0808 | 0.2474b |
| 育成时期 Time released | 品种数目 Variety number | 遗传距离 Genetic distance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 Range | 变异系数 CV (%) | 标准差 SD | 平均 Average | ||
| 2000年及以前 Before and during 2000 | 31 | 0.0783-0.3763 | 24.83 | 0.0558 | 0.2247a |
| 2000年以后 After 2000 | 58 | 0.0617-0.7223 | 31.59 | 0.0813 | 0.2574b |
Table 4 Parameters of genetic distance among varieties released in different periods
| 育成时期 Time released | 品种数目 Variety number | 遗传距离 Genetic distance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变化范围 Range | 变异系数 CV (%) | 标准差 SD | 平均 Average | ||
| 2000年及以前 Before and during 2000 | 31 | 0.0783-0.3763 | 24.83 | 0.0558 | 0.2247a |
| 2000年以后 After 2000 | 58 | 0.0617-0.7223 | 31.59 | 0.0813 | 0.2574b |
| 序号 No. | 品种名称 Accessions | 来源地 Source | 品种类型* Variety type | 育成年限 Year released | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 皖油14 Wanyou 14 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 1998 |
| 2 | 川油18 Chuanyou 18 | 四川 | Sichuan | OP | 1998 |
| 3 | 川油23 Chuanyou 23 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2002 |
| 4 | 川油16 Chuanyou 16 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 1994 |
| 5 | 东油1号 Dongyou 1 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2005 |
| 6 | 油201 You 201 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2006 |
| 7 | 富油668 Fuyou 668 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2006 |
| 8 | 华双2号 Huashuang 2 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1993 |
| 9 | 高油605 Gaoyou 605 | 浙江 | Zhejiang | H | 1998 |
| 10 | 核杂7号 Heza 7 | 上海 | Shanghai | H | 2003 |
| 11 | 红油3号 Hongyou3 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2006 |
| 12 | 沪油15 Huyou15 | 上海 | Shanghai | OP | 1997 |
| 13 | 沪油杂1号 Huyouza1 | 上海 | Shanghai | H | 2004 |
| 14 | 华91806 Hua 91806 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1998 |
| 15 | 华双3号 Huashuang 3 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1998 |
| 16 | 华双4号 Huashuang 4 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2003 |
| 17 | 华油杂7号 Huayouza 7 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2003 |
| 18 | 华杂5号 Huaza 5 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 19 | 华杂7号 Huaza 7 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2003 |
| 20 | 淮杂油3号 Huaizayou 3 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 21 | 汇油50 Huiyou 50 | 上海 | Shanghai | OP | 1975 |
| 22 | 两优586 Liangyou 586 | 江西 | Jiangxi | H | 2001 |
| 23 | 绵油11号 Mianyou 11 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2000 |
| 24 | 绵油12号 Mianyou 12 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2001 |
| 25 | 南油6号 Nanyou 6 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2001 |
| 26 | 宁油16号 Ningyou 16 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 27 | 蓉油10号 Rongyou 10 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2004 |
| 28 | 蓉油11号 Rongyou 11 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2004 |
| 29 | 蓉油4号 Rongyou 4 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 1996 |
| 30 | 蓉油8号 Rongyou 8 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2002 |
| 31 | 胜油1号 Shengyou1 | 安徽 | Anhui | OP | 1996 |
| 32 | 史力丰 Shilifeng | 江苏 | Nanjing | OP | 2002 |
| 33 | 蜀龙油2号 Shulongyou 2 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2004 |
| 34 | 蜀龙油3号 Shulongyou 3 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2006 |
| 35 | 苏油1号 Suyou 1 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2003 |
| 36 | 浙核选系 Zhehexuanxi | 浙江 | Zhejiang | OP | 2003 |
| 37 | 天禾油1号 Tianheyou 1 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 2003 |
| 38 | 皖油10号 Wanyou 10 | 安徽 | Anhui | OP | 1994 |
| 39 | 皖油18 Wanyou 18 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 2002 |
| 40 | 皖油19 Wanyou 19 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 2002 |
| 41 | 湘农油571Xiangongyou571 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 1998 |
| 42 | 湘油15号 Xiangyou 15 | 湖南 | Hunan | OP | 1997 |
| 43 | 湘油17号 Xiangyou 17 | 湖南 | Hunan | OP | 2003 |
| 44 | 湘杂油1号 Xiangzayou 1 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 1995 |
| 45 | 湘杂油3号 Xiangzayou 3 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 2001 |
| 46 | 湘杂油6号 Xiangzayou 6 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 2003 |
| 序号 No. | 品种名称 Accessions | 来源地 Source | 品种类型* Variety type | 育成年限 Year released | |
| 47 | 新甘油5号 Xinganyou 5 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 不详 Unknown |
| 48 | 兴选2号 Xingxuan 2 | 安徽 | Anhui | OP | 1992 |
| 49 | 扬油5号 Yangyou 5 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2003 |
| 50 | 扬油6号 Yangyou 6 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 51 | 阳光9558 Yangguang 9558 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1997 |
| 52 | 油研2号 Youyan 2 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 1992 |
| 53 | 油研6号 Youyan 6 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 1994 |
| 54 | 油研七号 Youyan 7 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 1999 |
| 55 | 渝黄一号 Yuhuang 1 | 重庆 | Chongqing | H | 2003 |
| 56 | 远杂九号 Yuanza 9 | 河南 | Henan | H | 不详 Unknown |
| 57 | 浙双72 Zheshuang 72 | 浙江 | Zhejiang | H | 2001 |
| 58 | 中乐油2号 Zhongleyou 2 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2006 |
| 59 | 中双6号 Zhongshuang 6 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2000 |
| 60 | 中双8号 Zhongshuang 8 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 61 | 中双9号 Zhongshuang 9 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2002 |
| 62 | 中油821 Zhongyou 821 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1987 |
| 63 | 中油杂12 Zhongyouza 12 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2006 |
| 64 | 中油杂1号 Zhongyouza 1 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 1999 |
| 65 | 中油杂3号 Zhongyouza 3 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 66 | 中油杂4号 Zhongyouza 4 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 67 | 中油杂5号 Zhongyouza 5 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 68 | 湘油15号 Xiangyou 15 | 湖南 | Hunan | OP | 1997 |
| 69 | 贵油7号 Guiyou 7 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 2004 |
| 70 | 贵杂5号 Guiza 5 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 2003 |
| 71 | 亚科28 Yake 28 | 青海 | Qinghai | H | 2001 |
| 72 | 陕油6号 Shanyou 6 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | H | 2000 |
| 73 | 成油1号 Chengyou 1 | 甘肃 | Gansu | H | 2004 |
| 74 | 华油1087 Huayou 1087 | 河南 | Henan | H | 2002 |
| 75 | 德油杂988 Dezayou 988 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2005- |
| 76 | 亚华油10号 Yahuayou 10 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2004 |
| 77 | 丰油701 Fengyou 701 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 2004 |
| 78 | 秦油三号 Qinyou 3 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | OP | 2001 |
| 79 | 德油5号 Deyou 5 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2001 |
| 80 | 青油14 Qingyou 14 | 青海 | Qinghai | H | 1994 |
| 81 | 陇油5号 Shanyou 5 | 甘肃 | Gansu | H | 2000 |
| 82 | 陕油8号 Shanyou 8 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | OP | 2001 |
| 83 | 扬油6号 Yangyou 6 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2004 |
| 84 | 垦鉴油2号 Kenjianyou 2 | 黑龙江 | Heilongjiang | H | 2005 |
| 85 | 红油杂2号 Hongyouza 2 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 86 | 秦优10号 Qinyou 10 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | H | 2004 |
| 87 | 豫油5号 Yuyou 5 | 河南 | Henan | H | 2002 |
| 88 | 秦优8号 Qinyou 8 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | H | 2001 |
| 89 | 垦油1号 Kenyou 1 | 黑龙江 | Heilongjiang | H | 1995 |
| 90 | 湘杂油2号 Xiangzayou 2 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 1998 |
| 91 | 垦油3号 Kenyou 3 | 黑龙江 | Heilongjiang | H | 2000 |
Appendix 1 Materials used in this experiment
| 序号 No. | 品种名称 Accessions | 来源地 Source | 品种类型* Variety type | 育成年限 Year released | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 皖油14 Wanyou 14 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 1998 |
| 2 | 川油18 Chuanyou 18 | 四川 | Sichuan | OP | 1998 |
| 3 | 川油23 Chuanyou 23 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2002 |
| 4 | 川油16 Chuanyou 16 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 1994 |
| 5 | 东油1号 Dongyou 1 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2005 |
| 6 | 油201 You 201 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2006 |
| 7 | 富油668 Fuyou 668 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2006 |
| 8 | 华双2号 Huashuang 2 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1993 |
| 9 | 高油605 Gaoyou 605 | 浙江 | Zhejiang | H | 1998 |
| 10 | 核杂7号 Heza 7 | 上海 | Shanghai | H | 2003 |
| 11 | 红油3号 Hongyou3 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2006 |
| 12 | 沪油15 Huyou15 | 上海 | Shanghai | OP | 1997 |
| 13 | 沪油杂1号 Huyouza1 | 上海 | Shanghai | H | 2004 |
| 14 | 华91806 Hua 91806 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1998 |
| 15 | 华双3号 Huashuang 3 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1998 |
| 16 | 华双4号 Huashuang 4 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2003 |
| 17 | 华油杂7号 Huayouza 7 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2003 |
| 18 | 华杂5号 Huaza 5 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 19 | 华杂7号 Huaza 7 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2003 |
| 20 | 淮杂油3号 Huaizayou 3 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 21 | 汇油50 Huiyou 50 | 上海 | Shanghai | OP | 1975 |
| 22 | 两优586 Liangyou 586 | 江西 | Jiangxi | H | 2001 |
| 23 | 绵油11号 Mianyou 11 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2000 |
| 24 | 绵油12号 Mianyou 12 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2001 |
| 25 | 南油6号 Nanyou 6 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2001 |
| 26 | 宁油16号 Ningyou 16 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 27 | 蓉油10号 Rongyou 10 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2004 |
| 28 | 蓉油11号 Rongyou 11 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2004 |
| 29 | 蓉油4号 Rongyou 4 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 1996 |
| 30 | 蓉油8号 Rongyou 8 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2002 |
| 31 | 胜油1号 Shengyou1 | 安徽 | Anhui | OP | 1996 |
| 32 | 史力丰 Shilifeng | 江苏 | Nanjing | OP | 2002 |
| 33 | 蜀龙油2号 Shulongyou 2 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2004 |
| 34 | 蜀龙油3号 Shulongyou 3 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2006 |
| 35 | 苏油1号 Suyou 1 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2003 |
| 36 | 浙核选系 Zhehexuanxi | 浙江 | Zhejiang | OP | 2003 |
| 37 | 天禾油1号 Tianheyou 1 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 2003 |
| 38 | 皖油10号 Wanyou 10 | 安徽 | Anhui | OP | 1994 |
| 39 | 皖油18 Wanyou 18 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 2002 |
| 40 | 皖油19 Wanyou 19 | 安徽 | Anhui | H | 2002 |
| 41 | 湘农油571Xiangongyou571 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 1998 |
| 42 | 湘油15号 Xiangyou 15 | 湖南 | Hunan | OP | 1997 |
| 43 | 湘油17号 Xiangyou 17 | 湖南 | Hunan | OP | 2003 |
| 44 | 湘杂油1号 Xiangzayou 1 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 1995 |
| 45 | 湘杂油3号 Xiangzayou 3 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 2001 |
| 46 | 湘杂油6号 Xiangzayou 6 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 2003 |
| 序号 No. | 品种名称 Accessions | 来源地 Source | 品种类型* Variety type | 育成年限 Year released | |
| 47 | 新甘油5号 Xinganyou 5 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 不详 Unknown |
| 48 | 兴选2号 Xingxuan 2 | 安徽 | Anhui | OP | 1992 |
| 49 | 扬油5号 Yangyou 5 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2003 |
| 50 | 扬油6号 Yangyou 6 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 51 | 阳光9558 Yangguang 9558 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1997 |
| 52 | 油研2号 Youyan 2 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 1992 |
| 53 | 油研6号 Youyan 6 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 1994 |
| 54 | 油研七号 Youyan 7 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 1999 |
| 55 | 渝黄一号 Yuhuang 1 | 重庆 | Chongqing | H | 2003 |
| 56 | 远杂九号 Yuanza 9 | 河南 | Henan | H | 不详 Unknown |
| 57 | 浙双72 Zheshuang 72 | 浙江 | Zhejiang | H | 2001 |
| 58 | 中乐油2号 Zhongleyou 2 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2006 |
| 59 | 中双6号 Zhongshuang 6 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2000 |
| 60 | 中双8号 Zhongshuang 8 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 61 | 中双9号 Zhongshuang 9 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 2002 |
| 62 | 中油821 Zhongyou 821 | 湖北 | Hubei | OP | 1987 |
| 63 | 中油杂12 Zhongyouza 12 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2006 |
| 64 | 中油杂1号 Zhongyouza 1 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 1999 |
| 65 | 中油杂3号 Zhongyouza 3 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 66 | 中油杂4号 Zhongyouza 4 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 67 | 中油杂5号 Zhongyouza 5 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2002 |
| 68 | 湘油15号 Xiangyou 15 | 湖南 | Hunan | OP | 1997 |
| 69 | 贵油7号 Guiyou 7 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 2004 |
| 70 | 贵杂5号 Guiza 5 | 贵州 | Guizhou | H | 2003 |
| 71 | 亚科28 Yake 28 | 青海 | Qinghai | H | 2001 |
| 72 | 陕油6号 Shanyou 6 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | H | 2000 |
| 73 | 成油1号 Chengyou 1 | 甘肃 | Gansu | H | 2004 |
| 74 | 华油1087 Huayou 1087 | 河南 | Henan | H | 2002 |
| 75 | 德油杂988 Dezayou 988 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2005- |
| 76 | 亚华油10号 Yahuayou 10 | 湖北 | Hubei | H | 2004 |
| 77 | 丰油701 Fengyou 701 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 2004 |
| 78 | 秦油三号 Qinyou 3 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | OP | 2001 |
| 79 | 德油5号 Deyou 5 | 四川 | Sichuan | H | 2001 |
| 80 | 青油14 Qingyou 14 | 青海 | Qinghai | H | 1994 |
| 81 | 陇油5号 Shanyou 5 | 甘肃 | Gansu | H | 2000 |
| 82 | 陕油8号 Shanyou 8 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | OP | 2001 |
| 83 | 扬油6号 Yangyou 6 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | OP | 2004 |
| 84 | 垦鉴油2号 Kenjianyou 2 | 黑龙江 | Heilongjiang | H | 2005 |
| 85 | 红油杂2号 Hongyouza 2 | 江苏 | Jiangsu | H | 2004 |
| 86 | 秦优10号 Qinyou 10 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | H | 2004 |
| 87 | 豫油5号 Yuyou 5 | 河南 | Henan | H | 2002 |
| 88 | 秦优8号 Qinyou 8 | 陕西 | Shaanxi | H | 2001 |
| 89 | 垦油1号 Kenyou 1 | 黑龙江 | Heilongjiang | H | 1995 |
| 90 | 湘杂油2号 Xiangzayou 2 | 湖南 | Hunan | H | 1998 |
| 91 | 垦油3号 Kenyou 3 | 黑龙江 | Heilongjiang | H | 2000 |
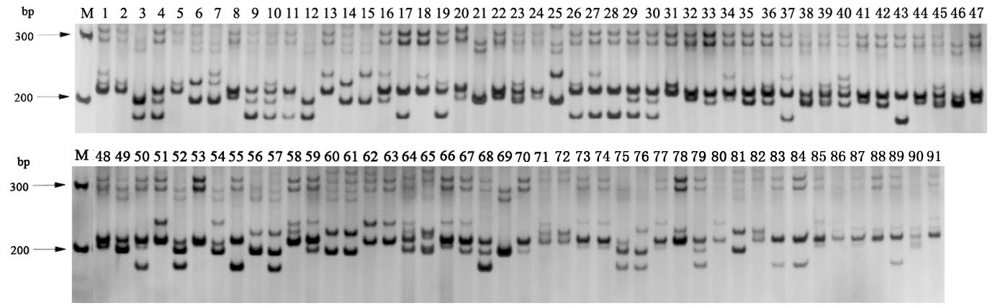
Appendix II Amplification by EST-SSR primer set P24 in 91varieties of oilseed rape. Lane M stands for DNA marker and other lanes stand for 91 varieties as listed in appendix I.
| [1] |
Barrett B, Griffiths A, Schreiber M, Ellison N, Mercer C, Bouton J, Ong B, Forster J, Sawbridge T, Spangenberg G, Bryan DW, Woodfield D (2004) A microsatellite map of white clover. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 109,596-608.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 32,314-331.
URL PMID |
| [3] |
Charters YM, Robertson A, Wilkinson MJ, Ramsay G (1996) PCR analysis of oilseed rape cultivars ( Brassica napus L. ssp. oleifera) using 5′-anchored simple sequence repeat (SSR) primers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 92,442-447.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Chen BY (陈碧云), Wu XM (伍晓明), Zhang DX (张冬晓), Liu FL (刘凤兰), Lu GY (陆光远), Xu K (许鲲), Gao GZ (高桂珍) (2008) SSR marker fingerprinting of winter rapeseed varieties in national field trail. Molecular Plant Breeding (分子植物育种), 6,709-716. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Chen LL (陈伦林), Zou XY (邹小云), Li SY (李书宇), Zou XF (邹晓芬), Zhang JM (张建模), Song LQ (宋来强) (2008) Analysis on the genetic diversity of rapeseed by SSR and SRAP with emphasis on the difference of this two kinds of markers. Molecular Plant Breeding (分子植物育种), 6,511-516. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Cho YG, Ishii T, Temnykh S, Chen X, Lipovich L, McCouch SR, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S (2000) Diversity of microsatellite derived from genomic libraries and gene-bank sequences in rice ( Oryza sativa L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 100,713-722. |
| [7] | Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin, 19,11-15. |
| [8] |
Ellis JR, Burke JM (2007) EST-SSRs as a resource for population genetic analyses. Heredity, 99,125-132.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Eujay I, Sorrells M, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2001) Assessment of genotypic variation among cultivated durum wheat based on EST-SSR and genomic SSRs. Euphytica, 119,39-43. |
| [10] | Hasan M, Seyis F, Badani AG, Pons-Kuhnemann J, Friedt W, Luhs W, Snowdon RJ (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity in the Brassica napus L. gene pool using SSR markers. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 53,793-802. |
| [11] | Jin JQ (金基强), Cui HR (崔海瑞), Gong XC (龚晓春), Chen WY (陈文岳), Xin Y (忻雅) (2007) Studies on tea plants ( Camellia sinensis) germplasms using EST-SSR marker. Hereditas (Beijing) (遗传), 29,103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Lei TG (雷天刚), Zhang XK (张学昆), Li JN (李加纳), Chen L (谌利), Xu XF (徐新福), Tang ZL (唐章林), Lu H (陆合) (2005) Genetic diversity of yellow-seeded rapeseed lines ( Brassica napus L.) based on SSR marker. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Science (中国油料作物学报), 27(1),41-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Li XB (李小白), Cui HR (崔海瑞), Zhang ML (张明龙) (2007a) Detecting the genetic diversity of Brassica napus by EST-SSRs. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology (农业生物技术学报), 15,661-667. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Li XB (李小白), Cui HR (崔海瑞), Zhang ML (张明龙) (2006) Molecular markers derived from EST: their development and applications in comparative genomics. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14,541-547. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Li XB (李小白), Zhang ML (张明龙), Cui HR (崔海瑞) (2007 b) Data mining for SSRs in ESTs and development of EST- SSR marker in oilseed rape. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology (分子细胞生物学报), 40,137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Li YQ (李永强), Li HW (李宏伟), Gao LF (高丽锋), He BR (何蓓如) (2004) Progress of simple sequence repeats derived from expressed sequence tags. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources (植物遗传资源学报), 5,91-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Ma CZ (马朝芝), Fu TD (傅廷栋), Tuevesson S, Gertsson B (2003a) Genetic diversity of Chinese and Swedish rapeseed ( Brassica napus L.) analysed by inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs). Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 36,1403-1408. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Ma CZ (马朝芝), Sakai T, Fu TD (傅廷栋), Meng JL (孟金陵), Yang GS (杨光圣), Tu JX (涂金星) (2003b) Genetic diversity of parents for hybrid breeding in Brassica napus L. detected by RAPDs and RFLPs. Acta Agronomic Sinica (作物学报), 29,701-707. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Meng JL (孟金陵), Sharpe A, Bowman C, Tian ZH (田志宏), Fu TD (傅廷栋), Qian XZ (钱秀珍), Lydiate D (1996) Genetic diversity of Brassica napus L. detected with RFLP markers. Acta Genetica Sinica (遗传学报), 23,293-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Nei M, Li W (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 76,569-573. |
| [21] | Poulsen GB, Kahl G, Weising K (1993) Abundance and polymorphisms of simple repetitive DNA sequence in Brassica napus L. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 85,994-1000. |
| [22] | Powell W, Machray GC, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends in Plant Science, 1,215-222. |
| [23] | Qiu F (邱芳), Fu JM (伏健民), Jin DM (金德敏), Wang B (王斌) (1998) The molecular detection of genetic diversity. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 6,143-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] |
Saha MC, Mian MA, Eujayl I, Zwonitzer JC, Wang LJ, May GD (2004) Tall fescue EST-SSR markers with transferability across several grass species. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 109,783-791.
URL PMID |
| [25] | Shen JX (沈金雄), Fu TD (傅廷栋), Yang GS (杨光圣) (2004) Relationship between hybrid performance and genetic diversity based on SSR and ISSR in Brassica napus L. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 37,477-483. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] |
Szewc-McFadden AK, Kresovich S, Bliek SM, Mitchell SE, McFerson JR (1996) Identification of polymorphic conserved simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in cultivated Brassica species. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 93,534-538.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Tan ZM (谭祖猛), Li YC (李云昌), Hu Q (胡琼), Mei DS (梅德圣), Cheng JH (程计华) (2008) Advances in molecular marker techniques for heterosis application in rapeseed. Chinese Bulletin of Botany (植物学通报), 25,230-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] |
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney K, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR markers in barley ( Hordeum vulgare L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 106,411-422.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genetic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends in Biotechnology, 23,48-55.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Wang ML, Mosjidis JA, Morris JB, Dean RE, Jenkins TM, Pederson GA (2006) Genetic diversity of Crotalaria germplasm assessed through phylogenetic analysis of EST-SSR markers. Genome, 49,707-715.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] | Wen YC (文雁成), Wang HZ (王汉中), Shen JX (沈金雄), Liu GH (刘贵华), Zhang SF (张书芬) (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity and genetic basis of Chinese rapeseed cultivars ( Brassica napus L.) by sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 39,246-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Xie H, Guan RX, Chang RZ, Qiu LJ (2005) Genetic diversity of Chinese summer soybean germplasm revealed by SSR markers. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50,526-535. |
| [33] | Yan J (闫娟), Chu HJ (楚海家), Wang HC (王恒昌), Li JQ (李建强) (2008) Genetic structure and diversity of Medicago lupulina populations in northern and central China based on EST-SSRs markers. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,263-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Yang XQ (杨新泉), Liu P (刘鹏), Han ZF (韩宗福), Ni ZF (倪中福), Liu WQ (刘旺清), Sun QX (孙其信) (2005) Comparative analysis of genetic diversity revealed by genomic-SSR, EST-SSR and pedigree in wheat (Triticum asetivum L.). Acta Genetica Sinica(遗传学报), 32,406-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Zhang ZF (张志峰), Shi HC (史洪才), Wu J (武坚), Jian ZJ (简子健) (2005) Advanced technique for silver staining of polyacrylamide gel of microsatellite DNA. Biotechnology (生物技术), 15(3),51-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [2] | Xiangzhang Wu, Fumin Lei, Yiyi Shan, Jing Yu. Distribution pattern of bryophyte diversity and environmental impact factors in urban parks of Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23364-. |
| [3] | Gang Ren, En Li, Shiye Zhao, Yanqiong Jiang, Shasha Wang, Sixian Tang, Huijian Hu. Correlation between color polymorphism and the MC1R gene of Lanius schach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(6): 688-694. |
| [4] | Dan Liu, Zhongling Guo, Xiaoyang Cui, Chunnan Fan. Comparison of five associations of Taxus cuspidata and their species diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(3): 340-349. |
| [5] | Fengzhen Wang, Yi Tang. Determination of key species in the food web and their impact on the robustness [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(10): 1132-1137. |
| [6] | Xingtong Wu, Lu Chen, Minqiu Wang, Yuan Zhang, Xueying Lin, Xinyu Li, Hong Zhou, Yafeng Wen. Population structure and genetic divergence in Firmiana danxiaensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(11): 1168-1179. |
| [7] | Jing Zhang, Yuan Li, Na Song, Longshan Lin, Tianxiang Gao. Species identification and phylogenetic relationship of Thryssa species in the coastal waters of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(8): 888-895. |
| [8] | Xiaozhi Lin, Dongmei Li, Huanzhang Liu, Hongsheng Lin, Shaorong Yang, Hanjin Fan, Rushu Wen. Fish species diversity and its seasonal variations in the Chaozhou section of Hanjiang River, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(2): 185-194. |
| [9] | Zhenna Qian, Qianwan Meng, Mingxun Ren. Pollination ecotypes and herkogamy variation of Hiptage benghalensis (Malpighiaceae) with mirror-image flowers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(12): 1364-1372. |
| [10] | Kunchi Lai, Youhua Cheng, Yuehchih Chen, Yousheng Li, Kwangtsao Shao. Applying cluster analysis and Google Maps in the study of large-scale species occurrence data [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(1): 76-85. |
| [11] | Hongzheng Ma, Shanshan Li, Song Ge, Silan Dai, Wenli Chen. Isolation of SSR markers for two related second-generation energy crop species, Miscanthus nepalensis and M. nudipes (Poaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(5): 535-542. |
| [12] | Bo Zhou, Haidong Jiang, Xiuxin Zhang, Jingqi Xue, Yantong Shi. Morphological diversity of some introduced tree peony cultivars [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(5): 543-550. |
| [13] | Chunnan Li, Hairui Cui, Weibo Wang. Genetic diversity in rhizosphere soil microbes detected with SRAP markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(4): 485-493. |
| [14] | Furong Xu, Enlai Zhang, Chao Dong, Luyuan Dai, Hongsheng Zhang. Comparison of phenotypic traits of rice landraces, grown in two different periods in Hani’s terraced fields in Yuanyang County, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(4): 365-372. |
| [15] | Longqian Xiao, Hua Zhu. Intra-genomic polymorphism in the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions of Cycas revoluta: evidence of incomplete concerted evolution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(5): 476-481. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()