



Biodiv Sci ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 796-805. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019394 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019394
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiangyan Shi1, Hai Yang2, Junqin Hua1, Yuze Zhao1, Jianqiang Li1, Jiliang Xu1,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-12
Accepted:2020-04-22
Online:2020-07-20
Published:2020-09-29
Contact:
Jiliang Xu
Jiangyan Shi, Hai Yang, Junqin Hua, Yuze Zhao, Jianqiang Li, Jiliang Xu. The relationship between the diurnal activity rhythm of Reeves’s pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesii) and human disturbance revealed by camera trapping[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(7): 796-805.
| 时间范围 Time range | 研究区 Study area | U2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 繁殖期 Breeding season | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.177 | < 0.1 |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.071 | > 0.1 | |
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.141 | > 0.1 | |
| 非繁殖期 Non-breeding season | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.190 | < 0.05* |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.092 | > 0.1 | |
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.174 | < 0.1 |
Table 1 Comparison of diurnal activity patterns of Reeves’s pheasants between different study areas
| 时间范围 Time range | 研究区 Study area | U2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 繁殖期 Breeding season | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.177 | < 0.1 |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.071 | > 0.1 | |
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.141 | > 0.1 | |
| 非繁殖期 Non-breeding season | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.190 | < 0.05* |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.092 | > 0.1 | |
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.174 | < 0.1 |
| 时间范围 Time range | 性别 Gender | 研究区 Study area | U2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 繁殖期 Breeding season | 雄性 Male | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.148 | > 0.1 |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.133 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.183 | < 0.1 | ||
| 雌性 Female | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.171 | < 0.1 | |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.052 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.225 | < 0.05* | ||
| 非繁殖期 Non-breeding season | 雄性 Male | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.132 | > 0.1 |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.061 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.157 | < 0.1 | ||
| 雌性 Female | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.203 | < 0.05* | |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.046 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.203 | < 0.05* |
Table 2 Comparison of diurnal activity patterns of same gender Reeves’s pheasants between different study areas in different time periods
| 时间范围 Time range | 性别 Gender | 研究区 Study area | U2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 繁殖期 Breeding season | 雄性 Male | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.148 | > 0.1 |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.133 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.183 | < 0.1 | ||
| 雌性 Female | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.171 | < 0.1 | |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.052 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.225 | < 0.05* | ||
| 非繁殖期 Non-breeding season | 雄性 Male | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.132 | > 0.1 |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.061 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.157 | < 0.1 | ||
| 雌性 Female | 中华山 vs. 连康山 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.203 | < 0.05* | |
| 中华山 vs. 平靖关 Zhonghua Mountain vs. Pingjingguan | 0.046 | > 0.1 | ||
| 平靖关 vs. 连康山 Pingjingguan vs. Liankang Mountain | 0.203 | < 0.05* |
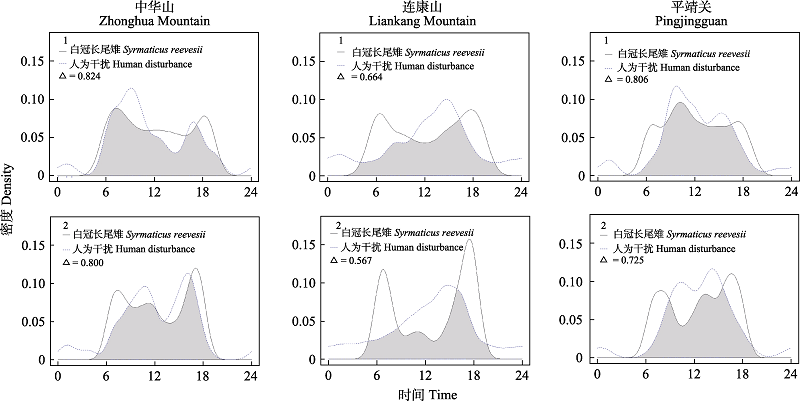
Fig. 4 Diurnal activity patterns of Reeves’s pheasants and human disturbance during breeding and non-breeding seasons. 1 represents breeding season, and 2 represents non-breeding season. The shadow areas show the overlap of diurnal activity patterns between Reeves’s pheasants and human disturbance.
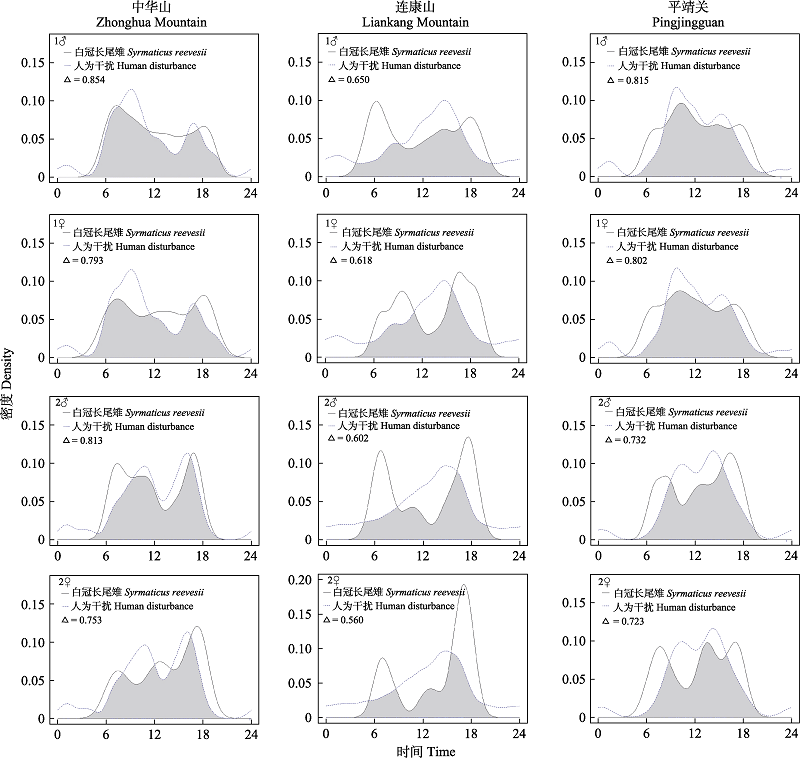
Fig. 5 Diurnal activity patterns of male and female Reeves’s pheasants and human disturbance during breeding and non-breeding seasons. 1♂ represents the males in breeding season, 1♀ represents the females in breeding season, 2♂ represents the males in non-breeding season, and 2♀ represents the females in non-breeding season. The shadow areas show the overlap of diurnal activity patterns between Reeves’s pheasants and human disturbance.
| [1] | Azlan JM, Sharma DSK (2006) The diversity and activity patterns of wild felids in a secondary forest in Peninsular Malaysia. Oryx, 40, 36-41. |
| [2] | Brodie JF, Pangau-Adam M (2015) Human impacts on two endemic cassowary species in Indonesian New Guinea. Oryx, 51, 354-360. |
| [3] | Chen LJ, Shu ZF, Xiao ZS (2019) Application of camera-trapping data to study daily activity patterns of Galliformes in Guangdong Chebaling National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 27, 266-272. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈立军, 束祖飞, 肖治术 (2019) 应用红外相机数据研究动物活动节律——以广东车八岭保护区鸡形目鸟类为例. 生物多样性, 27, 266-272.] | |
| [4] | Cheng SL, Lei P, Hu EY, Yuan RB, Zou SC (2015) Diurnal behavior of Cabot’s tragopan (Tragopan caboti) recorded by infrared-triggered cameras in Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 50, 695-702. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程松林, 雷平, 胡尔夷, 袁荣斌, 邹思成 (2015) 江西武夷山自然保护区黄腹角雉昼间行为的红外相机监测. 动物学杂志, 50, 695-702.] | |
| [5] | CITES (2019) Consideration of Proposals for Amendment of Appendices I and II. https://www.cites.org/eng/app/ appendices.php. (accessed on 2019-12-02) |
| [6] | Doherty TS, Dickman CR, Glen AS, Newsome TM, Nimmo DG, Ritchie EG, Vanak AT, Wirsing AJ (2017) The global impacts of domestic dogs on threatened vertebrates. Biological Conservation, 210, 56-59. |
| [7] | Fattorini N, Brunetti C, Baruzzi C, Chiatante G, Lovari S, Ferretti F (2019) Temporal variation in foraging activity and grouping patterns in a mountain-dwelling herbivore: Environmental and endogenous drivers. Behavioural Processes, 167, 1-9. |
| [8] |
Gaynor KM, Hojnowski CE, Carter NH, Brashares JS (2018) The influence of human disturbance on wildlife nocturnality. Science, 360, 1232-1235.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Greenberg JR, Holekamp KE (2017) Human disturbance affects personality development in a wild carnivore. Animal Behaviour, 132, 303-312. |
| [10] | Hughes J, Macdonald DW (2013) A review of the interactions between free-roaming domestic dogs and wildlife. Biological Conservation, 157, 341-351. |
| [11] | IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) (2019) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species https://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 2019-12-02) |
| [12] |
Karanth KU, Srivathsa A, Vasudev D, Puri M, Parameshwaran R, Kumar NS (2017) Spatio-temporal interactions facilitate large carnivore sympatry across a resource gradient. Biological Sciences, 284, 20161860.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Kovach WL (2012) Oriana—Circular Statistics for Windows, version. 4.02. Kovach Computing Services, Pentraeth, UK. |
| [14] | Lee HJ, Ha JW, Park SJ, Kim WY, Cha JY, Park JY, Choi SS, Chung CU, Oh HS (2019) A study on the analysis of mammals’ activity patterns and the effect of human hiker interference using camera trapping. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity, 12, 57-62. |
| [15] | Li S, Mcshea WJ, Wang DJ, Shao LK, Shi XG (2010) The use of infrared-triggered cameras for surveying Phasianids in Sichuan Province, China. Ibis, 152, 299-309. |
| [16] | Luo G, Yang C, Zhou H, Seitz M, Wu Y, Ran J (2019) Habitat use and diel activity pattern of the Tibetan snowcock (Tetraogallus tibetanus): A case study using camera traps for surveying high-elevation bird species. Avian Research, 10, 23-31. |
| [17] |
Markovchick-Nicholls L, Regan HM, Deutschman DH, Widyanata A, Martin B, Noreke L, Hunt TA (2008) Relationships between human disturbance and wildlife land use in urban habitat fragments. Conservation Biology, 22, 99-109.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Moretti L, Hentrup M, Kotrschal K, Range F (2015) The influence of relationships on neophobia and exploration in wolves and dogs. Animal Behaviour, 107, 159-173. |
| [19] | Ngoprasert D, Lynam AJ, Gale GA (2017) Effects of temporary closure of a national park on leopard movement and behaviour in tropical Asia. Mammalian Biology, 82, 65-73. |
| [20] | Nix JH, Howell RG, Hall LK, McMillan BR (2018) The influence of periodic increases of human activity on crepuscular and nocturnal mammals: Testing the weekend effect. Behavioural Processes, 146, 16-21. |
| [21] | O’Brien TG, Kinnaird MF, Wibisono HT (2003) Crouching tigers, hidden prey: Sumatran tiger and prey populations in a tropical forest landscape. Animal Conservation, 6, 131-139. |
| [22] | O’Connell AF, Nichols JD, Karanth KU (2011) Camera Traps in Animal Ecology: Methods and Analyses. Springer, New York, USA. |
| [23] | Oberosler V, Groff C, Iemma A, Pedrini P, Rovero F (2017) The influence of human disturbance on occupancy and activity patterns of mammals in the Italian Alps from systematic camera trapping. Mammalian Biology, 87, 50-61. |
| [24] | Reilly ML, Tobler MW, Sonderegger DL, Beier P (2017) Spatial and temporal response of wildlife to recreational activities in the San Francisco Bay ecoregion. Biological Conservation, 207, 117-126. |
| [25] | Ridout MS, Linkie M (2009) Estimating overlap of daily activity patterns from camera trap data. Journal of Agricultural Biological and Environmental Statistics, 14, 322-337. |
| [26] | Rowcliffe JM, Kays R, Kranstauber B, Carbone C, Jansen PA (2014) Quantifying levels of animal activity using camera trap data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 1170-1179. |
| [27] | Roy S, Ghoshal A, Bijoor A, Suryawanshi K (2019) Distribution and activity pattern of stone marten Martes foina in relation to prey and predators. Mammalian Biology, 96, 110-117. |
| [28] | Shamoon H, Maor R, Saltz D, Dayan T (2018) Increased mammal nocturnality in agricultural landscapes results in fragmentation due to cascading effects. Biological Conservation, 226, 32-41. |
| [29] | Sun QH, Zhang ZW, Zheng GM, Zhang KY, Ruan XF, Zhu JG (2003) Ranging behaviour of territorial male Reeves’s pheasants in the breeding season. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 49, 318-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙全辉, 张正旺, 郑光美, 张可银, 阮祥峰, 朱家贵 (2003) 繁殖期白冠长尾雉占区雄鸟的活动区. 动物学报, 49, 318-324.] | |
| [30] | Sun RY (2001) Principles of Animal Ecology, 3rd edn. Beijing Normal University Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 孙儒泳 (2001) 动物生态学 (第三版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] | Van Doormaal N, Ohashi H, Koike S, Kaji K (2015) Influence of human activities on the activity patterns of Japanese sika deer (Cervus nippon) and wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Central Japan. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 61, 517-527. |
| [32] | Wang QY, Zhao YZ, Luo X, Hua JQ, Li Z, Xu JL (2016) Potential nest predators of Syrmaticus reevesii based on camera traps and artificial nests. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 1968-1974. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王秦韵, 赵玉泽, 罗旭, 华俊钦, 李忠, 徐基良 (2016) 基于红外相机技术和人工巢试验分析白冠长尾雉巢潜在捕食者. 应用生态学报, 27, 1968-1974.] | |
| [33] | Wang ZX (2017) The Comprehensive Scientific Survey Report in Zhonghua Mountain Birds Nature Reserve. Hubei University Press, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [ 汪正祥 (2017) 湖北中华山鸟类自然保护区综合科学考察报告. 湖北大学出版社, 武汉.] | |
| [34] | Xue GQ (2016) Scientific Expedition of Liankang Mountain National Nature Reserve in Henan Province. Northeast Normal University Press, Changchun. (in Chinese) |
| [ 薛国庆 (2016) 河南连康山国家级自然保护区科学考察集. 东北师范大学出版社, 长春.] | |
| [35] | Yu JP, Qian HY, Chen XN, Li S, Shen XL (2017) Daily activity pattern of silver pheasant (Lophura nycthemera) using camera-traps. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 52, 937-944. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余建平, 钱海源, 陈小南, 李晟, 申小莉 (2017) 基于红外相机技术的白鹇日活动节律研究. 动物学杂志, 52, 937-944.] | |
| [36] | Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical Analysis, 4th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey. |
| [37] | Zhang JD, Hull V, Ouyang ZY, Li RG, Connor T, Yang HB, Zhang ZJ, Silet B, Zhang HM, Liu JG (2017) Divergent responses of sympatric species to livestock encroachment at fine spatiotemporal scales. Biological Conservation, 209, 119-129. |
| [38] | Zhang SS, Bao YX, Wang YN, Fang PF, Ye B (2012) Activity rhythms of black muntjac (Muntiacus crinifrom) revealed with infrared camera. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 32, 368-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 章书声, 鲍毅新, 王艳妮, 方平福, 叶彬 (2012) 基于红外相机技术的黑麂活动节律. 兽类学报, 32, 368-372.] | |
| [39] |
Zhao YZ, Wang ZC, Xu JL, Luo X, An LD (2013) Activity rhythm and behavioral time budgets of wild Reeves’s pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesii) using infrared camera. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 6021-6027. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 赵玉泽, 王志臣, 徐基良, 罗旭, 安丽丹 (2013) 利用红外照相技术分析野生白冠长尾雉活动节律及时间分配. 生态学报, 33, 6021-6027.] | |
| [40] | Zheng GM (2015) Pheasants in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑光美 (2015) 中国雉类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [41] | Zheng GM (2017) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录 (第三版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Zhou CF, Xu JL, Zhang ZW (2015) Dramatic decline of the vulnerable Reeves’s pheasant Syrmaticus reevesii, endemic to central China. Oryx, 49, 529-534. |
| [1] | Jiaqi Li, Yidi Feng, Lei Wang, Penyan Pan, Xiaoru Liu, Xueyang Li, Yihan Wang, Fang Wang. Diet and habitat selection of raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Shanghai, a rapidly urbanizing megacity in eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [2] | Xiaofan Shang, Jian Zhang, Haojie Gao, Weipeng Ku, Yuke Bi, Xiupeng Li, Enrong Yan. Island area and climate jointly impact seed plant richness patterns across the Zhoushan Archipelago [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [3] | Jinyu Yang, Wanlong Zhu. Impact of habitat variation and human activities on small mammal community structure and diversity in Diannan Town, Jianchuan County, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23246-. |
| [4] | Chaodan Guo, Jinfang Zhu, Xiaoyan Liu, Caiyun Zhao, Junsheng Li. Contrasting biodiversity of invasive herbs inside and outside nature reserves in Guizhou [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 596-604. |
| [5] | Zhi Yao, Jun Guo, Chenzhong Jin, Yongbo Liu. Endangered mechanisms for the first-class protected Wild Plants with Extremely Small Populations in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [6] | Ying Xiang, Suqun Liu, Xinglong Huang, Zhixiao Liu, Youxiang Zhang, Fangzhou Ma. Butterfly diversity and its influencing factors in the Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve and its surrounding area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(8): 940-949. |
| [7] | Min Deng, Mingwei Liao, Chenbin Wang, Chengqing Liao, Zujie Kang, Fangzhou Ma, Guohua Huang. Influence of human disturbance on butterfly diversity in the Hupingshan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(8): 931-939. |
| [8] | Xinhui Li,Yanhong Liu,Ye Liu,Yue Xu,Yang Yang,Zehao Shen. Impacts of geographical distances and environmental differences on the beta diversity of plant communities in the dry-hot valley of the Yuanjiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(4): 399-406. |
| [9] | Zhongqiu Li. Datasets of vigilance behavior for three rare ungulates [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(12): 1335-1340. |
| [10] | Wen Wu, Yuehui Li, Yuanman Hu, Long Chen, Yue Li, Zeming Li, Zhiwen Nie, Tan Chen. Suitable winter habitat for Cervus elaphus on the southern slope of the Lesser Xing’an Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(1): 20-29. |
| [11] | Wenhong Xiao, Limin Feng, Xiaodan Zhao, Haitao Yang, Hailong Dou, Yanchao Cheng, Pu Mou, Tianming Wang, Jianping Ge. Distribution and abundance of Amur tiger, Amur leopard and their ungulate prey in Hunchun National Nature Reserve, Jilin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(6): 717-724. |
| [12] | Yunzhu Liu,Linlu Shi,Hairui Duo,Boyong Peng,Cai Lü,Yi Zhu,Guangchun Lei. Disturbance-driven changes to landscape patterns and responses of waterbirds at West Dongting Lake, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(6): 666-676. |
| [13] | Fengying Zheng,Guanglong Qiu,Hangqing Fan,Wei Zhang. Diversity, distribution and conservation of Chinese seagrass species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(5): 517-526. |
| [14] | Yang Liu, Jian Zhang, Wanqin Yang. Responses of alpine biodiversity to climate change [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(1): 88-96. |
| [15] | Yuewei Yang, Guirong Xia, Ping Ding, Renfan Ma, Yuzhao Chen. Species diversity of water birds in the wetland of Yueqing Bay, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2005, 13(6): 507-513. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()