



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 22295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022295 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022295
黄永江1,*( ), 苏涛2, 朱海3,4, 贾林波1, 胡瑾瑾1, 纪运恒1, 周浙昆1,2
), 苏涛2, 朱海3,4, 贾林波1, 胡瑾瑾1, 纪运恒1, 周浙昆1,2
收稿日期:2022-06-01
接受日期:2022-08-12
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-08-19
通讯作者:
黄永江
作者简介: E-mail: huangyongjiang@mail.kib.ac.cn基金资助:
Yongjiang Huang1,*( ), Tao Su2, Hai Zhu3,4, Linbo Jia1, Jinjin Hu1, Yunheng Ji1, Zhekun Zhou1,2
), Tao Su2, Hai Zhu3,4, Linbo Jia1, Jinjin Hu1, Yunheng Ji1, Zhekun Zhou1,2
Received:2022-06-01
Accepted:2022-08-12
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-08-19
Contact:
Yongjiang Huang
摘要:
横断山南段复杂的地形地貌和多样的气候环境造就了高度丰富的植被多样性。这种植被多样性的演化与形成是植物学、生态学等领域共同关注的科学问题, 而植物化石是回答这一科学问题的重要媒介。本文基于横断山南段的9个上新世化石植物群, 根据其植物组成和优势成分, 分析其所代表的植被类型, 总结了该地区上新世的植被多样性与空间分布, 并结合古环境研究资料, 探讨该地区植被多样性的兴起, 植被分布格局的形成, 及其与环境变迁之间的关联。结果显示, 横断山南段在上新世时期已经具有了多种植被类型, 包括亚热带常绿阔叶林、亚热带落叶阔叶林、硬叶常绿阔叶林、针阔叶混交林、灌丛草地等, 体现了丰富的植被多样性; 植被类型从南面的偏热性植被向北面的偏温性植被逐渐转变, 反映了当时随纬度变化的海拔梯度, 植被类型与分布呈现出与现在高度相似的格局。同时, 小范围内也具有适应于不同气候的植被类型, 反映了当地较大的海拔落差, 可能与高大山体的存在有着密切关联。我们推测, 横断山南段现在丰富的植被多样性和随纬度变化的植被面貌最晚在上新世就已基本形成, 但形成时间是否更早则需要更多、更老化石植物群的发现与研究。
黄永江, 苏涛, 朱海, 贾林波, 胡瑾瑾, 纪运恒, 周浙昆 (2022) 横断山南段上新世的植被多样性与分布格局. 生物多样性, 30, 22295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022295.
Yongjiang Huang, Tao Su, Hai Zhu, Linbo Jia, Jinjin Hu, Yunheng Ji, Zhekun Zhou (2022) Vegetation diversity and distribution in the Pliocene of the southern Hengduan Mountains region. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022295.
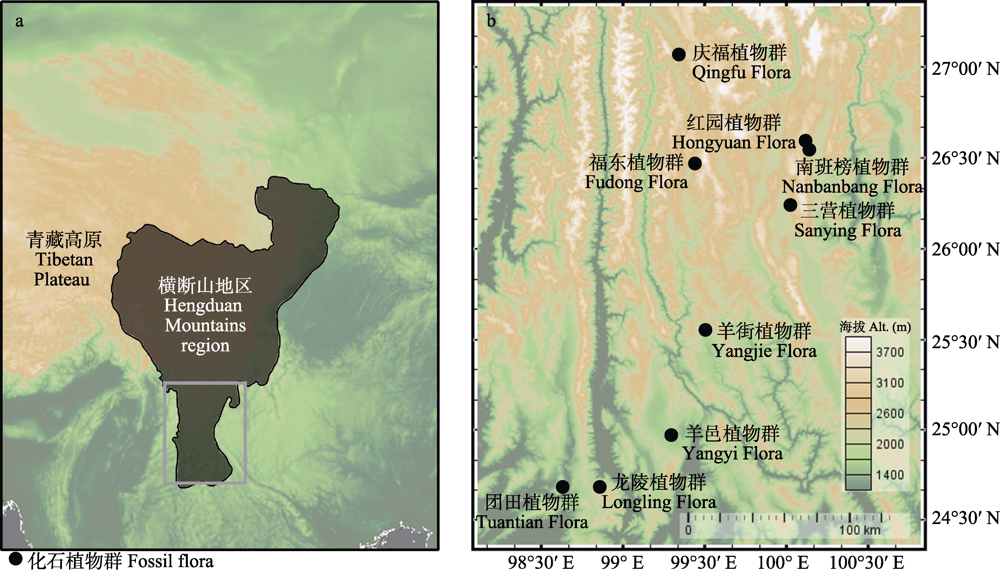
图1 横断山南段上新世化石植物群的地理分布。a: 横断山的地理位置与范围; b: 横断山南段上新世化石植物群的空间分布。地图基于GeoMapApp 3.6.10 (Ryan et al, 2009)生成。
Fig. 1 Maps showing the distribution of Pliocene fossil floras in the southern Hengduan Mountains region. a, Geographic position and range of the Hengduan Mountains region; b, Spatial distribution of Pliocene fossil floras in the southern Hengduan Mountains region. The maps were created using GeoMapApp 3.6.10 (Ryan et al, 2009).
| 植物群名称 Flora | 地理位置 Location | 经纬度 Geographical coordinate | 海拔 Altitude | 地层 Stratigraphic horizon | 化石类型 Fossil types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 庆福植物群 Qingfu Flora | 维西县永春乡 Yongchun, Weixi County | 99°21′ E, 27°05′ N | 2,476 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
| 红园植物群 Hongyuan Flora | 鹤庆县鹤庆盆地西南 Southwestern Heqing Basin, Heqing County | 100°08′ E, 26°34′ N | 2,291 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
| 南班榜植物 Nanbanbang Flora | 鹤庆县鹤庆盆地西南 Southwestern Heqing Basin, Heqing County | 100°10′ E, 26°31′ N | 2,200 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 果实、种子 Fruit and seed |
| 福东植物群 Fudong Flora | 兰坪县金顶镇 Jinding, Lanping County | 99°26′ E, 26°28′ N | 2,740 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片、果实、种子、炭屑 Leaf, fruit, seed, and charcoal |
| 三营植物群 Sanying Flora | 洱源县三营镇 Sanying, Eryuan County | 99°49′ E, 26°00′ N | 2,100 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片、孢粉 Leaf and spore/pollen |
| 羊街植物群 Yangjie Flora | 永平县永平盆地北 Northern Yongping Basin, Yongping County | 99°31′ E, 25°31′ N | 1,715 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
| 羊邑植物群 Yangyi Flora | 保山市保山盆地东南 Southeastern Baoshan Basin, Baoshan City | 99°15′ E, 24°57′ N | 1,650 m | 羊邑组 Yangyi Formation | 叶片、孢粉 Leaf and spore/pollen |
| 龙陵植物群 Longling Flora | 龙陵县龙陵煤矿 Longling Coal Mine, Longling County | 98°50′ E, 24°41′ N | 1,840 m | 羊邑组 Yangyi Formation | 孢粉 Spore/pollen |
| 团田植物群 Tuantian Flora | 腾冲县团田盆地 Tuantian Basin, Tengchong County | 98°38′ E, 24°41′ N | 1,250 m | 芒棒组 Mangbang Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
表1 横断山南段上新世化石植物群及其地理位置、地层划分与化石类型
Table 1 Pliocene fossil floras in the southern Hengduan Mountains region and their geographic location, stratigraphic horizon and fossil types
| 植物群名称 Flora | 地理位置 Location | 经纬度 Geographical coordinate | 海拔 Altitude | 地层 Stratigraphic horizon | 化石类型 Fossil types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 庆福植物群 Qingfu Flora | 维西县永春乡 Yongchun, Weixi County | 99°21′ E, 27°05′ N | 2,476 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
| 红园植物群 Hongyuan Flora | 鹤庆县鹤庆盆地西南 Southwestern Heqing Basin, Heqing County | 100°08′ E, 26°34′ N | 2,291 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
| 南班榜植物 Nanbanbang Flora | 鹤庆县鹤庆盆地西南 Southwestern Heqing Basin, Heqing County | 100°10′ E, 26°31′ N | 2,200 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 果实、种子 Fruit and seed |
| 福东植物群 Fudong Flora | 兰坪县金顶镇 Jinding, Lanping County | 99°26′ E, 26°28′ N | 2,740 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片、果实、种子、炭屑 Leaf, fruit, seed, and charcoal |
| 三营植物群 Sanying Flora | 洱源县三营镇 Sanying, Eryuan County | 99°49′ E, 26°00′ N | 2,100 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片、孢粉 Leaf and spore/pollen |
| 羊街植物群 Yangjie Flora | 永平县永平盆地北 Northern Yongping Basin, Yongping County | 99°31′ E, 25°31′ N | 1,715 m | 三营组 Sanying Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
| 羊邑植物群 Yangyi Flora | 保山市保山盆地东南 Southeastern Baoshan Basin, Baoshan City | 99°15′ E, 24°57′ N | 1,650 m | 羊邑组 Yangyi Formation | 叶片、孢粉 Leaf and spore/pollen |
| 龙陵植物群 Longling Flora | 龙陵县龙陵煤矿 Longling Coal Mine, Longling County | 98°50′ E, 24°41′ N | 1,840 m | 羊邑组 Yangyi Formation | 孢粉 Spore/pollen |
| 团田植物群 Tuantian Flora | 腾冲县团田盆地 Tuantian Basin, Tengchong County | 98°38′ E, 24°41′ N | 1,250 m | 芒棒组 Mangbang Formation | 叶片 Leaf |
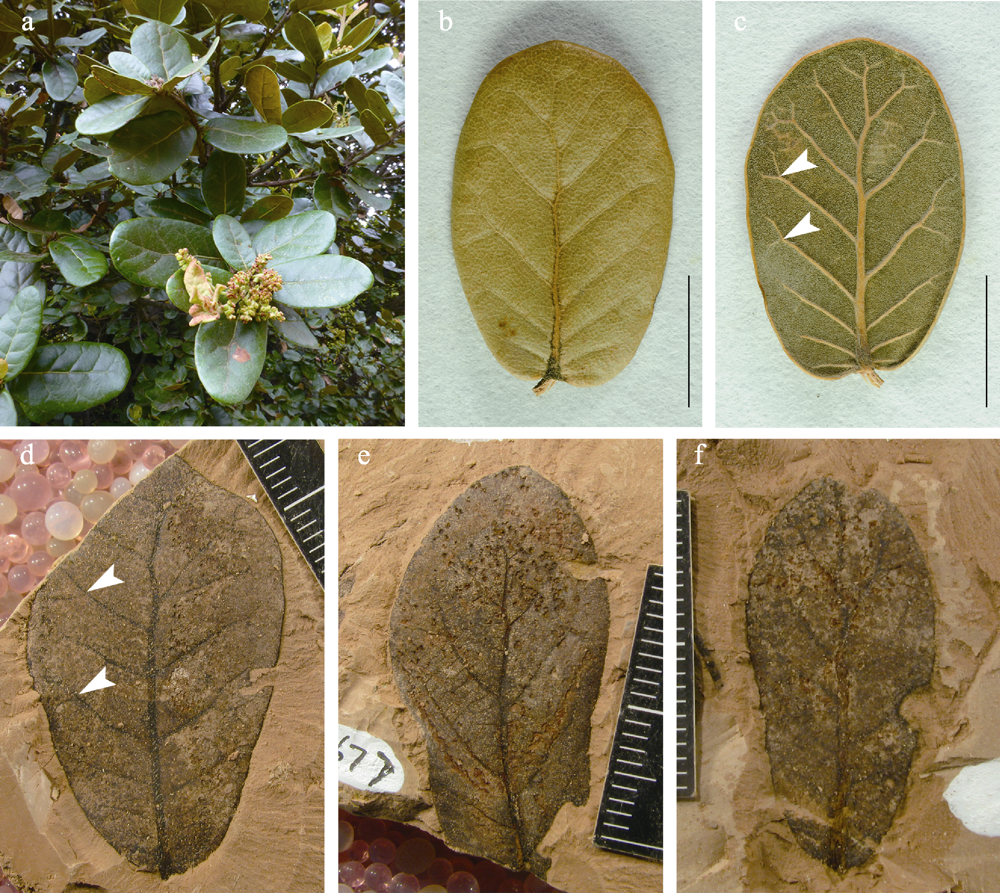

图2 高山栎组植物的现生和化石叶片(比例尺 = 1 cm)。a: 高山栎组植物的枝条(摄于西藏林芝); b, c: 高山栎组植物现生叶片的正反面及其近叶缘处分叉的二级脉(箭头所示); d-f: 上新世福东植物群的高山栎组叶片化石及其近叶缘处分叉的二级脉(箭头所示)。
Fig. 2 Extant and fossil leaves of Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (scale bars = 1 cm). a, Leafy twigs (picture taken in Linzhi, Xizang); b, c, An extant leaf, showing the upper and lower surfaces, respectively, with the secondary veins bifurcating near the leaf margin (arrows); d-f, Fossil leaves from the Pliocene Fudong flora, with the secondary veins bifurcating near the leaf margin (arrows).
| 植物群名称 Flora | 优势成分 Dominant element | 植被类型 Vegetation type | 主要相关文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 庆福植物群 Qingfu Flora | 高山栎组 Quercus sect. Heterobalanus | 硬叶常绿阔叶林 Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest | 2015 |
| 红园植物群 Hongyuan Flora | 高山栎组 Quercus sect. Heterobalanus | 硬叶常绿阔叶林 Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest | 2016; |
| 南班榜植物群 Nanbanbang Flora | 松科、蓼属、悬钩子属、黄芪属、苔草属等 Pinaceae, Polygonum, Rubus, Astragalus, Carex etc. | 灌丛草地、针阔叶混交林 Shrubby meadow, mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest | 2022 |
| 福东植物群 Fudong Flora | 高山栎组(叶片); 松科(炭屑) Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (leaves); Pinaceae (charcoals) | 硬叶常绿阔叶林(叶片); 针阔叶混交林(炭屑) Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest (leaves); mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest (charcoals) | 2021 |
| 三营植物群 Sanying Flora | 高山栎组(叶片); 松科、栎属、桦木科等(孢粉) Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (leaves); Pinaceae, Quercus, Betulaceae (spore/pollen) | 硬叶常绿阔叶林(叶片); 针阔叶混交林(孢粉) Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest (leaves); mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest (spore/pollen) | 2019 |
| 羊街植物群 Yangjie Flora | 高山栎组 Quercus sect. Heterobalanus | 硬叶常绿阔叶林 Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest | 2015 |
| 羊邑植物群 Yangyi Flora | 高山栎组(叶片); 桦木科、壳斗科、金缕梅科等(孢粉) Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (leaves); Betulaceae, Fagaceae, Hamamelidaceae etc. (spore/pollen) | 硬叶常绿阔叶林(叶片); 亚热带常绿阔叶林、亚热带落叶阔叶林(孢粉) Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest (leaves); subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest, subtropical deciduous broadleaved forest (spore/pollen) | 2004a |
| 龙陵植物群 Longling Flora | 壳斗科、杜鹃花科、冬青科等 Fagaceae, Ericaceae, Aquifoliaceae etc. | 亚热带常绿阔叶林 Subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest | 2004b |
| 团田植物群 Tuantian Flora | 樟科、壳斗科、金缕梅科等 Lauraceae, Fagaceae, Hamamelidaceae etc. | 亚热带常绿阔叶林 Subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest | 2009 |
表2 横断山南段上新世化石植物群的优势成分及其所代表的植被类型
Table 2 Dominant elements and vegetation types of the Pliocene fossil floras in the southern Hengduan Mountains region
| 植物群名称 Flora | 优势成分 Dominant element | 植被类型 Vegetation type | 主要相关文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 庆福植物群 Qingfu Flora | 高山栎组 Quercus sect. Heterobalanus | 硬叶常绿阔叶林 Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest | 2015 |
| 红园植物群 Hongyuan Flora | 高山栎组 Quercus sect. Heterobalanus | 硬叶常绿阔叶林 Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest | 2016; |
| 南班榜植物群 Nanbanbang Flora | 松科、蓼属、悬钩子属、黄芪属、苔草属等 Pinaceae, Polygonum, Rubus, Astragalus, Carex etc. | 灌丛草地、针阔叶混交林 Shrubby meadow, mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest | 2022 |
| 福东植物群 Fudong Flora | 高山栎组(叶片); 松科(炭屑) Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (leaves); Pinaceae (charcoals) | 硬叶常绿阔叶林(叶片); 针阔叶混交林(炭屑) Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest (leaves); mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest (charcoals) | 2021 |
| 三营植物群 Sanying Flora | 高山栎组(叶片); 松科、栎属、桦木科等(孢粉) Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (leaves); Pinaceae, Quercus, Betulaceae (spore/pollen) | 硬叶常绿阔叶林(叶片); 针阔叶混交林(孢粉) Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest (leaves); mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest (spore/pollen) | 2019 |
| 羊街植物群 Yangjie Flora | 高山栎组 Quercus sect. Heterobalanus | 硬叶常绿阔叶林 Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest | 2015 |
| 羊邑植物群 Yangyi Flora | 高山栎组(叶片); 桦木科、壳斗科、金缕梅科等(孢粉) Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (leaves); Betulaceae, Fagaceae, Hamamelidaceae etc. (spore/pollen) | 硬叶常绿阔叶林(叶片); 亚热带常绿阔叶林、亚热带落叶阔叶林(孢粉) Sclerophyllous evergreen broadleaved forest (leaves); subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest, subtropical deciduous broadleaved forest (spore/pollen) | 2004a |
| 龙陵植物群 Longling Flora | 壳斗科、杜鹃花科、冬青科等 Fagaceae, Ericaceae, Aquifoliaceae etc. | 亚热带常绿阔叶林 Subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest | 2004b |
| 团田植物群 Tuantian Flora | 樟科、壳斗科、金缕梅科等 Lauraceae, Fagaceae, Hamamelidaceae etc. | 亚热带常绿阔叶林 Subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest | 2009 |
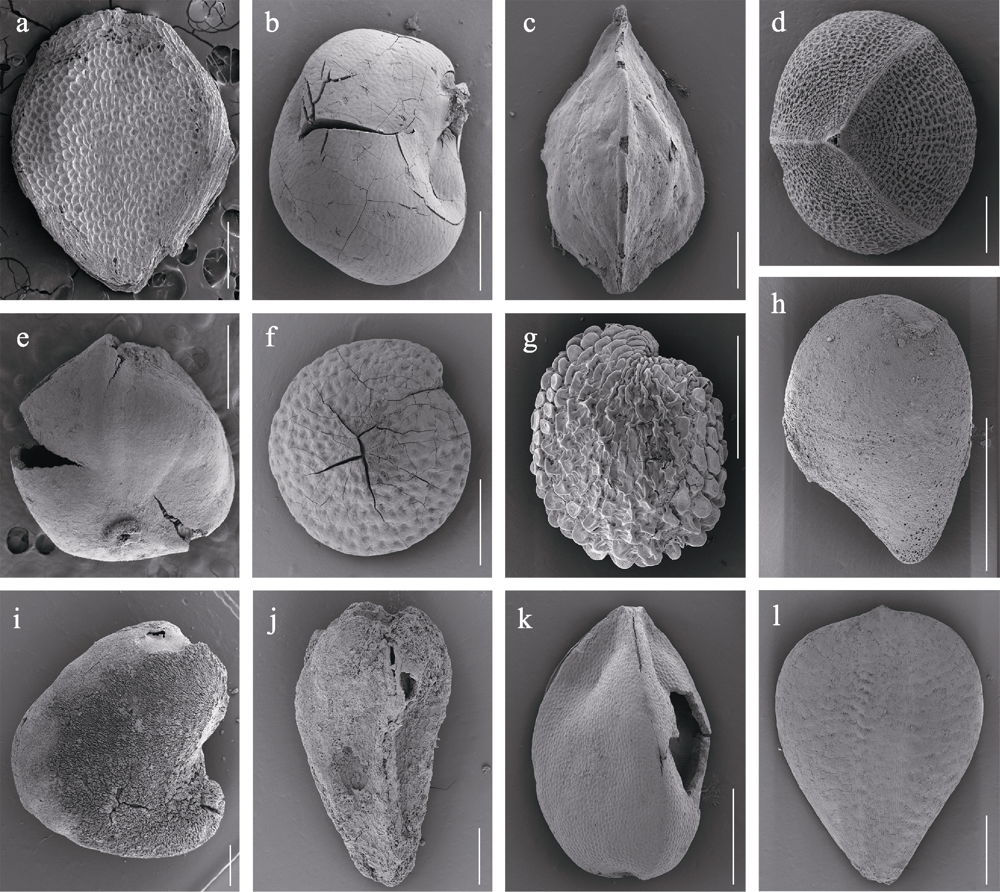
图3 上新世南班榜植物群的草本植物果实、种子化石(比例尺 = 0.5 mm)。a: 毛茛属; b: 紫菫属; c: 酸模属; d, e: 蓼属; f: 藜属; g: 繁缕属; h: 草莓属; i: 黄芪属; j: 紫菀属; k: 薹草属; l: 水葱属。b-d, h, j和l来自Huang等(2022), 并获得了出版商的使用许可。
Fig. 3 Fossil fruits and seeds of herbs from the Pliocene Nanbanbang flora (scale bars = 0.5 mm). a, Ranunculus; b, Corydalis; c, Rumex; d, e, Polygonum; f, Chenopodium; g, Stellaria; h, Fragaria; i, Astragalus; j, Aster; k, Carex; l, Schoenoplectus. Images b-d, h, j and l are based on Huang et al (2022) with the formal permission of the publisher.
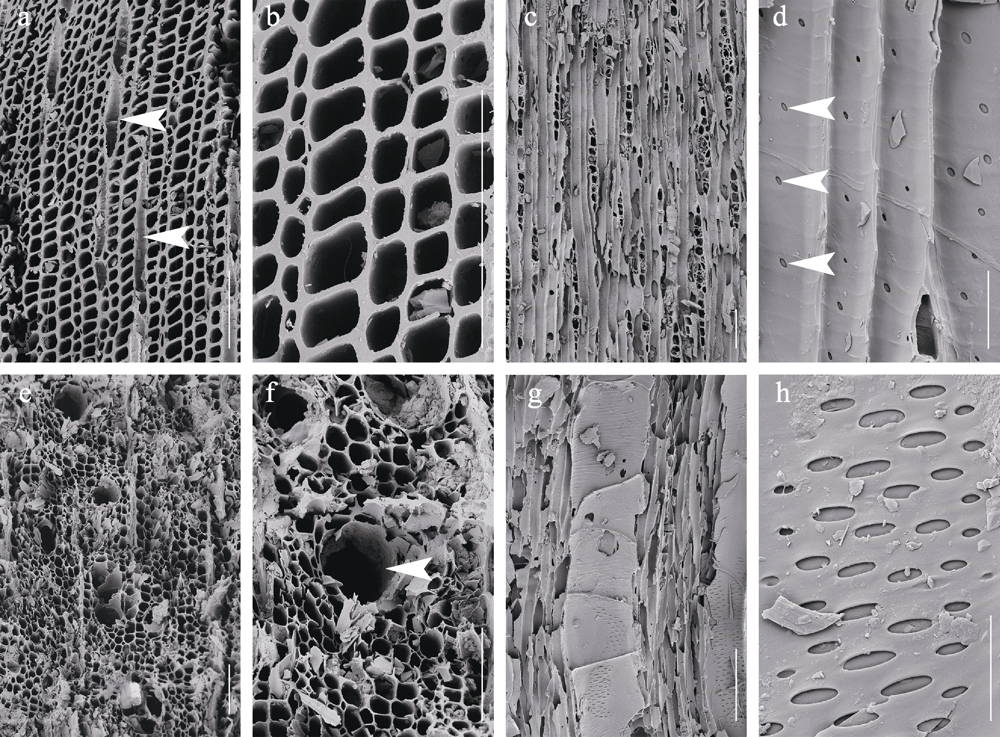
图4 上新世福东植物群的炭屑化石(比例尺: a-c, e-g, 50 μm; d, h, 10 μm)。a-d: 松柏类; a: 横切面, 显示形态、排列规则的腔隙(木纤维细胞横面观)及木射线(纵面观) (箭头所示); b: 横切面部分放大, 显示形态、排列规则的腔隙及相互联合的细胞壁; c: 纵切面, 显示木纤维细胞(纵面观)、管胞(纵面观)和单列细胞的木射线(横面观); d: 纵切面部分放大, 显示管胞壁上的单列圆形纹孔(箭头所示); e-h: 非松柏类; e: 横切面, 显示不规则的腔隙(导管细胞、木纤维细胞和薄壁细胞); f: 横切面部分放大, 显示导管的横面观(箭头所示); g: 纵切面, 显示单个导管的纵面观; h: 纵切面部分放大, 显示导管细胞壁上不规则排列的纹孔。
Fig. 4 Fossil charcoals from the Pliocene Fudong flora (scale bars = 50 μm (a-c, e-g); 10 μm (d, h)). a-d, Conifers; a, Transverse section, showing the homogenous, regular lumina (xylem cells; transverse view) and xylem rays (longitudinal view) (arrows); b, Amplified view of the transverse section, showing the regular xylem cells and homogenized adjacent cell walls; c, Longitudinal section, showing the xylem cells (longitudinal view), tracheid cells (longitudinal view) and uniseriate xylem rays (transverse view); d, Amplified view of the longitudinal section, showing the uniseriate, circular pits (arrows) on the tracheid wall; e-h, Non-conifers; e, Transverse section, showing the heterogenous, irregular lumina (vessel, xylem and parenchyma); f, Amplified view of the transverse section, showing the transverse view of a vessel (arrow); g, Longitudinal section, showing the longitudinal view of a vessel; h, Amplified view of the longitudinal section, showing alternative pits on the vessel cell wall.
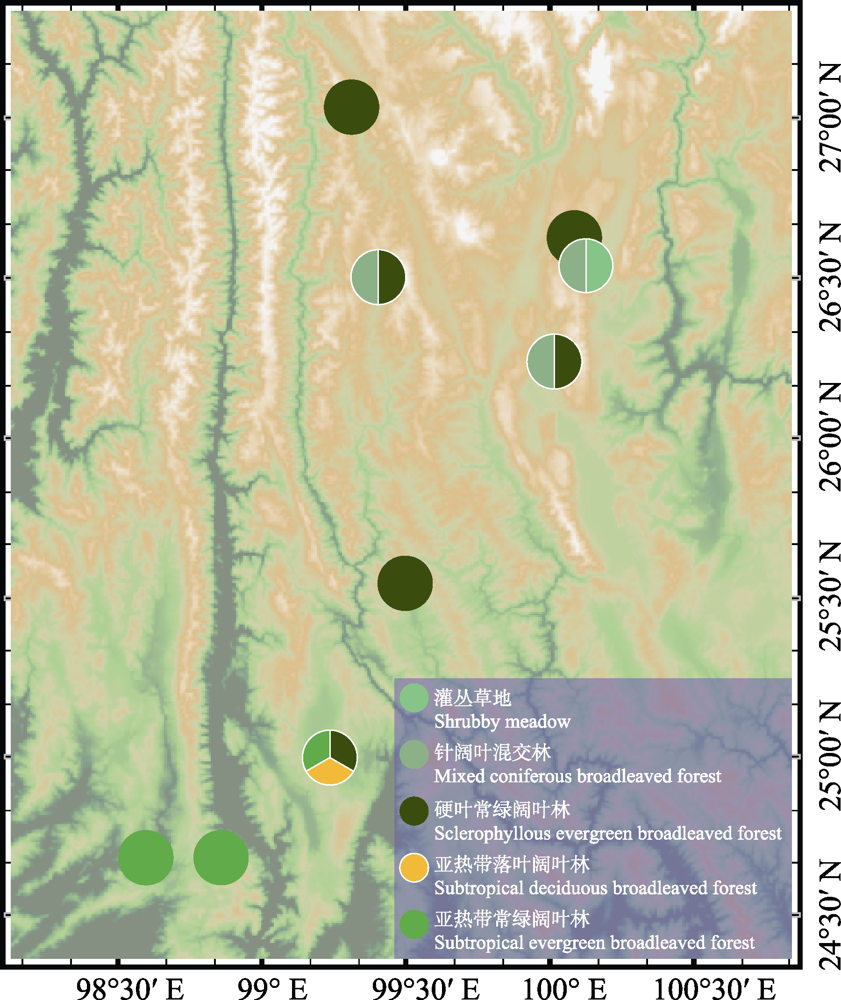
图5 上新世横断山南段的植被分布。地图基于GeoMapApp 3.6.10 (Ryan et al, 2009)生成。
Fig. 5 Vegetation distribution in the Pliocene of the southern Hengduan Mountains region. The map was created using GeoMapApp 3.6.10 (Ryan et al, 2009).
| [1] | Boufford DE (2014) Biodiversity hotspot: China’s Hengduan Mountains. Arnoldia, 72, 24-35. |
| [2] | Clark MK, House MA, Royden LH, Whipple KX, Burchfiel BC, Zhang X, Tang W (2005) Late Cenozoic uplift of southeastern Tibet. Geology, 33, 525-528. |
| [3] | Clark MK, Royden LH (2000) Topographic ooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow. Geology, 28, 703-706. |
| [4] | Ding WN, Ree RH, Spicer RA, Xing YW (2020) Ancient orogenic and monsoon-driven assembly of the world’s richest temperate alpine flora. Science, 369, 578-581. |
| [5] |
Feng L, Zheng QJ, Qian ZQ, Yang J, Zhang YP, Li ZH, Zhao GF (2016) Genetic structure and evolutionary history of three alpine sclerophyllous oaks in East Himalaya- Hengduan Mountains and adjacent regions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1688.
PMID |
| [6] | Ge HR, Li DY (1999) Cenozoic Coal-Bearing Basins and Coal-Forming Regularity in West Yunnan. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [戈宏儒, 李代芸 (1999) 云南西部新生代含煤盆地及聚煤规律. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [7] |
Harrison T, Ji XP, Su D (2002) On the systematic status of the late Neogene hominoids from Yunnan Province, China. Journal of Human Evolution, 43, 207-227.
PMID |
| [8] | He YL, Li N, Wang ZX, Wang HF, Yang GL, Xiao L, Wu JY, Sun BN (2014) Quercus yangyiensis sp. nov. from the late Pliocene of Baoshan, Yunnan and its paleoclimatic significance. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 88, 738-747. |
| [9] | Hoke GD, Jing LZ, Hren MT, Wissink GK, Garzione CN (2014) Stable isotopes reveal high southeast Tibetan Plateau margin since the Paleogene. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 394, 270-278. |
| [10] | Hu JJ, Xing YW, Turkington R, Jacques FMB, Su T, Huang YJ, Zhou ZK (2015) A new positive relationship between pCO2 and stomatal frequency in Quercus guyavifolia (Fagaceae): A potential proxy for palaeo-CO2 levels. Annals of Botany, 115, 777-788. |
| [11] | Huang HS, Hu JJ, Su T, Zhou ZK (2016) The occurrence of Quercus heqingensis n. sp. and its application to palaeo-CO2 estimates. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61, 1354-1364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄华生, 胡瑾瑾, 苏涛, 周浙昆 (2016) 鹤庆栎(Quercus heqingensis n. sp.)的发现及其在古大气CO2浓度重建中的应用. 科学通报, 61, 1354-1364.] | |
| [12] | Huang HS, Su T, Zhou ZK (2018) Fossil leaves of Buxus (Buxaceae) from the upper Pliocene of Yunnan, SW China. Palaeoworld, 27, 271-281. |
| [13] | Huang YJ (2012) Late Pliocene Fudong Flora in Lanping, Yunnan and Neogene Paleoclimate in Hengduan Mountains. PhD Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄永江 (2012) 云南兰坪晚上新世福东植物群及横断山新近纪的古气候. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院大学, 北京.] | |
| [14] | Huang YJ, Chen WY, Jacques FMB, Liu YS, Utescher T, Su T, Ferguson DK, Zhou ZK (2015) Late Pliocene temperatures and their spatial variation at the southeastern border of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111, 44-53. |
| [15] | Huang YJ, Jacques FMB, Liu YS, Su T, Xing YW, Xiao XH, Zhou ZK (2012) New fossil endocarps of Sambucus (Adoxaceae) from the upper Pliocene in SW China. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 171, 152-163. |
| [16] | Huang YJ, Jia LB, Su T, Zhu H, Momohara A, Gu ZJ, Zhou ZK (2020) A warm-temperate forest of mixed coniferous type from the upper Pliocene Sanying Formation (southeastern edge of Tibetan Plateau) and its implications for palaeoecology and palaeoaltimetry. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 538, 109486. |
| [17] | Huang YJ, Jia LB, Wang Q, Mosbrugger V, Utescher T, Su T, Zhou ZK (2016a) Cenozoic plant diversity of Yunnan: A review. Plant Diversity, 38, 271-282. |
| [18] | Huang YJ, Shen H, Jia LB, Li SF, Su T, Nam GS, Zhu H, Zhou ZK (2021) Macroscopic fossil charcoals as proxy of a local fire linked to conifer-rich forest from the late Pliocene of northwestern Yunnan, Southwest China. Palaeoworld, 30, 551-561. |
| [19] | Huang YJ, Su T, Zhou ZK (2016b) Late Pliocene diversity and distribution of Drynaria (Polypodiaceae) in western Yunnan explained by forest vegetation and humid climates. Plant Diversity, 38, 194-200. |
| [20] |
Huang YJ, Zhu H, Momohara A, Jia LB, Zhou ZK (2019) Fruit fossils of Rosoideae (Rosaceae) from the late Pliocene of northwestern Yunnan, Southwest China. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 57, 180-189.
DOI |
| [21] |
Huang YJ, Zhu H, Su T, Spicer RA, Hu JJ, Jia LB, Zhou ZK (2022) Rise of herbaceous diversity at the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: First insight from fossils. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 60, 1109-1123.
DOI |
| [22] | Jacques FMB, Su T, Spicer RA, Xing YW, Huang YJ, Zhou ZK (2014) Late Miocene southwestern Chinese floristic diversity shaped by the southeastern uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 411, 208-215. |
| [23] | Ji XP, Harrison T, Su D, Xue SR (2004) On the taxonomy of late Neogene hominids from Yunnan Province, China. Yunnan Geology, 23, 17-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吉学平, Harrison T, Su D, 薛顺荣 (2004) 云南古猿系统分类研究新进展. 云南地质, 23, 17-29.] | |
| [24] | Jiang NR, Xiao YF, Yang ZC (1983) The discovery of Stegolophodon yangyiensis sp. nov. Collected Works of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Geology, 11, 146-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [江能人, 肖永福, 杨正纯 (1983) 云南保山羊邑脊棱齿象的发现. 青藏高原地质文集, 11, 146-156.] | |
| [25] | Kou XY, Ferguson DK, Xu JX, Wang YF, Li CS (2006) The reconstruction of paleovegetation and paleoclimate in the late Pliocene of west Yunnan, China. Climatic Change, 77, 431-448. |
| [26] | Li BY (1989) Geomorphologic regionalization of the Hengduan Mountainous region. Mountain Research, 7, 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李炳元 (1989) 横断山区地貌区划. 山地研究, 7, 13-20.] | |
| [27] | Li DM, Li Q, Chen WJ (2000) Volcanic activities in the Tengchong volcano area since Pliocene. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16, 362-370. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李大明, 李齐, 陈文寄 (2000) 腾冲火山区上新世以来的火山活动. 岩石学报, 16, 362-370.] | |
| [28] | Li N, Sun BN, Wu JY, Yan DF, Xiao L, Dai J (2009) Cuticular structure of Quercus presenescens from the Pliocene in Baoshan, Yunnan, and its palaeoclimatic implications. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 48, 654-661. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李娜, 孙柏年, 吴靖宇, 闫德飞, 肖良, 戴静 (2009) 云南保山上新统前灰背栎Quercus presenescens角质层特征及古气候意义. 古生物学报, 48, 654-661.] | |
| [29] | Li SH, Deng CL, Yao HT, Huang S, Liu CY, He HY, Pan YX, Zhu RX (2013) Magnetostratigraphy of the Dali Basin in Yunnan and implications for late Neogene rotation of the southeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 118, 791-807. |
| [30] | Li SH, Ji XP, Harrison T, Deng CL, Wang SQ, Wang LR, Zhu RX (2020) Uplift of the Hengduan Mountains on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau in the late Miocene and its paleoenvironmental impact on hominoid diversity. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 553, 109794. |
| [31] | Li SY, Currie BS, Rowley DB, Ingalls M (2015) Cenozoic paleoaltimetry of the SE margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the region. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 432, 415-424. |
| [32] | Liu LH, Yu YD, Zhang JH (1984) The division of vertical vegetation zone in Hengduanshan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 6, 205-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘伦辉, 余有德, 张建华 (1984) 横断山自然植被垂直带的划分. 云南植物研究, 6, 205-216.] | |
| [33] | Liu LH, Yu YD, Zhang JH (1985) Discussion upon the regularities of vegetational distribution in the Hengduan Mountains. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 7, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘伦辉, 余有德, 张建华 (1985) 横断山地区植被分布规律的探讨. 云南植物研究, 7, 323-335.] | |
| [34] | Ma HJ (2013) Study on Cenozoic Stratigraphy and Paleoenvironmental Changes in the Hengduan Mountains, Southwest China. PhD Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马宏杰 (2013) 中国西南横断山地区新生代地层学及古环境变化研究. 博士学位论文, 昆明理工大学, 昆明.] | |
| [35] | Meng HH, Su T, Gao XY, Li J, Jiang XL, Sun H, Zhou ZK (2017) Warm-cold colonization: Response of oaks to uplift of the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains. Molecular Ecology, 26, 3276-3294. |
| [36] | Momohara A, Zhou Z, Li X, Setoguchi H (2006) Cenozoic flora with Quercus sect. Heterobalanus in the western Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Japanese Journal of Historical Botany, 14, 43-44. (in Japanese) |
| [37] | Schoenbohm LM, Burchfiel BC, Chen LZ (2006) Propagation of surface uplift, lower crustal flow, and Cenozoic tectonics of the southeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Geology, 34, 813-816. |
| [38] | Sherman R, Mullen R, Li HM, Fang ZD, Wang Y (2008) Spatial patterns of plant diversity and communities in Alpine ecosystems of the Hengduan Mountains, northwest Yunnan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 1, 117-136. |
| [39] | Spicer RA (2017) Tibet, the Himalaya, Asian monsoons and biodiversity—In what ways are they related? Plant Diversity, 39, 233-244. |
| [40] | Su T (2010) On the Establishment of the Leaf Physiognomy- Chinese Model and a Study of the Late Pliocene Yangjie Flora, Southwest China. PhD Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏涛 (2010) 叶相-气候中国模型的建立及上新世羊街植物群的研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院大学, 北京.] | |
| [41] | Su T, Adams JM, Wappler T, Huang YJ, Jacques FMB, Liu YS, Zhou ZK (2015) Resilience of plant-insect interactions in an oak lineage through Quaternary climate change. Paleobiology, 41, 174-186. |
| [42] | Su T, Jacques FMB, Liu YS, Xiang JY, Xing YW, Huang YJ, Zhou ZK (2011) A new Drynaria (Polypodiaceae) from the upper Pliocene of Southwest China. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 164, 132-142. |
| [43] | Su T, Spicer RA, Li SH, Xu H, Huang J, Sherlock S, Huang YJ, Li SF, Wang L, Jia LB, Deng WYD, Liu J, Deng CL, Zhang ST, Valdes PJ, Zhou ZK (2019) Uplift, climate and biotic changes at the Eocene-Oligocene transition in south-eastern Tibet. National Science Review, 6, 495-504. |
| [44] | Sun BN, Cong PY, Yan DF, Xie SP (2003) Cuticular structure of two angiosperm fossils in Neogene from Tengchong, Yunnan Province and its palaeoenvironmental significance. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 42, 216-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙柏年, 丛培允, 阎德飞, 解三平 (2003) 云南腾冲新近纪两种被子植物化石的角质层构造及其古环境意义. 古生物学报, 42, 216-222.] | |
| [45] | Sun BN, Wu JY, Liu YS, Ding ST, Li XC, Xie SP, Yan DF, Lin ZC (2011) Reconstructing Neogene vegetation and climates to infer tectonic uplift in western Yunnan, China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 304, 328-336. |
| [46] |
Sun H, Zhang JW, Deng T, Boufford DE (2017) Origins and evolution of plant diversity in the Hengduan Mountains, China. Plant Diversity, 39, 161-166.
DOI |
| [47] | Tang MY, Jing LZ, Hoke GD, Xu Q, Wang WT, Li ZF, Zhang JY, Wang W (2017) Paleoelevation reconstruction of the Paleocene-Eocene Gonjo basin, SE-central Tibet. Tectonophysics, 712/713, 170-181. |
| [48] | Tong YB, Yang ZY, Mao CP, Pei JL, Pu ZW, Xu YC (2017) Paleomagnetism of Eocene red-beds in the eastern part of the Qiangtang Terrane and its implications for uplift and southward crustal extrusion in the southeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 475, 1-14. |
| [49] | Tao JR (1986) Neogene flora of Lanping and its significance in middle watershed of Selween-Mekong-Yangtze Rivers. In: Studies in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau—Special Issue of Hengduan Mountains Scientific Expedition (II) (eds Team of Comprehensive Scientific Expedition to the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, Chinese Academy of Sciences), pp. 58-65. Science and Technology Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陶君容 (1986) 横断山区中段-兰坪新第三纪植物化石群及其意义. 见: 青藏高原研究-横断山科学考察专辑(中国科学院青藏高原综合科学考察队主编), 第58-65页 科技出版社: 北京.] | |
| [50] | Tao JR (2000) The Evolution of the Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic Floras in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English catalogue) |
| [陶君容 (2000) 中国晚白垩至新生代植物区系发展演变. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [51] | Tao JR, Kong ZC (1973) The fossil florule and sporo-pollen assemblage of the Shang-In coal series of Erhyuan, Yunnan. Acta Botanica Sinica, 15, 120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陶君容, 孔昭宸 (1973) 云南洱源三营煤系的植物化石群和孢粉组合. 植物学报, 15, 120-126.] | |
| [52] | Tao YL, Zhang HP, Ge YK, Pang JZ, Yu JX, Zhang JW, Zhao XD, Ma ZF (2020) Cenozoic exhumation and fault activities across the eastern Tibet: Constraints from low-temperature thermochronological data. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63, 4154-4167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陶亚玲, 张会平, 葛玉魁, 庞建章, 俞晶星, 张佳伟, 赵旭东, 马字发 (2020) 青藏高原东缘新生代隆升剥露与断裂活动的低温热年代学约束. 地球物理学报, 63, 4154-4167.] | |
| [53] | Wang SY, Zhang W (2002) Yunnan Geography. Yunnan Nationalities Publishing House, Kunming. (in Chinese with English catalogue) |
| [王声跃, 张文 (2002) 云南地理. 云南民族出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [54] | Wang Y (2006) Yunnan Mountain Climate. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [王宇 (2006) 云南山地气候. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [55] | Westaway R (2009) Active crustal deformation beyond the SE margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Constraints from the evolution of fluvial systems. Global and Planetary Change, 68, 395-417. |
| [56] | Wu FL, Gao SJ, Tang FJ, Meng QQ, An CR (2019) A late Miocene-early Pleistocene palynological record and its climatic and tectonic implications for the Yunnan Plateau, China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 530, 190-199. |
| [57] | Wu JY (2009) The Pliocene Tuantian Flora of Tengchong, Yunnan Province and Its Paleoenvironmental Analysis. PhD Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴靖宇 (2009) 云南腾冲上新世团田植物群及其古环境分析. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] | |
| [58] | Wu JY, Liu YS, Ding ST, Li J, An PC (2017) Late Pliocene Smilax (Smilacaceae) leaves from Southwest China: Phytogeographical and paleoecological implications. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 241, 26-38. |
| [59] | Wu JY, Sun BN, Liu YS, Xie SP, Lin ZC (2009) A new species of Exbucklandia (Hamamelidaceae) from the Pliocene of China and its paleoclimatic significance. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 155, 32-41. |
| [60] | Wu JY, Sun BN, Xie SP, Ding ST, Wen WW (2012) Dimorphic fronds and in situ spores of Drynaria (Polypodiaceae) from the upper Pliocene of Southwest China. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 172, 1-9. |
| [61] | Xiao L, Sun BN, Yan DF, Xie SP, Wei LJ (2006) Cuticular structure of Quercus pannosa Hand.-Mazz. from the Pliocene in Baoshan, Yunnan Province and its palaeoenvironmental significance. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 23, 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖良, 孙柏年, 阎德飞, 解三平, 韦利杰 (2006) 云南保山上新统黄背栎Quercus pannosa Hand.-Mazz.角质层特征及古环境意义. 微体古生物学报, 23, 23-30.] | |
| [62] | Xing YW, Ree RH (2017) Uplift-driven diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a temperate biodiversity hotspot. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, E3444-E3451. |
| [63] | Xiong ZY, Ding L, Spicer RA, Farnsworth A, Wang X, Valdes PJ, Su T, Zhang QH, Zhang LY, Cai FL, Wang HQ, Li ZY, Song PP, Guo XD, Yue YH (2020) The early Eocene rise of the Gonjo Basin, SE Tibet: From low desert to high forest. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 543, 116312. |
| [64] | Xu JX, Blackmore S, Wang YF, Li CS (2004a) Late Pliocene vegetation and climate of Yangyi region, Yunnan of China, based on palynological data. Palaeontographica Abteilung B, 269, 131-148. |
| [65] | Xu JX, Ferguson DK, Li CS, Wang YF, Du NQ (2004b) Climatic and ecological implications of Late Pliocene palynoflora from Longling, Yunnan, China. Quaternary International, 117, 91-103. |
| [66] | Xu JX, Wang YF, Du NQ (2003) Late Pliocene vegetation and palaeoclimate of Yangyi and Longling of western Yunnan Province. Journal of Palaeogeography, 5, 217-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐景先, 王宇飞, 杜乃秋 (2003) 云南西部羊邑和龙陵地区晚上新世植被和古气候. 古地理学报, 5, 217-223.] | |
| [67] | Yang QY, Zheng D (1989) An outline of physic-geographic regionalization of the Hengduan Mountains region. Mountain Research, 7, 56-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨勤业, 郑度 (1989) 横断山区综合自然区划纲要. 山地研究, 7, 56-64.] | |
| [68] | Yu HB, Miao SY, Xie GW, Guo XY, Chen Z, Favre A (2020) Contrasting floristic diversity of the Hengduan Mountains, the Himalayas and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau sensu stricto in China. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 136. |
| [69] | Yu YD, Liu LH, Zhang JH (1989) Vegetation regionalization of the Hengduan mountainous region. Mountain Research, 7, 47-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [余有德, 刘伦辉, 张建华 (1989) 横断山区植被分区. 山地研究, 7, 47-55.] | |
| [70] | Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (1990) Regional Geology of Yunnan Province. Geology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [云南省地质矿产局 (1990) 云南省区域地质志. 地质出版社, 北京.] | |
| [71] | Zhang QQ, Ferguson DK, Mosbrugger V, Wang YF, Li CS (2012) Vegetation and climatic changes of SW China in response to the uplift of Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 363/364, 23-36. |
| [72] | Zhang Y, Yin DC, Sun M, Wang H, Tian K, Xiao DR, Zhang WG (2017) Variations of climate-growth response of major conifers at upper distributional limits in Shika Snow Mountain, northwestern Yunnan Plateau, China. Forests, 8, 377. |
| [73] | Zheng Y, Jia J, Nie XK, Kong P (2014) Cosmogenic nuclide burial age of the Sanying Formation and its implications. Science China: Earth Sciences, 57, 1141-1149. |
| [74] | Zhou ZK, Pu CX, Chen WY (2003) Relationships between the distributions of Quercus sect. Heterobalanus (Fagaceae) and uplift of Himalayas. Advance in Earth Sciences, 18, 884-890. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[周浙昆, 普春霞, 陈文允 (2003) 青藏高原隆起和高山栎组(壳斗科)分布的关系. 地球科学进展, 18, 884-890.]
DOI |
|
| [75] | Zhu H (2016) The Late Pliocene Nanbanbang Carpoflora from Heqing, Yunnan, and Its Paleoenvironment. PhD thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱海 (2016) 云南鹤庆晚上新世南班榜古果实群及古环境. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院大学, 北京.] | |
| [76] | Zhu H, Huang YJ, Su T, Zhou ZK (2016) New fossil seeds of Eurya (Theaceae) from East Asia and their paleobiogeographic implications. Plant Diversity, 38, 125-132. |
| [77] | Zhu H, Jacques FMB, Wang L, Xiao XH, Huang YJ, Zhou ZK (2015) Fossil endocarps of Aralia (Araliaceae) from the upper Pliocene of Yunnan in southwest China, and their biogeographical implications. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 223, 94-103. |
| [1] | 戴静, 陈威兆, 金露露, 黄亮. 云南宜良上新世栎属植物研究及其古环境指示意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22553-. |
| [2] | 胡正艳, 郑全晶, 母其勇, 杜志强, 刘琳, 星耀武, 韩廷申. 不同纬度高蔊菜的交配系统和繁殖保障[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 712-721. |
| [3] | 李晟, William J. McShea, 王大军, 申小莉, 卜红亮, 官天培, 王放, 古晓东, 张晓峰, 廖灏泓. 西南山地红外相机监测网络建设进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1049-1058. |
| [4] | 胡茜茜, 郑维超, 李佳琦, 李晟, 杨晗, 陈星, 官天培. 四姑娘山国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性初步调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(12): 1325-1331. |
| [5] | 金效华, 向小果, 陈彬. 怒江河谷低海拔地区残存原生植被中兰科植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(1): 120-123. |
| [6] | 龚正达, 吴厚永, 段兴德, 冯锡光, 张云智, 刘泉. 云南横断山区蚤类物种丰富度与区系的垂直分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(4): 279-289. |
| [7] | 龚正达, 吴厚永, 段兴德, 冯锡光, 张云智, 刘泉. 云南横断山区蚤类物种多样性的地理分布趋势与重要环境因素的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(4): 319-328. |
| [8] | 龚正达, 吴厚永, 段兴德, 冯锡光, 张云智, 刘泉. 云南横断山区小型兽类物种多样性与地理分布趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(1): 73-79. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn