



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 445-454. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019356 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019356
姚志良1,2,温韩东1,3,邓云1,2,4,曹敏1,林露湘1,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-11-07
接受日期:2019-12-03
出版日期:2020-04-20
发布日期:2020-06-15
通讯作者:
林露湘
基金资助:
Zhiliang Yao1,2,Handong Wen1,3,Yun Deng1,2,4,Min Cao1,Luxiang Lin1,4,*( )
)
Received:2019-11-07
Accepted:2019-12-03
Online:2020-04-20
Published:2020-06-15
Contact:
Luxiang Lin
摘要:
Beta多样性通常指群落在时间和空间上物种组成的差异, 包括物种周转组分和物种丰富度差异组分。驱动beta多样性格局形成的生态过程决定了群落的时空动态, 然而关于beta多样性及其两个组分格局形成的驱动力还存在较多争议。以往研究表明, beta多样性的格局存在取样尺度的依赖性, 驱动其形成的生态过程在不同取样尺度下的相对重要性也随之改变。本研究以哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地为研究对象, 在不同取样尺度上, 将样方间的Bray-Curtis指数分解为物种周转组分和物种丰富度差异组分, 通过典范冗余分析和方差分解的方法揭示环境过滤和扩散限制对于beta多样性及其两个组分格局形成的相对重要性及其尺度依赖性。结果表明: (1) beta多样性、物种周转组分和物种丰富度差异组分均随取样尺度的增大而减小。在不同取样尺度下, 物种周转组分对于beta多样性的贡献始终占主导地位。(2)随着取样尺度的增大, 环境过滤驱动beta多样性格局形成的相对重要性逐渐增加, 而扩散限制的相对重要性逐渐降低。本研究进一步证实了取样尺度在beta多样性格局形成及其驱动力定量评价中的重要性, 今后的研究需要进一步解析上述尺度效应的形成机制。
姚志良,温韩东,邓云,曹敏,林露湘 (2020) 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林树种beta多样性格局形成的驱动力. 生物多样性, 28, 445-454. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019356.
Zhiliang Yao,Handong Wen,Yun Deng,Min Cao,Luxiang Lin (2020) Driving forces underlying the beta diversity of tree species in subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forests in Ailao Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 28, 445-454. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019356.
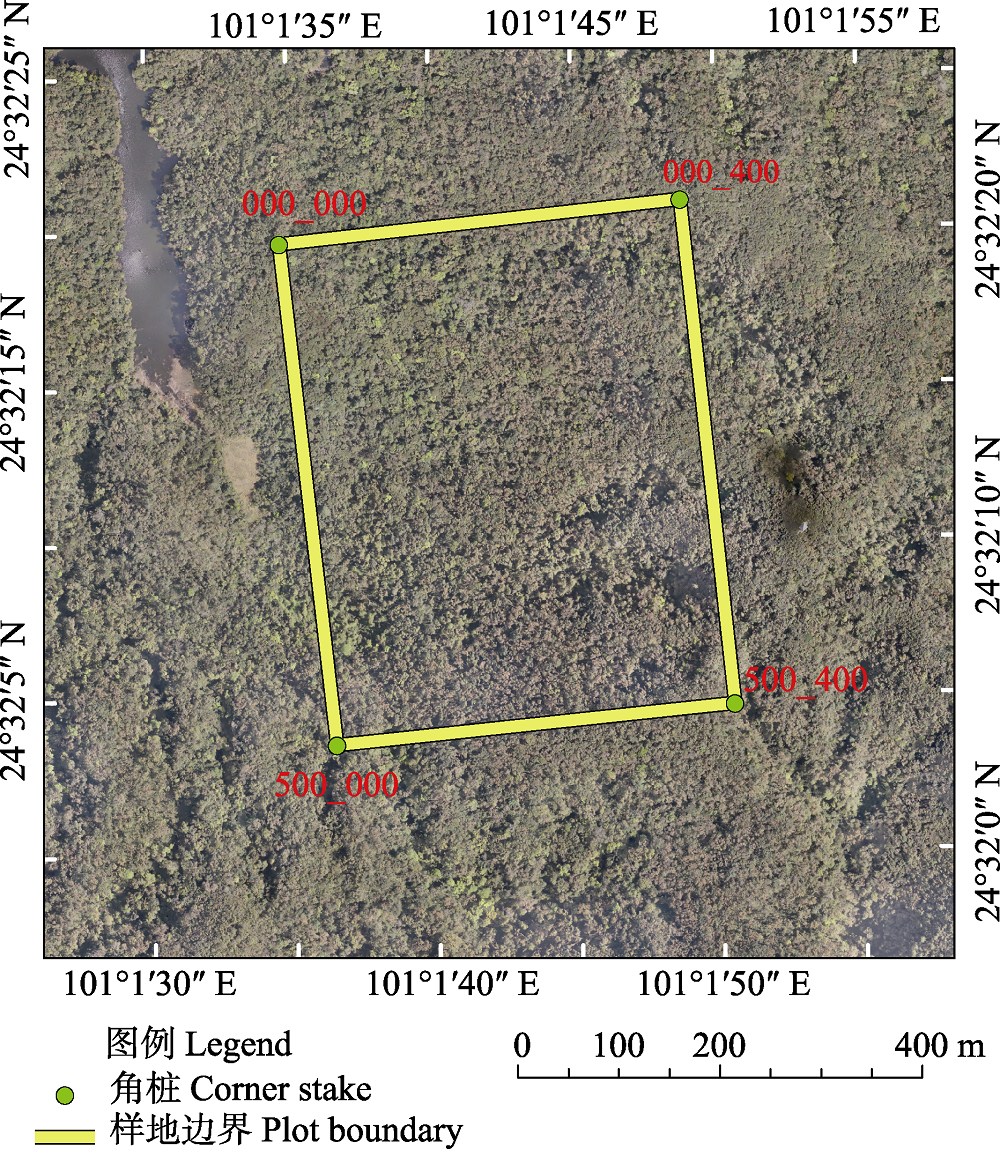
图1 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地示意图
Fig. 1 Diagrammatic of the 20 ha subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Ailao Mountains
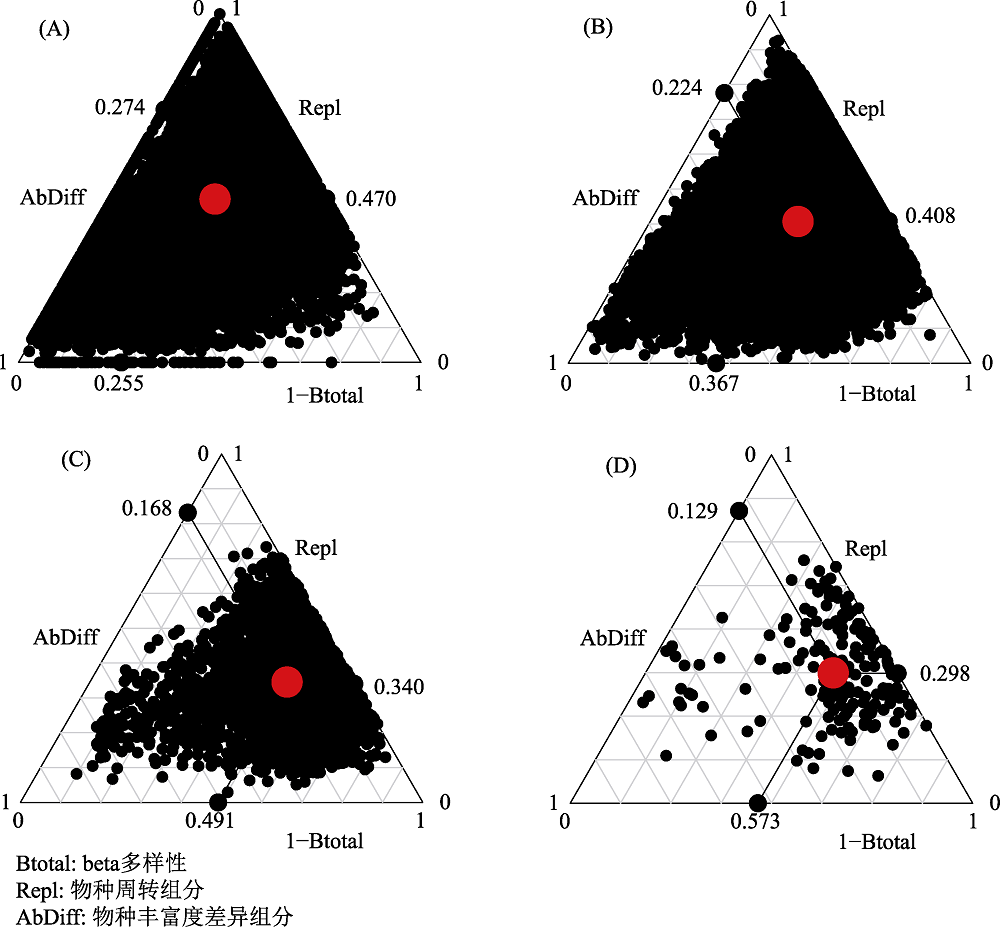
图2 不同取样尺度下的beta多样性及其两个组分的三元图。每一个黑点表示一个样方对, 它们的位置由物种组成相似性(1 - Btotal)、物种周转组分(Relp)、物种丰富度差异组分(AbDiff)三个值决定, 三个值之和等于1; 大圆点表示这些黑点的质心, 较大的黑点表示三个组分的平均值; A, B, C, D分别表示10 m、20 m、50 m、100 m取样尺度下的组分关系。
Fig. 2 Triangular plots of beta diversity and its two components at different cell sizes. Each black dot represents a pair of sites. Their positions were determined by a triplet of values from the species composition similarity (1-Btotal), species turnover component (Repl), species richness difference component (AbDiff); each triplet sums to 1. The large circular dot in each graph is the centroid of the points; the larger black dots represent the mean values of the 1-Btotal, Repl, and AbDiff components; A, B, C, and D represent the relationships of three components at 10 m, 20 m, 50 m, 100 m cell sizes, respectively.
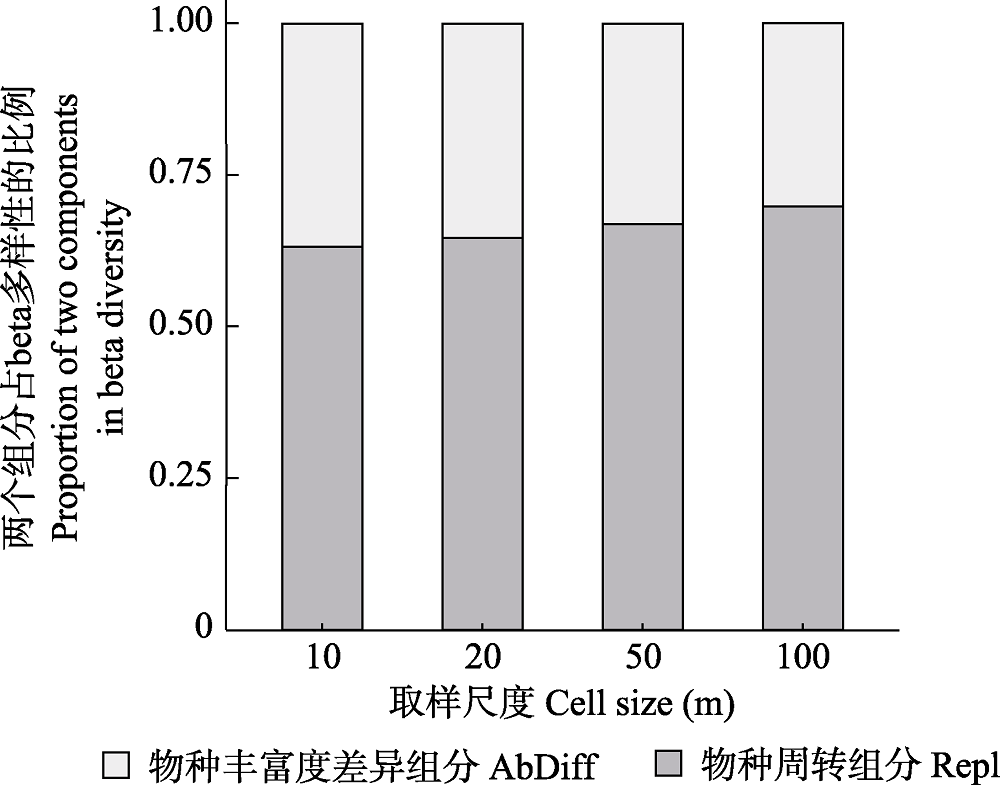
图3 不同取样尺度下两个组分占beta多样性的比例
Fig. 3 The proportion of two components in beta diversity at different cell sizes. AbDiff, Species richness difference component; Repl, Species turnover component.
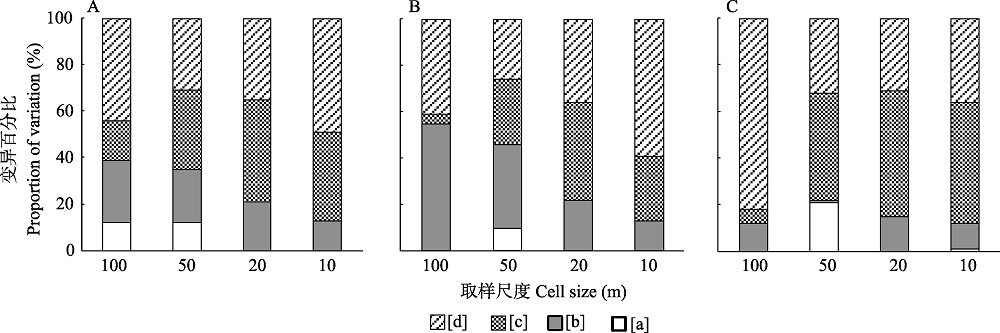
图4 beta多样性及其组分在不同取样尺度下的方差分解结果。A、B、C分别表示beta多样性、物种周转组分、物种丰富度差异组分在不同取样尺度下的方差分解结果; [a]单纯的环境变异; [b]环境的空间结构; [c]单纯的空间结构; [d]未明确的部分。
Fig. 4 Variation partitioning results of beta diversity and its components at different cell sizes. A, B, and C represent the variation partitioning results of total beta diversity, species replacement component, richness difference component at different cell sizes, respectively; [a] Pure environment variation; [b] Spatially structured of environment; [c] Pure spatially structured variation; [d] Unexplained variation.
| [1] |
Anderson MJ, Crist TO, Chase JM, Vellend M, Inouye BD, Freestone AL, Sanders NJ, Cornell HV, Comita LS, Davies KF, Harrison SP, Kraft NJB, Stegen JC, Swenson NG (2010) Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecology Letters, 14, 19-28.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Barton PS, Cunningham SA, Manning AD, Gibb H, Lindenmayer DB, Didham RK (2013) The spatial scaling of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 639-647.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143. |
| [4] |
Baselga A (2017) Partitioning abundance-based multiple-site dissimilarity into components: Balanced variation in abundance and abundance gradients. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 799-808.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Borcard D, Legendre P (2002) All-scale spatial analysis of ecological data by means of principal coordinates of neighbour matrices. Ecological Modelling, 153, 51-68.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Borcard D, Legendre P, Avois-Jacquet C, Tuomisto H (2004) Dissecting the spatial structure of ecological data at multiples scales. Ecology, 85, 1826-1832. |
| [7] | Bin Y, Wang ZG, Wang ZM, Ye WH, Cao HL, Lian JY (2010) The effects of dispersal limitation and topographic heterogeneity on beta diversity and phylobetadiversity in a subtropical forest. Plant Ecology, 209, 237-256. |
| [8] | Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Gomes P (2012) Determining the relative roles of species replacement and species richness differences in generating beta-diversity patterns. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 760-771. |
| [9] | Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.] | |
| [10] | Chase JM (2007) Drought mediates the importance of stochastic community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 17430-17434. |
| [11] | Chase JM, Myers JA (2011) Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 366, 2351-2363. |
| [12] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [13] | Condit R, Pitman N, Leigh EG, Chave J, Terborgh J, Foster RB, Nunez P, Aguilar S, Valencia R, Villa G, Muller- Landau HC, Losos E, Hubbell SP (2002) Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees. Science, 295, 666-669. |
| [14] | Cressie N (1990) The origins of Kriging. Mathematical Geology, 22, 239-252. |
| [15] |
De Cáceres M, Legendre P, Valencia R, Cao M, Chang LW, Chuyong G, Condit R, Hao ZQ, Hsieh CF, Hubbell S, Kenfack D, Ma KP, Mi XC, Noor MNS, Kassim AR, Ren HB, Su SH, Sun IF, Thomas D, Ye WH, He FL (2012) The variation of tree beta diversity across a global network of forest plots. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1191-1202.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Diggle PJ, Tawn JA, Moyeed RA (1998) Model-based geostatistics. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series C: Applied Statistics, 47, 299-326.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Dobrovolski R, Melo AS, Cassemiro FAS, Diniz-Filho JAF (2012) Climatic history and dispersal ability explain the relative importance of turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 191-197.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Dray S, Blanchet FG, Borcard D, Clappe S, Guénard G, Jombart T, Larocque G, Legendre P, Madi N, Wagner H (2018) adespatial: Multivariate Multiscale Spatial Analysis. R package version 0.2-0. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/adespatial/. (accessed on 2018-05-23) |
| [19] | Dray S, Legendre P, Peres-Neto PR (2006) Spatial modelling: A comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbour matrices (PCNM). Ecological Modelling, 196, 483-493. |
| [20] | Ellison AM (2010) Partitioning diversity. Ecology, 91, 1962-1963. |
| [21] |
Fang JY, Wang XP, Tang ZY (2009) Local and regional processes control species richness of plant communities: The species pool hypothesis. Biodiversity Science, 17, 605-612. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 方精云, 王襄平, 唐志尧 (2009) 局域和区域过程共同控制着群落的物种多样性: 种库假说. 生物多样性, 17, 605-612.]
DOI URL |
|
| [22] | Gianuca AT, Declerck SAJ, Lemmens P, De Meester L (2017) Effects of dispersal and environmental heterogeneity on the replacement and nestedness components of beta-diversity. Ecology, 98, 525-533. |
| [23] |
Greve M, Gremmen NJM, Gaston KJ, Chown SL (2005) Nestedness of southern ocean island biotas: Ecological perspectives on a biogeographical conundrum. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 155-168.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Guo YL, Xiang WS, Wang B, Li DX, Mallik AU, Chen HYH, Huang FZ, Ding T, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Li XK (2018) Partitioning beta diversity in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Southern China. Scientific Reports, 8, 17408. |
| [25] | Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [26] | Harrison S, Ross SJ, Lawton JH (1992) Beta-diversity on geographic gradients in Britain. Journal of Animal Ecology, 61, 151-158. |
| [27] |
Heino J, Nokela T, Soininen J, Tolkkinen M, Virtanen L, Virtanen R (2015) Elements of metacommunity structure and community-environment relationships in stream organisms. Freshwater Biology, 60, 973-988.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Hill MJ, Heino J, Thornhill I, Ryves DB, Wood PJ (2017) Effects of dispersal mode on the environmental and spatial correlates of nestedness and species turnover in pond communities. Oikos, 126, 1575-1585.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32). Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [30] | Jackson DA (1993) Stopping rules in principal components analysis: A comparison of heuristical and statistical approaches. Ecology, 74, 2204-2214. |
| [31] | Jones MM, Tuomisto H, Borcard D, Legendre P, Clark DB, Olivas PC (2008) Explaining variation in tropical plant community composition: Influence of environmental and spatial data quality. Oecologia, 155, 593-604. |
| [32] |
Jost L (2006) Entropy and diversity. Oikos, 113, 363-375.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Laliberté E, Paquette A, Legendre P, Bouchard A (2009) Assessing the scale-specific importance of niches and other spatial processes on beta diversity: A case study from a temperate forest. Oecologia, 159, 377-388.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Lande R (1996) Statistics and partitioning of species diversity, and similarity among multiple communities. Oikos, 76, 5-13. |
| [35] |
Legendre P, Anderson MJ (1999) Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecological Monographs, 69, 1-24.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Legendre P, De Cáceres M (2013) Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecology Letters, 16, 951-963.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Legendre P (2014) Interpreting the replacement and richness difference components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1324-1334.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Legendre P, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP, Yu MJ, Sun IF, He FL (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad- leaved forest of China. Ecology, 90, 663-674. |
| [39] | Lennon JJ, Koleff P, Greenwood JJD, Gaston KJ (2001) The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 966-979. |
| [40] | Leprieur F, Tedesco PA, Hugueny B, Beauchard O, Durr HH, Brosse S, Oberdorff T (2011) Partitioning global patterns of freshwater fish beta diversity reveals contrasting signatures of past climate changes. Ecology Letters, 14, 325-334. |
| [41] | Levine JM, Murrell DJ (2003) The community-level consequences of seed dispersal patterns. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34, 549-574. |
| [42] | Magurran AE (1988) Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement. Croom-Helm, London. |
| [43] | McArdle BH, Anderson MJ (2001) Fitting multivariate models to community data: A comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology, 82, 290-297. |
| [44] | McKnight MW, White PS, McDonald RI, Lamoreux JF, Sechrest W, Ridgely RS, Stuart SN (2007) Putting beta-diversity on the map: Broad-scale congruence and coincidence in the extremes. PLoS Biology, 5, e272. |
| [45] | Myers JA, Chase JM, Jiménez I, Jorgensen PM, Araujo- Murakami A, Paniagua-Zambrana N, Seidel R (2013) Beta- diversity in temperate and tropical forests reflects dissimilar mechanisms of community assembly. Ecology Letters, 16, 151-157. |
| [46] | Nekola JC, White PS (1999) The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology. Journal of Biogeography, 26, 867-878. |
| [47] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2018) vegan: Community Ecology Packagex. R package version 2.5-2. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/. (accessed on 2018-05-17) |
| [48] |
Page NV, Shanker K (2018) Environment and dispersal influence changes in species composition at different scales in woody plants of the Western Ghats, India. Journal of Vegetation Science, 29, 74-83.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Pebesma EJ (2004) Multivariable geostatistics in S: The gstat package. Computers & Geosciences, 30, 683-691. |
| [50] |
Podani J, Schmera D (2011) A new conceptual and methodological framework for exploring and explaining pattern in presence-absence data. Oikos, 120, 1625-1638.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Podani J, Ricotta C, Schmera D (2013) A general framework for analyzing beta diversity, nestedness and related community-level phenomena based on abundance data. Ecological Complexity, 15, 52-61.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Ponisio LC, M’Gonigle LK, Kremen C (2016) On-farm habitat restoration counters biotic homogenization in intensively managed agriculture. Global Change Biology, 22, 704-715.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Qiu XZ, Xie SC (1998) Study on the Forest Ecosystem in Ailao Mountains, Yunnan, China. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邱学忠, 谢寿昌 (1998) 哀牢山森林生态系统研究. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [54] | Seidler TG, Plotkin JB (2006) Seed dispersal and spatial pattern in tropical trees. PLoS Biology, 4, e344. |
| [55] | Si XF, Zhao YH, Chen CW, Ren P, Zeng D, Wu LB, Ding P (2017) Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 25, 464-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平 (2017) Beta多样性分解: 方法、应用与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 464-480.] | |
| [56] | Smith TW, Lundholm JT (2010) Variation partitioning as a tool to distinguish between niche and neutral processes. Ecography, 33, 648-655. |
| [57] | Soininen J, Heino J, Wang JJ (2018) A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 96-109. |
| [58] |
Steinbauer MJ, Dolos K, Reineking B, Beierkuhnlein C (2012) Current measures for distance decay in similarity of species composition are influenced by study extent and grain size. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1203-1212.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Svenning JC, Flojgaard C, Baselga A (2011) Climate, history and neutrality as drivers of mammal beta diversity in Europe: Insights from multiscale deconstruction. Journal of Animal Ecology, 80, 393-402.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Tisseuil C, Leprieur F, Grenouillet G, Vrac M, Lek S (2012) Projected impacts of climate change on spatio-temporal patterns of freshwater fish beta diversity: A deconstructing approach. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1213-1222.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Toledo M, Poorter L, Peña-Claros M, Alarcón A, Balcázar J, Chuviña J, Leaño C, Licona JC, Steege H, Bongers F (2011) Patterns and determinants of floristic variation across lowland forests of Bolivia. Biotropica, 43, 405-413.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Tonkin JD, Stoll S, Jähnig SC, Haase P (2016) Contrasting metacommunity structure and beta diversity in an aquatic- floodplain system. Oikos, 125, 686-697. |
| [63] |
Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M (2003) Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science, 299, 241-244.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Ulrich W, Almeida-Neto M, Gotelli NJ (2009) A consumer's guide to nestedness analysis. Oikos, 118, 3-17.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Valencia R, Foster RB, Villa G, Condit R, Svenning JC, Hernández C, Romoleroux K, Losos E, Magård E, Balslev H (2004) Tree species distributions and local habitat variation in the Amazon: Large forest plot in eastern Ecuador. Journal of Ecology, 92, 214-229.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Viana DS, Figuerola J, Schwenk K, Manca M, Hobæk A, Mjelde M, Preston CD, Gornall RJ, Croft JM, King RA, Green AJ, Santamaría L (2016) Assembly mechanisms determining high species turnover in aquatic communities over regional and continental scales. Ecography, 39, 281-288. |
| [67] |
Wang XG, Wiegand T, Anderson-Teixeira KJ, Bourg NA, Hao ZQ, Howe R, Jin GZ, Orwig DA, Spasojevic MJ, Wang SZ, Wolf A, Myers JA (2018) Ecological drivers of spatial community dissimilarity, species replacement and species nestedness across temperate forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 581-592.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Wen HD, Lin LX, Yang J, Hu YH, Cao M, Liu YH, Lu ZY, Xie YN (2018) Species composition and community structure of a 20 hm2 plot of mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forest on the Mts. Ailaoshan, Yunnan Province, China . Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42, 419-429. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 温韩东, 林露湘, 杨洁, 胡跃华, 曹敏, 刘玉洪, 鲁志云, 谢有能 (2018) 云南哀牢山中山湿性常绿阔叶林20hm2动态样地的物种组成与群落结构 . 植物生态学报, 42, 419-429.]
DOI URL |
|
| [69] |
Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 407-407.
DOI URL |
| [70] | Williams PH (1996) Mapping variations in the strength and breadth of biogeographic transition zones using species turnover. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 263, 579-588. |
| [71] |
Zobel M (1997) The relative role of species pools in determining plant species richness: An alternative explanation of species coexistence? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 266-269.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘志禹, 吉鑫, 隋国辉, 杨定, 李轩昆. 北京首都国际机场野牛草与杂草草坪无脊椎动物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [2] | 李华亮, 张明军, 张熙斌, 谭荣, 李诗川, 冯尔辉, 林雪云, 陈珉, 颜文博, 曾治高. 海南东寨港国家级自然保护区两栖类群落组成及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [3] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [4] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [5] | 周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平. 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| [6] | 杨欣, 姚志良, 王彬, 温韩东, 邓云, 曹敏, 张志明, 谭正洪, 林露湘. 亚热带常绿阔叶林林分结构对物种组成变异的驱动作用: 从局域到区域尺度[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22139-. |
| [7] | 王朝雅, 李金涛, 刘畅, 王波, 苗白鸽, 彭艳琼. 西双版纳热带植物园蝴蝶多样性稳定的年际变化及幼虫与植物的互作网络结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23305-. |
| [8] | 刘金花, 李风, 田桃, 肖海峰. 土壤细菌和线虫对热带雨林优势植物凋落物特性和多样性的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23276-. |
| [9] | 王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23144-. |
| [10] | 张超, 李娟, 程海云, 段家充, 潘昭. 秦岭西段地区蝴蝶群落多样性与环境因子相关性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22272-. |
| [11] | 董建宇, 孙昕, 詹启鹏, 张宇洋, 张秀梅. 莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落beta多样性格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21388-. |
| [12] | 陈胜仙, 张喜亭, 佘丹琦, 张衷华, 周志强, 王慧梅, 王文杰. 森林植物多样性、树种重要值与土壤理化性质对球囊霉素相关土壤蛋白的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21115-. |
| [13] | 刘笑彤, 田艺佳, 刘汉文, 梁翠影, 姜思维, 梁文举, 张晓珂. 下辽河平原农田土壤线虫群落组成的季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22222-. |
| [14] | 曲梦君, 努尔依拉·阿巴拜克, 邹旭阁, 赵航, 朱威霖, 王健铭, 李景文. 地理距离和环境因子对阿拉善戈壁植物群落β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22029-. |
| [15] | 任淯, 陶胜利, 胡天宇, 杨海涛, 关宏灿, 苏艳军, 程凯, 陈梦玺, 万华伟, 郭庆华. 中国生物多样性核心监测指标遥感产品体系构建与思考[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22530-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()