



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 24476. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024476 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024476
收稿日期:2024-10-31
接受日期:2025-02-26
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-03-13
通讯作者:
*E-mail: wangyanping@njnu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2024-10-31
Accepted:2025-02-26
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-13
Contact:
*E-mail: wangyanping@njnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
生物的生活史和生态学特征在一定程度上决定了物种的种群动态和生存策略, 并深刻影响着它们对环境变化的适应能力。蛇类是一类形态高度特化的爬行动物类群, 截至2024年9月全球共有4,145种。但是, 由于蛇类的隐秘性及独居性, 其宏观生态学研究与其他脊椎动物类群相比相对较少, 目前也没有专门针对蛇类生活史、生态学和生物地理特征的数据集。本研究通过系统查阅已出版的蛇类专著、文献、在线数据库等数据资源, 收集整理了全球4,145种蛇类的28个特征数据。这些特征包括生活史特征(体重、体长、猎物等8个特征)、生态学特征(分布地区、微生境、海拔分布等7个特征)和生物地理特征(年平均温度、年平均降水、归一化植被指数等13个特征), 其完整度为42.41%-99.90%。与已发表的数据集相比, 本数据集物种数更多、特征的完整度更高, 而且新增加了3个生活史和生态学特征数据(食物宽度、分布地区和致危因子), 以及13个生物地理特征数据。该数据集是目前全球蛇类最新和最全的特征数据集, 可为全球和特定地区蛇类的生态学、生物地理学和保护生物学等领域研究提供数据支持。
数据库(集)基本信息简介
| 数据库(集)名称 | 全球蛇类生活史、生态学和生物地理特征数据集 |
|---|---|
| 作者 | 赵一凡, 王彦平 |
| 通讯作者 | 王彦平(wangyanping@njnu.edu.cn) |
| 时间范围 | 截止到2024年9月6日 |
| 地理区域 | 全球 |
| 文件大小 | 1.7 MB |
| 数据格式 | *.xlsx |
| 数据链接 | https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.16435 https://www.biodiversity-science.net/fileup/1005-0094/DATA/2024476.zip |
| 数据库(集)组成 | 数据集共包括1个数据文件和2个描述文件, 包括全球4,145种蛇类的28个生活史、生态学和生物地理特征 |
赵一凡, 王彦平 (2025) 全球蛇类生活史、生态学和生物地理特征数据集. 生物多样性, 33, 24476. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024476.
Zhao Yifan, Wang Yanping (2025) A database of life-history, ecological, and biogeographical traits of snakes worldwide. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24476. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024476.
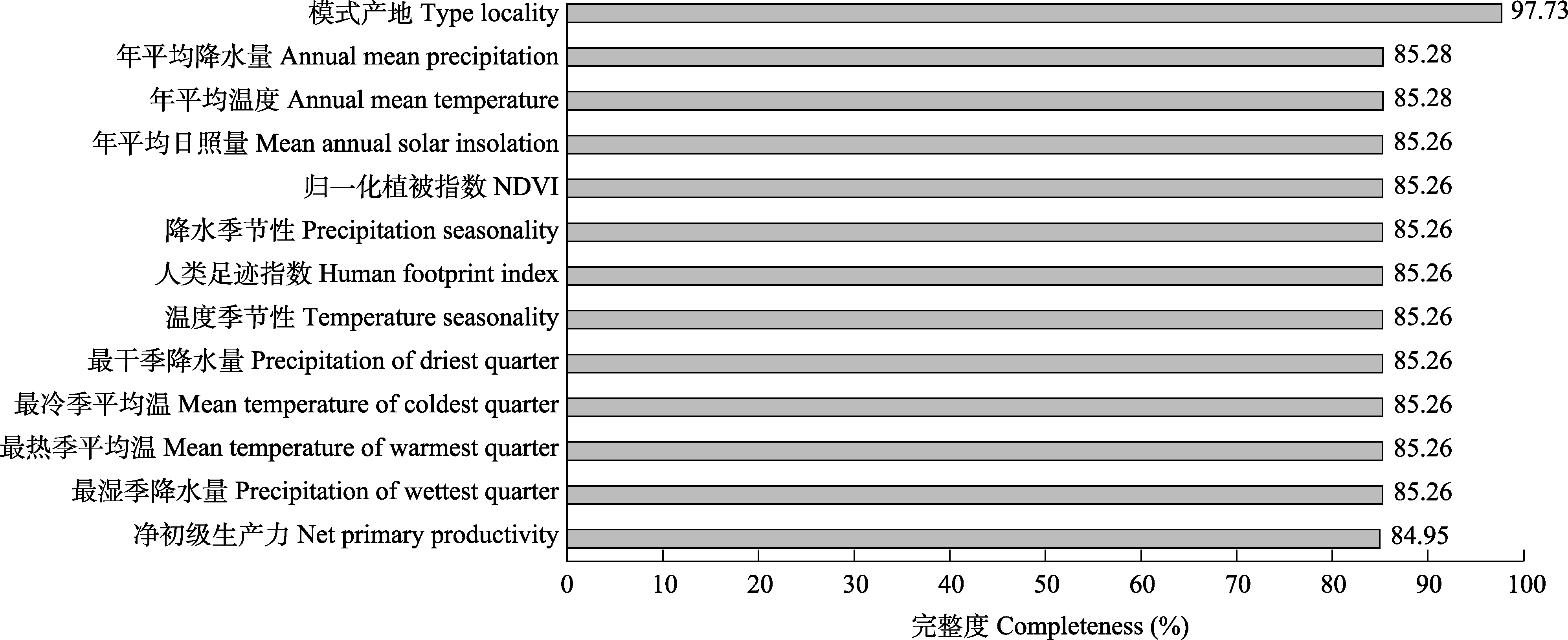
图2 全球4,145种蛇类13个生物地理特征数据的完整度
Fig. 2 Data completeness of the 13 biogeographical characteristics for the 4,145 snakes worldwide. NDVI, Normalized difference vegetation index.
| [1] |
Ashton KG, Feldman CR (2003) Bergmann’s rule in nonavian reptiles: Turtles follow it, lizards and snakes reverse it. Evolution, 57, 1151-1163.
PMID |
| [2] | Böhm M, Collen B, Baillie JEM, Bowles P, Chanson J, Cox N, Hammerson G, Hoffmann M, Livingstone SR, Ram M,..., Wearn OR, Werner YL, Whiting MJ, Wiewandt T, Wilkinson J, Wilson B, Wren S, Zamin T, Zhou KY, Zug G (2013) The conservation status of the world’s reptiles. Biological Conservation, 157, 372-385. |
| [3] | Böhm M, Cook D, Ma HD, Davidson AD, García A, Tapley B, Pearce-Kelly P, Carr J (2016) Hot and bothered: Using trait-based approaches to assess climate change vulnerability in reptiles. Biological Conservation, 204, 32-41. |
| [4] | Böhm M, Kemp R, Williams R, Davidson AD, Garcia A, McMillan KM, Bramhall HR, Collen B (2017) Rapoport’s rule and determinants of species range size in snakes. Diversity and Distributions, 23, 1472-1481. |
| [5] | Brosse S, Charpin N, Su GH, Toussaint A, Herrera-R GA, Tedesco PA, Villéger S (2021) FISHMORPH: A global database on morphological traits of freshwater fishes. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 2330-2336. |
| [6] | Burbrink FT, Myers EA (2015) Both traits and phylogenetic history influence community structure in snakes over steep environmental gradients. Ecography, 38, 1036-1048. |
| [7] | Caetano GHO, Chapple DG, Grenyer R, Raz T, Rosenblatt J, Tingley R, Böhm M, Meiri S, Roll U (2022) Automated assessment reveals that the extinction risk of reptiles is widely underestimated across space and phylogeny. PLoS Biology, 20, e3001544. |
| [8] | Camaiti M, Evans AR, Hipsley CA, Hutchinson MN, Meiri S, Anderson RO, Slavenko A, Chapple DG (2022) A database of the morphology, ecology and literature of the world’s limb-reduced skinks. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 1397-1406. |
| [9] |
Chen CW, Qu YF, Zhou XF, Wang YP (2019) Human overexploitation and extinction risk correlates of Chinese snakes. Ecography, 42, 1777-1788.
DOI |
| [10] | Dayrat B (2005) Towards integrative taxonomy. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 85, 407-415. |
| [11] | Díaz S, Lavorel S, de Bello F, Quétier F, Grigulis K, Robson TM (2007) Incorporating plant functional diversity effects in ecosystem service assessments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 20684-20689. |
| [12] |
Escudero A, Valladares F (2016) Trait-based plant ecology: Moving towards a unifying species coexistence theory. Oecologia, 180, 919-922.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Feldman A, Bauer AM, Castro-Herrera F, Chirio L, Das I, Doan TM, Maza E, Meirte D, de Campos Nogueira C, Nagy AT, Torres-Carvajal O, Uetz P, Meiri S (2015) The geography of snake reproductive mode: A global analysis of the evolution of snake viviparity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 1433-1442. |
| [14] | Feldman A, Meiri S (2014) Australian snakes do not follow Bergmann’s rule. Evolutionary Biology, 41, 327-335. |
| [15] | Fontana RB, Furtado R, Zanella N, Debastiani VJ, Hartz SM (2021) Linking ecological traits to extinction risk: Analysis of a Neotropical Anuran database. Biological Conservation, 264, 109390. |
| [16] | Fosseries G, Herrel A, Godoy-Diana R, Gaucher P, Traimond M, Joris A, Daoues K, Gouygou A, Chateau O, Gossuin H, Banzept P, Banzept C, Lefebvre D, Bonnet X (2024) Can all snakes swim? A review of the evidence and testing species across phylogeny and morphological diversity. Zoology, 167, 126223. |
| [17] | Fukami T, Bezemer TM, Mortimer SR, van der Putten WH (2005) Species divergence and trait convergence in experimental plant community assembly. Ecology Letters, 8, 1283-1290. |
| [18] | Gibbons JW, Scott DE, Ryan TJ, Buhlmann KA, Tuberville TD, Metts BS, Greene JL, Mills T, Leiden Y, Poppy S, Winne CT (2000) The global decline of reptiles, Déjà Vu amphibians. BioScience, 50, 653-666. |
| [19] | Isaac NJB, Cowlishaw G (2004) How species respond to multiple extinction threats. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 271, 1135-1141. |
| [20] | Jones KE, Bielby J, Cardillo M, Fritz SA, O’dell J, Safi K, Sechrest W, Boakes EH, Carbone C, Connolly C, Cutts MJ, Foster JK, Grenyer R, Habib M, Plaster CA, Price SA, Rigby EA, Rist J, Teacher A, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Gittleman JL, Mace GM, Purvis A (2009) PanTHERIA: A species-level database of life history, ecology, and geography of extant and recently extinct mammals. Ecology, 90, 2648. |
| [21] | Keinath DA, Doak DF, Hodges KE, Prugh LR, Fagan W, Sekercioglu CH, Buchart SHM, Kauffman M (2017) A global analysis of traits predicting species sensitivity to habitat fragmentation. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 26, 115-127. |
| [22] | Lapaine M (2011) Mollweide map projection. KoG, 15, 7-16. |
| [23] | Lepage D, Vaidya G, Guralnick R (2014) Avibase—A database system for managing and organizing taxonomic concepts. ZooKeys, 420, 117-135. |
| [24] | López-Luna MA, Hidalgo-Mihart MG, Aguirre-León G, del C González-Ramón M, Rangel-Mendoza JA (2015) Effect of nesting environment on incubation temperature and hatching success of Morelet’s crocodile (Crocodylus moreletii) in an urban lake of Southeastern Mexico. Journal of Thermal Biology, 49, 66-73. |
| [25] | Luiselli L (2006) Resource partitioning and interspecific competition in snakes: The search for general geographical and guild patterns. Oikos, 114, 193-211. |
| [26] | Luría-Manzano R, Serrano FC, Böhm M, Sawaya RJ, Haddad CFB, Martins M (2024) Tadpoles in lotic waters, habitat specialization, and human population density lead tree frogs (Hylinae) to higher extinction risk. Biological Conservation, 290, 110439. |
| [27] | Mace GM (2004) The role of taxonomy in species conservation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 359, 711-719. |
| [28] | McGill BJ, Enquist BJ, Weiher E, Westoby M (2006) Rebuilding community ecology from functional traits. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 178-185. |
| [29] | Meiri S (2024) SquamBase—A database of squamate (Reptilia: Squamata) traits. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 33, e13812. |
| [30] |
Murray KA, Verde Arregoitia LD, Davidson A, Di Marco M, Di Fonzo MMI (2014) Threat to the point: Improving the value of comparative extinction risk analysis for conservation action. Global Change Biology, 20, 483-494.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Oliveira BF, São-Pedro VA, Santos-Barrera G, Penone C, Costa GC (2017) AmphiBIO, a global database for amphibian ecological traits. Scientific Data, 4, 170123. |
| [32] | O’Shea M (2005) Venomous Snakes of the World. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [33] |
Oskyrko O, Mi CR, Meiri S, Du WG (2024) ReptTraits: A comprehensive dataset of ecological traits in reptiles. Scientific Data, 11, 243.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Petchey OL, Gaston KJ (2006) Functional diversity: Back to basics and looking forward. Ecology Letters, 9, 741-758.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Poos MS, Walker SC, Jackson DA (2009) Functional-diversity indices can be driven by methodological choices and species richness. Ecology, 90, 341-347.
PMID |
| [36] | Reed RN, Shine R (2002) Lying in wait for extinction: Ecological correlates of conservation status among Australian elapid snakes. Conservation Biology, 16, 451-461. |
| [37] | Rincón-Aranguri M, Toro-Cardona FA, Galeano SP, Roa-Fuentes L, Urbina-Cardona N (2023) Functional diversity of snakes is explained by the landscape composition at multiple areas of influence. Ecology and Evolution, 13, e10352. |
| [38] | Roll U, Feldman A, Novosolov M, Allison A, Bauer AM, Bernard R, Böhm M, Castro-Herrera F, Chirio L, Collen B,..., Tallowin OJS, Torres-Carvajal O, Torres-Carvajal J, Vidan E, Uetz P, Wagner P, Wang YZ, Orme CDL, Grenyer R, Meiri S (2017) The global distribution of tetrapods reveals a need for targeted reptile conservation. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 1677-1682. |
| [39] | Rugiero L, Milana G, Petrozzi F, Capula M, Luiselli L (2013) Climate-change-related shifts in annual phenology of a temperate snake during the last 20 years. Acta Oecologica, 51, 42-48. |
| [40] | Sobral M (2021) All traits are functional: An evolutionary viewpoint. Trends in Plant Science, 26, 674-676. |
| [41] |
Song YF, Chen CW, Wang YP (2022) A dataset on the life-history and ecological traits of Chinese amphibians. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22053. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 宋云枫, 陈传武, 王彦平 (2022) 中国两栖类生活史和生态学特征数据集. 生物多样性, 30, 22053.]
DOI |
|
| [42] | Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest S (2010) Ecotoxicology of Amphibians and Reptiles, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| [43] |
Swenson NG, Weiser MD (2010) Plant geography upon the basis of functional traits: An example from eastern North American trees. Ecology, 91, 2234-2241.
PMID |
| [44] | Ten Caten C, Lima-Ribeiro MS, Yañez-Arenas C, Villalobos F, Díaz-Gamboa L, Terribile LC (2023) Robustness of Bergmann’s and Rapoport’s rules to different geographical range estimates in New World pit vipers. Journal of Biogeography, 50, 365-379. |
| [45] | Tilman D, Knops J, Wedin D, Reich P, Ritchie M, Siemann E (1997) The influence of functional diversity and composition on ecosystem processes. Science, 277, 1300-1302. |
| [46] | Uetz P, Freed P, Aguilar R, Reyes F, Kudera J, Hošek J (2024) The Reptile Database. http://www.reptile-database.org.(accessed on 2024-09-06) |
| [47] |
Venter O, Sanderson EW, Magrach A, Allan JR, Beher J, Jones KR, Possingham HP, Laurance WF, Wood P, Fekete BM, Levy MA, Watson JEM (2016) Sixteen years of change in the global terrestrial human footprint and implications for biodiversity conservation. Nature Communications, 7, 12558.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Wallach V, Williams KL, Boundy J (2014) Snakes of the World:A Catalogue of Living and Extinct Species. CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| [49] |
Wang J, Zhao YF, Qu YF, Zhang CW, Zhang L, Chen CW, Wang YP (2023) A dataset of the morphological, life-history, and ecological traits of snakes in China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 王江, 赵一凡, 屈彦福, 张财文, 张亮, 陈传武, 王彦平 (2023) 中国蛇类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集. 生物多样性, 31, 23126.]
DOI |
|
| [50] | Wang YP, Song YF, Zhong YX, Chen CW, Zhao YH, Zeng D, Wu YR, Ding P (2021) A dataset on the life-history and ecological traits of Chinese birds. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1149-1153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 王彦平, 宋云枫, 钟雨茜, 陈传武, 赵郁豪, 曾頔, 吴亦如, 丁平 (2021) 中国鸟类的生活史和生态学特征数据集. 生物多样性, 29, 1149-1153.]
DOI |
|
| [51] | Zhao EM (2006) Snakes of China. Anhui Science & Technology Press, Hefei. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵尔宓 (2006) 中国蛇类. 安徽科学技术出版社, 合肥.] |
| [1] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [2] | 王江, 赵一凡, 屈彦福, 张财文, 张亮, 陈传武, 王彦平. 中国蛇类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23126-. |
| [3] | 钟雨茜, 陈传武, 王彦平. 中国蜥蜴类生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 22071-. |
| [4] | 宋云枫, 陈传武, 王彦平. 中国两栖类生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 22053-. |
| [5] | 丁晨晨, 梁冬妮, 信文培, 李春旺, 蒋志刚. 中国哺乳动物形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21520-. |
| [6] | 王彦平, 宋云枫, 钟雨茜, 陈传武, 赵郁豪, 曾頔, 吴亦如, 丁平. 中国鸟类的生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1149-1153. |
| [7] | 宋永昌, 阎恩荣, 宋坤. 中国常绿阔叶林8大动态监测样地植被的综合比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 139-148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn

